Renal Histology and Physiology I
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
What is the path of renal blood flow? (8)
Renal artery → Segmental Artery → Interlobar Artery→ Arcuate Artery→ Cortical radiate → Afferent arteriole → Glomerulus → Efferent arteriole → Peritubular capillaries/vasa recta → Venous return. (Renal Science Is Actually Cool And Generally Exciting) last two are less important.
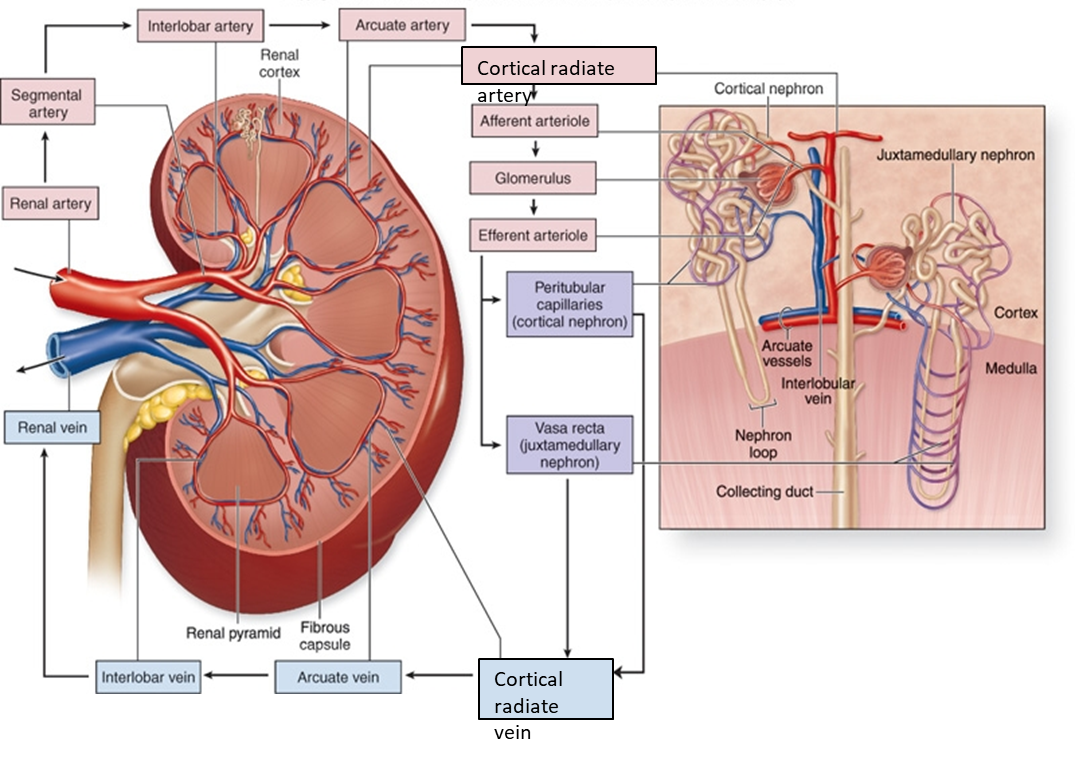
What are the functions of the Kidney? (WEEEB)
Water homeostatis(conc or dilute urine with ADH), Electrolyte levels(balance input and output of ions), Excrete wastes(urea, uric acid, creatinine), Endocrine action(erythropoietin production and activation of Vitamin D to calcitriol), Blood pressure(NA+ reabsorption and renin secretion and the RAAS system(Renin, angiotensin, aldosterone system)
What forms the glomerular filtration barrier?
Fenestrated endothelium, basement membrane, podocyte foot processes, mesangial cells(macrophages)
What is paracellular transport?
Movement of substances BETWEEN (rather than through) epithelial cells via tight junctions, driven by gradients.
