Lumbopelvic Quizzes: Key Terms & Definitions in Medicine
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Which of the following s/s must be present to diagnose cauda equina syndrome?
- low back pain
- radicular leg pain
- motor loss in lower leg
- reduced sensation in saddle area
Reduced sensation in saddle area (S2-S4 nerve roots do not really go into our leg and anyone can have LBP)
CES primarily affects which of the following nerve roots?
- L1
- L2
- S1
- S4
S4
CES is most likely the result of which condition?
Disc herniation (really any space-occupying lesion, but a disc herniation is the most common)
Patient presents w/ localized axial LBP with aggs & easing factors that are easily ID by the client. Symptoms are described as intermittent and improve with rest. He describes his pain as sharp and achy. Which pain mechanism is most likely?
- Nociceptive
- Neurogenic
- Nociplastic
- Radicular
Nociceptive
Which of the following muscles is most likely to atrophy w/ acute and/or chronic LBP?
- Longissimus
- Iliocostalis
- Multifidus
- Spinalis
Multifidus
Which of the following explanations is most accepted for the increased fatiguability of lumbar paraspinal musculature during and after an episode of LBP?
Longer duration of pain, more type IIB and less IIA oxidative fibers
A 62 y.o. patient reports a gradual onset of unilateral axial LBP that is described as "deep" and "achy." Symptoms are reproduced during extension, rotation, and sidebending. Which of the following nociceptive tissues is most likely involved?
- Muscles
- Discs
- Facets
- Ligaments
Facets (age & aggravating factors are key indicators here)
Which of the following hormones released during pregnancy contributes to increased laxity in the SI joint that may result in SI joint related pain?
Relaxin
Which of the following statements best describes the SI joint?
Strong & stable
What model helps clinicians organize and make sense of the complexity of LBP while providing a framework to guide the selection of person-centered interventions?
Pain and disability drivers model
A patient presents to PT w/ an acute episode of LBP without leg pain. They have low psychosocial risk factors and low medical comorbidities. Because of this presentation, which of management strategy is appropriate?
Self-care management
Which of the following tissues is most affected by spondyloarthropathy?
Entheses
A 32 y.o. Native American male presents to PT w/ a 6 month hx of LBP of insidious onset. He reports significant morning stiffness and feels better w/ movement than with rest. Which of the following clinical exam findings is most likely?
- Limited chest wall expansion
- Sensory loss in lower legs
- Motor loss in lower legs
- Hypermobility during motion assessment
Limited chest wall expansion (spondyloarthropathy is the most likely diagnosis based on age, race, and gender)
A patient reports of a 3 month hx of LBP that is constant and increasing in intensity over the past 3 weeks. He reports pain at night, recently visited a TB endemic country, and smokes 20 cigarettes a day. The neuro exam is normal. Which condition is most likely?
Infection
Symptom in the abdominal area are reproduced by coughing or sneezing or doing activities such as bending, twisting, or lifting indicate which of the following body systems?
MSK
16 y.o. female presents w/ unilateral low back pain. *insert x-ray image of a bone defect in the pars interarticularis (vertebral arch)* Which of the following conditions is most likely?
