Abdominal X-Ray
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
- Bowel obstruction
- Abdominal distention
- r/o foreign body
AXRs are pretty out dated because we have better imaging, but there are some indications including...
CXR
What should be ordered in patient with suspected pneumoperitoneum?
AXR
The chest region has more air. The abdomen has more organs. Therefore, you need more radiation for an AXR.
Is there greater radiation exposure when performing an AXR or CXR?
Supine
AXR view that displays the overall appearance of the gas pattern.
Upright/erect
AXR view that displays free air in the peritoneal cavity, used to show air fluid levels in obstruction or ileus. Diaphragm, liver and spleen tend to become more visible because fluid moves down into pelvis. Remaining mid and lower abdominal contents tend to become less visible.
Left lateral decubitis
AXR view that is used to look for free air on the outside edge of the liver.
- View, age, sex, date
- Technically satisfactory
- Overall gas patterns
- Extraluminal air
- Abnormal calcifications
- soft tissues outline size and shape
- other incidental findings
Framework for assessment and presenting the AXR...
black: gas
white: calcified structures
grey: soft tissues
darker grey: fat
intense white: metallic objects
the 5 densities on AXR are...
black: ______
white: _______
grey: _______
darker grey: ______
intense white: ________
11th thoracic spinous process
A "Technically Satisfactory" AXR extends superiorly to the ______
obturator foramen (ischial tuberosity, greater trochanter too)
A "Technically Satisfactory" AXR extends inferiorly to the ______
Lateral rib margins and iliac crest
A "Technically Satisfactory" AXR extends laterally to the _________.
look for clear bone edges of lumbar spine
How to assess penetration of AXR...
Coverage
Penetration
Rotation
Things to assess for technical satisfaction...
Supine AP
in a ______ AXR, fluid lies posteriorly within the gut and the gas in the bowel will float anteriorly on top of it.
