Dental Anatomy and Morphology
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
Homodont
having only one tooth form (ex. sharks)
Heterodont
having multiple tooth forms (ex. humans)
Diphyodont
Having two separate sets of teeth (2 dentitions)
Monophyodont
Having only one dentition
Polyphyodont
Having more than two dentitions
Dentulous/Dentate
having teeth
Edentulous
having no teeth
Partially Edentulous
missing some teeth
Maxilla
upper jaw
mandible
lower jaw
Anterior teeth
incisors and canines
Functions of anterior teeth
esthetics - smiling
phonetics - speaking
incising - biting
Posterior teeth
premolars and molars
Functions of posterior teeth
limited esthetics - broad smile
mastication (tearing, holding, grinding)
Functions of incisors
biting, incising, shearing, cutting
Functions of canines
cutting, piercing, tearing, holding
Functions of premolars
tearing, holding, grinding
Functions of molars
grinding
Primary dentition
deciduous
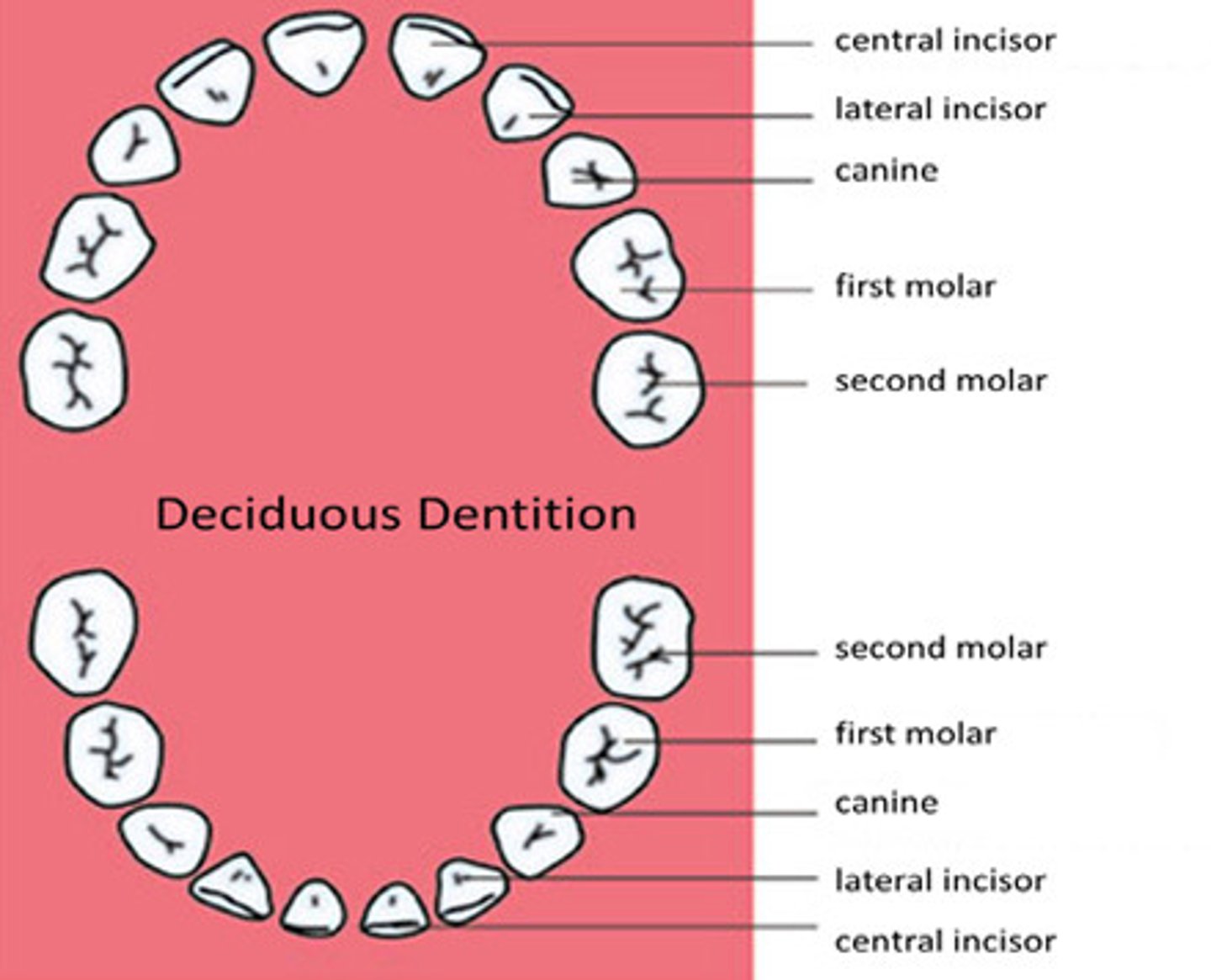
Permanent dentition
secondary dentition
how many deciduous teeth are there?
20
how many permanent teeth are there?
32
Primary dentition lasts from ______ to ______
6 months old to 6 years old
Mixed dentition lasts from ______ to ______
6 years old to 12-13 years old
Permanent dentition begins at
12 years old
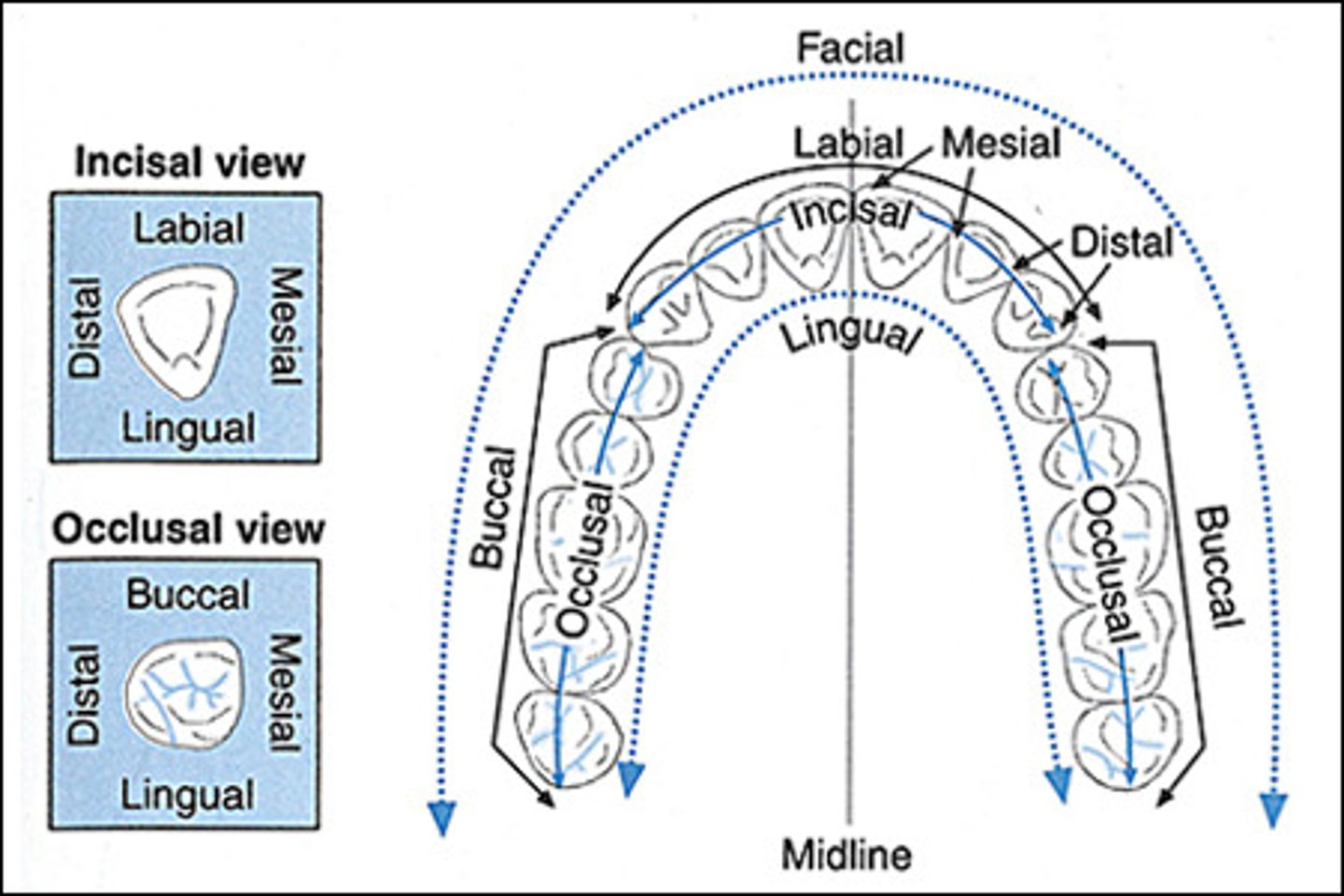
Labial surface
tooth surface facing the lips
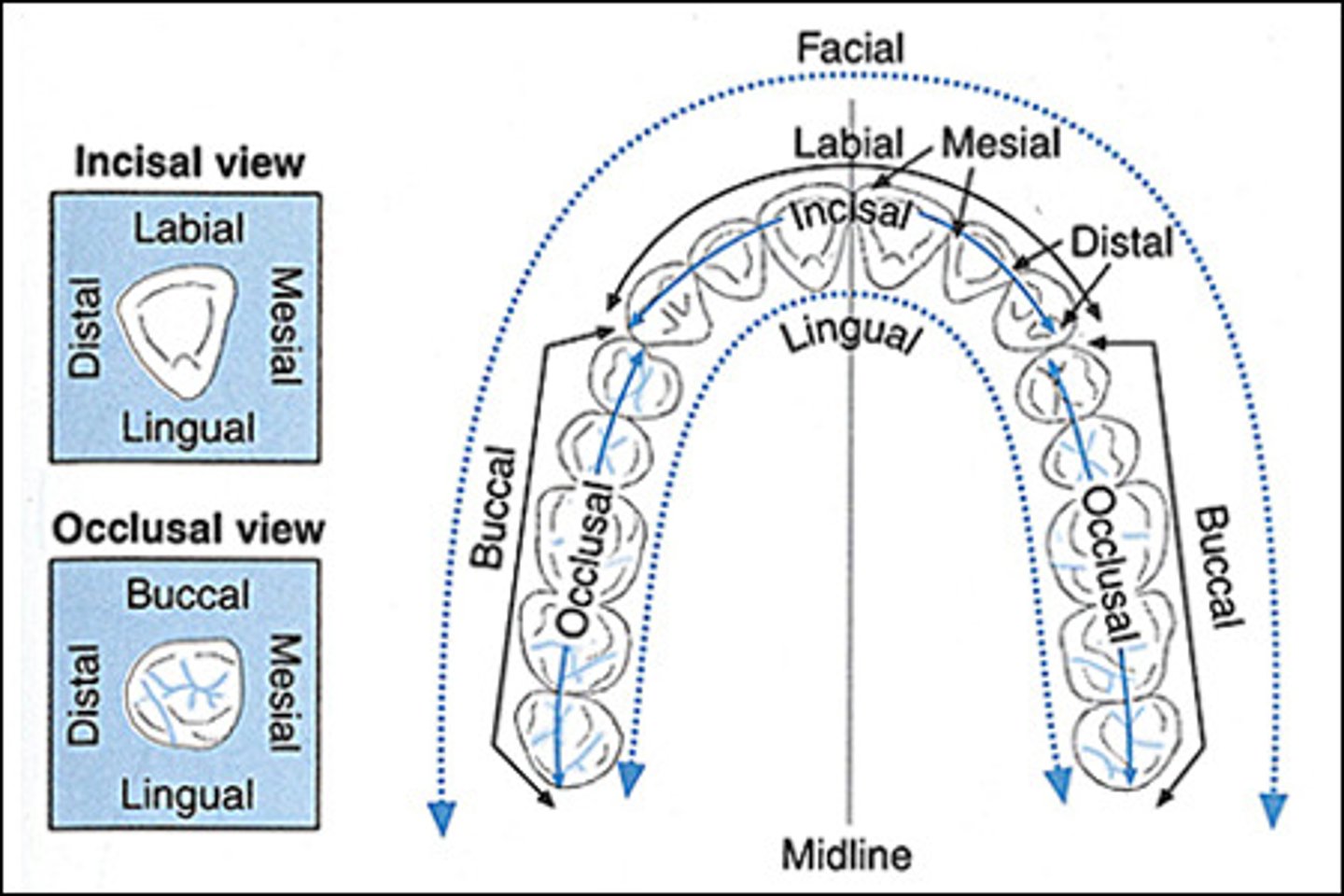
Facial surface
same as labial surface
buccal surface
Tooth surface closest to the inner cheek
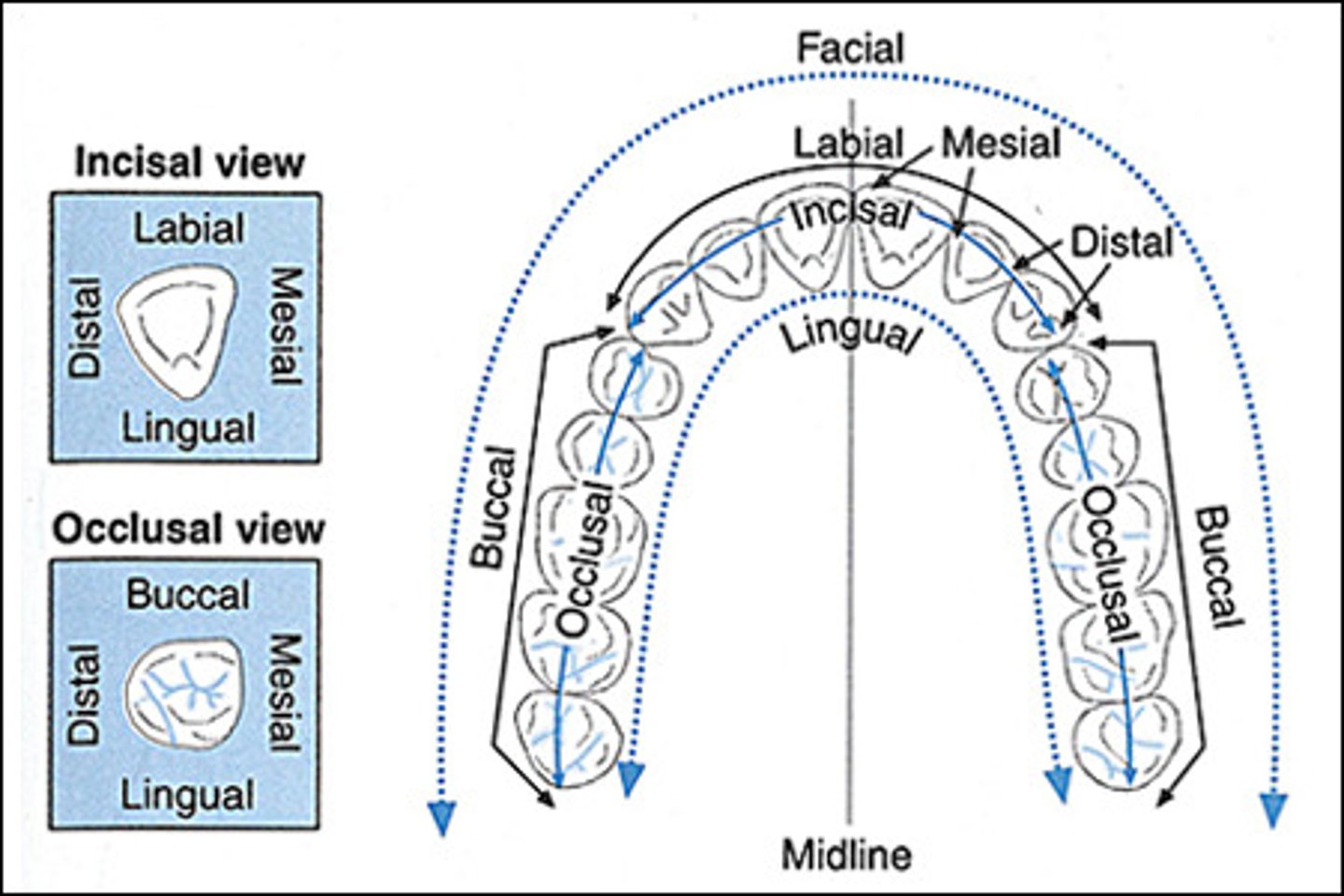
