Biology- photosynthesis and respirtation
4.0(1)
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/59
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
1
New cards
The Energy needed by plants ultimately comes from where?
solar energy
2
New cards
What is the energy transport molecule used to do cellular work? (usable form of cellular energy)
ATP
3
New cards
How many phosphate groups are in ATP?
3
4
New cards
How many phosphate groups are in ADP?
2
5
New cards
Where is the chemical energy stored in the ATP molecules?
phosphate bonds
6
New cards
Which one is like a charged battery?
ATP
7
New cards
When a phosphate bond is broken, energy is -
released
8
New cards
Which one has less energy ATP or ADP?
ADP
9
New cards
Which organelle is responsible for recharging ATP molecules?
mitochondria
10
New cards
Organisms that can make their own food are classified as
autotrophs
11
New cards
Organisms like a cow and wolf are classified as
Heterotrophs
12
New cards
The body's response to maintain a constant internal balance of conditions is known as
Homeostasis
13
New cards
In the following equation the reactants would be what? - ADP + P + energy -->ATP
ADP + P + energy
14
New cards
absorb or take in energy
Endergonic (Endothermic)
15
New cards
photosynthesis
Endergonic (Endothermic)
16
New cards
ADP changed to ATP
Endergonic (Endothermic)
17
New cards
release energy
Exergonic (Exothermic)
18
New cards
ATP changed to ADP
Exergonic (Exothermic)
19
New cards
cellular respiration
Exergonic (Exothermic)
20
New cards
In the following equation the products would be what? - ADP + P + energy -->ATP
ATP
21
New cards
In the following equation what is happening to the energy? - ADP + P + energy -->ATP
Energy is being stored
22
New cards
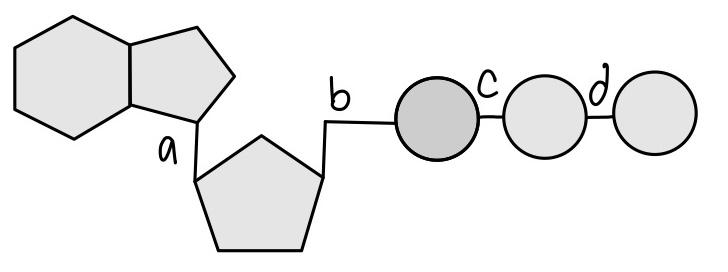
With which bond is the MOST energy contained in this molecule?
D
23
New cards
A net total of _____ATP molecules are created during glycolysis
two
24
New cards
\n Why is glycolysis an anaerobic process?
Glycolysis does not utilize oxygen in its steps
25
New cards
\n To maximize ATP production, glycolysis must be followed by\*
the krebs cycle
26
New cards
During cellular respiration
The complete breakdown of glucose yields ATP molecules
27
New cards
inner membrane
where the electron transport chain is located
28
New cards
decarboxylation
removal of a carbon
29
New cards
phosphorylation
addition of a phosphate
30
New cards
intermembrane
space where protons (Hydrogens) build up
31
New cards
During cellular respiration oxygen is ___________ to ____________.
reduced; water
32
New cards
Select the formula for cellular respiration (e represents energy)
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
33
New cards
In eukaryotic cells, ,most ATP is produced in the
Mitochondria
34
New cards
Cellular respiration is considered to be an _____________ reaction because it ____________ energy.
exergonic; releases
35
New cards
Oxidizing which of the following substances yields the most energy?
Glucose
36
New cards
\n During cellular respiration, carbohydrates are ultimately broken down into
carbon dioxide
37
New cards
Products of glycolysis include
Pyruvate
ATP
NADH
ATP
NADH
38
New cards
Glucose is broken down into ______ during _______
pyruvate; glycolysis
39
New cards
The oxidized form of NADH and FADH2 are:\*
NAD+ and FAD+
40
New cards
The electrons stored in NADH and FADH2 are passed along to
the electron transport chain
41
New cards
A net of 32 ATP molecules are produced during what process of cell respiration?
electron transport chain
42
New cards
\n The final electron acceptor in aerobic respiration is:
oxygen
43
New cards
Which stage of aerobic respiration produces ATP and NADH and releases carbon dioxide?
krebs cycle
44
New cards
\n The electron transport chain pumps protons
out of the matrix and into the inter-membrane space
45
New cards
\n Which process of cellular respiration generates the most ATP?
Chemiosmosis
46
New cards
\n Water is formed during the electron transport chain when __________ is reduced
oxygen
47
New cards
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Metabolic pathway that uses energy released by the oxidation of nutrients to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
48
New cards
Chemiosmosis
movement of protons down the concentration gradient through ATP synthase
49
New cards
Cellular Respiration is a(an) _________________ reaction, meaning it breaks down molecules
catabolic
50
New cards
What do scientists call an organism that puts ATP together using light energy?
Photoautotroph
51
New cards
Cellular respiration is considered to be an _____________ reaction because it ____________ energy.
exergonic; releases
52
New cards
What do scientists call an organism that uses inorganic molecules as a source of carbon to build organic molecules like carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids?
Autotroph
53
New cards
Ultimately all energy on earth comes from the _________
sun
54
New cards
\n The energy released from ATP is used to
perform life activities
build new molecules
power chemical reactions
build new molecules
power chemical reactions
55
New cards
Oxidizing which of the following substances yields the most energy?
glucose
56
New cards
\n What do scientists call an organism that takes in organic matter (food) from other organisms and gets their carbon by breaking down organic carbon compounds from their food?
Heterotroph
57
New cards
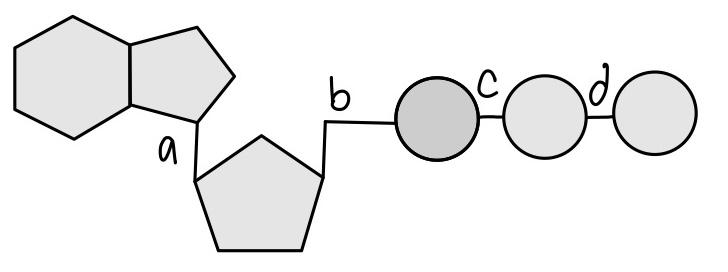
With which bond is the MOST energy contained in this molecule?
D
58
New cards
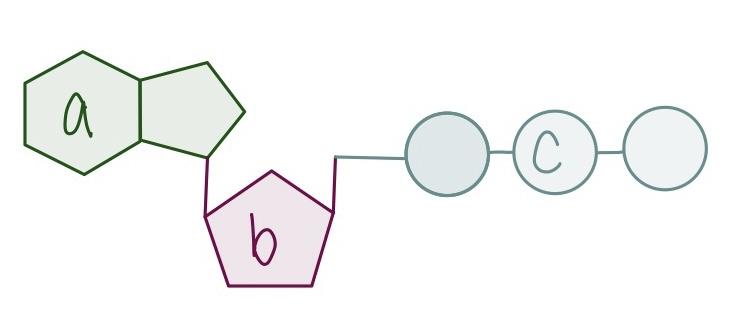
Label the ATP molecule
a-adenine base B-ribose sugar C-phosphate
59
New cards
Breaking the outer phosphate bond of ATP
releases energy
60
New cards
During cellular respiration oxygen is ___________ to ____________
reduced; water