Tour Of The Cell ch 6.
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
159 Terms
magnification
makes an object look bigger
resolution
how clear an object is
relationship btwn magnification and resolution
as magnification increases, resolution decreases
contrast
accentuation of differences in parts of the object
how can you see contrast easier
staining
microscope development has focused on improving magnification and resolution via...
- Beller glass
- quartz lenses used w uv light and camera
- electron microscopy
electron microscopy
uses electrons instead of light, the shorter wavelength of electrons gives greater resolution
galileo galilei + microscope
1600s: arranged 2 glass lenses to form primitive microscope
robert hooke + microscope
1665: viewed cells in mediterranean oak bark using microscope and called them "cellulae"
Antoni van Leeuwenhoek + microscope
viewed drops of water and called protists animalcules
schiden and shwaann
cell theory w microscope
abbe and zeiss + microscope
1900: first perfect microscope--> first to resolve many organelles including mitochondria and chloroplasts
- today's scopes are abt the same
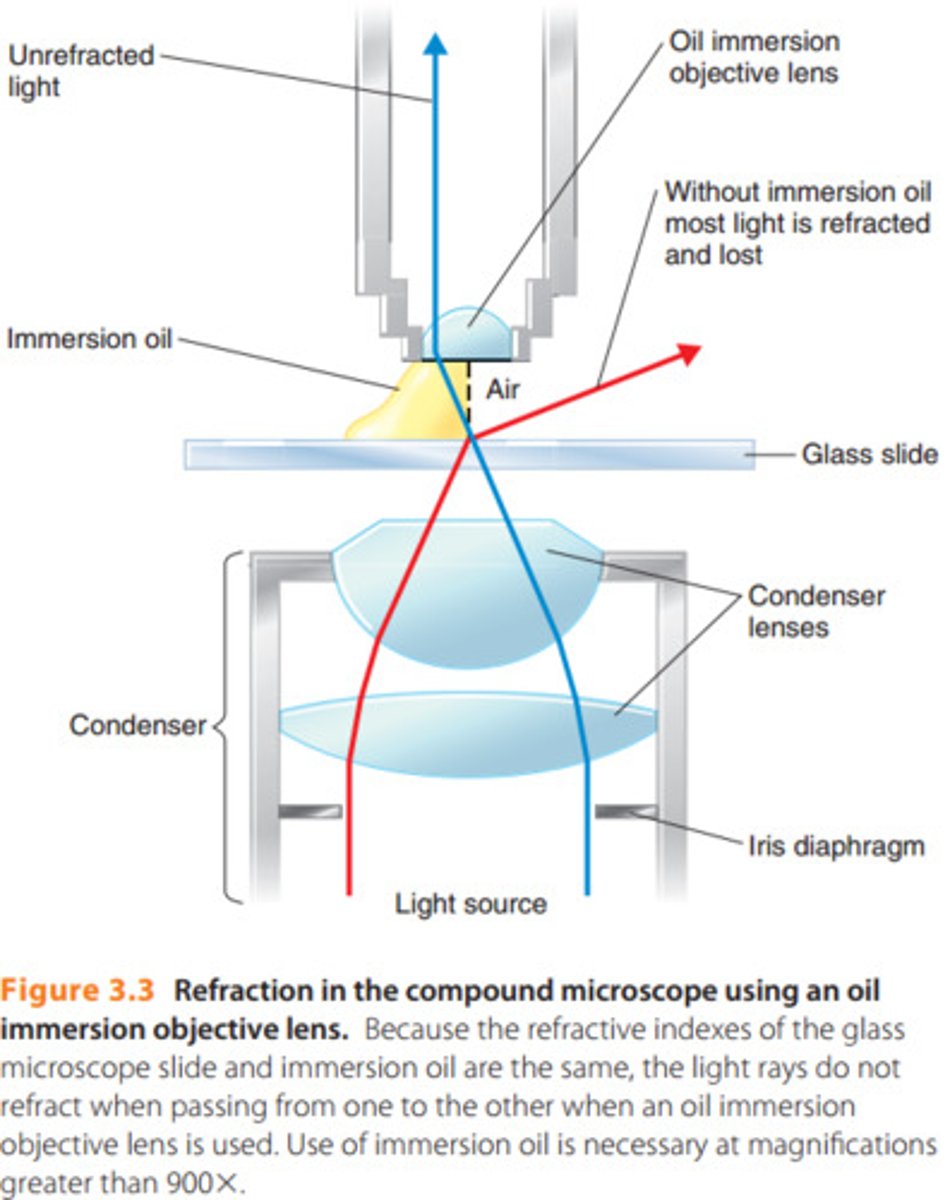
why is oil immersion needed for 1000x microscope lenses?
oil has higher refraction index than air so gathers more light--> higher resolution
electron microscope
1930s: originally developed in germany
- used e- beam as opposed to light to view images, specimen coated with gold to conduct electricity
what was a disadvantage of the electron microscope
cells viewed are dead since it would have to be frozen to view under the electron microscope--> can't unfreeze specimen
2 types of modern microscopes
scanning e- microscope and transmission e- microscope
scanning e- microscope (SEM)
runs a beam of e- across the surface of a specimen; 3 dimensional images
transmission e- microscope
you see the inside of the specimen so you can study the internal parts
functions of cell membranes
-Keep damaging materials out of the cell
-Allow entry of materials needed by the cell
-sending/receiving chemical messages from other cells
importance of surface area to volume ratio in cells
if the ratio is too low, there is not enough cell membrane and the cell cannot carry on its normal metabolic functions efficiently enough to survive
the larger the cell, the _____ (lower/higher) the surface area:volume ratio
the larger the cell, the lower/higher the surface area: volume ratio
how do larger cells increase their surface area
they're elongated or folded
all cells have
plasma membrane, cytosol, chromosomes, ribosomes
cytosol
semi-fluid portion of the cytoplasm
what are chromosomes composed of?
DNA and protein
function of ribosomes
protein synthesis
do prokaryotic cells have a nucleus
no, dna is not bound by a membrane
Nucleoid
A non-membrane-bounded region in a prokaryotic cell where the DNA is concentrated.
structure of DNA in prokaryotic cells
short, circular and not associated with proteins
do prokaryotic cells have membrane bound organelles
no
importance of cytoplasm in prokaryotic cells
cytoplasm contains all structures needed for life
are prokaryotes unicellular or multicellular
unicellular
why do most prokaryotic cells have a cell wall
for shape and protection
what are the 2 domains of prokaryotes
Bacteria and Archaea
where is the DNA enclosed in eukaryotic cells
nucleus
Do eukaryotic cells have membrane bound organelles?
yes
organelles
internal membrane-bound compartments for specialized functions
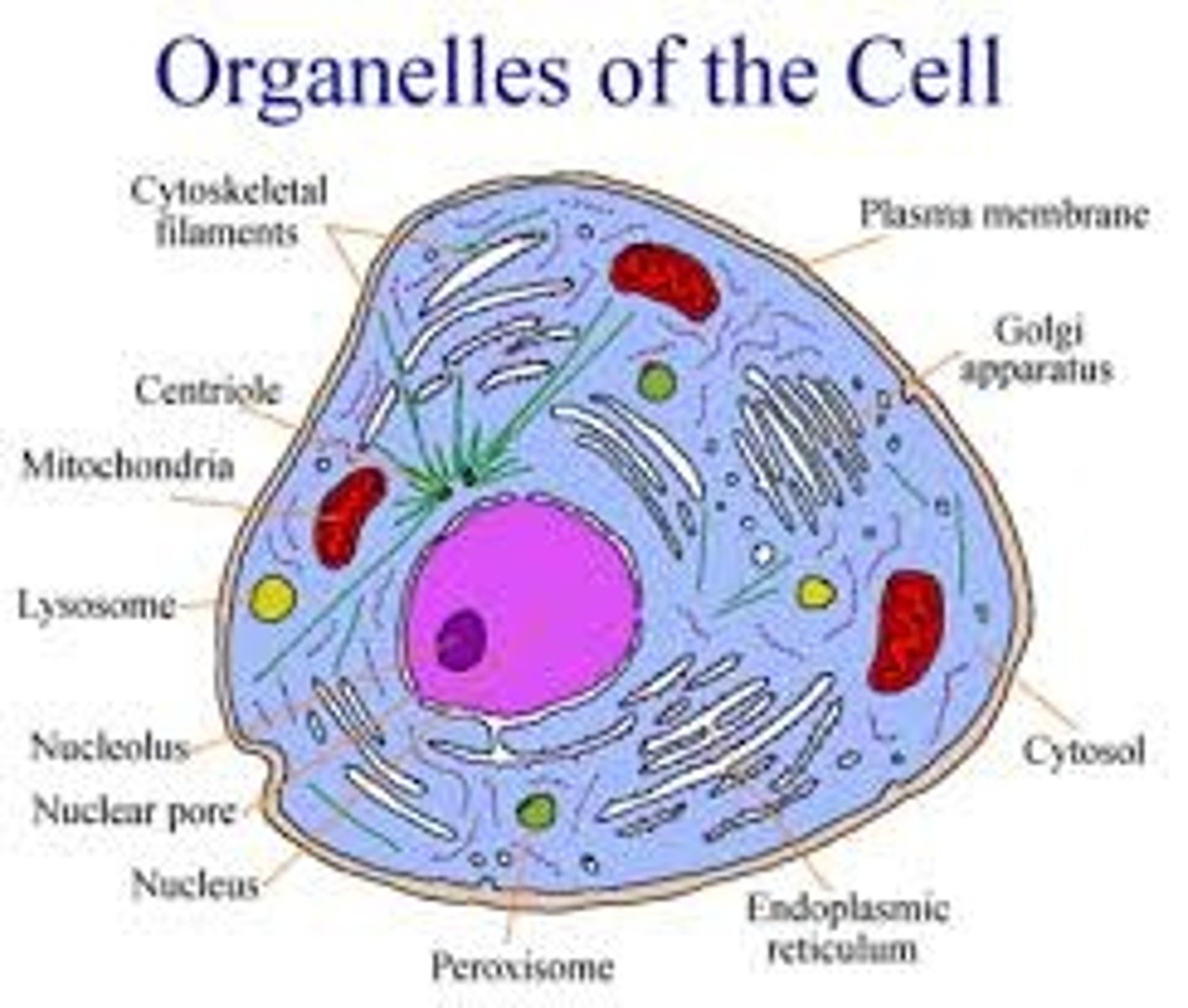
Why is compartmentalization important?
