Lecture 12: Extremophiles and Bacterial Growth Conditions
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Extremophiles
Organisms thriving in extreme environmental conditions.
Growth Rate
Slope of line during exponential growth phase.
Growth Yield
Height of line in stationary growth phase.
Mesophiles
Bacteria thriving at 37°C, optimal for growth.
Thermophiles
Bacteria with optimal growth between 50°C-80°C.
- proteins fold properly at high temp
-membranes with long, straight-chain fatty acids (low fluidity)
Hyperthermophiles
Bacteria thriving at temperatures 80°C-113°C.
"Hypersaline"
- Extremely cold
Psychrophiles
Bacteria with optimal growth at 4°C-10°C.
- low temp
- membrane fatty acids have extensive unsaturation or branching (more fluid)
Obligate Aerobe
organism that requires a constant supply of oxygen in order to live
faculative halophiles
Organisms that do not require high salt concentrations but can tolerate salt concentrations at 2 percent
Aerotolarant anaerobes
can tolerate the presence of oxygen but can't use it for growth
strict anaerobes
die in the least bit of oxygen
Microaerophiles
Aerobes that require Oxygen levels from 2-10% and have a limited ability to detoxify Hydrogen Peroxide and Superoxide Radicals
Halophiles
Organisms thriving in high salt concentrations.
- Ponds > 2m NaCl
