Thorax and Lungs | Chapter 19 | NURS 122
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
144 Terms
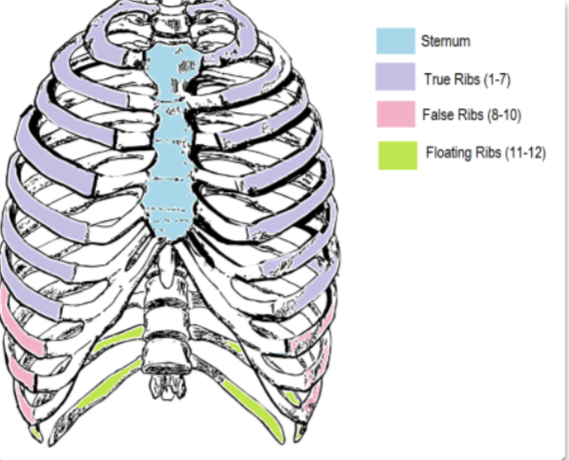
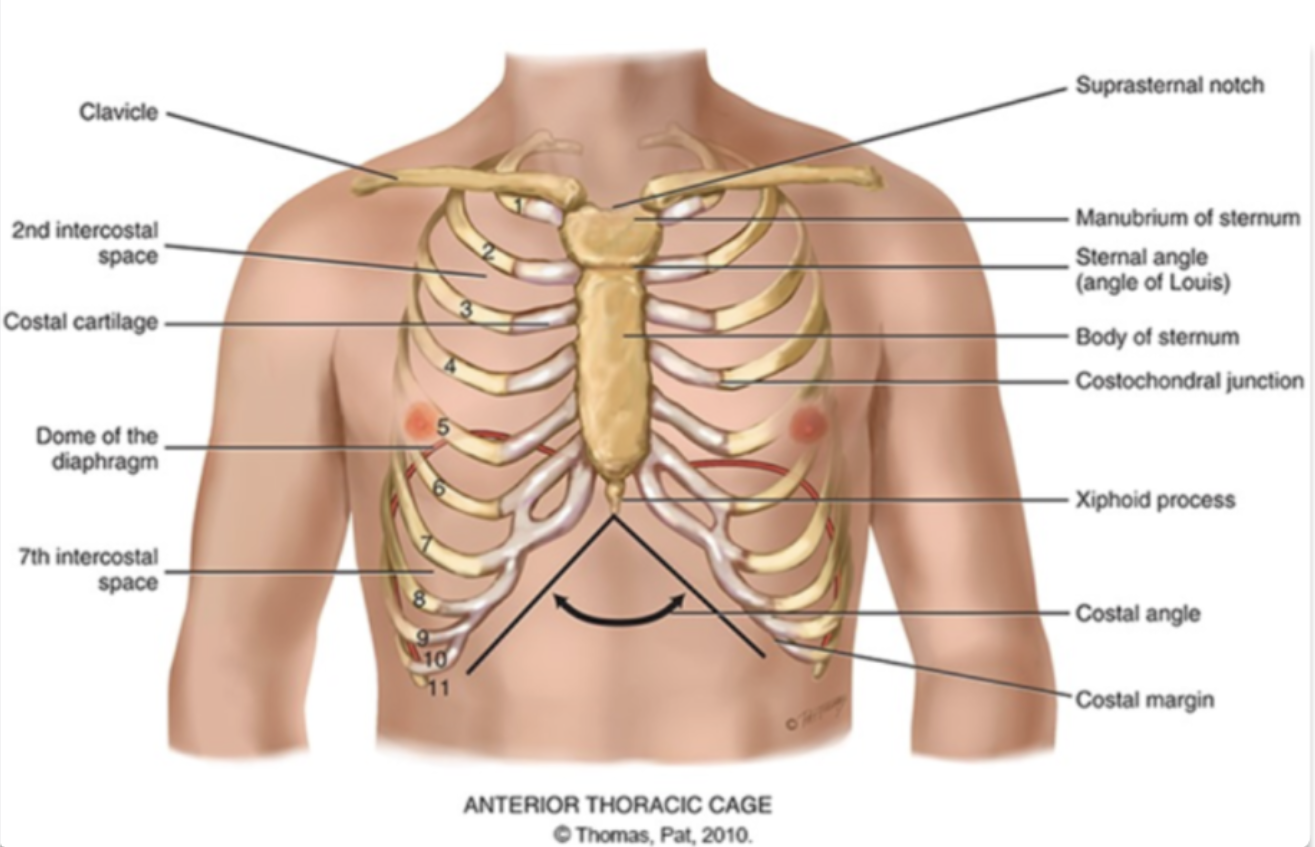
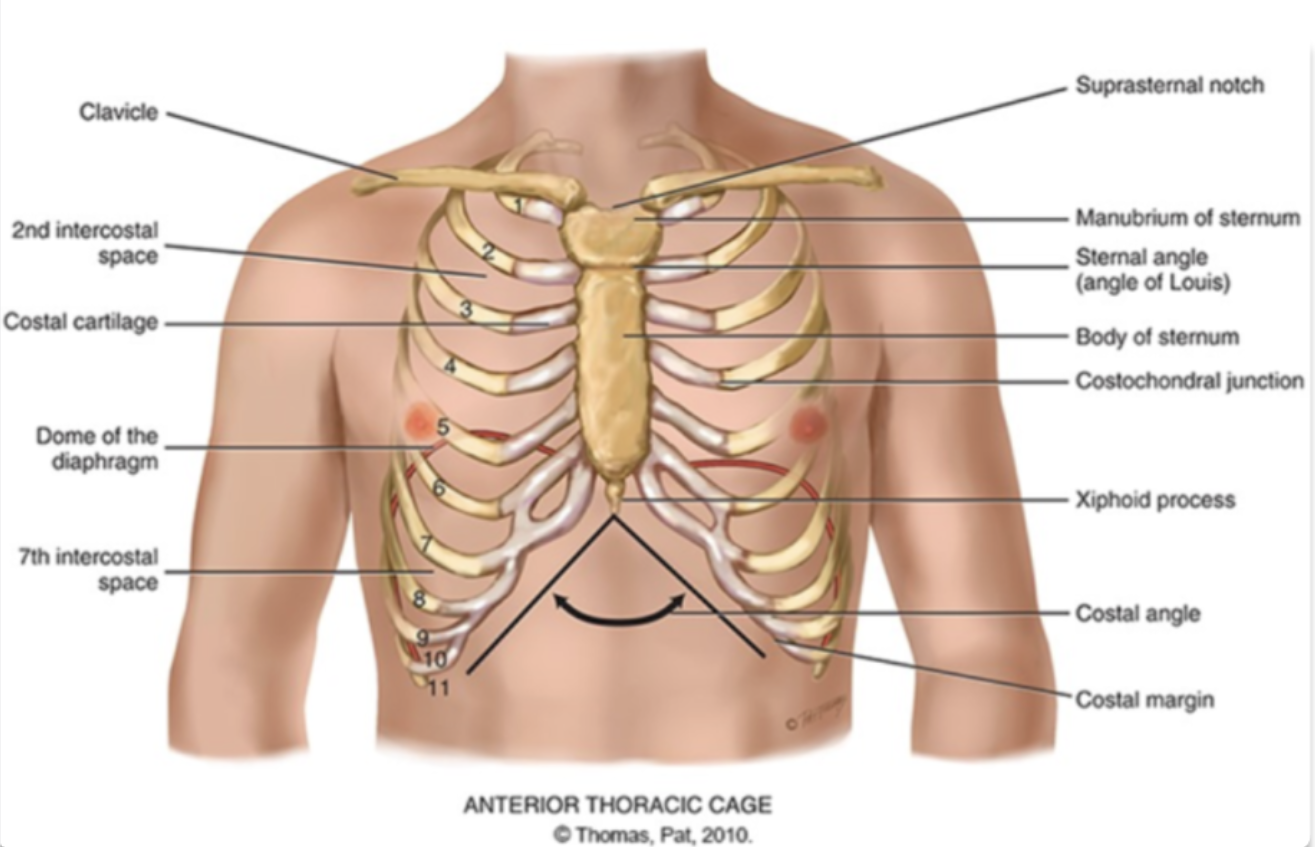
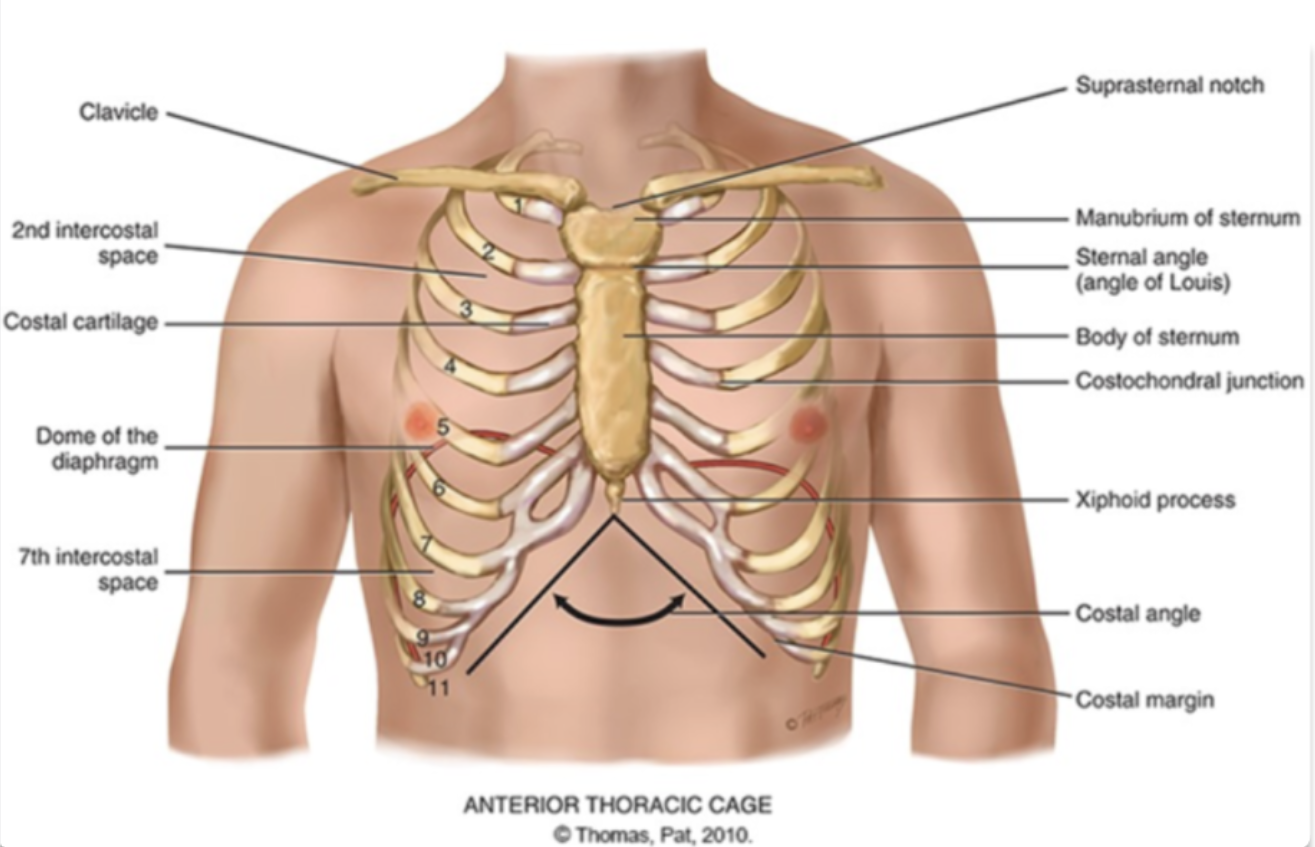
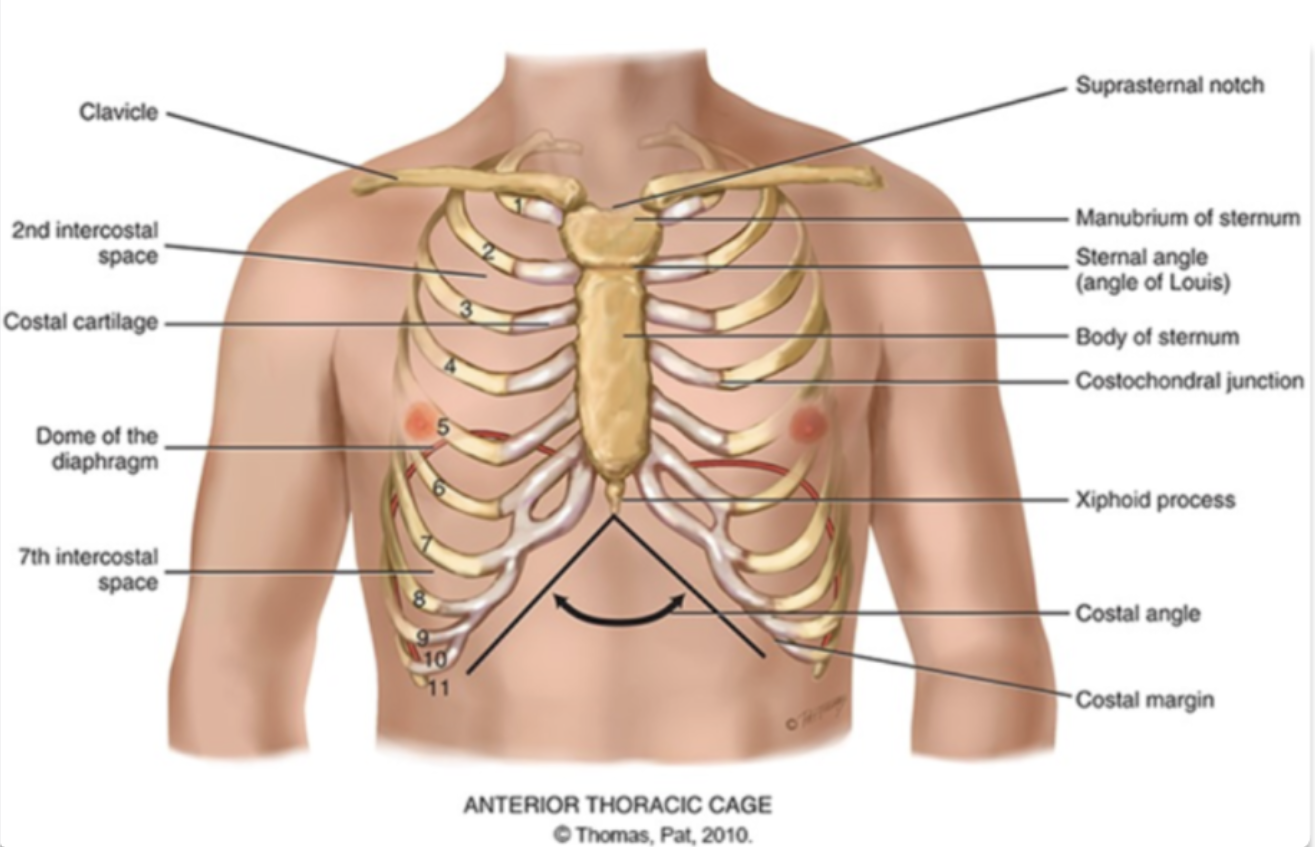
what are the different compositions of the ribcage?
sternum
true ribs
falses ribs
floating ribs
costal cartilage
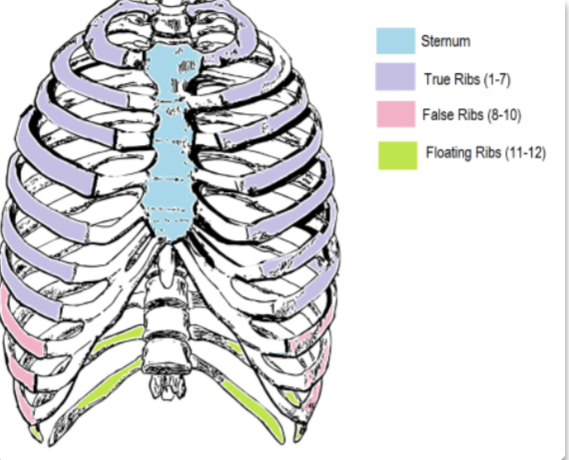
why is true ribs, ‘true’ and why is false ribs, ‘false’?
true ribs are ribs where it costal cartilage individually and directly attaches to the sternum while false ribs are ribs does not individually and directly attaches to the sternum
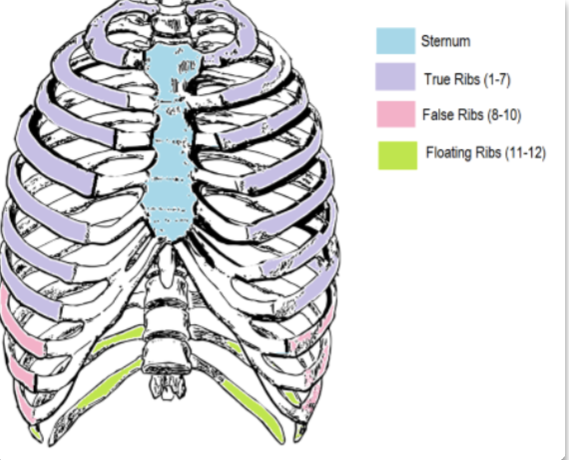
why is floating ribs, ‘floating’?
they are floating because they have no costal cartilage to attach them to the sternum
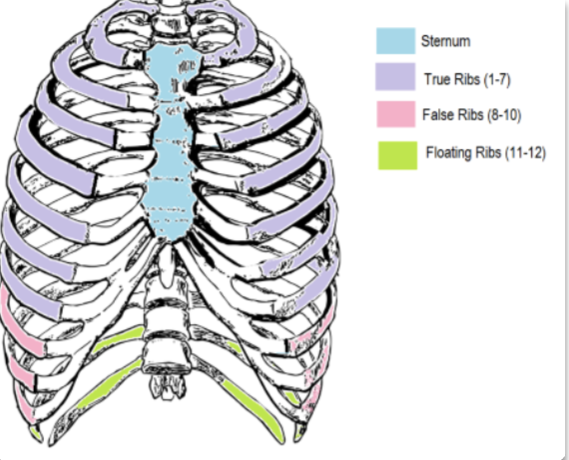
how many pairs of ribs do human have?
