AP Bio Evolution 1 Review/Study Guide
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
How do the ideas of Darwin and Lamarck differ?
Darwin- believed organisms changed by chance when they are born & before there was a change in the environment
Lamarck- believed organisms changed out of necessity and after a change in the environment
What is the raw material for natural selection?
Why are adaptations so necessary in Darwin’s theory of evolution by way of natural selection?
Genetic variation is the raw material for natural selection.
Adaptations are so necessary because organisms that are more adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and pass on the genes that aided them.
What is decent with modification?
Also known as:a process by which species accumulate differences from their common ancestors as they adapt to different environments over time.
Also: A change in the genetic composition of a population from generation to generation.
If and organism is “biologically fit” what does that mean?
It can survive/thrive in its environment, find a mate, and produce offspring.
What is genetic drift and gene flow?
What is the founder effect?
Does genetic drift have a greater effect in larger or smaller populations?
Genetic drift is a chance event that causes allele frequencies to fluctuate unpredictably from generation to generation (especially in small populations because they have less genetic variation and therefore ability to adapt)
Gene flow is the transfer of alleles into and out of a population due to movement of fertile individuals/their gametes
The founder effect is when a few individuals become isolated from a larger population and create a new population whose gene pool different from the OG population
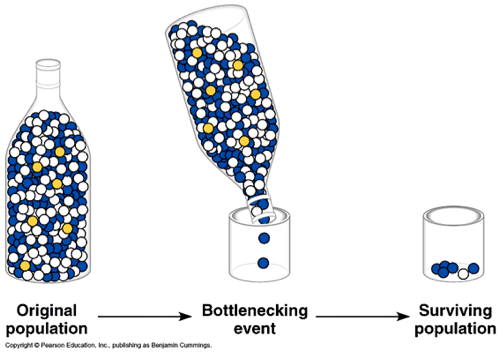
What is the “bottleneck” effect?
When a sudden chance event causes a sudden drop in population size so the species is squeezed through a “bottle-neck” and the frequency of alleles changes (can be overpopulated, underpopulated, or lost completely”
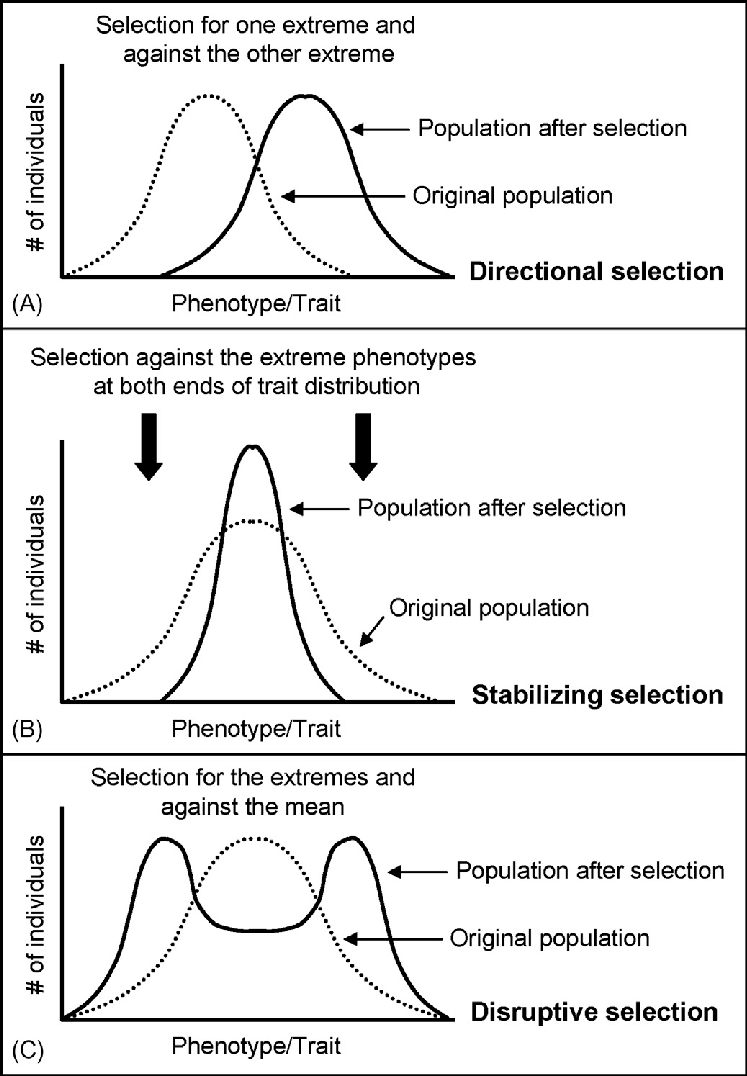
What is the difference between directional selection, disruptive selection, and stabilizing selection? What do the graphs look like?