breaks up work amongst organelles keeping things more organized; allows many reactions to proceed simultaneously in a very small space
_____ and _____ cells contain many of the same organelles
plant and animal
plasma membrane
A selectively-permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of the cells
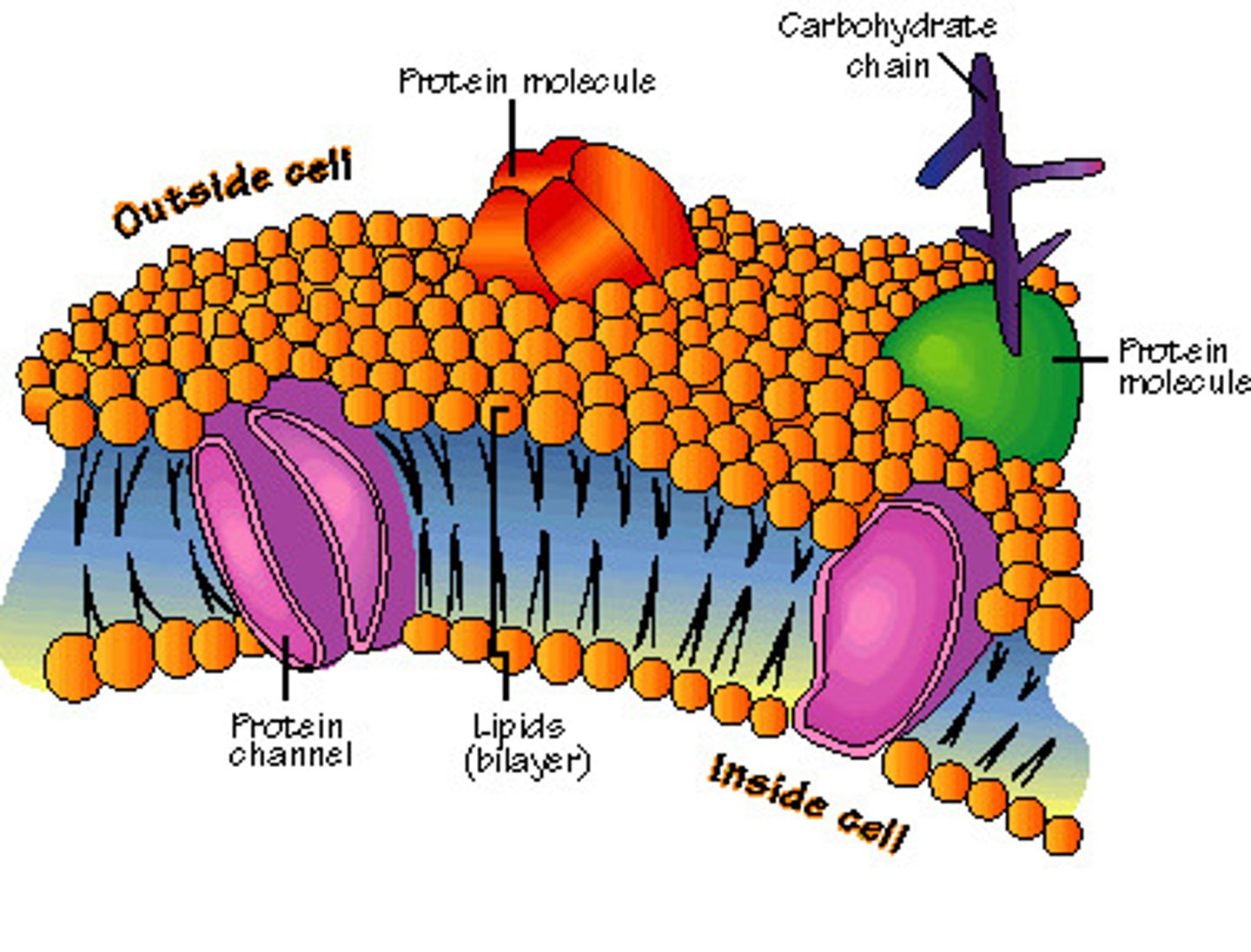
functions of plasma membrane
- separates cell from outside
- regulates the flow of materials in and out of the cell
- allows interaction with other cells through receptors and signaling molecules
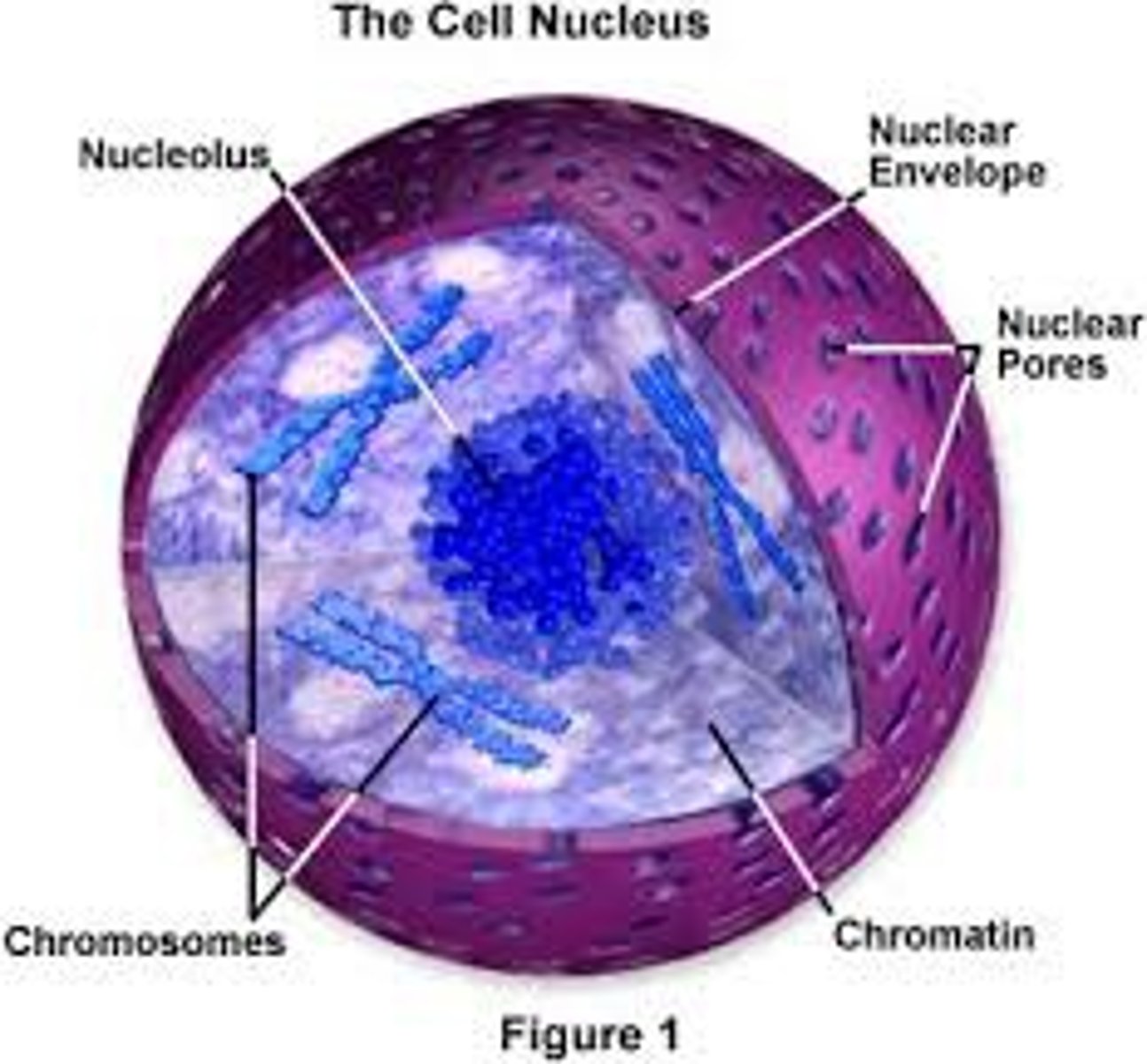
chromatin
loosely wound DNA and associated proteins inside nucleus
chromosomes
distinct unit of DNA and proteins
metaphase chromosome
dna tightly coiled around histone proteins
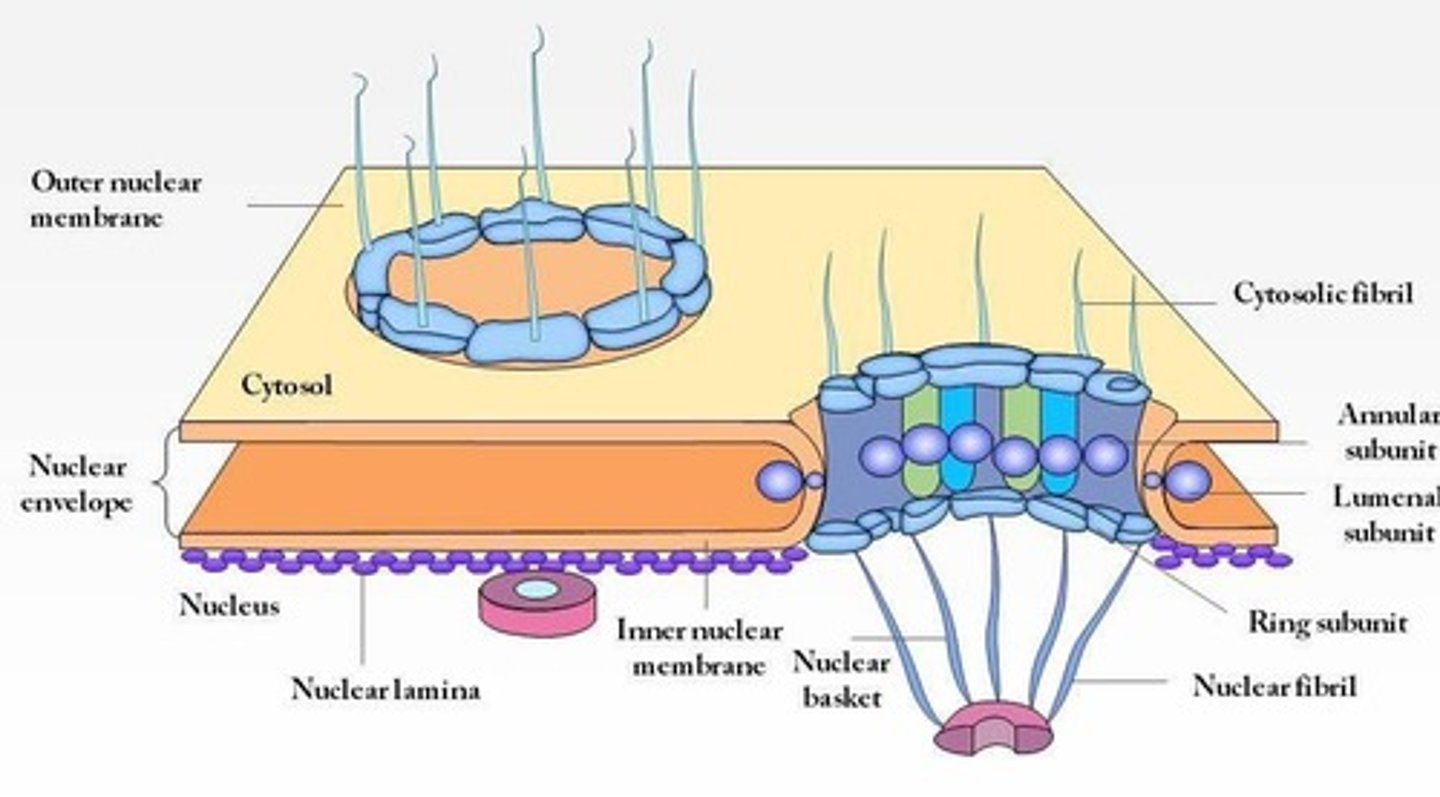
nuclear envelope
seperates nuclear material from cytoplasm
structure of nuclear envelope
2 lipid bilayers with small nuclear pores
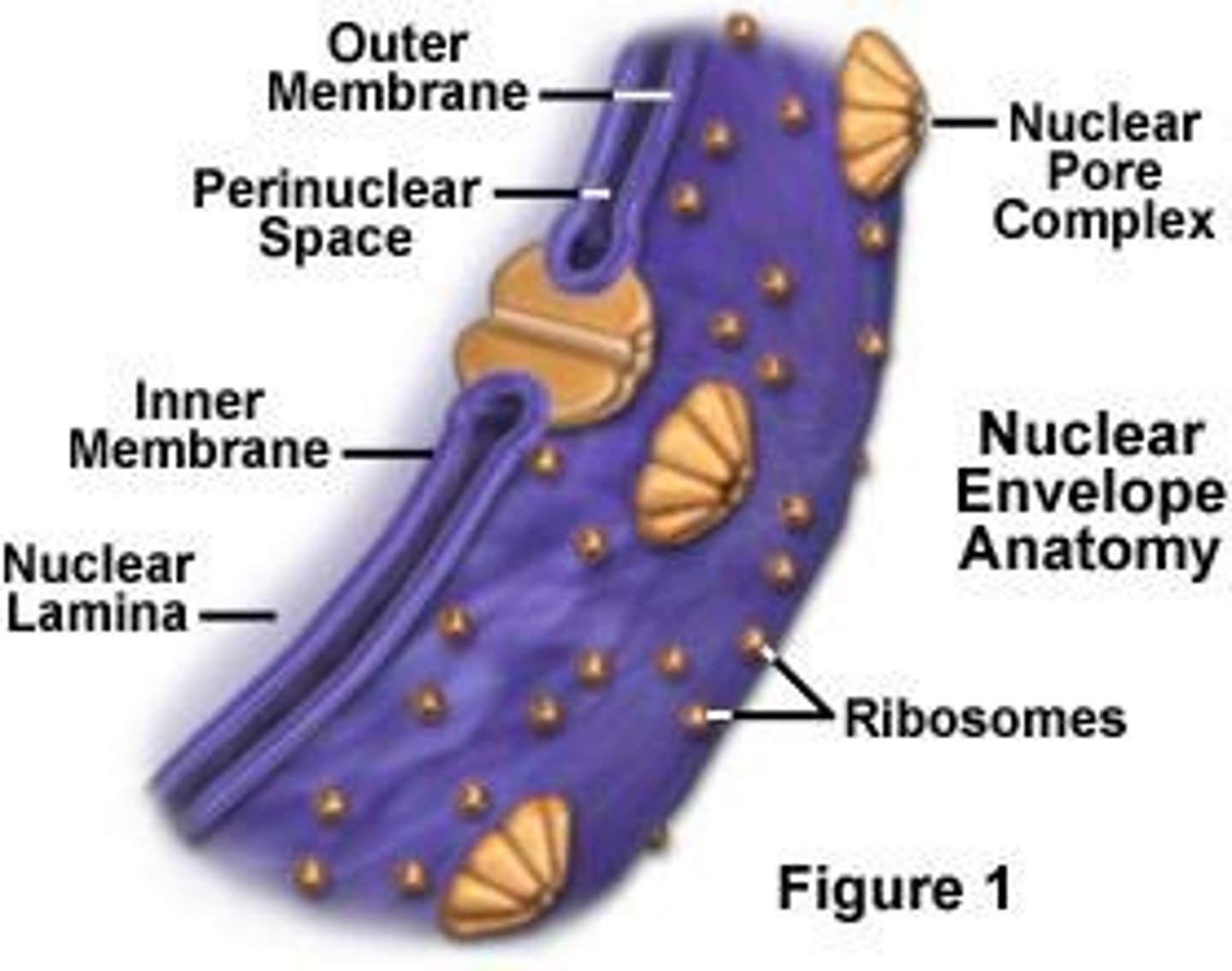
function of nuclear envelope
- let water and small molecules pass through freely
- regulate movement of large molecules like protein+RNA
pore complexes
line the nuclear envelope; regulate information flow between the nucleus and cytoplasm
Where is the nucleolus found?
inside the nucleus
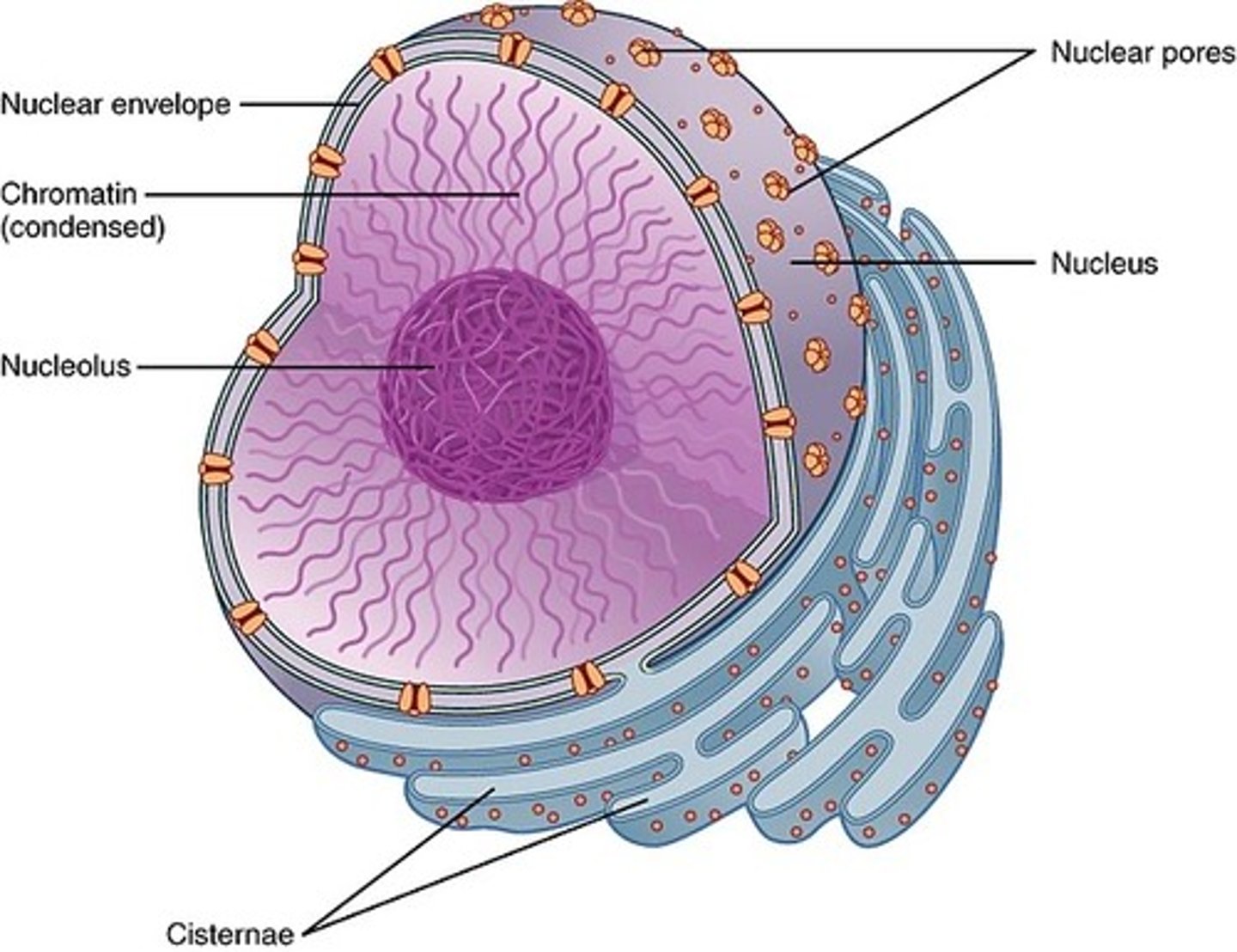
how many nucleolus are there in a cell
can be one or more per nucleus
what is the nucleolus made of
ribosomal RNA, proteins, ribosomes, and DNA
function of nucleolus
site of rRNA synthesis and assembly of ribosomal subunits
nucleoplasm
soluble (aqueous) part of the nucleus