Erect
in a ___ AXR, fluid lies inferiorly and te bowel will have an air fluid level.
intraluminal
gas inside the bowel
Stomach
____ almost always has intraluminal air.
small bowel
____ has 2-3 loops of air
extraluminal
____ air is never normal. This is air outside the bowel lumen.
Bowel distension
bowel filled with air within normal limits.
Bowel dilation
bowel filled beyond its normal capacity, usually indicative of a bowel obstruction.
centrally
small bowel is located _____
peripherally
large bowel is located _____
2.5 cm
normal size of the small bowel is less than _____
6 cm
normal size of the large bowel is less than _____
valvulae conniventes
folds of the small bowel are called ______. These are coiled spring shaped folds, 1-2 mm thick that appear like stacked coins, and completely traverse the width of the colon.
Haustra
folds of the large bowel are called ____ and only partially traverse the bowel.
Small bowel
there is often very little ____ gas seen on plain films.
stool
___ may be present in the large bowel, will appear as multiple small bubbles within soft-tissue type of structure.
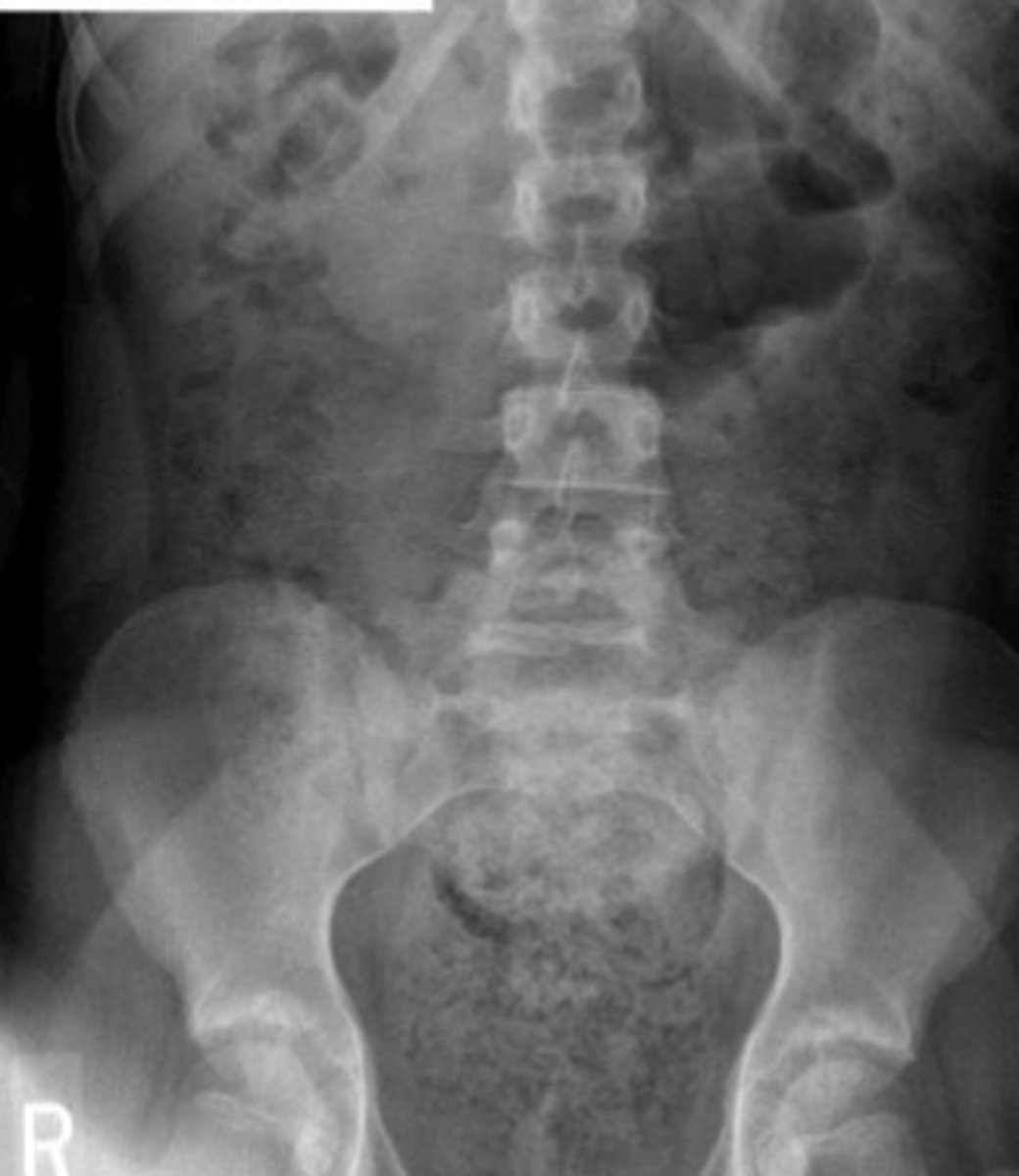
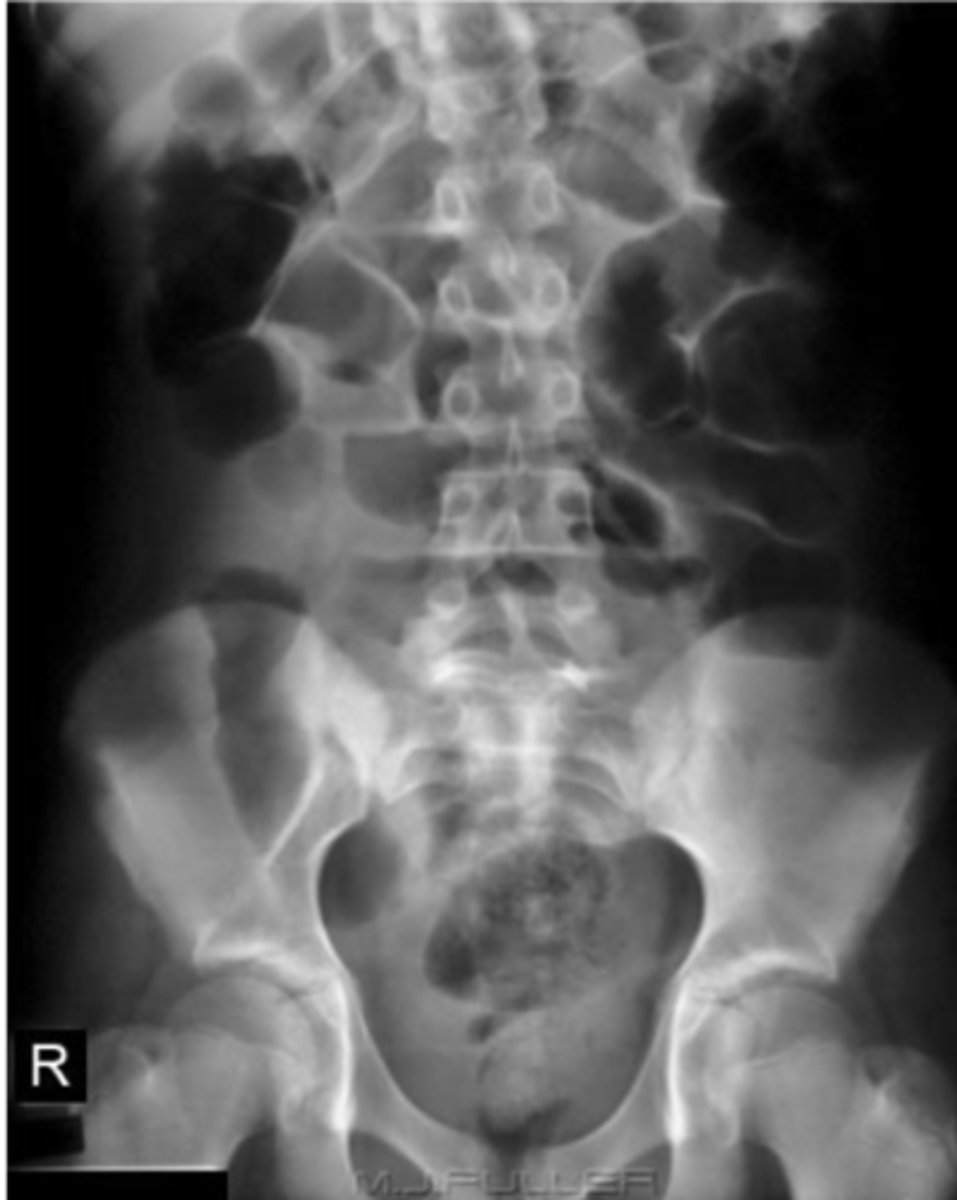
Normal AXR
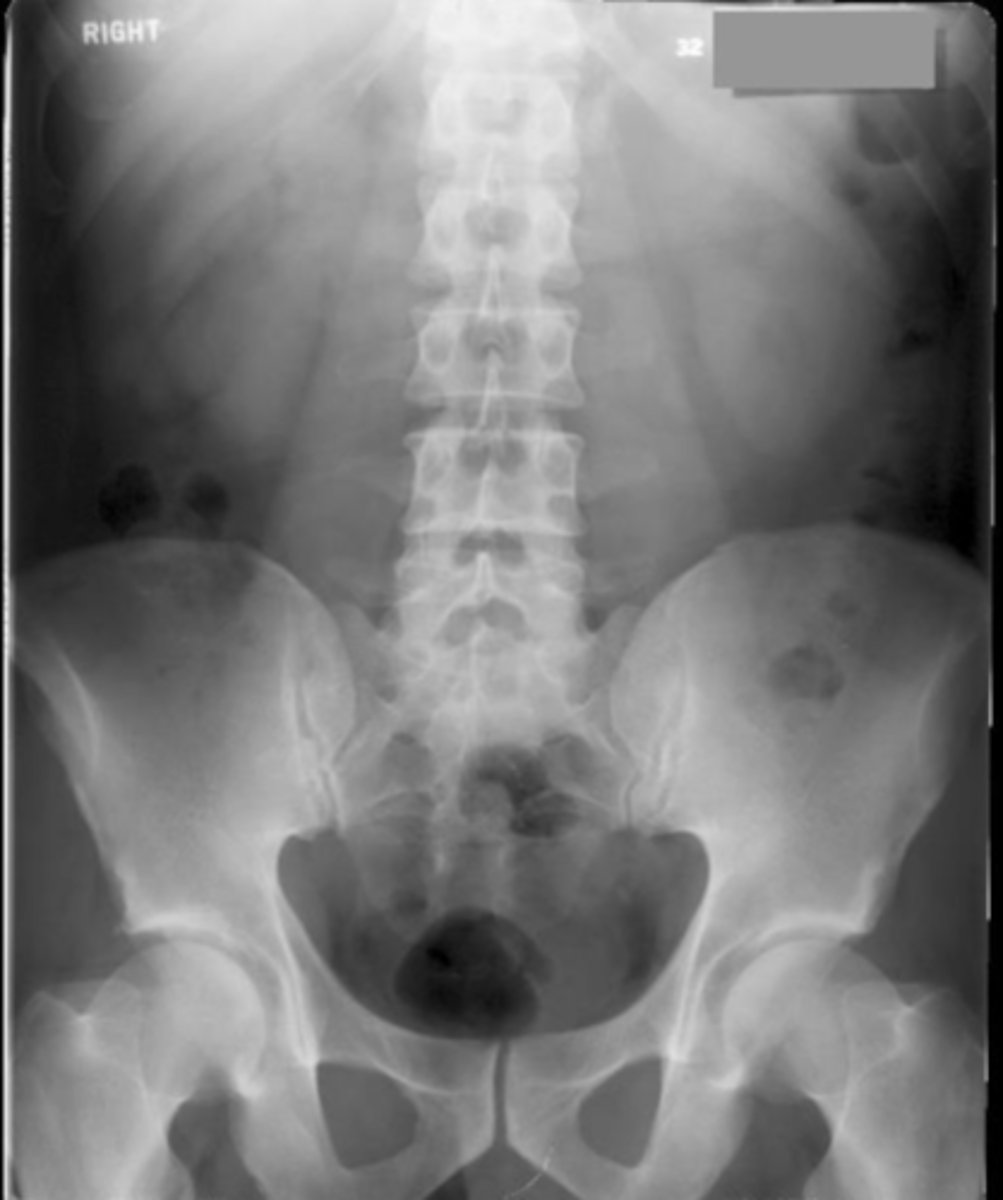
Large Bowel Distension
no dilation, less than 6cm
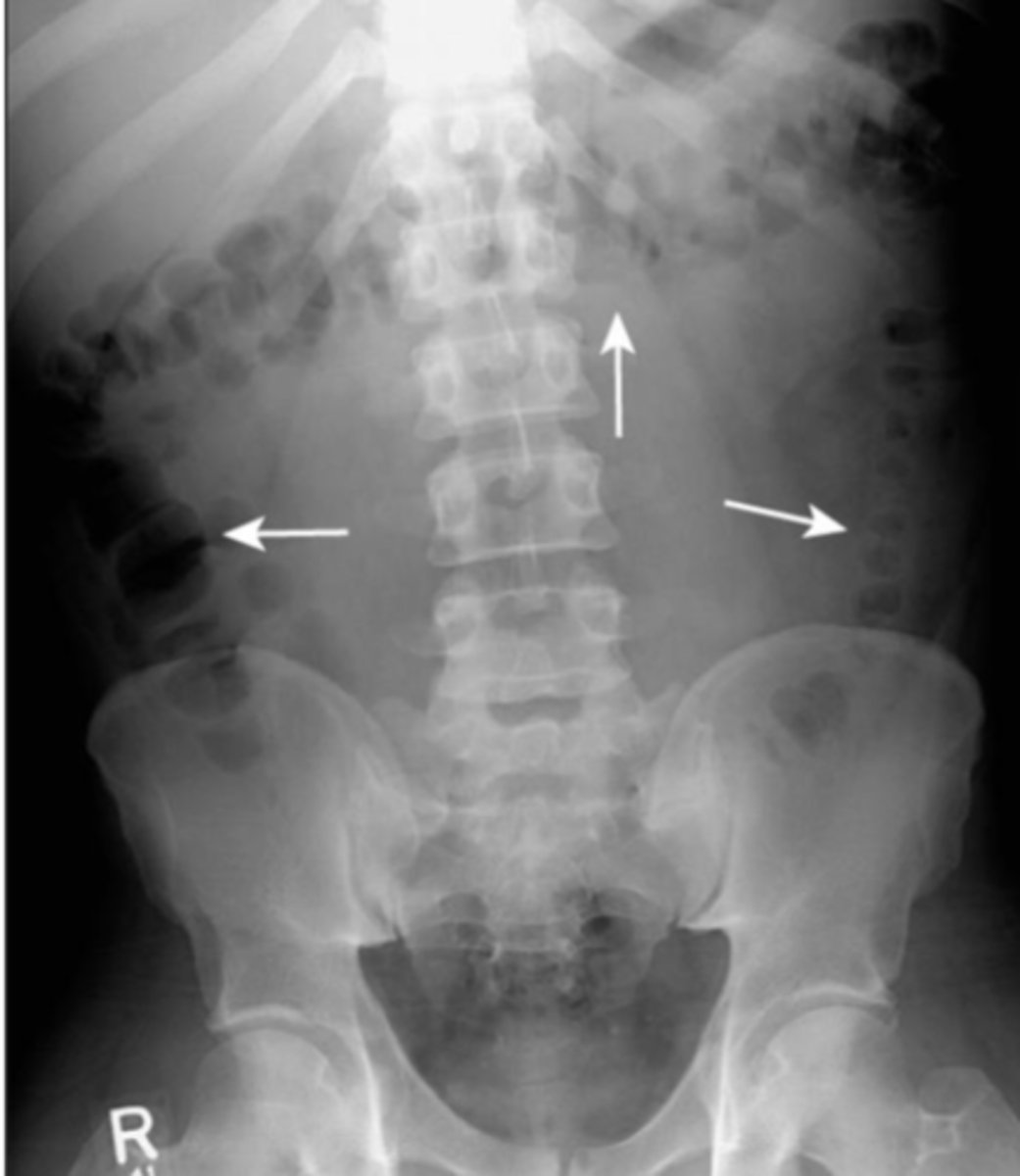
Small bowel obstruction
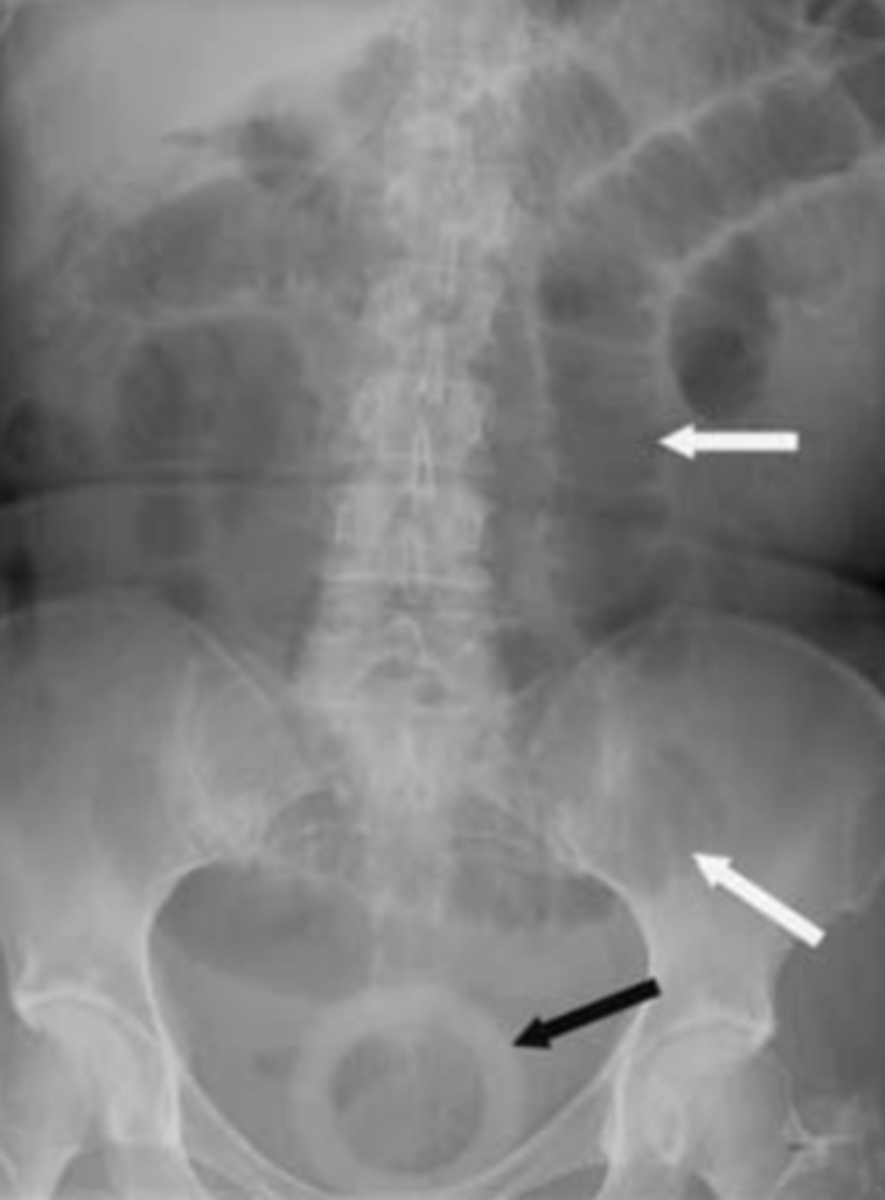
Large bowel obstruction
Aerophagia
patient swallows a lot of air, excess gas diffusely, but air in rectum is present so no obstruction
- Functional ileus
- Mechanical obstruction
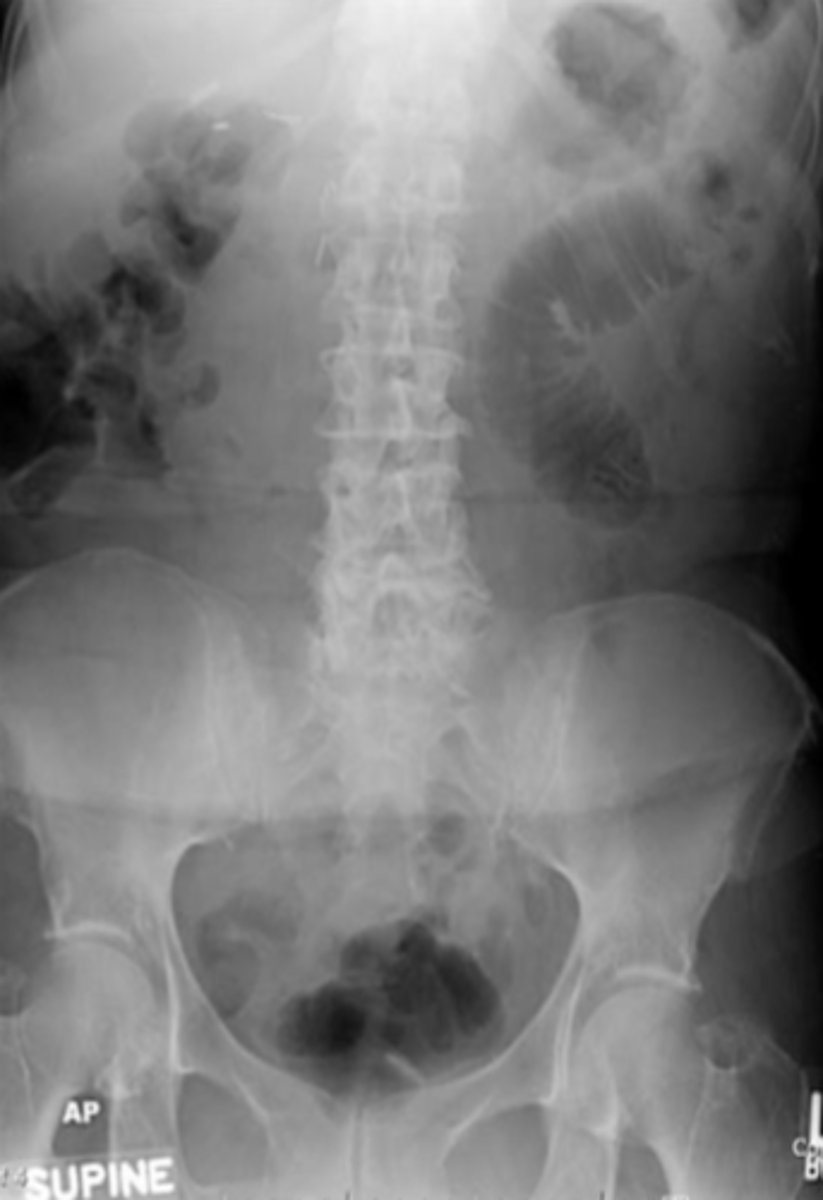
Ogilvie syndrome
causes of intraluminal gas
- pneumoperitoneum
- abcesses
causes of extraluminal air
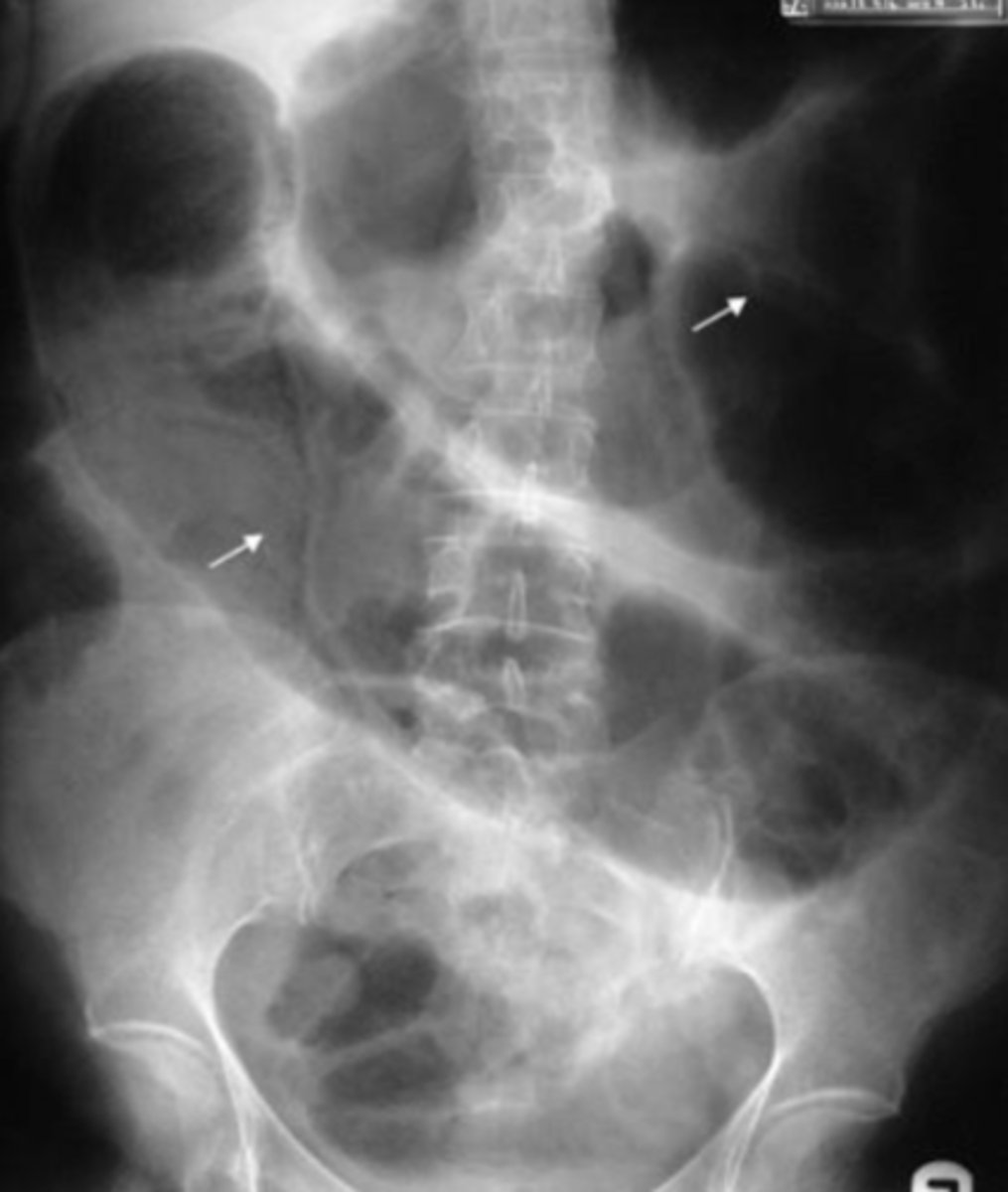
Functional ileus
one or more loops of bowel lose their ability to propagate peristaltic waves, causing a functional "obstruction" proximally, seen as gas-filled loops of bowel.