12 pairs
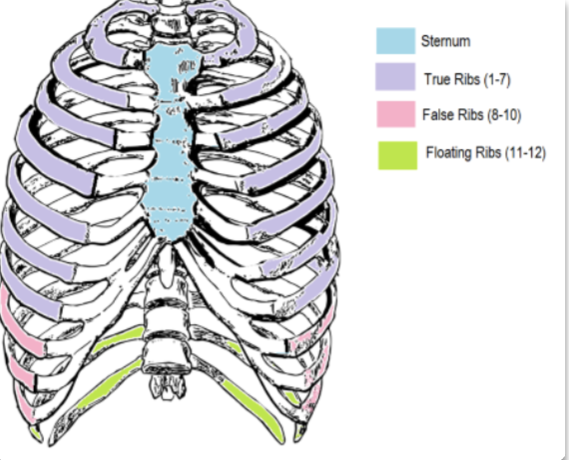
what are the ribs that are true ribs, false ribs, and floating ribs?
true ribs: 1-7
false ribs: 8-10
floating ribs 11-12
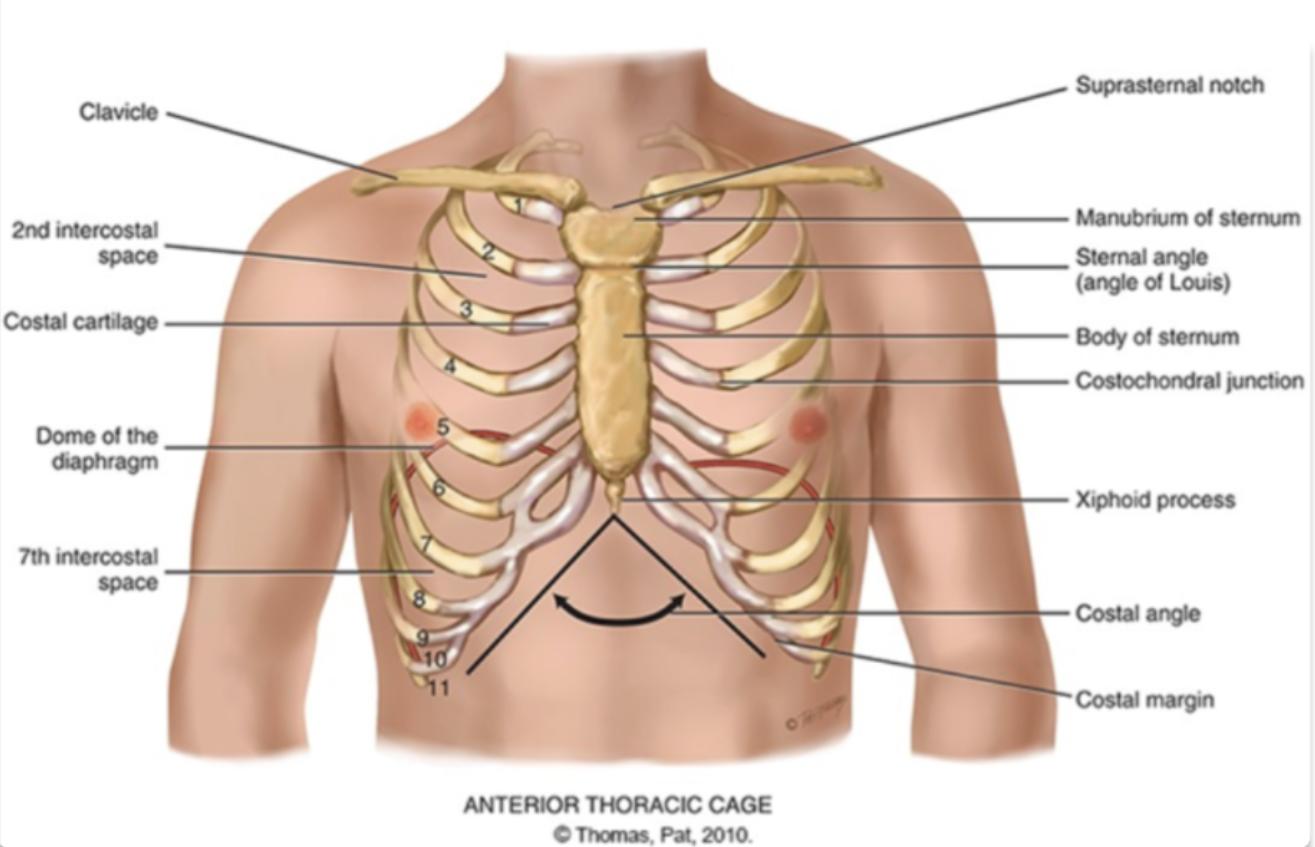
what are the different areas making up the sternum?
manubrium (head of the tie)
body (the tie)
xiphoid process (the pointy part of the tie)
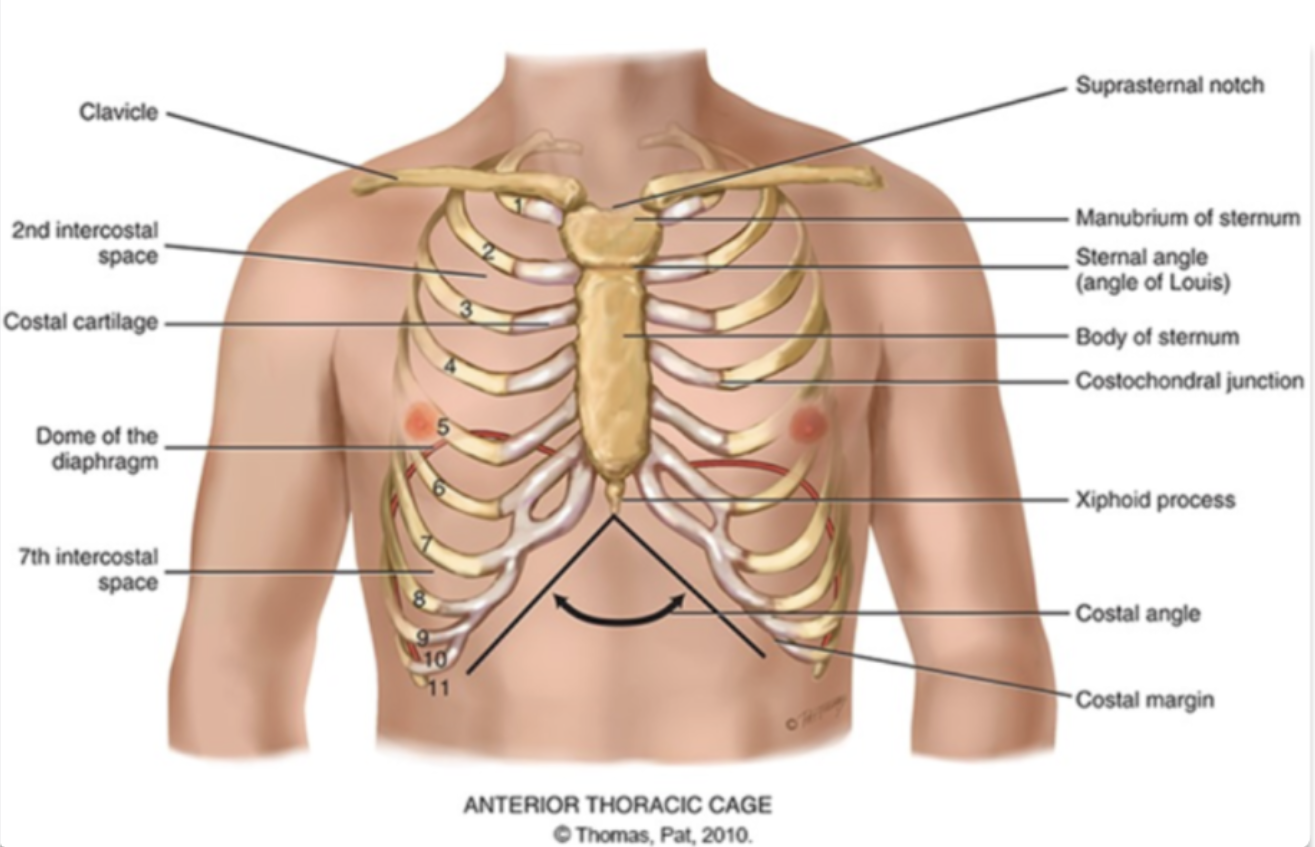
sternum is also known as the…
the breast bone
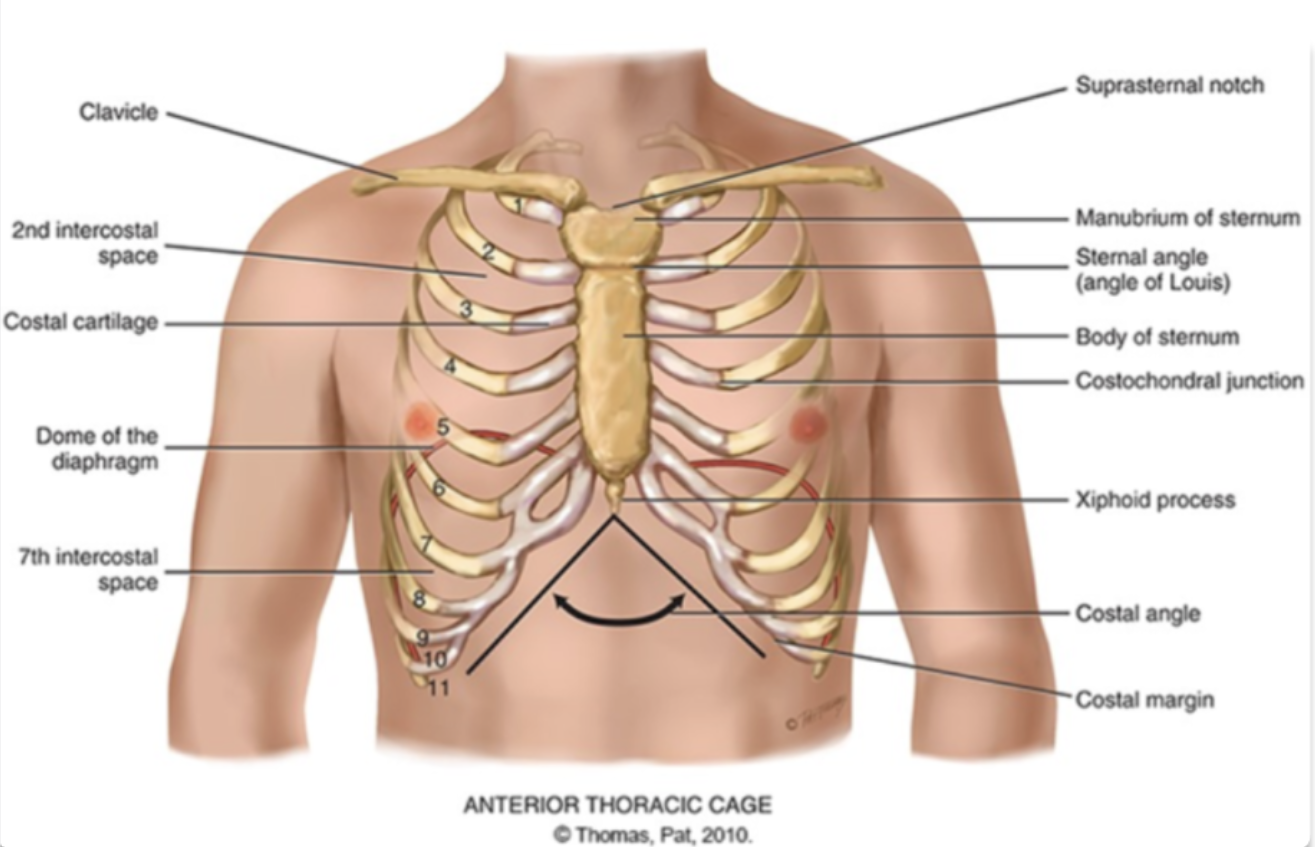
sternal angle (angle of louis)
the articulation between the manubrium and the body of the sternum and the second rib
true or false: angle of louis mark the site of tracheal bifurcation where the trachea split into the left and right bronchi and is above the fourth thoracic vertebra on back
true
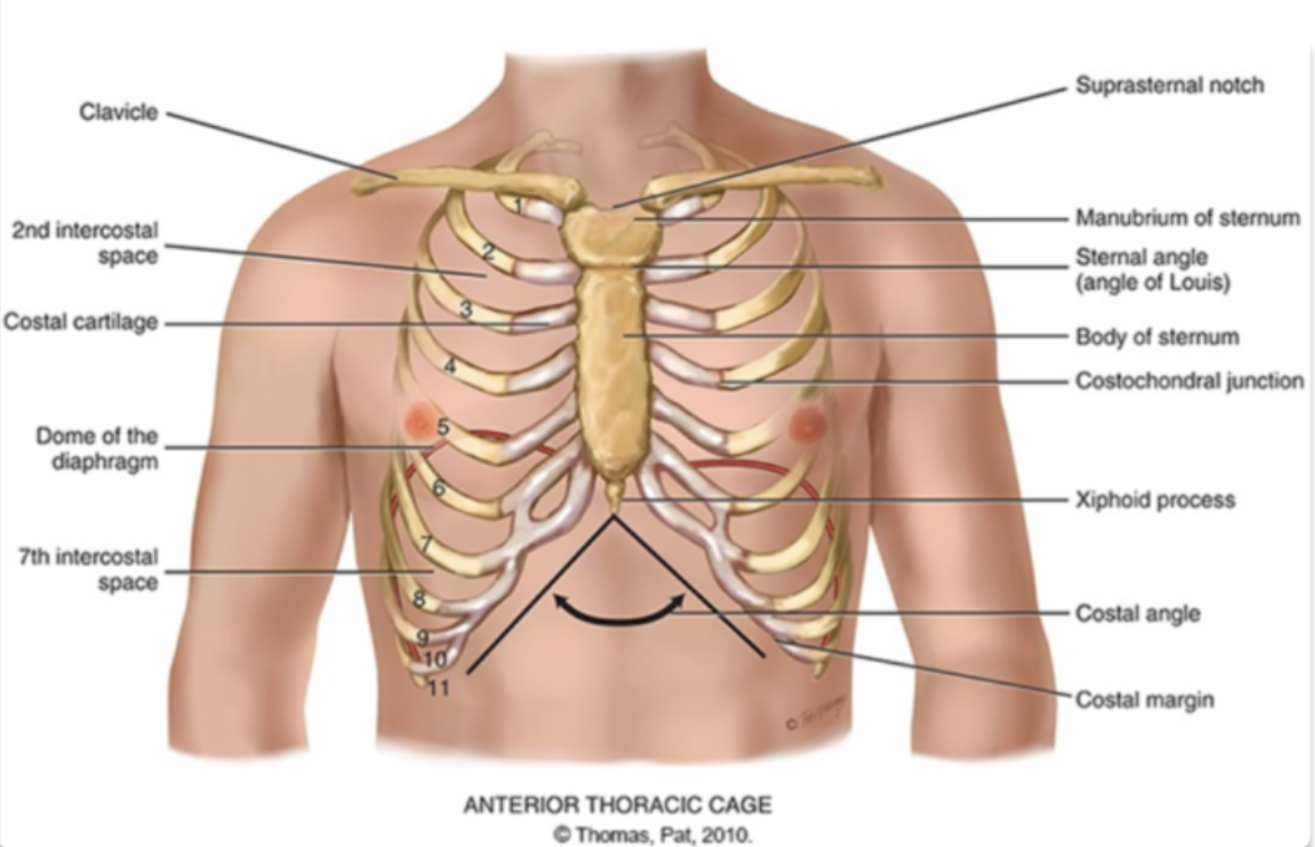
how can the student nurse palpate for the angle of louis?