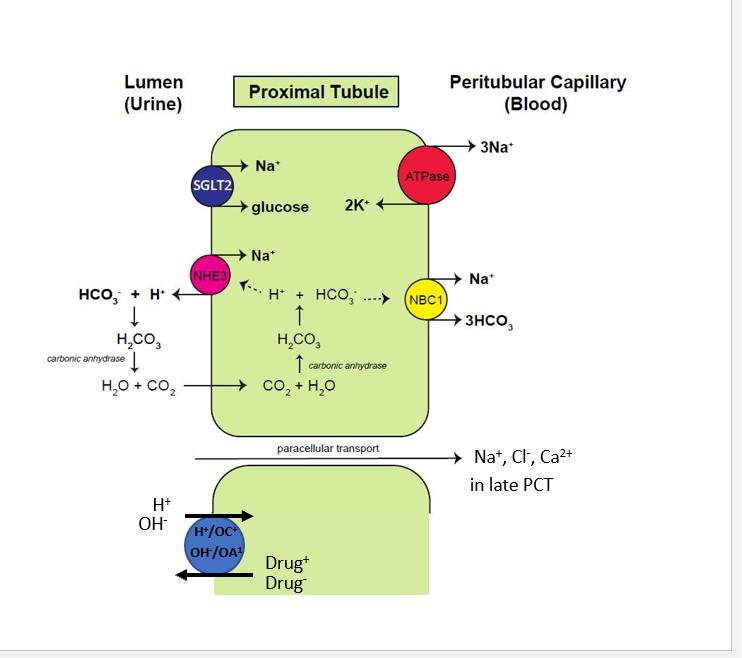
What does the PCT reabsorb?
65–70% Na⁺, water, K⁺; 80–90% HCO₃⁻; 100% glucose and amino acids; significant Ca²⁺, Cl⁻, PO₄³⁻. (Not much Mg2+)
What does the PCT secrete?
Creatinine, urate, drugs, NH₃ (via glutamine metabolism).
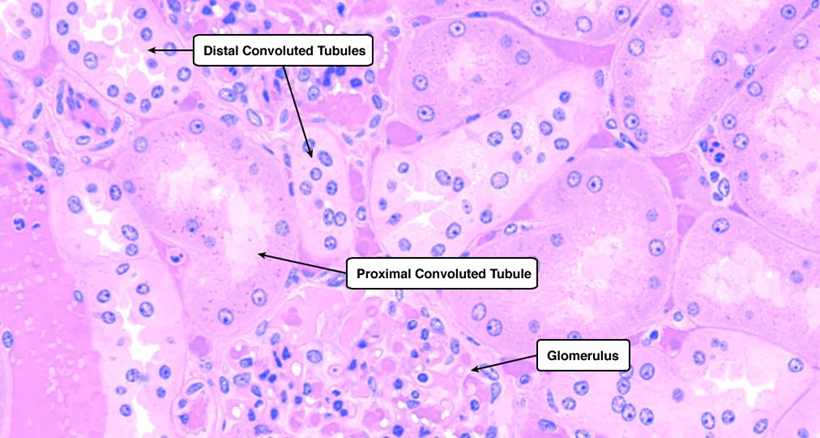
What is the histology of the PCT?
Simple cuboidal epithelium with long microvilli (brush border); lumen often obscured.
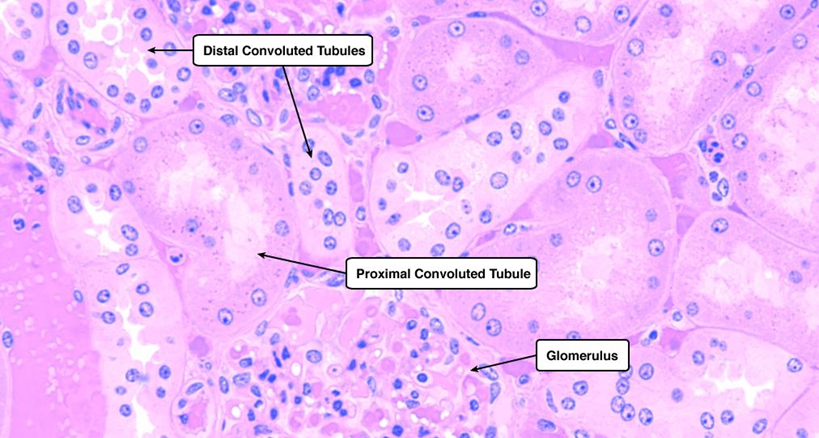
What is Fanconi syndrome?