lingual surface
surface of the tooth that faces the tongue
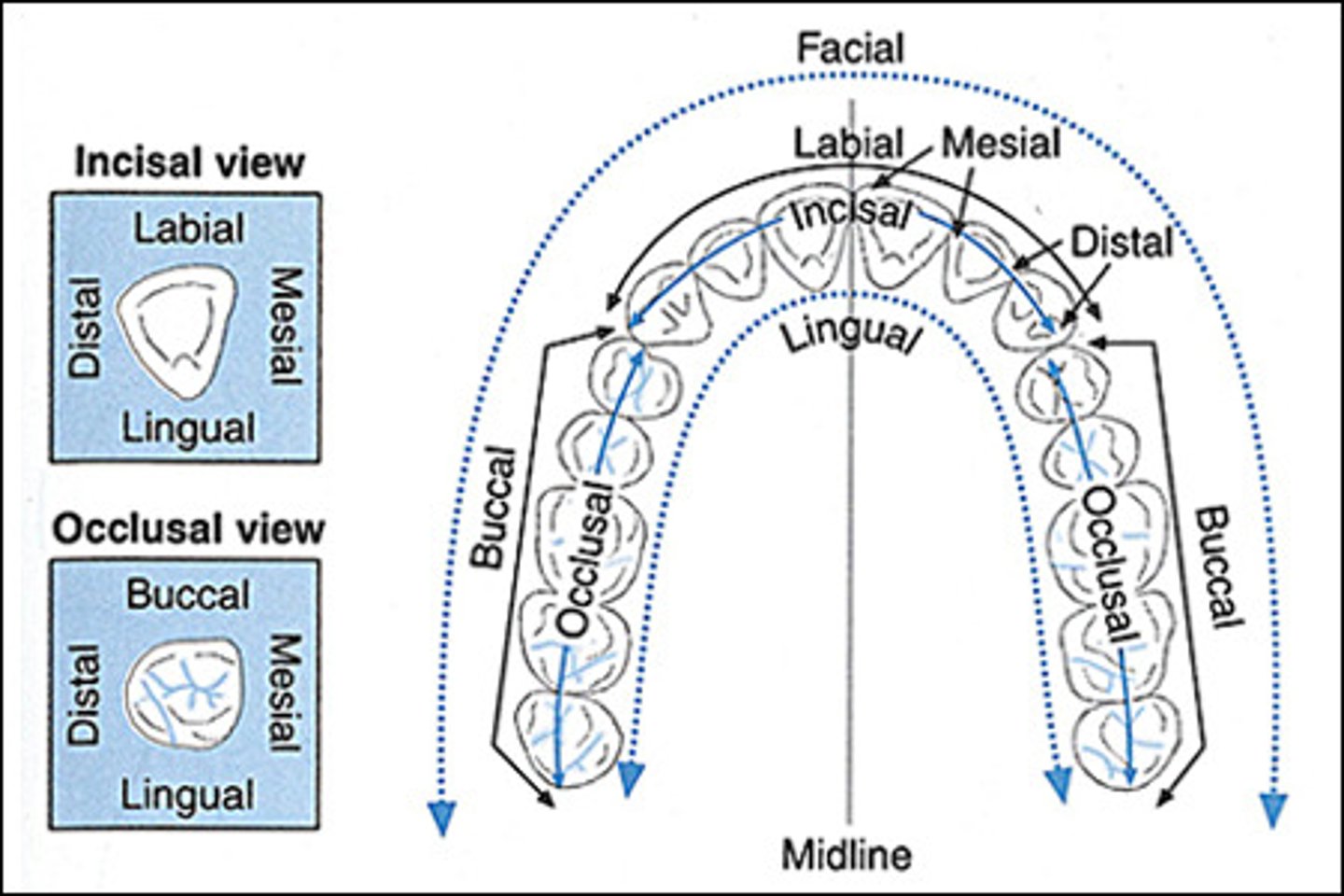
mesial surface
Surface of the tooth toward the midline
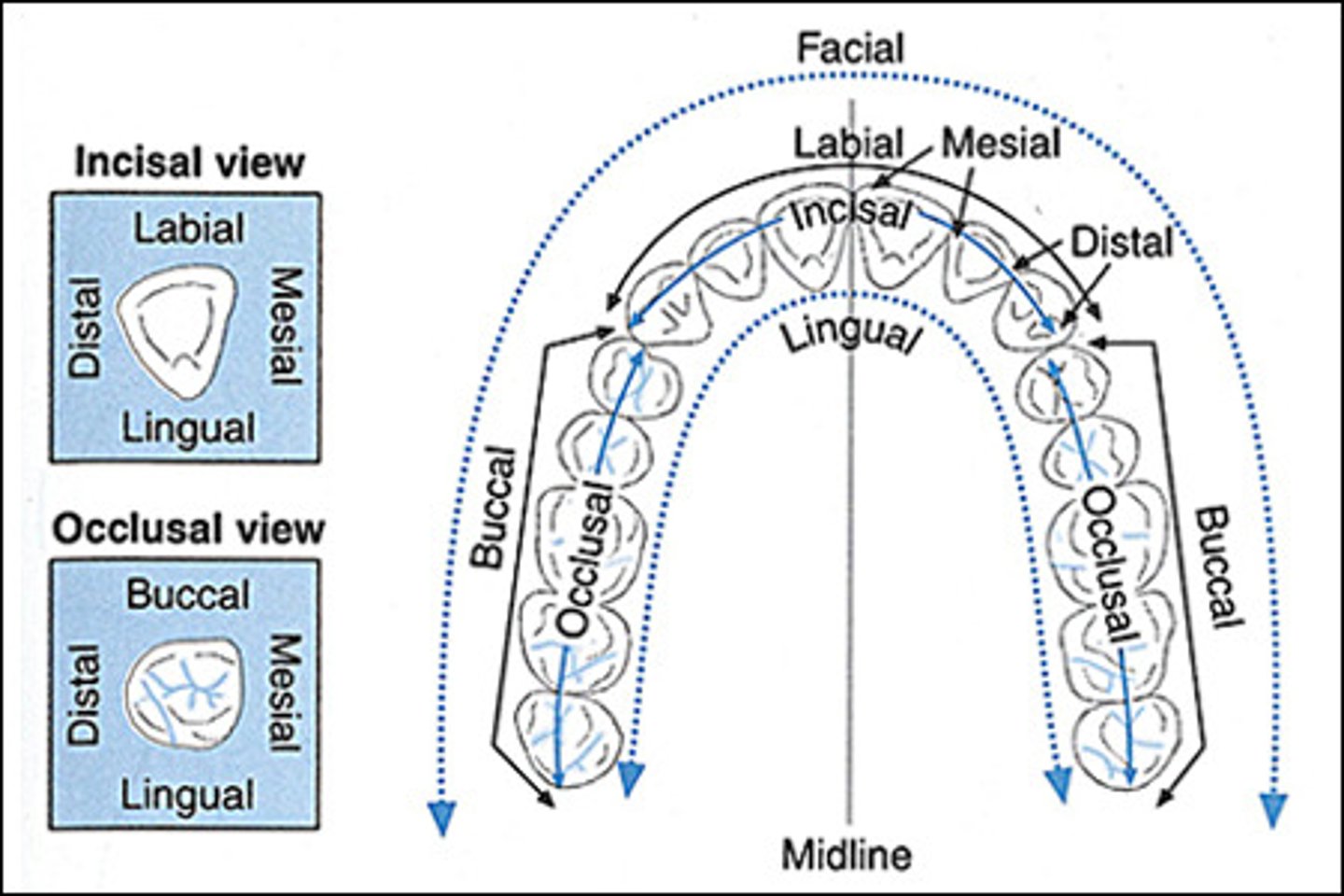
distal surface
Surface of tooth distant from the midline
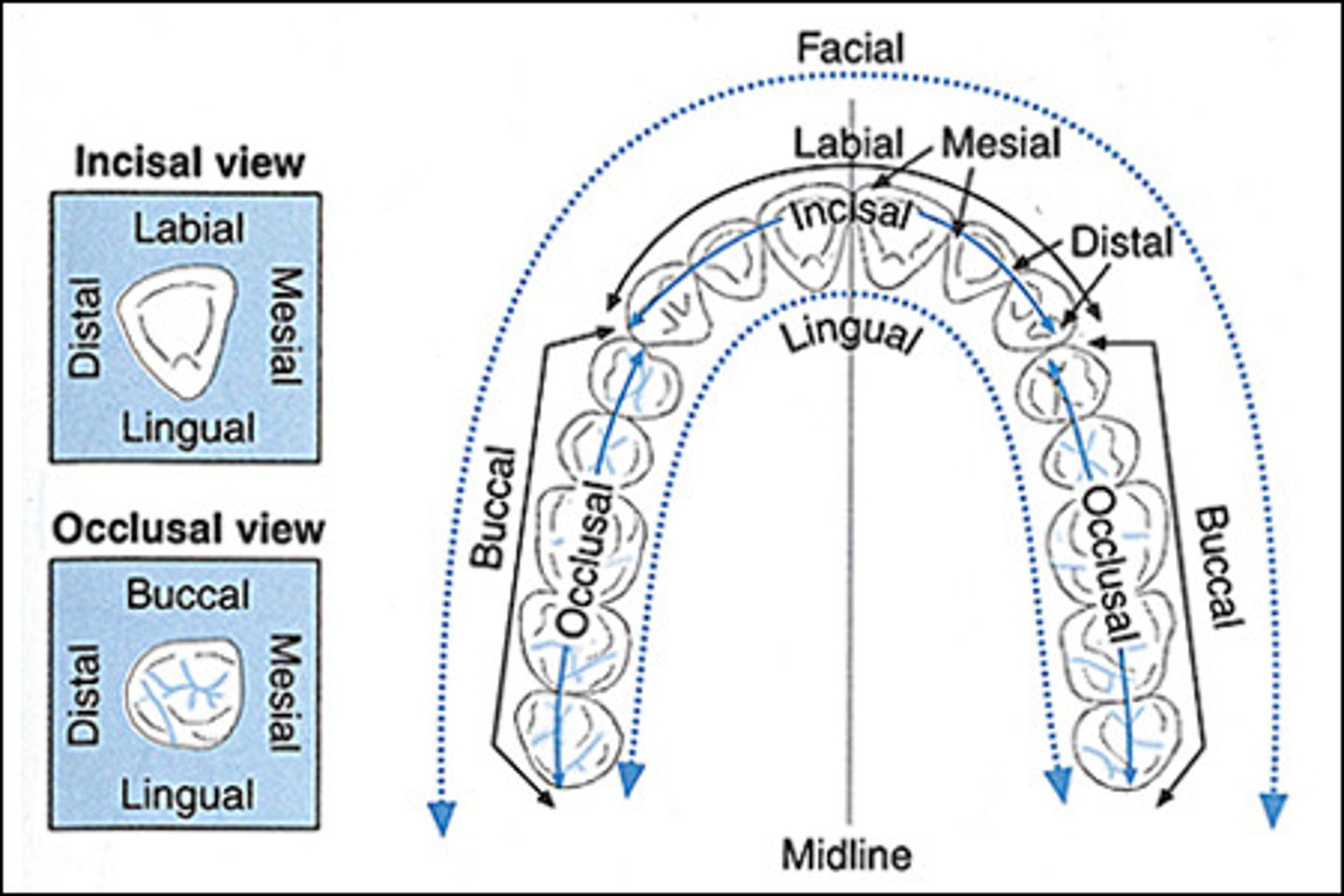
occlusal surface
Chewing surface of posterior teeth
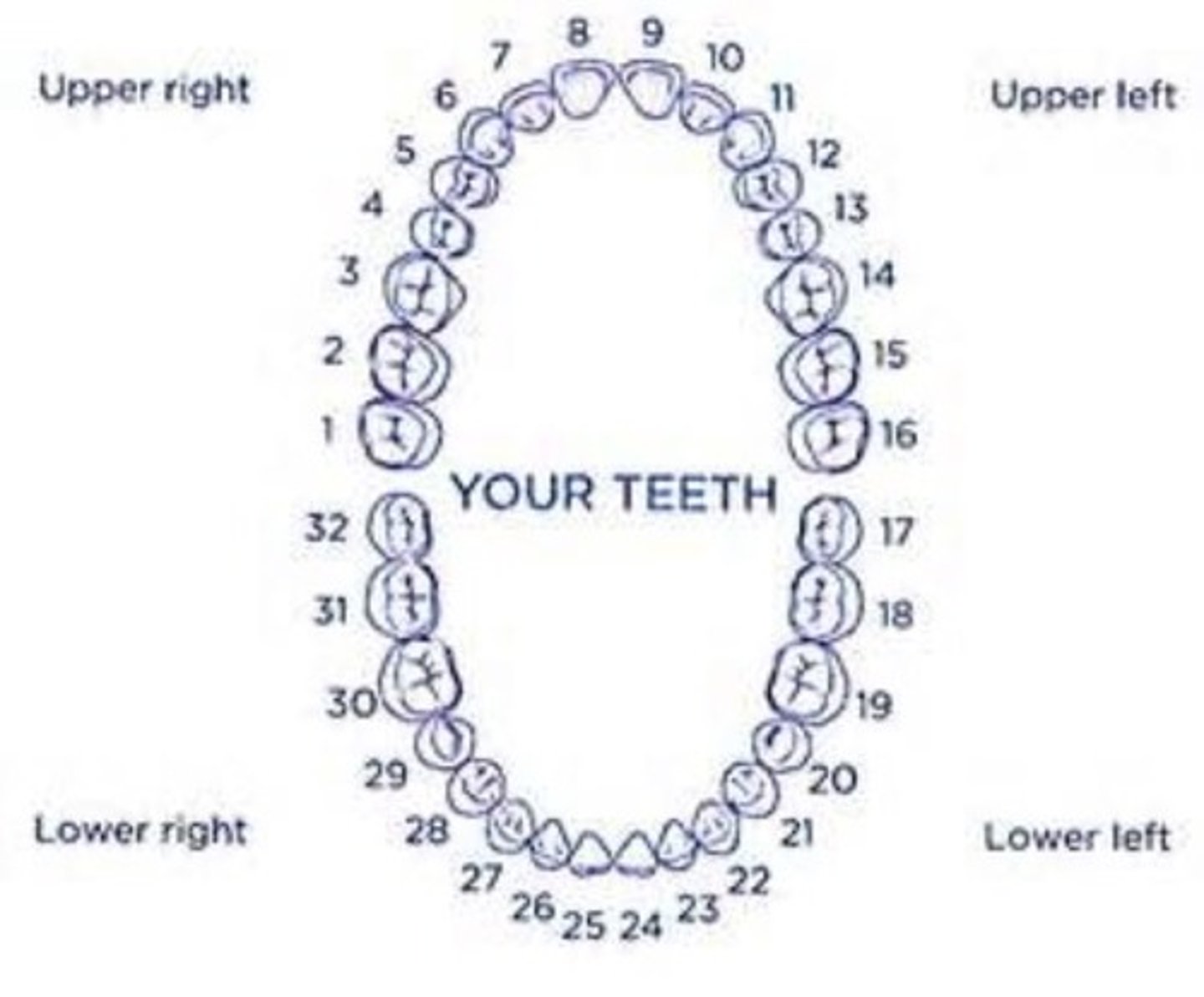
Incisors
7, 8, 9, 10, 23, 24, 25, 26
Canines
6, 11, 22, 27
Premolars
4, 5, 12, 13, 20, 21, 28, 29
Molars
1, 2, 3, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 30, 31, 32
6 year old molars
3, 14, 19, 30
12 year old molars
2, 15, 19, 31
3rd molars (wisdom teeth)
1, 16, 17, 32
UL means
Upper Left (2nd Quadrant)
UR means
Upper Right (1st Quadrant)
LR means
Lower Right (4th Quadrant)
