PC3 Module 5.4 (medchem)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
A. contact activation pathway
What pathway leading to coagulation is this describing?
- intrinsic
- used for maintenance of homeostasis
- its initiation involves the sequential activation of factors FXII, FXI, and FIX
A. contact activation pathway
B. tissue factor pathway
B. tissue factor pathway
What pathway leading to coagulation is this describing?
- extrinsic
- caused by trauma
- TF glycoprotein is a major initiating factor of arterial thrombogenesis
A. contact activation pathway
B. tissue factor pathway
A. coumarin derivatives
This is the pharmacophore for what drug class?
A. coumarin derivatives
B. heparin
C. Hiruden
D. argatroban
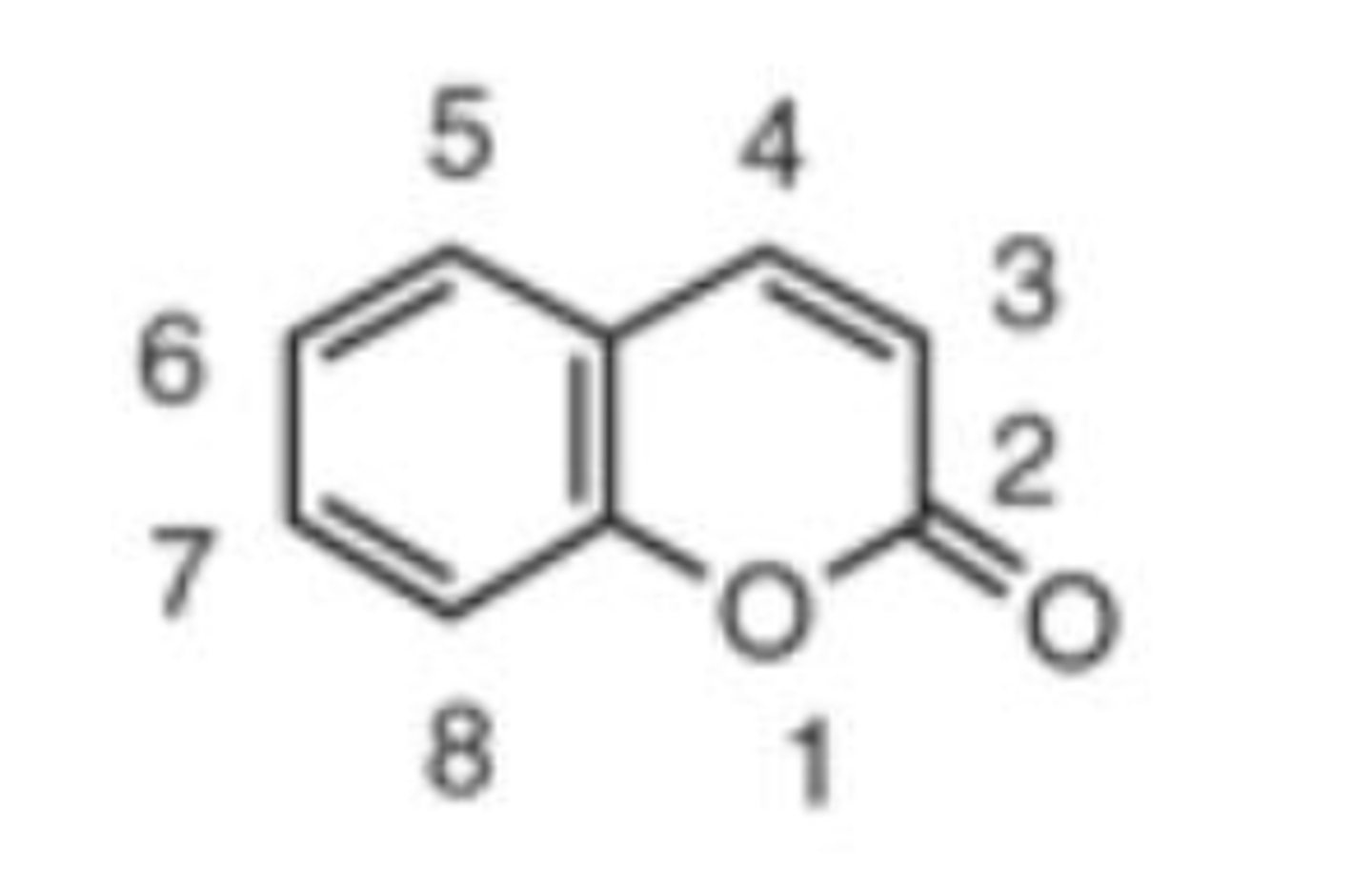
A. coumarin derivatives
This is the MOA of what drug class?