PCT dysfunction causing glucosuria, aminoaciduria, phosphaturia, bicarbonaturia. Kidney fails to reabsorb electrolytes and nutrients
What transporter reabsorbs glucose in the PCT?
Na⁺/glucose cotransporter
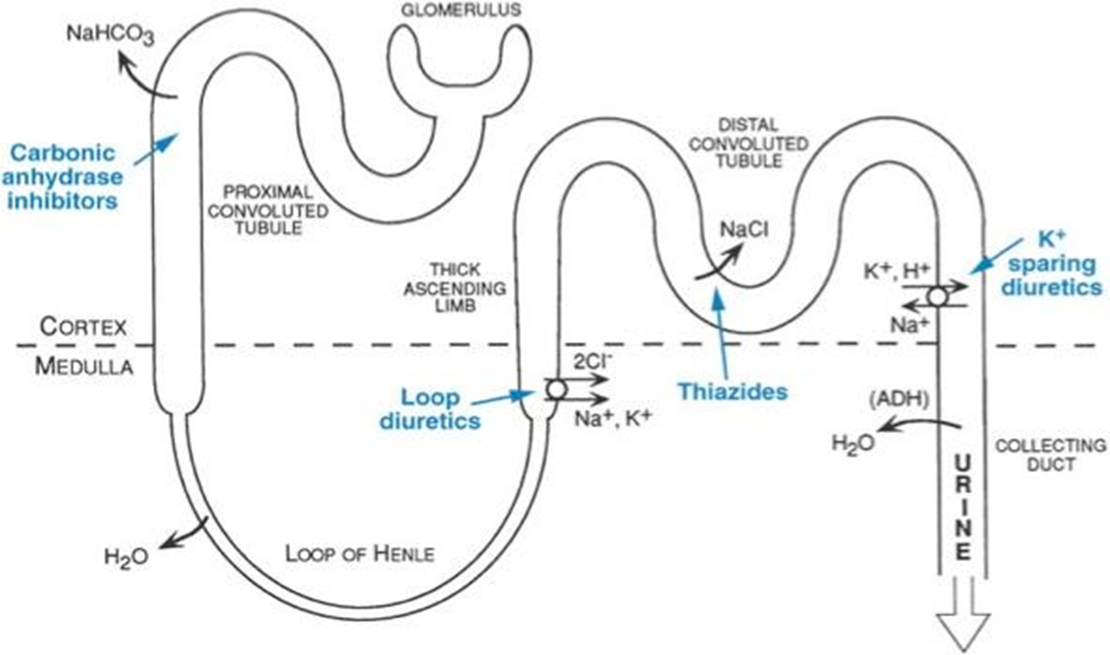
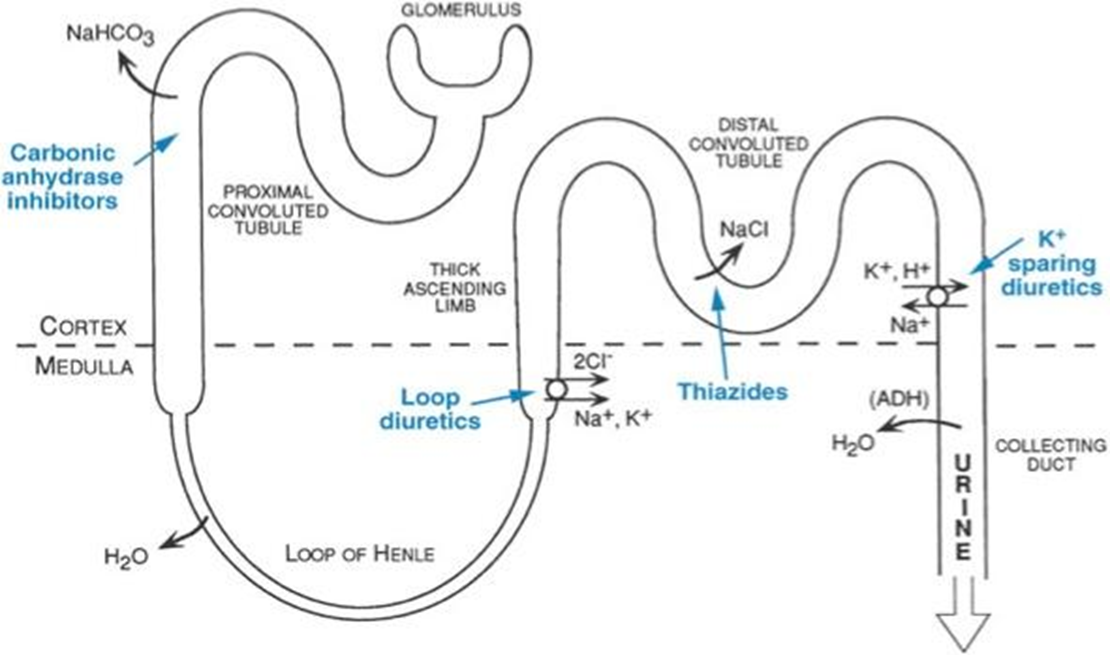
What is the role of carbonic anhydrase in the PCT?