LL means
Lower Left (3rd Quadrant)
Enamel
surrounds the dentin of the anatomical crown
anatomical crown
Portion of the tooth that is covered with enamel
clinical crown
portion of the tooth that is visible in the mouth
anatomical root
portion of the tooth covered with cementum
clinical root
portion of the tooth not visible in the mouth
dentin
hard tissue that makes up the majority of the tooth; surrounds pulp cavity; is covered by enamel and cementum
cementum
layer of hard tissue that covers the dentin of the anatomic root
pulp
living soft tissue which is within the pulp cavity; contains nutrients and nerve supply
periodontal ligament
attaches tooth to jaw
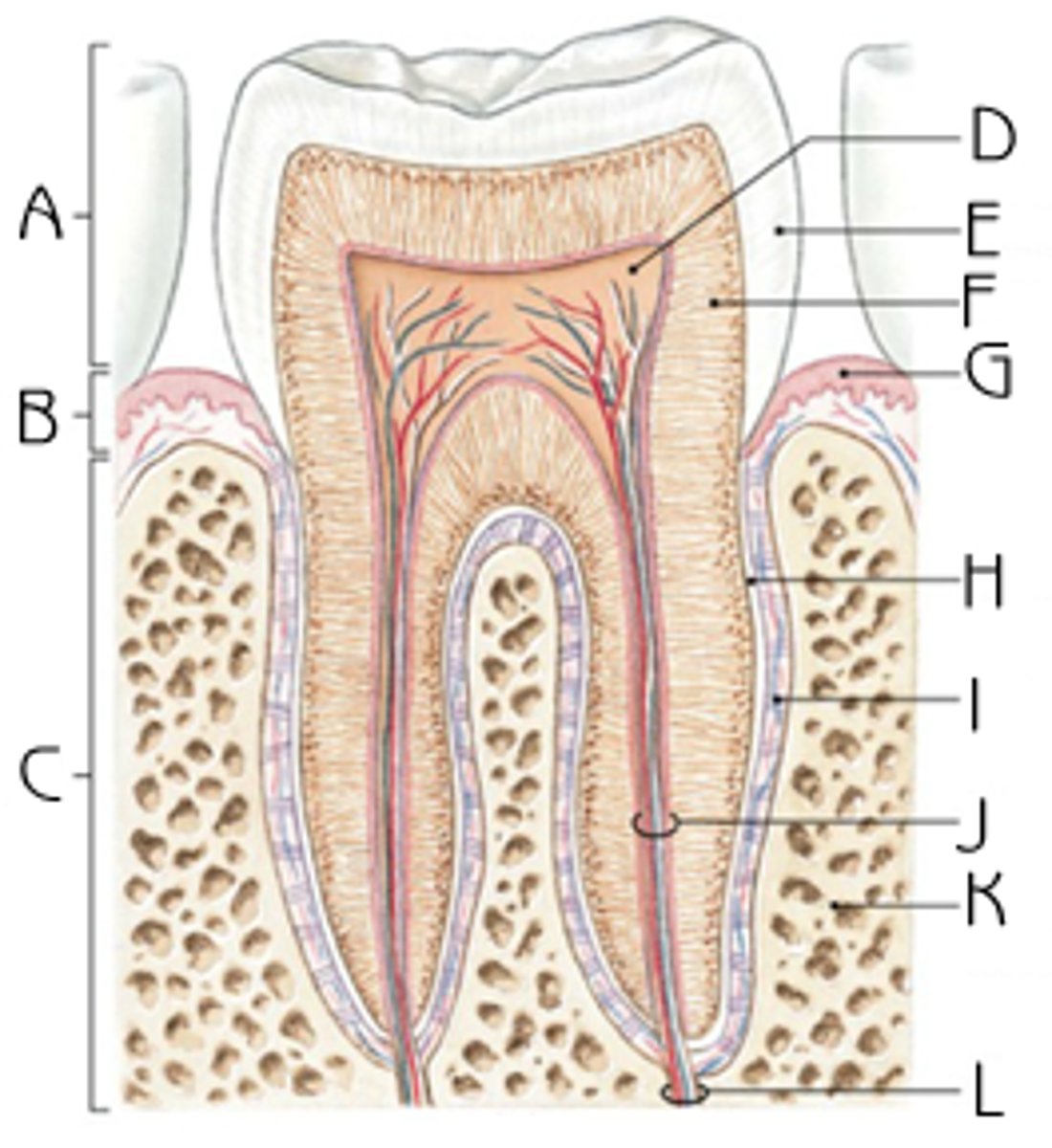
dentinoenamel junction
Line marking the junction of the dentin and the enamel.