Red color due to Archaea Halobacterium are extreme halophile
Osmotic Stress
Pressure from solute concentration affecting cell function.
Desiccation
Extreme dryness limits bacterial growth and function.
- water squeezes out of the cell
- Atacama desert Chile
-Low water concentration limits protein function and causes chromosomes to shear into fragments (lethal)
Radiation
Ultraviolet and ionizing radiation damage DNA.
- powerful mutagen- forms thymine-thymine dimmers in DNA
-ionizes most common molecules in the cell (water) to attack the largest molecule
Deinococcus radiodurans
• isolated from an irradiated can of meat
• extremely radiation-resistant
• tolerance - 5,000,000 rad
• Human tolerance - 100 rad
• multiple chromosomes/cell (4-10)
• nucleoid compacted into a torus
Deinococcus is also very desiccation resistant. Why?
1. Can quickly and efficiently repair DNA
2. Has proteins that acts as antioxidants that provide a shield
3. Has a tightly packed genome structure that protects DNA from damage
Pressure
High pressure conditions affecting DNA replication.
Superoxide Dismutase (SodA)
enzyme that detoxifies radicals
Catalase (KatF)
Enzyme converting hydrogen peroxide to water.
Deinococcus radiodurans
Radiation-resistant bacterium with multiple chromosomes.
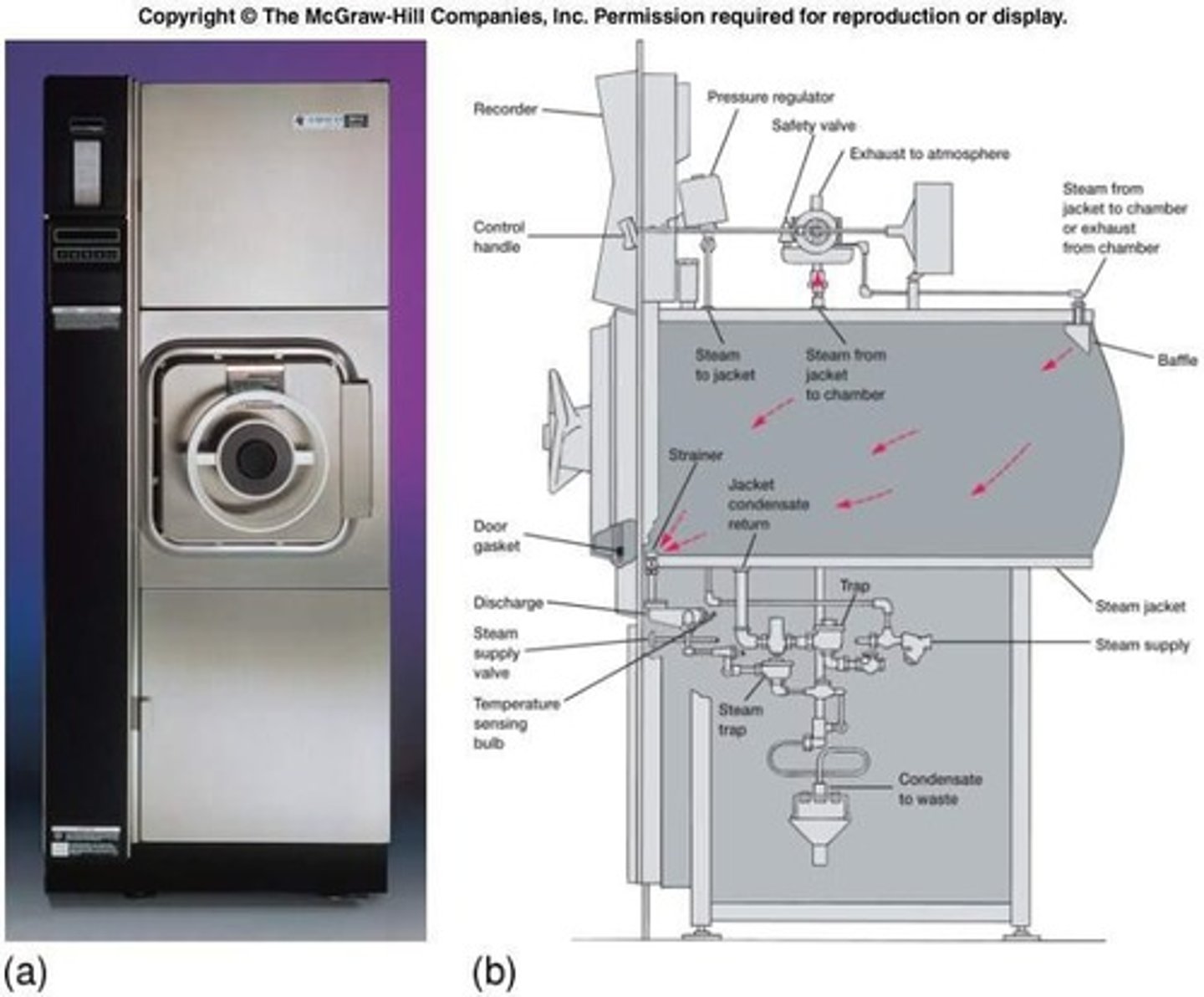
Autoclave
