CP Biology Midterm Review
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/111
Last updated 7:46 PM on 1/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
1
New cards
Eyepiece
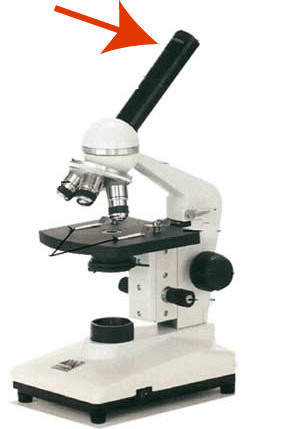
2
New cards
Coarse Adjustment
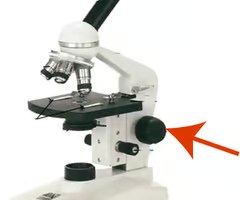
3
New cards
Fine Adjustment
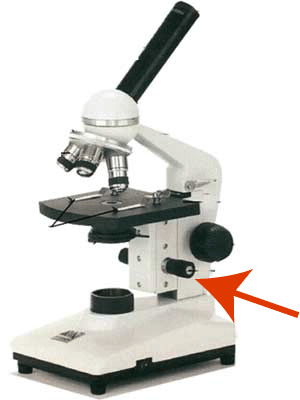
4
New cards
Arm
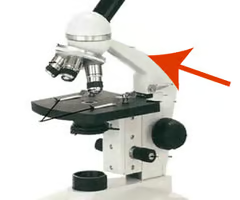
5
New cards
Bodytube

6
New cards
Revolving Nosepiece
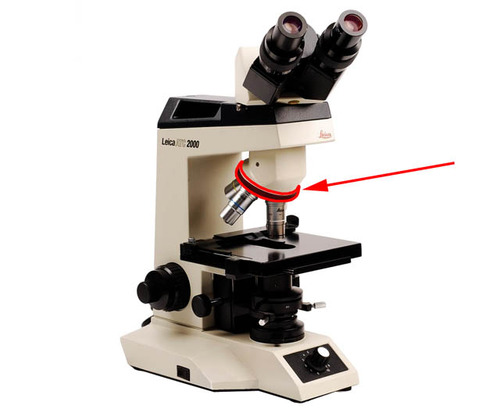
7
New cards
Objective Lenses
Scanning (4x), Low (10x), and High (40x)
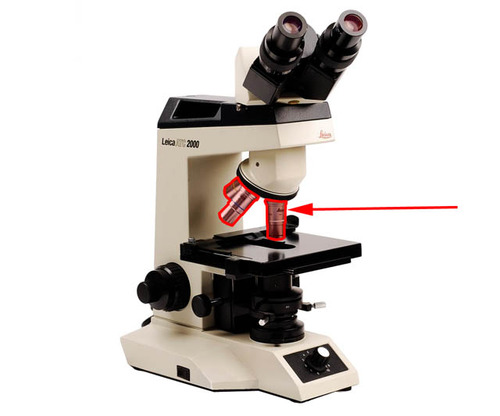
8
New cards
Stage
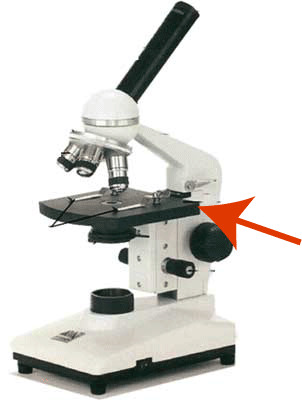
9
New cards
Illuminator