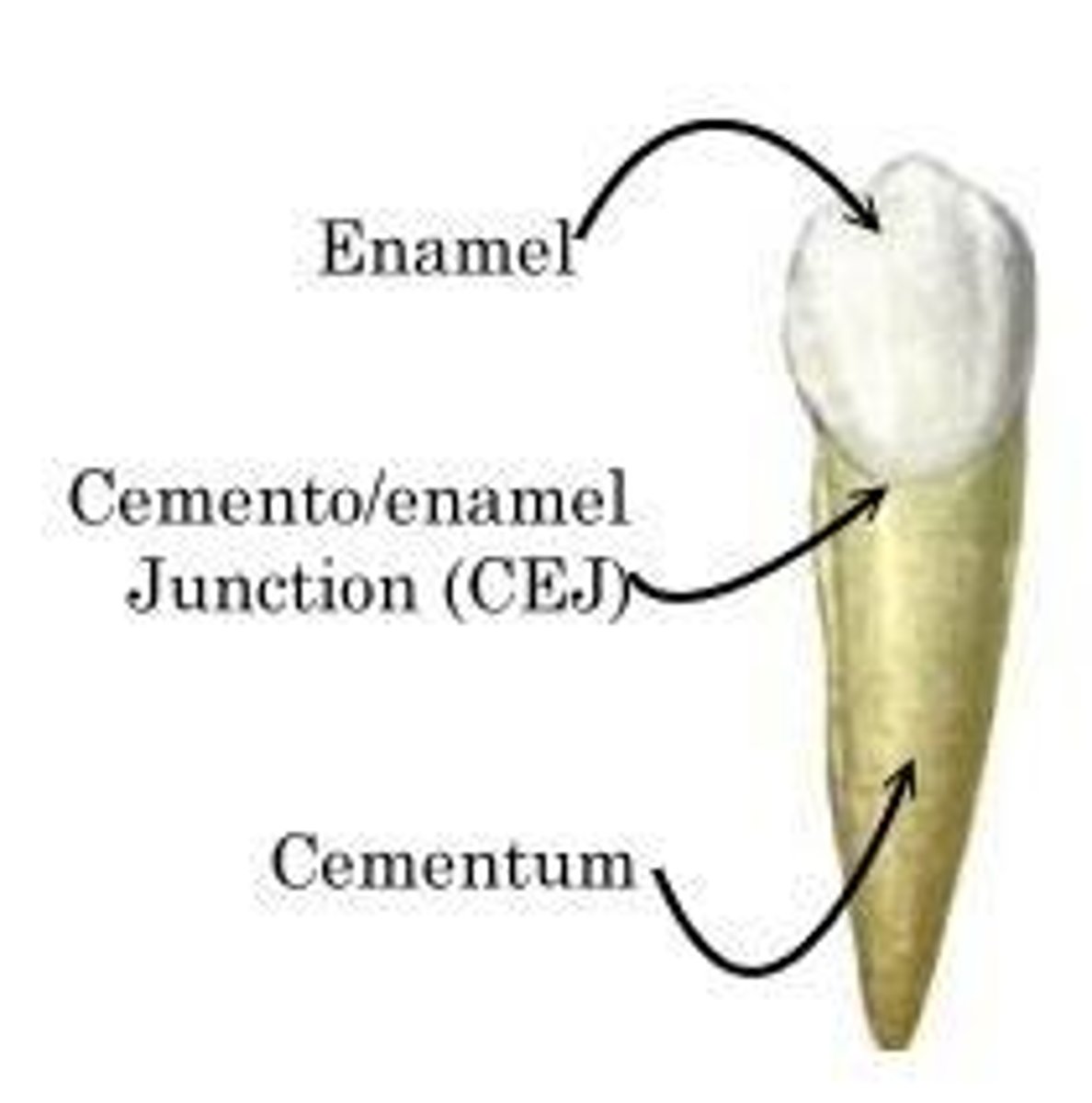
cementoenamel junction
The location where the enamel, which covers the crown of a tooth, and the cementum, which covers the root of a tooth, meet.
Alveolar process
Portion of the maxillary bones that form the support for teeth of the maxillary arch
Root Apex
tip of the root
Cementodentinal junction
inner surface of cementum where cementum joins dentin
Cervical Line
where the anatomical crown and root join (CEJ)
Diastema
A space between two teeth
Six sextants of teeth
Anterior (maxillary and mandibular)
Posterior (left and right; maxillary and mandibular)
Upper left permanent first molar
14
lower left central incisor
24
Palmer Notation
System to identify teeth that uses quadrant symbol and number indicating position from midline
FDI Notation
1) First digit denotes quadrant (1, 2, 3 , 4) for permanent dentitions (5, 6, 7, 8) for deciduous dentitions
2) Second digit denotes tooth number 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 (for deciduous) + 6, 7, 8 for permanent dentition, 37 pronounced "three-seven"