ribosomes
small particles of rRNA and proteins involved in protein synthesis
how can any ribosome be used to synthesize any protein
The same ribosome can move from one mRNA to another, producing different proteins depending on the mRNA sequence it reads.
Ribosomes are like a factory machine.
mRNA is like the instruction manual.
tRNAs bring parts (amino acids).
The ribosome assembles the protein by reading the instructions.
where can ribosomes be found
cytoplasm and rough ER
are the ribosomes in the cytoplasm actually just free
no; they're attached to the cytoskeleton
endoplasmic reticulum
series of interconnected membrane enclosed tubes and sacs in the cytoplasm
how is the ER connected to the nucleus
one of the nuclear pores open up into the ER
what makes the rough er rough
ribosomes
how are proteins transported through er
Ribosomes attached to the RER synthesize proteins destined for:
- Secretion (export out of the cell)
- Insertion into the plasma membrane
- Use in lysosomes or organelles
As the protein is synthesized, it's threaded directly into the lumen (inside) of the RER through a pore in the RER membrane.
This is called co-translational translocation—the protein enters the RER while it's still being made.
Inside the RER, the protein begins folding into its 3D shape.
Some modifications (like adding sugar groups—glycosylation) may occur here.
The protein collects in pockets or cisternae of the RER.
These pockets bud off from the RER as transport vesicles, which are small membrane-bound sacs containing the protein.
