Zoo-Lab (Sem-1) - Exercise 13: Phylum Nemathelminthes (Nematoda)
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Phylum Nemathelminthes (Nematoda)
unsegmented roundworms; bilaterally symmetrical; usually so elongated and slender that they are called thread/hair worms; complete digestive system; covered with a tough cuticle and sensory organs; free-living in soil and water, parasitic to animals
amphids
anterior sensory organs
phasmids
posterior sensory organs
Phasmida; Aphasmida
representative classes of Phylum Nematoda
Class Phasmida
parasitic roundworms that live in the intestine of mammals, including man; both amphids and phasmids present
Ascaris lumbricoides
human Ascaris; cylindrical body with four longitudinal lines running from the anterior to the posterior end
median dorsal line; medial ventral line; two lateral lines
four longitudinal lines of the Ascaris
mouth
part of the Ascaris; at the anterior end, bordered by 3 lip-folds: one dorsal, two ventral lips
gonophore/reproductive pore
a tiny opening; situated at the mid-ventral line about one third from the anterior end of the female; the equivalent for males is the anus, which lie on the ventral line also
pineal setae
in males; a pair of needle-like chitinoid bodies; may project from the anus
Ascaris lumbricoides (male)
smaller than the female; curved ventrally at its posterior end
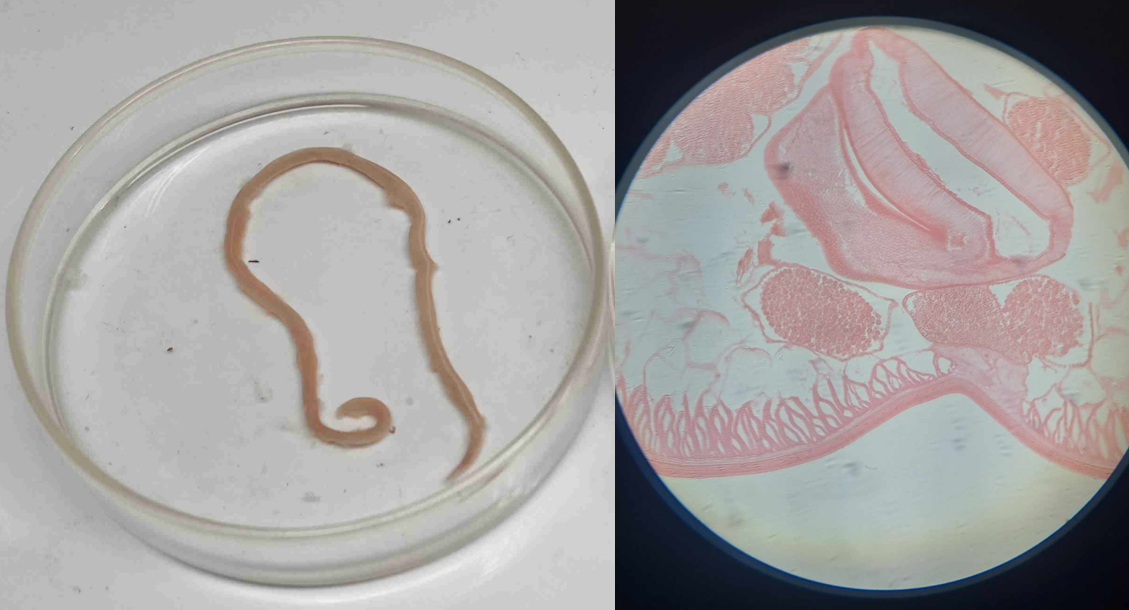
Ascaris lumbricoides (female)
larger than the male; have two big mass: uteri; distinguishable oviducts and ovaries
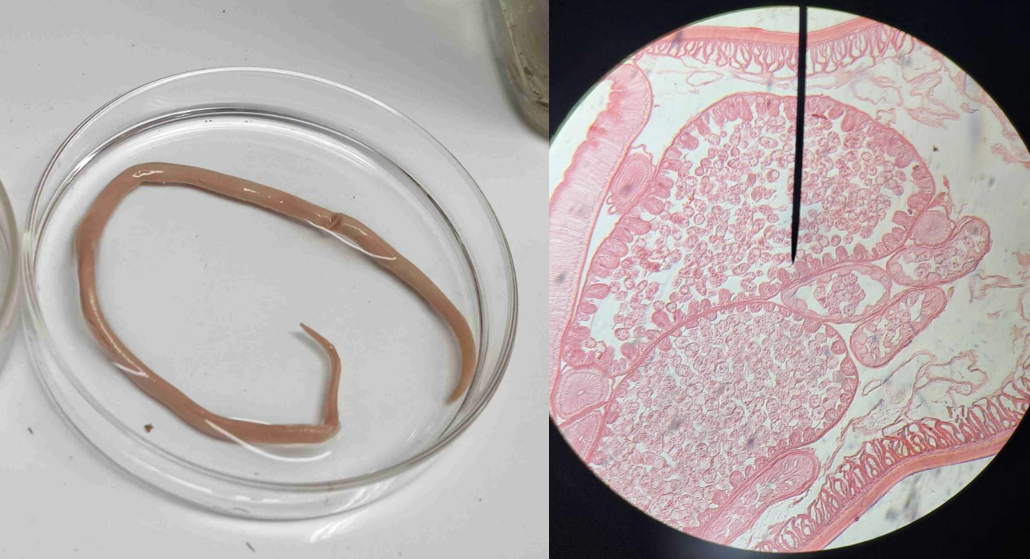
Turbatrix aceti
vinegar eel; non-parasitic nematode found in native vinegar; ovoviviparous animal; female bigger than male; cylindrical body
Class Aphasmida
posterior sense organs are absent; only amphids are present; they possess caudal adhesive glands
Trichiuris trichiura
whipworm; small nematode in which the esophagus is not muscular but consists of a long chain of cells forming a narrow tube; body is made up of 2 portions, a very slender anterior portion (esophagus), and a thick posterior portion containing the reproductive organs
spicule
structural elements found in most sponges; the meshing of many spicules serves as the sponge's skeleton and thus it provides structural support and potentially defense against predators