The Nursing Process (3 & 4)
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
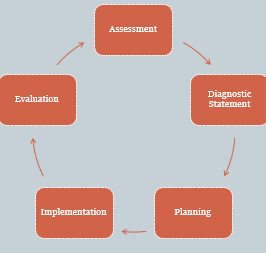
What are the 5 Steps in the nursing process?
Assessment
Diagnostic statement
Planning
Implementation
Evaluation
A good way to remember this by is…?
A.D.P.I.E.
What is it important to remember about the ORDER of the nursing process…?
The order is not linear because assessment never stops.
Nursing Process —> Step 1: Assessment:
It is critical to conduct a comprehensive assessment as this phase will impact the ENTIRE NURSING PROCESS.
_________ ________ of data related to client’s past and current health status or situation.
What is the chief complaint (what would ask)?
Systemic collection
Priority issue, “What brings you here today?”
Nursing Process —> Step 1: Assessment:
An assessment database includes what kinds of data?
What senses would you used when conducting an assessment?
Both subjective and objective
Sight, hearing, smell, and touch. (all except taste)
Nursing Process —> Step 1: Assessment:
What is subjective data?
What is Objective data?
Subjective data is what the patient tells you, a verbal description of health concerns
Objective data are observations or measurements of a client’s health status
Nursing Process —> Step 1: Assessment:
Subjective and Objective data can also be known respectively as what?
Subjective - symptoms
Objective - signs
Nursing Process —> Step 1: Assessment:
Validating Data includes two steps leading to an “educated guess” what are they?
a cue and an Inference
Nursing Process —> Step 1: Assessment:
Validating Data:
What is a cue?
What is an inference? (can only be validated by asking patient more questions)
Cue - information nurse obtains through the use of senses (both objective and subjective)
Inference - nurse’s judgement or interpretation of the cues
Nursing Process —> Step 1: Assessment:
Validating Data:
Give the Cue below as an example, say the inference based on it.
“I have trouble moving my bowels”
Blood pressure is 60/50 and client is lightheaded
Client may be constipated
Client may have orthostatic hypotension
Nursing Process —> Step 1: Assessment:
Sources of Data:
Name the three sources of data.
Primary source
Secondary source
Tertiary source
Nursing Process —> Step 1: Assessment:
Sources of Data:
Names the Primary source(s).
Why would that be the primary source?
The Client
Patient is the expert of their own health
Nursing Process —> Step 1: Assessment:
Sources of Data:
What are the THREE Secondary sources?
Family and significant others
Health care team members
Medical records
Nursing Process —> Step 1: Assessment:
Sources of Data:
What are the TWO Tertiary sources?
Relevant literature (like textbooks and studies)
Nurse’s experience
Nursing Process —> Step 1: Assessment:
What are the FOUR Data Collection Methods?
Client interview
Nursing health history
Physical examination findings
Results of laboratory and diagnostic tests
Nursing Process —> Step 1: Assessment:
What type of data is collected in a Client Interview?
What kinds of questions should be asked?
Subjective data
open and closed ended questions.
Nursing Process —> Step 1: Assessment:
Which of these examples is an open ended question and which is a closed ended?
“Do you have any pain right now?”
“Can you tell me how you’ve been feeling lately?”
Closed ended question
Open ended question
Nursing Process —> Step 1: Assessment:
What is a Nursing Health history?
A collection of data of all health dimensions
Nursing Process —> Step 1: Assessment:
What does a Physical Examination Findings include doing? (what kind of data)
A head to toe examination (objective data)
Nursing Process —> Step 1: Assessment:
The last part of the assessment in the nursing process is…?
Organizing / Cluster Data Collection
Nursing Process —> Step 1: Assessment:
A Data Cluster is a group of…?
group of signs or symptoms we group together in a logical way
Nursing Process —> Step 1: Assessment:
Clustering Data can be done using what two models?
Client Dimensions Mode
Body Systems Model
Nursing Process - Step 1: Assessment:
What DATA is included in the Data Clustering Client Dimensions Model? (6)
Physical
Social
Spiritual
Development
Emotional
Intellectual
Nursing Process - Step 1: Assessment:
What Physical Dimensions are used for data in the Data Clustering Body Systems Model? (8)
Respiratory
Cardiovascular
Circulatory
GI
Neurological
Genital (inc. Urinary)
Integumentary
Reproductive
Nursing Process - Step 2: Diagnostic Statement
Diagnostic Reasoning is…
Used to inform…?
