Database Applications 🗄️
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GCSE CCEA Specification GCSE Digital Technology Unit 1: Digital Technology (Core)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Logical operators
Analysing two values to return either true or a false result
What are the logical operators
AND, OR, BETWEEN
Comparison operators
Comparing a value against other data when queried
What are the comparison operators?
< | Less than |
<= | Less than or equal to |
> | Greater than |
>= | Greater than or equal to |
= | Equal to |
<> | Not equal to |
Database
Collection of data items and links between held together in a structured way so it can be accessed by different applications
Where might databases be used?
Schools
Police
Government
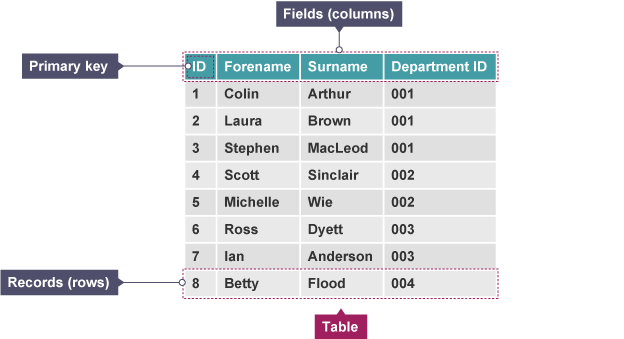
Table
structure where data is organised in rows and columns
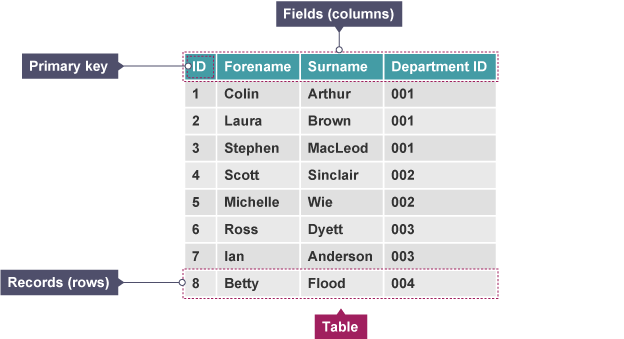
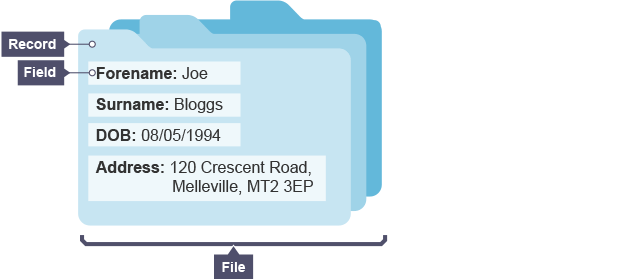
Record
collection of data items (may be different types) relating to individual or object
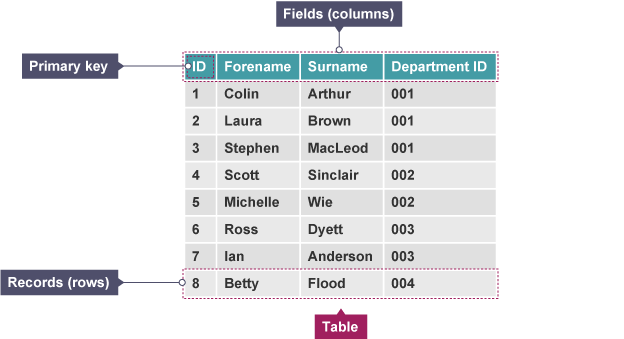
Field
part of a record designed to hold a single data item about an individual or object
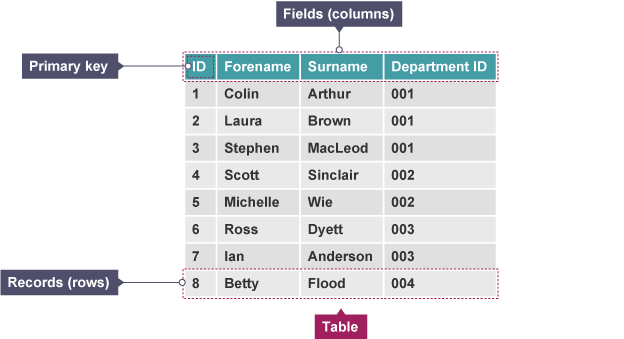
Key field/ primary key
field within record used to uniquely identify a record e.g Customer ID
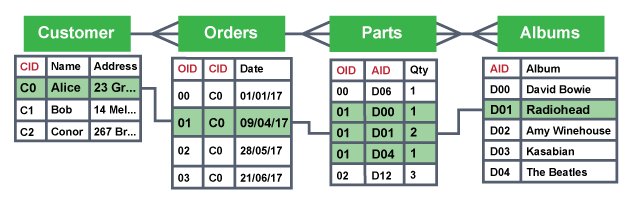
Foreign key
primary key from another table appears as field in current
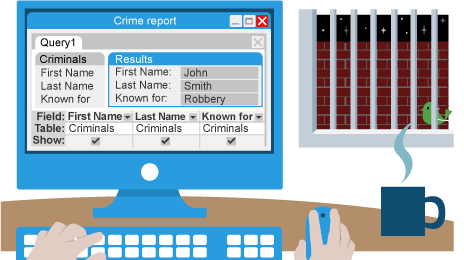
Query
question used to retrieve selected information from a database that satisfies criteria
Form
Collects data to create, modify or view records
Report
presentation of selected data from database in an effective manner
Macro (button)
small programs to perform repetitive task automatically by executing code when clicked, can be stored for later use
Relationship
Link two or more tables in a database
Export
create data file so it can be read by different piece of software
Import
corresponding read process to accept file produced by other software (exported)
Why do we import data?