Spondylolysis (note: when you get bilateral par defects, you could develop spondylolythesis--this is especially common in extension-based athletes like gymnasts or offensive linemen)
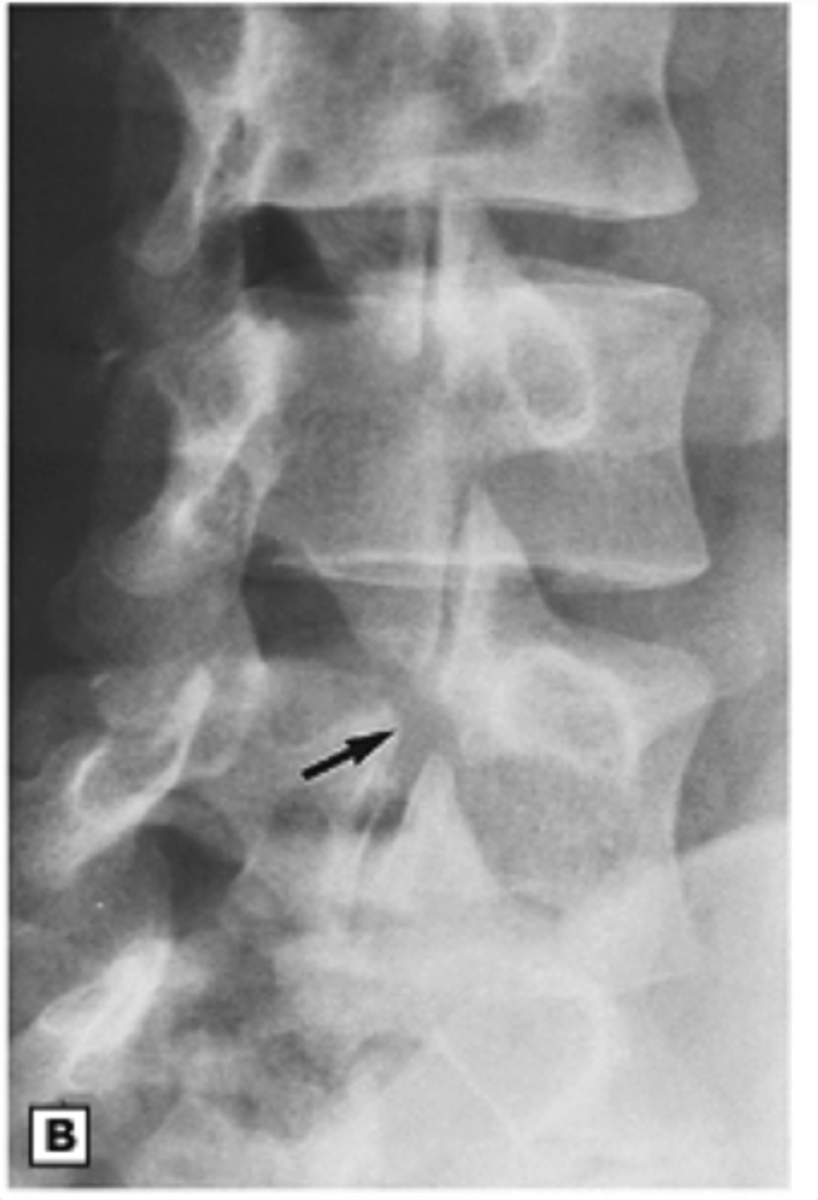
Which of the following types of disc herniations will resorption of disc material most likely occur?
Extrusion (however, this type of herniation is usually highly uncomfortable and will have some type of leg pain associated w/ the inflammatory response --> irritates the nerve root)
Which of the following types of disc herniations involves the nucleus pulposus bulging outwards but not escaping from the annulus fibrosis or PLL?
Protrusion
A 43 y.o. female presents w/ gradual onset of low back and buttock pain. No symptoms were reproduced during the lumbar spine or hip motion assessment. Neurodynamic tests were negative. Distraction and thigh thrust tests were positive. Based on this information, which of the following conditions is most likely?
SI joint related pain
A 72 y.o. patient presents w/ gradual onset of LBP and bilateral leg pain. Symptoms in the leg are exacerbated by activities such as walking or bike riding but are relieved w/ the cessation of those activities. He describes these symptoms are "tight" and "cramping." There is also an absence of pulses bilaterally. Which of the following conditions is most likely?
Vascular claudication
Which of the following symptoms is most common w/ a lumbar central spinal stenosis?
Neurogenic claudication
A patient presents w/ low back pain. Physical exam findings include decreased sensation in the anterior lower leg and dorsal surface of the foot and extensor hallucis longus strength 2/5. There is an intact patellar and achilles reflexes. Which of the following vertebral segments is most likely involved?
L4/L5
What of the following findings is the STRONGEST risk factor for the development of chronic LBP?
Cognitive and emotional problems
Which of the following maladaptive cognitions is associated w/ fear-avoidance beliefs?
Fear of movement
Which of the following mood disorders is related to LBP?
Depression
Which of the following patient variables is the strongest predictor of success vs. non-success in PT?
Expectations
Which of the following patient characteristics has the highest association w/ outcomes in PT?
