Reptiles external morphology (Bolded)
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Scute
Scale alternative for turtle
Anapsid
Synapsid
Diapsid
Top to bottom skull type
Carapace
Endochondral ribs and vertebrae
Top shell of a turtle and where it’s fused
Plastron
remaining elements of pectoral girdle
bottom shell of turtle and where what it incorperates
Scutes
Bone of carapace except close to neck
thin bone surrounding edge
In leatherback turtles: what is lost (2), what has plastron ones become
Manus, antebrachium, brachium, pes, shank, thigh FINISH NICE RIGHT OK
tetrapod limb divisions
Claws
Specialization of the epidermis in all higher vertebrates
Anus opens beyond end of carapace
Front foot claws longer than on hind foot vs even
Plastron slight to concave vs convex
Differentiating a male vs female turtle 3 external ways
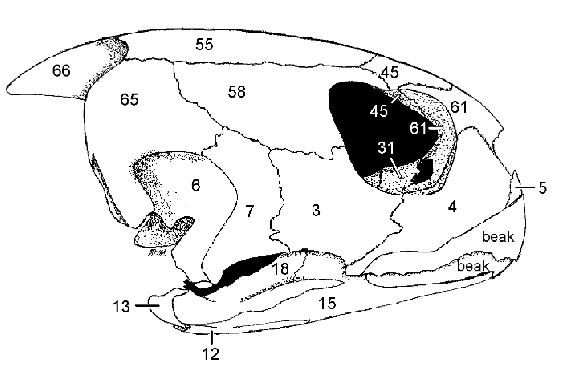
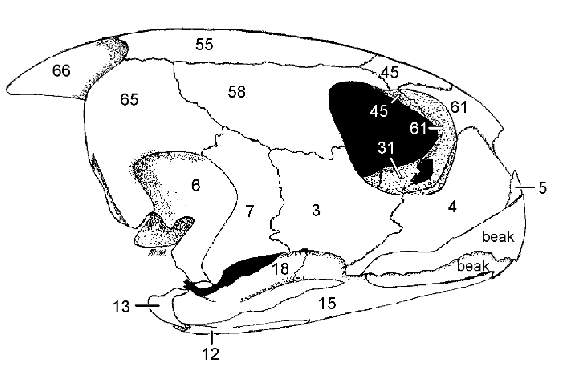
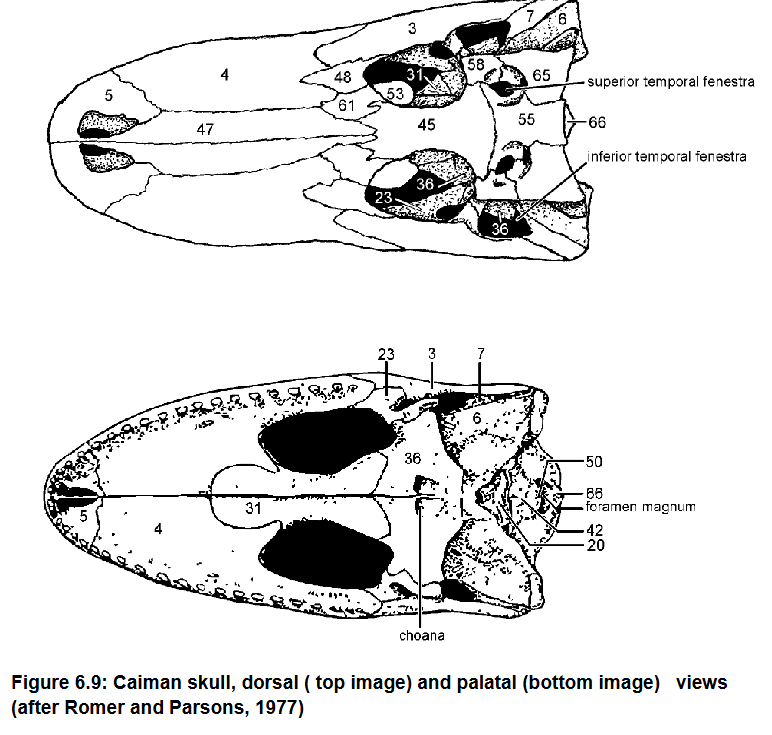
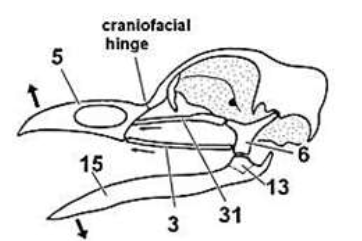
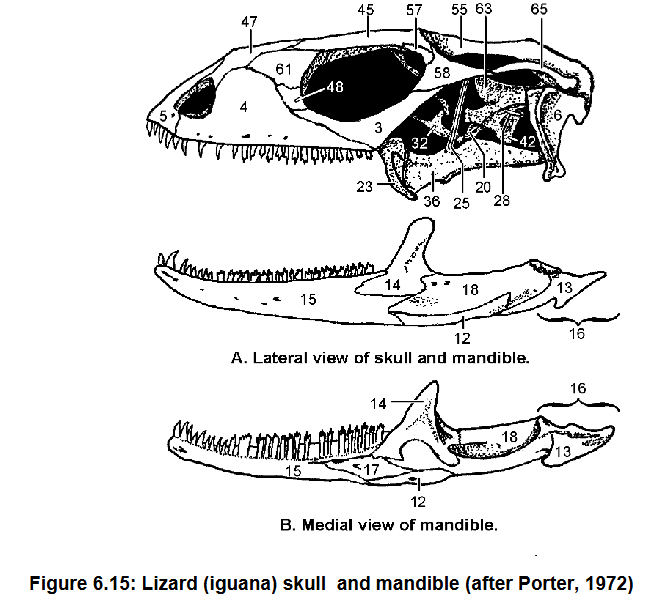
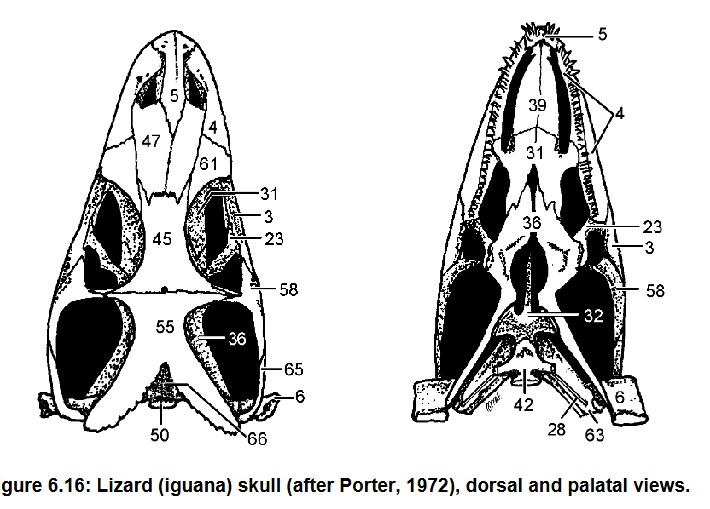
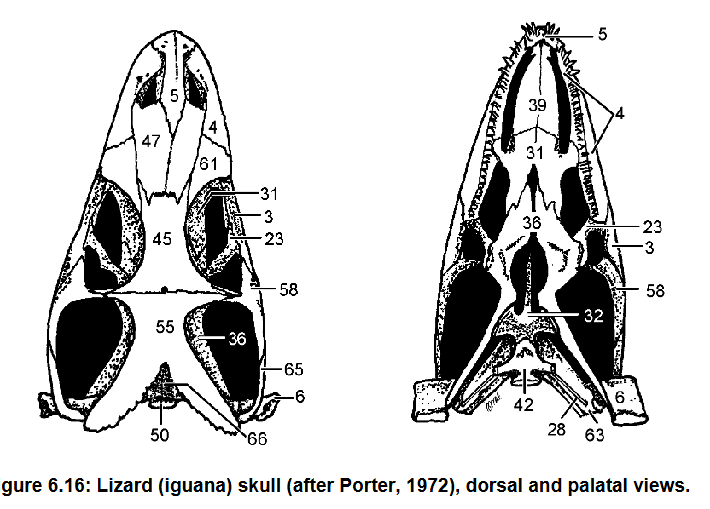
4: Maxilla
3: Jugal
Contribute to lateral floor of the orbit
Articulate with the Palatine (31)
4, 3, what they do, what they articulate with
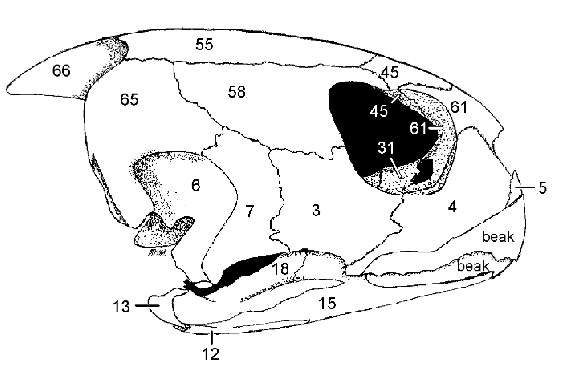
Postorbital forms dorsocaudal edge of orbit
58 and function
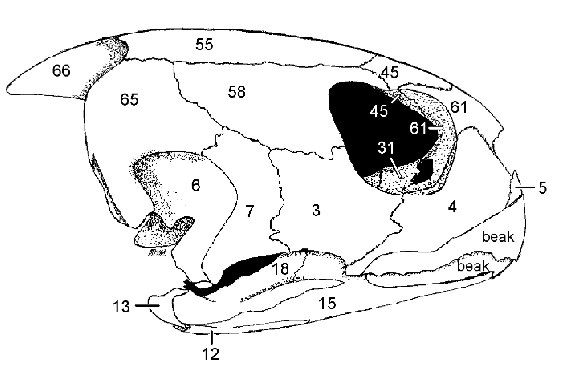
Orbit
Term denoting the eye socket in the skull
Quadrate, most of the inner wall of the tympanic cavity, sutured to squamosal (65)
