Topic 7- DNA Replication
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Primary Structure of DNA
Phosphate group attached to the 5’ carbon, hydroxyl on the, and a nitrogen base attached to the 1’ carbon
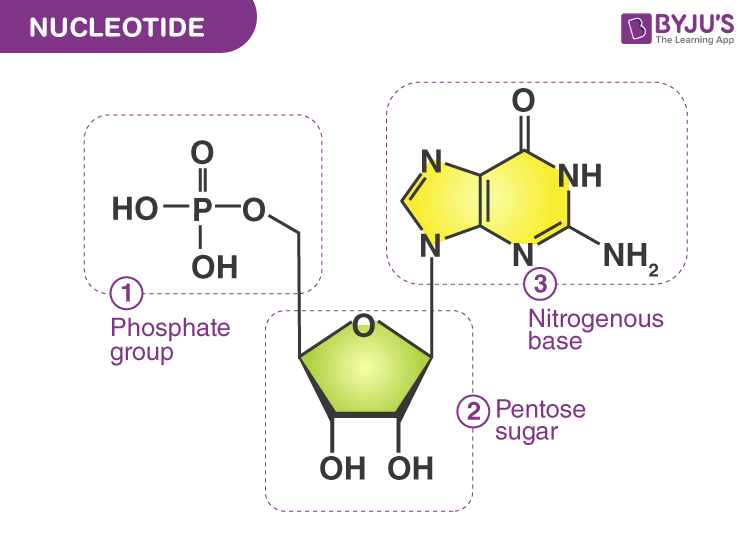
Purine
Double-ring structure (adenine and guanine)
Pyrimidine
Single-ring structure (thymine and cytosine)
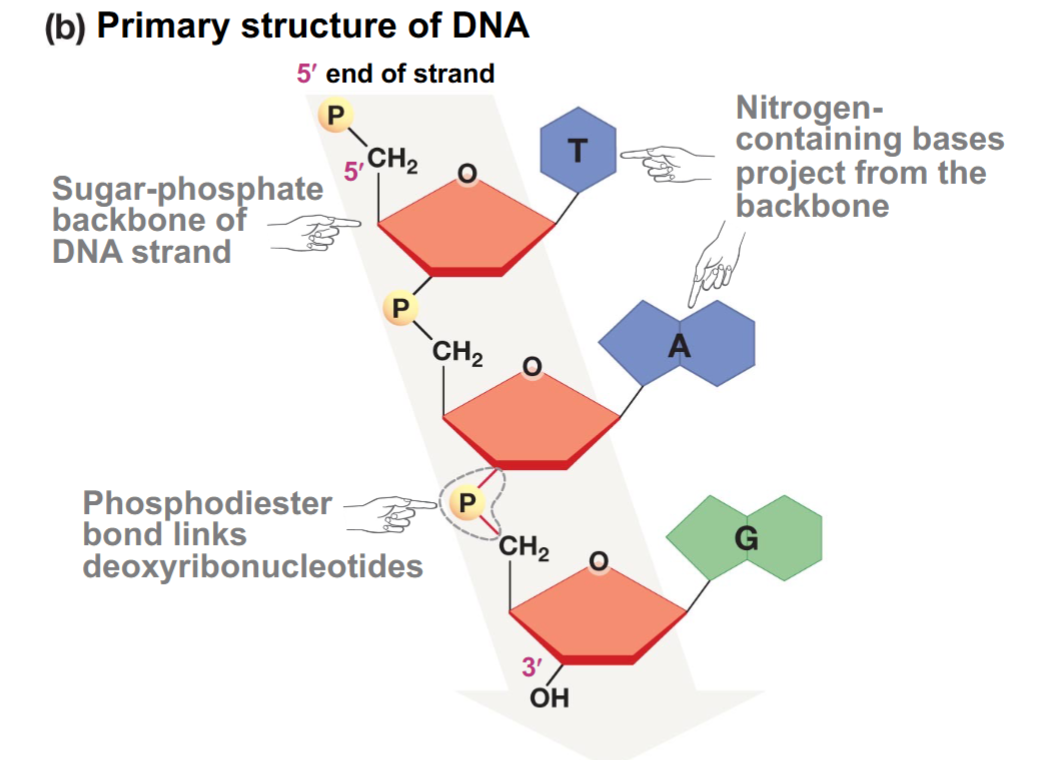
Primary structure of a DNA strand
Phosphate-sugar backbone of DNA strand; phosphodiester bond links deoxyribonucleotides
Watson and Crick
Proposed that two DNA strands line up in the opposite direction of each other, in what is called antiparallel fashion; suggested that existing DNA strands could serve as a template for the production of new strands according to complementary base pairing
Chargaff’s Rules
A hydrogen binds to T, and C hydrogen bonds to G
Semiconservative replication
Each old DNA strand is copied to generate a new strand; each new chromosome is composed of one strand of old DNA and one strand of newly synthesized DNA
Conservative replication
The original chromosome is copied but remains unchanged; one chromosome is composed of old DNA and the other is composed of new DNA
Dispersive replication
Replication process generates two new chromosomes randomly mixed with old and new sections of DNA
Meselson-Stahl Experiment
Provided strong evidence that DNA replication is semi-conservative when future generation of E. Coli had both 14N and 15N content
dNTPs
deoxynucleotide triphosphates; building blocks of DNA
What direction is DNA synthesis?
5’ —> 3’
Prokaryotes and points of origin
Prokaryotes have one point of origin for DNA synthesis; theta structure
Eukaryotes and points of origin
Eukaryotes have multiple points of origin due to their linear structure
Helicase
Catalyzes the breaking of hydrogen bonds between base pairs and opening of DNA’s double helix
Single-stranded DNA binding proteins
Stabilizes single-stranded DNA by preventing base-pairs from pairing up again
Topoisomerase
-Breaks and rejoins the DNA double helix to relive twisting forces caused by the opening of the helix
Primase
Makes an RNA primer, or a short stretch of nucleic acid complementary to the DNA template, that provides a 3’ end for the DNA polymerase to work on (lagging strand)
DNA polymerase III
Elongation
Sliding clamp
Holds DNA polymerase in place during strand extension
DNA polymerase I
removes the RNA primer and replaces it with DNA
DNA ligase
Catalyzes the joining of Okazaki fragments into a continuous strand; seals nicks left behind by DNA polymerase I
Why do telomeres shorten during DNA replication?
When the last primer is removed, DNA synthesis cannot occur (because it needs a primer), so the place where the primer was remains unreplicated
Telomerase
Adds more repeating bases to the end of the lagging strand, catalyzing the synthesis of DNA from an RNA template that it carries with it
Result of telomerase
The lagging strand becomes slightly longer than it actually was
How does DNA polymerase III proofread?
It has an epsilon subunit that acts as an exonuclease that removes deoxyribonucleotides from DNA; goes in the 3’ —> 5’ direction
Exonuclease
An enzyme that removes nucleotides from the ends (exo) of a polynucleotide chain