- y-glutamyl carboxylase converts glutamic acid of factors II, VII, IX, and X to Gla (y-carboxyglutamic acid) which chelates Ca2+ to activate these factors
- KH2 is an essential cofactor of GGCX and is oxidized to vitamin K epoxide
- VKOR (vitamin K reductase) converts KO to vitamin K and further to KH2
A. coumarin derivatives
B. heparin
C. Hiruden
D. argatroban
B. KH2
In the MOA of coumarin derivatives, _____________ is an essential cofactor of GGCX and is oxidized to vitamin K epoxide
A. O2
B. KH2
C. NH2
D. BOH
B. water insoluble
All of the coumarin derivatives are ____________________ lactones
A. water soluble
B. water insoluble
C. salt
D. 4-OH
The ___________________ on coumarins makes the drugs weakly acidic, allowing formation of water soluble sodium salts
A. 1-OH
B. 2-OH
C. 3-OH
D. 4-OH
A. S/R
_____________ warfarin is 4-fold more potent than ______ warfarin
A. S/R
B. R/S
C. thrombin
____________ is a serine protease that converts soluble fibrinogen into insoluble strands of fibrin, as well as catalyzing many other coagulation related reactions. It is the central effector of coagulation and amplifies its own production; it is a natural target for pharmacologic intervention
A. plasmin
B. factor xa
C. thrombin
D. thromboxane
B. heparin
__________ is composed of a heterogenous mixture of straight-chain, sulfated, and negatively charged polysaccharides of a molecular weight range of 5-30 kd.
A. coumarin derivatives
B. heparin
C. Hiruden
D. argatroban
salt
under physiological conditions, heparin exists primarily as polysulfate anions, and therefore, usually is adminstered as a ________
A. high molecular weight heparin
_____________ contains mucopolysaccharides
A. high molecular weight heparin
B. low molecular weight heparin
C. fondaparinux
B. low molecular weight heparin
_____________ typically are isolated as fractions from heparin; more selective and have more favorable pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles
A. high molecular weight heparin
B. low molecular weight heparin
C. fondaparinux
C. fondaparinux
_____________ is a synthetic, highly sulfonated pentasaccharide. It has improved pharmacokinetics and a more selective anticoagulant action
A. high molecular weight heparin
B. low molecular weight heparin
C. fondaparinux
B. heparin
MOA of what drug:
- antithrombin III inhibits clotting factor proteases, thrombin, IXa, Xa, XIa, and XIIa by forming stable complexes
- by binding to ATIII it causes a conformational change which enhances the action of ATIII by 2000 fold
A. coumarin derivatives
B. heparin
C. Hiruden
D. argatroban
B. low molecular weight heparin
__________ predominantly inhibits factor Xa
A. high molecular weight heparin
B. low molecular weight heparin
C. fondaparinux
B. fibrin
Thrombin contains 3 binding sites: E1, E2, and the active site. What binds to E1?
A. thrombinogen
B. fibrin
C. heparin
C. heparin
Thrombin contains 3 binding sites: E1, E2, and the active site. What binds to E2?
A. thrombinogen
B. fibrin
C. heparin
C. active site
Thrombin contains 3 binding sites: E1, E2, and the active site. What binds to E2? Where do univalent DTIs bind?