Pterygoid, forms part of floor of middle ear cavity
Quadratojugal, jugal (3)
6, what it forms, what it’s sutured to
36, what it forms
7, what it forms it is caudal to what
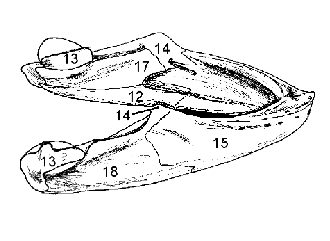
Quadrate (6) and Articular (13)
What forms the jaw suspension
Dentary
Coronoid
Surangular
Splenial
Angular
Articular
15
14
18
17
12
13
Palatal
View given
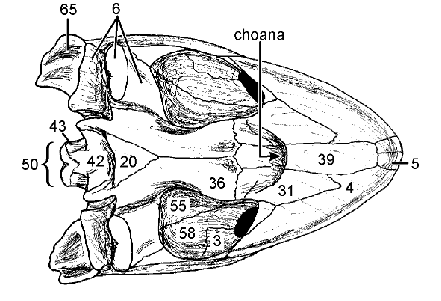
Premaxilla (5), Maxilla (4), palatine (31)
Bones that form the secondary palate in green sea turtle
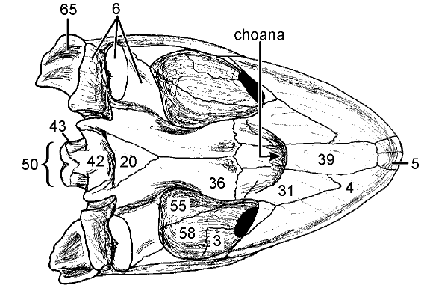
Basisphenoid
Pterygoid: Forms much of palate caudal to Choanae
20
36 what it forms
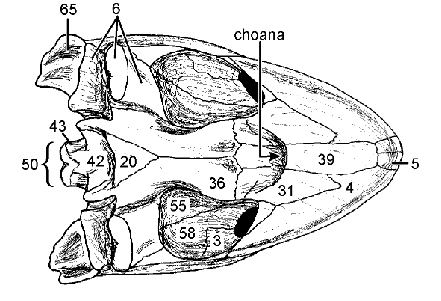
Choanae
Internal opening of nasal cavity
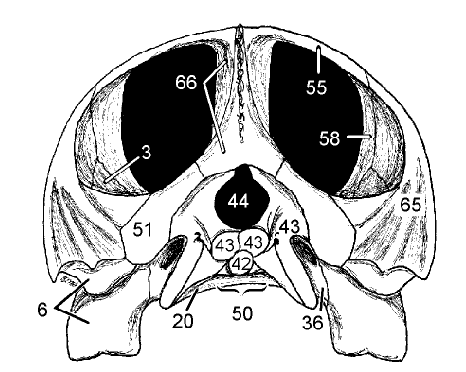
(caudal) Foramen magnum: Spinal cord enters it