Device using high pressure and temperature for sterilization for endospores
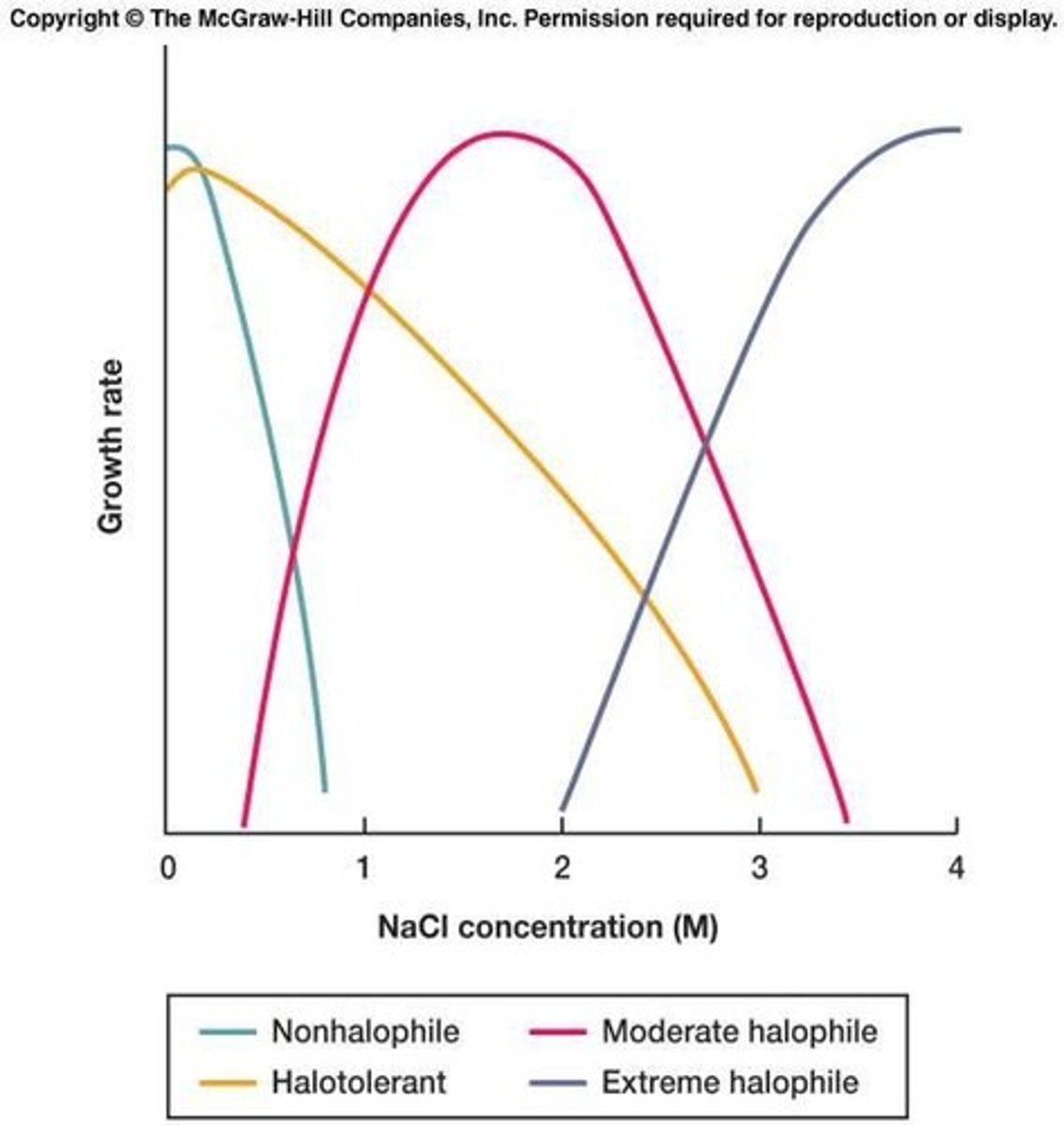
Halotolerance Curves
Graphs showing bacterial growth in varying salt concentrations.
- similar to desiccation
- Jellies (sugar), Brines (salt), curing (salt).
Endospores
Dormant, resistant structures formed by some bacteria.
- need very high heat
Limiting Bacteria growth
1. Rise temp (Cooking/pasteurizing)
-From dsDNA to melted ssDNA
- Damage protein structure
- disrupts membranes
2. Lower temp (fridge)
Nutrient Limitation
Insufficient nutrients hindering bacterial growth.
Thermostable Proteins
Proteins that maintain structure at high temperatures.
Membrane Fluidity
Degree of lipid mobility in cellular membranes.
Thymine Dimers
DNA damage caused by ultraviolet light.
Hydrogen Peroxide
Reactive oxygen species damaging cellular components.
Oxygen Radicals
Reactive molecules generated during aerobic respiration.
Desiccation Resistance
Ability to survive extreme dryness.
Barophiles
Organisms thriving under high pressure conditions.
Antibiotics
Substances targeting bacterial growth without harming humans.
Functional Proteins
Proteins maintaining activity under specific conditions.
Chromosome Melting
Denaturation of DNA at high temperatures.
Cell Wall
Structure providing shape and protection to bacteria.