10
New cards
Base

11
New cards
Scientific Method
A logical, systematic approach to the solution of a scientific problem
12
New cards
Organism
Any living thing
13
New cards
Species
Any group of organisms that can interbreed
14
New cards
Variable
A factor that can influence the results of an experiment
15
New cards
Hypothesis
A possible explanation for a set of observations
16
New cards
Theory
A hypothesis that has been supported many times, by different types of evidence
17
New cards
Control
Part of an experiment without a variable
18
New cards
Adaptations
Features that allow an organism to survive changing environments
19
New cards
Controlled Experiment
An experimental setup where only one factor is altered at a time
20
New cards
Covalent Bond
A chemical bond that involves sharing a pair of electrons between atoms in a molecule
21
New cards
Ionic Bond
Formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another
22
New cards
Peptide Bond
A covalent bond formed between amino acids
23
New cards
Hydrogen Bonding
Bonds between hydrogen atom and oxygen atom of another water molecule
24
New cards
Macromolecule
A very large organic molecule composed of many smaller molecules
25
New cards
Monomer
A simple compound whose molecules can join together to form polymers
26
New cards
Polymer
A long molecule consisting of many similar or identical monomers linked together.
27
New cards
Carbohydrates
The starches and sugars present in foods
28
New cards
Proteins
Nutrients the body uses to build and maintain its cells and tissues
29
New cards
Lipids
Energy-rich organic compounds, such as fats, oils, and waxes, that are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
30
New cards
Nucleic Acids
DNA and RNA
31
New cards
Monosaccharides
Simple Sugars
32
New cards
Polysaccharides
Carbohydrates that are made up of more than two monosaccharides
33
New cards
Amino Acids
Building blocks of proteins (20 different kinds)
34
New cards
Polypeptides
Polymers of amino acids
35
New cards
Fatty Acids
Building Blocks of Lipids
36
New cards
Nucleotides
Building blocks of nucleic acids
37
New cards
DNA
A complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes
38
New cards
RNA
Single-stranded nucleic acid that contains the sugar ribose
39
New cards
Activation Energy
The minimum amount of energy needed for reactants to form products in a chemical reaction
40
New cards
Catalyst
A substance that speeds up a chemical reactions by lowering activation energy (without being changed)
41
New cards
Enzyme
A type of protein that speeds up chemical reactions in a living thing
42
New cards
Substrate
Reactant that binds to the enzyme
43
New cards
Active Site
The specific location where a substrate binds on an enzyme
44
New cards
Denature
Inactive or non-functioning enzymes
45
New cards
Product
A substance produced in a chemical reaction
46
New cards
Osmosis
Diffusion of Water
47
New cards
Diffusion
Passage of materials from a region of high concentration to low concentration
48
New cards
Hypertonic
A solution with more solute than another solution
49
New cards
Hypotonic
A solution with less solute than another solution
50
New cards
Isotonic
A solution with the same amount of solute as another solution
51
New cards
Active Transport
Movement across a membrane against a diffusion gradient. Requires energy
52
New cards
Selectively-Permeable
Allows only passage of certain materials
53
New cards
Passive Transport
Movement across a membrane without the use of energy
54
New cards
Cytoskeleton
Network of filaments that maintain cell chape
55
New cards
Centrioles
Involved in cell division
56
New cards
Microtubules
Tiny protein tubes that help support cells
57
New cards
Lysosomes
Sacs that contain hydrolytic enzymes
58
New cards
Nucleus
Control center for cell activity
59
New cards
Nucleolus
Assembles Ribosomes
60
New cards
Cell Membrane
Selectively permeable lipid layer
61
New cards
Prokaryotes
Cells with no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles
62
New cards
Eukaryotes
Cells with a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
63
New cards
Cytoplasm
Jelly-like suspension that organelles float in
64
New cards
Chromatin
DNA material located in the nucleus
65
New cards
Chloroplast
Converts sunlight energy into glucose
66
New cards
Vacuole
Provides Storage area for water, ions and other organic molecules
67
New cards
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, organelle that is the site of ATP (energy) production
68
New cards
Golgi Body
Packages proteins for use
69
New cards
Ribosome
Assembles amino acids into proteins
70
New cards
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
An endomembrane system where lipids are synthesized, calcium levels are regulated, and toxic substances are broken down
71
New cards
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
An endomembrane system covered with ribosomes where many proteins for transport are assembled
72
New cards
mRNA
Messenger RNA; type of RNA that carries instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome
73
New cards
tRNA
Transfer RNA; type of RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome
74
New cards
rRNA
Ribosomal RNA; type of RNA that makes up part of the ribosome
75
New cards
pH Scale
A scale with values from 0 to 14, used to measure the concentration of H+ ions in a solution; a pH of 0 to 7 is acidic, a pH of 7 is neutral, and a pH of 7 to 14 is basic
76
New cards
Carbon
All of the organic molecules are based on the element \_________
77
New cards
Saturated Fats
A type of fat in which the fatty acid chains have all single bonds
78
New cards
Unsaturated Fats
A type of fat containing a high proportion of fatty acid molecules with at least one double bond
79
New cards
Radioactive Isotopes
It helps doctors diagnose disease and locate certain types of cancer
80
New cards
Isotopes
Atoms of the same elements with different number of neutrons
81
New cards
Ions
Atoms that have a positive or negative charge
82
New cards
Homeostasis
A tendency to maintain a balanced or constant internal state; the regulation of any aspect of body chemistry, such as blood glucose, around a particular level
83
New cards
Polarity
Molecules having uneven distribution of charges
84
New cards
Cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance
85
New cards
Adhesion
Attraction between molecules of different substances
86
New cards
Capillary Action
The attraction of the surface of a liquid to the surface of a solid
87
New cards
High Heat Capacity
Water's ability to absorb and retain heat
88
New cards
Surface Tension
A measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid
89
New cards
Cellulose
Carbohydrate component of plant cell walls
90
New cards
Mutation
A random error in gene replication that leads to a change
91
New cards
Semiconservative
Method of replication that implies that each new strand of DNA is half original and half new
92
New cards
Antiparallel
The opposite arrangement of the sugar-phosphate backbones in a DNA double helix
93
New cards
DNA Helicase
An enzyme that unwinds the DNA double helix during DNA replication
94
New cards
RNA Primase
An enzyme that creates a short RNA primer for initiation of DNA replication
95
New cards
DNA Polymerase
Enzyme involved in DNA replication that joins individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule
96
New cards
DNA Ligase
Enzyme that chemically links DNA fragments together
97
New cards
Replication
Copying process by which a cell duplicates its DNA
98
New cards
Transcription
Synthesis of an RNA molecule from a DNA template
99
New cards
Translation
Process by which mRNA is decoded and a protein is produced
100
New cards
Substitution
A mutation in which a nucleotide or a codon in DNA is replaced with a different nucleotide