Dorsal formed by supraoccipital (66)
44 and what it does, what forms its dorsal margin
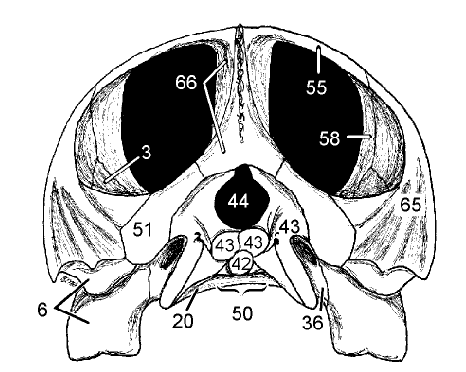
Exoccipitals (43) laterally and basioccipital (42) in other directions
What surrounds the foramen mangum
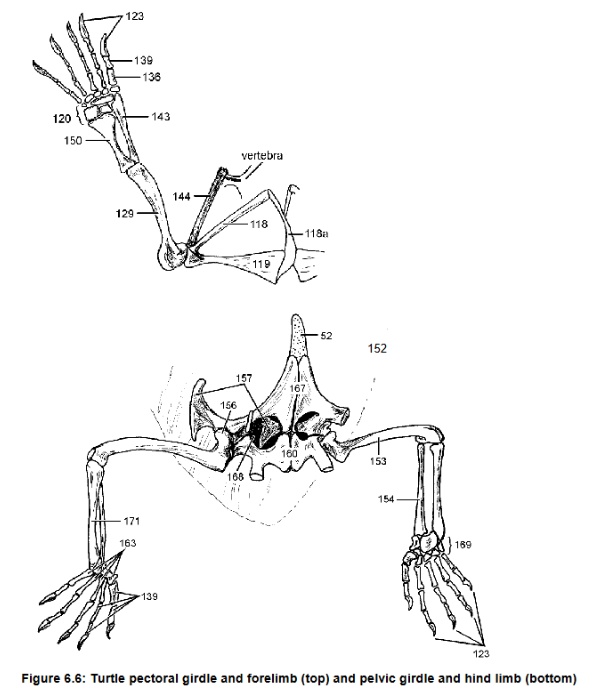
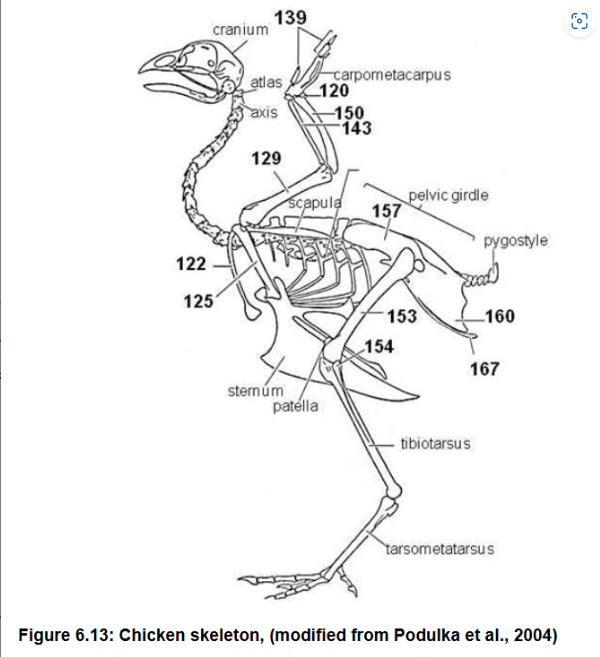
Humerus and femur
Move on horizontal plane when walking to maximize stability over speed
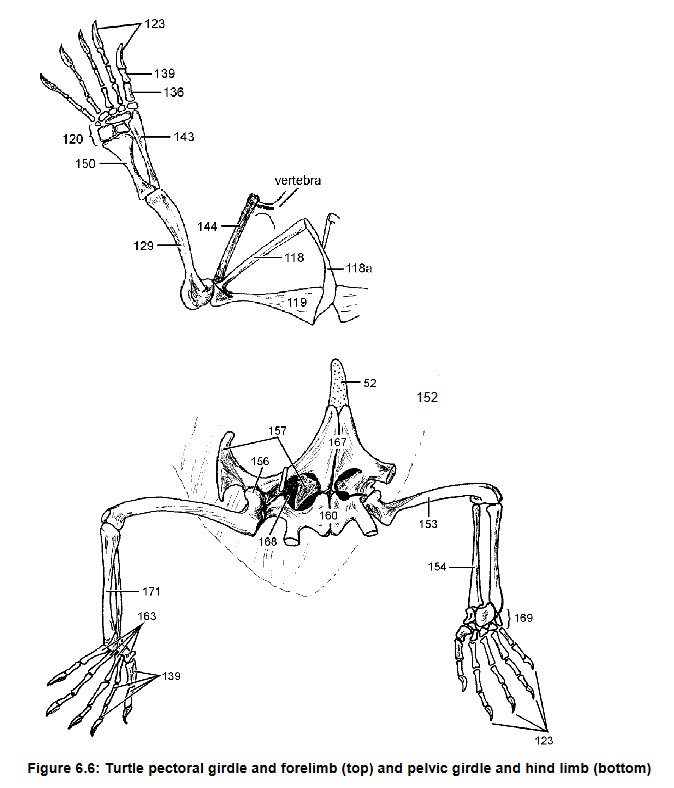
129 and 153 and their uniqueness in turtles and why
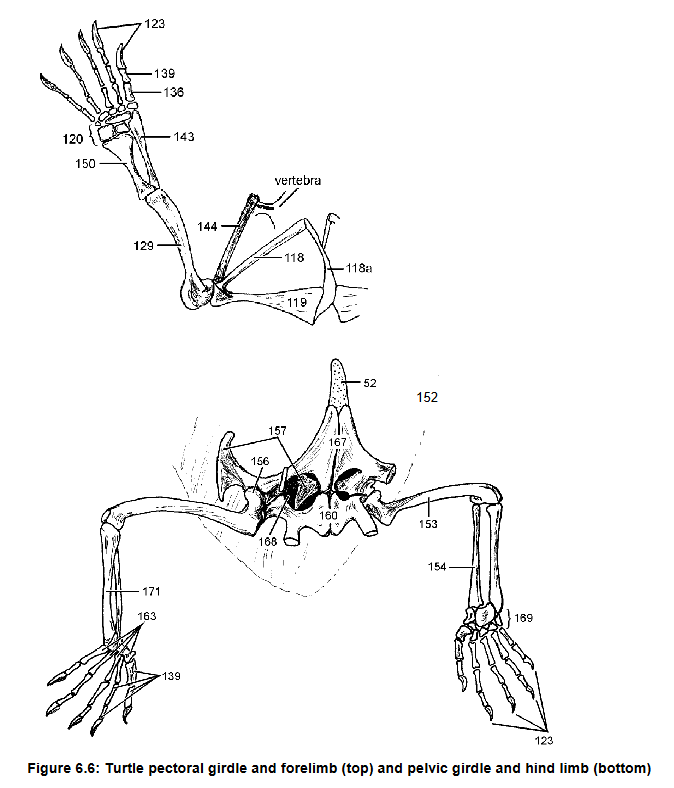
Acromion, connects scapula (144) to plastron via ligament
118, what it does
125 what it forms
129, what it articulates with
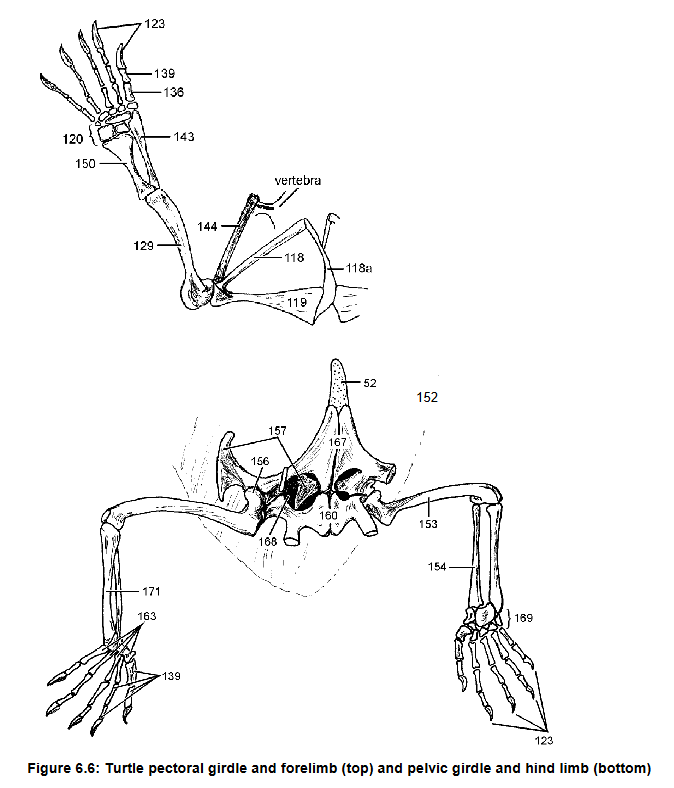
Humerus, radius, ulna, metacarpal
Separate articulations w/ carpals
129, 143, 150, 136