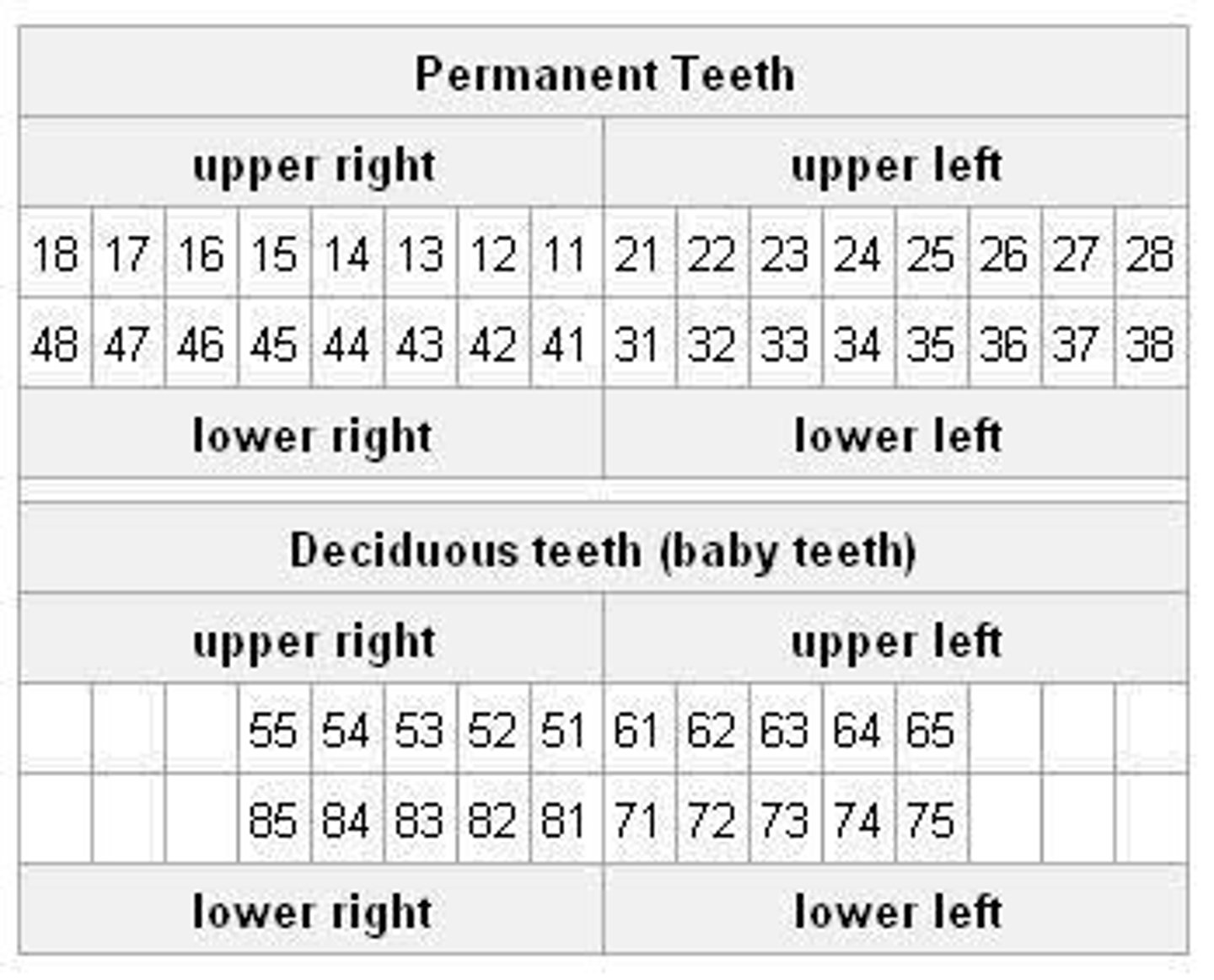
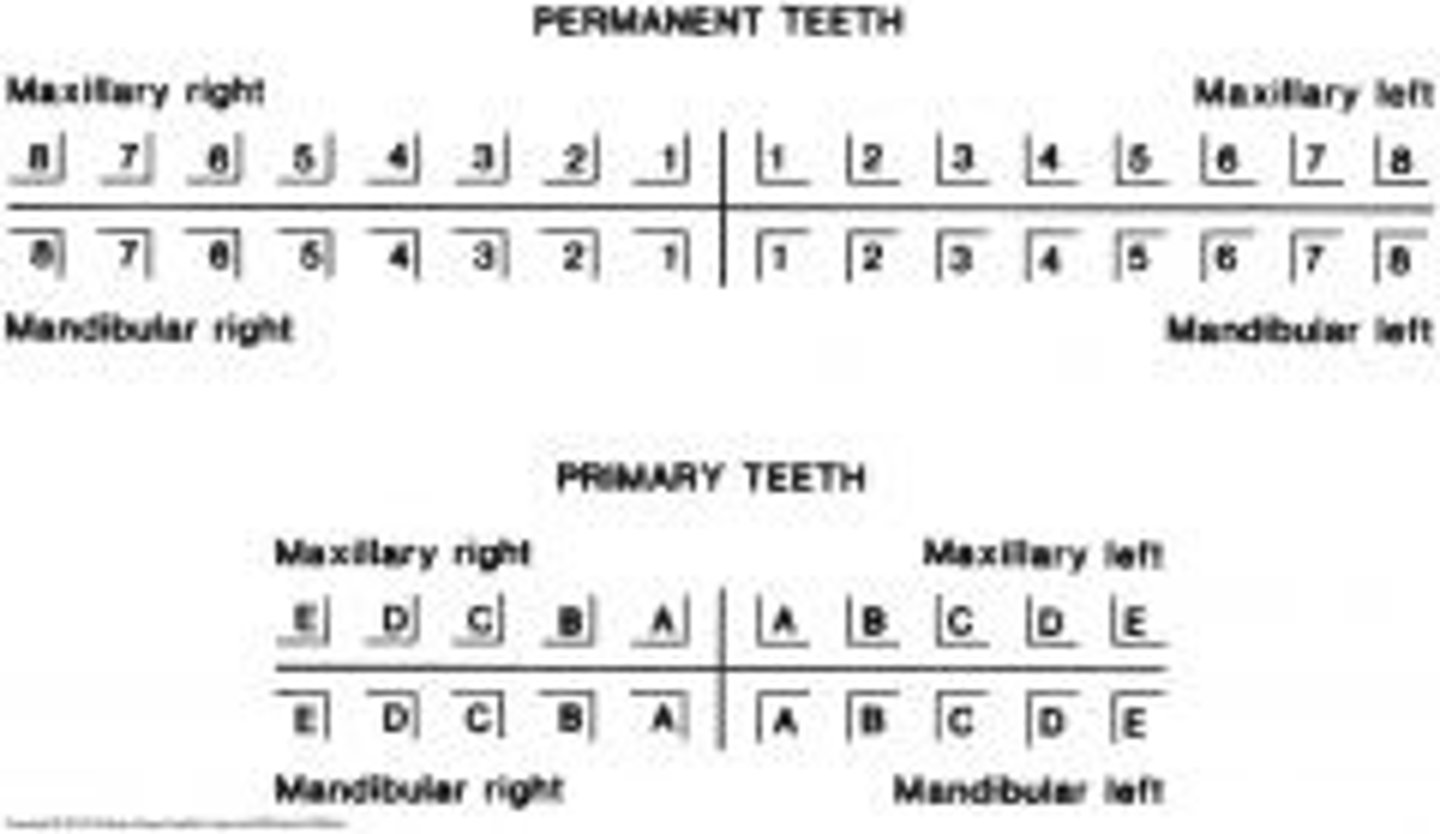
Primary Dentition Naming
20 teeth named A-T
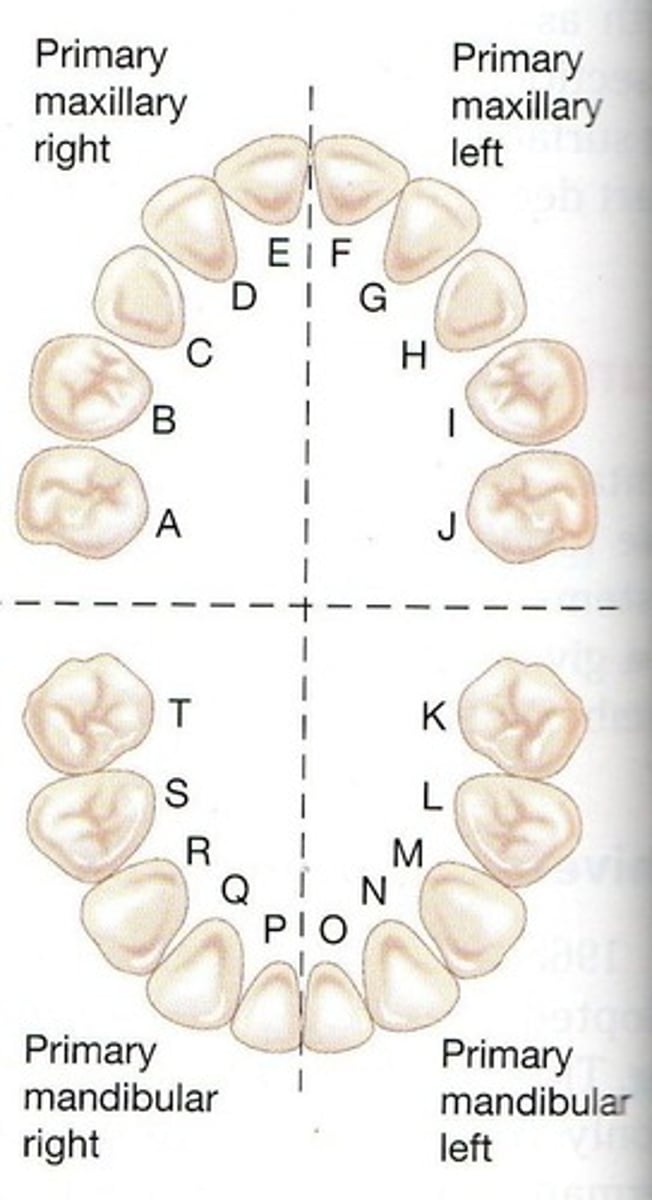
Each quadrant of primary dentition is made up of
2 incisors, 1 canine, and 2 molars
dental formula for the deciduous dentition
I 2/2 + C 1/1 + M 2/2
Mid-Root Axis Line (Long Axis)
imaginary line through the center of the tooth root
Axial surface
any surface of a tooth that is parallel to the long axis of the tooth (B, L, M, D)
Proximal surfaces
mesial and distal
Mesiodistal
axis running from mesial to distal
Line Angle
When two surfaces of a tooth meet
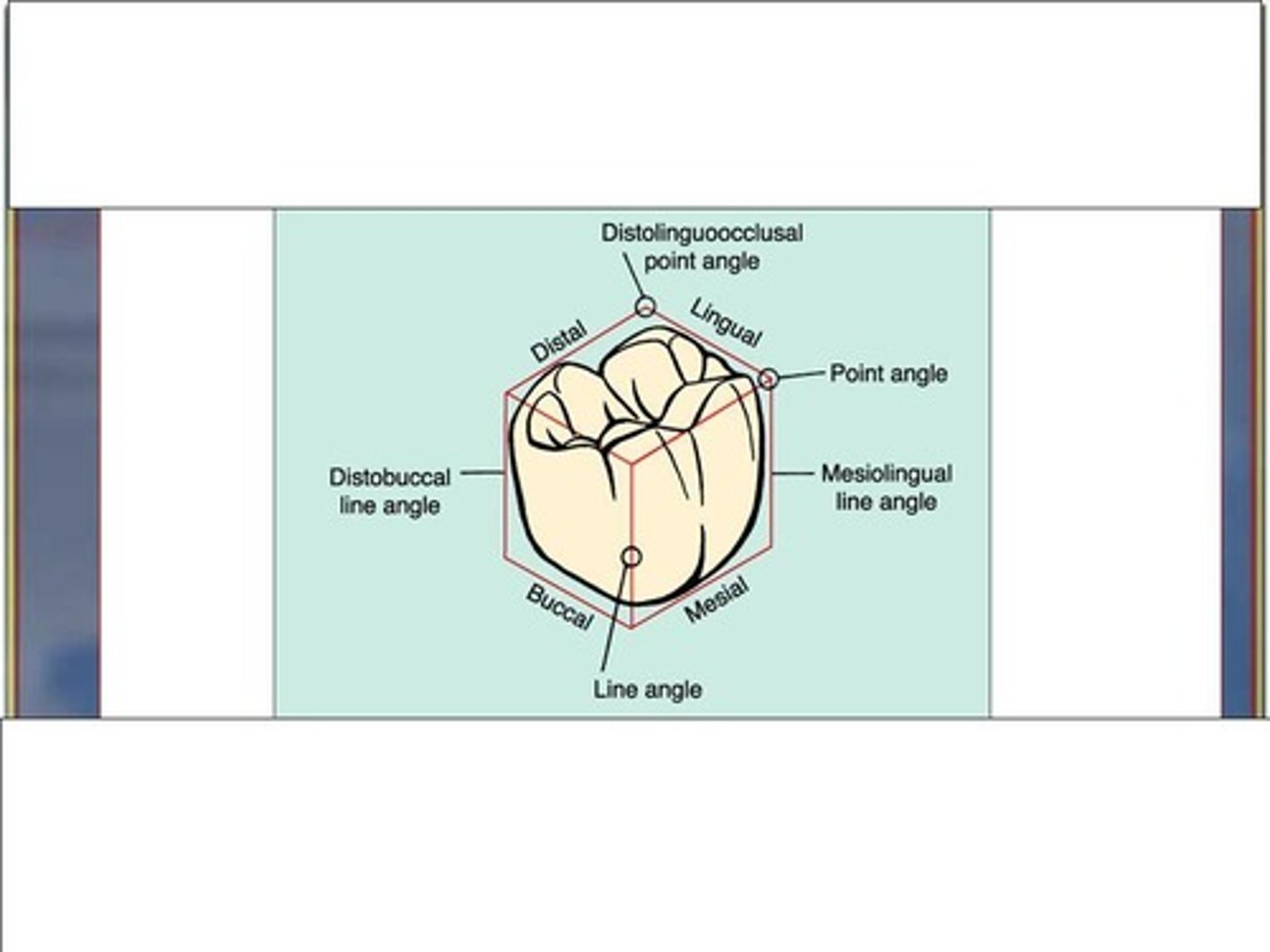
Mesiofacial Line Angle
angle created where the mesial and facial surfaces meet
Mesio-occlusal line angle
angle created where the mesial and occlusal surfaces meet
point angle
Angle formed by the junction of three surfaces
mesiobuccal-occlusal point angle
Where the Mesial meets the buccal and the occlusal
Pulpal
