Biomechanics (Topic 1B, Scalars, Vectors + Newtons laws of motion)
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Scalar quantity (defintition)
Has magnitude (size) but no direction.
Examples of scalar quantities + Unit
Time (seconds)
Length (meters)
Speed (ms-1)
Mass (kg)
Area (m2)
Vector Quantity (defintion)
Has magnitude (size) and acts in a particular direction
Examples of vector quantities + Unit
Force (N)
Weight (N)
Acceleration (ms-2)
Velocity (ms-1→)
Displacement (m→)
Velocity (definition)
The speed of an object in a particular direction
Distance (definition)
The length covered by an object moving from one point to another. (scalar quantity)
Displacement (defintion)
A vector quantity and describes how an object has moved a distance away from its starting point in a given direction.
Speed (definition)
How fast a body moves in relation to time
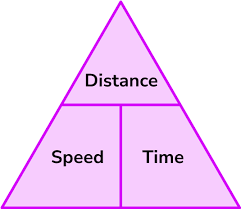
Speed, distance, Time formulas
Distance = speed x time
Speed = Distance over Time
Time = Distance over speed
Velocity (m/s) Formula
Distance over Time (with Direction →)
Acceleration (definition)
The rate of change of a bodies velocity (vector quantity)
Deceleration (definition)
Opposite of acceleration. it is the rate of decrease in a bodies velocity.
Mass (definition)
The amount of matter a body possesses(Kg).
Weight (definition)
The force exerted on a body by gravity.
Weight (formula)
Mass(kg) x Gravity(m/s)
Motion
The action of changing location or position. Motion is described in terms of displacement, velocity, acceleration, speed and time.
Newtons Laws of motion + Benefit
Forms the basis for principles used in sports movements.
Purpose/Benefits: Athletes and coaches can gain a greater understanding of human biomechanics and how the human bodies motion can be influenced by external factors.
Newtons 1st law of Inertia (e.g. of external forces) (1,2,3 = I,A,C)
An object at rest will remain at rest unless acted on by an external force.
If an object is in motion, it will remain in motion until something stops it.
Gravity
Friction
Weather
Braking on a bike
Newtons 2nd law of Acceleration(1,2,3 = I,A,C)
The velocity of a body is changed only when acted upon by an additional force.
The acceleration or deceleration is produced proportional to and in the same direction of the force. e.g. tackling in rugby can slow down, stop, or reverse in direction depending on the force of the tackle.
Newtons 3rd law of Counterforce (1,2,3 = I,A,C)
The production of any force will create another force opposite and equal to the first force.
e.g. in rowing the oar moves through the water, the force produced created counterforce that pushes the boat in the opposite direction.