A. E1
B. E2
C. active site
A. E1
C. active site
Thrombin contains 3 binding sites: E1, E2, and the active site. What binds to E2? Where do bivalent DTIs bind?
A. E1
B. E2
C. active site
univalent
Is this drug a univalent or a bivalent DTI?
- argatroban
univalent
Is this drug a univalent or a bivalent DTI?
- dabigatran
bivalent
Is this drug a univalent or a bivalent DTI?
- lepirudin
bivalent
Is this drug a univalent or a bivalent DTI?
- bivalirudin
C. Hiruden
_______________ forms 1:1 complex with the thrombin and inhibits its activity; the binding is ionic interaction at its highly anionic C terminus
A. coumarin derivatives
B. heparin
C. Hiruden
D. argatroban
C. Hiruden
_______________ and its derivatives bind and inactivate both free thrombin and thrombin bound to fibrin
A. coumarin derivatives
B. heparin
C. Hiruden
D. argatroban
B. heparin
unlike ___________, DTIs bind directly and reversibly to the active site of thrombin (do not require an activated ATIII as a cofactor for their anticoagulant therapy)
A. coumarin derivatives
B. heparin
C. Hiruden
D. argatroban
A. lepirudin
B. desirudin
What drug: (select all)
- bivalent DTI
- bind to both the active site and the E1 site of thrombin
- nearly irreversible inhibition of thrombin
- inhibit both free thrombin and thrombin bound to fibrin
A. lepirudin
B. desirudin
C. dabigatran
D. argatroban
D. argatroban
What drug?
A. lepirudin
B. desirudin
C. dabigatran
D. argatroban
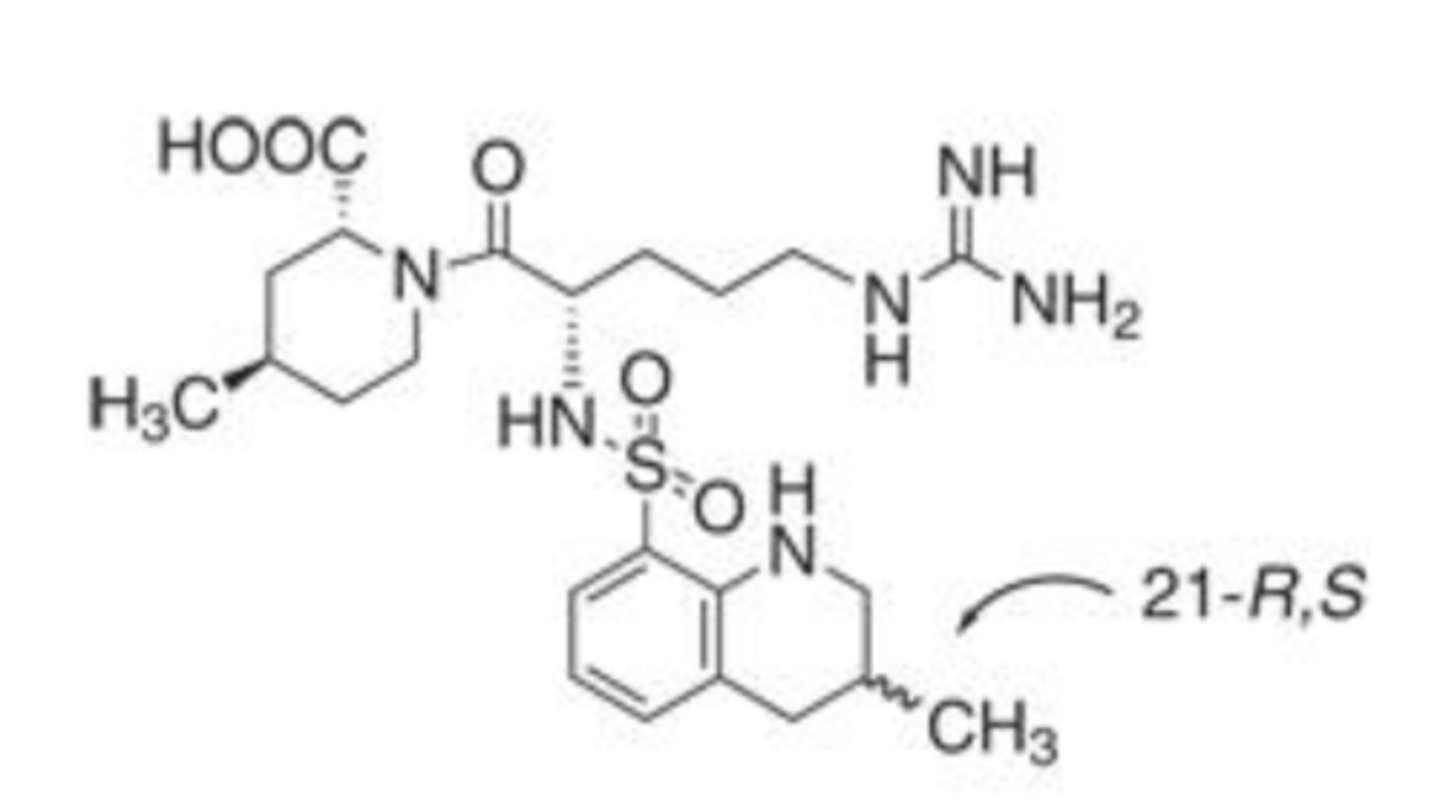
D. argatroban
What drug?
- peptidomimetic that binds selectively to the catalytic site of thrombin
- univalent competitive DTI
- reversible inhibitor of both free thrombin and clot bound thrombin
A. lepirudin
B. desirudin
C. dabigatran
D. argatroban
C. dabigatran
What drug is this?
A. lepirudin
B. desirudin
C. dabigatran
D. argatroban
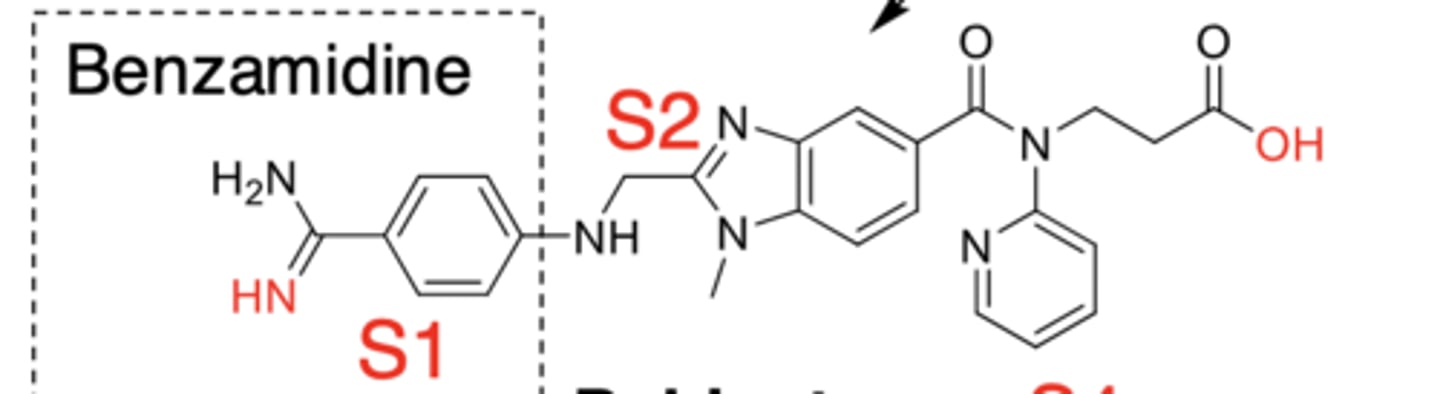
C. dabigatran
What drug?