The transport vesicles move to the Golgi apparatus, where they fuse with the Golgi's cis face (the receiving side).
which ER is responsible for synthesizing lipids
smooth er
functions of smooth er
Synthesizes lipids
Metabolizes carbohydrates
Detoxifies drugs and poisons
Stores calcium ions
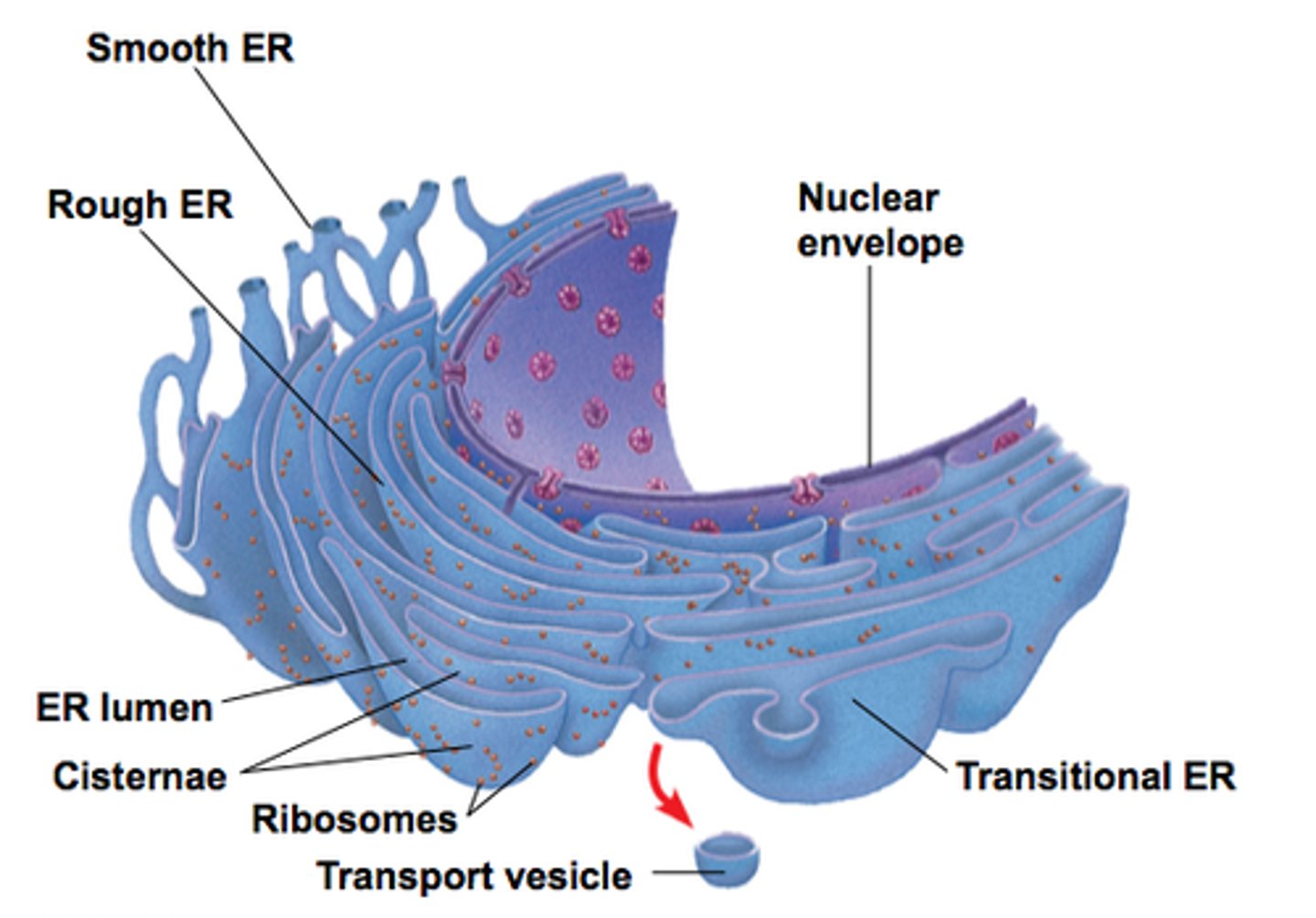
why can the ER form membranes
cuz the smooth er can make lipids and the rough er can make proteins
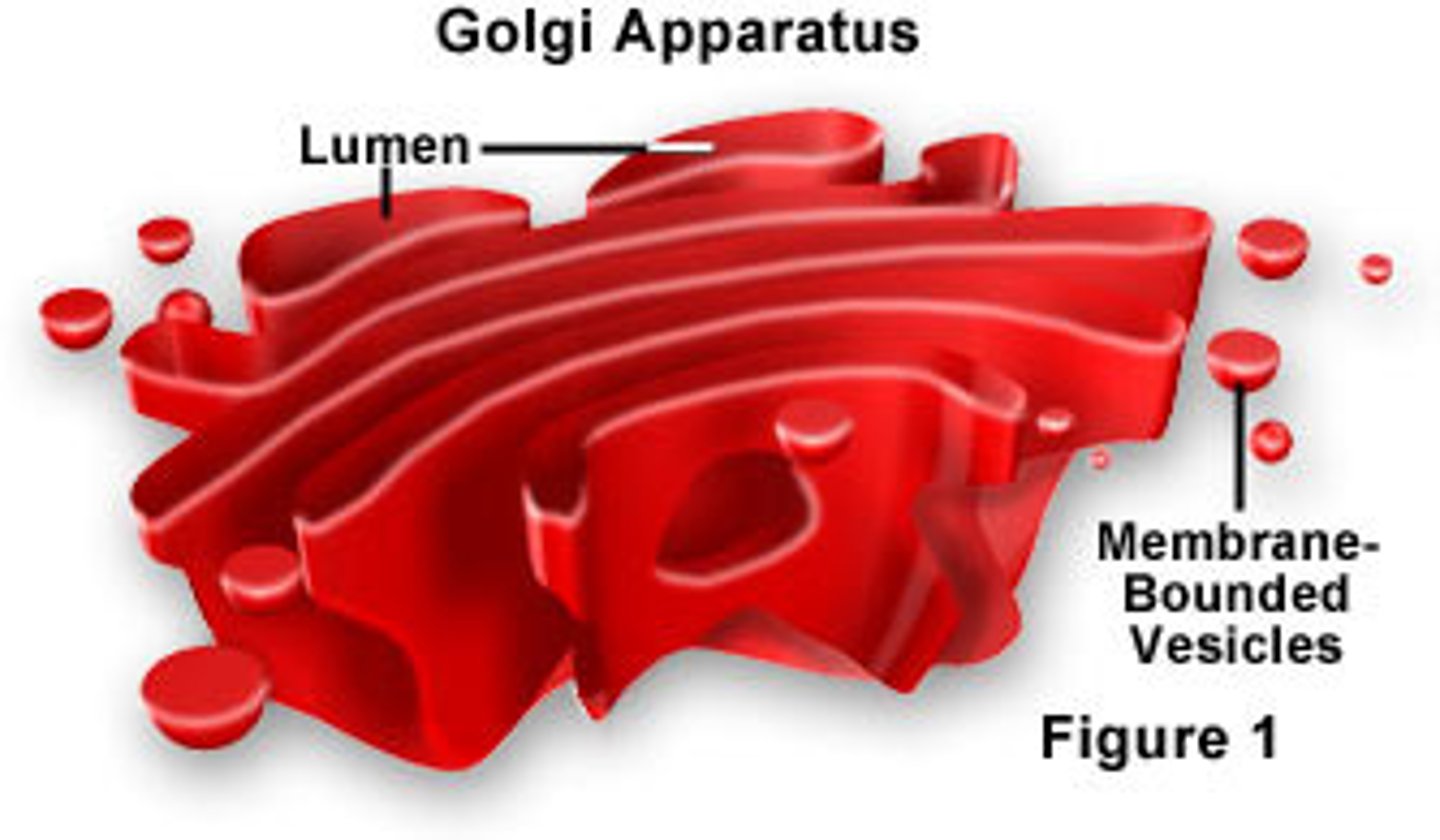
golgi apparatus
A system of membranes that modifies and packages proteins for export by the cell
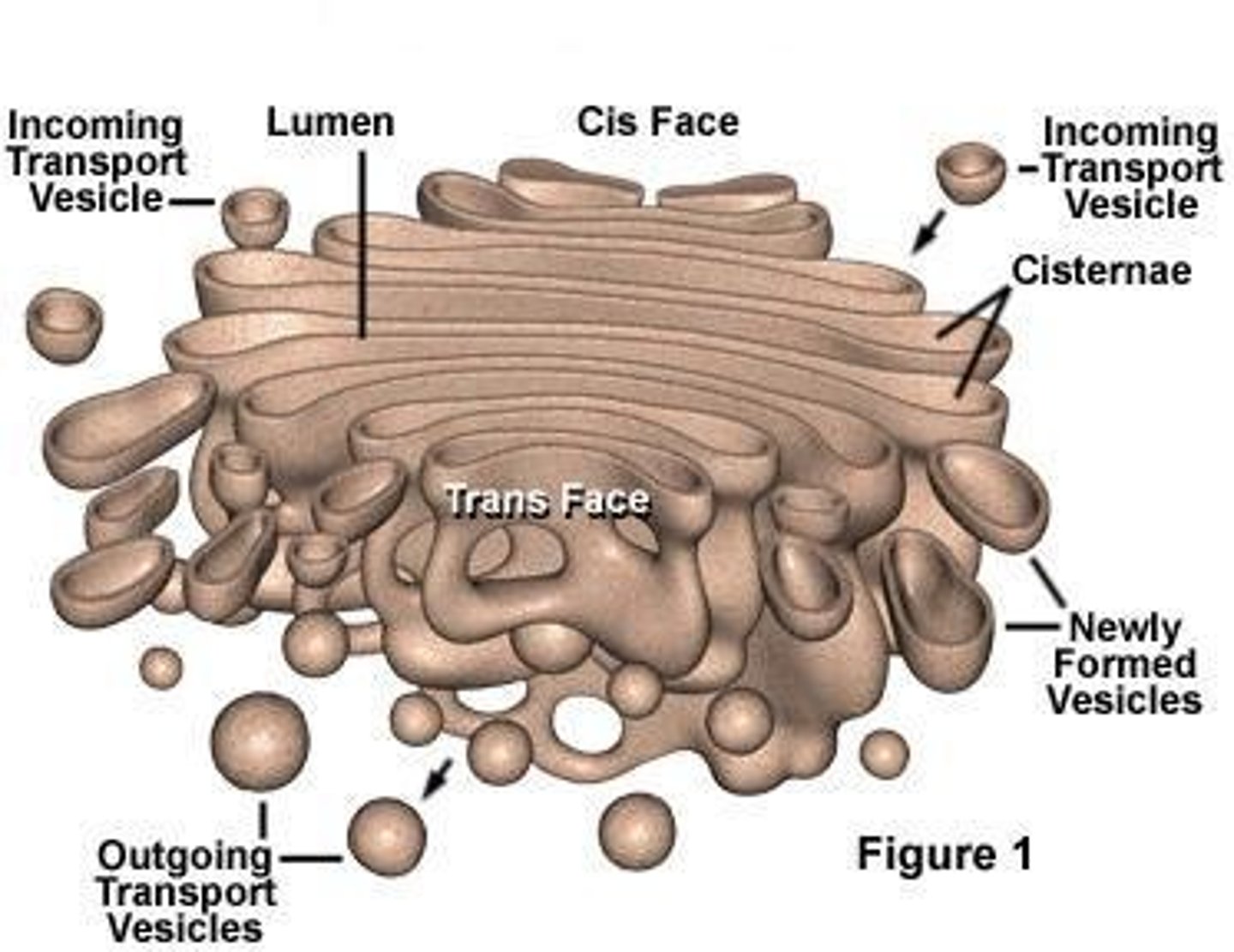
Dictyosomes
stacks of cisternae in the golgi apparatus
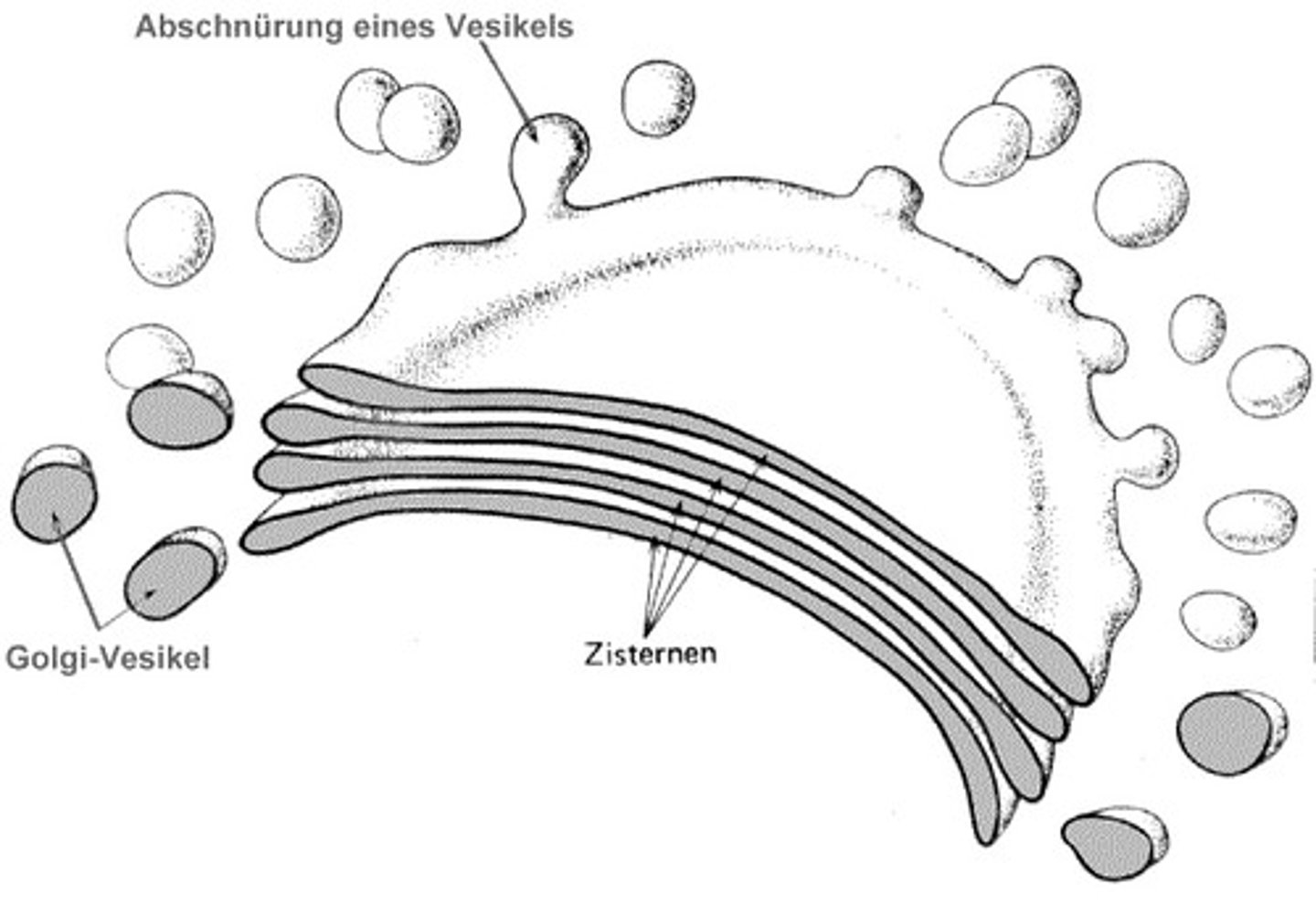
how are vesicles transported through the golgi
