Chapter 19
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Where is glycolysis done in the cell? Citric acid cycle?
Cytosol
Mitochondria: most done in matrix
Describe precursor step in citric acid cycle:
reactants/products
enzyme
redox reaction? reduced/oxidized
What was released?
Control step?
Pyruvate + NAD+ + CoA-SH → Acetyl-CoA
pyruvate dehydrogenase
NAD is reduced to NADH. Pyruvate is oxidized to acetyl-CoA
1 NADH and 1 CO2 (each molecule)
control
Describe step 1: formation of citrate
reactants/products
enzyme
redox reaction? reduced/oxidized
What was released?
Control step?
Oxaloacetate + acetyl CoA → citrate + CoA-SH
citrate synthase
N/A
N/A
Control
Describe step 2: isomerization of citrate
reactants/products
enzyme
redox reaction? reduced/oxidized
What was released?
Control step?
citrate → isocitrate
aconitase
N/A
N/A
Not control
Describe step 3: formation of α-ketoglutarate and CO2 - First Oxidation
reactants/products
enzyme
redox reaction? reduced/oxidized
What was released?
Control step?
isocitrate → α-ketoglutarate + CO2
isocitrate degydrogenase
NAD is reduced to NADH. Isocitrate is oxidized to α-ketogluterate
1 NADH and 1 CO2 (each molecule)
Control
Describe step 4: formation of succinyl CoA and CO2
reactants/products
enzyme
redox reaction? reduced/oxidized
What was released?
Control step?
α-ketogluterate + CoA-SH + NAD+ → succinyl-CoA
α-ketogluterate dehydrogenase complex
NAD is reduced to NADH. α-ketogluterate is oxidized to succinyl-CoA *uses redox energy to attach CoA
1 CO2 (each molecule)
Control
Describe step 5: formation of succinate
reactants/products
enzyme
redox reaction? reduced/oxidized
What was released?
Control step?
succinyl CoA → succinate
succinyl CoA synthetase
N/A
CoA and 1 GTP (each molecule)
not control
Describe step 6: formation of fumerate
reactants/products
enzyme
redox reaction? reduced/oxidized
What was released?
Control step?
succinate → fumarate
succinate dehydrogenase * takes place in inner mitochondria membrane
FAD is reduced to FADH2. Succinate is oxidized to fumerate
1 FADH2 (each molecule)
not control
Describe step 7: formation of L-malate
reactants/products
enzyme
redox reaction? reduced/oxidized
What was released?
Control step?
fumerate + H2O → L-malate
fumerase
N/A
N/A
not control
Describe step 8: regeneration of oxaloacetate
reactants/products
enzyme
redox reaction? reduced/oxidized
What was released?
Control step?
L-malate + NAD+ → oxaloacetate + NADH
malate dehydrogenase
NAD is reduced to NADH. Malate is oxidized to oxaloacetate
1 NADH (each molecule)
not control
What are the control steps in citric acid cycle?
precursor
1
3
4
What citric acid cycle steps release CO2?
