Topic 5 - Homeostasis and response
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Nervous system responses
-stimulus is detected by receptors
-information from receptors is transferred through sensory neurons to the CNS via electrical impulses
-the CNS containing the brain and spinal cord coordinates the body's response to the stimulus
-the electrical impulses passes from relay neurons to motor neurons to the effector
-the effector carries out a response which is usually a muscle contraction or a gland secreting a hormone
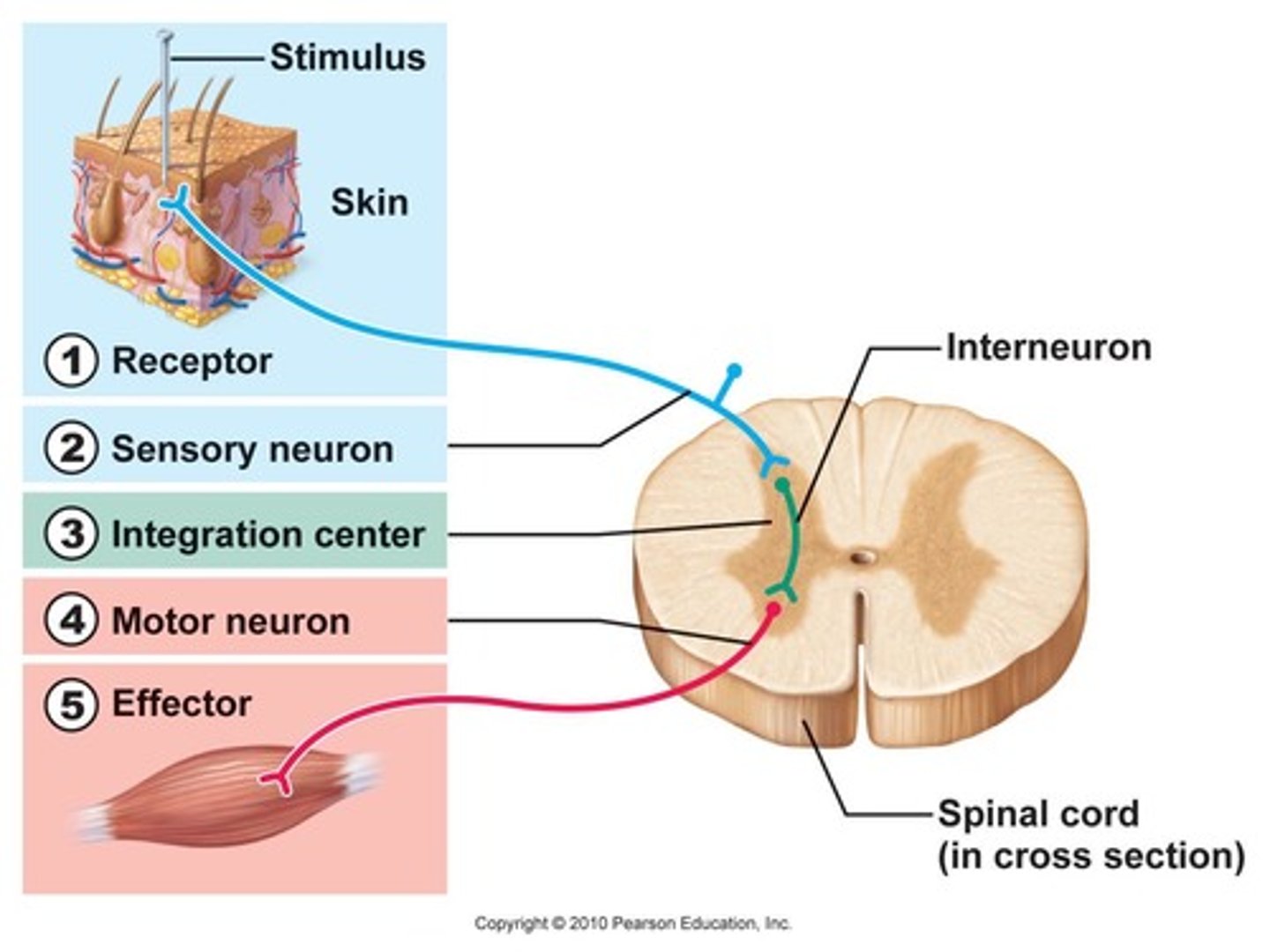
Reflex arcs
-automatic and rapid
-do not involve the conscious part of the brain
-bypass the brain and go straight through the spinal cord
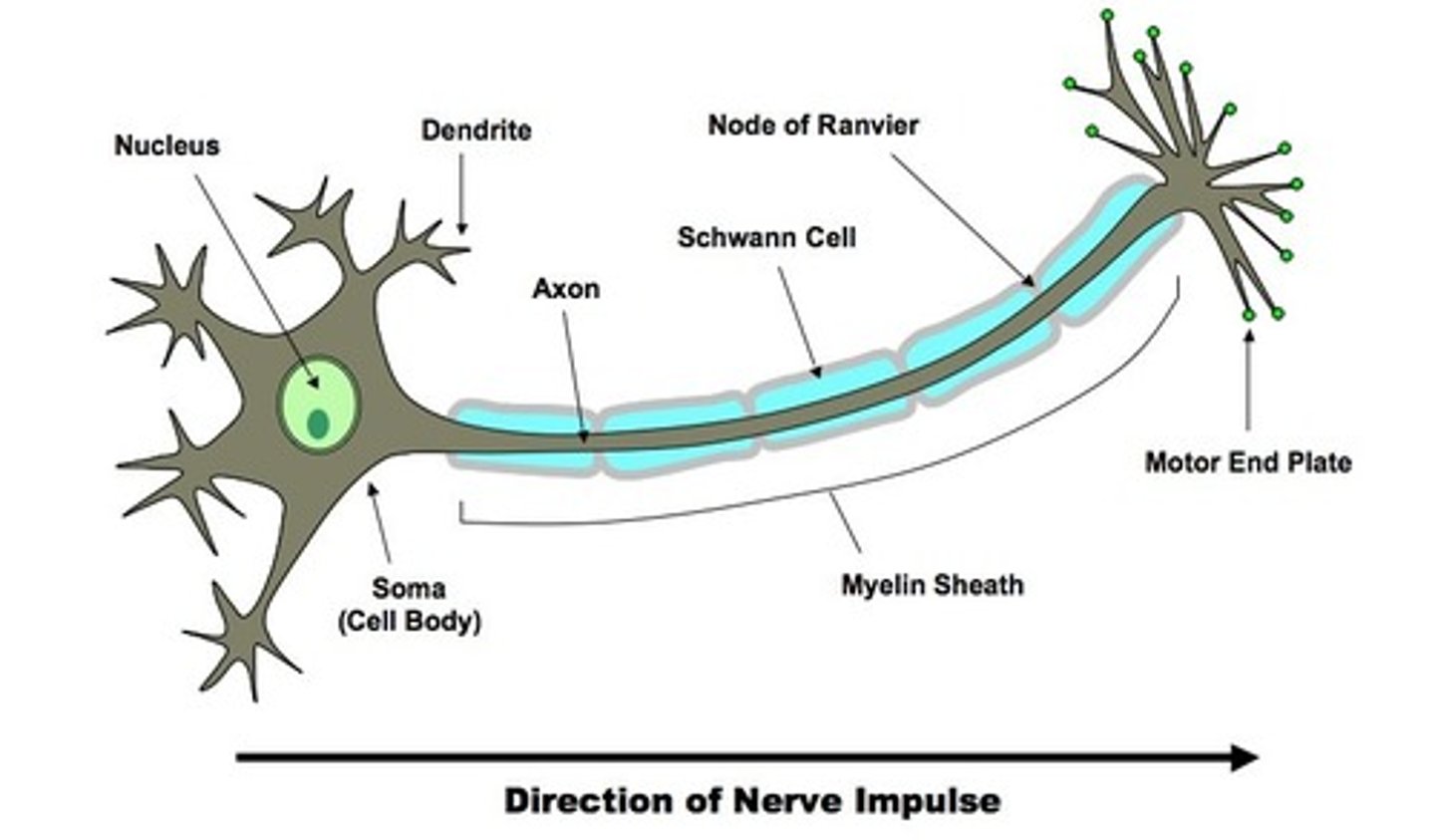
Neurone structure
-branched connections which make connections with other neurons or effectors
-myelin sheath insulates the axon making electrical impulses travel faster
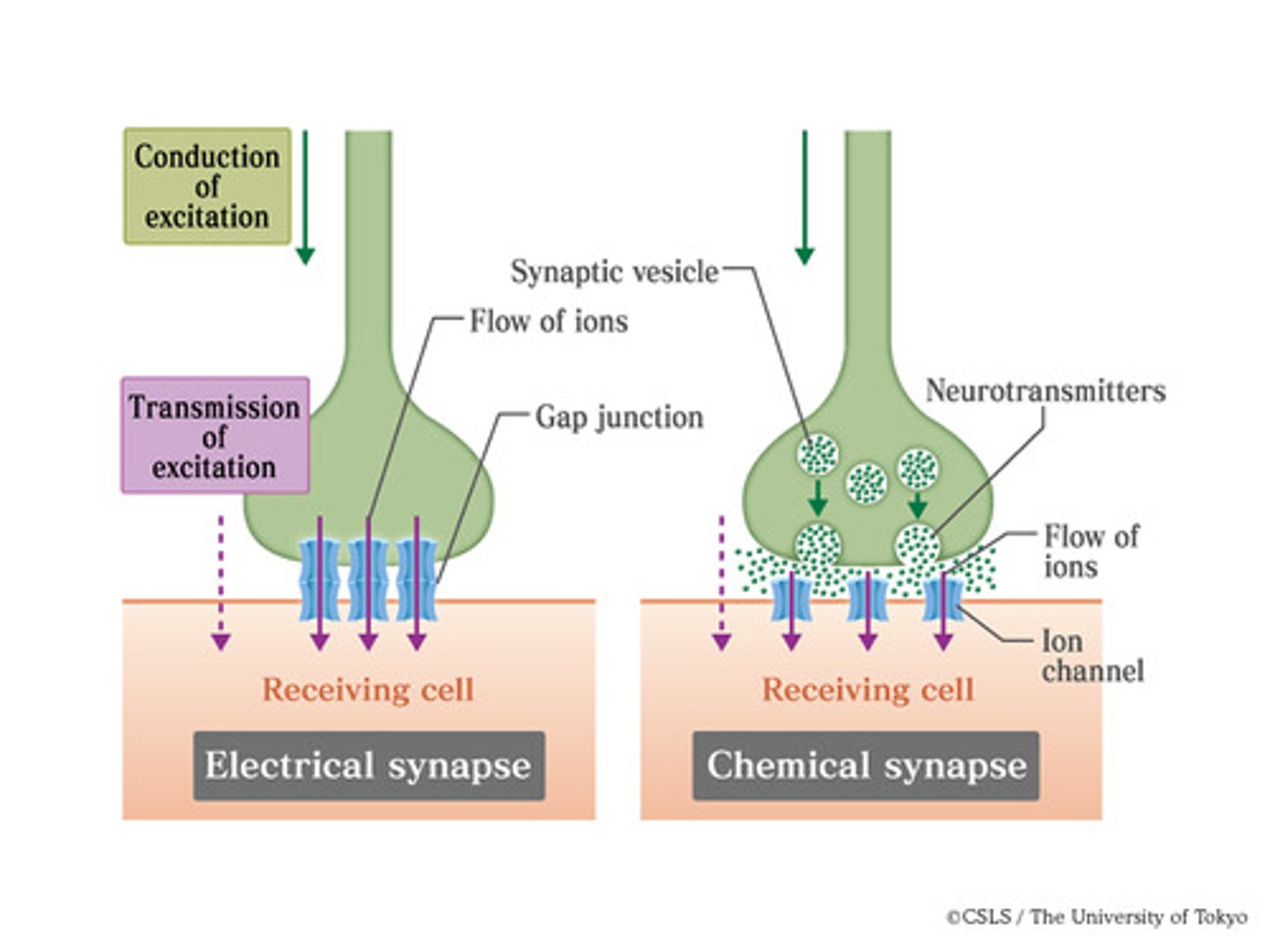
Synapses
-gaps between neurones which electrical impulses to cross between neurones
-neurotransmitters are released into the gap between minerals by small sacs containing chemicals
-chemicals attach to the next surface of the next surface to set up a new electrical impulse
