PCE - Multisystems
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
134 Terms
AIDS results in..
loss of immune system fxn
decreased CD4+ helper T-cells (200-500/ml; norm is 800-1200/ml)
Guillian-Barre Syndrome (GBS) general presentation
Begins in LE and ascends bilaterally:
- weakness
- ataxia
- bilateral paresthesia progress to paralysis
- stocking and glove pattern of loss (aka distal limb affected)
- absent DTR
GBS causes problems with:
respiration
talking
swallowing
bowel and bladder fxn
GBS risk factors
- possibly autoimmune
- association with immunization
- frequently preceded by mild respiratory or intestinal infection
immunoglobins
bind with specific antigens to aid in their destruction
Dx for lupus
+ve serum "antinuclear antibodies (ANA)" symmetric arthritis
lupus S&S
butterfly (malar) rash
localized erythema
localized edema, joint effusion
alopecia
photosensitivity
mucosul ulcers
raynaud's
Haemophilia
body unable to control blood clotting/coagulation
Haemophilia - if mom doesn't have it but father has it what will the son/daughter have?
son - won't have it (dad gives y)
daughter - obligated carrier (dad gives x)
joint bleed symptoms
if not treated leads to?
jt tight + no pain -->
jt tight + pain, no bleed -->
swollen + hot to touch, hard to move -->
*all ROM lost + severe pain -->
bleeding slows in few days (jt full of blood)
leads to arthritis
Normal Sodium Values?
High vs low
135-145 mmol/L
Role: extracellular excitation aka flud shift
Hypoatremia (too much water retention): postural hypotension, syncope, weight loss, loss skin elasticity, confuse, muscle spasm, seizure
Hyperatremia (dehydrated): edema, pulmonary edema, hypertension, effusions rmb salty food --> puffy
Normal potassium levels
High vs low
3.4-5.2 mmol/L
Role: intracellular excitation
Hypokalemia (too little excitation): weak, nausea/vomit, faint, palpitation, hypotonia, arrythmia
Hyperkalemia (too much exciation): cardiac issues
Normal calcium levels
High vs low
2.1-2.6 mmol/L (8.4-10.2 mEqL)
high calcium in blood = decrease muscle contraction
Hypocalcemia: vit D deficient, increased urine excretion (too much calcium peed out), respiratory acidosis, prolonged QT on ECG
Hypercalcemia: stones, groans, bones (muscle weak, bone loss), thrones, psychiatric over tones (decreased cognition), shortened QT
^*they all rhyme! think how high calcium in blood = low in bones = bone loss)
Normal magnesium levels
High vs low
0.7-1.0 mmol/L (1.6-24 mEqL)
Role: relaxes muscles
Hypomagnesemia: muscle cramp, hyperactive reflex, tremor, overall weakness
Hypermagnesemia: nausea/vomit, muscle weakness
Glucose: fasting, impaired glucose tolerance, dx of DM
fasting 3-5.5 mmol/L
5.5-7.8 impaired glucose tolerance
>7.8 diagnostic of diabetes mellitus
international normalized ratio (INR) values
High vs low
0.89-1.3 (2-3 for pt on warfarin)
low = increase risk of thrombosis/clotting
high = excessive bleeding tendencies
RBC levels
High vs low
male: 4.5-6.5
female: 3.5-5.8
low = anemia, leukemia, hemorrhage
high = polycythemia, decreased plasma volume (=increase concentration of RBC)
erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and implications of fast rate
measures the rate erythrocytes settle to the bottom of a test tube
fast rate = inflammation
normally it settles quite slowly
Main feature of RA
Synovitis (symmetrical pattern)
RA Criteria (8)
- normal stiffness >1 hr (6 wks)
- arthritis of >3 jts (6 wks)
- arthritis of hand jts
- symmetric arthritis (6 wks)
- rheumatoid nodules
- serum rheumatoid factor
- radiographic changes
- abnormal antibody HLA-DR4 (80% of those w/ RA)
think 3-arthritis, 2-rheumatoid, RAS
Questions to ask for rheumatic diseases (4)
1. Red flags: #, septic arthritis, malignancy, central cord, muscle wkness, paresthesia
2. inflammation in jt or around jt
3. focal (<3 jt) or widespread (>3 jt)
4. acute (<6 wks) or chronic (>6 wks)
RA acute phase rx
energy conservation, ice, splints, gentle ROM
NO STRETCHING (may stretch the synovial membrane & cause irreversible damage)
What are the types of surgeries for RA?