palpate lightly and locate the second ribe and slide down to second intercostal space toward the middle of the chest where the sternum is
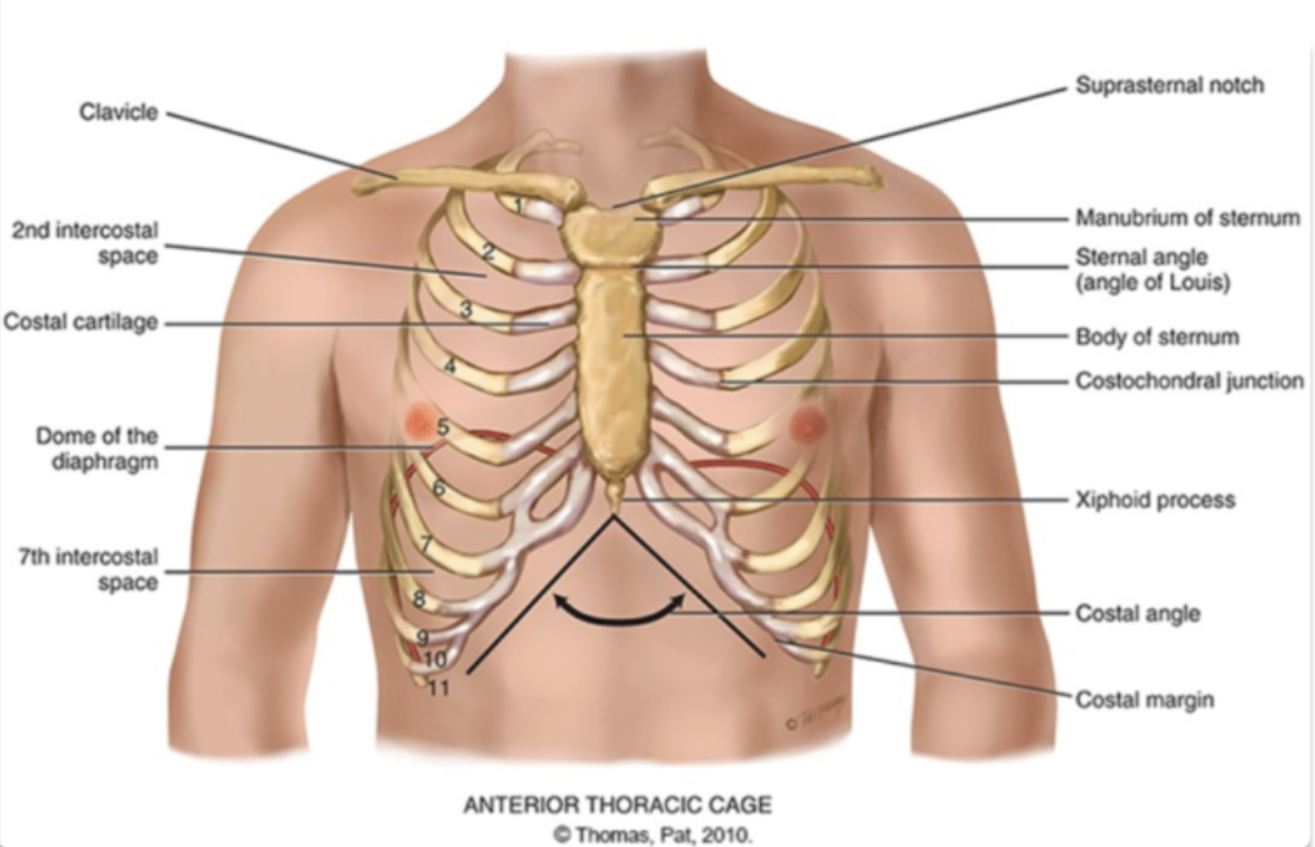
costal angle
the slanted degree of articulation of the false ribe cartilage
another definition: right and left costal margins from an angle where they meet at xiphoid process
vertebra prominens
the most prominent bony spur protruding at the base of the neck at the cervical vertebrae 7
spinous process
the other bony spur protrusion excluding the C7 which is the vertebra prominens
where is the inferior border of the scapula located?
the level of the 7th or 8th rib in most individual
how can the student nurse palpate for the inferior border of the scapula?
follow the spine of the scapula
move downward along the medial edge of the scapula until you feel the inferior border
how can the student nurse palpate for the twelth rib?
locate the lowest point of the rib cage on the lateral aspect of the torso
gently press in and follow the bony contour downward from the 10th ribs down to the 11th and then the 12th
identify where the 12th ribs end - the free tip where should located somewhere within the back
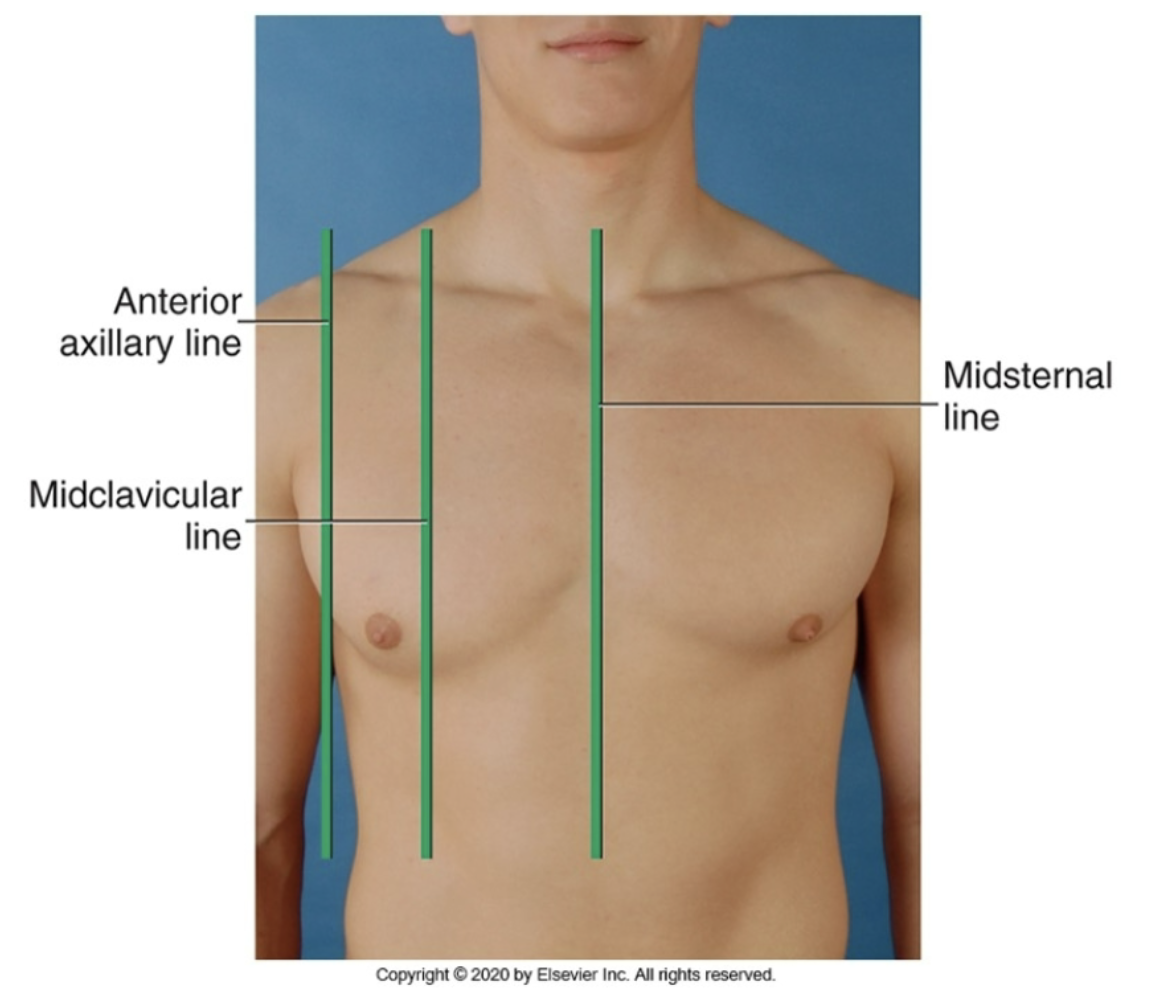
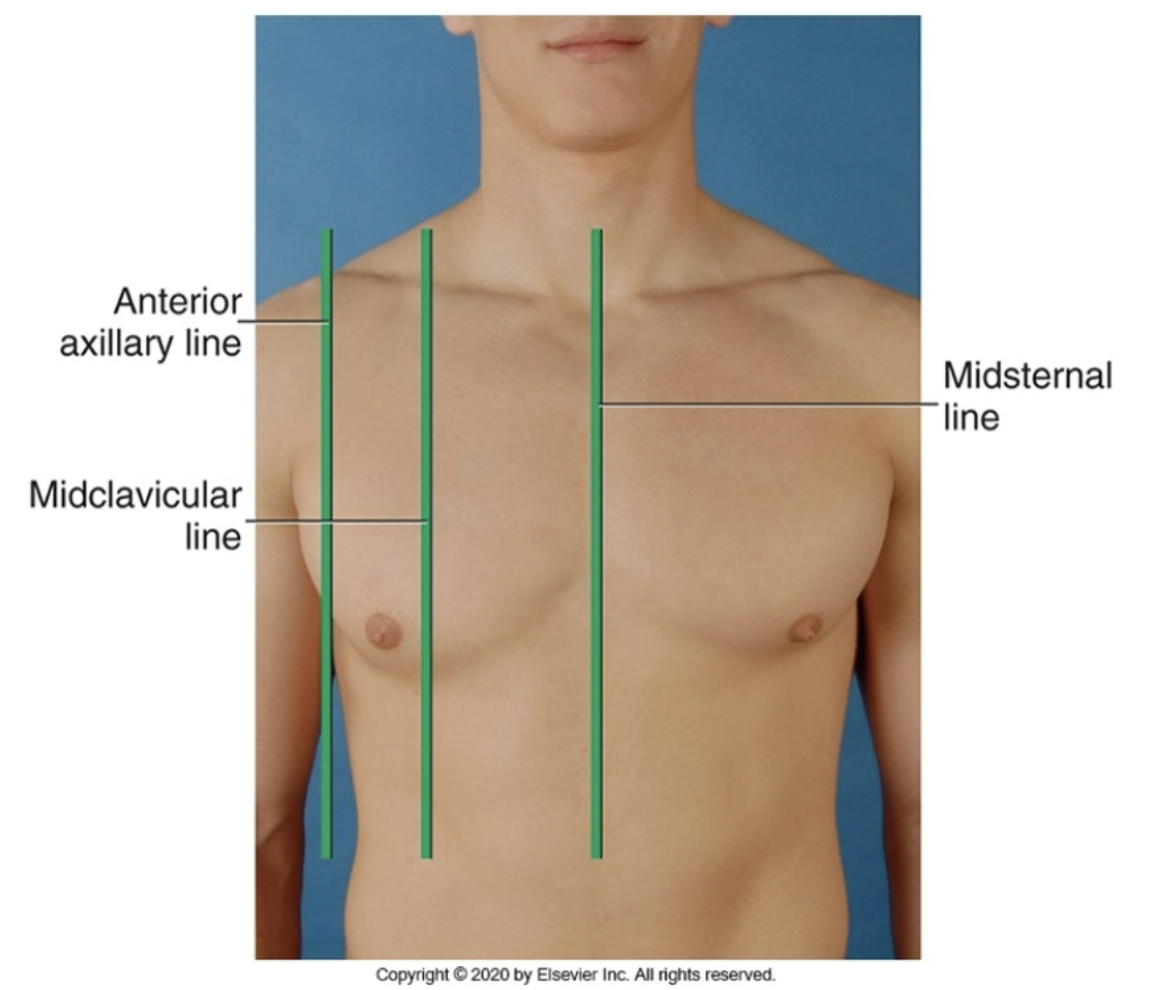
midsternal line
anterior reference line running down the middle of the chest (middle of the sternum)