-this is called chemical diffusion of nerves
Cerebal cortex
outer layer of the brain important for consciousness intelligence memory and language
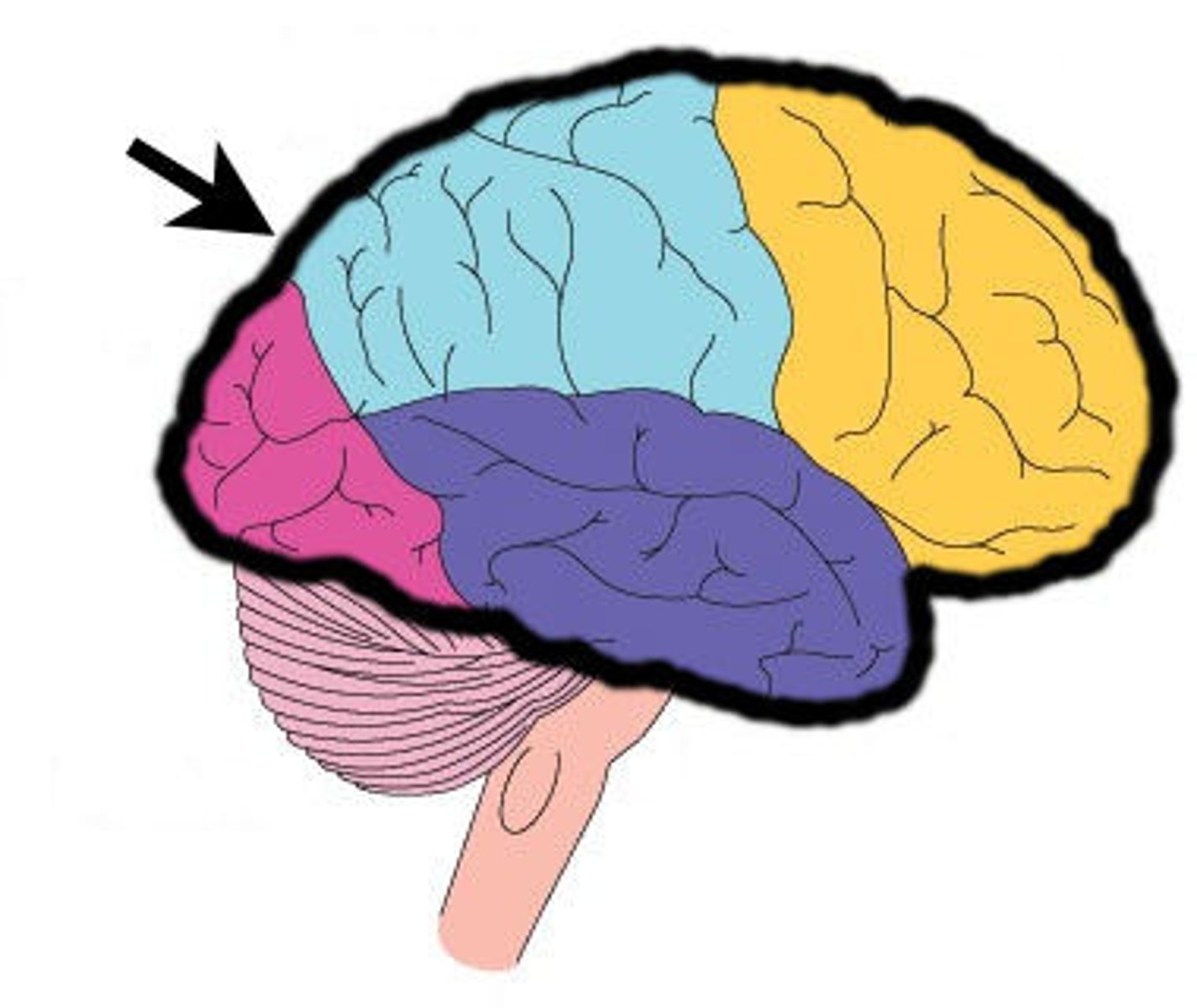
Cerebellum
at the back of the brain controlling balance coordination and muscle activity
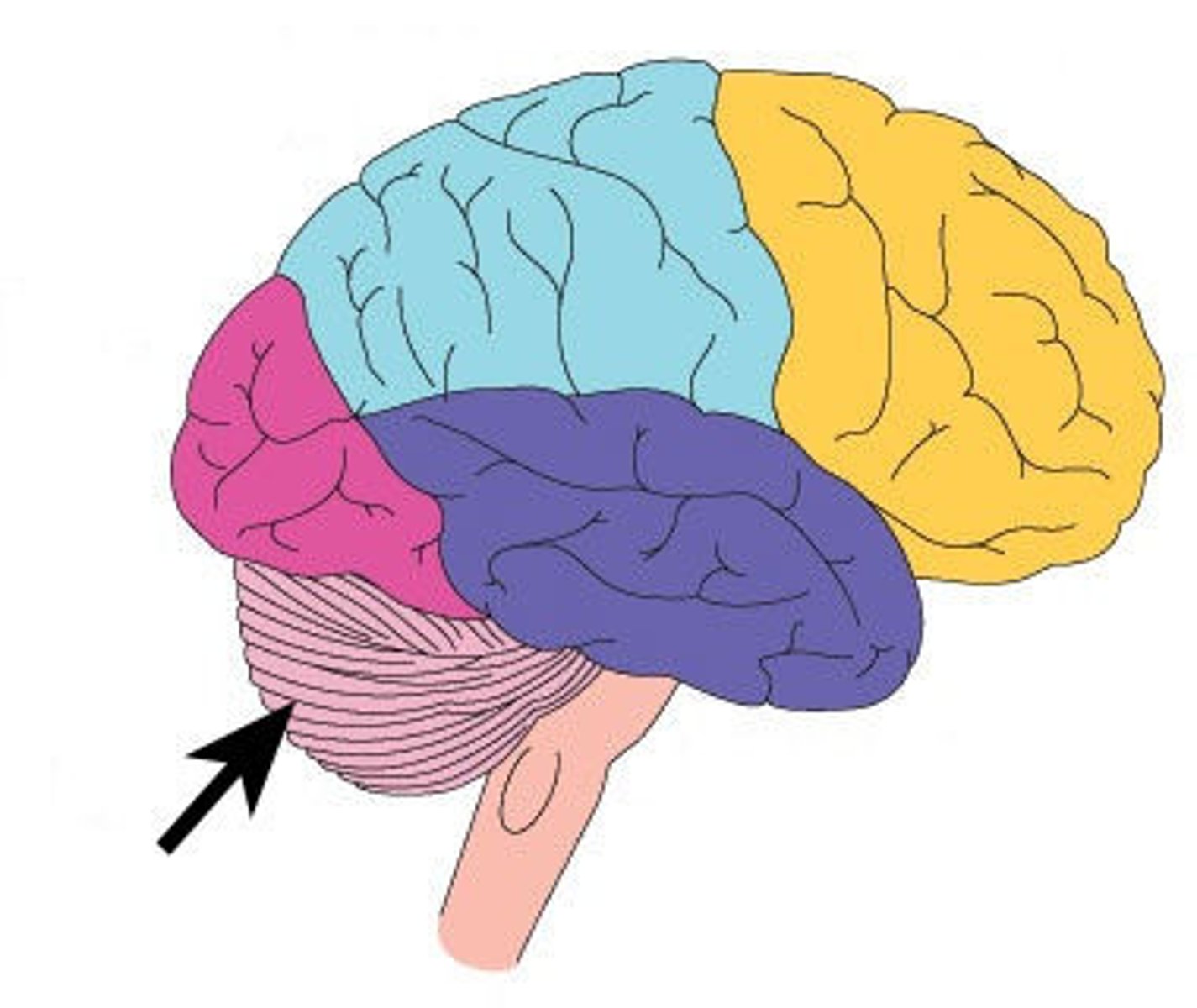
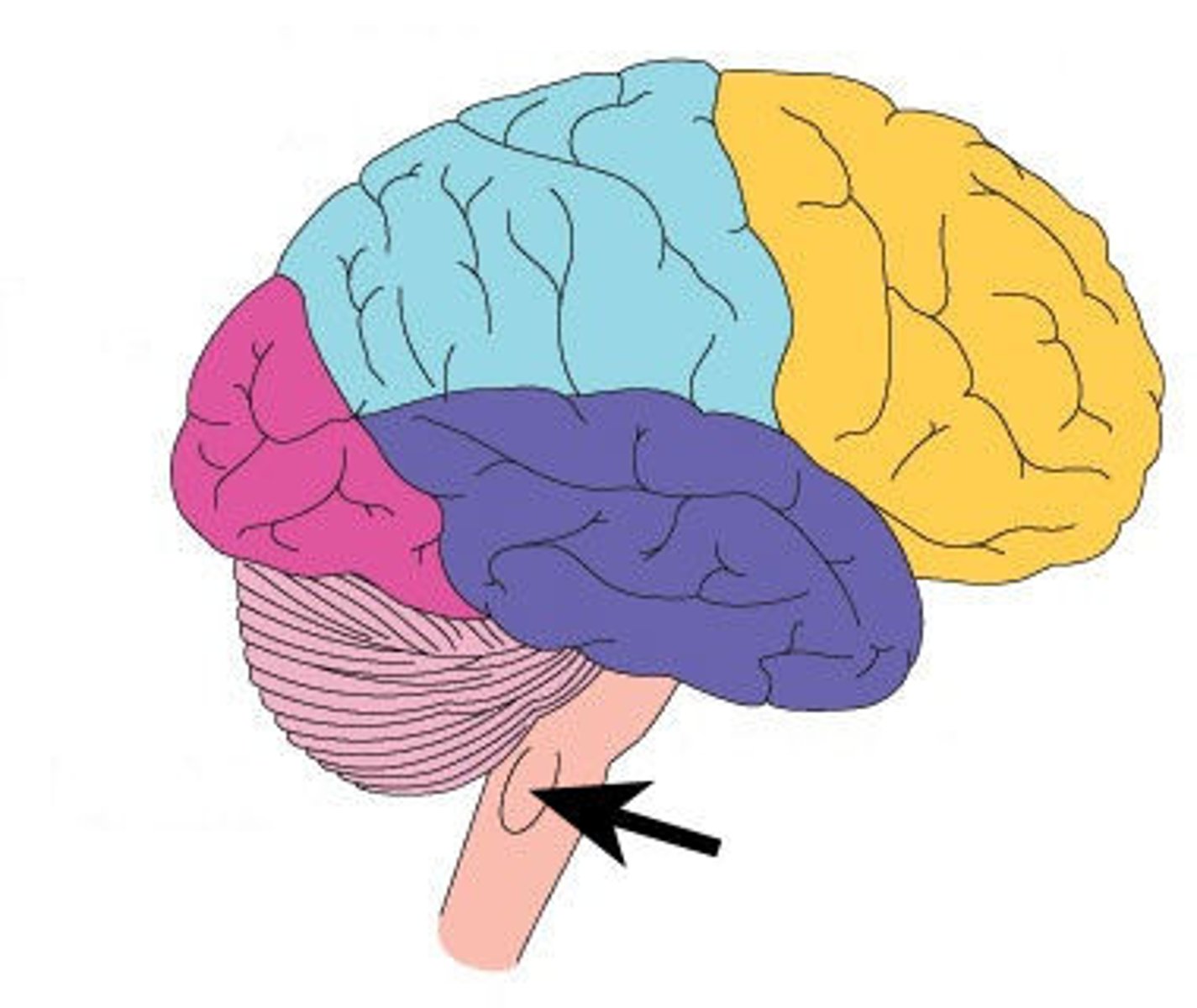
Medulla oblongata
above the spinal cord controlling unconscious activities such as breathing and heart rate
Why treatment of the brain is difficult
-the brain function in each area is not fully understood
-drugs do not always reach the brain through its membrane's
-surgery can cause unintended damage as the brain is very delicate and the cranium is very strong
How science attempt to research brain functions
-studying patients with brain damage
-MRI scans
-electrically stimulating parts of the brain
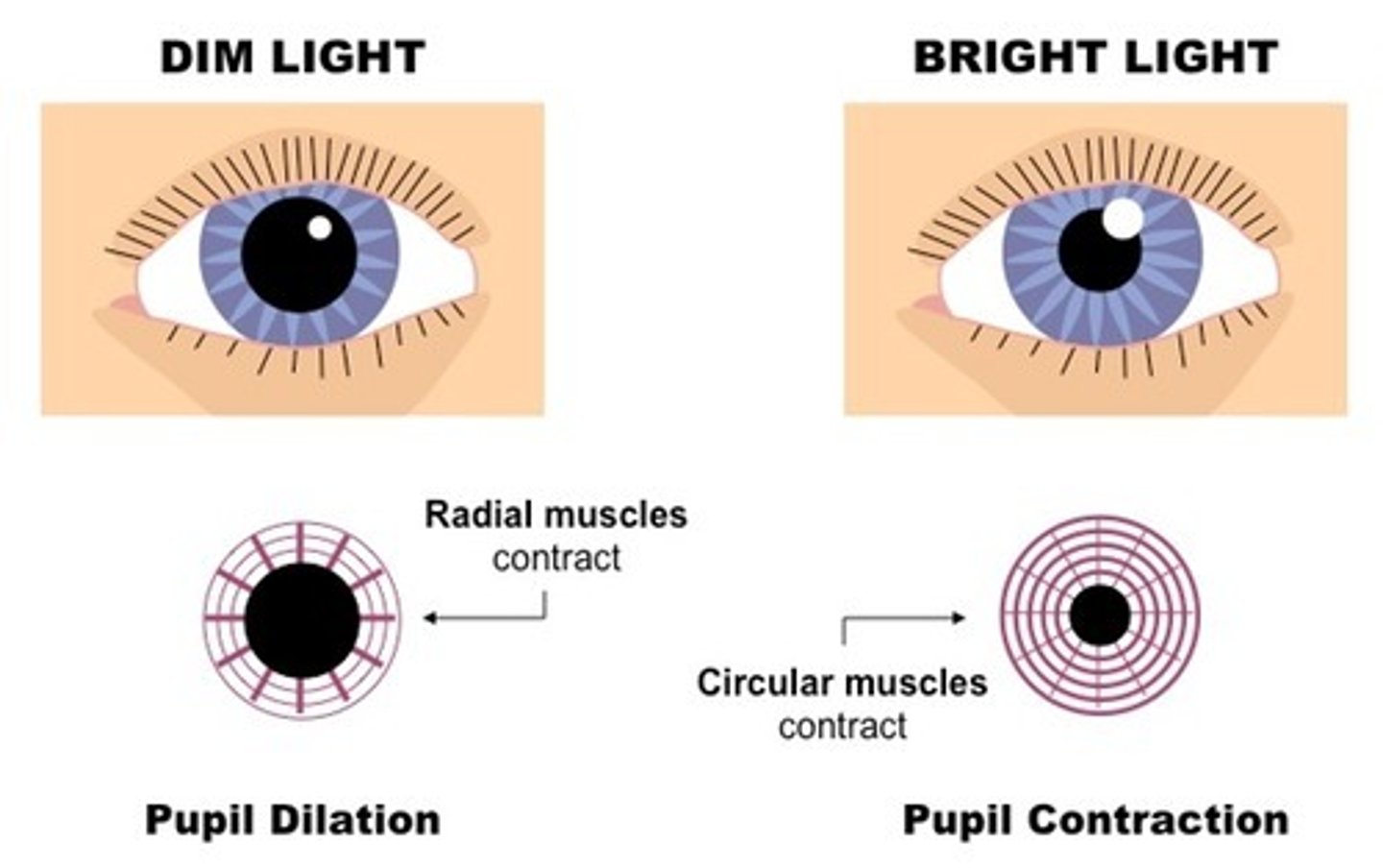
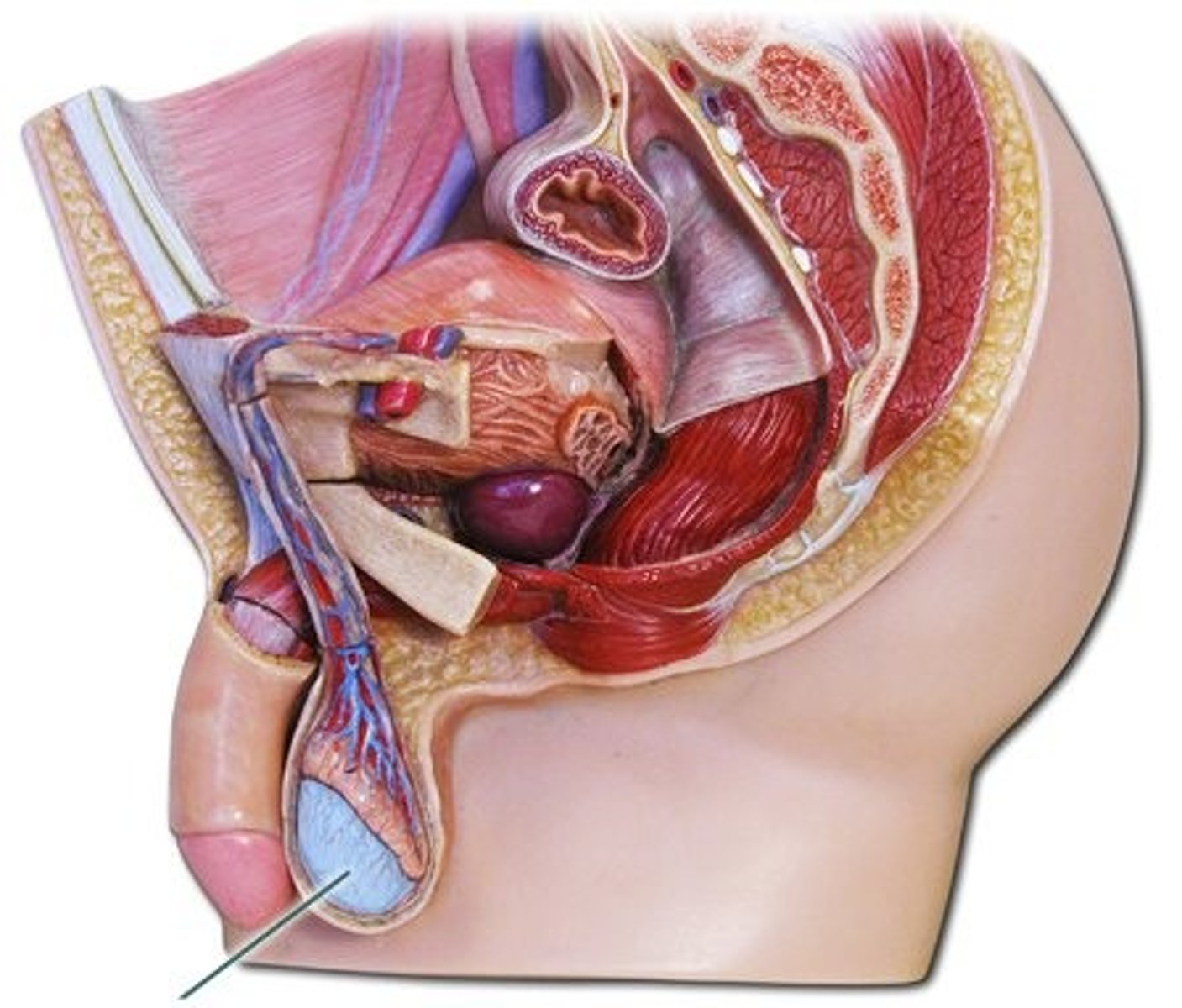
Iris and Iris reflex
-coloured part of the eye containing radial and circular muscles
-in bright light circular muscles contract and radial muscles relax making the pupil smaller
-in dim light circular muscles relax and radial muscles contract making the pupil smaller
Cornea
