System Failures
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Entire System Perspective
Technical components
People, knowledge, processes
Organisational context
Environment
Different Levels of Failure (Multi-Causal Approach)
Regulatory failures - lack of information; undertrained personnel; lack of regulation
Managerial Failures -safety climate, lines of command and responsibility, quality control
Hardware Failures - design failure; requirements failure; implementation failure
Software Failures - requirements failures; specification failures
Human Failures - slips, lapses & mistakes; team factors, human error
Failure in Complex Systems
Failure in one part may coincide with the failure of a different part
This combination can cause cascading failures of other parts
In complex systems these are many possible combinations
What Characterises a Complex System
Complex interactions:
Unfamiliar, unplanned, or unexpected sequences which are not visible or immediately comprehensible
Tightly coupled:
Time-dependent processes
Rigidly ordered processes (sequence B must follow sequence A)
Very little slack
If a system has interactive complexity and is tightly coupled it is particularly prone to failure
Reason’s Swiss Cheese Model
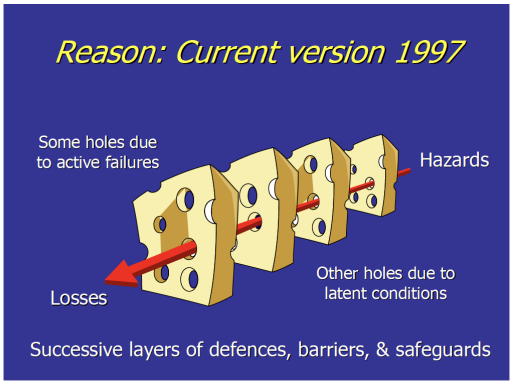
Reason’s Swiss Cheese Model - Limitations
Leveson (2004) critique of the model: “Note that independence of the barriers is assumed and some randomness in whether the “holes” line up”
Dekker (2002): “layers of defence are not static or constant, and not independent of each other either. They can interact, support or erode one another”
Dekker: the Swiss Cheese Model doesn’t explain what the holes are, how and why they got there, how the holes line up, etc
The Concept of Dependability
For most complex socio-technical systems, dependability is the most important property
Judgement about the user’s trust in a system
Reflects the extent of the user’s confidence that it will operate as expected and will not ‘fail’ in normal use
“Dependability is defined as that property of a computer system such that reliance can justifiably be placed on the service it delivers.” (Mellor)
Laprie’s Model
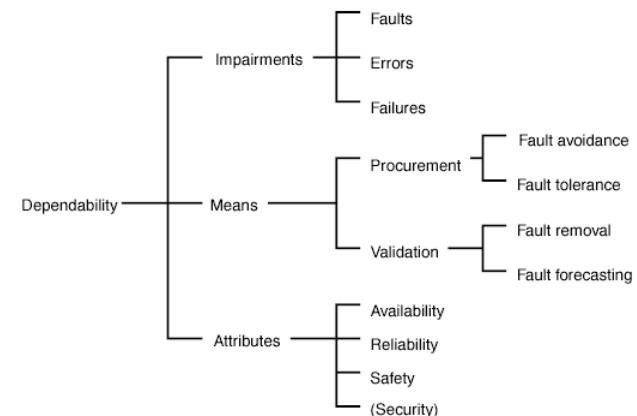
Laprie’s Model - Impairments
Faults, errors and failures:
System failure – when the system does not deliver the service its users expect
System error – where the behaviour of the system does not confirm to its specification
System fault – incorrect system state not expected by the designers of the system
Human error or mistake – human behaviour that results in faults being introduced into a system
Laprie’s Model - Means
Fault avoidance – preventing the occurrence or introduction of faults
Fault tolerance – delivering correct service, though faults are present
Fault removal – reducing number or severity of faults
Fault forecasting – estimating number of faults, future occurrence, consequences
Laprie’s Model: Primary Attributes of Dependability
Availability – ability of system to deliver services when requested
Reliability – ability of the system to deliver services as specified
Safety – ability of the system to operate without catastrophic failure
Security – ability of the system to protect itself against accidental or deliberate intrusion
Laprie’s Model: Secondary Attributes of Dependability
Timeliness – the ability of the system to respond in a timely way to user requests
Survivability – the ability of a system to continue to deliver its services to users in the face of deliberate or accidental attack
Recoverability – the ability of the system to recover from user or system errors
Maintainability - the ease of repairing the system after a failure has been discovered or changing the system to include new features