How 143 and 150 connect to 120
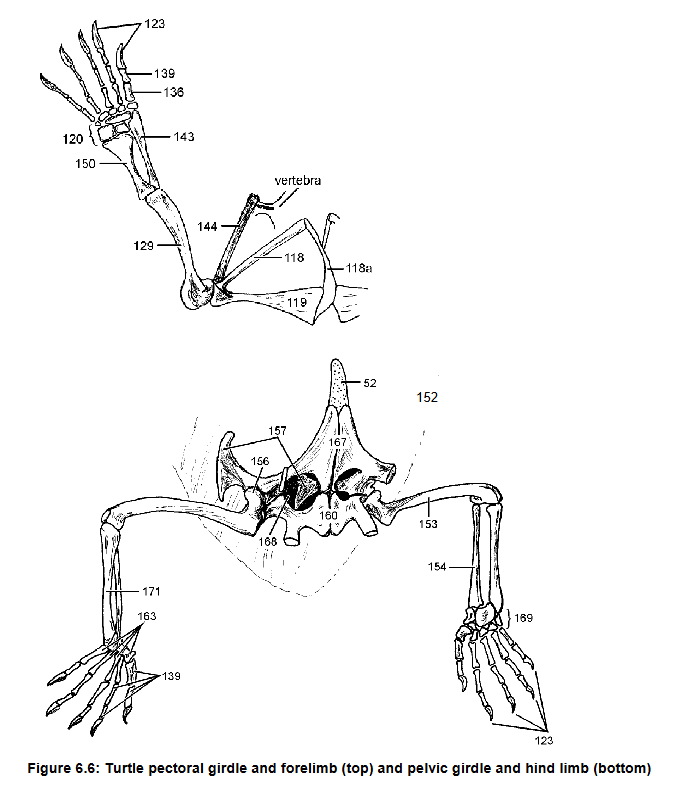
Claw on phalynx, first on reptiles
136 what it is attached to, which species it first appears
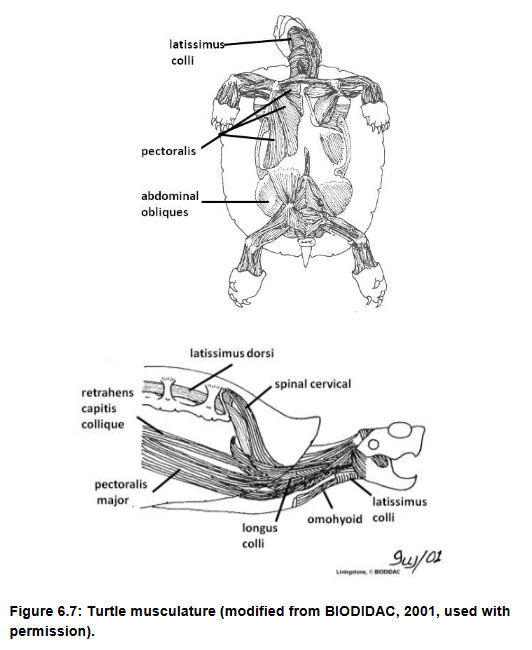
Pectoralis group, originates on plastron, inserts on had of humerus, draws humerus toward the body (retracts and abducts)
Latissimus Dorsi: originates on the ventral carapace and scapula, insnerts on humerus, pulls forelimb dorsally and anteriorly
M-95, origin and insertion, function
M-78, origin and insertion, function
157 - ilium: connects pelvic girdle to axial skeleton
ishium
femur
pubis
Pubioschiadic fenestra
157 function
160
153
167 and its cartilage extension
168
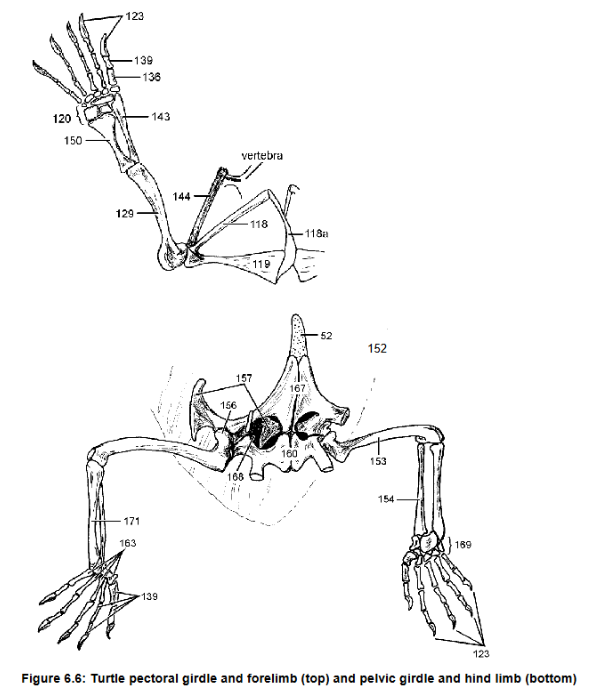
Tarsals, fully
Metatarsal
169, Are they ossified?