A _______.
Used to inform real-time decision making and communication
It is a process
Nursing Process - Step 2: Diagnostic Statement
Diagnostic Reasoning is…
What does it result in?
Whom does it inform?
Involves _________.
Results in diagnostic statements
Informs appropriate nursing intervention (determines action!)
involves reflection
Nursing Process - Step 2: Diagnostic Statement
What framework is used as a tool to support diagnostic reasoning?
How many parts does it consist of?
The R.E.D. Framework
consists of two or three parts
Nursing Process - Step 2: Diagnostic Statement
What are the three parts to the RED framework?
R - human Response
E - Etiology
D - Defining characteristics
Nursing Process - Step 2: Diagnostic Statement
Based on the R.E.D. Framework what does R stand for and what does it mean?
What phrase is used following listing your R?
human Response - This is the what? What is the patient’s problem, risk, or strength
“related to”
Nursing Process - Step 2: Diagnostic Statement
Based on the R.E.D. Framework what does E stand for and what does it mean?
What phrase is used following listing your E?
Etiology - Answers the why? Why is this response occurring and attributing factors.
“as evidence by”
Nursing Process - Step 2: Diagnostic Statement
Based on the R.E.D. Framework what does D stand for and what does it mean?
What is D this proof of?
Defining Characteristics - subjective and objective data
proof of the human response
Nursing Process - Step 2: Diagnostic Statement
Using RED Framework, provide a diagnostic statement for the following scenario:
A student comes in saying he has been having frequent headaches and is crying each day. He is very stressed, he also mentions midterms are around the corner, stating he is studying a lot late into the night. This is resulting in the student only getting 5 hours of sleep each night.
Stress related to increased school workload as evidence by sleeping 5 hours per night, frequent headaches, and crying each day.
Nursing Process - Step 2: Diagnostic Statement
Using the RED framework there are THREE types of diagnostic statements that can be made. What are they?
Three-part statement - (Actual Statement)
Two-part statement - (Risk for Statement)
One-part statement - (Wellness)
Nursing Process - Step 2: Diagnostic Statement
Using the RED framework there are THREE types of diagnostic statements that can be made.
Actual (three part)
Risk for (two part)
Wellness (one part)
What parts of R-E-D would each include?
Actual Statement - human response + etiology + defining characteristics
Risk For Statement - human response + etiology
Wellness Statement - ONLY human response
Nursing Process - Step 2: Diagnostic Statement
Using the RED framework there are THREE types of diagnostic statements that can be made. Based on the example below, name the TYPE of diagnostic statement.
“Risk for injury related to lack of awareness of hazards”
Risk For Statement (two-part)
Nursing Process - Step 2: Diagnostic Statement
Using the RED framework there are THREE types of diagnostic statements that can be made. Based on the example below, name the TYPE of diagnostic statement.
“Readiness for enhanced nutrition”
Wellness Response (one-part)
Nursing Process - Step 2: Diagnostic Statement
Using the RED framework there are THREE types of diagnostic statements that can be made. Based on the example below, name the TYPE of diagnostic statement.
“Pain related to inflammation in joints (secondary to osteoarthritis) as evidence by client grimacing when ambulating and client verbalizing, “my joints hurt so much”.
Actual Statement (three-part)
10 Rules for Writing a Diagnostic Statement:
The First rule is to…
State a….?
State a human response, not a clients need
10 Rules for Writing a Diagnostic Statement:
The Second rule is to…
Start the diagnostic statement with…?
a human response
10 Rules for Writing a Diagnostic Statement:
The Third rule is to…
Connect…?
Hint: NOT “due to” or “caused by”
Connect human response to etiology using a “related to”
10 Rules for Writing a Diagnostic Statement:
The Fourth rule is to…
Be sure that….?
Be sure that the first two parts aren’t restatements of each other
10 Rules for Writing a Diagnostic Statement:
The Fifth rule is to…
Do not mention a…
How ever you can state that is…?
Medical diagnosis in the first two parts
Can state (Secondary to a medical diagnosis)
10 Rules for Writing a Diagnostic Statement:
The Sixth rule is to…
Include all factors in…
Include all factors involved in the etiology of human response
10 Rules for Writing a Diagnostic Statement:
The Seventh rule is to…
Select an _______ that can be changed by…?
Select an etiology that can be changed by a nursing intervention
10 Rules for Writing a Diagnostic Statement:
The Eighth rule is to…
Avoid judging the….