ER vesicles fuse with the cis side of the Golgi, adding their membrane to the Golgi and exporting their contents into the golgi sacs.
other vesicle buds off golgi on the trans side and leave, carrying away proteins, lipids, and other molecules
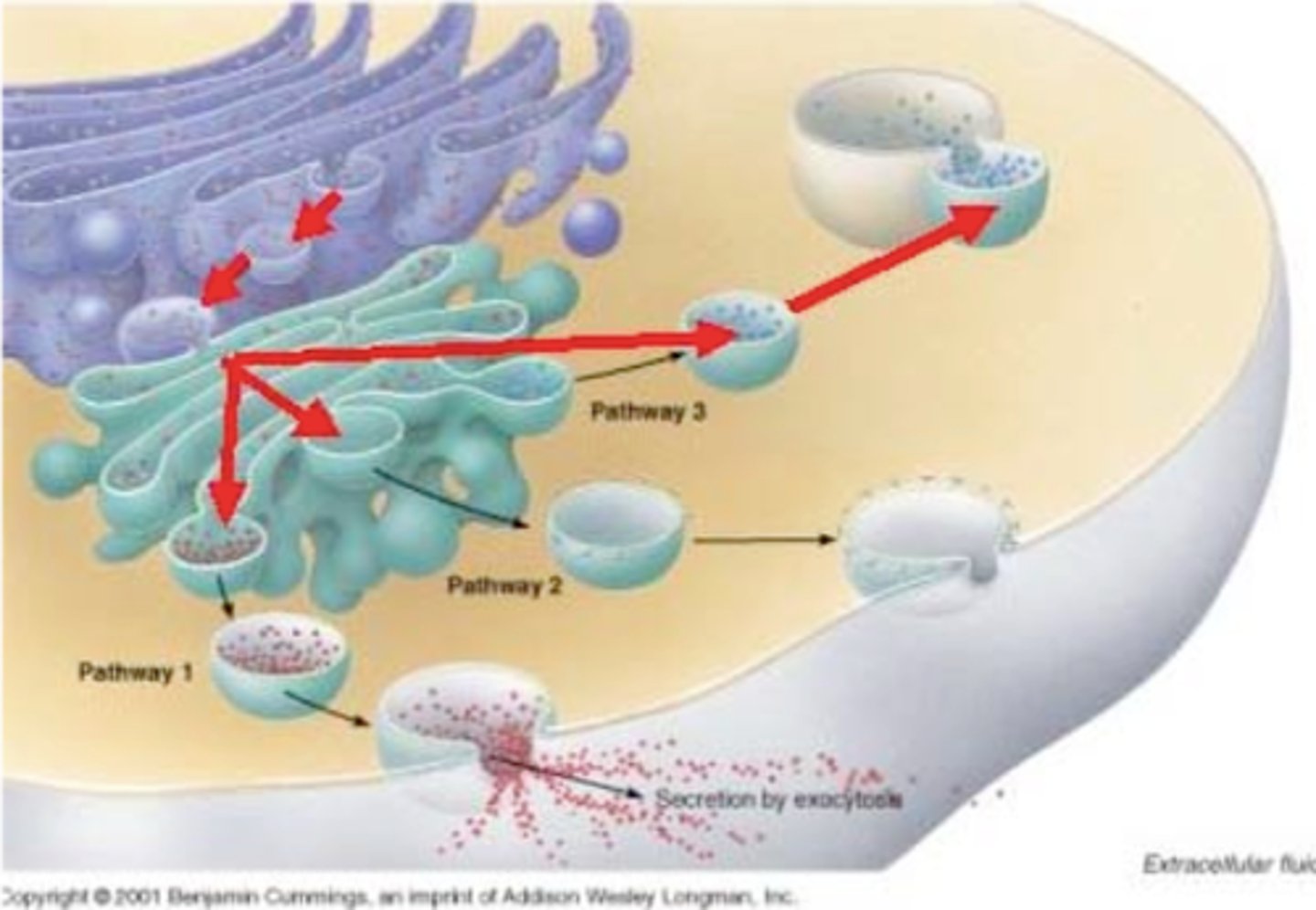
functions of golgi
- receives transport vesicles from ER
- sorts: separates proteins and lipids from the ER according to their destinations
- alters: modifies molecules and makes carbs through processes like glycosylation
- packages material into vesicles that are transported to other parts of the cell
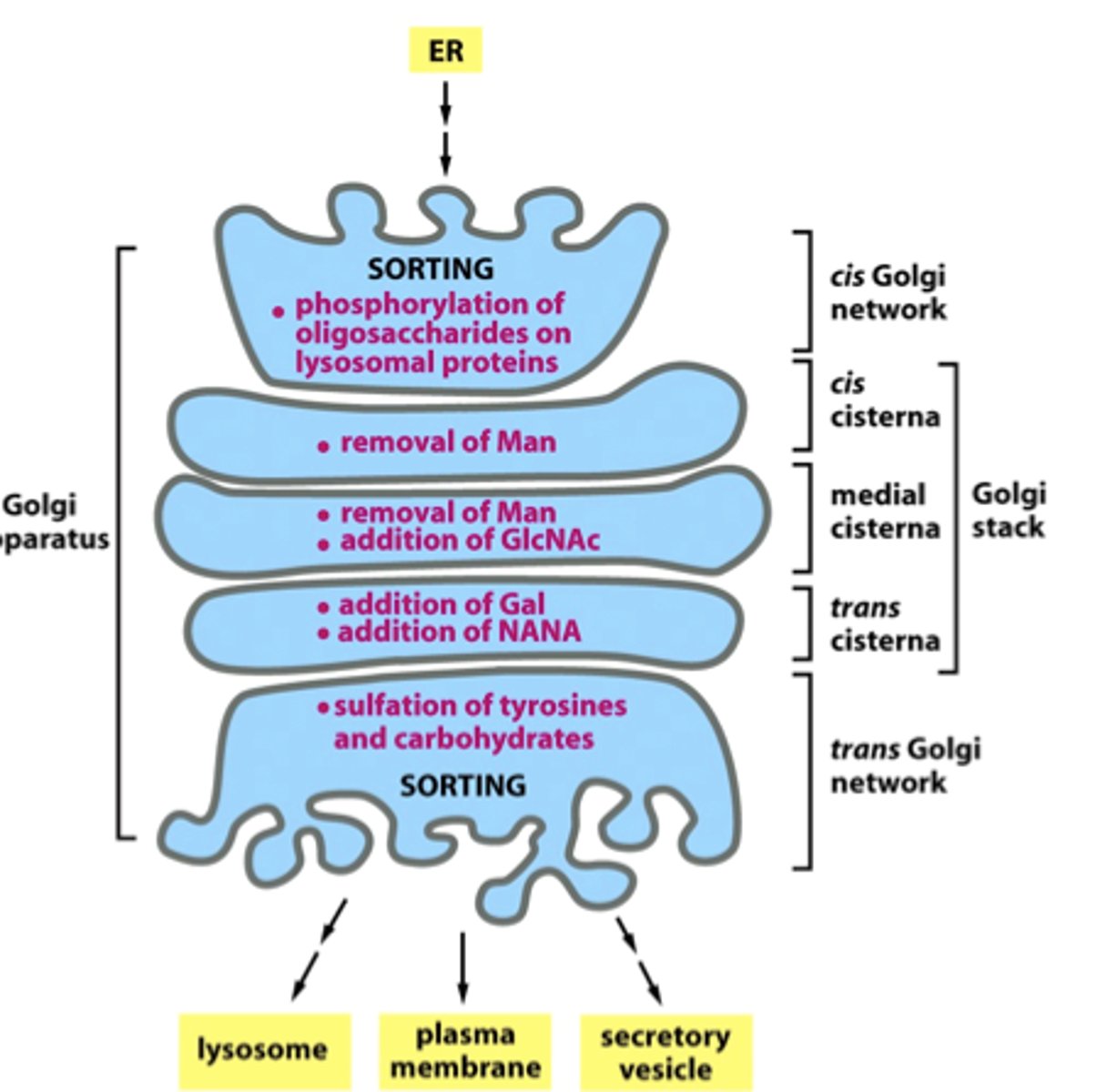
glycosylation
adds or modifies carbohydrate (sugar) groups on proteins and lipids, turning them into glycoproteins or glycolipids.