4 R'S
• remove (MTP resection)
• re-align (tendon rupture)
• rest (arthrodesis)
• replace (arthroplasty)
Steps of joint count ax
1. joint effusion (2/4 finger technique)
2. joint line tenderness
3. stress pain
indicator of RA disease activity of RA --> STOP
MTP subluxation
synovitis, displacement of flexors, unopposed extensors pull proximal phalanx into hyperextn, metatarsal head prolapse and get dislocation and lateral drift of toes
Swan neck deformity
Cause? Test?
hyperextension of PIP joint and flexion of DIP joint
caused by contracture of intrinsic muscles with dorsal subluxation of lateral extensor tendons
test --> bunnel litter's
Bunnel-Littler test
PIP flexion ROM increase w/ MCP jt flex = instrinsic muscles restriction
no increase in flex = capsular restriction
Boutonniere deformity
cause?
flexion of PIP joint and hyperextension of DIP joint
caused by rupture of central tendinous slip of extensor hood
Ulnar Drift Deformity
test?
volar subluxation/laxity of MCP in radial collateral ligaments
radial collateral ligament test
radial collateral ligament test
passive flex MCP to 90 degrees, apply ulnar force to feel laxity (+ is >45 degrees deviation)
Most common hand deformity
ulnar drift
duck-bill thumb
test?
rx?
MCP at 0, IP at 90 (90/90 position)
grind and crank test
- grind = axial load + MC rot
- crank = axial load + flex/extn
rx: web space massage/stretch, opposition and abduction exercises
Distal Radial Ulnar Joint (DRUJ) instability
synovitis at joint, stretches ulnar carpal ligaments, ulnar head will sublux dorsally, ECU is displaced and more becomes a flexor tendon
TEST: ballottement test
Ballottement test
aka piano key sign - stabilize distal radius and move distal ulnar up/down
Dupuytren's contracture
Thickening and shrinking of the fascia of the palm with fingers being drawn into a flexed position
MCP's + PIP's of 4th and 5th digit
Ape hand
how is it formed?
Thenar muscle wasting with first digit moving dorsally until in line with second (can't abduct thumb)
Results from median nerve dysfunction
List the RA deformities of the feet
hallux valgus
MTP subluxation
claw toe
hammer toe
mallet toe
List the RA deformities of the hand
swan neck
boutonniere
ulnar drift deformity
BD thumb or swan neck
DRUJ instability
Mallet finger
Rupture or avulsion of extensor tendon at its insertion into distal phalanx (generally with trauma)
Causes flexion of DIP
Gamekeeper's Thumb (Skier's Thumb)
Sprain/rupture of ulnar collateral ligament of MCP of first digit leading to medial instability
Caused by falls (ie. while skiing when pole increases forces on thumb)
Gout
most affected joint
• genetic disorder of purine metabolism
• increased serum uric acid (hyperuricemia)
• Acid ▲ to crystals and deposits into joints
• Most affected JOINTS: KNEE, GREAT TOE
Osteoarthritis
release of enzymes + abnormal biomechanical forces = fibrillation + articular cartilage damage
RA rx:
Meds - DMARDS/biologics, methotrexate, NSAIDS/tylenol/cortiosone
Rehab
Lifestyle modification/self mgmt
Surgery
OA dx
x-ray findings 4 features: *jt space, osteophytes, 2subchondral
1. jt space narrowing
2. osteophytosis
3. subchondral cyst
4. subchondral sclerosis
(Grading: Kellgren - Lawrence System (0-4)
4 QUESTIONS
- Pain most days of the last month?
- Pain over the last year?