- nonpeptidomimetic prodrug
- reversible, basic benzamidine based DTI
- binds to S1, S2, and partially to S4 sites
A. lepirudin
B. desirudin
C. dabigatran
D. argatroban
A. aspirin
What drug?
A. aspirin
B. triflusal
C. heparin
D. warfarin
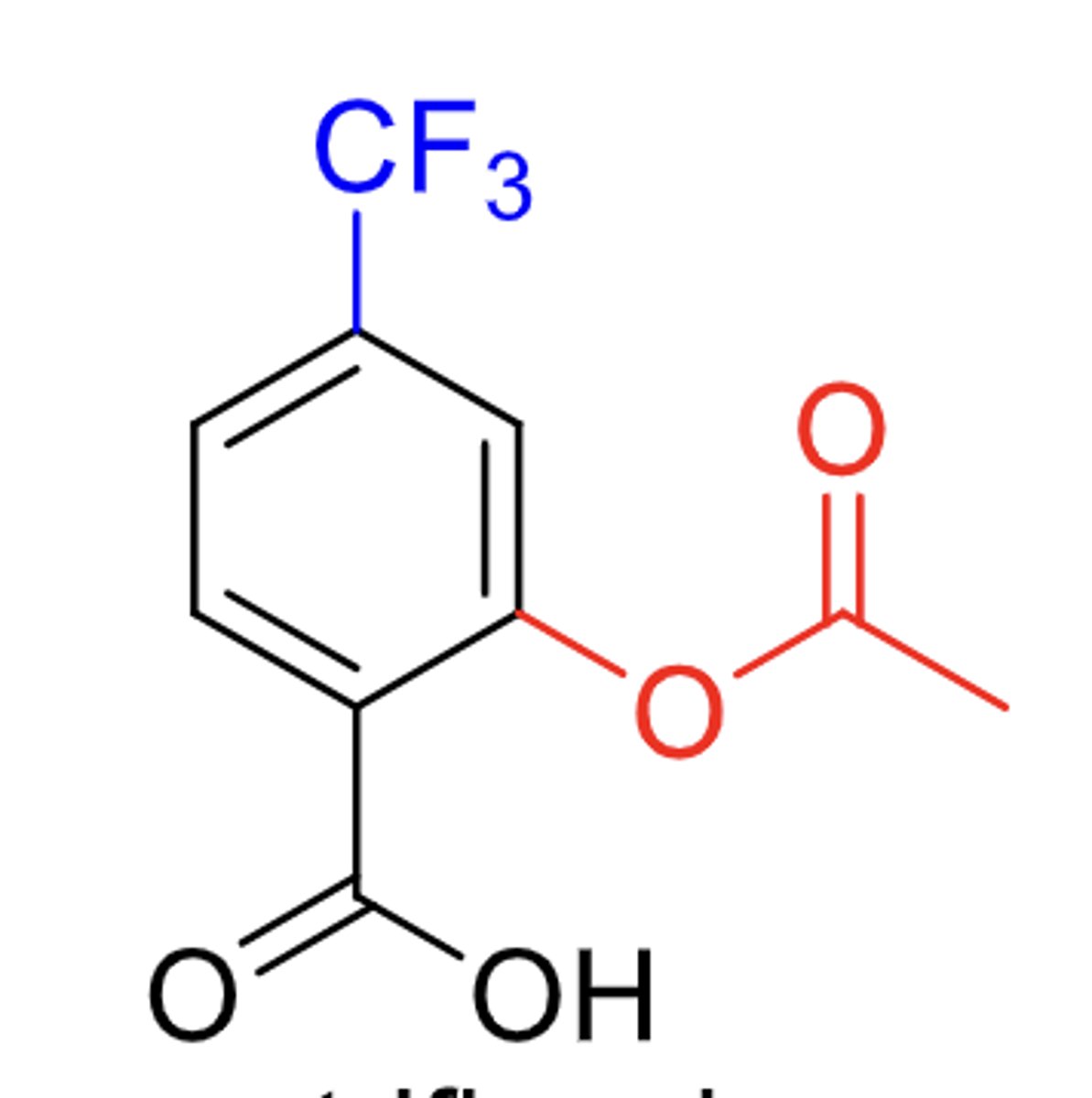
B. triflusal
What drug?