transparent structure refracting light that enters in order for it to focus on the retina
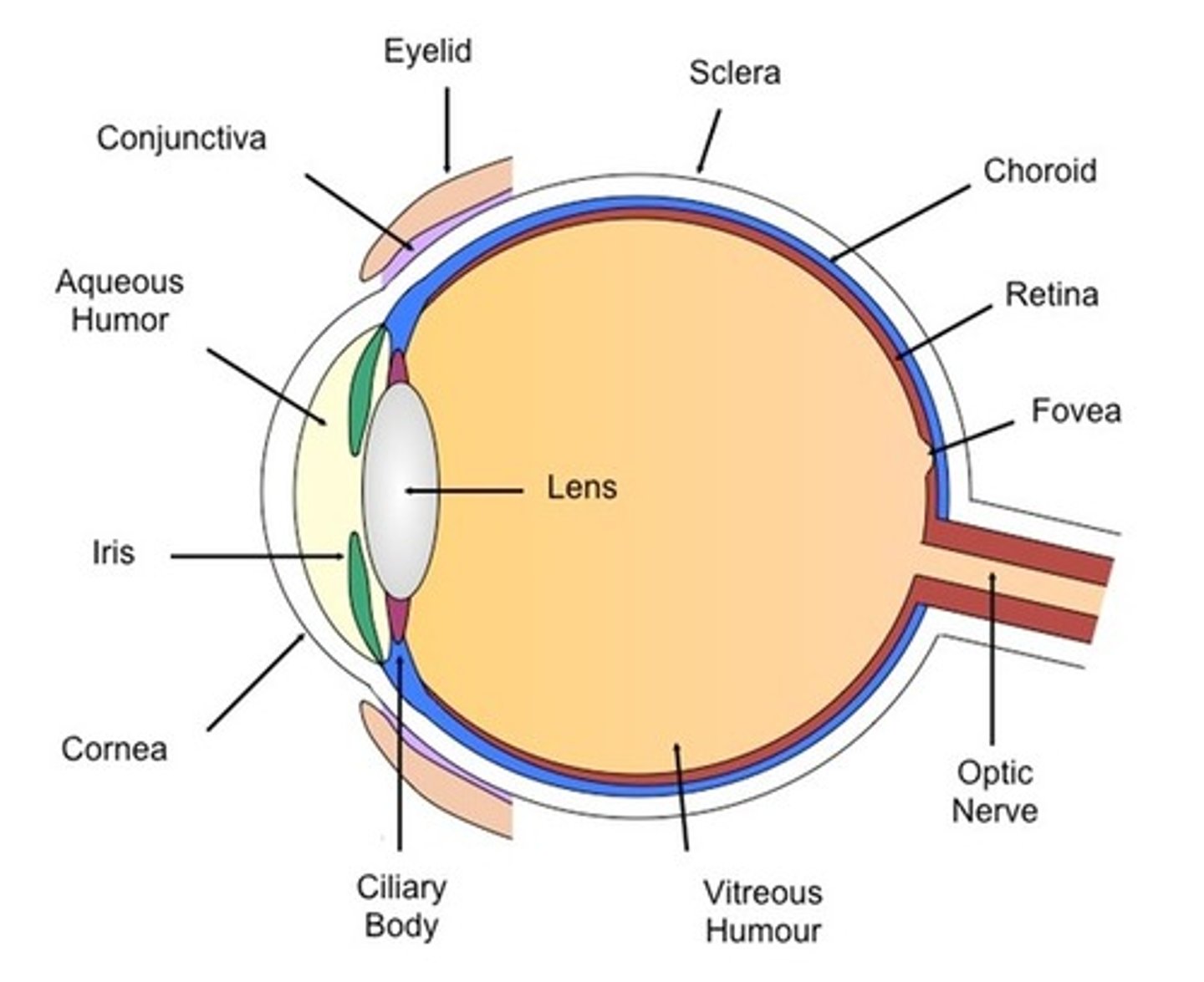
Retina
-layer of receptors at the back the eye
-rods are sensitive to light
-cones are sensitive to colour
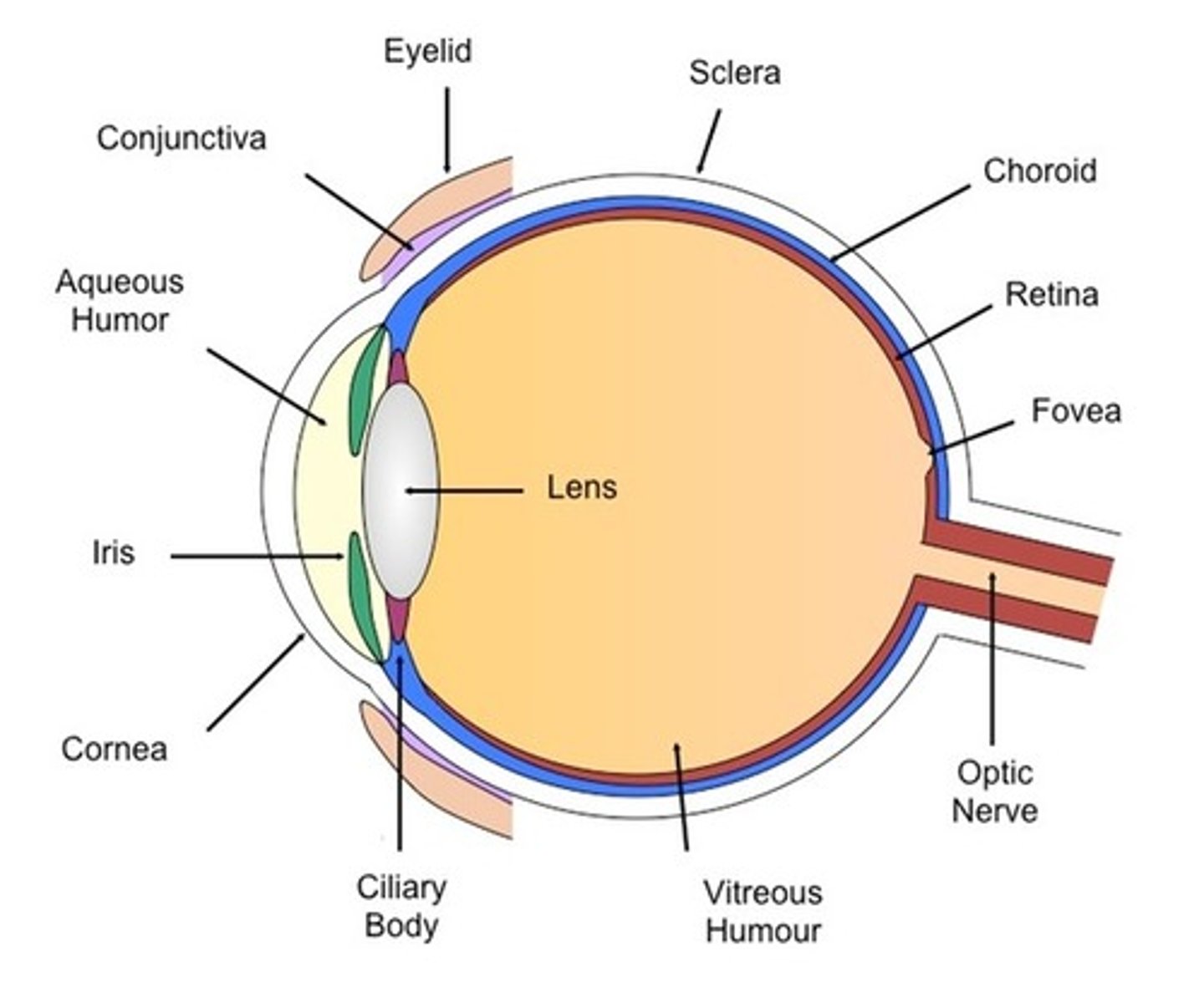
Optic nerve
-carries electrical impulses from the eye to the brain
Sclera
-tough white outer layer protecting the eye
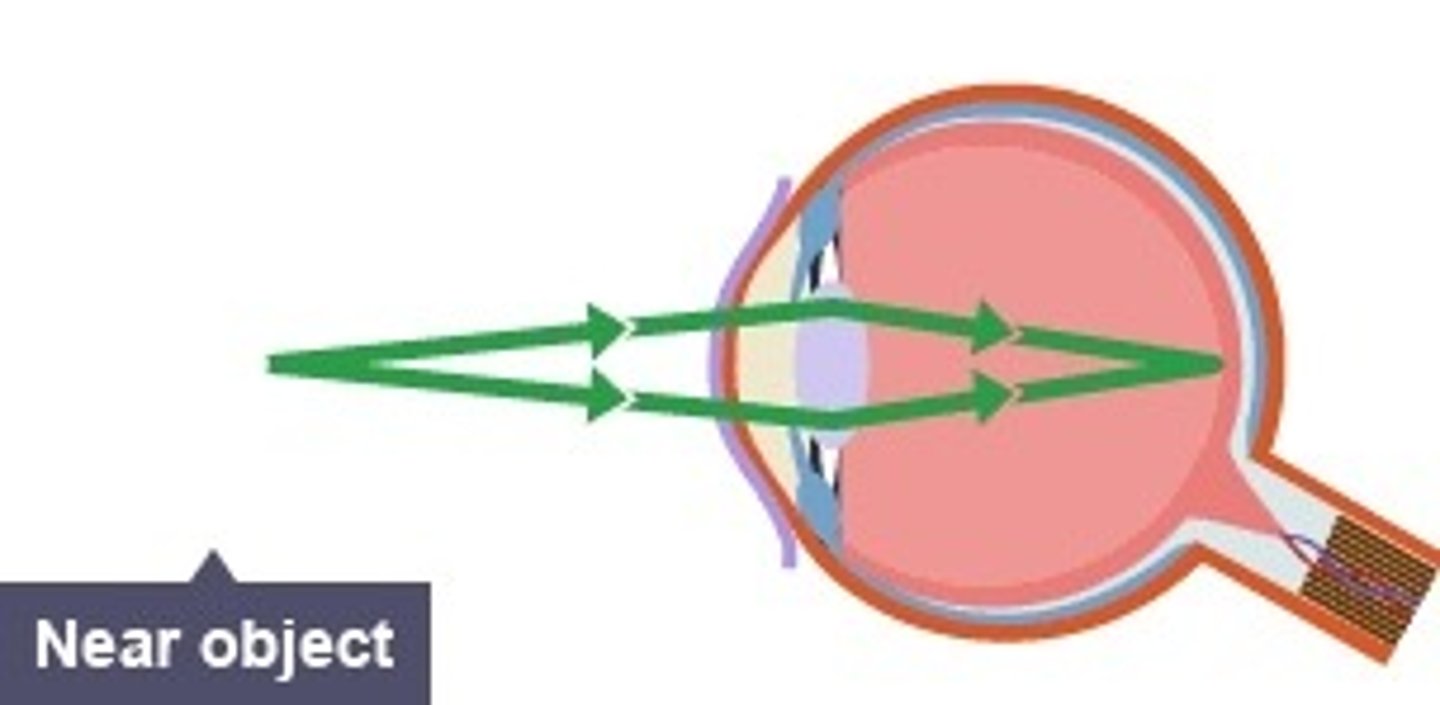
Focusing on near objects
-ciliary muscles contract
-suspensory ligaments slacken
-lens becomes thicker and refracts light more strongly
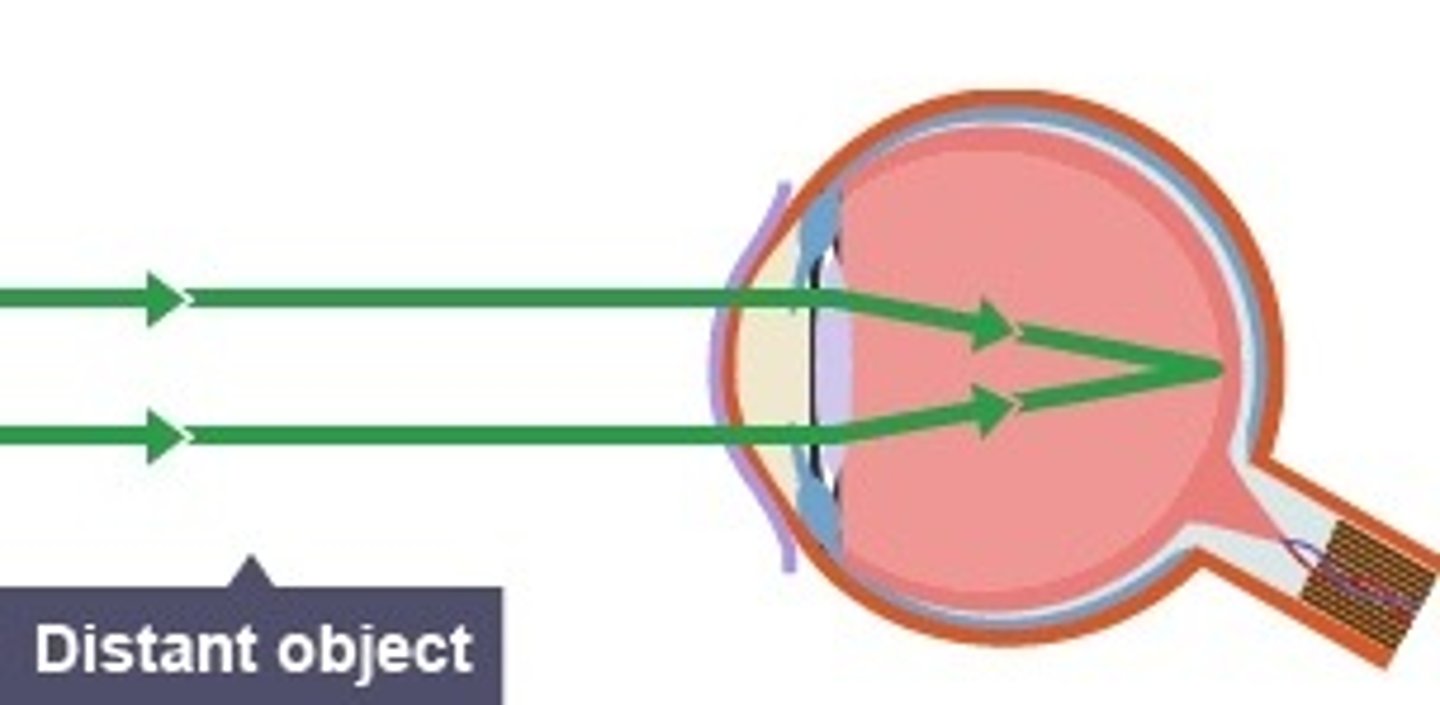
Focusing on distant objects
-ciliary muscles relax
-suspensory ligaments tighten
-lens is thinner and weakly refracts light
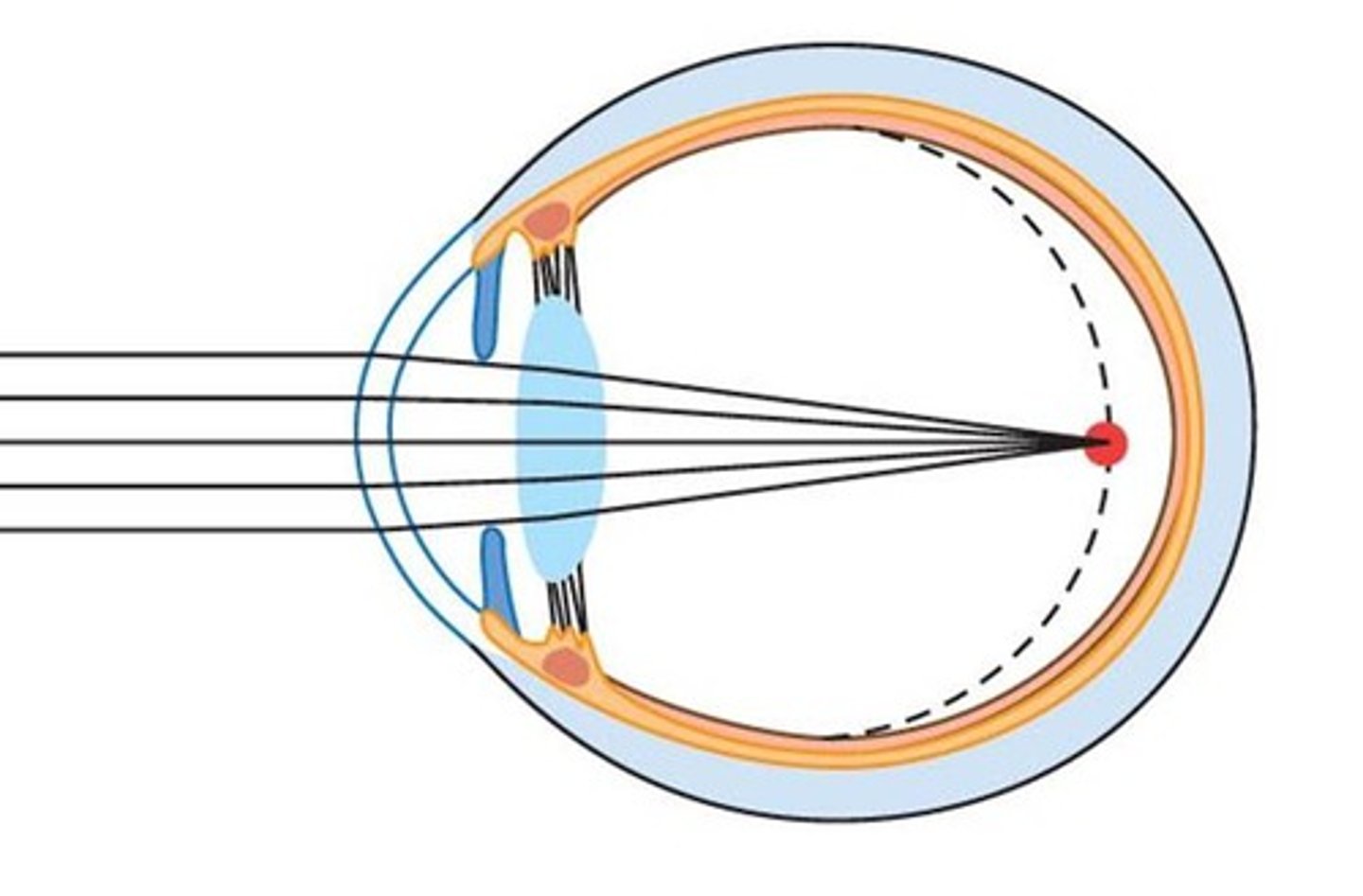
Myopia
-short sightedness due to light rays being focused in front of the retina
-issue is corrected using a concave lens
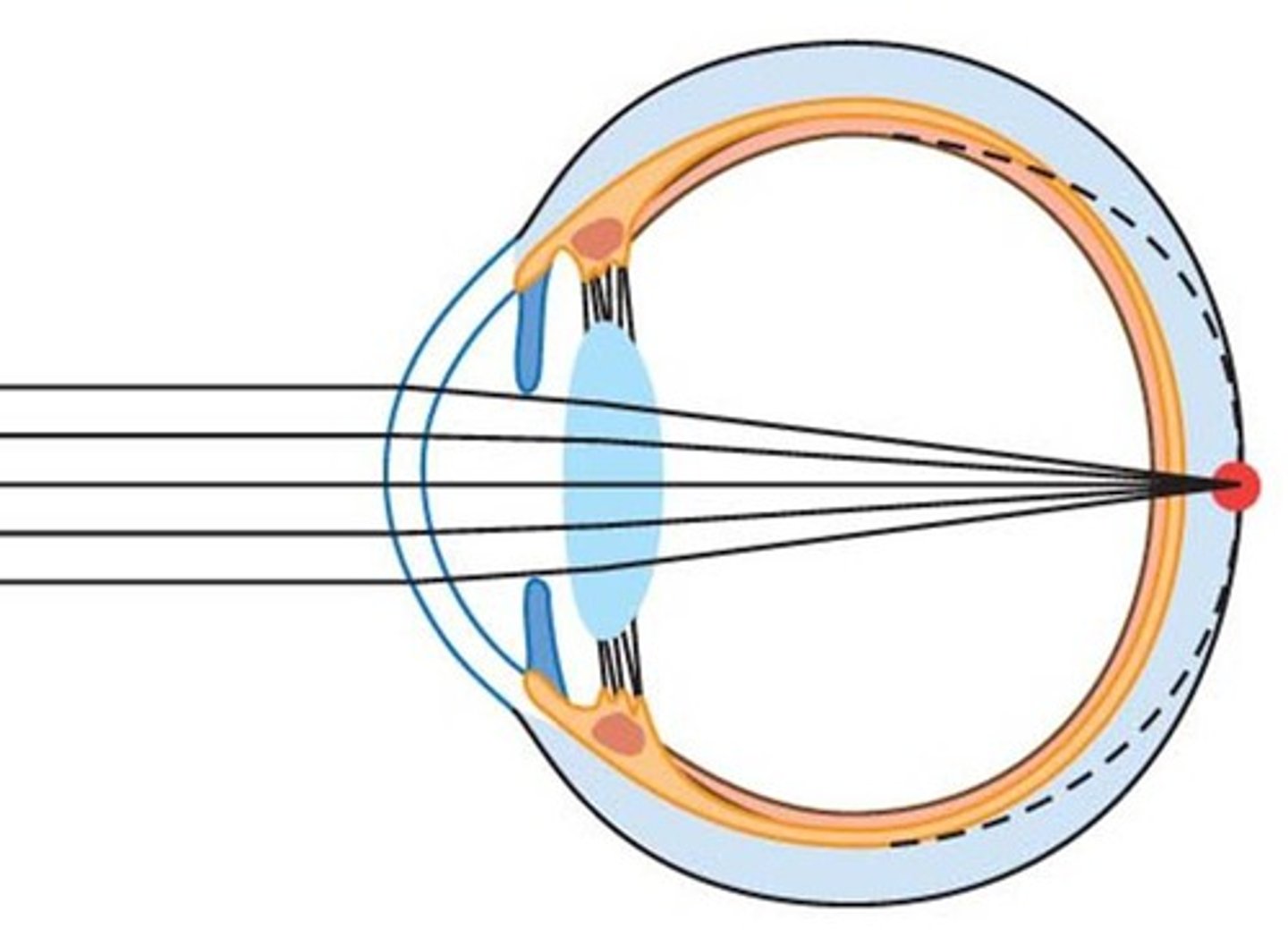
Hyperopia
-long sightedness due to light rays being focused in behind the retina
-issue is corrected with a convex lens
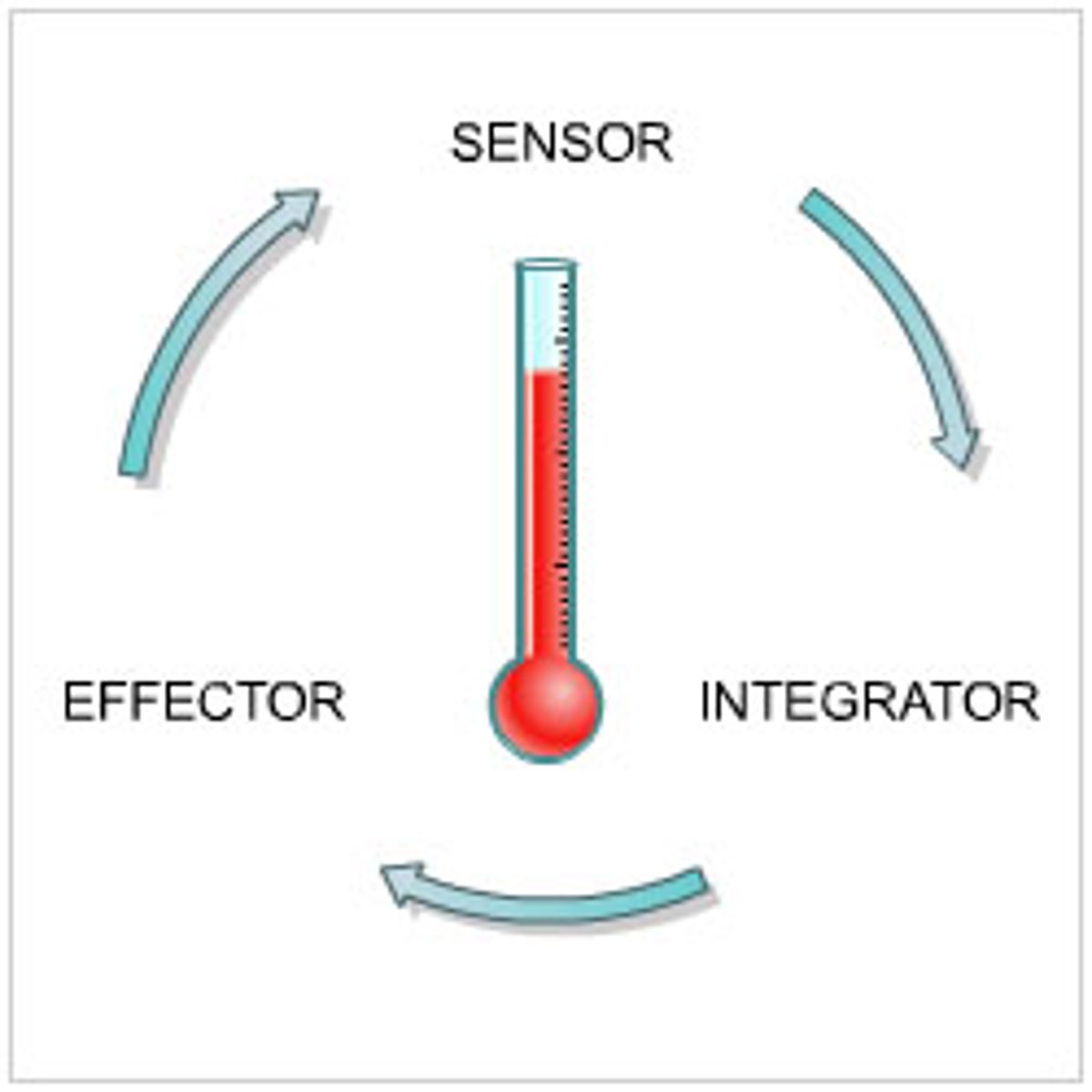
Homeostasis
-the regulation of internal conditions of a cell or organism in response to external changes in order to maintain optimum conditions for functions of enzymes and cells