- Worse with activity - stairs (doing down worse), overdoing it
- Relieved with rest - may have 'gelling' after inactivity period
OA Rx
Weight loss (1 lb loss = 4 lb decrease knee jt stress)
Exercise: 30 min mod aerobic (10 min bouts), LE resistance
Protective aids
Medications: aceteminophen (non-inflammation)
Electromodalites: TENS
dactylitis
sausage fingers d/t swelling
Enthesitis
Inflammation of tissue at muscle insertion on bone
usually in heels and back
Meds for psoriatic arthritis
acetaminophen, NSAIDs, DMARDs, corticosteroids, biological response modifiers
DMARDS is used for what conditions?
IA/RA, JIA, psoriatic arthritis, lupus (NOT AS)
IA = inflammatory arthritis
JIA = juvenile idiopathic arthritis
Biological response modifiers is used for what conditions?
RA, axial spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis
Grading: Kellgren - Lawrence System (0-4) for OA
Gr 0 - no features
Gr 1 - minute osteophyte
Gr 2 (minimal; OA Dx) - definite osteophyte; unimpaired jt. space;
Gr 3 (moderate) - moderate diminution of jt space; Gr 4 (severe) - jt space greatly impaired, sclerosis of subchondral bone
ulcerative colitis
same as crohn's but no skipped lesions, only affects colon, significant bleeding/anemia
Crohn's disease - s/s, rx
affects entire GI tract from mouth-anus, small and large intestines
can have skipped lesions
ulcers, fissure (narrow tear from spincter to canal), fistulas (tract from anal canal --> hole in skin near anus), alterations in digestion and absorption --> malnutrition
rx: antinflammatory drug for bowel, prednisone (immunosupressant), antibiotics, biologic therapy
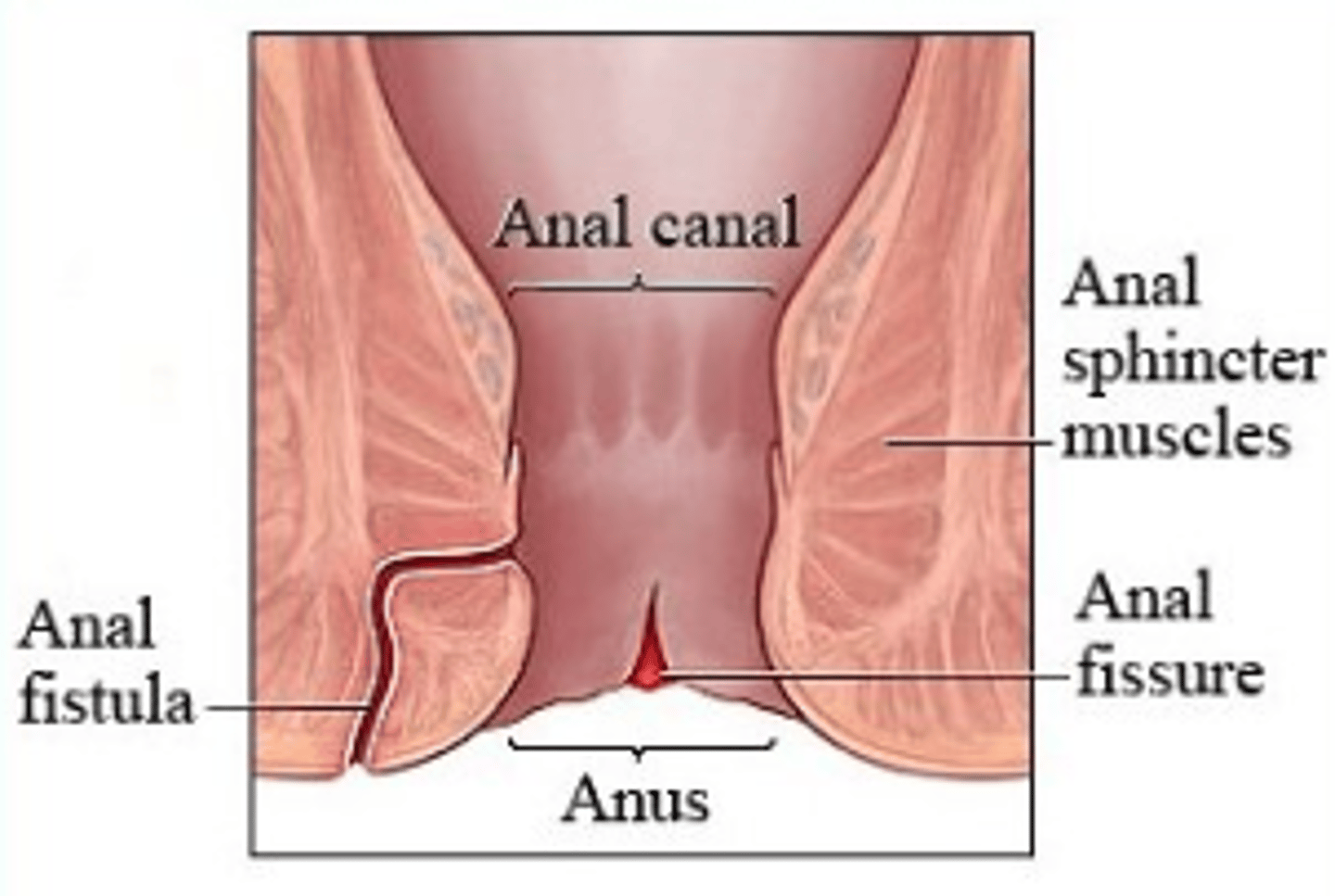
Reactive arthritis
triggered by infection (possibly STI) in bowel/GI tract
dx for ankylosing spondylitis
HLA-B27
ankylosing spondylitis
a form of rheumatoid arthritis that primarily causes inflammation of the joints between the vertebrae
stiffness/fusing of spine d/t inflammation
ankylosing spondylitis onset?
before 40 disease of young adults
M>F
ankylosing spondylitis features