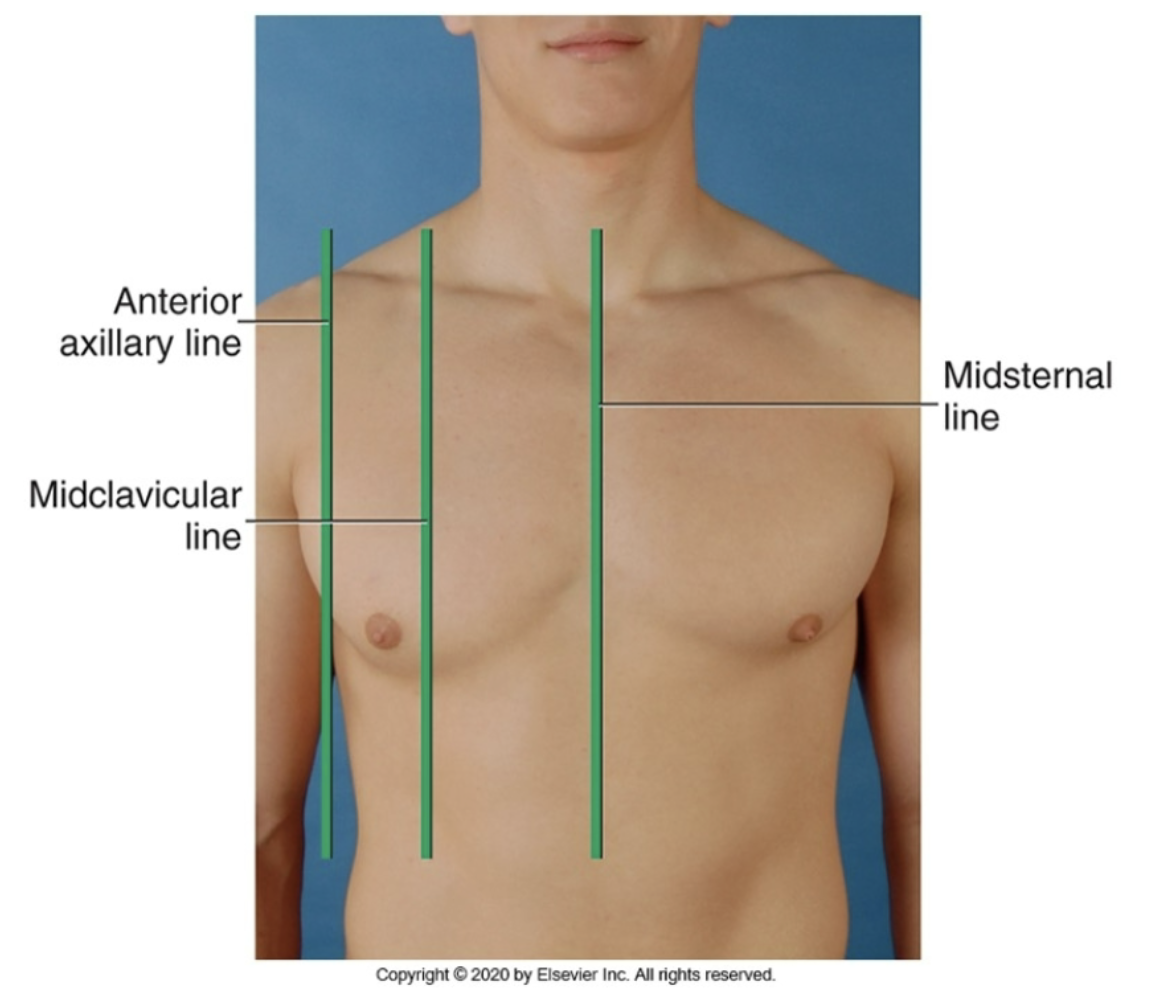
anterior axillary line
anterior reference line running down area a little medial to the armpit
midclavicular line
anterior reference line running down the middle of the clavicle and the torso
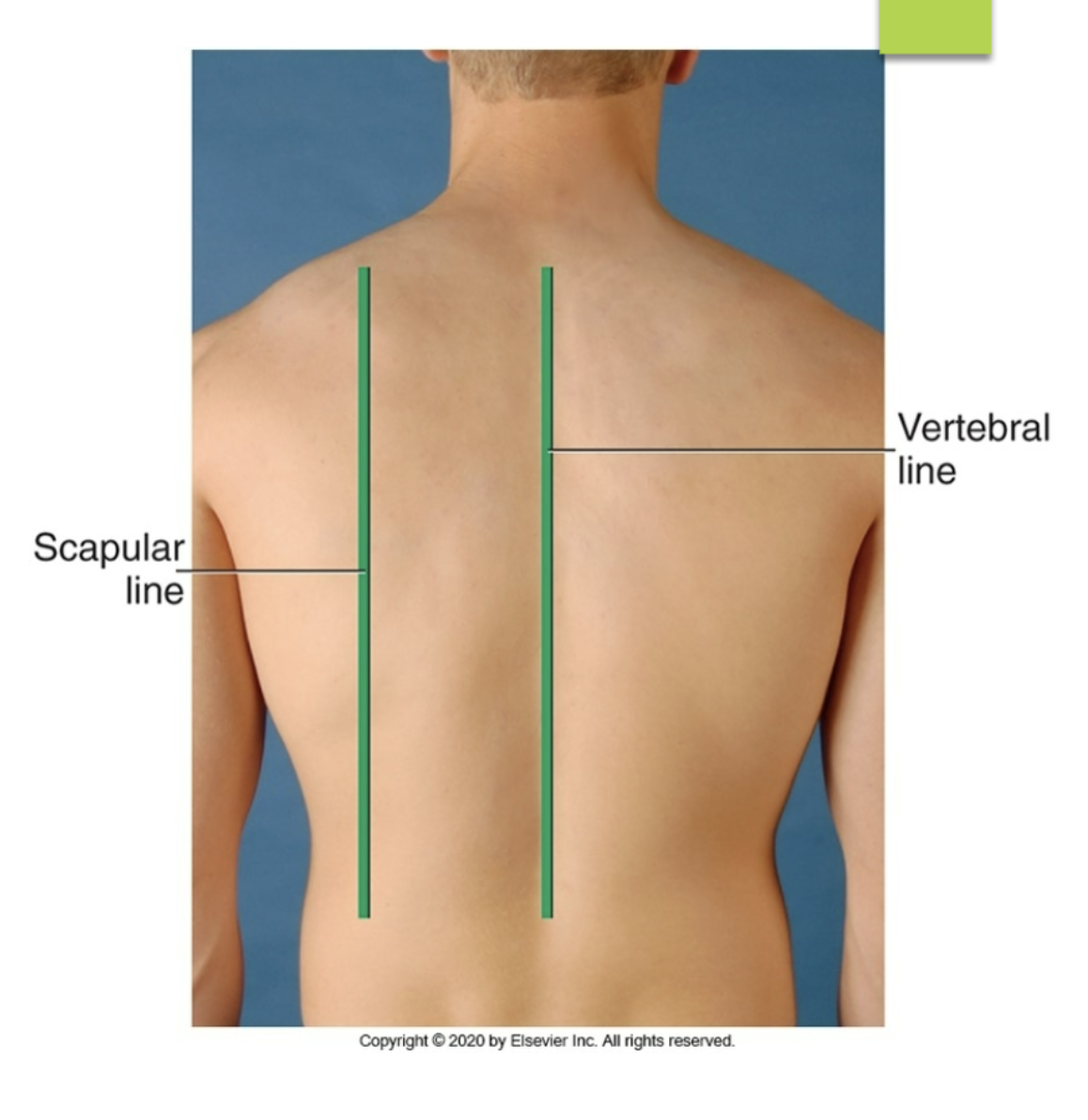
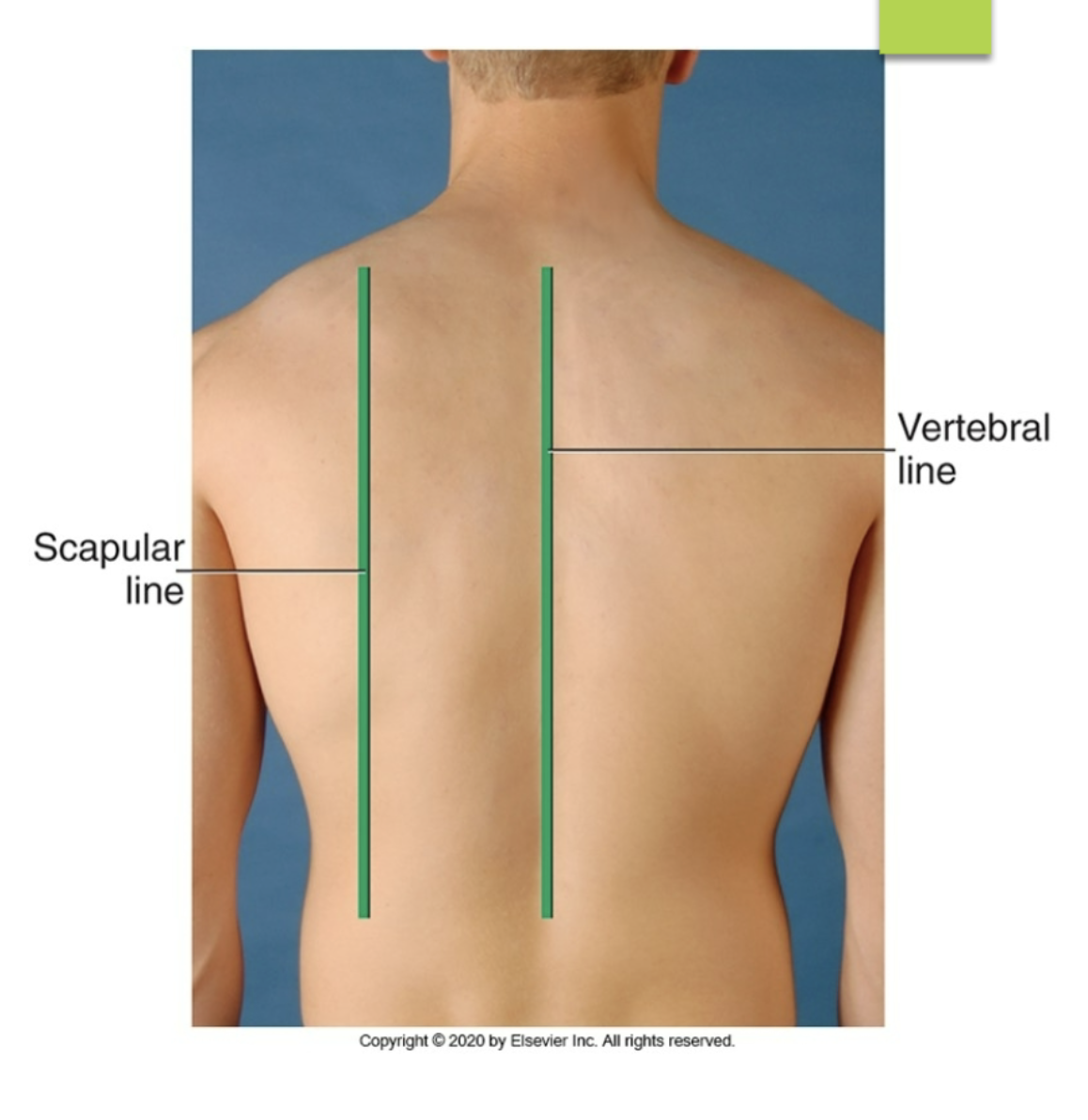
scapular line
posterior reference line running down near the medial ridges of the scapula
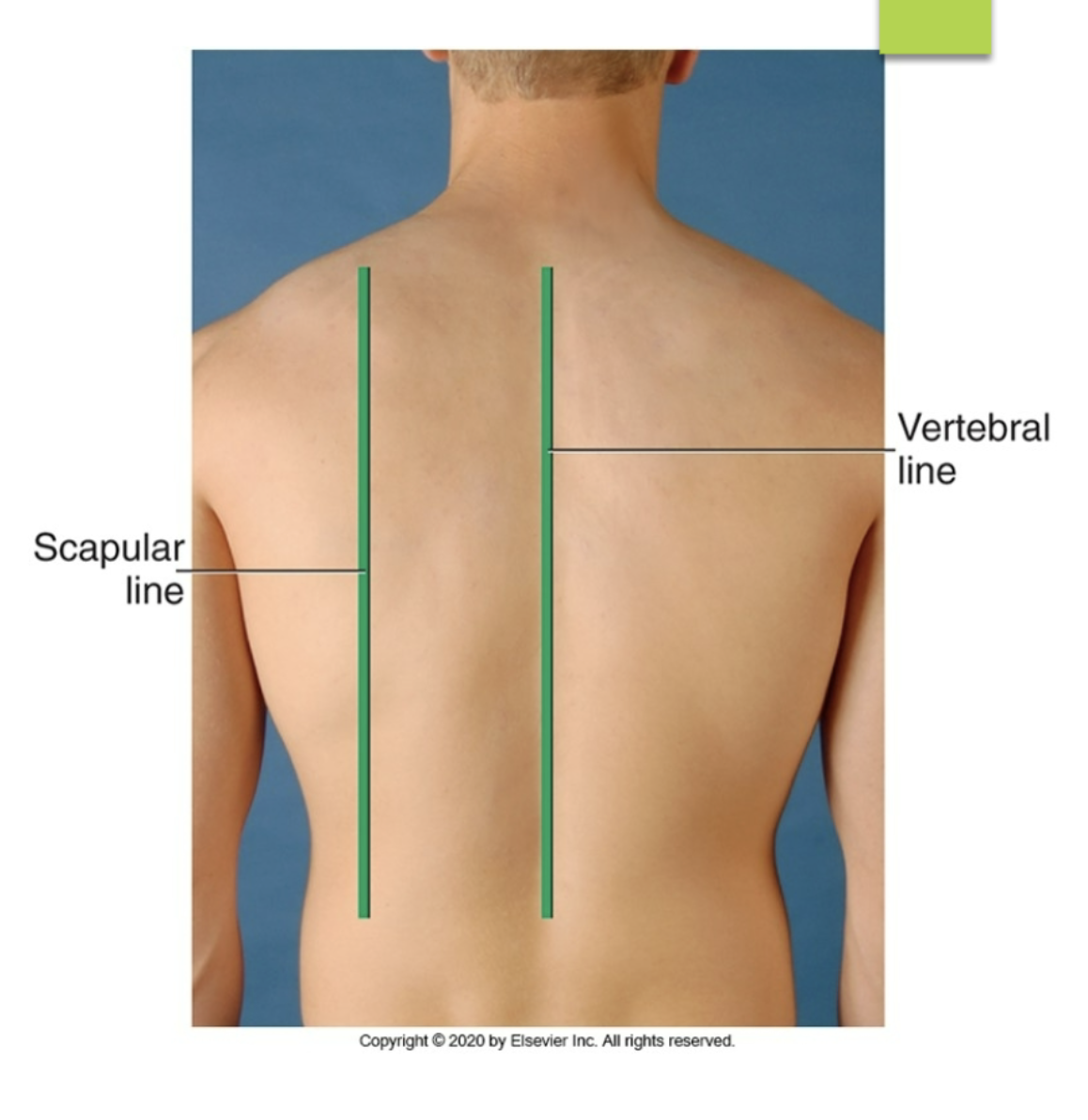
vertebral line
posterior reference line running down the spine
what are the different anterior reference line
anterior axillary line
midclavicular line
midsternal line
what are the different posterior reference line?
scapular line
vertebral line
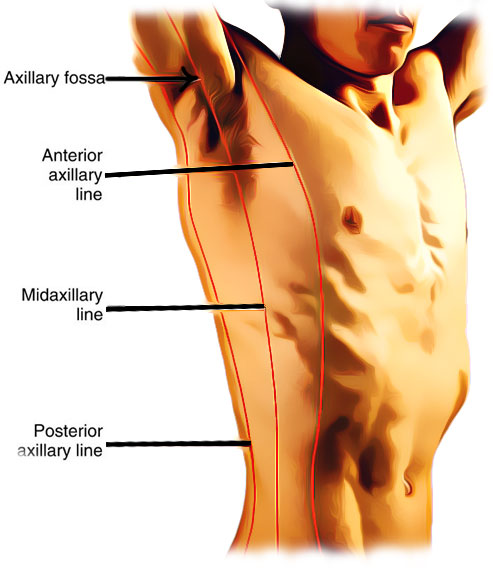
what are the different lateral reference lines
anterior axillary line
posterior axillary line
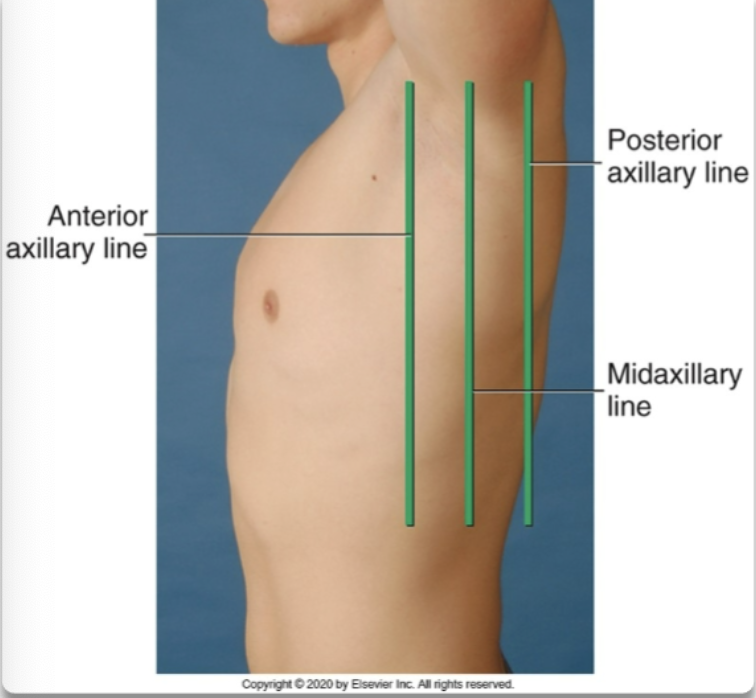
midaxillary line
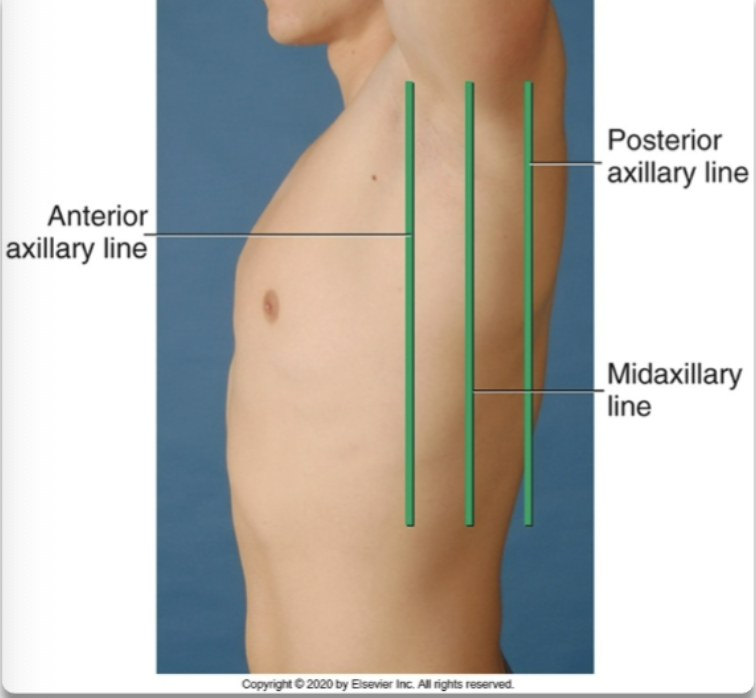
midaxillary line
lateral reference line that runs along the sides of the torso
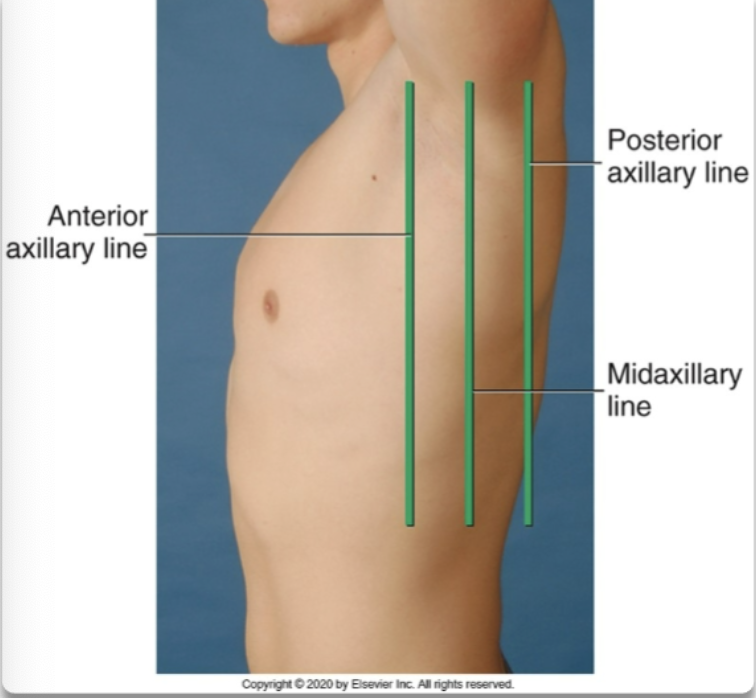
posterior axillary line
lateral reference line that runs near the marginal ends of the laterals side of the torso
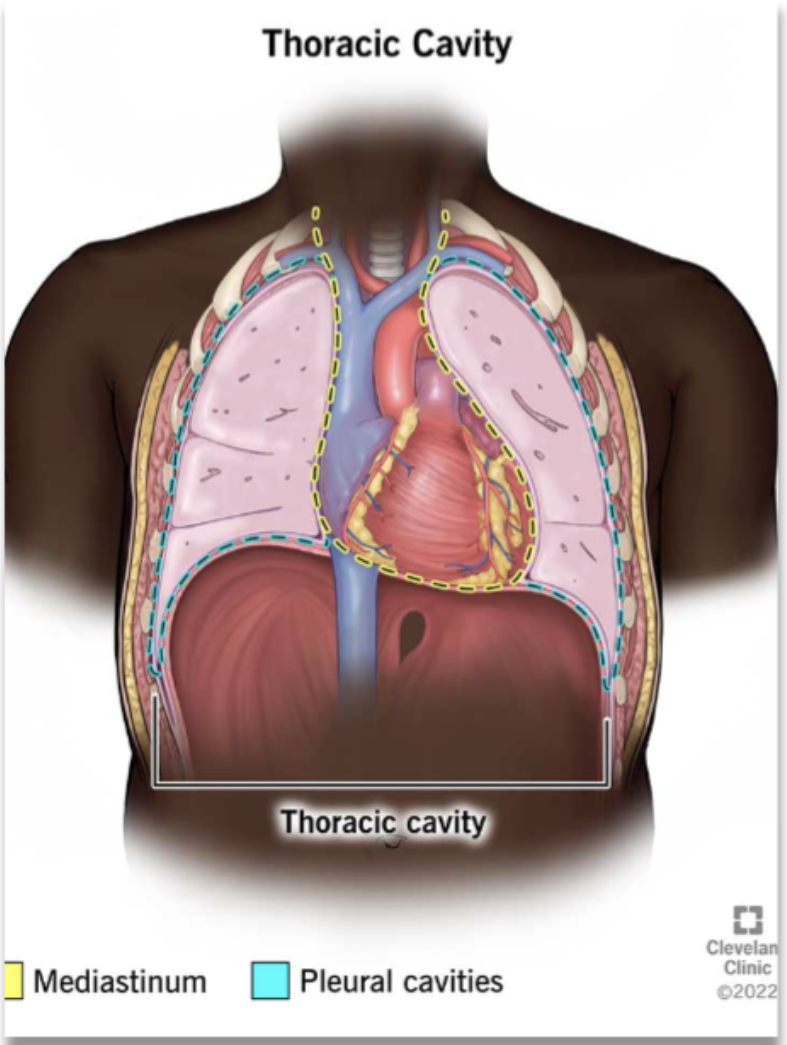
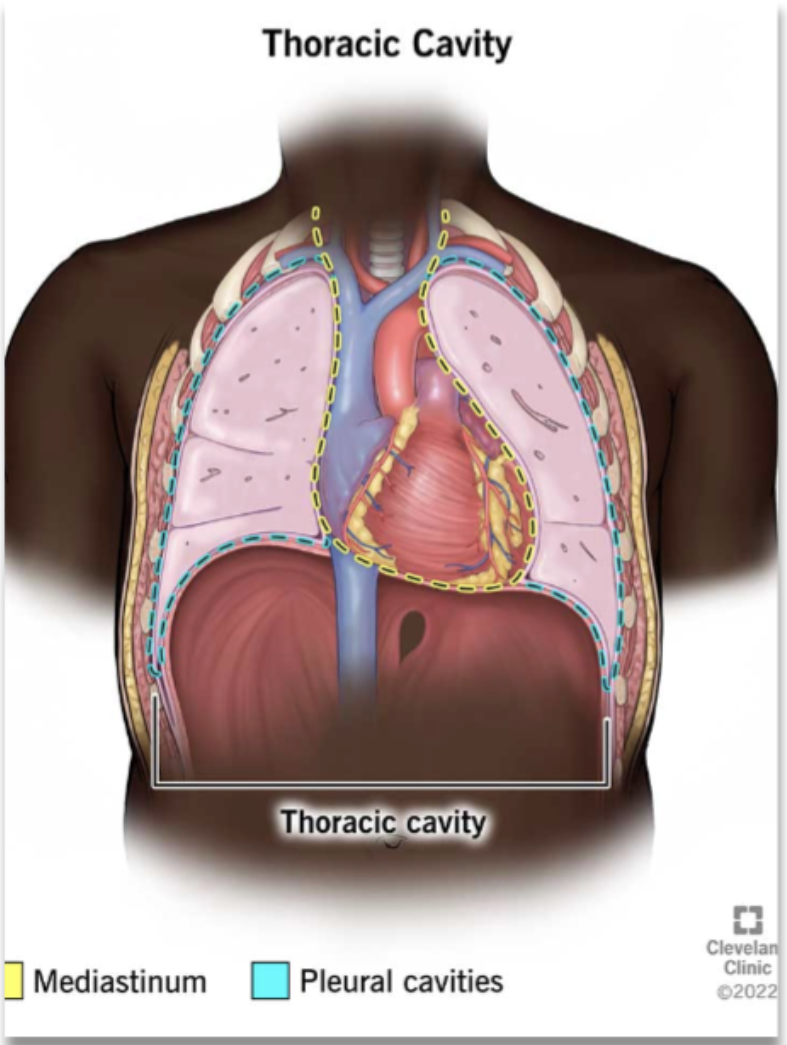
mediastinum (location and compositions)
middle section of thoracic cavity
