Higgins- SBS
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
PAY ATTENTION TO OBJECTIVES!!!!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What is Short Bowel Syndrome (SBS)?
malabsorptive state after extensive surgical resection of the small intestine
What are the indications for Short Bowel Syndrome (SBS)?
re-surgery performed due to complications from a previous abdominal surgery
massive small intestine surgical resection
others: vascular complications, intra-abdominal trauma/neoplasm, radiation injury, small bowel obstruction
Symptoms of SBS:
abdominal pain
diarrhea/steatorrhea
dehydration/electrolyte imbalance
weight loss
What are the 2 classifications of SBS and their corresponding categories?
Anatomical
Type I: End-jejunostomy
Type II: Jejunocolonic anastomosis
Type III: Jejuno-ileal anastomosis
Pathophysiologic
SBS without colon
SBS with colon in continuity
What are the 4 Phases of SBS Development? What is the duration of each phase if applicable?
Acute: 3-4 weeks
Adaptation: 1-2 years
Chronic intestinal failure
Maintenace
Describe the acute phase of SBS.
HOSPITALIZATION IS REQUIRED!!!!!!!!!!!!
metabolic derangement/ intestinal losses + increased gastric secretions (due to loss of hormonal neg feedback)
Describe the adaptation phase of SBS.
structural AND functional adaptative changes of the remaining small bowel
The chronic intestinal failure phase of SBS occurs when…
adaptation phase fails
Describe the early management of SBS? (before the acute and adaptation phase etc.)
early parenteral nutrition
enteral nutrition when ileus resolved/harder stooler
replace fluids/electrolytes IV (separate from TPN)
avoid hypo- and hypervolemia
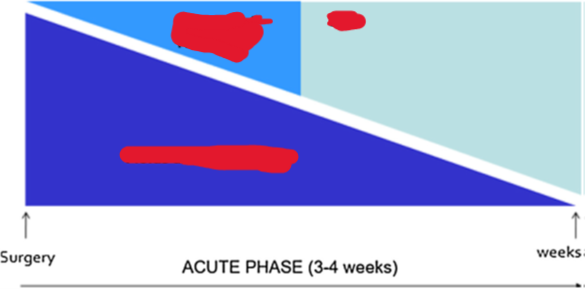
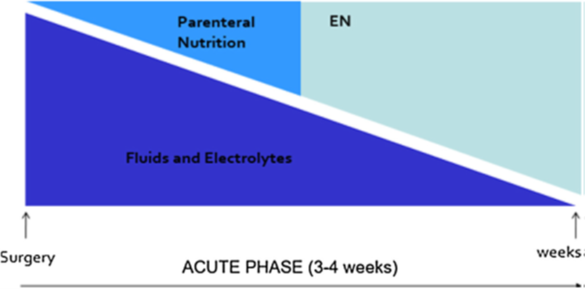
How is the acute phase of SBS managed? (aka describe how fluids, TPN, and EN are managed from right after surgery to weeks after.)
RIGHT AFTER SURGERY: Give lots of fluids/electrolytes and little TPN.
As weeks go by, start decreasing fluid/electrolyte amounts and increasing nutrition!!!
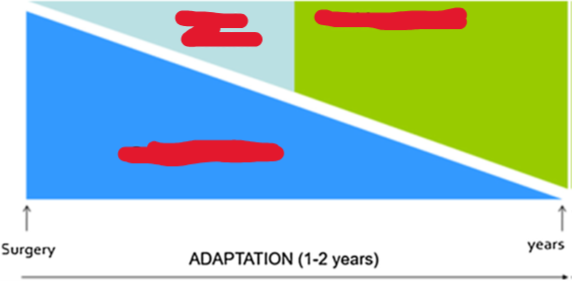
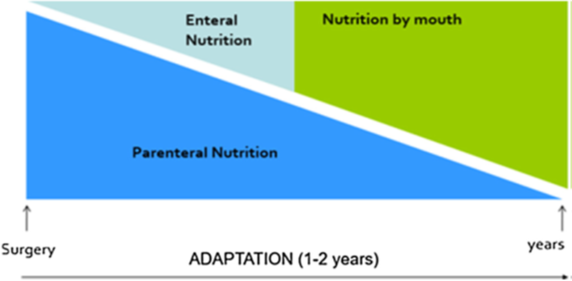
How is the adaptation phase of SBS managed? (aka describe how PN, EN, and Nutrition by mouth are managed from surgery to 1-2 years after)
right after surgery during acute phase, pt. is on parenteral nutrition only
as time passes, slowly decrease PN and start introducing EN and eventually nutrition by mouth (aka increase EN, decrease PN)
nutrition by mouth is OUR GOAL!!!!! (promotes adaptation and stimulates intestinal adaptation)
Nutrition wise—> try to eat at least 5 or more small meals/day, avoid sugars, supplement vitamins/minerals, and use oral rehydration to correct fluid balances
How is the chronic intestinal failure stage of SBS managed? (aka what are the 2 types, and what can we do to address symptoms)
can be irreversible or reversible
irreversible: lifelong TPN
reversible: TPN over months—> years, wean off of it
ADDRESS SYMPTOMS WITH MEDICATIONS!!!!! (prior to this, in the acute/adaptation phases the focus was fluids and nutrition, but now we want to initiate more)
What meds can be used during the late phases of SBS?
