Part 4: 3D (conventional) localization films
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Name all types of 3D (conventional) localization films
Orthogonal Films
Stereo Film Technique
Cross Table Lateral Film
Scout Film
term. Orthogonal Films
def. 2 images taken at right angles to each other to give a 3D view
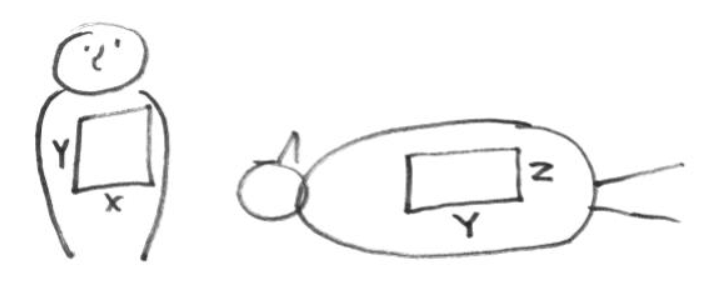
What dimensions can you see in orthogonal films
x: width
y: length
z: depth
In orthogonal films, you take __ films which let you see in ___ dimensions
1 AP: x, y
1 Lateral: y, z
Stereo Film Technique aka
Stereo Shift Technique
term. Stereo Film Technique
def. Filming technique where patient remains stationary , while the tube rotates

Stereo Film Technique:
# of films
Taken at __ degree gantry intervals
3 separate films (new film for each exposure)
15
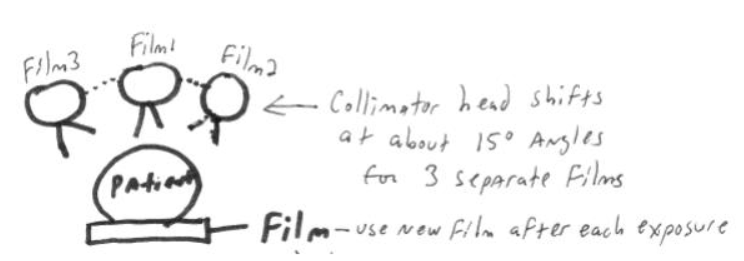
term. Cross Table Lateral Film
An attempt at 3D filming using:
1 lateral film, and
an opaque marker placed on the anterior and posterior skin surfaces
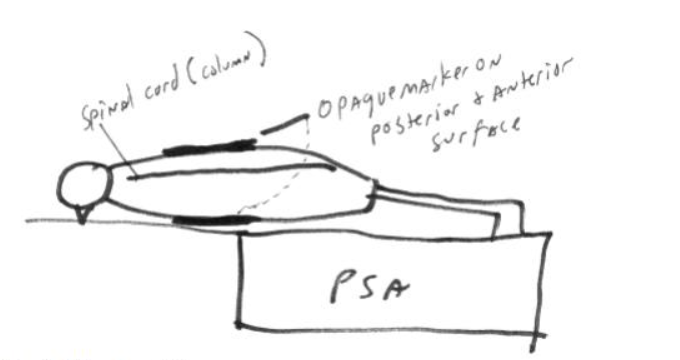
What types of opaque markers are used for Cross Table Lateral Films?
Wire
coin
etc.
Why do we place an opaque marker on the anterior and posterior skin surfaces? Give an example.
To measure relative distances to other structures in the body. For example. When treating a PA spine, we use this to verify the depth of the spinal cord
Purposes of Cross Table Lateral Film
Shows us the depth of critical structures relative to the skin surface
Shows us the magnification and divergence on the film compared to isocenter
term. Scout Film
def. A preliminary image (film) used for localization or verification e
Example of a scout film
Take a scout film before the 1st tx to verify you are in the right area
True or False: Scout Films are the same as weekly-port films
False
Field size is defined at
isocenter