precursor, 3, 4
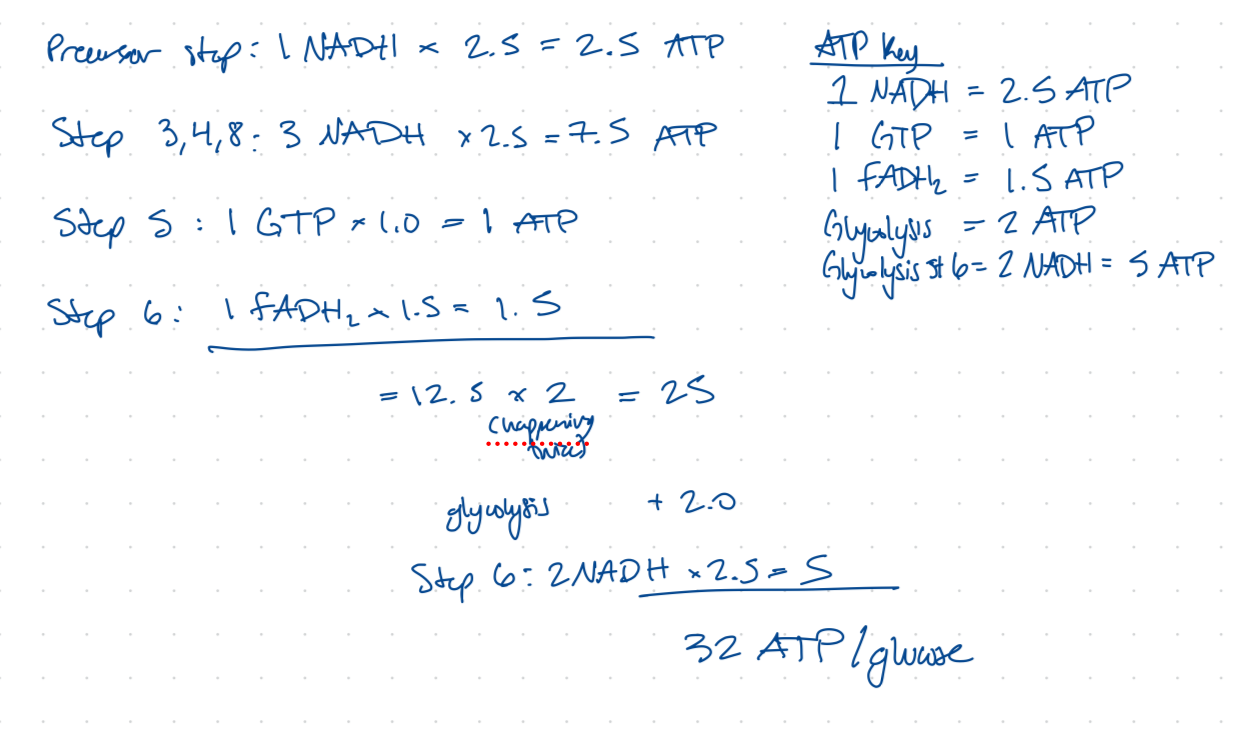
Calculate the amount of ATP in the citric acid cycle
Which steps of the citric acid cycle are redox reactions?
steps 3, 4, 6, 8
Which steps of the citric acid cycle produce NADH?
steps 3, 4, 8
Which steps of the citric acid cycle produce FADH2?
step 6
Which steps of the citric acid cycle produce GTP?
step 5
If fructose 6 phosphate is fed into glycolysis, how much energy would be producted under aerobic conditions?
33 ATP

How does ATP affect citric acid cycle?
increased levels of ATP turn off control steps: precursor, 1, 3, 4
How does NADH affect citric acid cycle?
increased levels of NADH turn off control steps
What are the negative and positive allosteric receptiors
Negative:ATP, NADH
Positive: ADP + NAD+
What is the ATP/ADP and NADH/NAD+ ratio for cells in a resting state? *EXAM
High ATP, low ATP = ATP ratio is high
High NADH, low NAD+ = NADH ratio is high
What is the ATP/ADP and NADH/NAD+ ratio for cells in an active state? *EXAM
Low ATP, high ATP = ATP ratio is low
Low NADH, high NAD+ = NADH ratio is low
Glyoxylate cycle
Where it occurs
Main purpose
plant and bacteria
gains carbohydrate from acetyl CoA
If valine is fed into the citric acid cycle as succinyl CoA, how much ATP would be made?
5 ATP

Describe oxaloacetate (beginning reactant for citric acid cycle)
only comes from carbohydrates for animals
uses enzyme pyruvate carboxylase and CO2 to make oxaloacetate
acetyl CoA gets oxaloacetate in plants and bacteria
Oxaloacetate is apart of which step(s) of the citric acid cycle?
step 1 and 8
Which control enzyme is responsible for activating pyruvate dehydrogenase?
pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase
What are the control enzymes of the citric acid cycle?
citrate synthase
isocitrate dehydrogenase
α- keglutarate dehydrogenase
For the control enzymes, which of the following are allosteric inhibitors?
NADH and ATP
When glutamine is degraded it enters the citric acid cycle as the product of step 3, how much ATP would result from glutamate?
7.5 ATP