antidiarrheals
pancreatic enzyme replacement
bile-acid resions
H2RAs, PPIs
abx
lactase supplements
What meds can be used to reduce parenteral nutrition? Describe each.
oral glutamine- anti-inflammatory
recombinant growth hormone w/ glutamine (somatropin)- early dumping—> GI hormones, late dumping—> pancreas (insulin)
glucagon-like peptide-2 analogues (GLP-2 analogues) like Teduglutide- SQ injection that reduces IV TPN, reduces stool weight, and increases villus height, crypt depth, and mitotic index
What are the complications of SBS?
diarrhea
intestinal failure-associated liver disease
cholelithiasis (gallstones)
oxalate nephropathy
acidosis
What are the VITAMIN/MINERAL DEFICIENCES in SBS?
Deficiency | Disease |
Vitamin C | |
Calcium | |
Vitamin A | |
Vitamin E | |
Vitamin K | |
Iron | |
Zinc |
Deficiency | Disease |
Vitamin C | scurvy |
Calcium | osteoporosis |
Vitamin A | night blindness, corneal ulcerations |
Vitamin E | paresthesia (tingling/numb), ataxia (trouble coordinating muscles) |
Vitamin K | bleeding |
Iron | anemia, glossitis (tongue inflammation) |
Zinc | stomatitis (mouth inflammation), alopecia |
WHAT ARE THE COMPLICATIONS OF LONG-TERM PARENTERAL NUTRITION?
IV catheter infections
thrombosis
metabolic bone disease
iron deficiency anemia
What is an ostomy? What is a stoma? Are ostomies permanent or temporary?
ostomy- opening or outlet through abdominal wall for eliminating waste
the “opening” is called a stoma
can be temporary or permanent
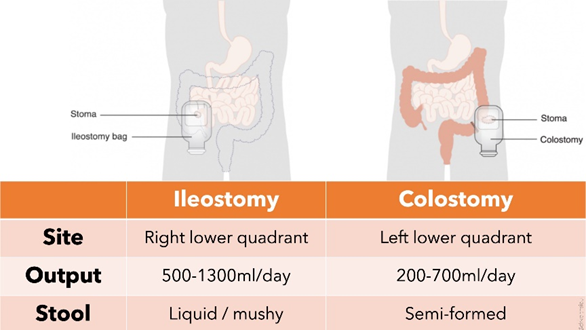
What are the 2 types of ostomies, where are they located, and what stools come out the hole?
ILLEOSTOMY—> right side/ liquid, mushy stool
COLOSTOMY—> left side/ semi-formed stool
What are some things to think about if you have an ostomy? (i don’t think that important)
types of pouching systems (1 piece, 2 piece, drainable, closed end)
fit and application
wear time
use of skin barrier rings, powder, paste
avoid moisturizers
food choices
What are complications of ostomies?
psychological
fluid/electrolyte imbalances
vitamin/mineral deficiencies
constipation/diarrhea
intestinal gas
skin irritation
stoma complications
What are the medication considerations with ostomies?
avoid SR, XR, and enteric coated meds
check pouch for undissolved tablets
medications can change the color of stool
review meds for ADRs
WHAT ARE COMMON ostomy medication side effects?
(focus on indentifying the interacting drugs first then the side effects)
antibiotics- diarrhea
sulfa drugs- risk of crystallization in kidneys
diuretics- increase fluid/electrolyte loss
laxatives- use under close supervision
antacids- diarrhea w/ Mg based products OR constipation w/ Al based
opioids- constipation
SBS might end in needing a…
intestinal transplant