localized ileus
occurs when part of a bowel is aperistaltic (usually due to irritation). Affected small bowel usually remains persistently dilated on subsequent images. Some gas continues to pass through the affected bowel because there is not a true obstruction, so there is visible air in the rectum.
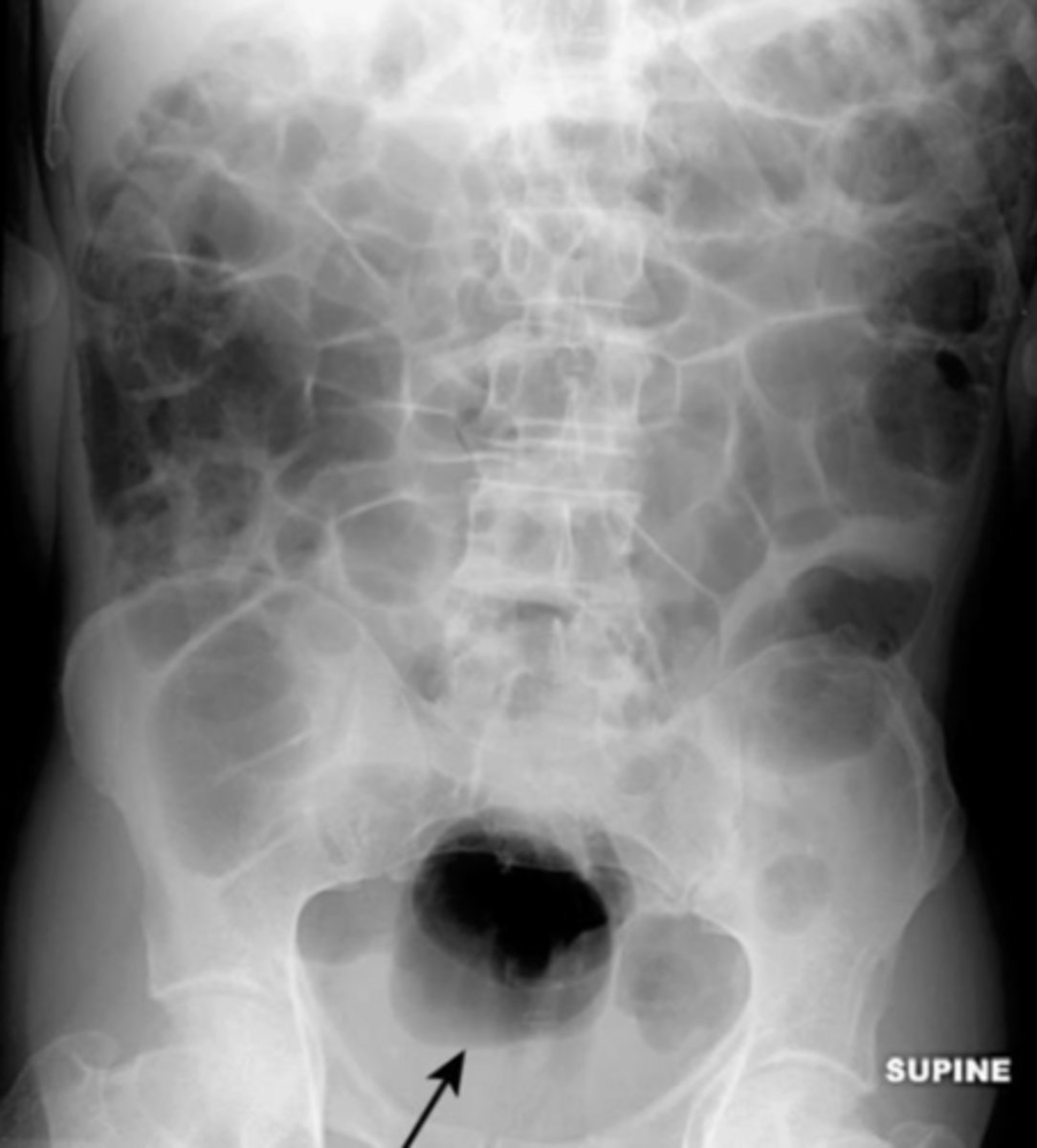
generalized adynamic ileus (Paralytic Ileus)
generalized dilation of the small and large bowel. Entire bowel is aperistaltic. Most often seen postoperatively. Air visible in the rectum/sigmoid since this is not a mechanical obstruction.
proximal
d/t the Law of the Gut, ____ to an obstruction becomes dilated because of swallowed air.
Distal
d/t to the Law of the Gut, ____ to an obstruction shows absence of air.
irritation
localized ileus is most commonly due to _____
postoperatively
generalized adynamic ileus is most commonly due to ______
Localized ileus
Generalized Adynamic ileus
Ogilvie's Syndrome
acute intestinal pseudo obstruction commonly of the right colon that affects older immobile patient on medications.