Avoid judging the client as bad in any part of the diagnostic
10 Rules for Writing a Diagnostic Statement:
The Ninth rule is to…
Avoid suggesting that some member…
Avoid suggesting that some member of the healthcare team is not doing their job.
10 Rules for Writing a Diagnostic Statement:
The Tenth rule is to…
Put the CUES that led to diagnosis in…
Hint: /or proof of human response.
the third part (defining characteristics)
Recognizing incorrectly stated nursing diagnostic statements:
Example:
Impaired comfort; acute pain related to gastritis as evidence by the client saying, “my stomach hurts”
Which rule was broken and why?
Rule 5 - do not mention medical diagnosis in either of the first two parts (gastritis in etiology)
Recognizing incorrectly stated nursing diagnostic statements:
Example:
Self-care deficit: hygiene related to laziness as evidence by strong foot odor.
Which rule was broken and why?
Rule 8 - avoid judging the client as bad in any part of the diagnostic statement (i.e. laziness)
Recognizing incorrectly stated nursing diagnostic statements:
Example:
Risk for injury related to insufficient nurse-patient ratio as evidence by 1 nurse for 20 patients.
Which rule was broken and why?
Rule 9 - avoid suggesting that some member of the healthcare team is not doing their job. (i.e.1 nurse for 20 patients)
Nursing Process - Step 2: Diagnostic Statement
Diagnostic Statements for Year one nursing students may include…
Anxiety, dehydration, constipation, malnutrition, fatigue, insomnia, Pain (be specific - include location)
Risk for infection, risk for falls, risk for disease
Optimal self-care, effective stress management, readiness for learning
Based on the involving factors name which types of statement it would be included in.
Actual Statement - Three part
Risk for Statement - Two part
Wellness Statement - One part
Nursing Process - Step 3: Planning
Is the overarching function of the Planning step in the nursing process?
What is the product that is produce from the Planning step?
To develop goals to address the diagnostic statement
product of the planning phase is a nursing care plan
Nursing Process - Step 3: Planning
There are THREE components of Planning, what are they based on the hint below…?
What is prioritized?
What is established?
What is selected to achieve the goals and expected outcomes?
Nursing diagnostic statements
Client-centered goals and expected outcomes
Nursing interventions
Nursing Process - Step 3: Planning
There is also THREE different types of priorities in the Planning Phase, what are they?
High Priority
Intermediate Priority
Low Priority
Nursing Process - Step 3: Planning
Based on the priorities in the planning phase…
High Priority - (Impaired gas exchange)
Intermediate Priority - (risk for infection)
Low Priority - (client wants to improve sleep habits)
Give a brief definition of each// how they’re established.
High - diagnosis that are life-threatening or essential for survival and safety
Intermediate - diagnosis involve the nonemergency, non-life-threatening needs of patient
Low - diagnosis for patients long term health care needs, not always related to illness
What is a Client Centered Short Term Goal?
An objective behavior or response the client is expected to achieve in less than a week or as a stepping stone towards a long-term goal.
When is a Client Centered Short Term goal most often used?
Immediate client needs (acute care) - (ex. shortness of breath)
What is a Client Centered Long Term Goal?
An objective behavior or response that the client is expected to achieve over a longer period, like several days, weeks or months
When is a Client Centered Long Term Goal most often used?
Used most often for clients at home or in long term care (ex. lose weight)
All Goals must be S.M.A.R.T. meaning…
S - specific
M - measurable
A - attainable
R - relevant
T- time-limited
Example of a SMART goal…
Client will be able to verbalize three stress management techniques by the end of the 30-minute teaching session
Is it SMART worthy bro?
yeeeee
Nursing Process - Step 3: Planning
When are nursing interventions identified in the nursing process?
Identified during the planning phase of the nursing process
Nursing Process - Step 3: Planning
Nursing interventions is also considered to be?
what are they based on…?
Overall nursing care
based on clients needs (goals)
Nursing Process - Step 3: Planning
Nursing Interventions outline…?…that the nurse performs to achieve the goals and expected outcomes of the client.
What should nursing interventions be based on?
outlines actions / activities
must be evidence based (research findings)
What step in the nursing process initiates or completes planned actions or nursing interventions?
Implementation
Nursing Process - Step 4: Implementation:
The implementation phase of the nursing process involves:
__________ the client.
Determining the nurse’s need for…?