contains the esophagus, trachea, heart, and great vessels (vena cava and aorta)
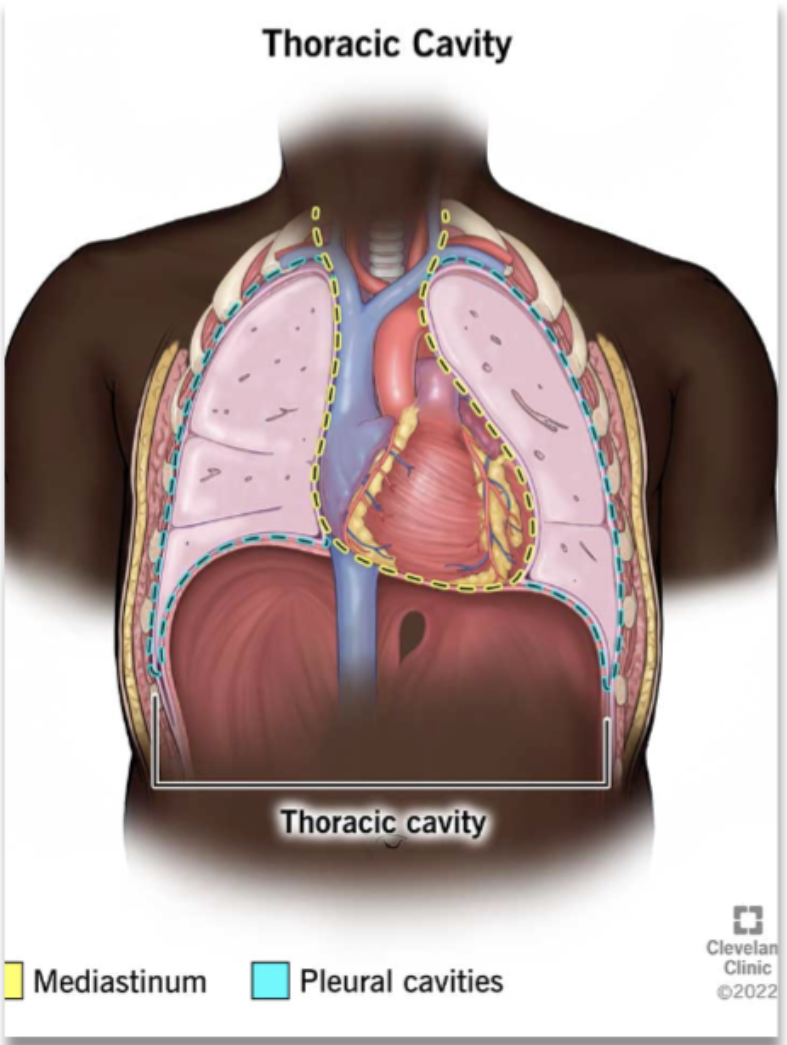
lung borders and its different regions
pleural cavities surrounding the lungs
apex: extends 2-4 cm above the clavicle
base: rest on the diaphragm (6th rib anteriorly, 10th rib posteriorly) - the base of the lung extend lower the more posterior it gets
lateral: reaches the 8th rib at the midaxillary line
anterior: refer the medial edge where left and right lungs come closest to the sternum - edge with the mediastinum
posterior: extend o the 10th ribs (rest) and 12th rib (deep inspiration)
true or false: the left lung is shorter than the right lung because of underlying liver
false: the RIGHT lung is SHORTER than the LEFT lung because of the underlying liver
true or false: left lung is narrower than the right lung because the heart bulges to the left
true
true or false: the bronchial tree is wider on the right side, increasking the risk of aspiration going down that bronchi
true
true or false: right lung have 2 lobes while left lung have 3 lobes
false: RIGHT lung have THREE while LEFT lung have TWO
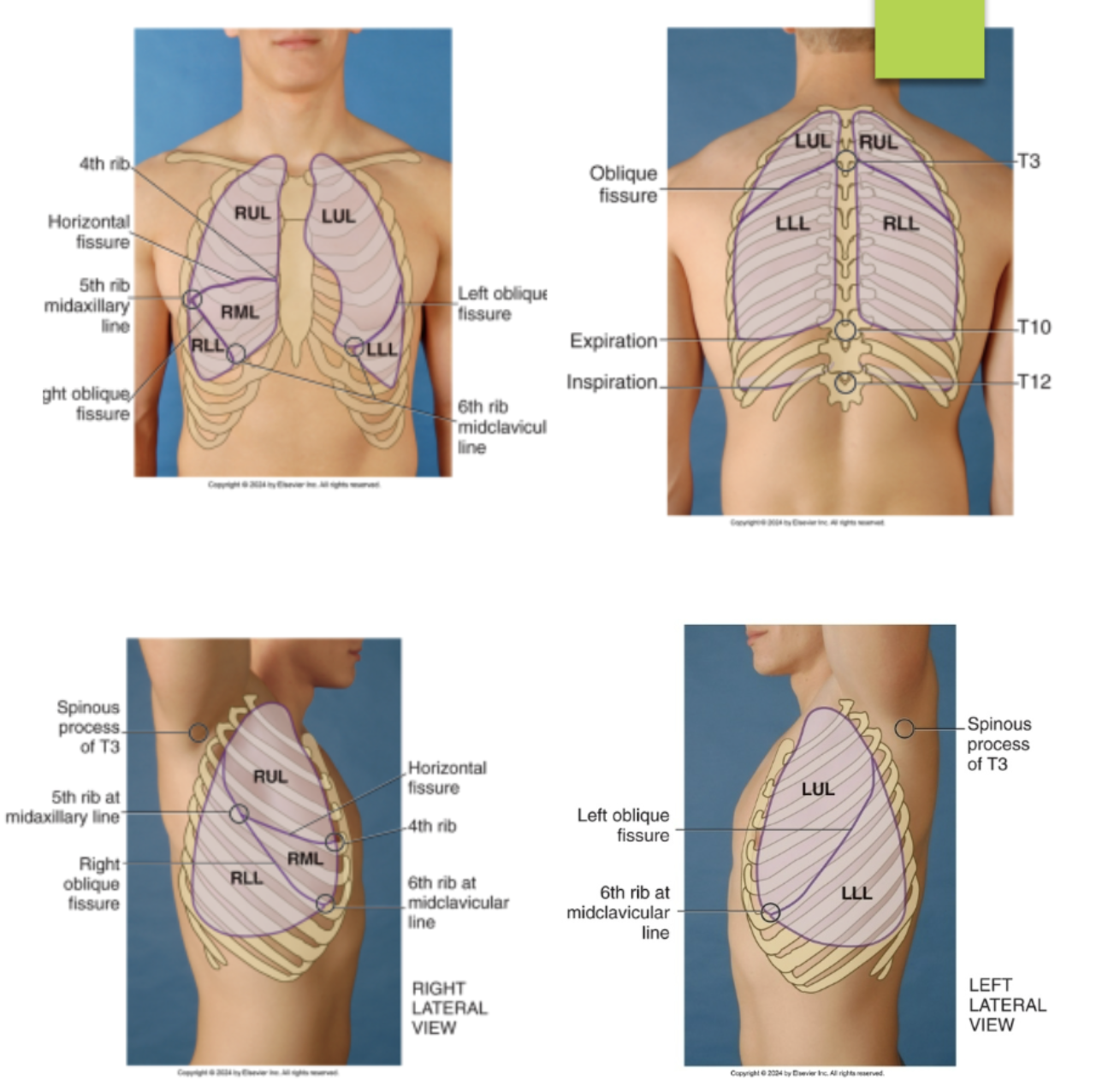
identify the lobes and fissures of the right lungs from the anterior view of the chest…(identify from top to bottom)
right upper lobe
horizontal fissures @ the 4th rib and 5th ribe at the midaxillary line
right middle lobe