Ogilvie's Syndrome
older immobile patient on medications
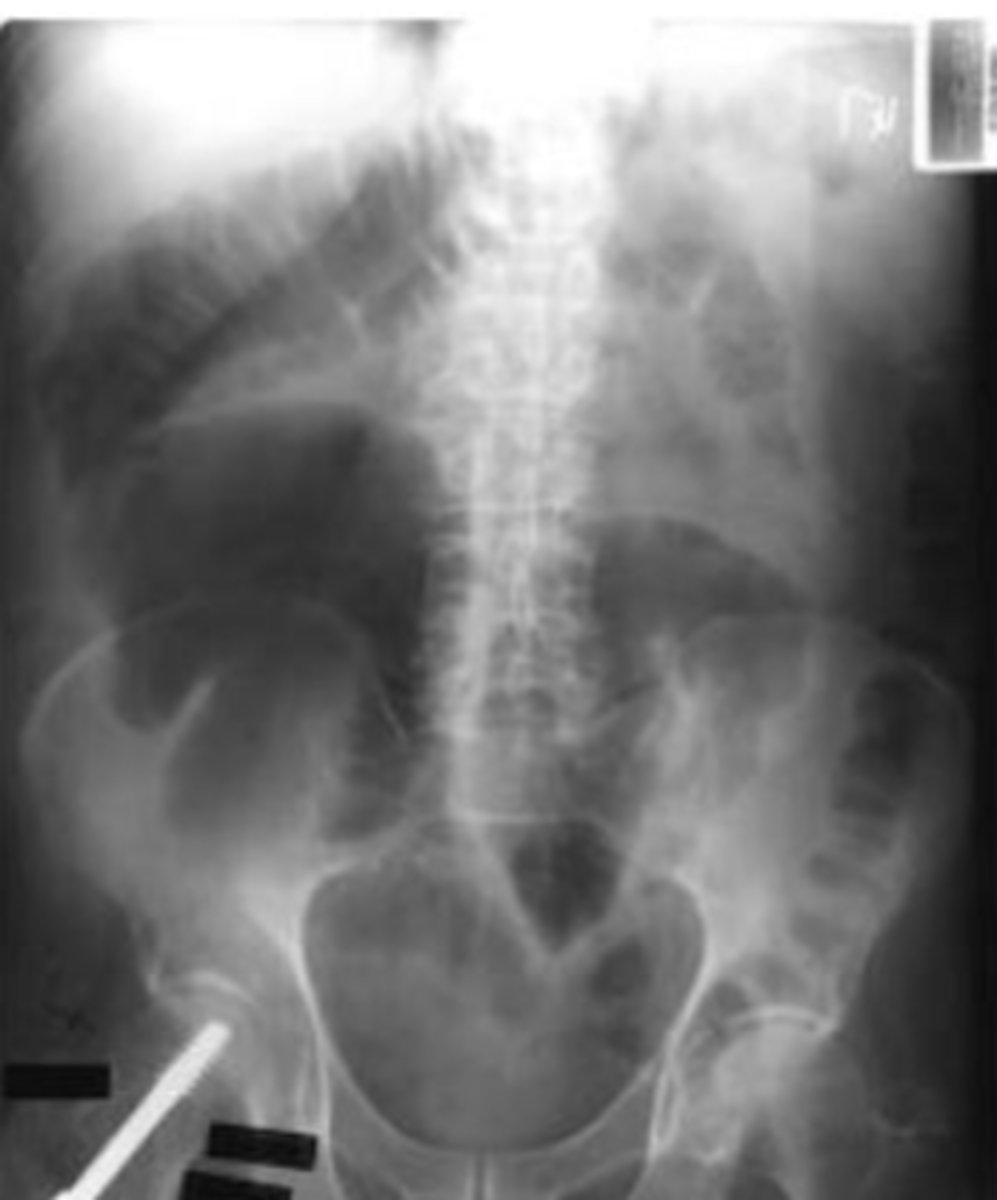
Small Bowel Obstruction
manifested by dilated centrally lcoated bowel greater than 3 cm in diameter, high pitched hyperactive bowel sounds, visible valvulae conniventes, stepladder configuration on erect view, no gas distally
adhesions
History of abdominal surgery
number one cause of small bowel obstruction
Small Bowel Obstruction
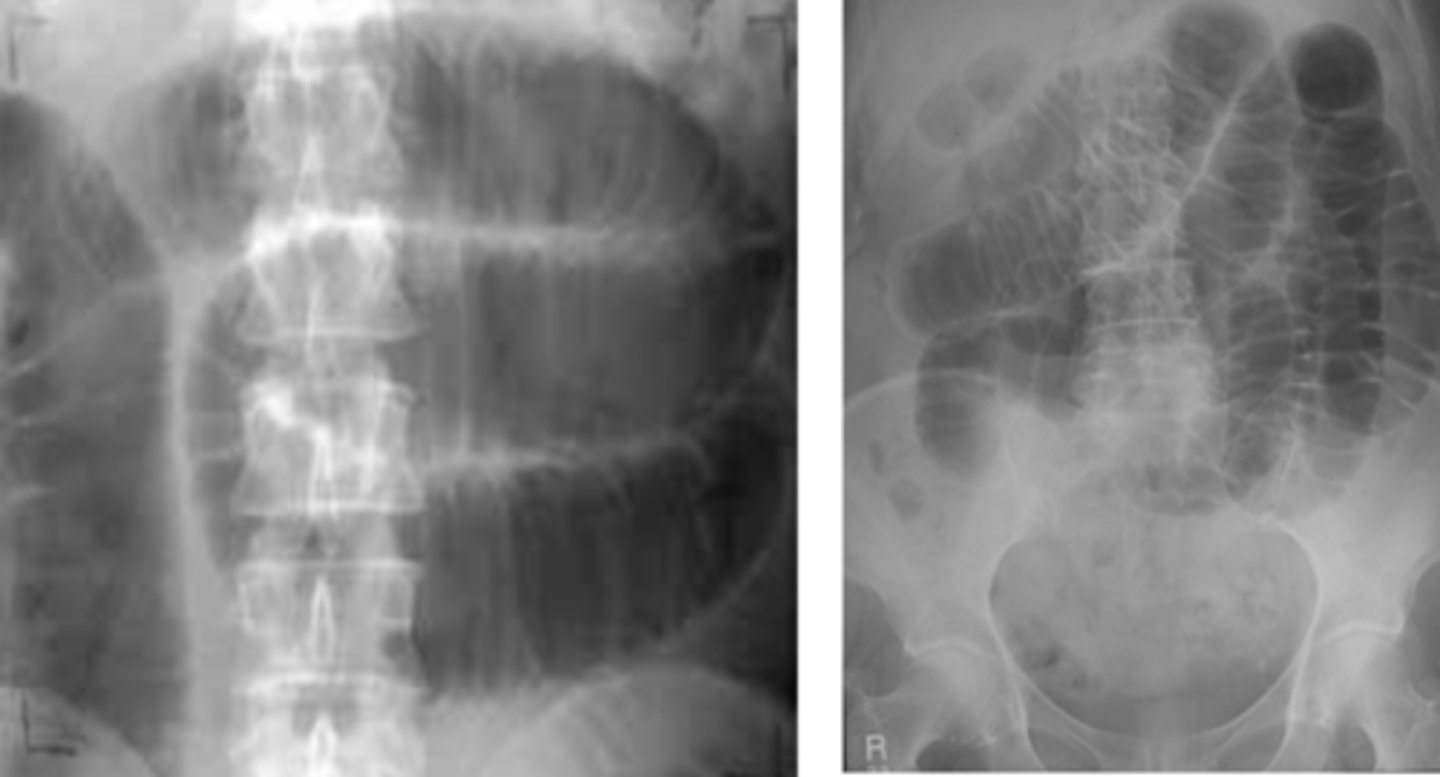