lysosome
membranous vesicles containing digestive enzymes: breaks down proteins, fats, nucleic acids, and carbs
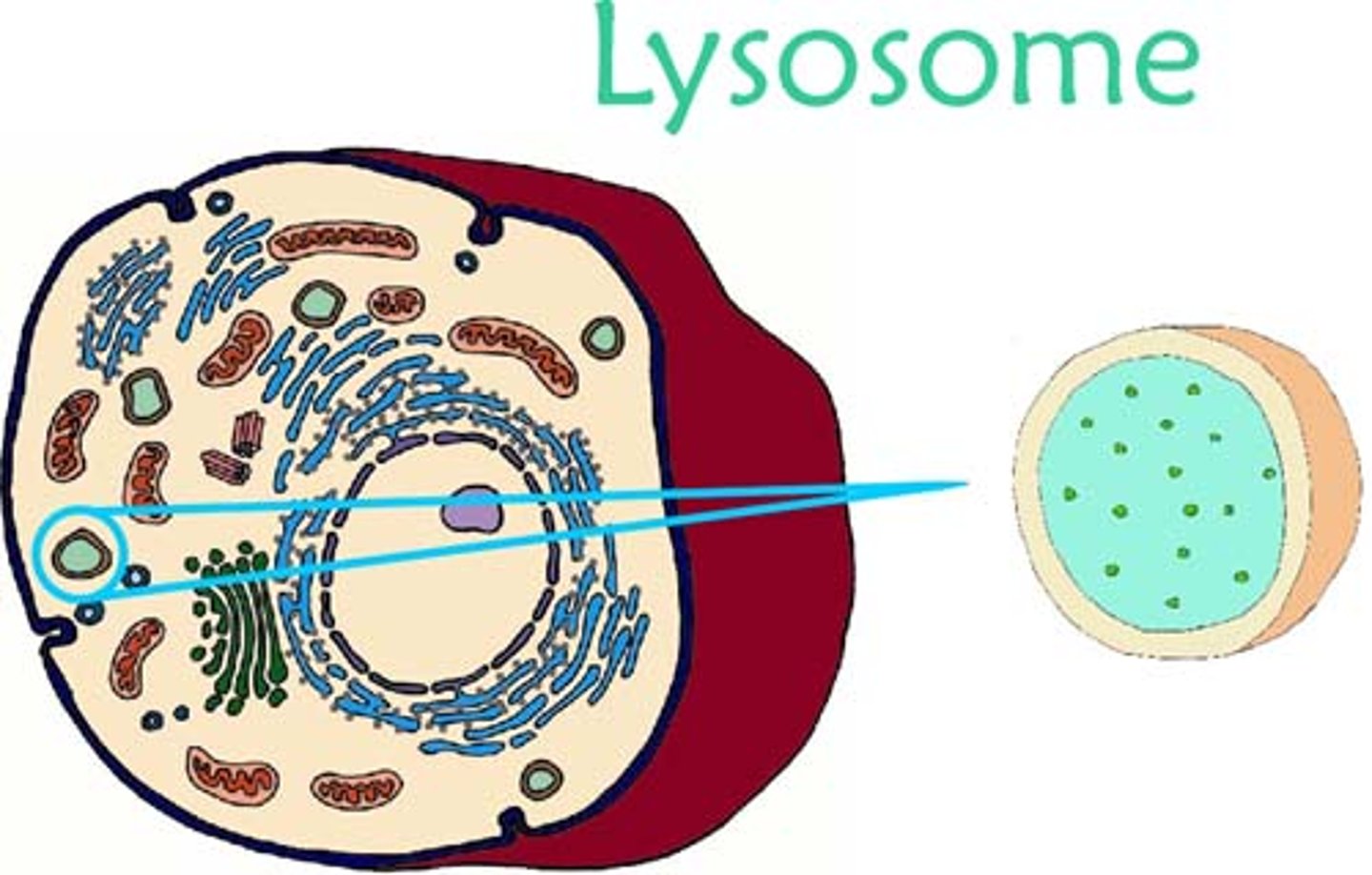
which type of cells are lysosomes usually found in?
animal cells
??? where are the enzymes found in lysosomes made
made by the ER
lysosome functions
phagocytosis and autophagy
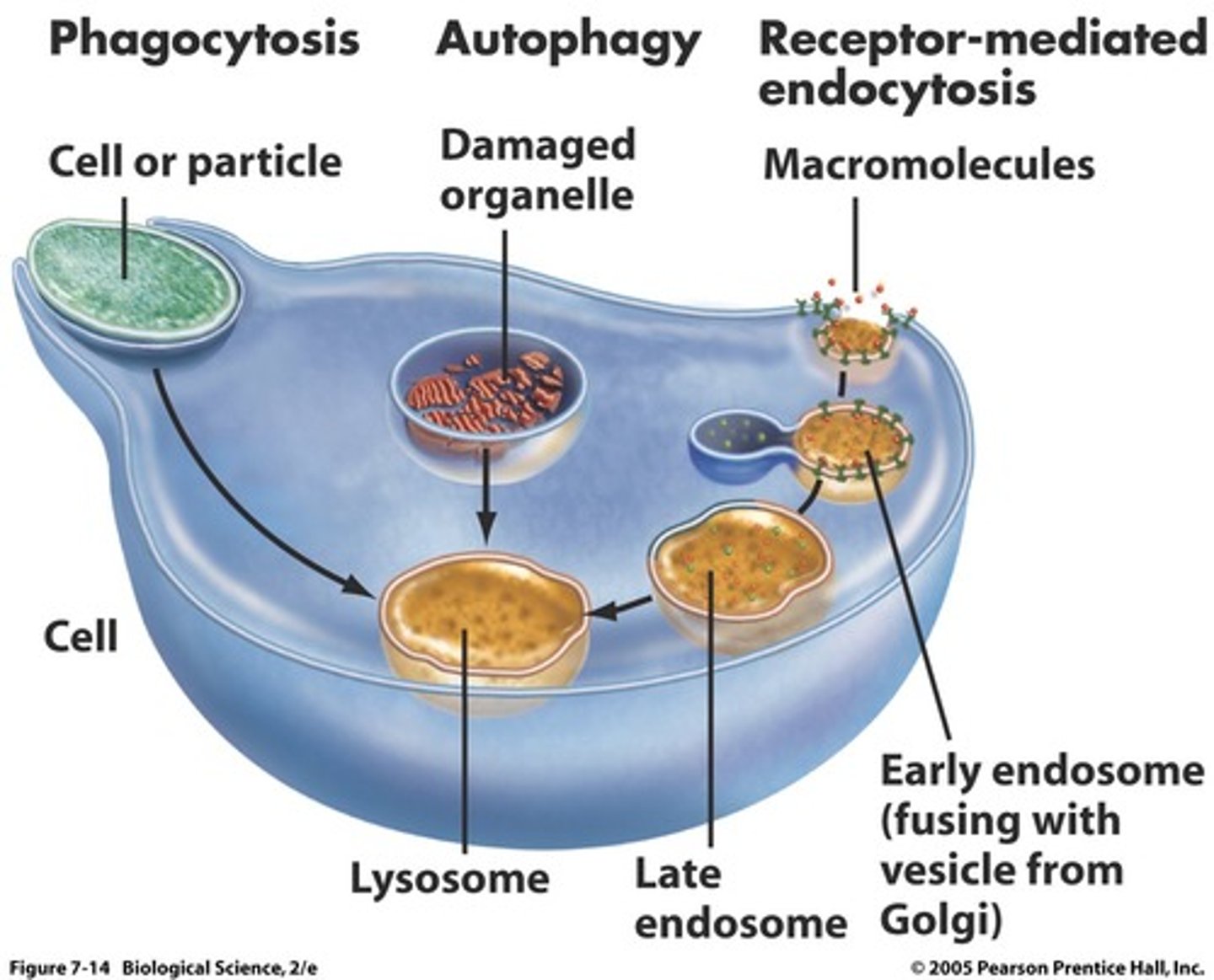
Describe how lysosomes digest food particles or invading organisms
phagocytosis by a cell--> these particles enclosed in vesicles called food vacuoles--> lysosome fuses w contents of food vacuoles--> lysosome enzymes digest the food into smaller molecules that diffuse out of the lysosome and into the cytoplasm
autophagy
lysosomes break down damaged organelles
explain how autophagy works
a cell identifies the defective organelles and encloses them in 2 membranes with a peroxisome--> a lysosome fuses with the vesicle--> organelles are digested
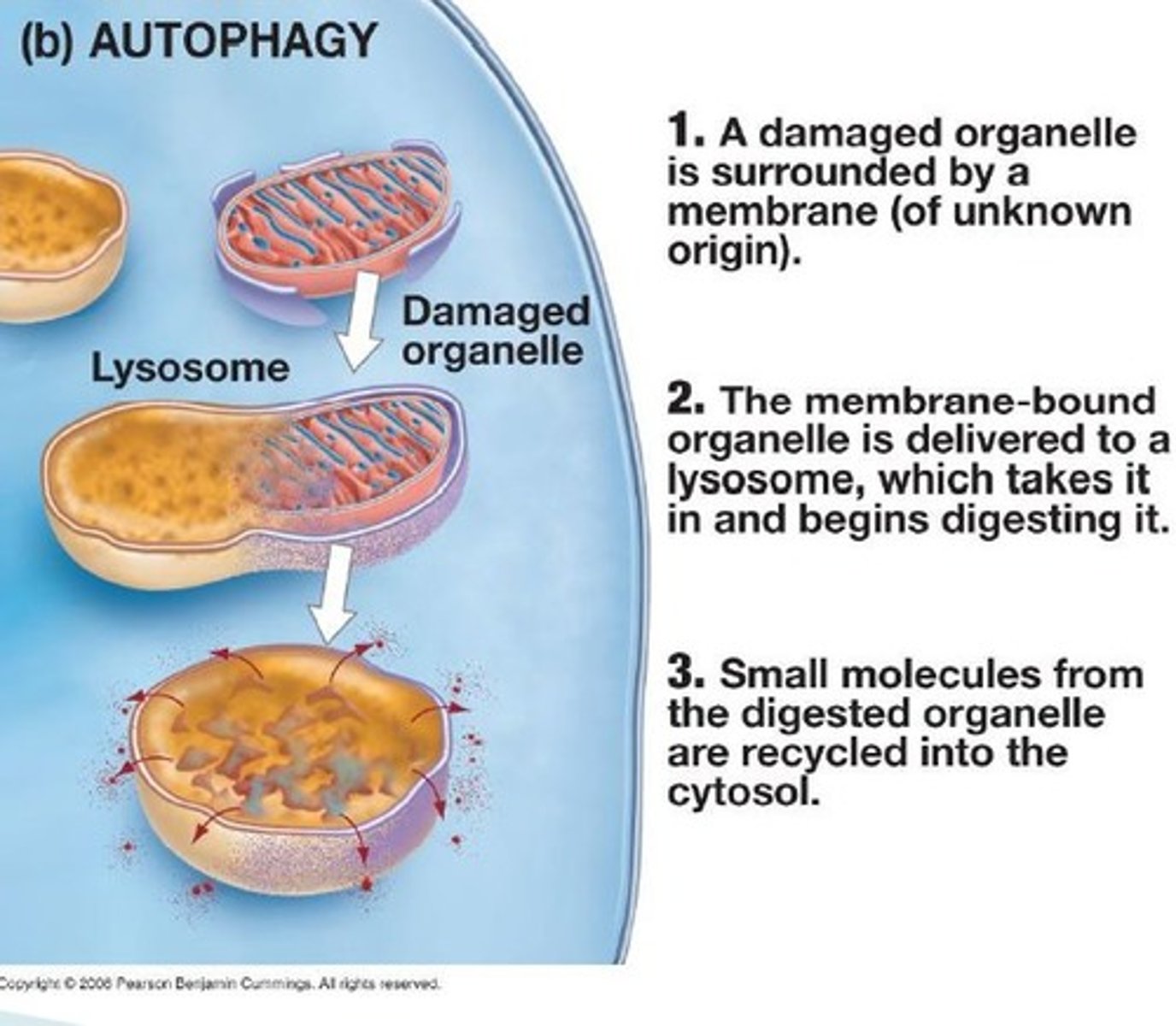
after molecules are digested, can they be reused in cellular processes
yes