-includes control of blood glucose concentration body temperature and water levels
Thermoregulatory centre response to low body temperature
-vasoconstriction of blood vessels so less heat is transferred to the skin and out to surroundings
-skeletal muscles frequently contract causing shivering
-During shivering, your muscles require energy to contract rapidly. This energy is released through aerobic respiration
Thermoregulatory system response to high body temperature
-vasodilation of blood vessels so more blood is transferred to the skin and lost through the surroundings
-sweat glands produce sweat which can evaporate of the skin
Treatment of eye defects
-lenses to alter refraction of light in order for it to focus on the retina
-laser eye surgery to change the shape of the cornea
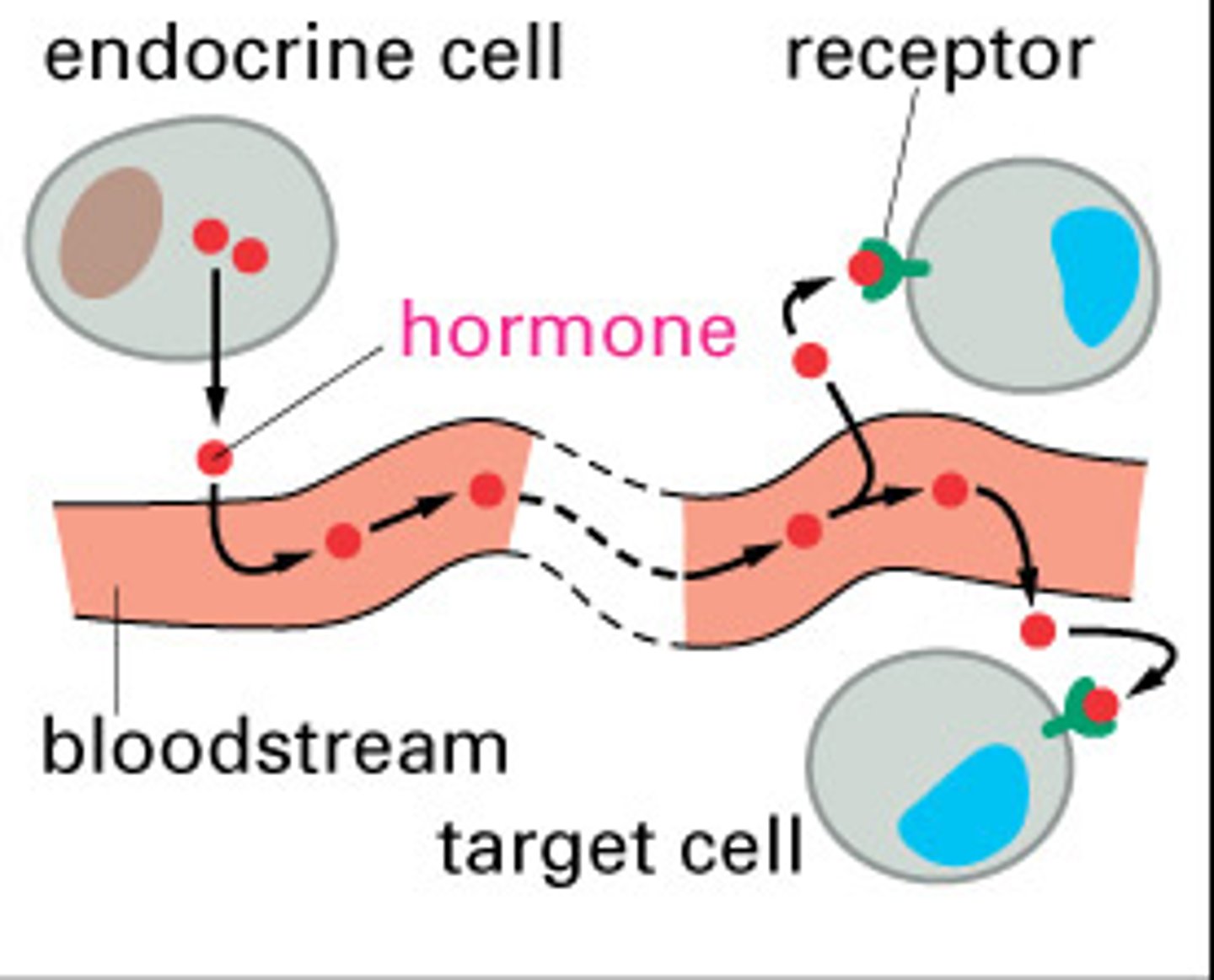
The endocrine system
-composed of glands that secrete chemicals called hormones into the bloodstream
-the blood carries the hormone to the target organ where an effect is carried out
-hormones secreted by the pituitary gland act on other glands stimulating release of other hormones that bring about effects
Response to high blood glucose levels