SBO
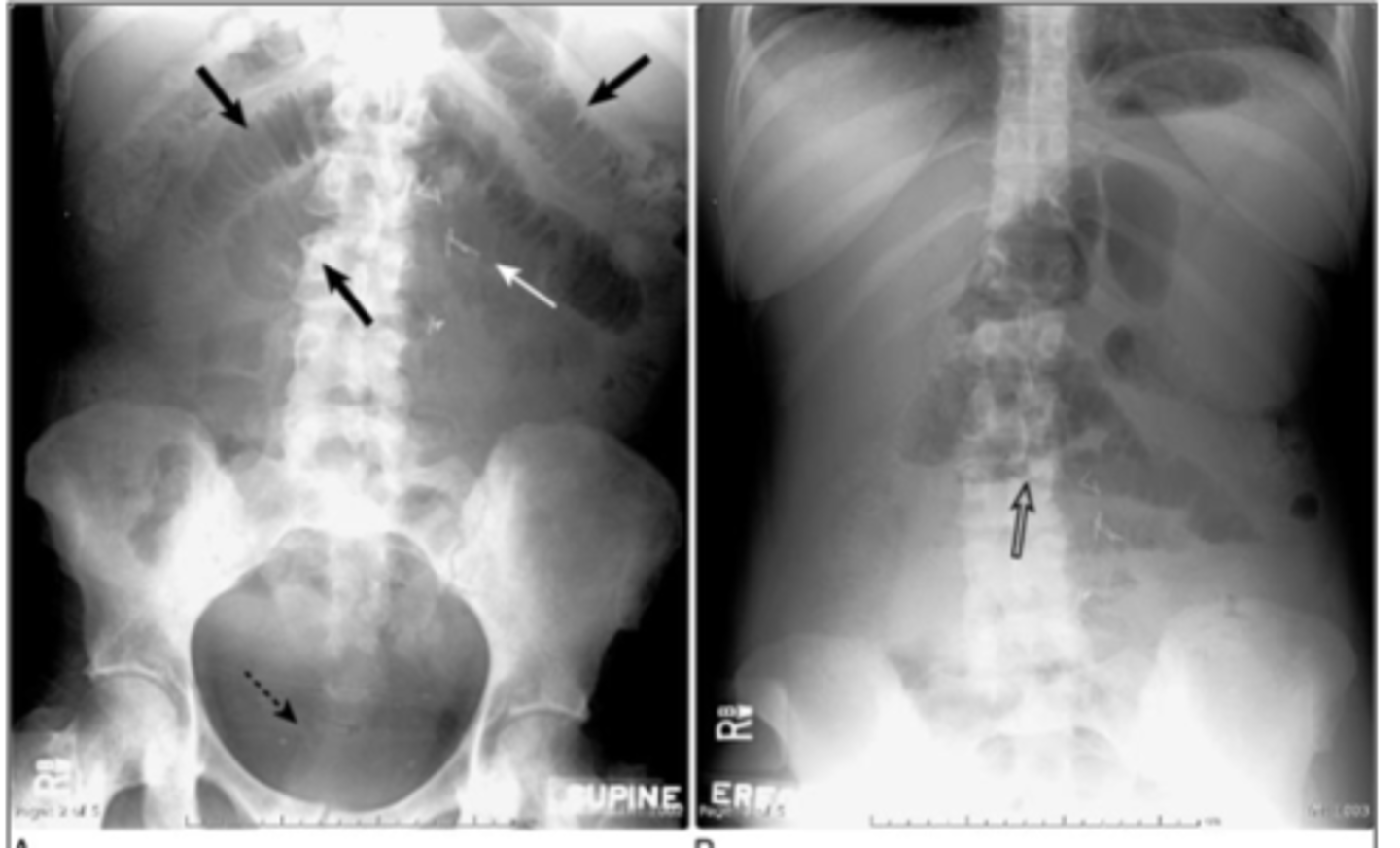
SBO with Step ladder appearance on erect AXR
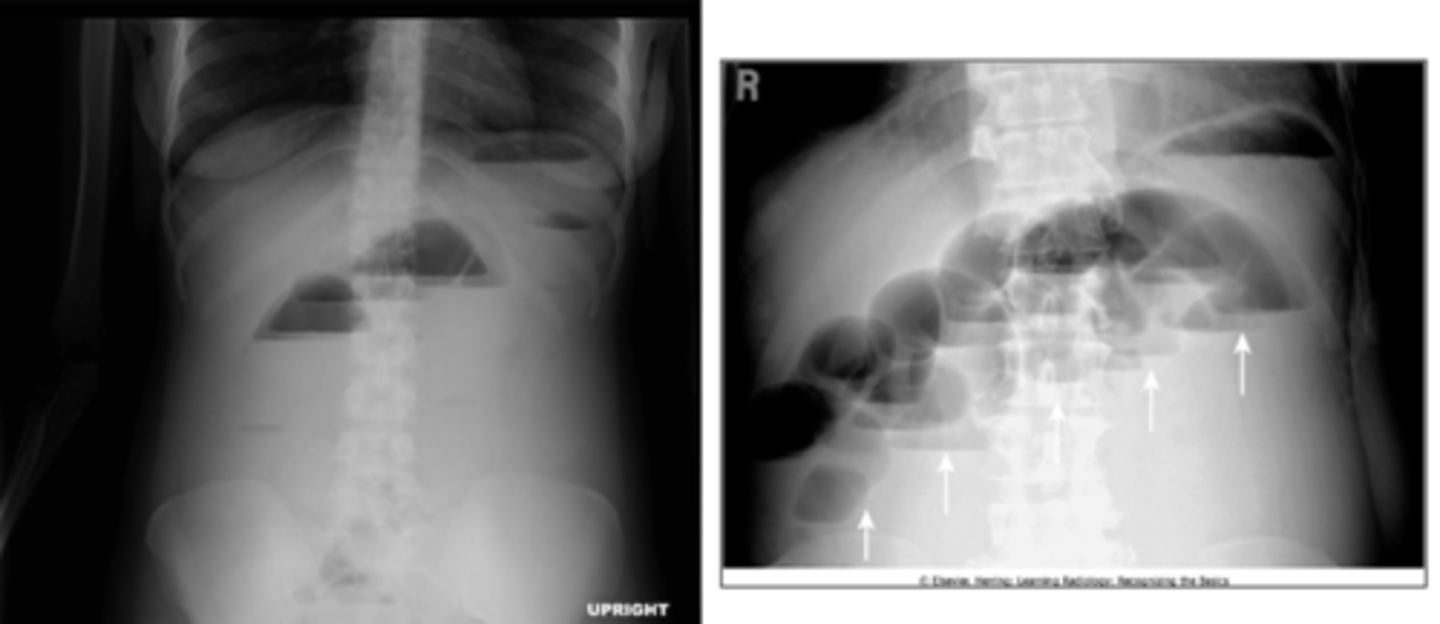
large bowel obstruction
persistent dilation of a bowel segment in the periphery. Few or no air fluid levels in upright film because most contents of this bowel are solids. Cuf off point due to passage of gas and feces distal to blockage. Visible haustra. No air in rectum
Cancer
number one cause of Large Bowel Obstruction.