vacuole
a fluid-filled sac used for the storage of materials needed by a cell
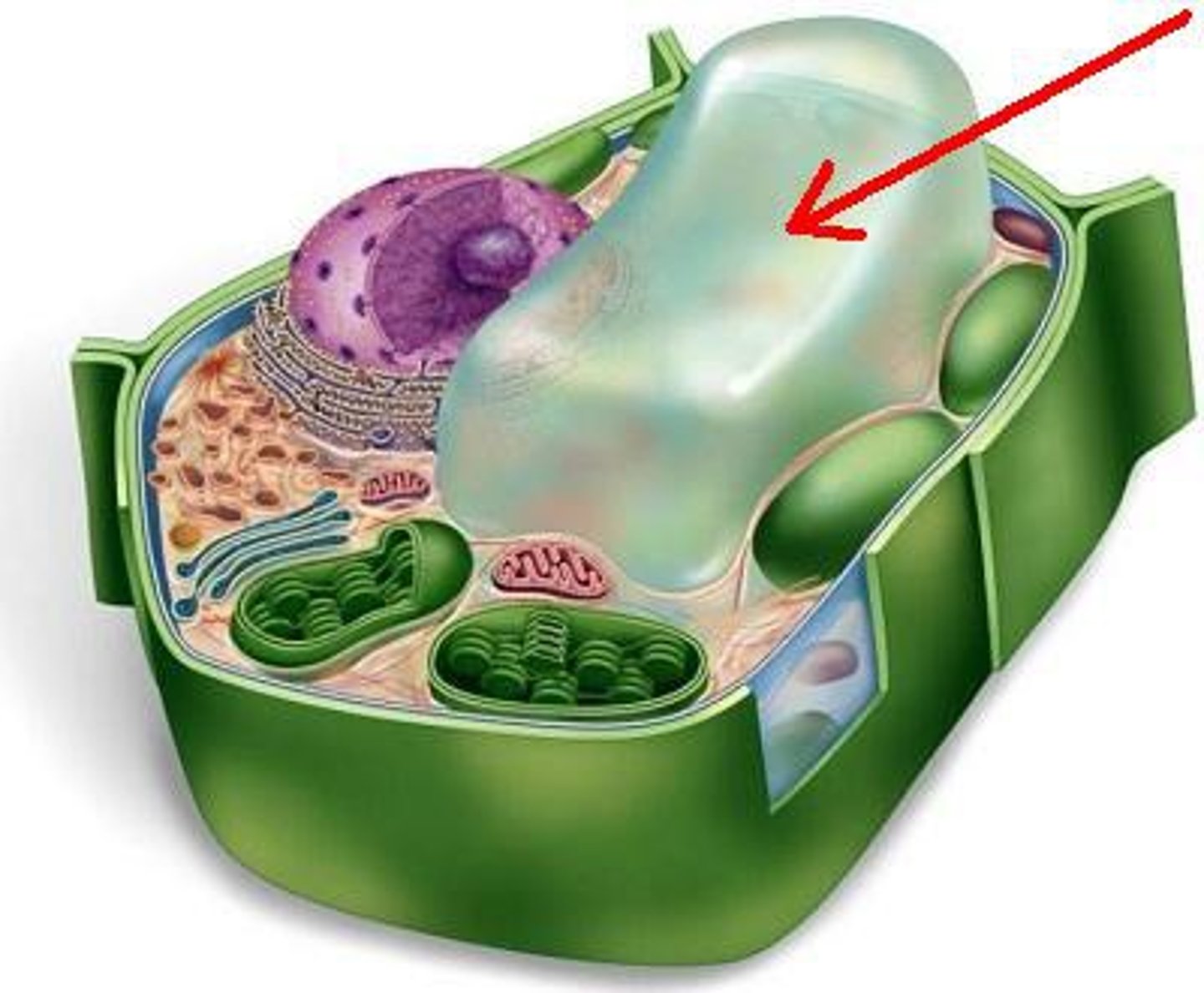
how many membranes does a vacuole have
1
how many vacuoles do most cells have
1 or more
contractile vacuole
removes water from a cell; permanent
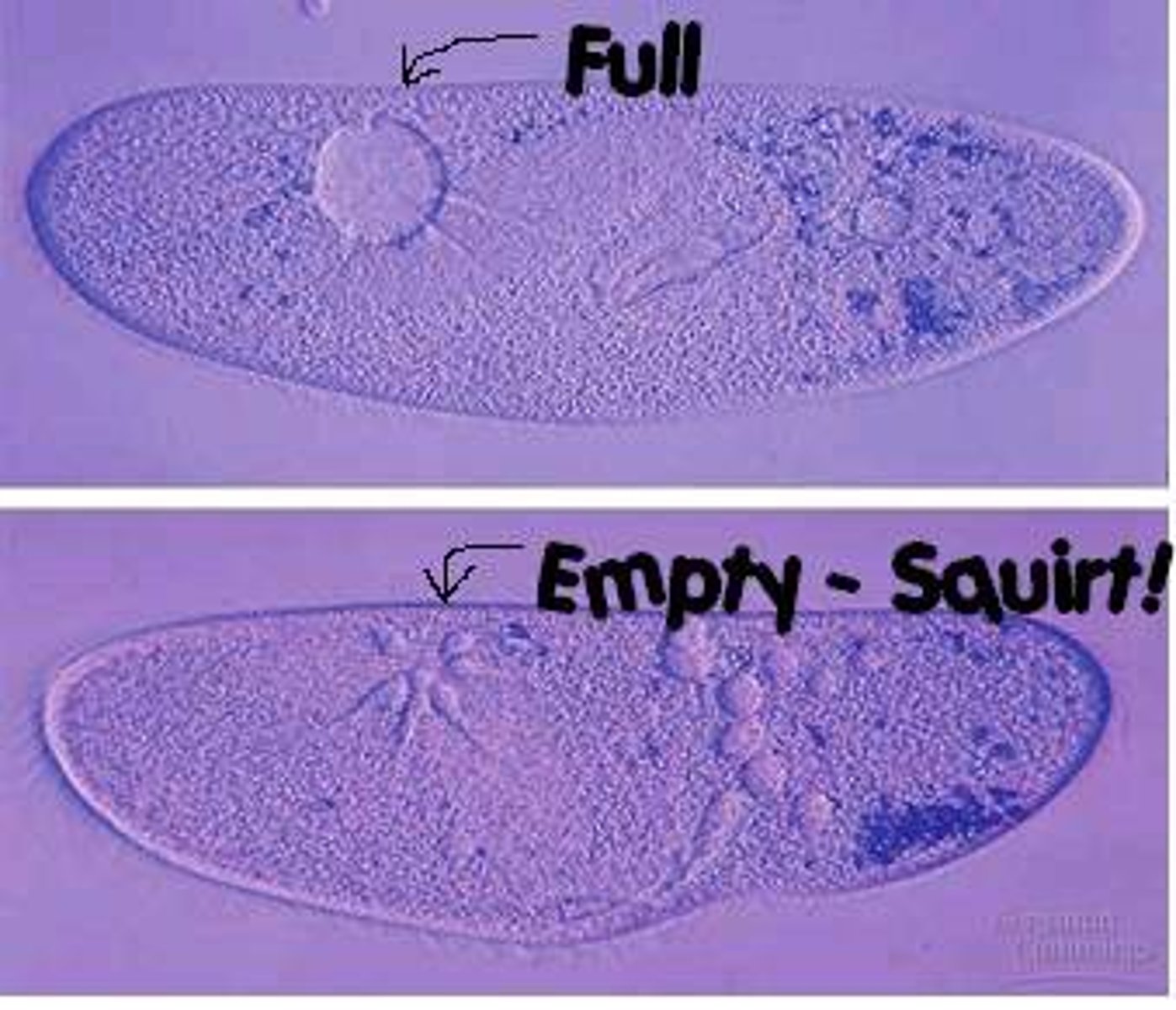
explain how contractile vacuoles work
purer water enters the cell through the cell membrane (osmosis)--> cell would keep taking up more water until it bursts if it didnt have a way to get rid of the water--> protists pump salts into the vacuole--> water enters the vacuoles cuz of osmosis--> when the reservoir is full, it contracts, squeezing water out through a pore in the membrane
how much of the cell does the centralized vacuole take up
around 75%
why's it important that the central vacuole forces organelles to be pushed against the plasma membrane
creates TURGOR PRESSURE
- Maintains cell rigidity and structure: The pressure keeps the plant cell firm and helps the plant stay upright. Without it, plants would wilt.