-pancreas secretes insulin
-this causes the glucose to move from blood into cells
-excess glucose is converted to glycogen in the liver and muscles for storage
Response to low blood glucose levels
-pancreas secretes glucagon
-this causes glycogen to be converted back into glucose and released into the blood
Type 1 diabetes
-early onset
-pancreas doesn't produce a sufficient amount of insulin
-treated mainly though insulin injections but also diet and exercise
Type 2 diabetes
-usually later onset
-obesity is a risk factor
-the cells in the blood become resistant and no longer respond to insulin
-usually treated by a carbohydrate controlled diet
Loss of water urea and salt ions
-water is lost through inhalation
-water salt ions and urea are lost through sweat
-excess water ions and urea are removed by the kidneys in urine
Filtration of the kidneys
-the level of water in the body must be balanced so cells don't burst from too much ester or swell from too little
-kidneys produce urine by filtration and selective reabsorption of substances
-all glucose is selectively reabsorbed
-some water and some ions are selectively reabsorbed
-no urea is selectively reabsorbed
Negative feedback by ADH in the kidneys
-when water concentration is too high less ADH is released causing less water to be selectively reabsorbed meaning a higher volume of urine is produced that is less concentrated
-when water concentration is too low the kidneys selectively reabsorb more water causing a lower volume of urine being produced that is more concentrated
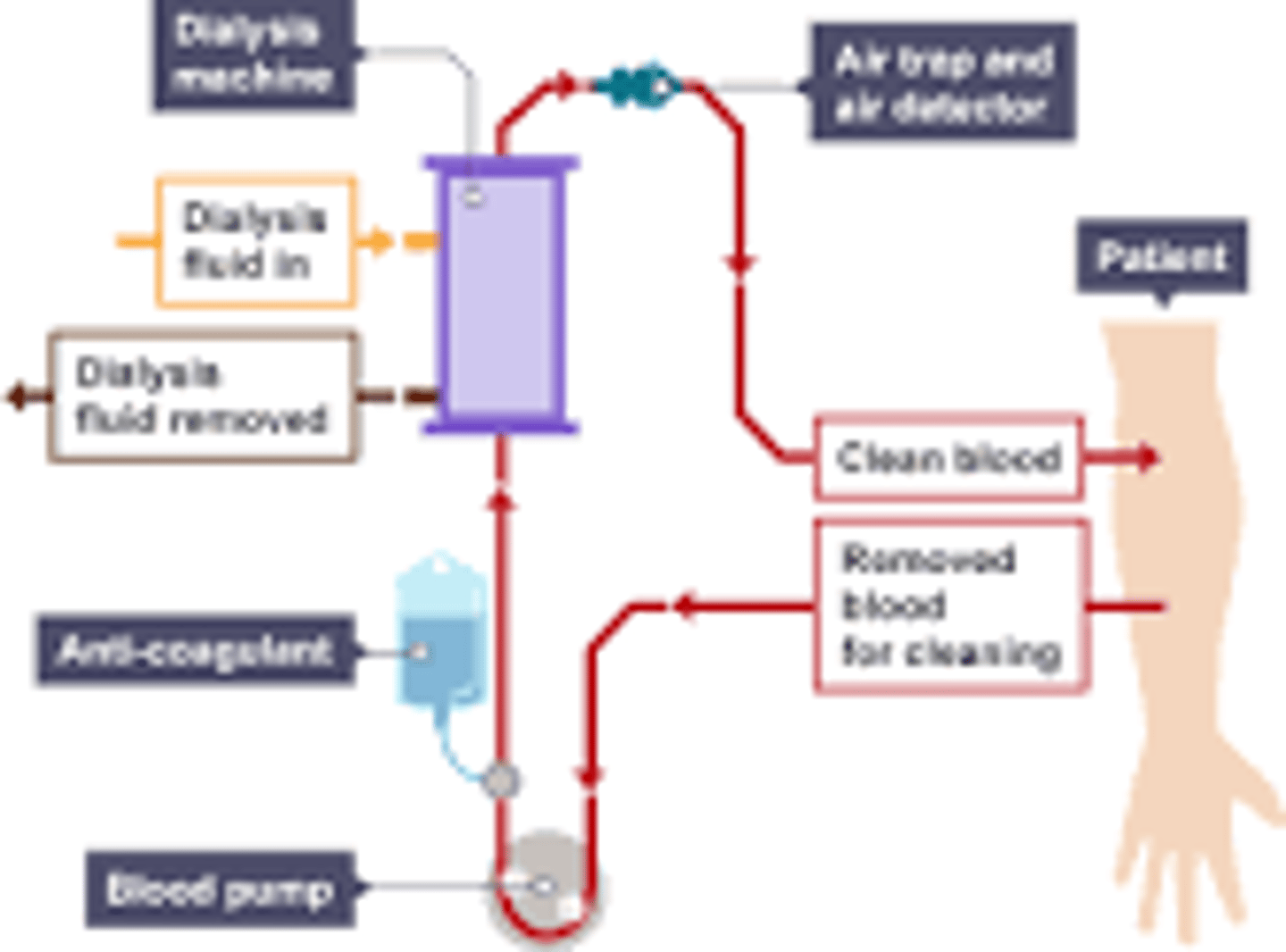
Process of kidney dialysis
-blood is temporarily removed from the patient's body and filtered through a dialysis machine
-the patients blood passes through dialysis fluid which has no urea
-urea and other waste products diffuse from a high concentration in the blood to a low concentration in the fluid
-patients blood is then returned to the body
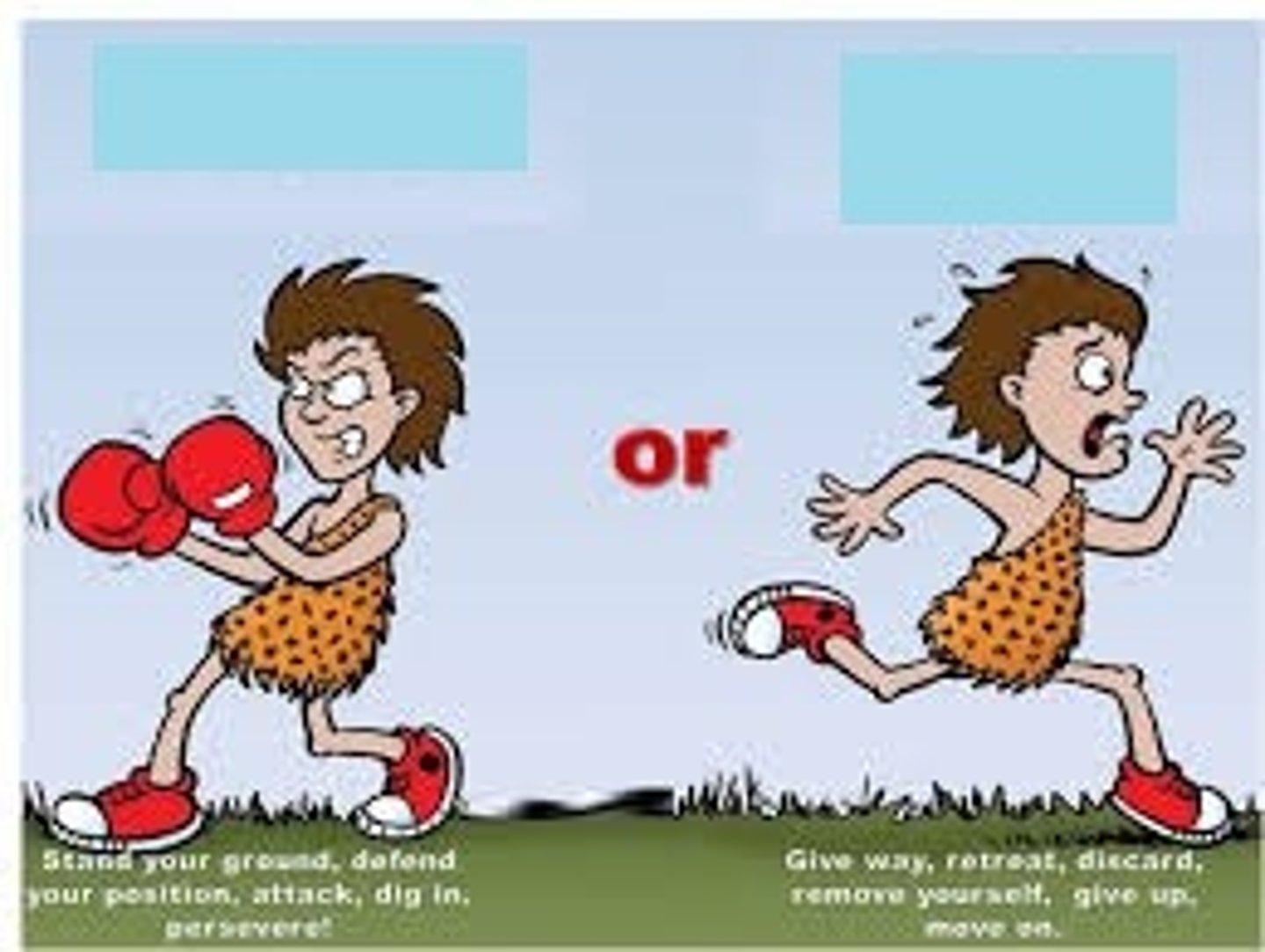
Adrenaline
-produced by the adrenal gland in fight or flight scenarios
-increases heart rate
-boosts delivery of oxygen and glucose to the brain and muscles
-not a negative feedback reaction as the adrenal glands will stop producing adrenaline

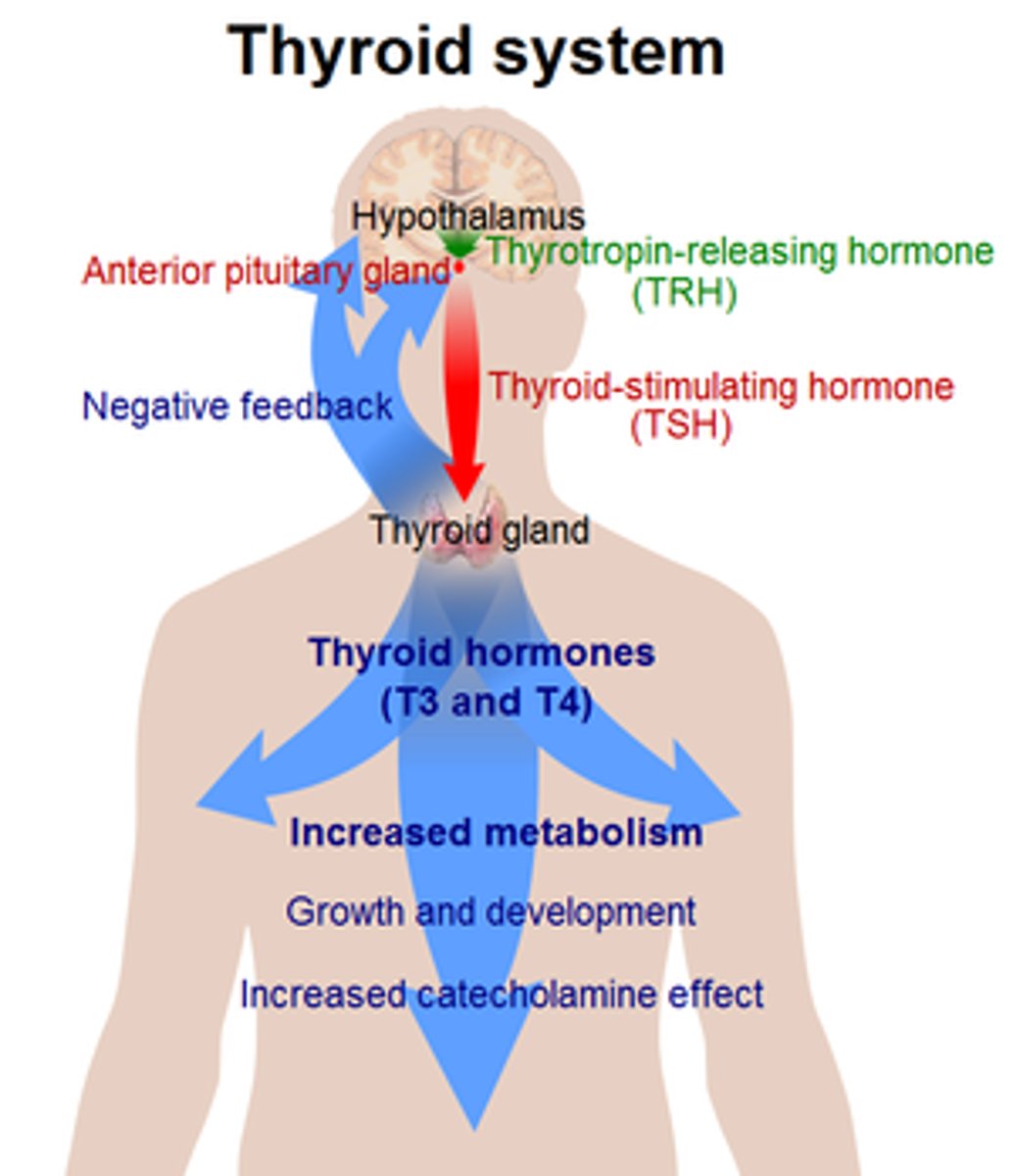
Thyroxine
-produced by the thyroid gland
-regulates how quickly uses energy and makes proteins known as regulating metabolic rate (BMR)
-controlled by negative feedback
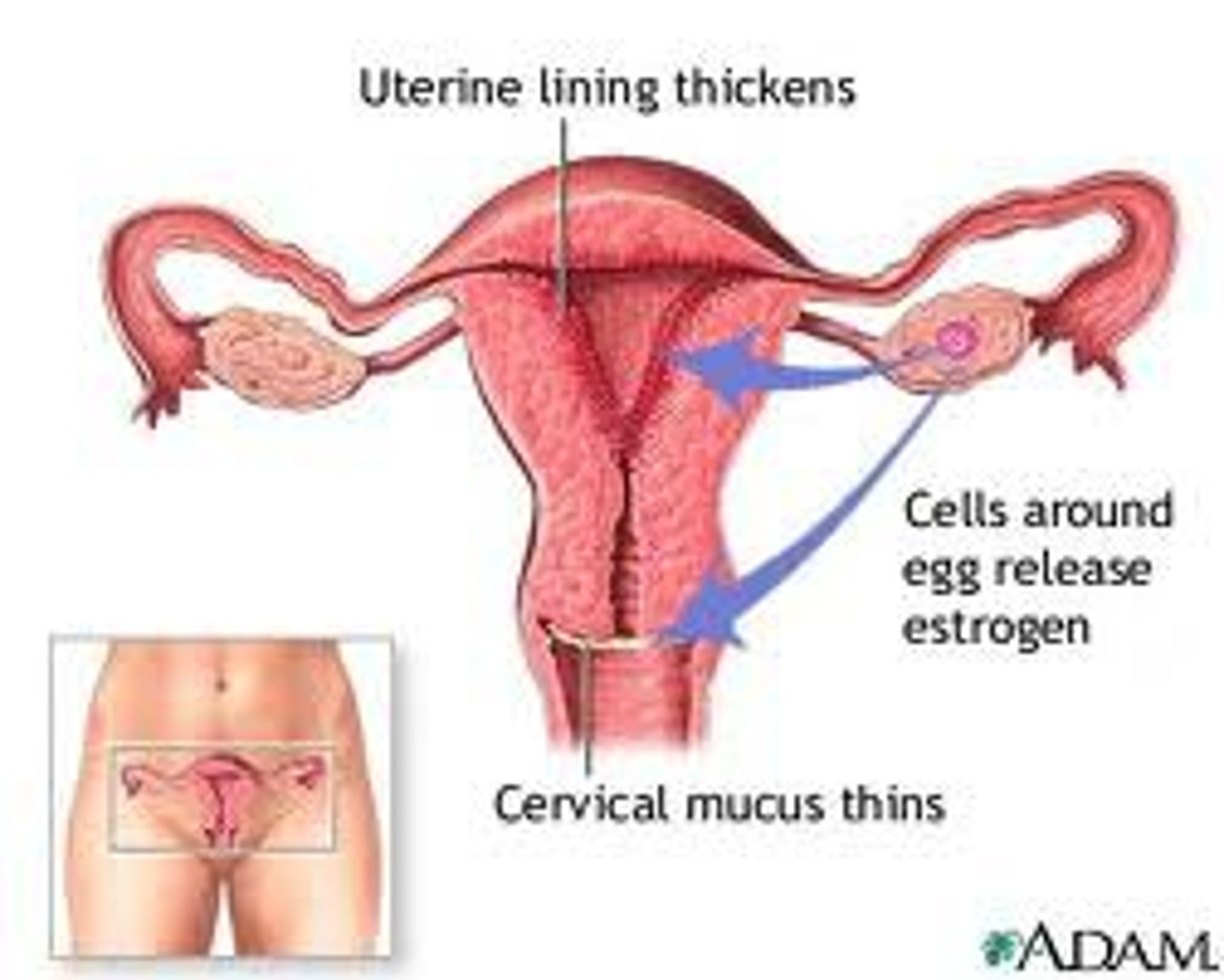