A. aspirin
B. triflusal
C. heparin
D. warfarin
COX-1 inhibitors
What drug class?
- thromboxane A2 is a labile platelet aggregation inducer. inhibition of its production effectively blocks platelet aggregation
- inhibit COX-1, by acetylating and irreversibly deactivates platelet COX-1, and its antithrombotic effect remains for the life span of the platelet
because of the formation of a covalent bond into the binding site with the alcoholic amino acid residue, serine 529
Why do COX-1 inhibitors antithrombotic effects remain for the life span of the platelet?
A. PDE-3 inhibitor
What drug class?
- degrades cAMP to AMP in platelets and blood vessels
- selective __________________ inhibit the degradation of cAMP, thereby increasing cellular concentration of cAMP and leading to inhibition of platelet aggregation and vasodilation
A. PDE-3 inhibitor
B. P2Y12 inhibitor
C. Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor antagonist
A. PDE-3 inhibitor
What drug class?
A. PDE-3 inhibitor
B. P2Y12 inhibitor
C. Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor antagonist
B. P2Y12 inhibitor
Drug class?
ticlopidine, clopidogrel, and prasugrel are thienopyridines, which exhibit selective, irreversible inhibition of ADP-induced platelet aggregation
A. PDE-3 inhibitor
B. P2Y12 inhibitor
C. Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor antagonist
prodrugs
thienopyridines are __________. Ticlopidine and clopidogrel require CYP450 for their activation. P450 isoforms produces the 2-oxo derivative, which in turn is hydrolyzed to the thiol. Prasugrel's activation requires esterases
D. thiol
the ___________ binds irreversibly to P2Y12 by forming a disulfide bridge to a cysteine in P2Y12, therefore blocking the binding of the agonist
A. alcohol
B. flourine
C. chlorine
D. thiol
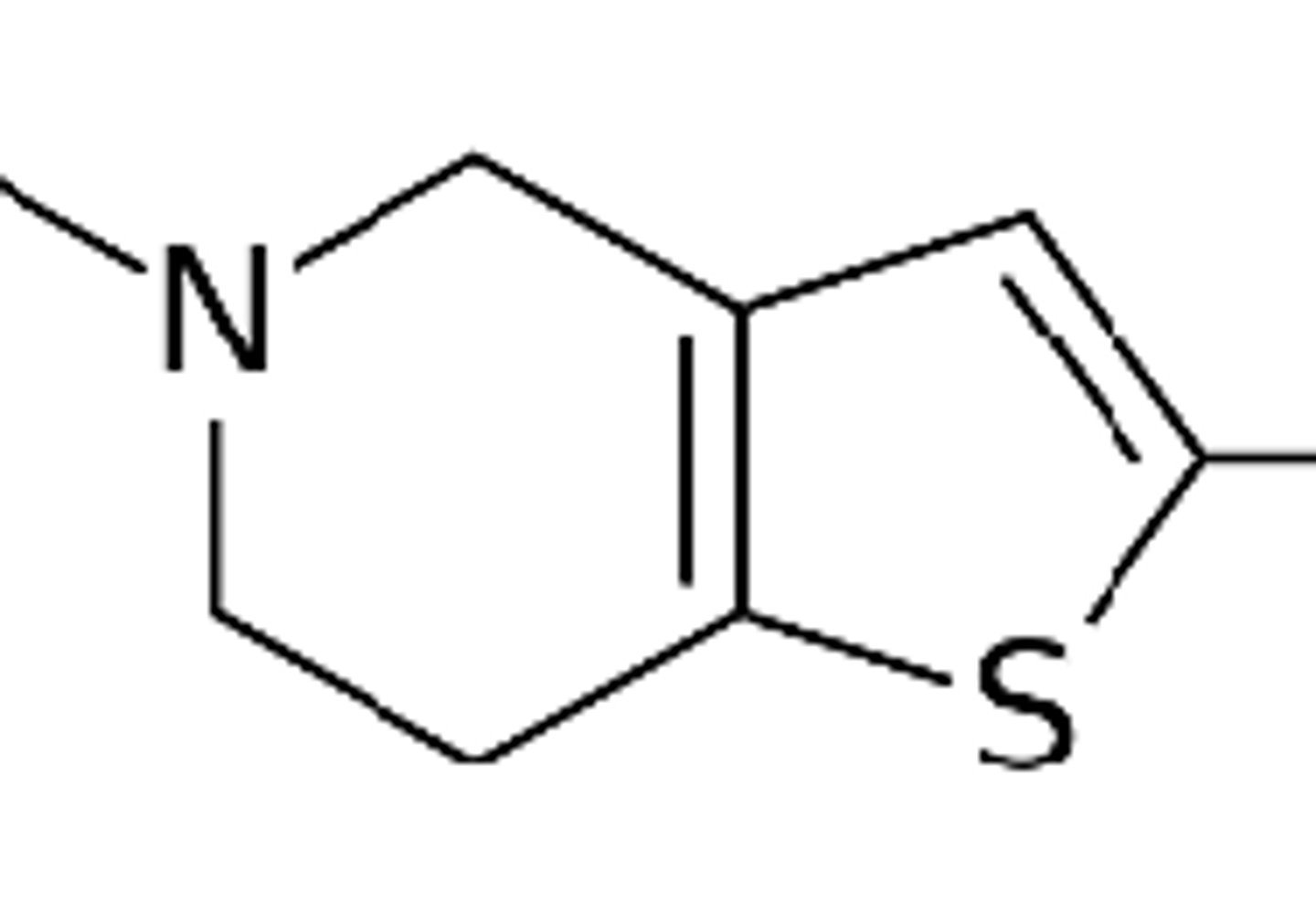
thienopyridine P2Y12 inhibitors
pharmacophore of what drug
A. ticagrelor