Sacroilitis HALLMARK SIGN
Enthesitis - common sites: spine, hip, peripheral regions
Synovitis - peripheral jts usually (shoulder, hip, knee, ankles)
lungs - apical fibrosis, restrictive lung disease, avoid smoking
heart (inflammation), eyes, bowels
AS Diagnostic Criteria (3)
A diagnosis is made if radiologic criterion of sacroiliitis grade 2 bilaterally or grade 3-4 unilaterally is present with at least one clinical criterion:
- Low back pain and stiffness for >3months that improves with exercise, but is not relieved with rest
- Limitation of motion of L-spine in both sagittal and frontal planes
- Limitation of chest expansion relative to normal values correlated for age and sex
Typical AS posture
HFP, thoracic kyphosis, flattening of anterior chest wall, protrusion of abdomen, flattening
of lumbar lordosis, slight hip flex
Criteria for Inflammatory Back Pain (IBP)
If back pain > 3 months, and 4/5 of below:
- Improvement with exercise
- No improvement with rest
- Insidious onset, age <40 years at onset
- Pain at night
AS breathing mechanics
decreased chest expansion
diaphragmatic breathing pattern
decreased vital capacity
AS physical assessment
posture (tragus to wall), lateral trunk flexion, trunk flexion (modified Schober's), trunk extension
(Smythe test), trunk rotation, chest expansion, cervical mobility, muscle length and strength, enthesitis sites, peripheral joint scan
smythe test
mark X at PSIS w/ pt bent forward
make 3 consecutive 10cm marks above
measure difference when pt in prone/extn
Modified Shober Test
mark X at PSIS, 5cm below, 10 cm above
measure change from 15cm during flexion
Outcome measures for AS
Bath ankylosing spondylitis functional index (BASFI) - impact on disease on fxn in last week
Bath ankylosing spondylitis disease activity index (BASDAI) - how disease is managed
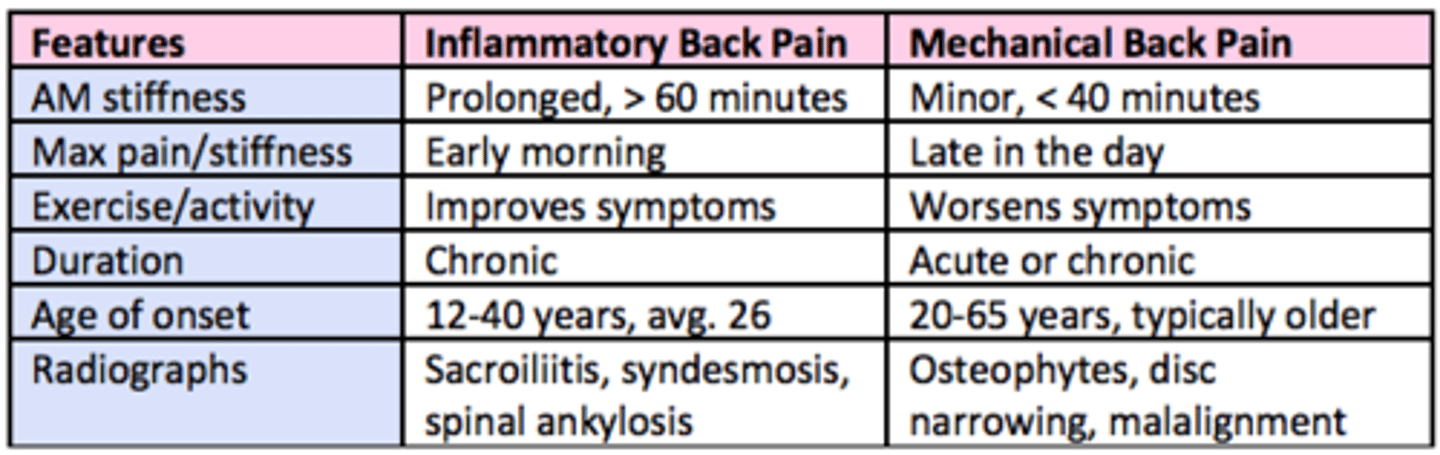
inflammatory vs mechanical back pain
- duration
- age of onset
- max P/stiffness
- type of condition
- x-ray
RA primarily affects
primarily affects MCP + PIP, rheumatoid cachexia (breakdown of muscle fibers), fatigue!!!