Facilitates H⁺ secretion and HCO₃⁻ reabsorption; inhibited by CA inhibitors.

What hormone stimulates vitamin D activation in the PCT?
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)»increases Ca2+ from bones
What cells near the PCT produce erythropoietin?
Interstitial fibroblasts in response to hypoxia.
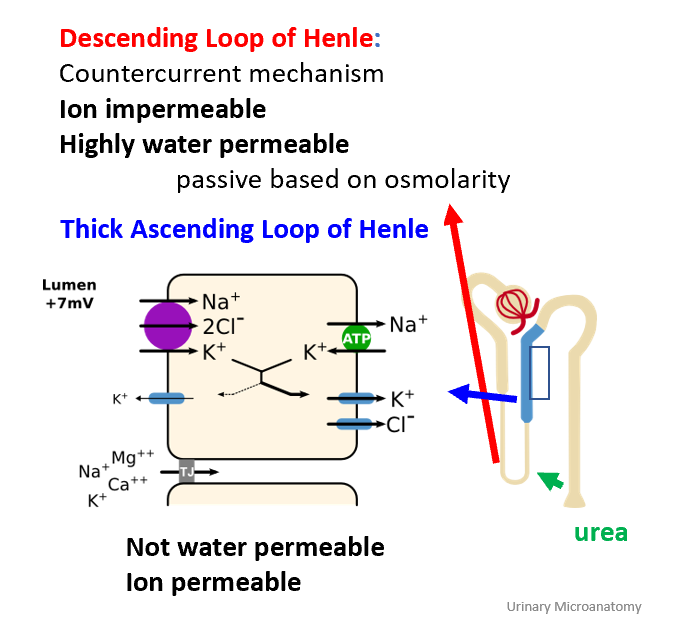
What does the descending limb of LoH do? Histology?
Reabsorbs water; impermeable to ions; concentrates filtrate. Simple squamous
What does the thin ascending limb of LoH do? Histology?
Passive ion reabsorption; impermeable to water; dilutes filtrate. Simple squamous
What does the thick ascending limb of LoH do? Histology
Active reabsorption of Na⁺, K⁺, Cl⁻ via NKCC2, and majority of Mg2+; impermeable to water. Simple cubodial to low columnar, no microvilli
What ion is mostly reabsorbed in the LoH?
Magnesium (70%).
What diuretic targets the thick ascending limb?