163
On top
Crocodilian nare modification
Surangular (18) above
Angular (12) below
Dentary (15) anteriorly
What bounds the fenestra above, below, and anteriorly
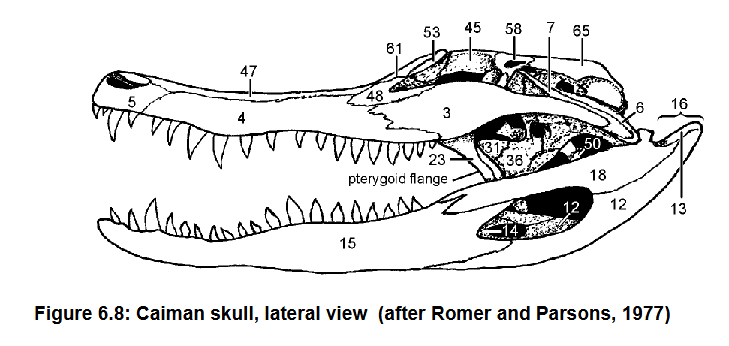
Articular (13)
What is dorsal, caudal, and medial to the angular, more visible in back view
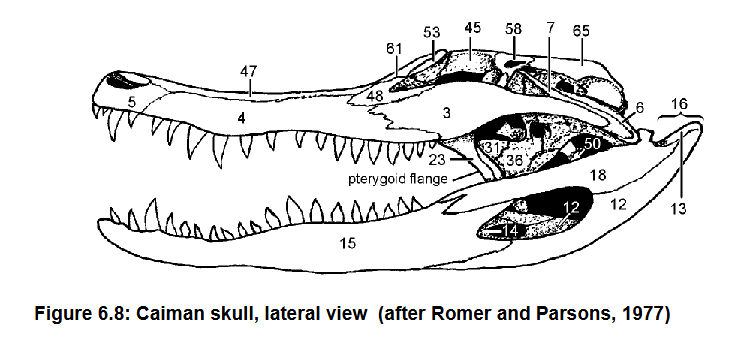
Coronoid (14) forms anteromedial border of lateral fenestra
Ectyopterygoid (36) sutured to anterior edge of pterygoid flange (written) which is distinctive feature of crocodilians
14 and what it forms
36 and what it’s sutured to and why it’s important
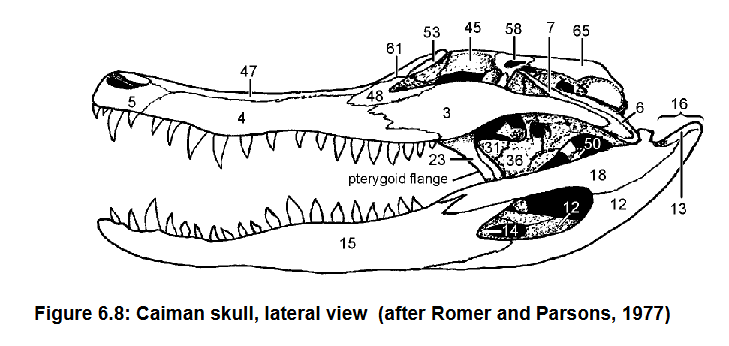
Jaw articulates b/w articular (13) and surangular (18) of lower jaw and quadrate (6) of upper jaw
Retroarticular process (!6)
How the jaw articulates in crocodilians
Lower jaw projection
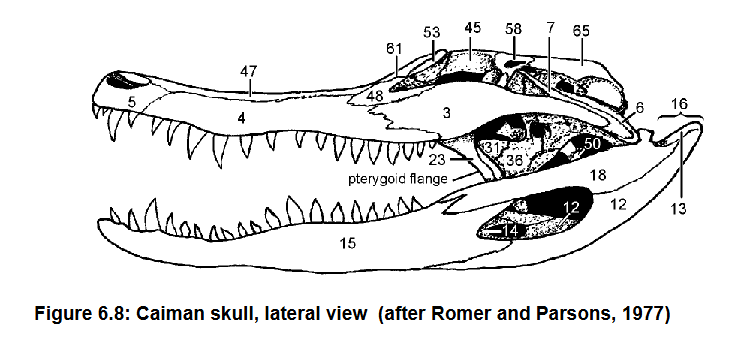
Vomer, separates two halves of the nasal cavity
39, function
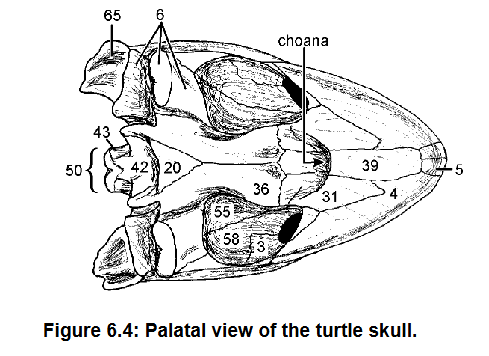
Palatine (31) articulates w/ maxilla (4) anterior, pterygoid (36) posteriorly
Choanae
31 and what it articulates with, what are holes in 36 called
Neck articulation
Exoccipitals, occipital condyle
43, 50, function
Cervicle, thoracic, lumbar, sacral
Cranial to caudal the vertebrae of crocodilia
Ilium (157), pubis (not visible), ischium (160)
Parts of the pelvic girdle
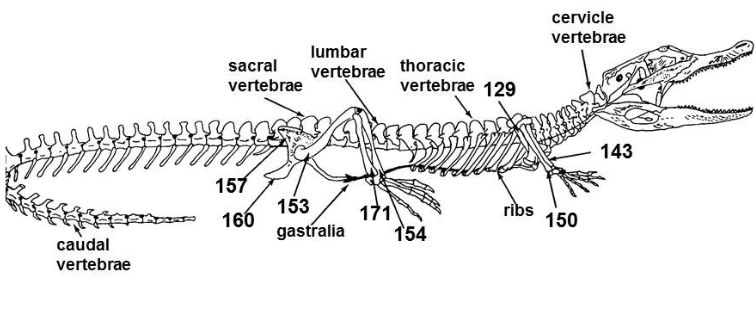
Floating dermal ribs, gastralia
Type of ribs and other name in crocodilia
Flat
Concave
Round
Pointed
Types of tail in following
Swallow
grouse
hawk
gull
Upper: Premaxilla (5)
Lower: Dentary (15)
Cere, fleshy covering
What forms upper and lower beak
Nares covered by what?