gives more flexibility in handling data
Referential integrity
Prevents addition of a new record to ensure data is consistent
Data redundancy
When data is repeated unnecessarily
Data integrity
The correctness, reliability and accuracy of the data
How do relationships work?
link two tables with a common field, the key field from one table is stored as the foreign key another
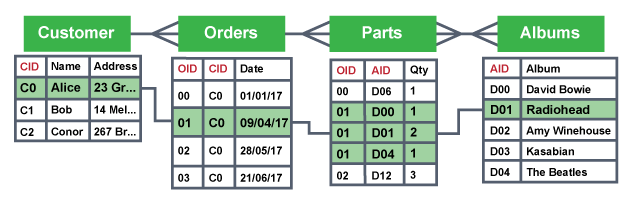
How are relationships defined?
One-one, one-many, many-many
Data validation
automatic checking input to ensure data entered is sensible, reasonable and within acceptable limits
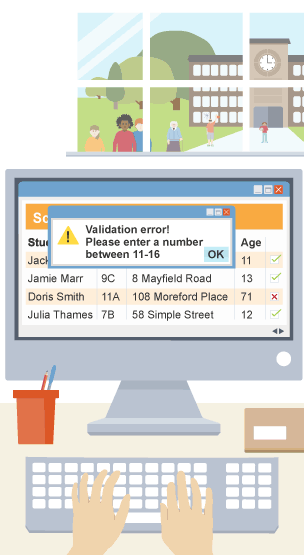
Why do we use data validation?
to ensure data integrity and reduce errors, inconsistences or mistakes
Ensure it is present in the field and not left blank e.g compulsory field in a form
Ensure data is the correct number of characters e.g phone number be is 11 digits
Ensure it is the correct data type e.g Name should be text only
Ensure it is in the correct format that matches a predefined pattern e.g Postcode should be AABB ABB
Ensure it is within upper and lower limits e.g Percentage should range from 1-100
Big data
large amounts of data that have the potential to be mined for information
What are the 3 V’s
volume, variety and velocity
Volume
amount of data stored by organisations, large amounts of data require large storage capacity hardware
Vareity
different types and varieties of data, in many formats which can be structured, semi structured or unstructured
Velocity
speed data can be processed, large volumes need more powerful computers to process data quicker
Data analytics
applies algorithms to raw data in order to spot patterns, relationships and trends so it can produce information
Need for data analytics
beneficial to organisations for making decisions and planning for future growth
What makes data analytics harder?
different formats makes preparing and processing the data more challenging
What is used to speed up analytics?
Specialised software such as data mining are designed to process vast quantities
Data type
defines the type of data associated with the field
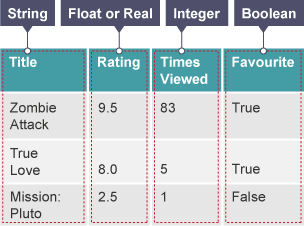
Text/ string
a mixture of letters and numbers e.g address
Monetary data that includes 2 decimal places e.g £34.56
Binary value that can either be yes/no
Link to a web address e.g email address
A file attached to a record e.g image
A value can be selected from a predefined list e.g dropdown menu