Loop diuretics (e.g., furosemide) inhibit NKCC2 (Na, K, Ca, Cl)
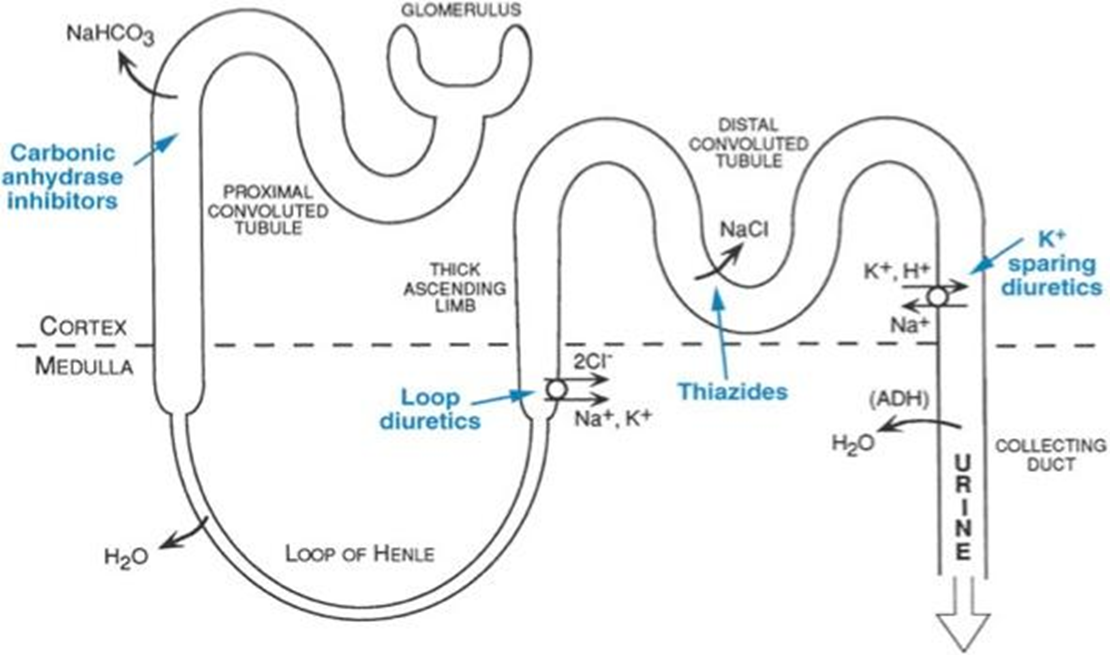
What is the histology of the LoH?
Thin limbs: simple squamous; Thick ascending: cuboidal to low columnar, no microvilli.
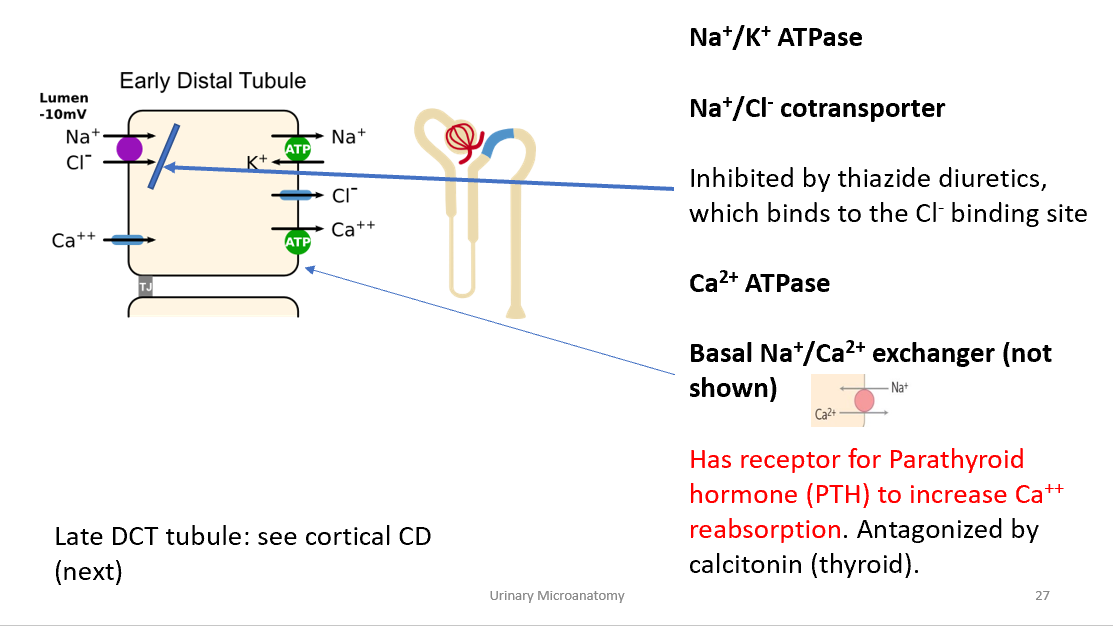
What does the early DCT reabsorb?