Oestrogen
-main female reproductive hormone
-produced in the ovaries
-eggs begin to mature at puberty and are released once every 28 days
Testerone
-main male reproductive hormone
-produced by the testes
-stimulates sperm production
Menstrual cycle
-FSH is released by the pituitary gland which causes eggs to mature in the ovaries and stimulates the ovaries to produce oestrogen
-LH is produced by the pituitary gland which stimulates ovulation of the mature egg
-oestrogen is produced by the ovaries which causes the uterus lining to thicken inhibits FSH production and stimulates LH production
-progesterone is produced by the ovaries which maintains the uterus lining and inhibits FSH and LH production
Hormonal contraception
-oral contraceptives contain hormones to inhibit FSH production so no eggs can mature
-injections, implants or skin patches slow the release of progesterone to inhibit maturation and release of eggs
Non-hormonal methods of contraception
-barrier contraceptives such as condoms and diaphragms that prevent sperm to reach the egg
-IUD coils prevent implantation of an embryo or release hormones such
-spermicide agents kill or disable sperm
-abstaining from sex when an egg may be in the oviduct
-surgical methods of male and female sterilisation
IVF treatment
1 - mother is given FSH and LH to stimulate the maturation of several eggs
2 - the eggs are collected from the mother and are fertilised by sperm from the father in a laboratory
3 - the fertilised eggs develop into embryos
4 - one or two embryos are inserted into the mother's uterus when the embryos are tiny
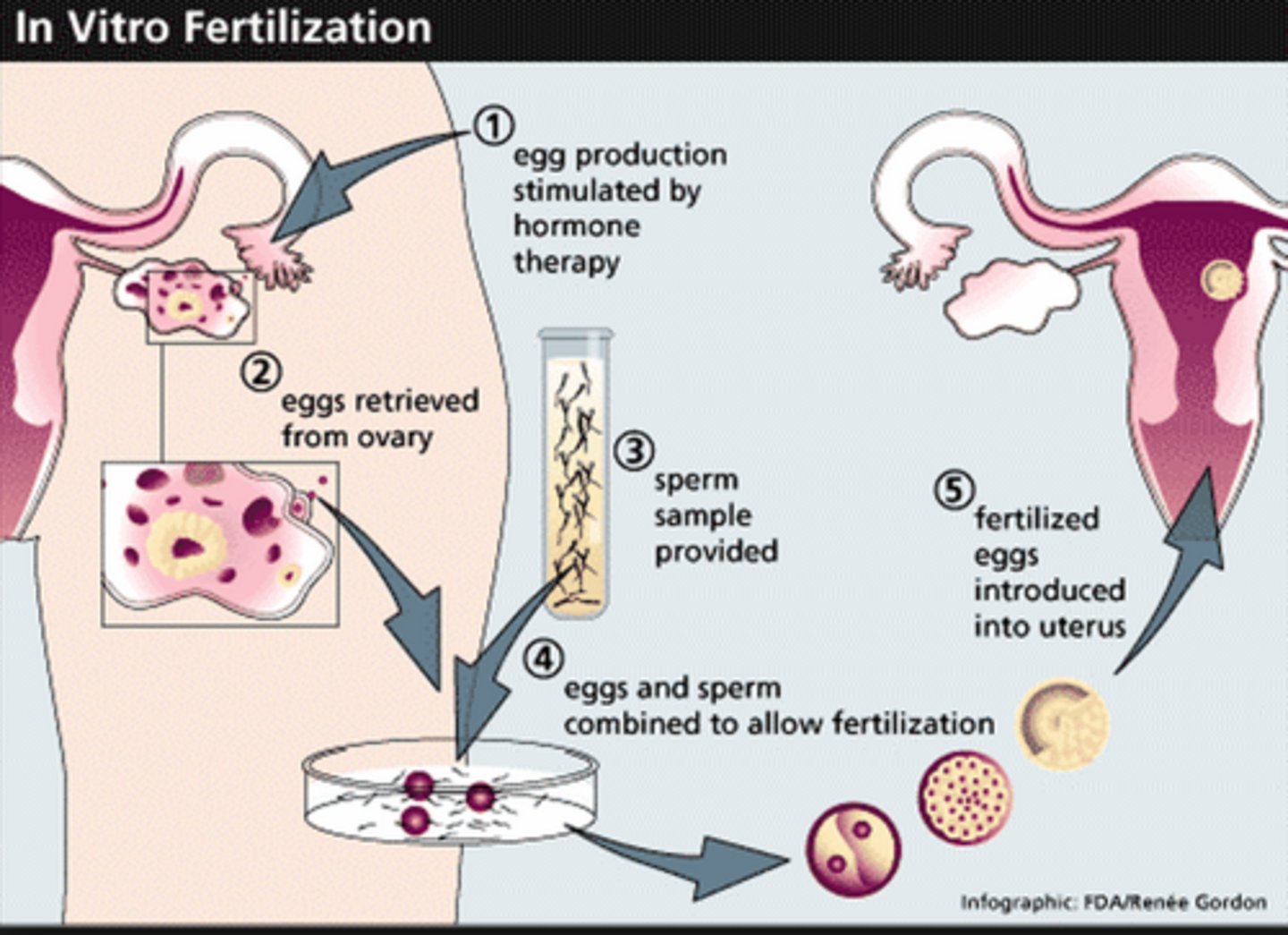
Disadvantages of IVF
-emotionally and physically stressfully
-it has a low success rate
-can lead to multiple births putting both the mother and babies at risk
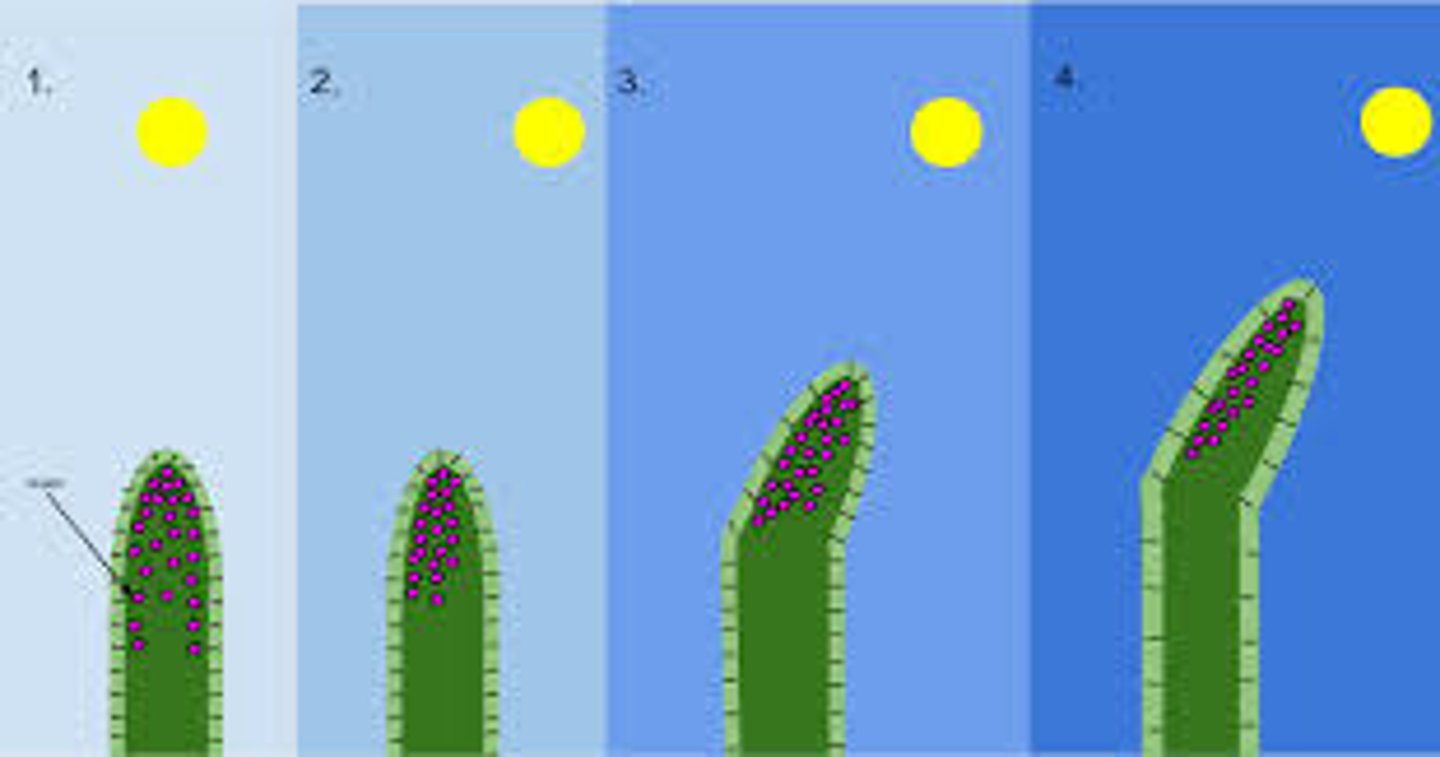
Plant hormones
-plants produce hormones to coordinate and control growth
-phototropism is the growth of plants in response to light
-geotropism is the growth of plants in response to gravity
Auxins
-stimulate growth in shoots and inhibit growth in roots
-used as weedkillers, rooting powder and promoting growth in tissue cultures
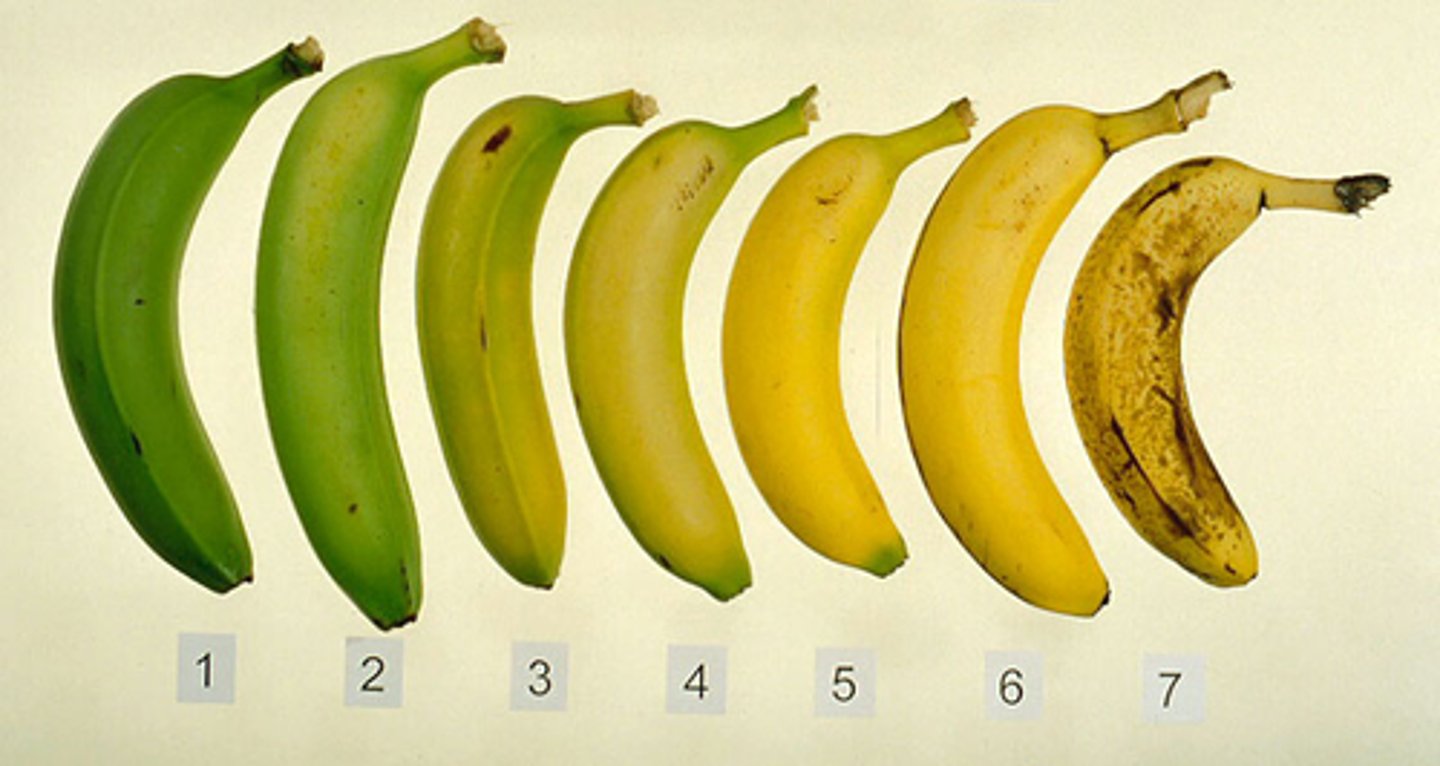
Ethene
-acts as a hormone to control cell division
-used to control ripening of fruit during storage and transport

Gibberellins
-regulates developmental processes
-used to end seed dormancy promote flowering and to increase fruit sizes