D. cangrelor
What two drugs are reversible inhibitors of P2Y12?
A. ticagrelor
B. prasugrel
C. clopidogrel
D. cangrelor
B. P2Y12 inhibitor
MOA of what drug class:
- ADP binding to the P2Y12 receptor results in conformational change and G-protein activation
- irreversible binding of the clopidogrel active metabolite to the P2Y12 receptor prevents the ADP binding
A. PDE-3 inhibitor
B. P2Y12 inhibitor
C. Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor antagonist
A. ticagrelor
____________ binds reversibly to P2Y12 at a site distinct from the ADP binding site and inhibits ADP signaling and receptor conformational change by locking the receptor in an inactive state; ADP can still bind at its binding site
A. ticagrelor
B. prasugrel
C. clopidogrel
D. RGD
For glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor antagonists, what amino acid sequence is important for their function?
A. KDR
B. GDR
C. DKG
D. RGD
thrombolytic drugs
What drug class
- plasmin is a relatively nonspecific protease that can digest newly formed blood clots
- the fibrinolytically active plasmin is produced from the circulating inactive proenzyme plasminogen by a group of trypsin-like serine proteases. the principal activator is tissue type plasminogen activator tPA
- plasmin activity is regulated by tPA inhibitors 1 and 2
- ____________ are plasminogen activator mimics
A. alteplase
What drug:
- unmodified human tPA
- fibrin specific agent
A. alteplase
B. reteplase
C. tenecteplase
B. reteplase
What drug:
- recombinant deletion mutant of tPA
- has reduced fibrin selectivity but has a longer half life
A. alteplase
B. reteplase
C. tenecteplase
C. tenecteplase
What drug:
- three mutations T103N, N117Q, KHRR296-299AAAA
- mutations result in a prolonged half life
- change the binding to PAI-1 by 80 fold, thus improving activity.
- 15 fold higher fibrin specificity
A. alteplase
B. reteplase
C. tenecteplase