Na⁺ (5%), Cl⁻ (5%), Ca²⁺ (10%); fine-tunes electrolyte balance.
What transporter is inhibited by thiazide diuretics?
Na⁺/Cl⁻ cotransporter in early DCT.
What hormone acts on early DCT?
PTH increases Ca²⁺ reabsorption; antagonized by calcitonin.

What is the histology of the early DCT?
Simple cuboidal cells, smaller than PCT, short microvilli, clear lumen.
What does the late DCT and cortical CD reabsorb?
Na⁺, water, bicarbonate; secretes K⁺ and H⁺.
What cells are found in the CD?
Principal cells (Na⁺/water reabsorption, K⁺ secretion); Intercalated cells (H⁺ secretion, HCO₃⁻ reabsorption).
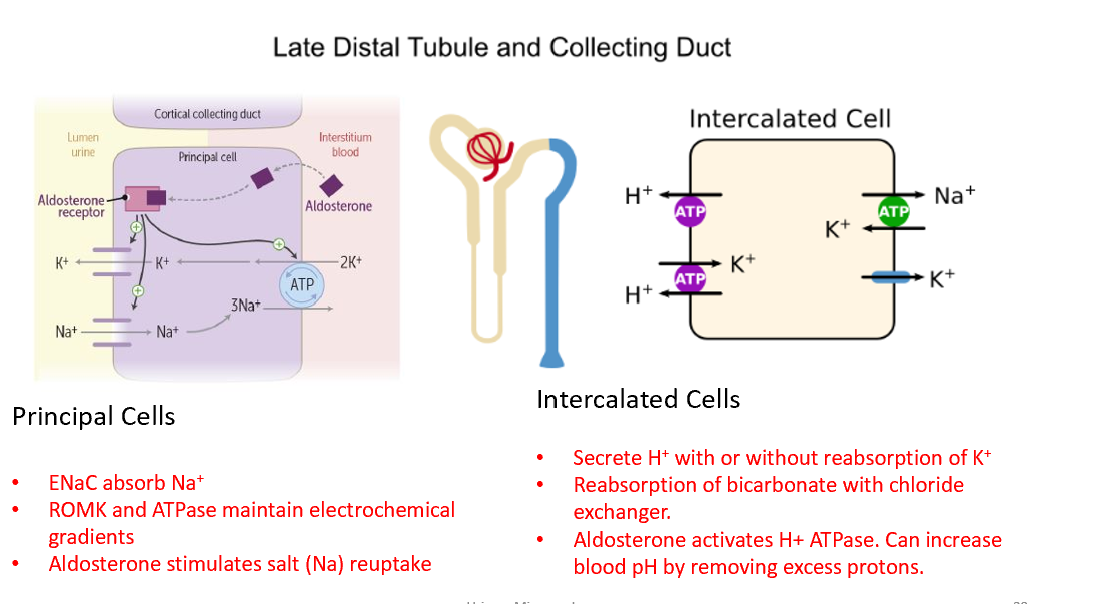

What hormone acts on principal cells?
Aldosterone → ↑ Na⁺ reabsorption, ↑ K⁺ secretion via ENaC and ROMK.
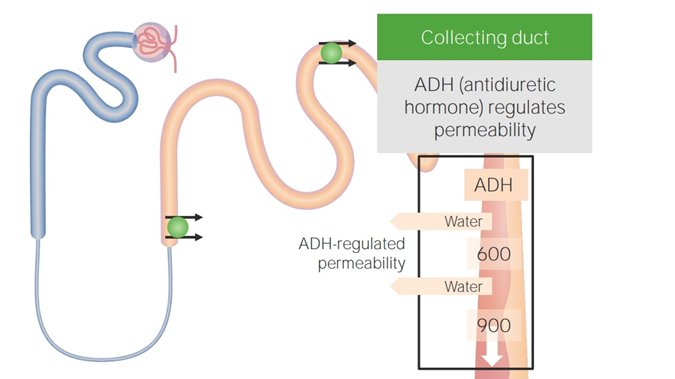
What hormone acts on medullary CD?