right oblique (diagonal) fissures running from the 5th rib midaxillary line to the 6th rib midclavicular line
right lower lobe
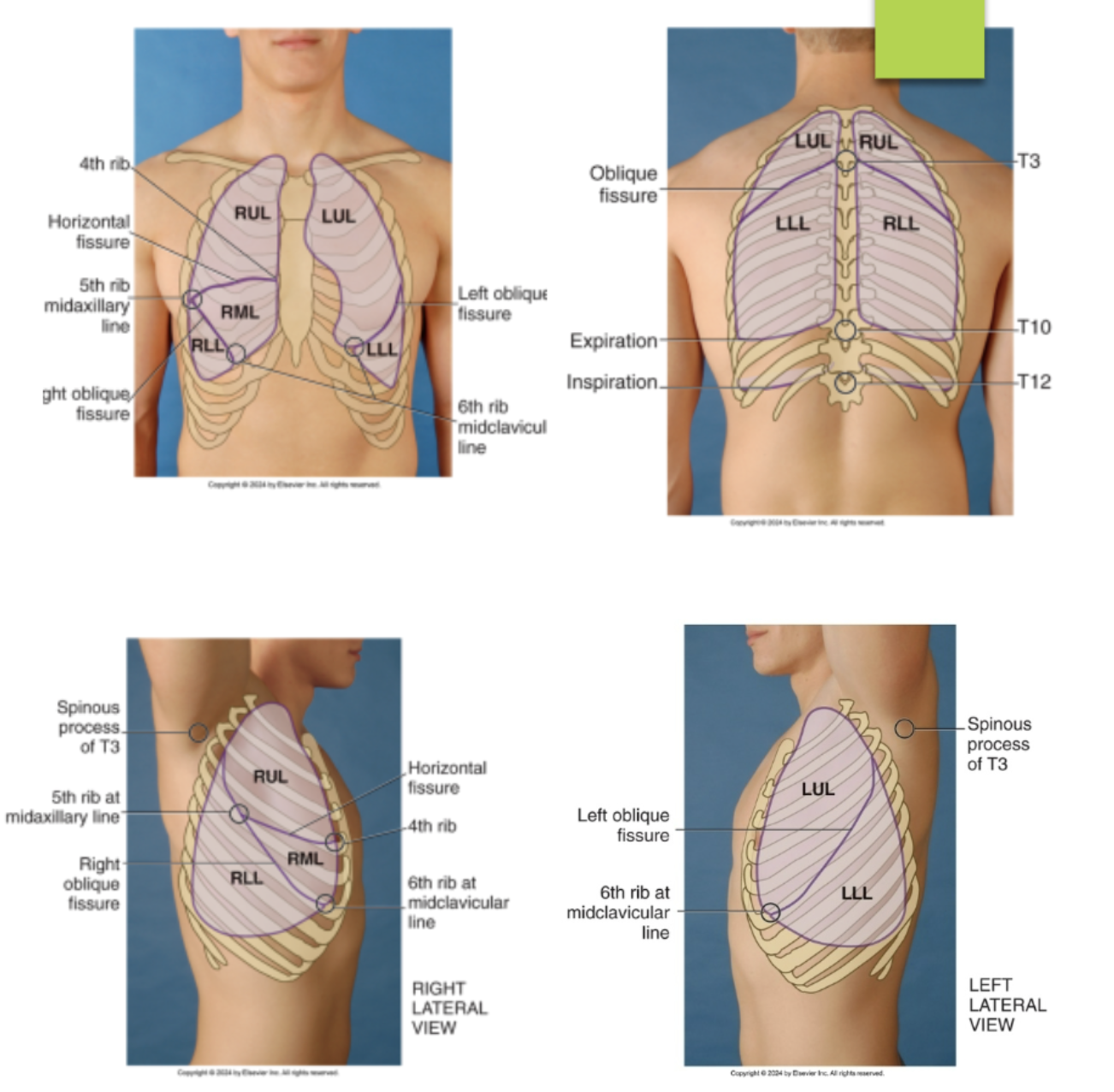
identify the lobes and fissures of the left lung from the anterior view of the chest…(identify from top to bottom)
left upper lobe
left oblique fissure (5th rib midaxillary to the 6th rib midclavicular line)
left lower lobe
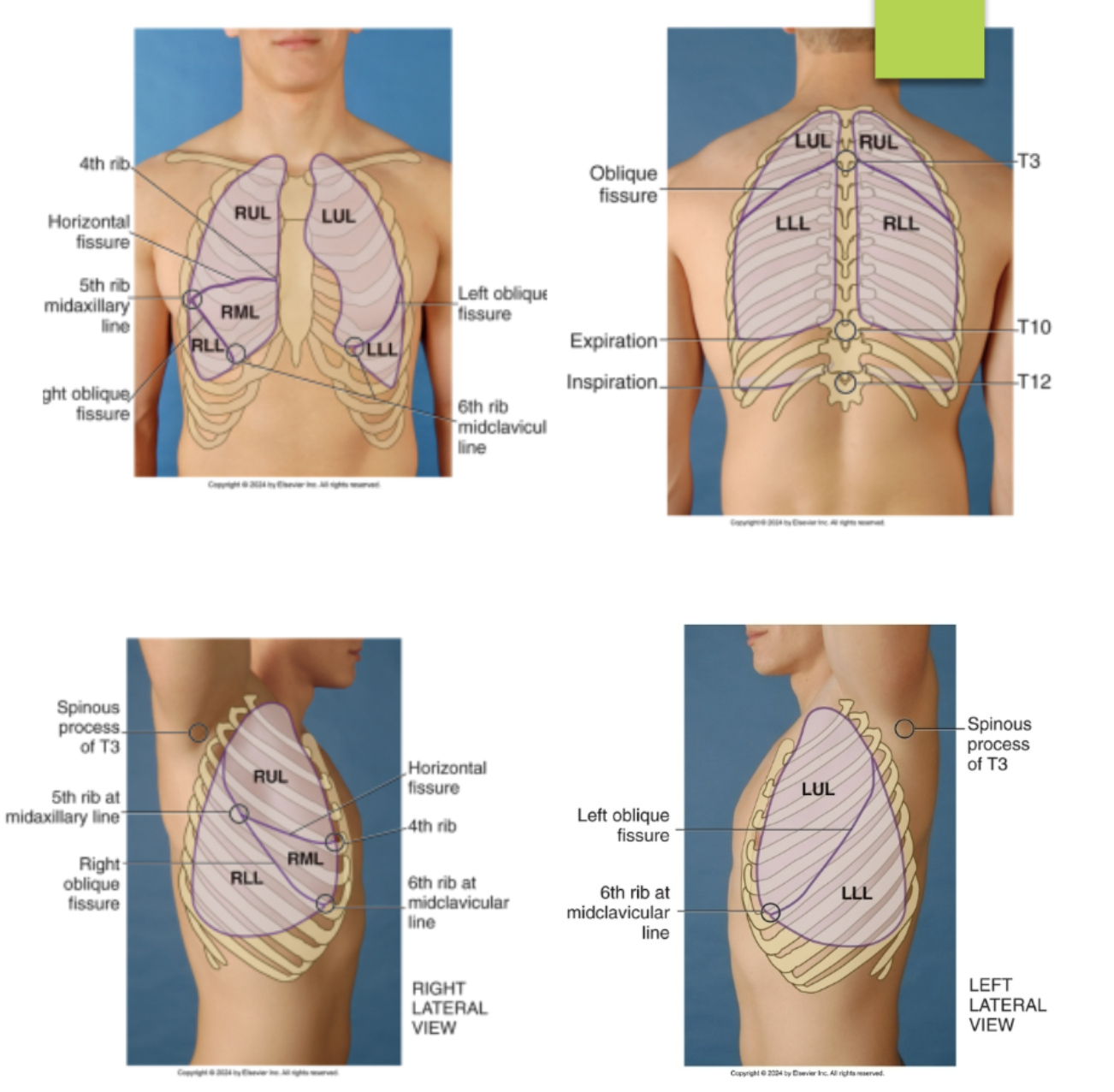
identify the lobes and fissures of the right lung from the posterior view of the chest…(identify from top to bottom)
right upper lobe
right oblique fissures (T3 to 5th rib posterior axillary line)
right lower lobe
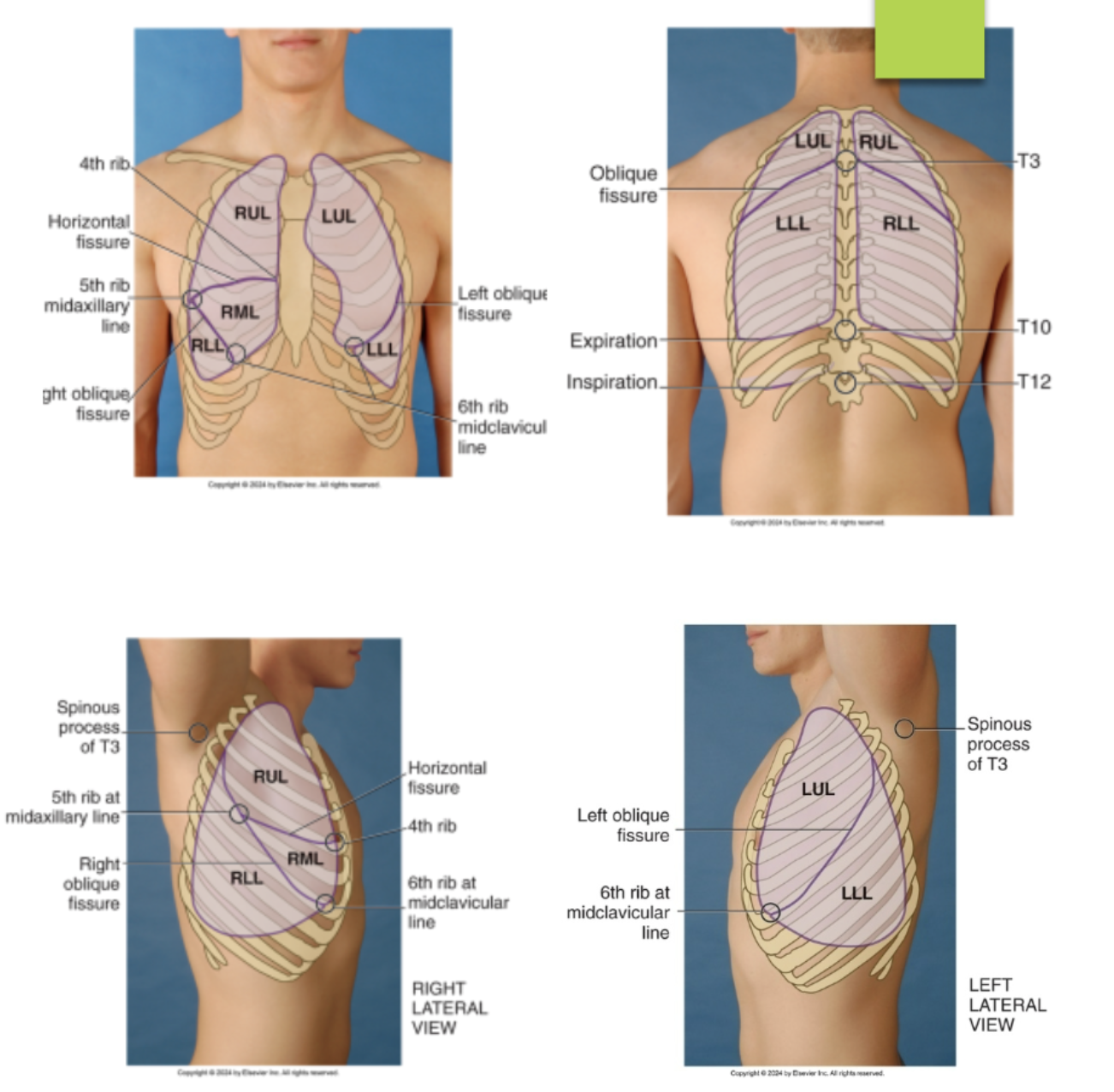
identify the lobes and fissures of the left lung from the posterior view of the chest…(identify from top to bottom)
left upper lobe
left oblique fissures (T3 to 5th rib posterior axillary line)
left lower lobe
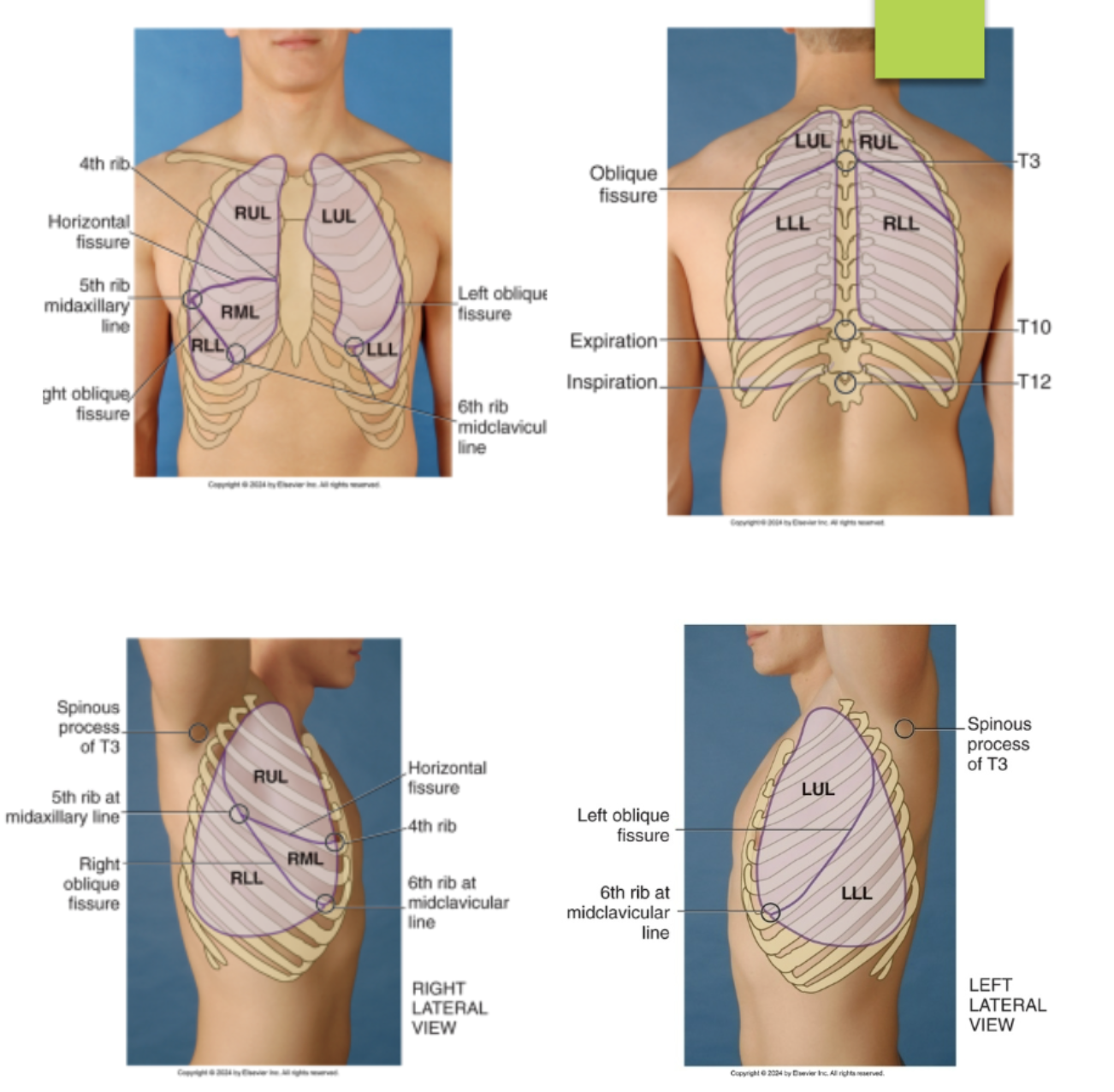
identify the lobes and fissures of the right lung from the lateral view of the chest…(identify from top to bottom)
right upper lobe
horizontal fissures @ the 4th rib and 5th ribe at the midaxillary line
right middle lobe
left oblique (diagonal) fissures running from the T3 to the 6th rib midclavicular line (meet with the horizontal fissures at the 5th rib midaxillary line)
right lower lobe
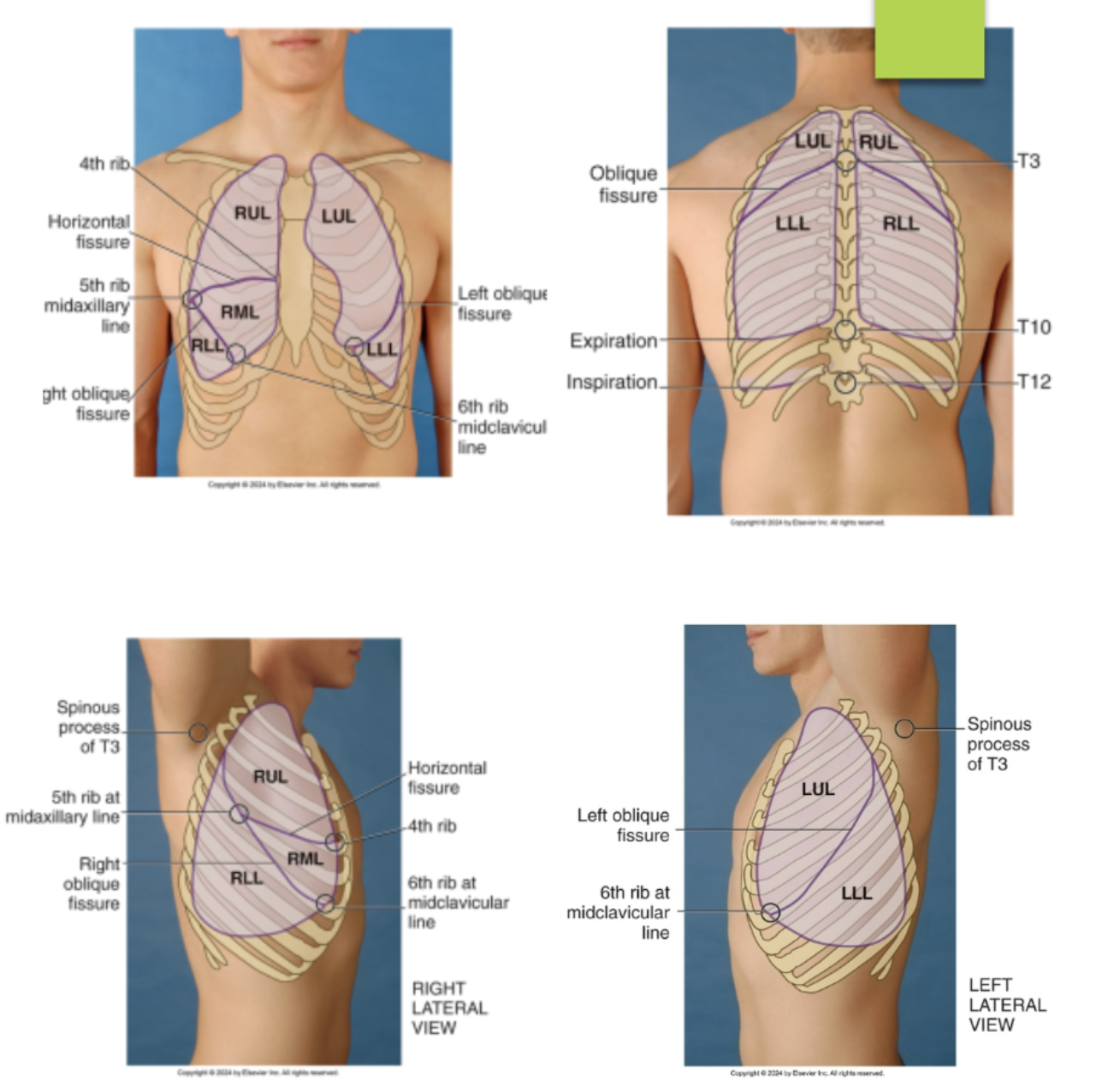
