GEO 135 Unit 4 Latin America (Key terms)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Agrarian reform
A set of policies, laws, or movements aimed at redistributing land and improving the social and economic conditions of people who work in agriculture—especially landless farmers, tenants, or smallholders.
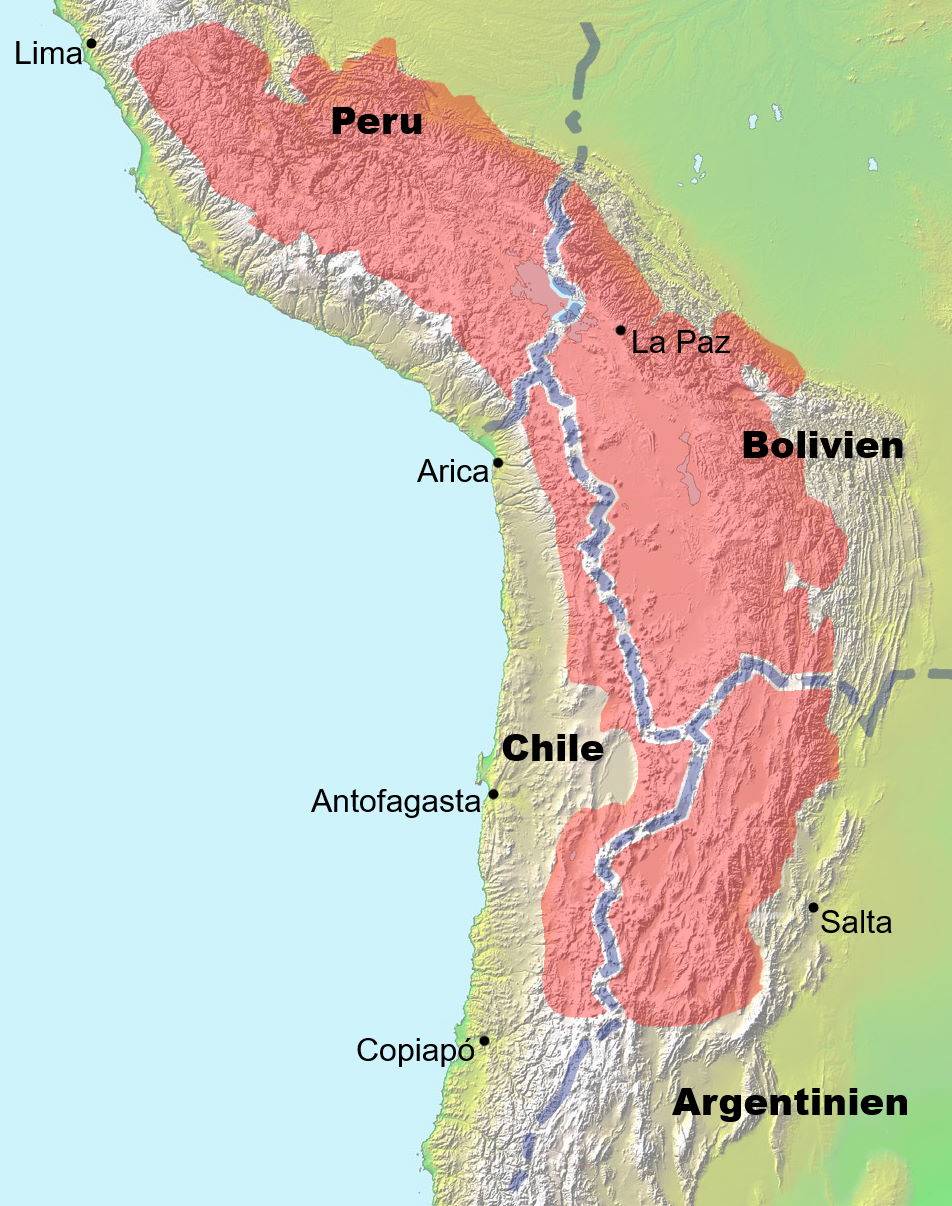
Altiplano
a high plateau in the central Andes Mountains of South America.
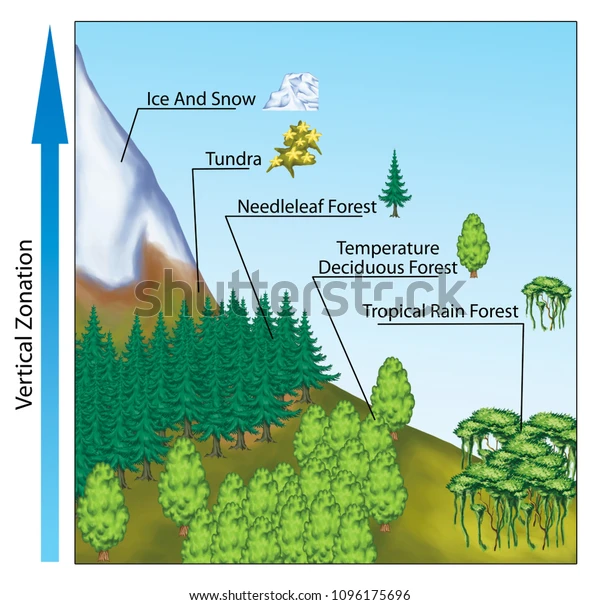
Altitudinal Zonation
the natural layering of ecosystems that occurs at different elevations in mountainous regions.