OA primarily affects
affects weight bearing joints - hip, spine, DIP, PIP, first CMC, first MTP
Exercise in OA and RA
aerobic, resistance, and stretching/ROM --> pool is great for both
follow ACSM general but based on individual pattern presentation
CI/red flags for exercise in RA/OA
- Increase pain, fatigue or AM stiffness
- sudden pain at joint or joint deformity
- joint becomes red, swollen and hot after doing exercise (within 24 hrs)
- decrease muscle strength and function (local myositis)
- neurological SSx (CV involvement)
- SOB on mild exertion
What are the 3 domains of the ICF?
aka International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF)
- body function & structure (impairment)
- activity (limitation)
- participation (restrictions)
type 1 vs type 2 diabetes
Type 1 (insulin deficiency): juvenile onset, require insulin, decrease circulating insulin
- weight loss, increase urination, dehydration
Type 2 (insulin resistance): adult onset, don't need insulin b/c DOESN'T RESPOND TO IT --> cause insulin resistance in peripheral tissues
- obese, acanthosis nigricans (hyperpigmented skin in axilla, groin, back of neck), HTN
hypoglyecemia
dizzy, nausea, weak, sweating profusely (rules out orthostatic hypotension), fatigue, irritability, confusion, fainting
hyperglycemia
blurred vision, fatigue, thirst, frequent urination, weakness, abnormal breathing, acetone breath
*think of too much sugar making you thirsty, pee alot, blurry vision, etc
long term effects of hyperglycemia
Damage to:
- small blood vessels (retinopathy, diabetic nephropathy)
- large blood vessels: increased cholesterol levels --> vessel wall damage --> atherosclerosis, MI, stroke
- peripheral nerves (diabetic neuropathy)
Normal glucose levels for fasting - normal vs DM
normal: 5.6 mmol/L
diabetes: >7 mmol/L
impaired = <5.6, >7
DM Rx
- regular ex
- talk to MD about insulin levels for ex
- snack before ex
- monitor blood sugar levels pre, during, and post ex
- avoid ex at night --> may sleep and slip in hypoglycemic coma and die!!!!