Reassessing the client
assistance
Nursing Process - Step 4: Implementation:
Within the implementation phase obviously involves implementing the nursing interventions. But, it doesn’t stop there, nurses then need to…
__________ the delegated care
And, ___________ nursing activities
Supervising the delegated care
Documenting nursing activities
Nursing Process - Step 4: Implementation:
Implementation of Nursing Interventions involves what TWO types of Interventions techniques?
Direct care interventions
Indirect care interventions
Nursing Process - Step 4: Implementation:
What is a Direct Care Intervention? (examples)
Treatments that are performed through direct interactions with patients. (ex. changing positions in bed, CPR, teaching)
Nursing Process - Step 4: Implementation:
What is Indirect Care Interventions? (examples)
Treatment or care that is performed away from patient but on their behalf. (ex. documentation, delegation between team members, interdisciplinary collaboration)
Nursing Process - Step 4: Implementation:
There are also different TYPES of nursing interventions, what are the three?
Independent Intervention
Dependent Interventions
Collaborative Interventions
Nursing Process - Step 4: Implementation:
What is an Independent Intervention initiated by?…
…Meaning it doesn’t require…?
Initiated by the nurse
does not require directions or order from other healthcare providers.
Nursing Process - Step 4: Implementation:
Independent Intervention def: The nurse acts independently for the care based on…?
Example of independent intervention?
evidence that is based on findings and critical thinking
Teaching side effects of medications
Nursing Process - Step 4: Implementation:
Dependent intervention is initiated by?
… to give?
Physicians or NP initiated
to give orders or directions
Nursing Process - Step 4: Implementation:
What is Direct Intervention aimed to do?
give an example of direct intervention.
aimed at treating or managing a medical diagnosis
administering medication, dressing change
Nursing Process - Step 4: Implementation:
What is Collaborative Intervention initiated by?
This means it’s mostly prevalent in…?
Interdependent (collaboration between health care professionals)
Therapies or care
Nursing Process - Step 4: Implementation:
Collaborative Intervention requires…?
combined knowledge of skills and expertise of numerous healthcare providers
Nursing Process - Step 4: Implementation:
Selection of Nursing Interventions has SIX factors involved that every nurse should consider. What are they?
Nursing Diagnostic Statements
Goals and Expected Outcomes
Evidence base
Feasibility
Acceptability
Capability (competence of a nurse)
Nursing Process - Step 4: Implementation:
Preparatory activities for Implementation include:
Reassessing the client
Reviewing and revising the existing nurse care plan
Organizing resources and care delivery
Equipment, Personnel, Environment, Client
Anticipating and preventing complications
Implementation skills
Cognitive, Interpersonal, and Psychomotor
What do these preparatory activities address?
Addresses the basic needs before intervention
Nursing Process - Step 4: Implementation:
During the ACTUAL implementation of nursing interventions…
Nursing care activities are delivered to…?
In most clinical settings ________ ___________ are necessary to achieve selected outcomes.
meet client centered goals and outcomes
multiple interventions
Nursing Process - Step 4: Implementation:
What are 7 important skills that nurses can use during the implementation phase?
Care coordination
Good time management
Organization
Appropriate use of resources
Priority setting
Health teaching
Discharge planning
Nursing Process - Step 4: Implementation:
One of the seven important skills during the implementation phase is “Discharge Planning” - what does this mean?
Where does it begin?
a discharge plan is used when transitioning a patient from one facility to another
starts in assessment phase of nursing process
Nursing Process - Step 5: Evaluation
Evaluation is the final step of the nursing process that determines…?
determines the effectiveness of nursing care
Nursing Process - Step 5: Evaluation
The evaluation phase involves 2 Components, what are they?
Examination of client condition/situation
Judgement regarding whether change has occurred
Nursing Process - Step 5: Evaluation
In the “Judgement regarding whether a change has occurred” component of the evaluation phase, what does it mean by “change”?
Did the patient meet the goal, partially meet it, or not meet it
Nursing Process - Step 5: Evaluation
Who is the main source of data in the evaluation process?
What is important to remember about the evaluation phase during the nursing process?
The client
Evaluation happens during the entire process
What are the Five Elements of the Evaluation Process?
Identifying evaluation criteria and standards
Collecting evaluation data
interpreting and summarizing findings
Documenting findings and clinical judgement
Terminating, continuing, or revising the nursing care plan
What is an important component of each step of the nursing process?
Critical thinking