Sclerotic ring
Structure in bird orbit that supports but limits movement
Jugal (3)
Thin bar
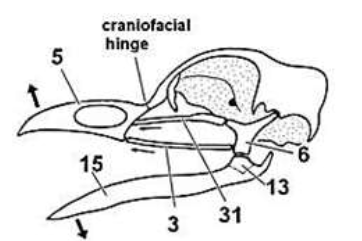
Between articular (13) and quadrate (6)
Location of jaw suspension
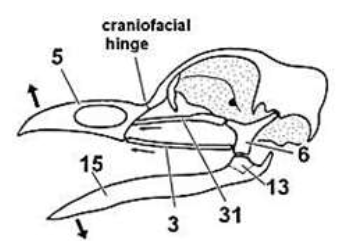
Atlas articulating with Occipital condyle (50)
Multifidid cervices: complex group of small muscles for neck flexibility
What allows head movement
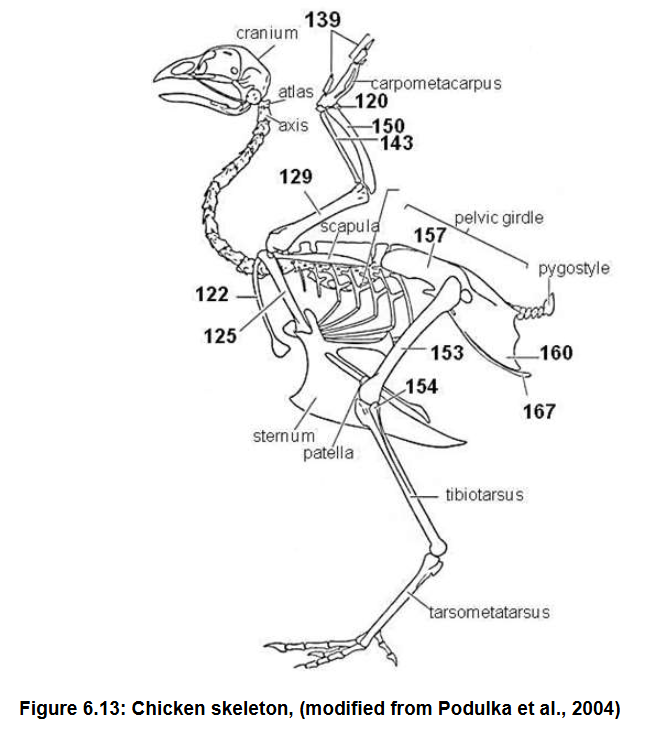
Humerus (129)
Radius (143)
Ulna (150)
Carpometacarpus (fusion of two carpals)
Phalanges (139)
Bones that make up the wing
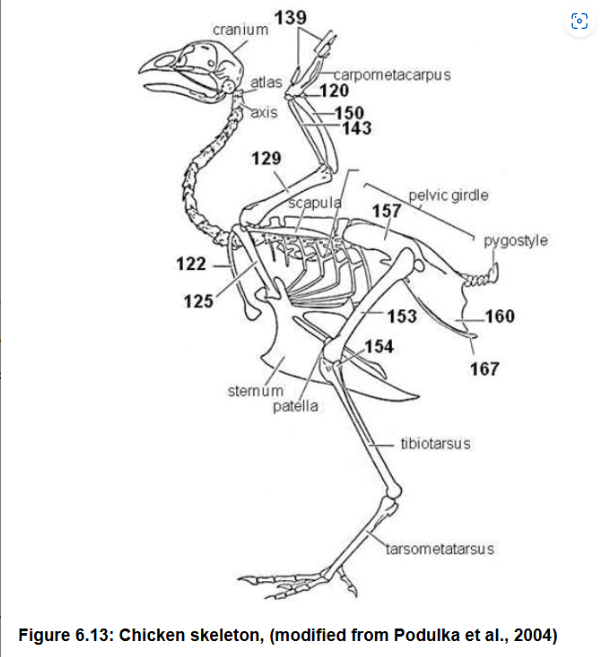
Scapula (144)
Coracoids (125) link scapula to sternum
Clavicles (122) left and right fused into V called Furcula, attached to sternum
prevent collapse of chest cavity during wing beats
Pectoral girdle bones and modification of 122
Function of 125
Pectoralis (95) powers downstroke by adduction of humerus (129). Origin on furcula and keel of sternum, inserts on ventral surface of humerus (129)
Supracoracoides (underlying, not shown), powers upstroke, smaller. Originates on sternum, inserts on dorsal of humerus.