PT always monitor pt for S&S of hyper/hypoglycemia
A delta fibers vs C fibers
A delta fibers are large and myelinated, these respond to sharp pain., localized, fasting adapting - meds work well
C fibers are small and unmyelinated, these respond to dull pain, diffuse, slow adapting and persistent. - meds don't work
*think D for deanne - super sharp/fast
*think C for calvin - dull and slow
explain conduction of pain
- at spinal cord --> go up lateral spinothalamic tract (pain/temp) --> thalamus --> cortex
-periaqueductal grey (primary control center for descending pain modulation) releases endorphins --> inhibits subs P and glutamate release --> no pain
Explain chronic pain and it's rx
chemical change in brain --> receptors hypersensitive --> allodynia + hyperalgesia --> increase activity in pain pathways
Rx: desensitive area, education, restore normal fxn (meds but not our scope, electrotherapy, cryotherapy, thermotherapy, ex/stretch (reduce pain caused by muscle spasm)
Allodynia
Pain due to a stimulus that does not normally provoke pain
Hyperalgesia
excessive sensitivity to painful stimuli
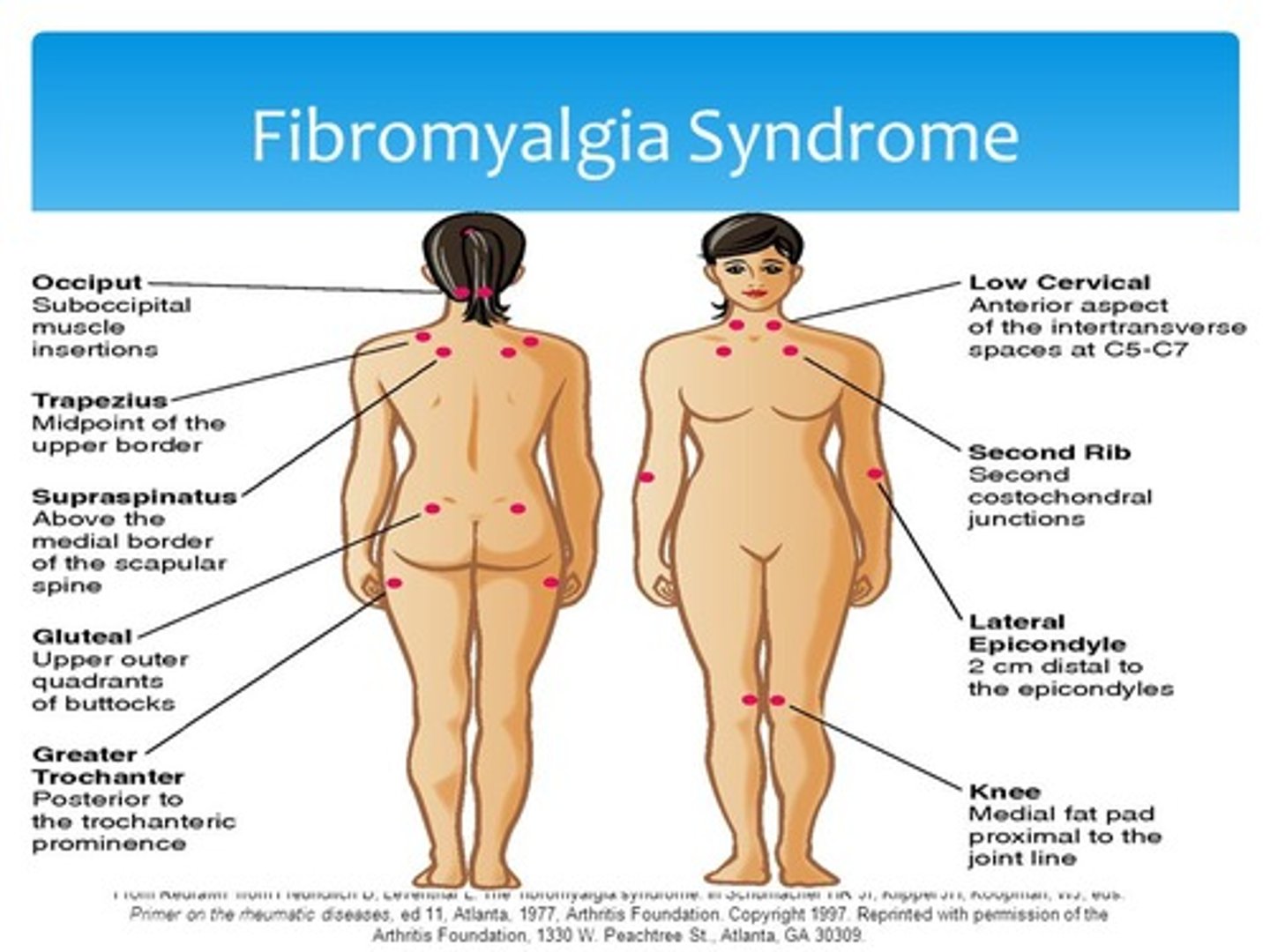
Fibromyalgia
chronic condition with widespread aching and pain in the muscles and fibrous soft tissue
etiology unknown (F>M) *rmb pt from community placement
Dx of fibromyalgia
11/18 of the points are tender
Rx for fibromyalgia
anti-inflammatories, mm relaxants, pain meds, psychological support, nutrition, like heat and not ice
PT rx: energy conservation, aquatic therapy
sepsis
presence of whole body inflammatory state (SIRS) + presence of known or unknown infection
septic shock
severe sepsis but hypoperfusion abnormalities in spite of adequate fluid resuscitation
normal response to infection is local, but then causes widespread vasodilation and vascular permeability
shock
types of shock (4)
- poor distribution of blood at microcirculation level
- decrease tissue perfusion --> cell death
Types:
- hypovolemic aka blood loss
- cardiogenic aka heart damage