ADH → inserts aquaporins, ↑ water reabsorption; ↑ urea reabsorption.
What diuretics target the late DCT/CD?
Potassium-sparing diuretics (e.g., amiloride, spironolactone).
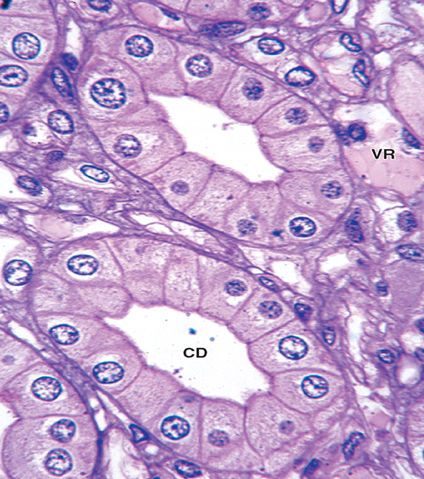
What is the histology of the CD?
Simple cuboidal to columnar; principal cells pale with distinct boundaries; intercalated cells darker.
What hormone is produced near the CD under hypoxia?
Erythropoietin (EPO) by interstitial fibroblasts.
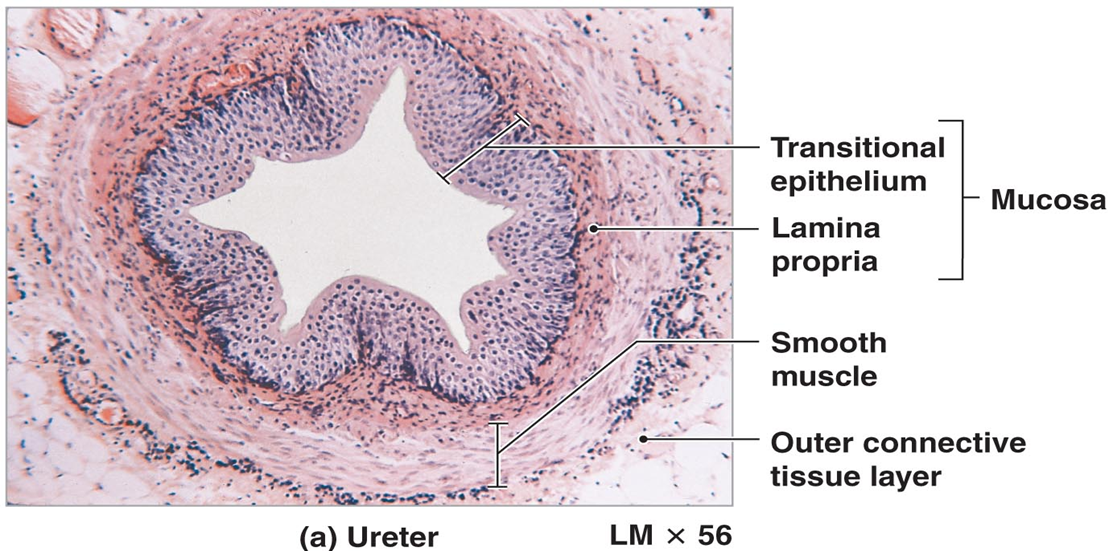
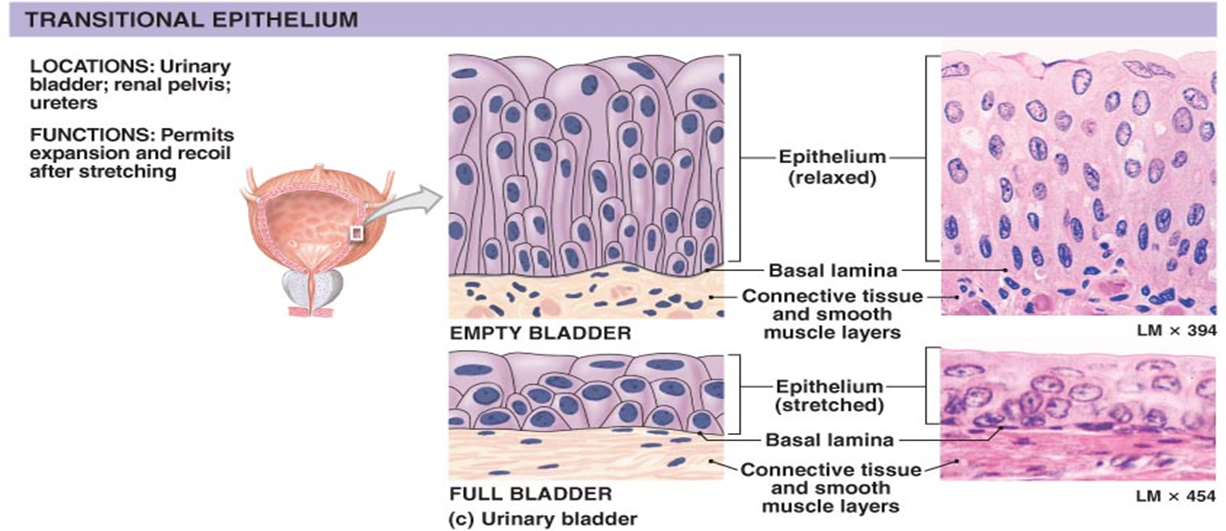
What is transitional epithelium?