Stability
Two main flight muscles, origin and insertion, function
Coracoid function
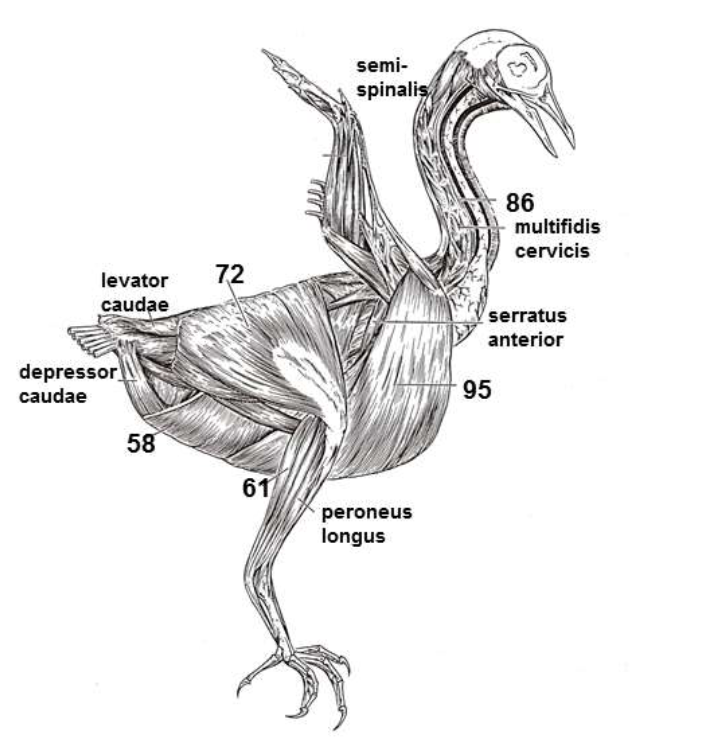
Biceps brachii
Articulation of the elbow via the humerus (129), radius (143), and ulna (150)
Muscle that folds wing during flight and it’s articulation
Originates on dorsal, inserts on ventral ribs (116) and scapula (144)
Support rib cage and thus pectoral girdle, movement in respiration
Serratus anterior origin and insertion, function
Pygostyle
Fused vertebrae of the tail
Levator and Depressor caudae
Both originate on pelvis, insert on caudal vertebrae
Two muscles for tail steering in flight and origin and insertion
Ilium (157)
Ischium (160)
Pubis (167)
Parts of the pelvis
Tibiotarsus
Fusion in birds of tibia
Tarsometatarsus
In birds, fusion of 2nd 3rd and 4th metatarsals
Iliotibais, originates on anterior ilium (157), inserts on patella ligament
Peroneus longii
Gastrocnemius
Muscle that extends tibiotarsus, origin and insertion
Muscle that flexes digits
Muscle that extends foot
Dewlap, unfolded by special muscles
Intraspecies communication, predator deterence
Fold of skin on hyoid of some lizards, function
Quadrate attached to tympanum for transmitting sound
Lower bar of inferior temporal fenestra lost for quadrate mobility
One modification of a lizard quadrate for the body and one body modification for the quadrate
Coronoid, process for muscle attachment
Articular (13) with quadrate (6)
Retroarticular process (16)
14 and what it forms
What two form the jaw joint
projection of 6
Streptostyly
Increases gape size, keeps jaws parallel for biting, maintains tympanum tension
Phenomenon where when the lower jaw drops the quadrate swings forward, snout rotates downwards around a joint with the skull roof, function
Vomer (39)
Palatine (31), articulates vomer (39) anteriorly, pterygoid (36) anteriorly
What forms anterior palate
What forms much of the floor of the orbit and what it articulates with
Basioccipital (42) forms lower border of foramen magnum (44)
Basioccipital (42) and exoccipitals (43) make occipital condyle
42 and function
What makes 50
Both temporal arches
Quadrate
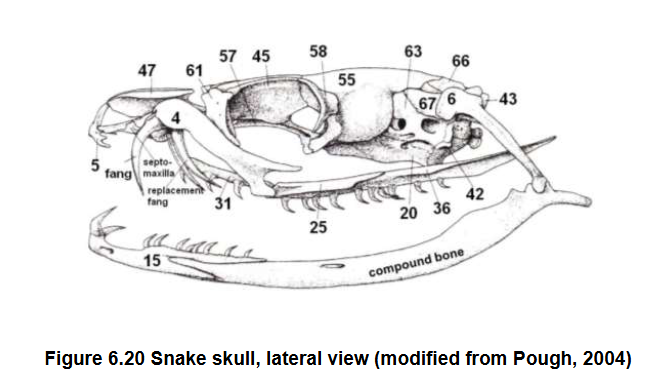
What is lost in snake skull
6
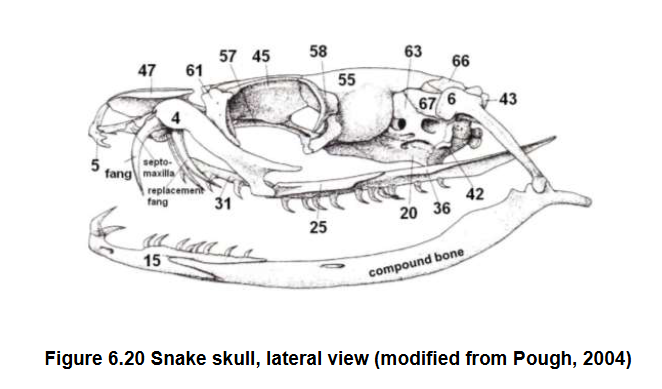
Elongated quadrate (6) and pterygoids (36)
Maxilla (4), palatine (31), pterygoid (36)
Feeding adaptations
Which bones bear teeth