Number of comorbidities
Which of the following TBCs is the MOST appropriate for a patient with high disability and high severity?
Symptom modulation
Which of the following symptom-modulatory interventions is used in clients with reports of LBP w/ referred leg pain?
Specific exercises
Which of the following directional preferences is MOST common in clients presenting w/ LBP w/ referred leg pain?
Extension
A patient has progressed their low back extension exercises to performing prone on elbow. Which of the following extension exercises preceded this?
Prone lying
A 72 y.o. male presents w/ LBP and neurogenic claudication. Which of the following directional preferences SHOULD the PT expect to find during repeated movement?
Flexion
A 42 y.o. patient presents w/ LBP and leg pain extending to the distal lower leg. During the physical exam, the patient did not have directional preferences. Symptoms were peripheralized during repeated extension. Which of the following interventions is MOST appropriate?
Lumbar traction
Which of the following clinical exam findings favors the use of lumbar manipulation?
LBP only, more recent onset of symptoms, hypomobility w/ lumbar accessory motion (looking for 3+/5 variables)
A PT is determining which intervention is most appropriate to use for a 21 y.o. female who presents w/ LBP only. The exam findings reveal a SLR of 94 deg, an instability catch during motion assessment, and a (+) prone instability test. Which of the following TBCs is most appropriate?
Stabilization
A patient presents with an acute episode of LBP that they rate an 8/10 with activity. The pain is significantly impacting their ability to perform daily activities. Which of the following core stabilization/motor control exercises should the PT start with?
Pelvic tilts
A client w/ acute LBP is now able to tolerate an increase in the vigor of their core stabilization program. They are currently performing a bent-leg fallout in a hook-lying position. Which of the following interventions should the patient progress to?
Lift bent leg to 90 deg of hip flexion while in hook-lying position
Which of the following exercises has the HIGHEST EMG activity for the gluteus medius?
Sidelying hip abduction
Which of the following adverse events should a patient be aware of regarding a high-velocity, low amplitude thrust targeted at the lower lumbar spine?
Mild soreness <24 hours
Which of the following patient variables is the STRONGEST predictor for a favorable response to a HVLAT at the lower lumbar spine?
Recent onset of symptoms (<16 days)
A PT is initiating a core stabilization program that focuses on motor control. Which of the following basic principles of motor control should the patient start with?
Developing awareness of muscle contractions, muscle relaxations, and spine positions (similar to the concept of quad sets following a TKA)
A PT is working with a patient who injured their back lifting forty-five 60 lb. sandbags 3 months ago. Currently, the patient has low severity and irritability of their symptoms and has progressed to functional optimization. Which intervention would be appropriate for them?
Single arm carry
The health of the nervous system depends on which 3 variables?
Space, movement, and blood
Which analogy is most appropriate to use when discussing axoplasmic flow with a patient?
Nerve lubricant
What is the role of movement with neurogenic pain? What is the benefit?
Movement of peripheral nerves is needed for axoplasmic flow (side note: this is why the term neural tension switched to neural dynamics--MOVEMENT IS MEDICINE)
When treating a patient with neuropathic pain, which statement is the most accurate when it comes to using stretching as an intervention?
- should be provided
- increases blood flow
- decreases mechanosensitivity
- should be avoided
Should be AVOIDED
Which intervention is used to apply tension at both ends of the peripheral nerve?
Tensioners
A patient presents to your clinic w/ LBP and leg pain that started 12 days ago. They report that it feels like a buzzing and tingling sensation and rates it as a 7/10. Which intervention is MOST appropriate?
Sliders 15-30 reps every hour
A patient presents to your clinic w/ LBP and leg pain AND a (+) SLUMP test. Which intervention is MOST appropriate?
Slump stretching
Which intervention is MOST effective to improve lumbar spinal stenosis?
Individualized exercise
A patient presents to your clinic w/ LBP and leg pain that radiates to the lateral knee. Which exam technique assesses for centralization of these symptoms?
Repeated motion
While examining a patient, you note that repeated motion does not cause centralization of symptoms, but it does decrease the intensity of the leg pain. Which intervention is most appropriate?
Directional preference