Stratified epithelium with dome-shaped umbrella cells; found in ureters and bladder.
How does bladder epithelium change with distention?
Transitional cells flatten; umbrella cells become squamous to accommodate volume.
What are the layers of the ureter?
Mucosa (transitional epithelium), muscularis (inner longitudinal, outer circular), adventitia.
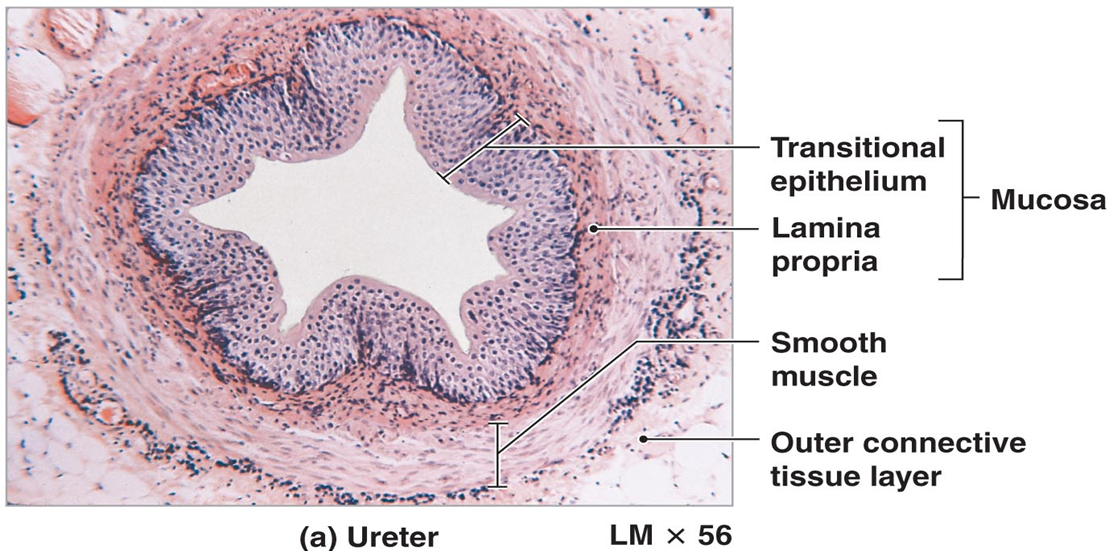
How does ureter histology differ from kidney tubules?
Ureter has transitional epithelium and muscularis layers; kidney tubules have simple cuboidal/squamous epithelium.