Directional- conditions favor individuals exhibiting one extreme of a phenotypic range which shifts a population frequency curve for the phenotypic character in a specific direction
Disruptive- conditions favor individuals with both extremes of a phenotypic range over individuals with inheritable phenotypes
Stabilizing- acts against both extreme phenotypes and favors the intermediate variants which reduces variation and maintains the status quo for a particular phenotype character
What is the Hardy-Weinberg formula and what does each variable represent?
Formula": p² + 2pq + q² = 1(percentage) p + q = 1 (frequencies)
p² - Homozygous Dominant
2pq - Heterozygous
q² - Homozygous Recessive
What five conditions that must be present for Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium to be met?
1) No mutations 2) must have random mating 3) no natural selection 4) very large populations 5) No gene flow
Why do bacteria become antibiotic resistant?
Because they can develop defense mechanisms against antibiotics depending on environment and use, and through mutations/selection
Describe artificial selection and natural selection. What role do humans play in artificial selection?
Artificial Selection- is human involvement/forced selection for desired traits and or characters in organisms (for example: dog breeding)
Natural Selection- the mechanism that chooses the most “fit” organisms to withstand harsh life through which evolution occurs
What is the difference between convergent and divergent evolution? Provide examples of homologous and analogous structures.
Convergent- It’s the independent evolution of similar features in different lineages
Divergent- It’s the accumulation of differences between closely related populations within a species →speciation
Homologous (similarity due to shared ancestry) - human arms, whale fins, bat wings
Analogous (share similar function but not common ancestry) - wings in birds/bats and fins in penguins/fish
What is Genetic Variation? How does it make evolution possible?
It is the difference in DNA among individuals or the difference between populations among the same species.
It makes evolution possible by introducing new traits to an organism/making advantageous traits more likely to be passed down to the next generation.
How is evolutionary fitness measured?
It is measured by an organism’s ability/inability to mate and produce offspring and pass on their genes to the next generation.
Which philosophy of evolution is based on a theory of use and disuse?
*research later* pangenesis
What is one of the principles that Darwin learned from the writing of Thomas Malthus?
*research later* more animals were born that can survive
Explain the order of events of natural selection beginning with a population
containing genetic variation.
1) a change occurs in the environment 2) the less suited organisms begin to die out 3) well adapted organisms have more offspring 4) genetic frequencies within a population change
What is the strongest evidence that all living organisms have descended from
a common ancestor?
Similar DNA sequences
When classifying organisms on a phylogenetic tree, what is the most
important consideration to examine?
Parsimony - fewest total changes
What type of structure are your wisdom teeth, or your appendix?
vestigial
If, in a gene pool, 56% of the individuals are heterozygous, what percentage
is homozygous?
homozygous - 44%
Natural selection cannot act upon a population that has no ________ ___________.
genetic variation
If, in a population, the frequency of the recessive allele is 0.2, what is the
percentage of the population that would be aa?
4%
Evolution can occur by natural selection, but also by which effect?
genetic drift
Which is a random event- mutation or natural selection
mutation
What are the 3 mechanisms that alter allele frequencies directly and will
cause the most evolutionary change?
genetic drift, gene flow, natural selection