- distributive - hypotension and general tissue hypoxia
- obstructive (great vessel of heart)
Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS)
whole body inflammatory state
How to dx SIRS (4)
With: body temp, HR, RR, WBC
Need to have 2+ signs:
- body temp: >38, <36
- HR >90bpm
- RR >20 or PaCO2 <32 (35-45 normal)
- WB count >12000 or <4000
What to be mindful for exercise in obese pt?
mindful of response to heat (used therapeutically) or in response to exercise - excess fat leads to heat insulation --> overheating
postural changes in pregnancy
- increased thoracic kyphosis, lumbar lordosis
- HFP
- increase breast size
- shoulder protraction
- decreased form/force closure - pelvic floor on stretch, lig laxity (hypermobile SI jt)
PT antepartum (before birth) concerns
antepartum bleed, preterm labour (mini contractions), ruptured membrane (slow trick of fluid), incompetent cervix/changes
varicose veins
abnormally swollen, twisted veins with defective valves; most often seen in the legs
heaviness, dull pain/ache in legs with standing/walking
Rx for varicose veins
- posture, positioning elevation, limit cross leg time
- pressure grades stockings/tights/underwear, circulatory ex
Stress vs urge incontinence
Stress - leakage of urine when coughing, sneezing, laughing, lifting, jogging, or doing anything that causes the abdominal pressure transmitted to the bladder pressure to be stronger than the bladder's closure mechanism
Urge - sudden involuntary contraction of the bladder muscle and is associated with a strong desire to urinate and the inability to delay voiding long enough to get to a toilet.
Gestational DM
Rx - what to avoid
Do: 20 min walk post meal
Avoid:
- valsalva (stress PF/ab)
- rapid uncontrolled movements
- positions of inversion (aka downward dog)
- manual therapy (take care with end feels)
- positioning - supine okay for short period of time, prone not well tolerated
- glute strategy for rolling and STS
cystocele
protrusion of the bladder
rectocele
protrusion of the rectum