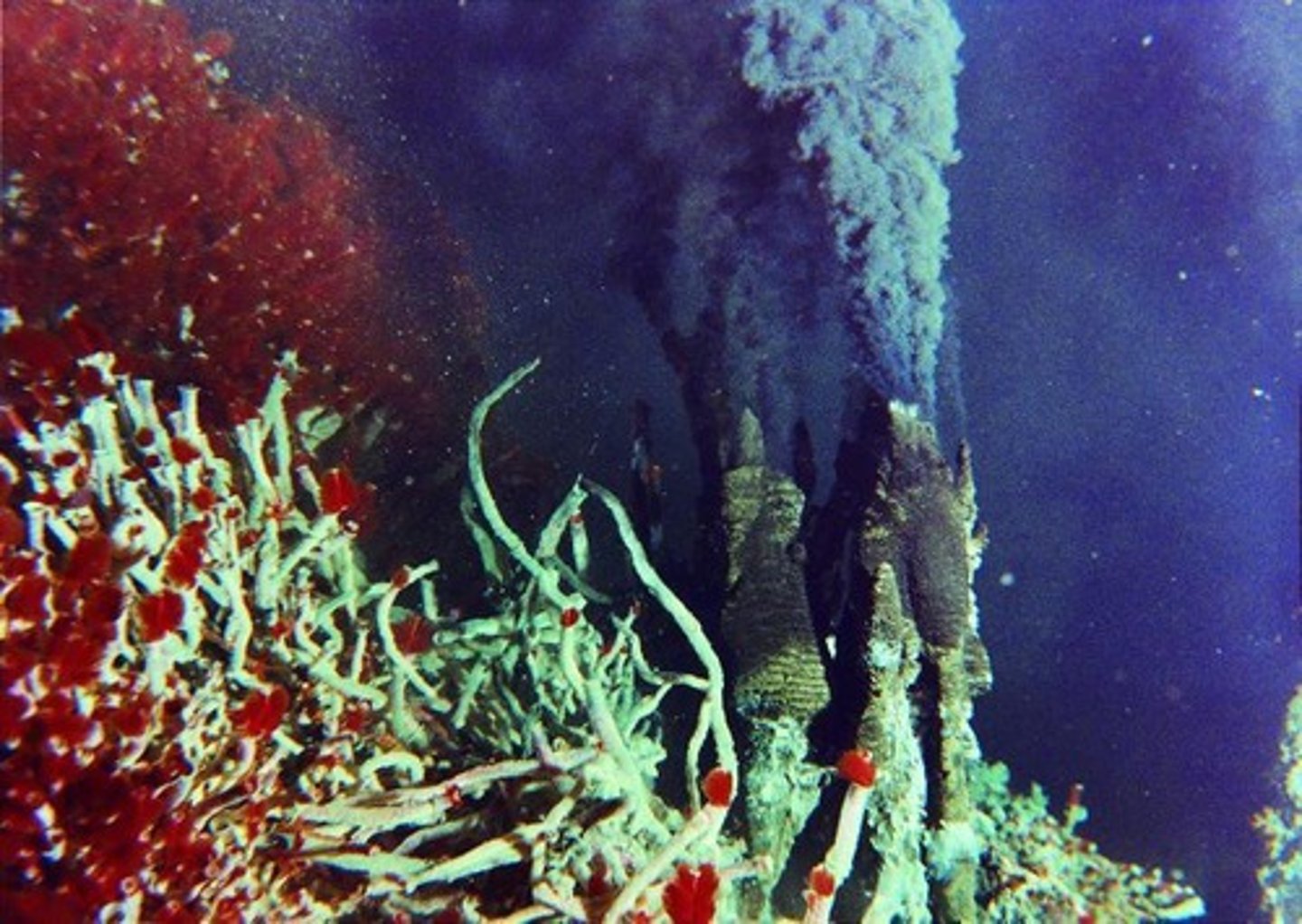
Hydrothermal Vents
Underwater openings supporting unique microbial life.
-life around "black smoker"
- animals feed on microbial biomass growing near the smoker
- steep temp gradient in rock

Microbial Biomass
Total mass of microorganisms in a given area.
Nucleoid
Compact structure of bacterial chromosome.
Oxygen Tolerance
Ability of bacteria to survive in oxygen presence.
Oxygen Damage
- Superoxide (Radical O-) reacts with and damages all macromolecules it encounters
- DNA (largest) common target
- Difficult to repair
- halt DNA replication
GasPak
Anaerobic chamber for growing oxygen-sensitive bacteria.
Psychrophile Adaptations
Membrane adaptations for low-temperature survival.
Halobacterium
Extreme halophile known for red pigmentation.
Sodium Hypochlorite
Chemical compound used as a disinfectant.
Heavy Metals
Toxic elements affecting protein function.
Cold Temp
1. causes the membrane to shatter
2. proteins inflexible leading to denaturation
3. slow metabolism to crawl
Phenolics
Chemical compounds disrupting cellular membranes.
Protein Denaturants
-alcohols (ethanol, isopropanol)
-halogens (iodine)
Poisons (inactivate proteins)
heavy metals (silver, mercury, arsenic)
membrane disruptors
phenolics (Lysol)
detergents (soap)
Antibiotics
Specifically, target structures or reactions required for bacterial but not human growth