Surface of the cavity preparation perpendicular to the pulp of a tooth
Cusps
pointed or rounded mounds on the crown of the tooth
Cingulum
Raised, rounded area on the cervical third of the lingual surface
Mamelons
three bulges on the incisal edge of a newly erupted central incisor
Marginal ridges
Elevated areas of enamel that form the mesial and distal borders of the lingual surface on the anterior teeth and the mesial and distal borders of the occlusal surface of the posterior teeth
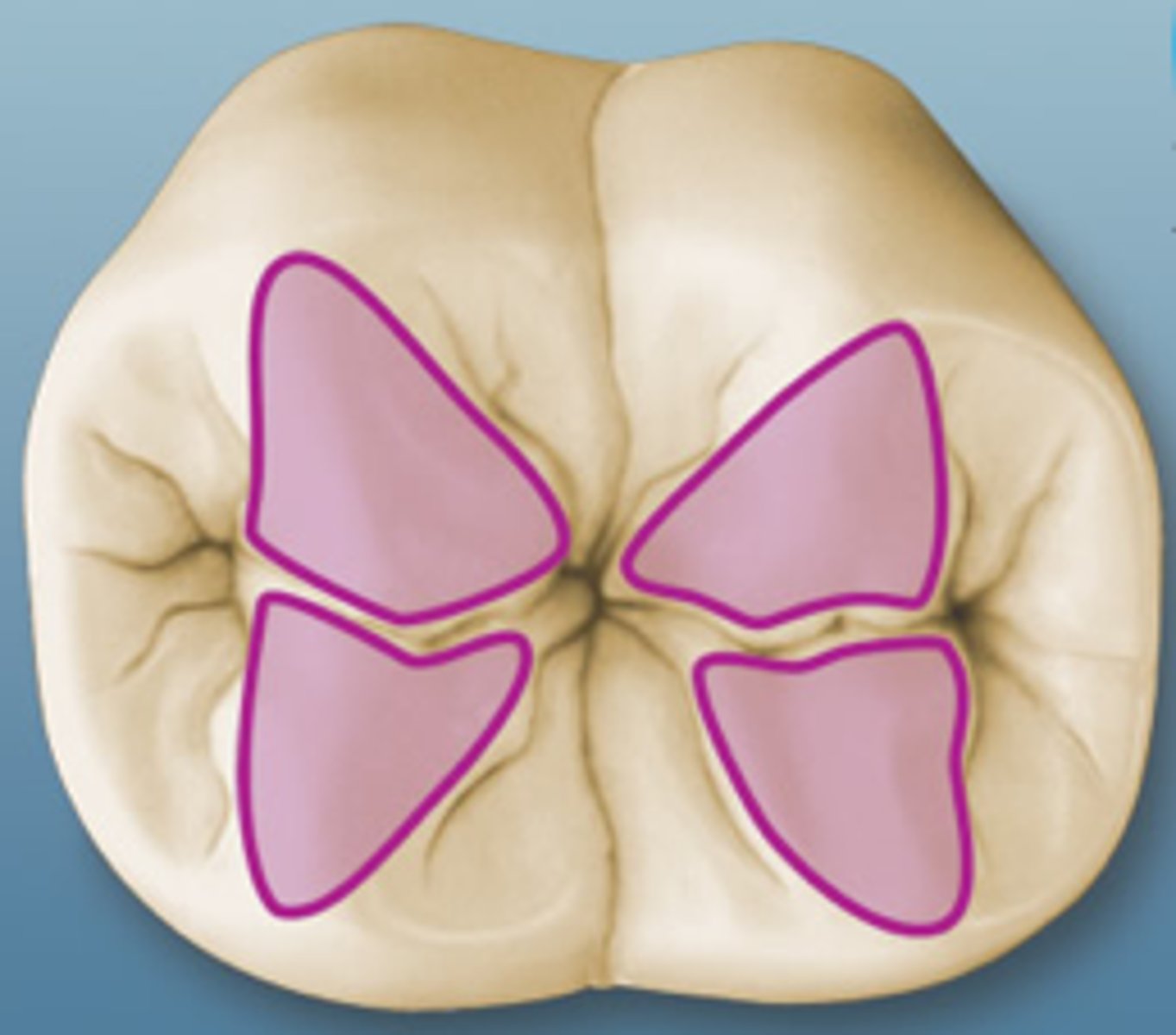
Triangular ridges
cusp ridges that descend from the cusp tips toward the central part of the occlusal table
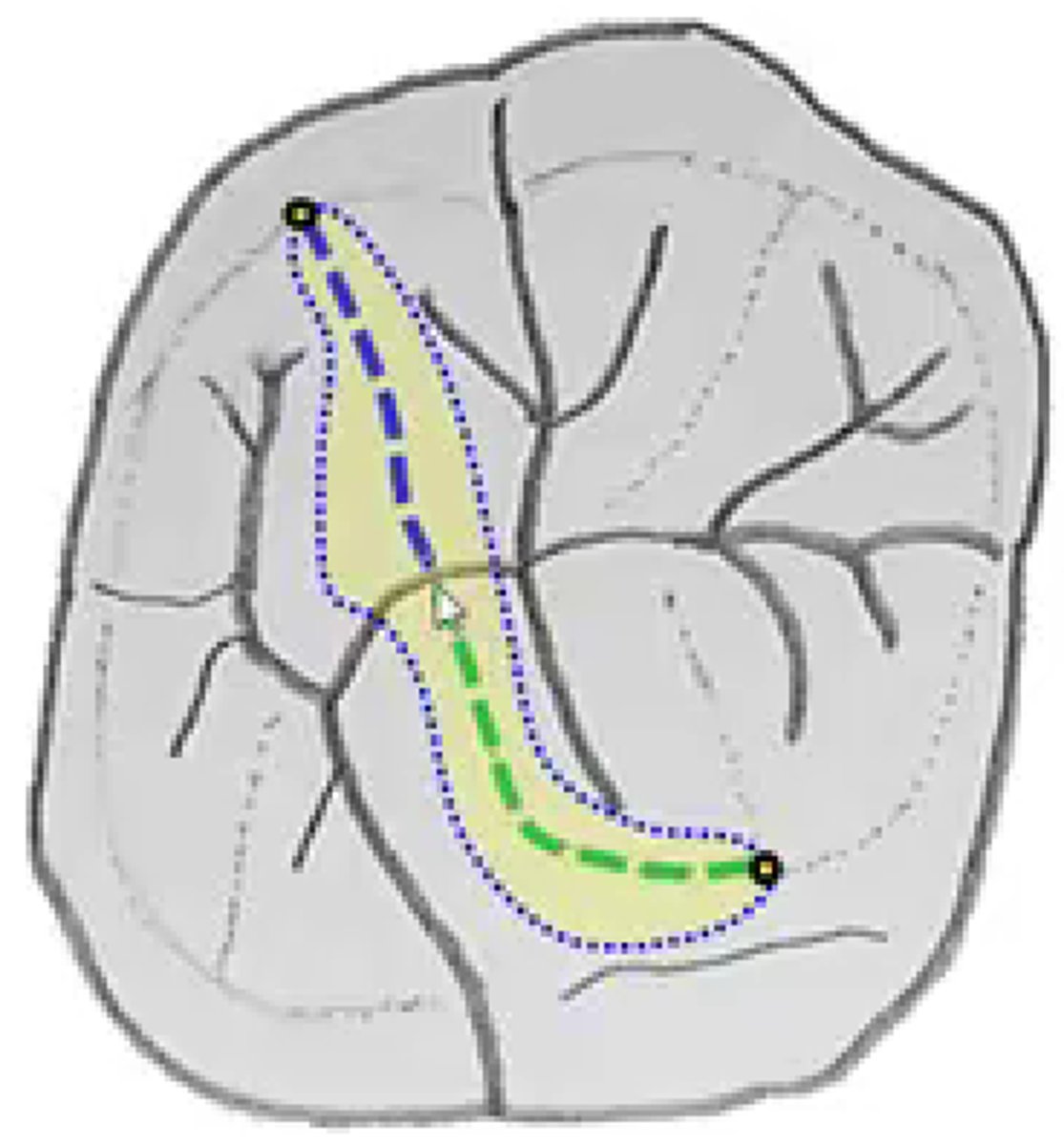
Oblique ridges
Elevated prominences on the occlusal surfaces of a maxillary molar extending obliquely from the tips of the mesiolingual cusp to the distobuccal cusp
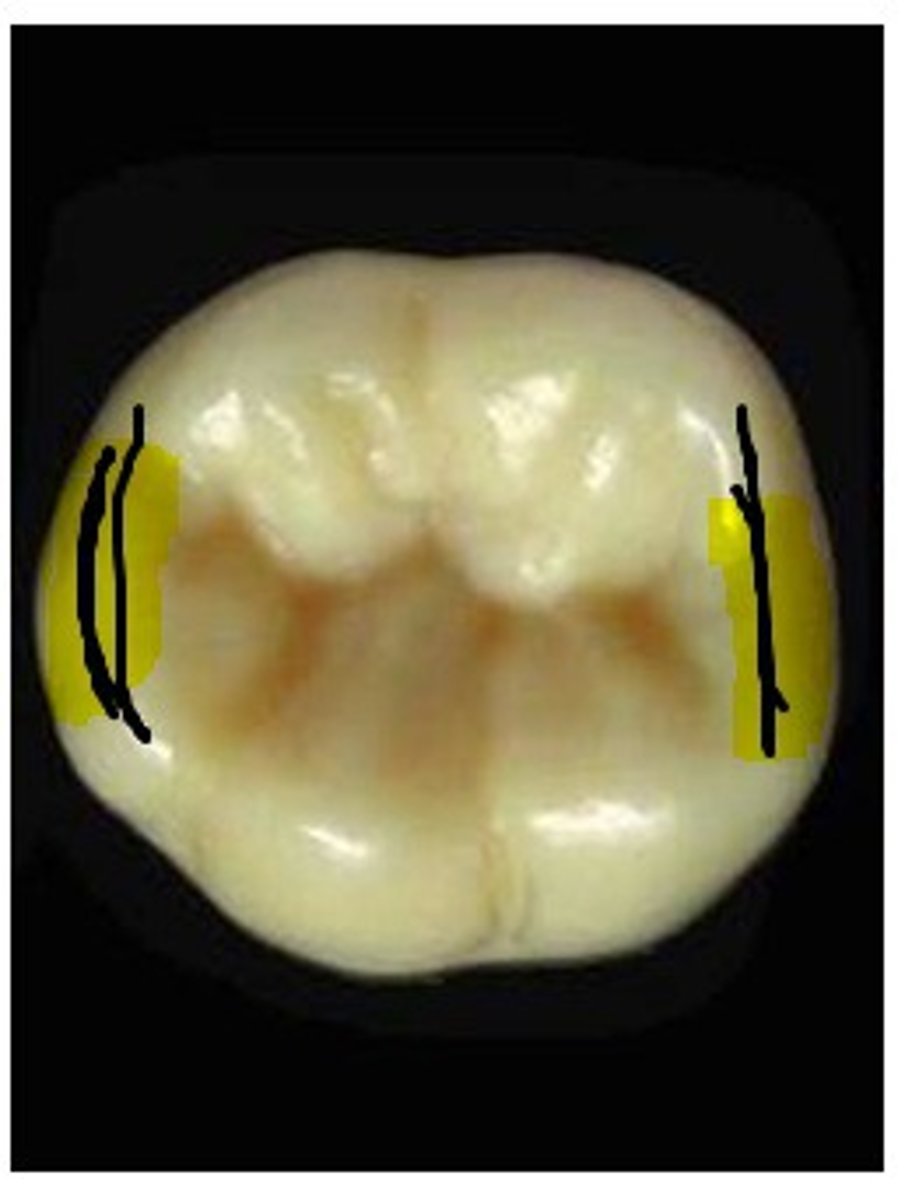
Cusp ridges
Ridge that descends from each cusp tip on the posterior teeth
canines have ____ cusp(s)
1
Premolars have ___ cusp(s)
2 or 3
Molars have ___ cusp(s)