identify the lobes and fissures of the left lung from the lateral view of the chest…(identify from top to bottom)
left upper lobe
left oblique fissure (T4 to the 6th rib midclavicular line)
left lower lobe
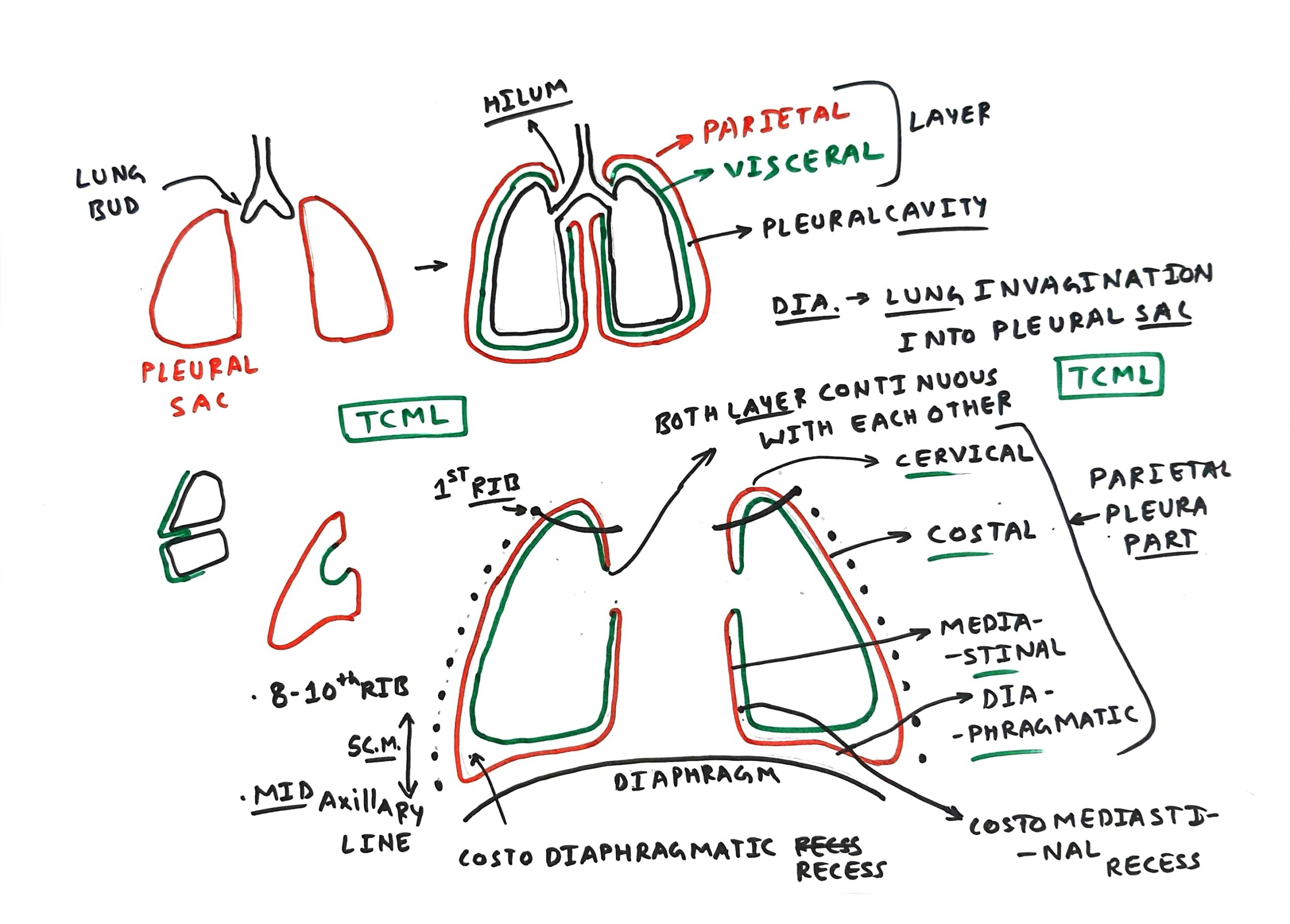
visceral pleura
the deep layer of the pleura that directly attaches to the lung
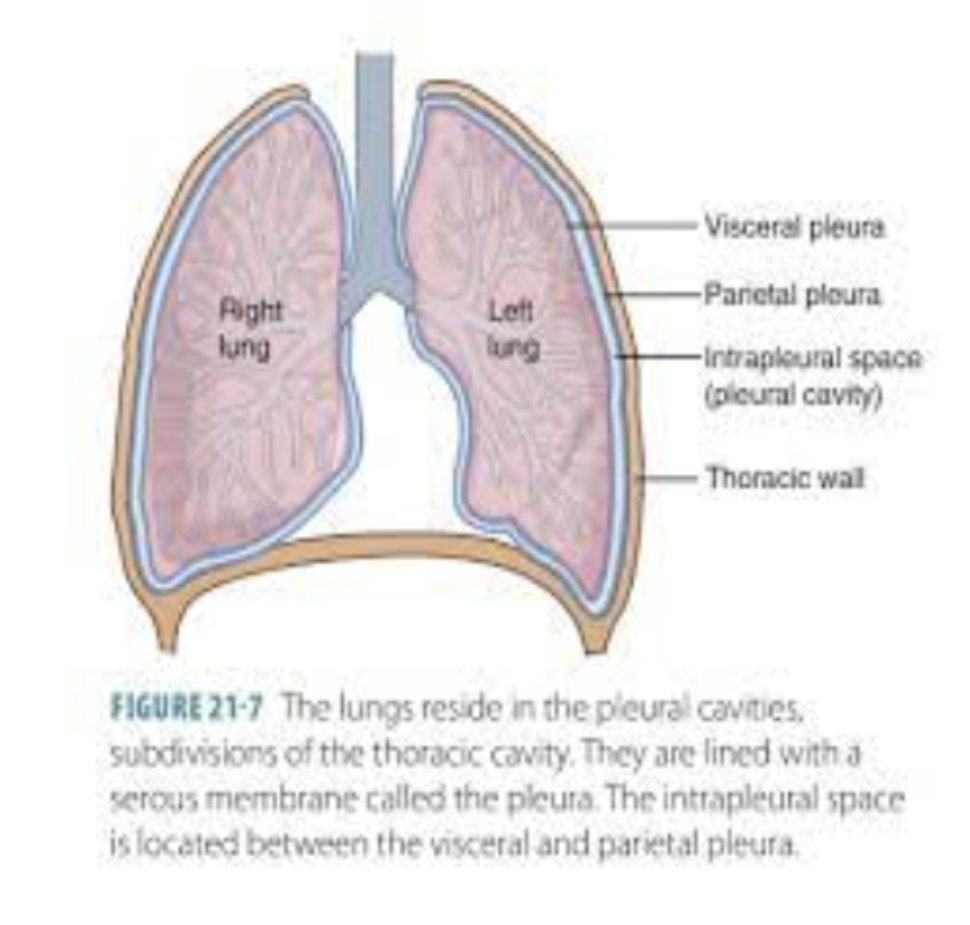
parietal pleura
the superficial layer of the pleura that directly attaches to the thoracic wall
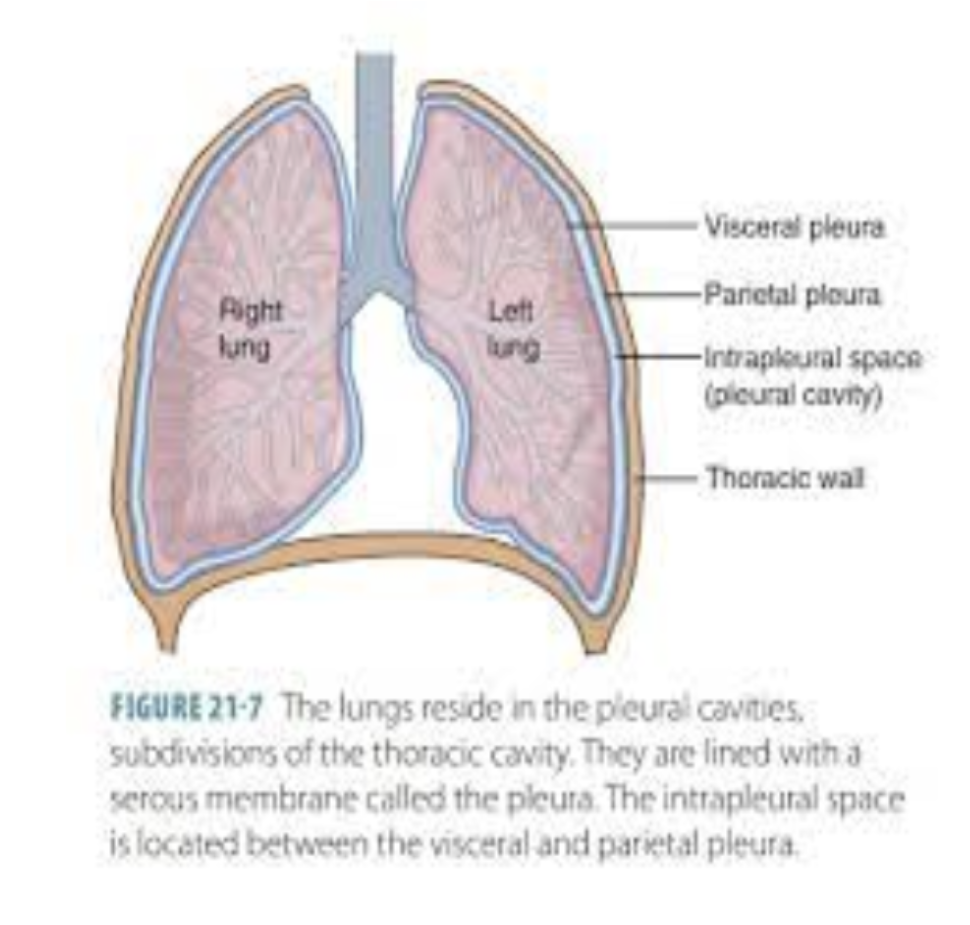
what is the area between the parietal and visceral pleura?
intrapleural space
why do the pleural cavity have negative pressure vacuum?
the negative pressure of the pleural cavity is lower than the pressure inside the lung which create a suction effect that helps the lungs stay expanded and attaches to the chest wall
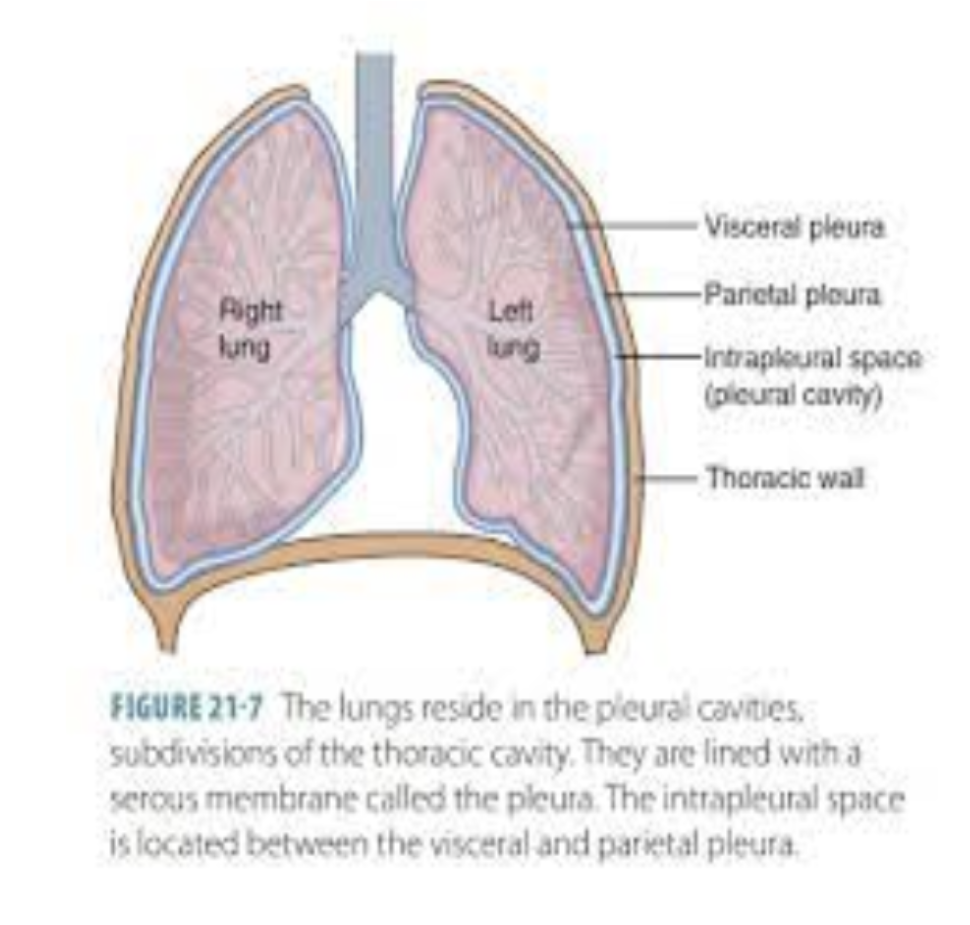
true or false: pleural cavity is a potential space that is usually very thin and filled with only a small amount of pleural fluid
true
costodiaphragmatic recess
potential space that extend 3cm below the level of the lungs contained within the parietal layers
allow for optimal lung expansion
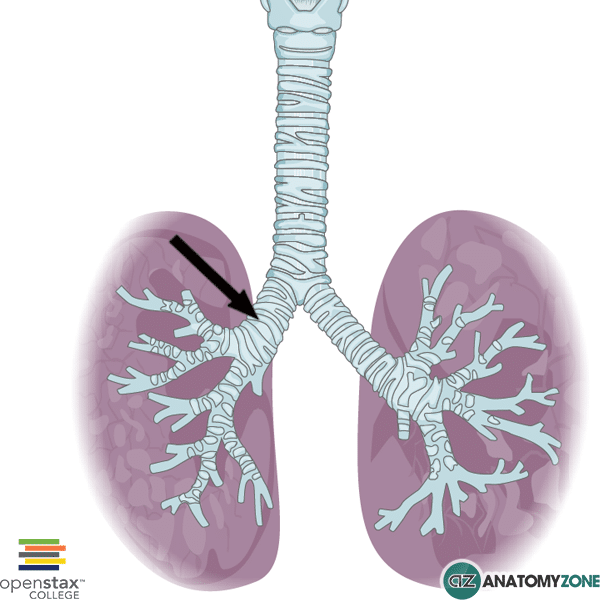
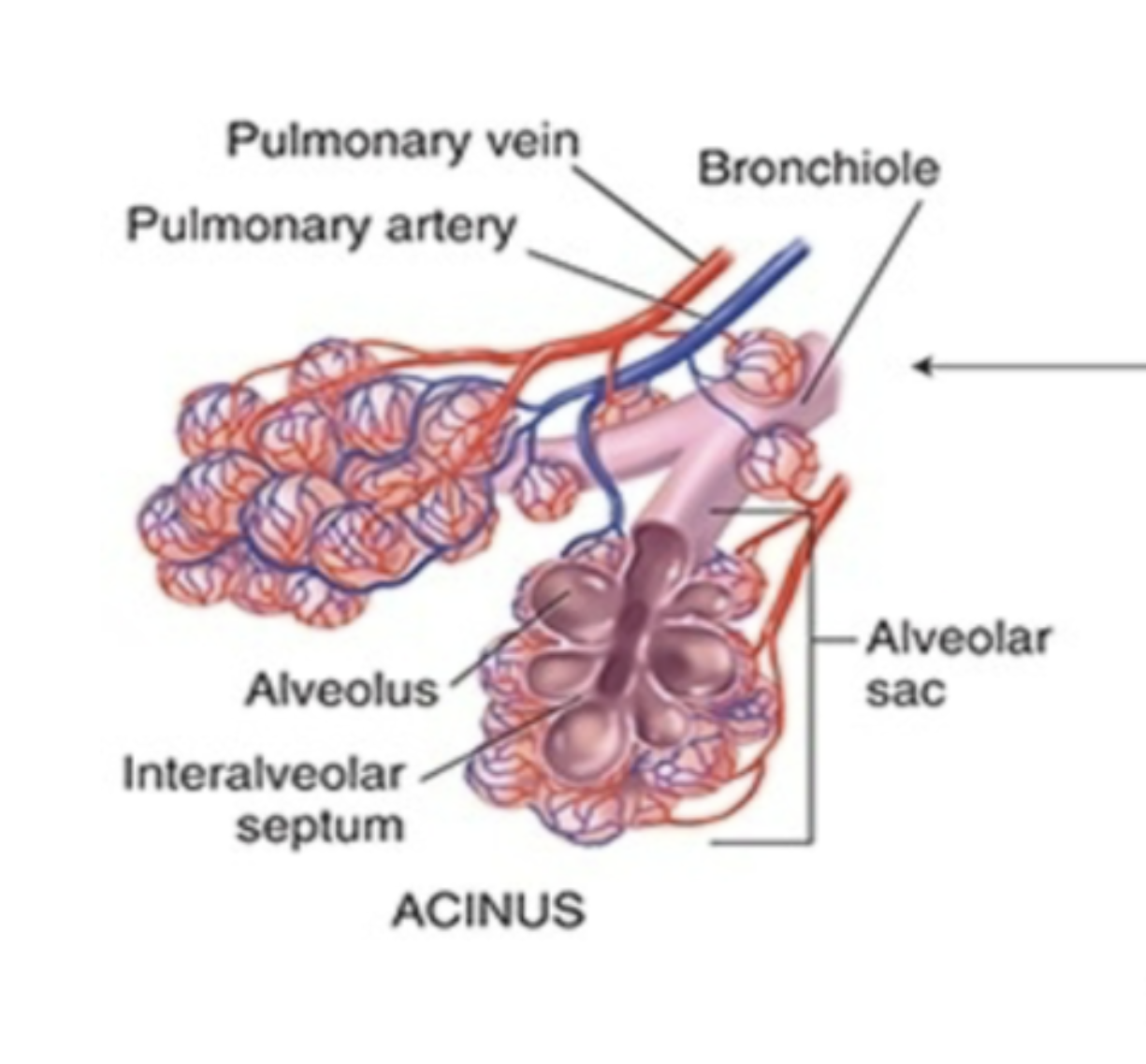
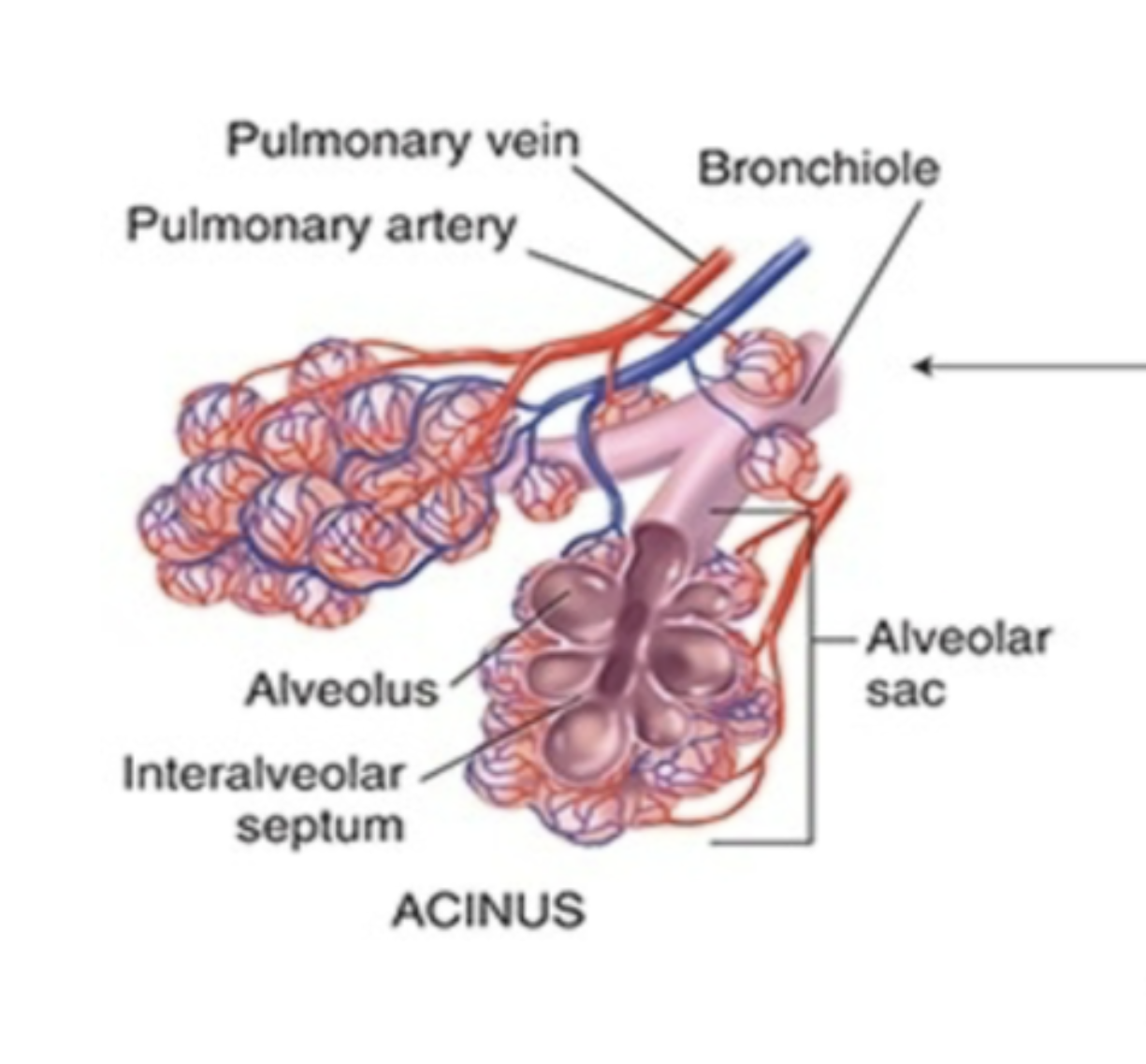
what is the primary difference between the left main and right main bronchus?