- Optimizes surface area for exchange: Pushing organelles toward the plasma membrane allows efficient exchange of nutrients, gases, and waste between the cell and its environment.
- Supports growth: The vacuole's pressure helps cells expand during growth without having to produce more cytoplasm.
functions of centralized vacuole
- involved in cell's water balance
- dump site for hazardous wastes, which cells often cannot excrete
- storage
importance of turgor pressure
In plant cells to gives rigidness to stand straight and do normal activities
are food vacuoles temporary
yes
hydrolytic vacuoles
basically lysosomes for plants
endomembrane system consists of
nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles and the plasma membrane.
are peroxisomes involved in endomembrane system
no
Explain the endomembrane system of protein modification and transport.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) - Ribosomes on the RER make proteins, which enter the RER for folding and initial modification (like adding sugar chains).
Transport Vesicles - Carry proteins from the RER to the Golgi apparatus.
Golgi Apparatus - Further modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for their final destination.
Vesicles - Transport the modified proteins to the plasma membrane (for secretion), to lysosomes, or to other parts of the cell.
peroxisome
vesicles with enzymes to break form fatty acids (lipids), amino acids (proteins), and alcohol (toxin)
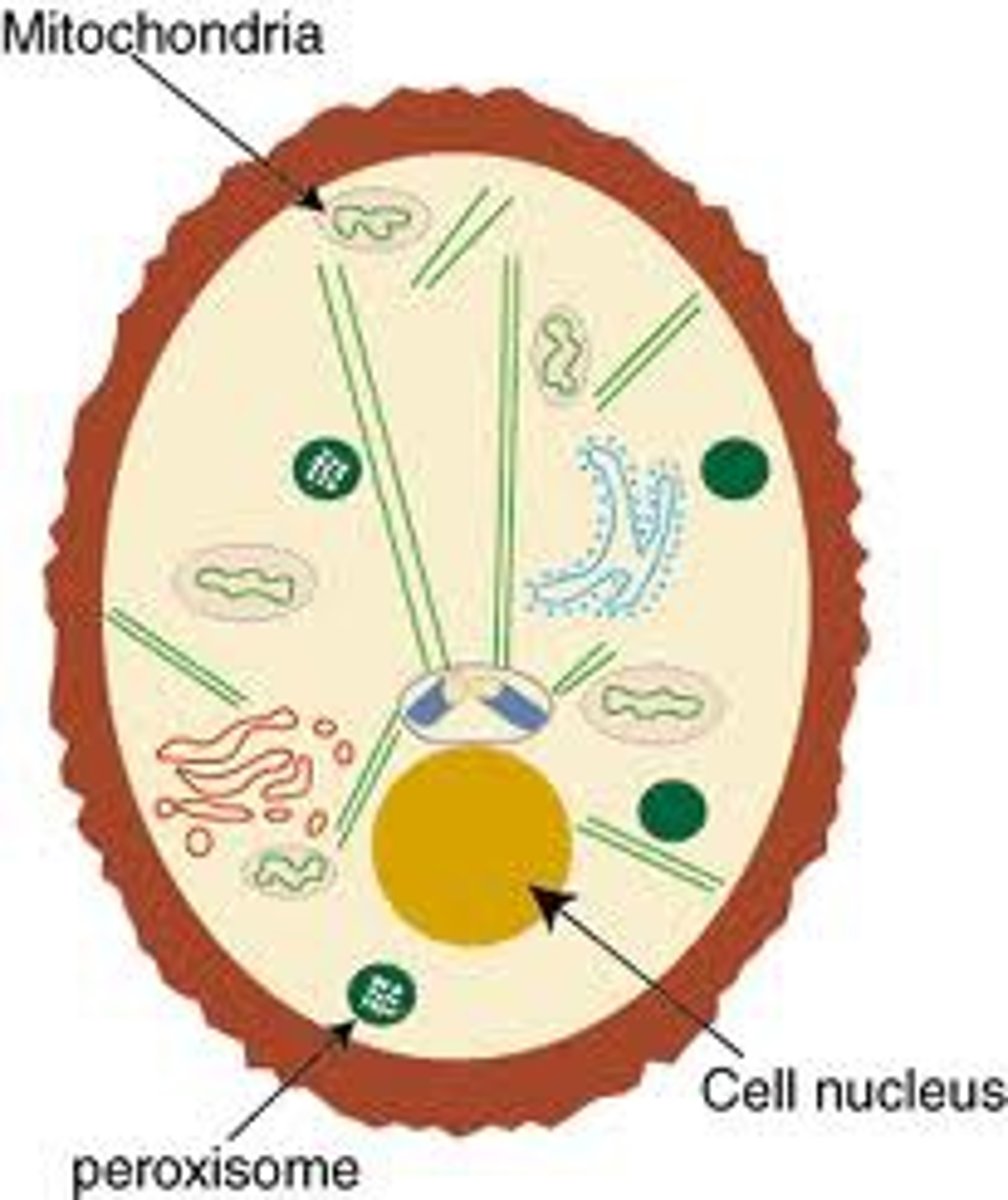
How does peroxidase neutralize hydrogen peroxide?
it does not produce oxygen gas just water
H2O2 + 2H --------->2H2O
function of mitochondria
provides energy for cells via cellular respiration
what part of the body is there an abundance of mitochondria
metabolically active cells like in muscle tissue
endosymbiotic theory
mitochondria and chloroplasts may have been dervied from bacteria that took up residence within eukaryotic cells 1 billion years ago
evidence for endosymbiotic theory
Mitochondria and chloroplasts possess their own DNA similar to prokaryotes
double membrane
reproduce by fission independent of cell
mobile within cell
structure of mitochondria
- outer membrane
-cristae- inner membrane that is folded
- inner membrane divides into: outer compartment and the matrix
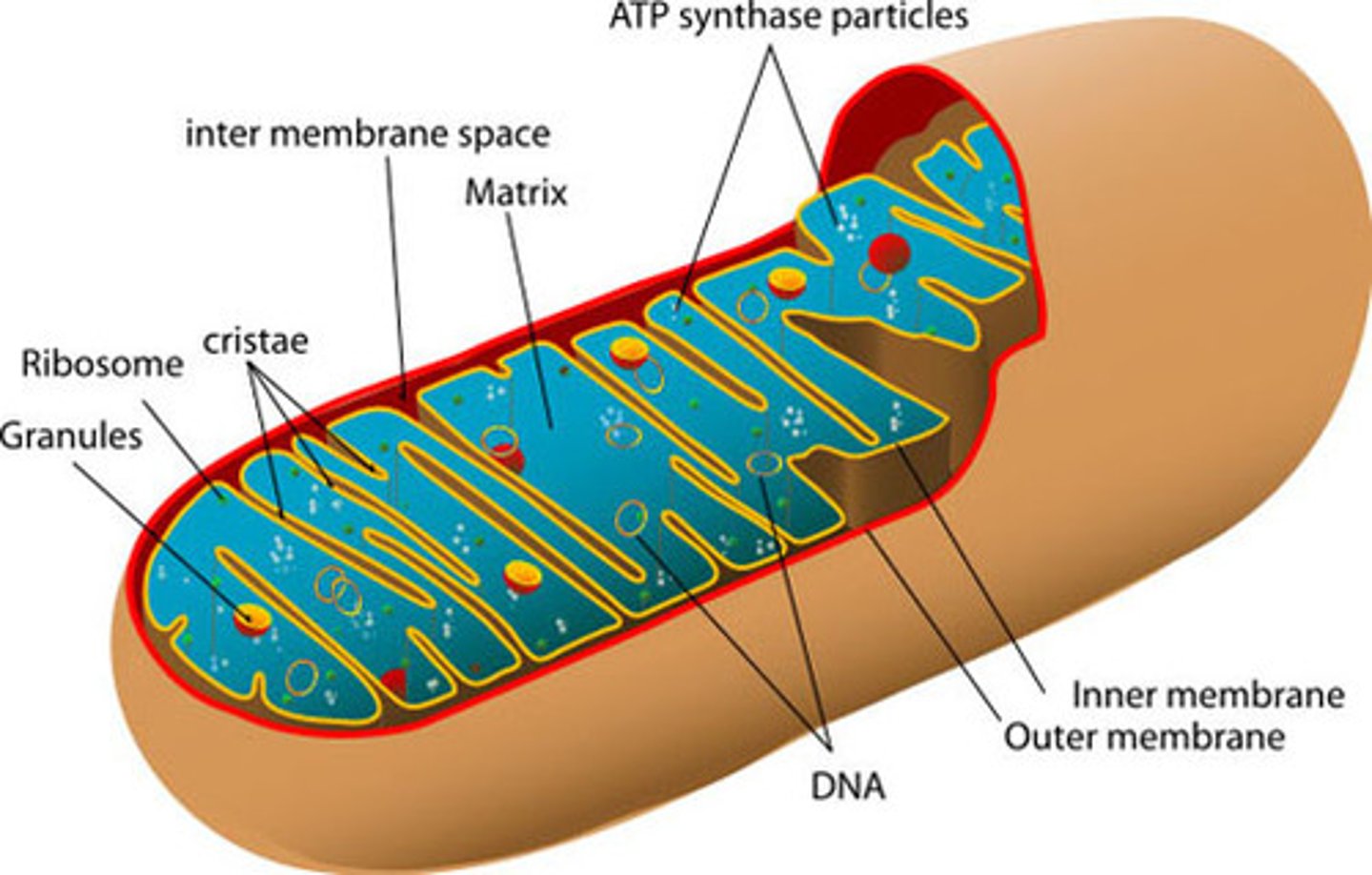
where in the mitochondria do the metabolic functions happen
within the matrix fluid and along membrane cristae
what kind of organelles are plastids found in
photosynthetic organisms (plants and protists)