4 or 5
tranverse ridge
goes across the tooth
buccal triangular ridge plus lingual triangular ridge
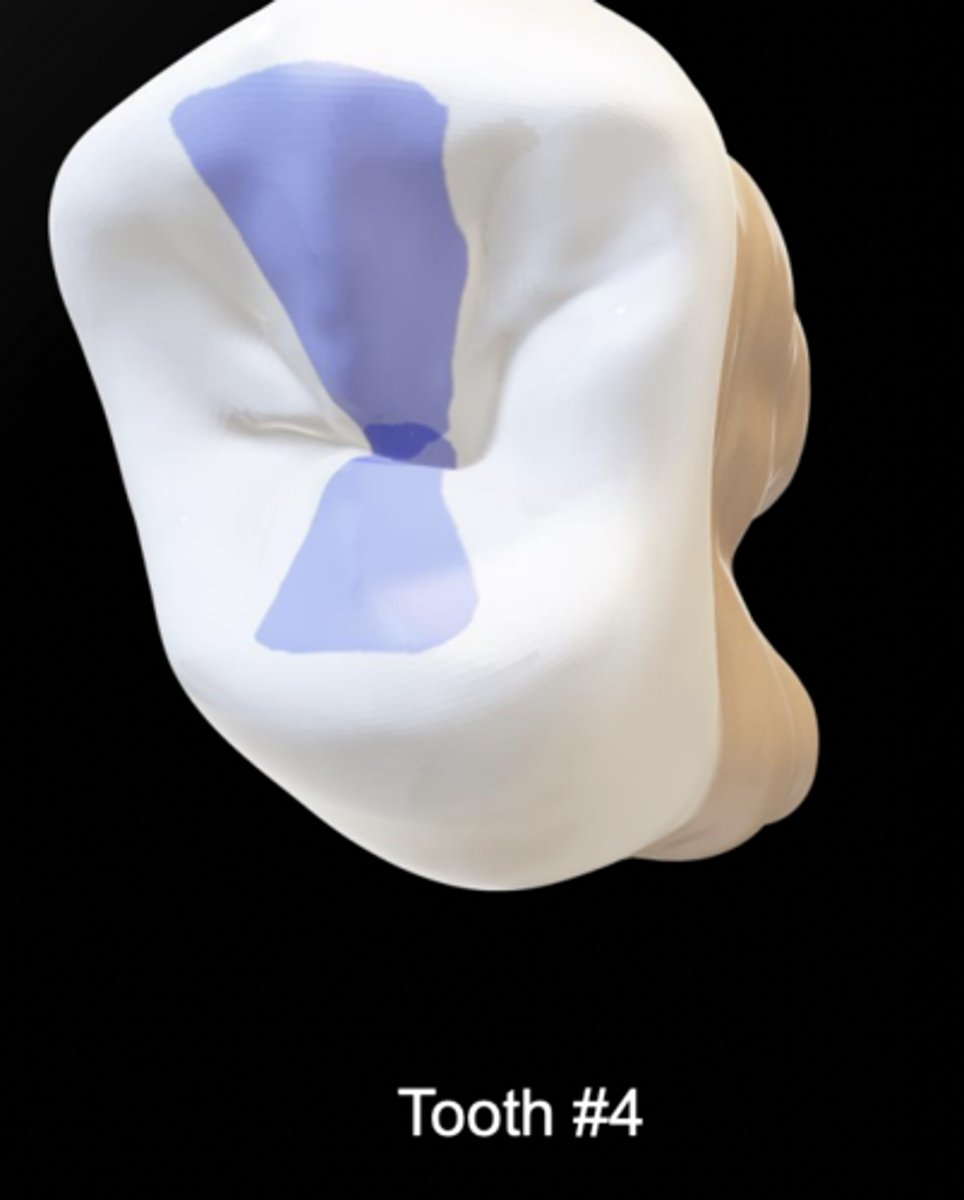
a cusp has ___ ridges
4
mesial cusp ridge
extends from cusp tip toward mesial surface
distal cusp ridge
extends from cusp tip toward distal surface
facial cusp ridge
extends from cusp tip toward facial surface (facial cusps only)
lingual cusp ridge
extends from cusp tip toward lingual surface (lingual cusps only)
can be triangular in posterior teeth
occlusal table
part of occlusal surface of posteriors bordered by marginal ridges
tubercle
projections of the crowns of teeth
may be rounded or pointed
variable in size and shape
perikymata
small grooves noted on some teeth
cervical ridge
the bulge in the gingival third of the facial surface of an anatomic crown
Fossa
shallow depression
Developmental groove
Groove formed by the uniting of lobes during development of the crown of the tooth
Pit
pin point depression on occlusal surface
sometimes located apical to fossa in anterior teeth