the right main bronchus is shorter, wider, and more vertical than the left main bronchus (picture is of the right main bronchus)
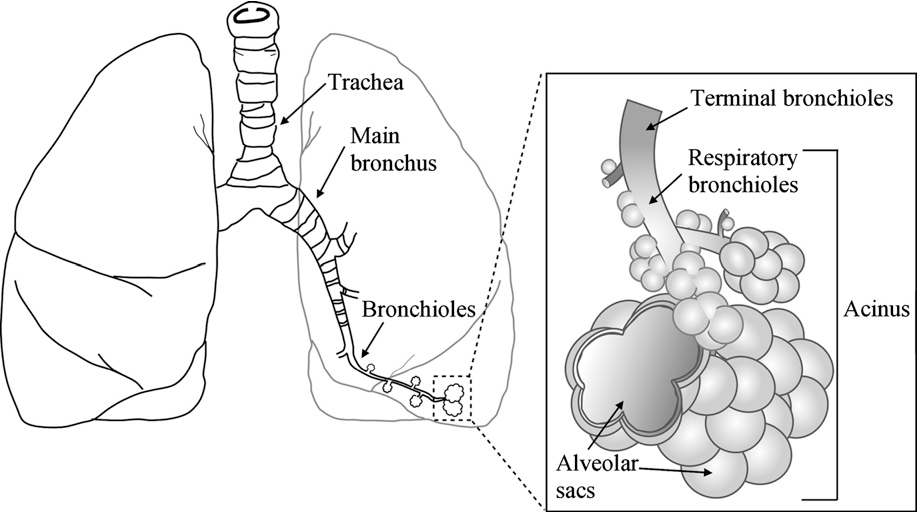
lung parenchyma
refer to the functional tissues within the lungs that allow for gas exchange, AKA the collections of alveoli that helps with gas exchange
why is the space within the trachea and bronchi are considered to be dead space?
they are considered dead space as they hold air but doesn’t participate in gas exchange, only the air sacs within each alveoli are space that participate in the gas exchange
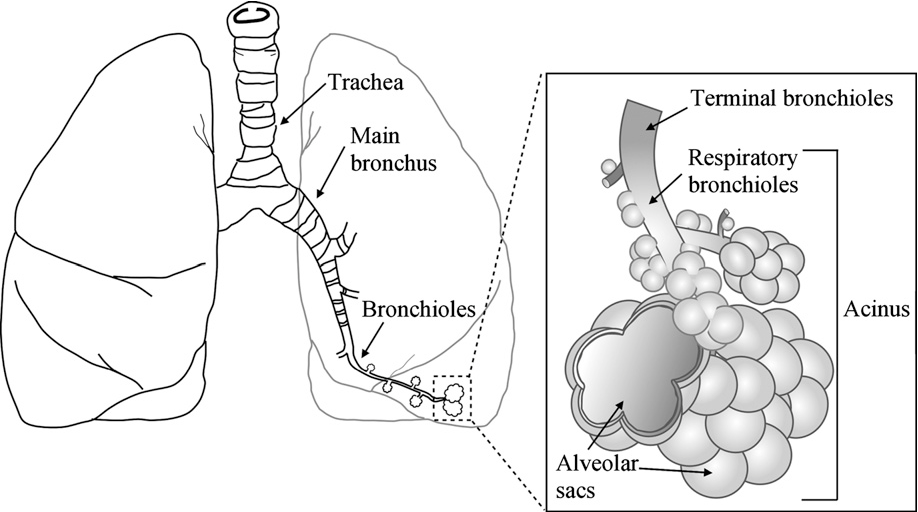
what are the protective mechanisms within each bronchial tree?
secretion of mucus from goblet cells to trap dust, bacteria, and other particles
coordinated movement of the cilia to sweep trapped particles and mucus upward toward the throat where they can be swallowed or expelled
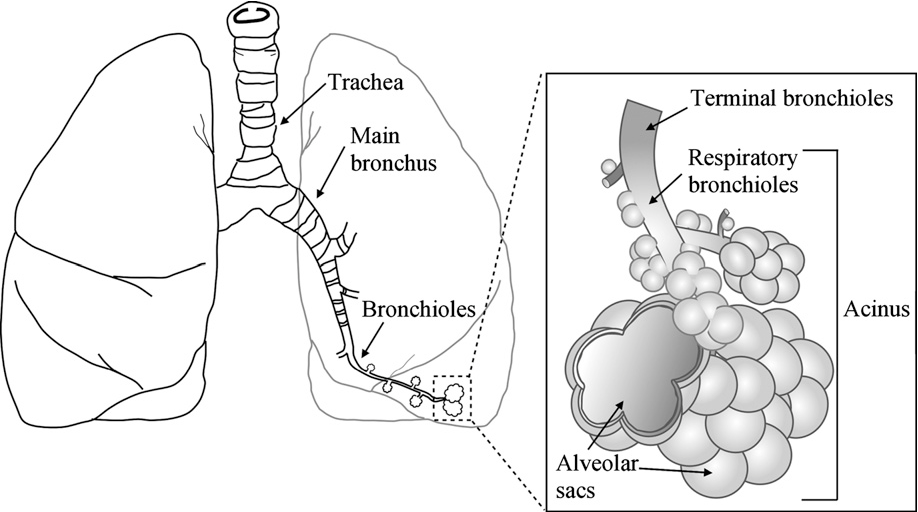
acinus of the lung
functional unit of the lung that involved in gas exchange comprised of the
bronchioles
alveolar ducts (branches off the bronchioles)
alveolus (each of the bulbous area) - where gas exchange happen between the capillaries and the membrane
alveolar sac (which is the collection of alveoli)
what is the four major functions of the respiratory system?
supplying oxygen for energy production
removing carbon dioxide
maintaining homeostasis of the acid-base balance of arterial blood
maintaining heat exchange
what is the feedback loop that control respirations and give a brief description…
humoral regulation (AKA changes in carbon dioxide and oxygen levels in blood, and some hydrogen ions level)
increased carbon dioxide in blood (hypercapnia) trigger the brain NS to let the diagram go down so the lung can expand and allow us to breath in
ventilation (or pulmonary ventilation)
the physical act of breathing
true or false: actual “respiration” occurs at the cellular level
true
vital capacity
the maximum amount of air a person can move into and out of their lungs in a single respiratory cycle after taking the deepest breath in and out possible
total lung capacity
the total volume of a person lung
inspiratory capacity
the amount of air a person can move into their lung after they have completed a quiet (normal/not forced) respiratory cycle
tidal volume
amount of air a person can move into or out of their lung during a normal relaxed breath
residual volume
the volume of air remaining after maximum exhalation
expiratory reserve volume
the volume of air that can be voluntarily expel after a single complete quiet and normal repsiration cycle
true or false: as individual age, we have a decreased vital capacity and increased residual volume
true; less air is being move in and out of the lung
what is the 2nd most diagnosed cancer in both genders and leading cause of cancer death in the U.S?
lung
true or false: tuberculosis affected more than 1/3 of the world’s population as it is the “social and migratory” disease
true
what is the most common chronic disease in childhood?
asthma
true or false: highest burden of asthma correlated with those living at or below poverty level with ethnic and environmental factors playing a significant role in the development of asthma
true
review some of the questions the student nurse can and should use when inquiring about the patient’s cough…
do you have a cough?
when did it start/stop?
how often is the cough?
when does the cough seem to start/get worse/get better?
is the cough gradual (there is a trend) or sudden (onset of a fever, etc)?
productive or non-productive?
can you describe your cough? (the quality —> wheezing, hacking, rattling, etc)
what seem to make the cough better or worse (any triggers)?
have the patient tried any form of treatments to treat the cough?
how have the cough impacted the patient ability to carry on with daily activities and their quality of life?
VERY SIMILAR to the PQRST for pain
review some of the questions the student nurse can and should use when inquiring about the patient’s shortness of breath…
have you ever experienced SOB in the past?
are you aware of any possible triggers?
how would you rate the severity of the shortness of breath from 1-10
how long does these episodes of SOB usually last for?
does changing your positions (e.g., laying down, sitting, standing, etc) help/worsen the SOB
is there a specific time where the SOB seem to start/get better/get worse
are there any other symptoms following the SOB?
do you take any medications or seek any type of treatment during each episode of SOB?
how have the SOB affect your daily lives and our quality of life?
can you give me a brief timeline of your SOB (when it start and where it is now)
review some of the questions the student nurse can and should use when inquiring about the patient’s chest pain with breathing…
when did this chest pain with breathing began?
is the chest pain with breathing constant like after each breath or is it on and off with some breath causing chest pain
does changing how you breath (deeply or shallow) help or worsen the pain?
how would you describe the pain?
how intense would you rate the pain on a scale of 1 to 10
are there any other symptoms that happens along with the chest pain?
what kind of treatment, if any, have you seek and implemented to decrease the pain?
rely on the PQRST with some additional for breathing
review some of the questions the student nurse can and should use when inquiring about the patient’s past history of breathing trouble or lung diseases (e.g., bronchitis, emphysema, asthma, pneumonia, etc)…
have you have any unusually frequent or unusually severe colds? (like starting suddenly or some that get worse very fast?)
are you aware of any family history of allergies, tuberculosis, or asthma?
review some of the questions the student nurse can and should use when inquiring about the patient’s smoking history…
when did you began to smoke? or how long have you been smoking for?
how often do you smoke per day/week? (they can also give an approximate of how many cigarettes packs they go through per month)
when do you usually smoke (setting/time)?
are you aware of any triggers that might cause you to smoke or smoke more than usual?
are you living with anybody else where your smoking might be expose to those individuals?
(if yes to above) are you aware of the risk poses by secondhand exposure to smoke?
(if applicable) when did you stop smoking?
counseling using the five A’s: Ask, Advice, Assess, Assist, and Arrange
review some of the questions the student nurse can and should use when inquiring about the patient’s environmental exposure that might have had an effect on their breathing…
are you aware of any factors from your workplace that might effects your breathing?
if yes to the above, do you have adequate form of protection like wearing a well fitted mask to protect you from the exposure?
have you been monitoring and following-up on your symptoms?
are there any symptoms that usually happen before that might signal breathing problems before it worsen?
review some of the questions the student nurse can and should use when integrating patient-centered care for respiratory conditions?
ask about the patient screening and follow-up testing like TB skin test, chest X-Ray study, pneumonia/influenza immunization, and COVID status and/or vaccination to ensure the patient is well-protected
review some of the questions the student nurse can and should use when inquiring about the patient’s SOB or fatigue (for AGING ADULTS) …
can you tell me about your usual amount of physical activity?
how is your usual energy level? —> do you get tired more easily? how does your change in breathing affect you at home and at work
do you have any chest pain with breathing?
do you have any chest pain after a bout of coughing or after a fall
what is the purpose of visual inspection during the physical assessment of the thorax (chest)?
look for symmetry, deformities, or signs of respiratory distress (e.g., use of accessory muscles, abnormal breathing patterns, etc)
what is the purpose of visual palpation during the physical assessment of the thorax (chest)?
feel for any tenderness, lumps, or abnormalities in the chest wall (e.g., rib fractures, muscle tenderness, etc)
what is the purpose of visual percussion during the physical assessment of the thorax (chest)?
help access the density of underlying tissues by using finger or instrument to produce sounds that would help identify the density (hollow = filled with air, thud/dull = fluid or solid mass or collapsed lung, booming = excess air, drum-like = large area of air)
what is the purpose of auscultation during the physical assessment of the thorax (chest)?
to listen to breathing sounds with a stethoscope to evaluate lung function and detect abnormalities like wheezes, crackles, or absence of breathing sounds (which can indicate pneumothorax or consolidation) and also heart sounds (e.g., murmur, irregular rhythm, etc)
what should the student nurse note when visually inspecting the posterior chest?
note shape and configuration of chest wall
note the position the person takes to breath
assess skin color and conditions
note any lesions; inquire about changes
what should the student nurse note when palpating the posterior chest
symmetric chest expansion
tactile or vocal fremitus (using hand to feel for vibration while patient talk/repeating phrases like “99” or “blue moon”) —> look for areas of increased or decreased lung capacity
how can the student nurse perform percussion for lung assessment?
using straight fingers of one hand spread out and use two finger of the other hand to tap on the intermediate phalange of the middle finger of the spread out hand on the patient skin
start at the apices - the topmost part of the lungs
work downward
after finished with the entire lung area (front = 6th rib, back = 10th rib) work across the tops of both shoulders
resonance
normal, low-pitched, clear, and hollow sound whe assessment healthy lung tissue
true or false: resonance varies slightly between individual during percussion (if so, how?)
thin people: resonance might be more pronounce as there are less tissue between the chest wall and lungs (less thick)
obese or muscular individual: resonance may be less obvious and may sound duller due to thicker chest wall
what should the student nurse look for when auscultating the anterior and posterior chest?
set of noise as from the passage of air through tracheobronchial trees audible through the chest wall
use flat diaphragm of stethoscope and listen to at least one full respiration in each location
perform bilateral comparison of each lung sound
what are the types of breath sounds heard normally in adults and older child?
bronchial (AKA trchael or tubular) = loud and high-pitched with hollow quality
bronchovesicular = medium-pitched and moderately loud
vesicular = soft, low-pitched, and gentle rustling (e.g., winds blowing through trees)
adventitious lung sounds and the types
abnormal lung sounds
crackles (rales): short, popping sounds commonly heard in pt with pneumonia or heart failures
wheezes (rhonchi): high-pitched whistling sounds or low-pitched snoring sounds common heard in pt with narrowed airways (e.g., asthma, bronchitis, etc)
atelectatic crackles: temporary crackling sounds - fine crackles that are not caused by a disease and go away after the person take a few deep breath
true or false: hearing enhanced voice sounds that is supposed to be soft, muffled, and indistinct could be a possibly indication of increased lung density
true
review some examples of enhanced voice sounds that is indicative of increased lung density…
bronchophony: voice sounds become louder and clearer when saying “99”
egophony: the sound of “eee” is heard as “ay”
whispered pectoriloquy: whispered sounds become unusually loud and clear
what should the student nurse take note of when inspecting the anterior chest?
note shape and configuration of chest wall
note patient’s facial expression
assess level of consciousness (examin for oxygenation and possible respiratory distress) - early signs of hypoxia can be restless/confusion/anxiety and alert but anxious can suggest mild to moderate distress, etc
note skin color and condition
assess quality of respirations (note respiratory effort, observe for symmetry, determine if accessory muscle are being used)
what should the student nurse look for when palpating the anterior chest?
symmetric chest expansion
—> it is easier to detect any limitation in thoracic expansion as there are greater range of motion with breathing from the anterior chest
access tactile (vocal fremitus)
—> compare vibrations from one side to other as the person repeats “99”
note any tenderness or lumps
note skin mobility, turgor, temperature, and moisture
true or false: when percussing the anterior chest of a female patient, we can percuss over the female breast tissue
false: doing this would produce a dull note, of which, shifting the breast tissue over slightly using edge of the stationary hand would be most efficient
true or false: percussing over the heart region normally produce a dull sound and is not indicative of any lung pathology
true
true or false: percussing over the upper border of the liver in the right hemithorax located in the 5th intercostal space in the right midclavicular line will produce a dull sound
true
true or false: percussing over the left hemithorax space will produce a tympanic quality of sounds due to the presence of the gastric space
true
forced expiration time
the number of seconds it takes to exhale from total lung capacity to residual volume
why do the student nurse measure forced expiration time?
to screen for airway obstruction and pulmonary functions
spirometer
a device that help to measure lung health by measuring how much air can the patient lung hold and how much they can expel and retain
6-minute walk test (6 MWT)
clinical measure of functional status in aging adults
cardiopulmonary functions
disease progression/treatment efficiency
pre and post surgical assessment
set baseline and rehabilitation goal
what are the respiratory changes seen in pregnant women?
thoracic cage may appear wider
deeper respirations
tidal volume increased by 40%
faster breathing rate
what is the respiratory changes seen in aging adults?
increased anteroposterior (AP) diameter (wider upper chest) and kyphosis (outward curve of the thoracic spine)
chest expansion may be somewhat decreased but remains symmetric
tend to tire easily during auscultation requiring deep mouth breathing
decreasing lung capacity
decreased gas exchange
chest wall stiffen
increased risk for respiratory infections
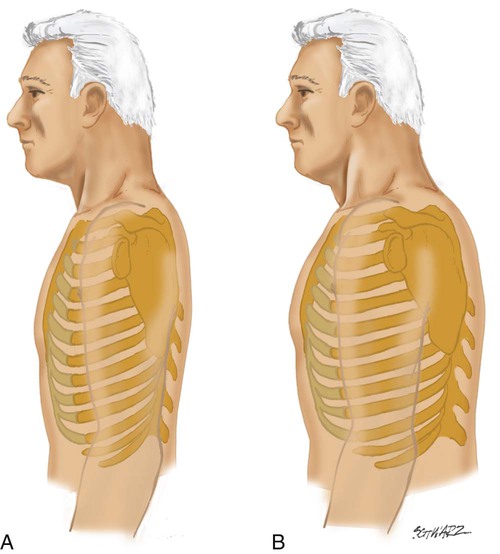
how can the student nurse adapt respiratory assessment for an acutely ill person?
use of second examiner to assist with positional changes
use of rolling technique if solo examiner but can interfere with bilateral comparison