Bolsa familia
a social welfare program in Brazil that provides cash transfers to low-income families, with the goal of reducing poverty and breaking its cycle across generations.
Columbian exchange
the widespread transfer of plants, animals, people, technology, culture, and diseases between the Americas (New World) and Europe, Africa, and Asia (Old World) after Christopher Columbus’s voyages (starting in 1492).
Dollarization
when a country adopts the U.S. dollar (USD) as its official currency
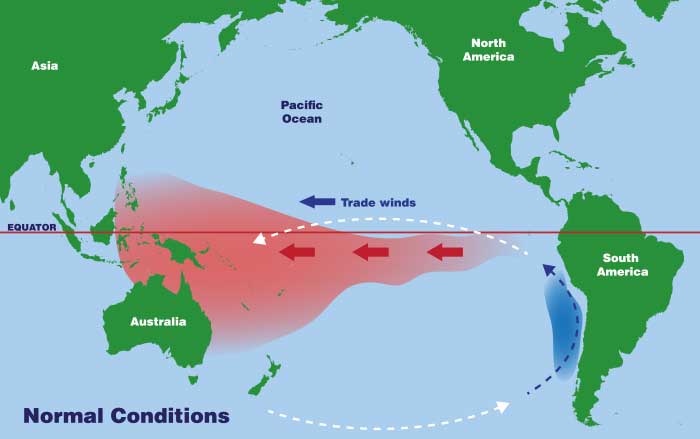
El Niño
a climate phenomenon that happens when the surface waters of the central and eastern Pacific Ocean become unusually warm, disrupting normal weather patterns around the world.
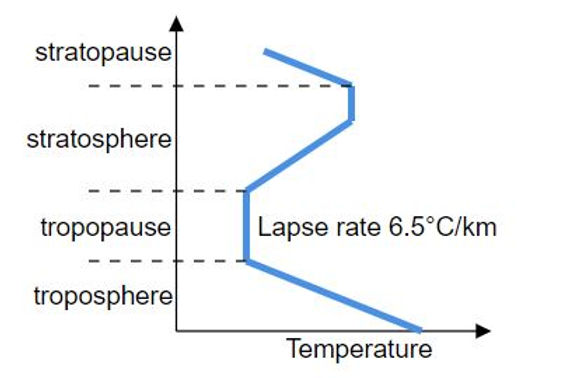
Environmental lapse rate
the rate at which air temperature decreases with an increase in altitude in the atmosphere.
Grassification
the process of converting forested land or other ecosystems into grasslands, usually for cattle ranching or other grazing purposes.
Informal sector
the part of the economy made up of jobs and businesses that are not regulated, taxed, or protected by the government.
Maquiladoras
factories in Mexico, often near the U.S. border, that are run by foreign companies and import materials duty-free to assemble or manufacture products for export.
Mestizo
a person of mixed European (usually Spanish) and Indigenous American ancestry.
Minifundia
a very small plot of farmland, usually too small to support a family efficiently.
Neoliberalism
an economic and political approach that emphasizes free markets, privatization, deregulation, and reducing the role of the state in the economy.
Neotropics
one of Earth’s major biogeographic regions, covering the tropical areas of the Americas.
Organization of American States (OAS)
a regional international organization that brings together countries from North, Central, and South America, plus the Caribbean, to promote cooperation.
Outsourcing
when a company hires another company (often abroad) to perform tasks, services, or produce goods that it could otherwise do itself.
(Usually for cheaper labor costs)
Pacific Alliance
a regional trade bloc in Latin America that promotes economic integration and free trade among its member countries on the Pacific coast.
Pristine Myth
the idea that the Americas were mostly untouched, wild, and sparsely populated by humans before Europeans arrived in 1492.
Remittances
money that immigrants send back to their home countries, usually to support family members.
Rural to urban migration
the movement of people from the countryside to cities, usually in search of better jobs, education, and living conditions.
Shields
a shield is a large area of exposed, ancient, and stable rock, usually part of a continent’s craton (the old, stable interior).

Subnational organizations
groups or governing bodies that operate below the national (federal) level, such as within a state, province, region, or city.
Supranational organizations
entities made up of multiple countries that cooperate and give up some national authority to achieve common goals. (Ex. EU & the UN)
Syncretic religions
belief systems that blend elements from two or more different religions or cultural traditions into a new, combined faith.
Treaty of Tordesillas
an agreement between Spain and Portugal in 1494 to divide newly discovered lands outside Europe.
Union of South American Nations (UNASUR)
a regional organization aimed at promoting integration and cooperation among South American countries.
Urban primacy
a situation where one city in a country is much larger and more important than all the others, dominating the economy, politics, and culture.