LBO
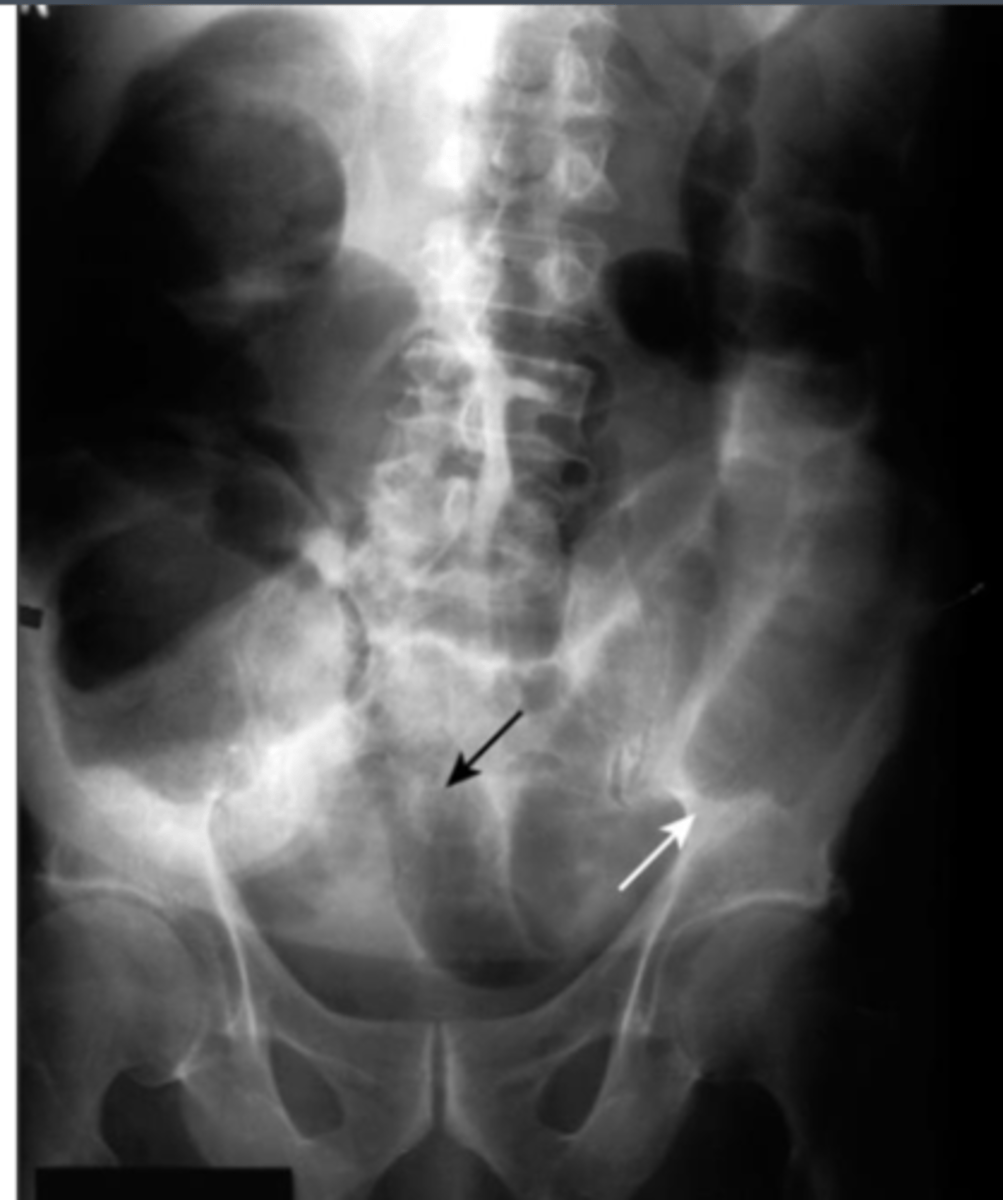
LBO
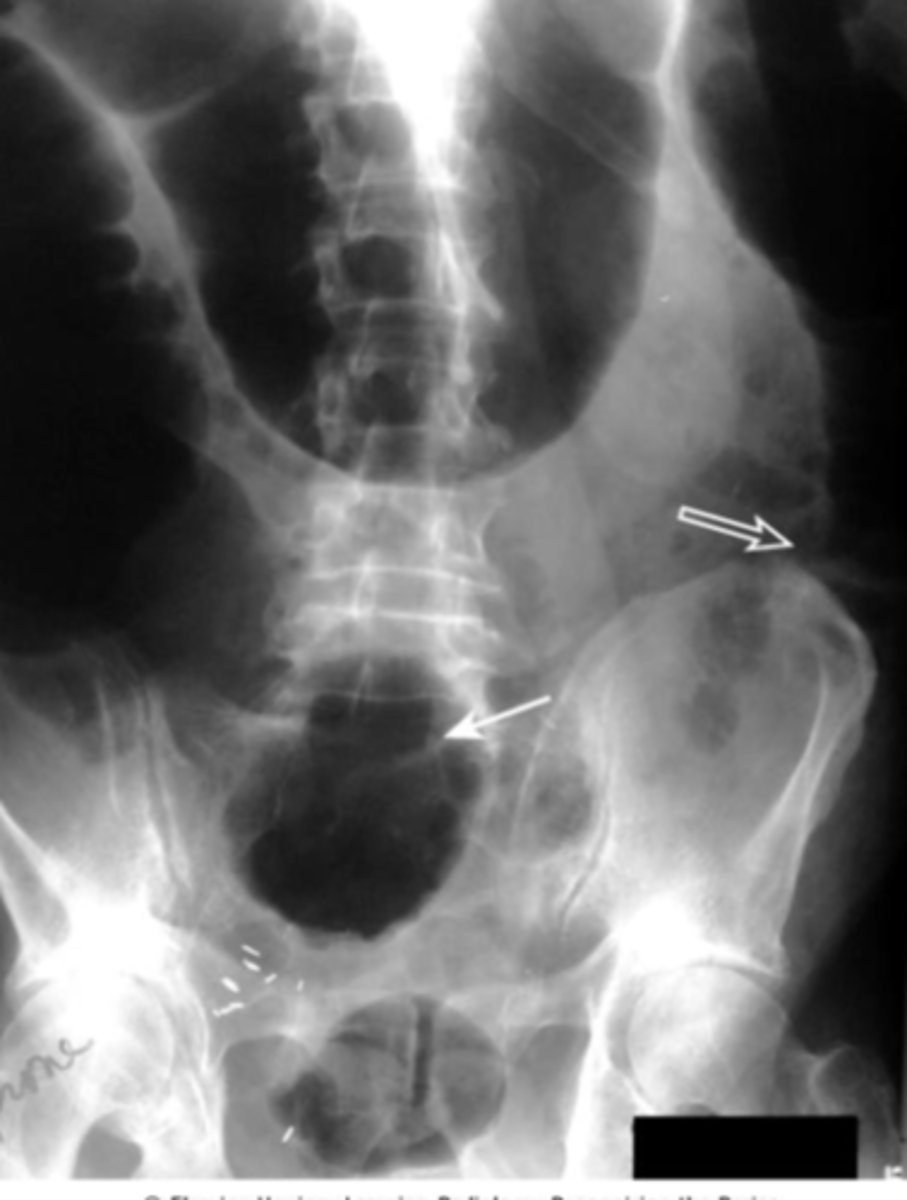
Colonic Volvulus
the twisting of the colon upon itself. Occurs when part of the colon twists on its mesentery, resulting in acute, subacute, or chronic colonic obstruction. Colon is distended with gas and has an inverted U appearance.
Cecum
frequently has the largest diameter of the large intestine
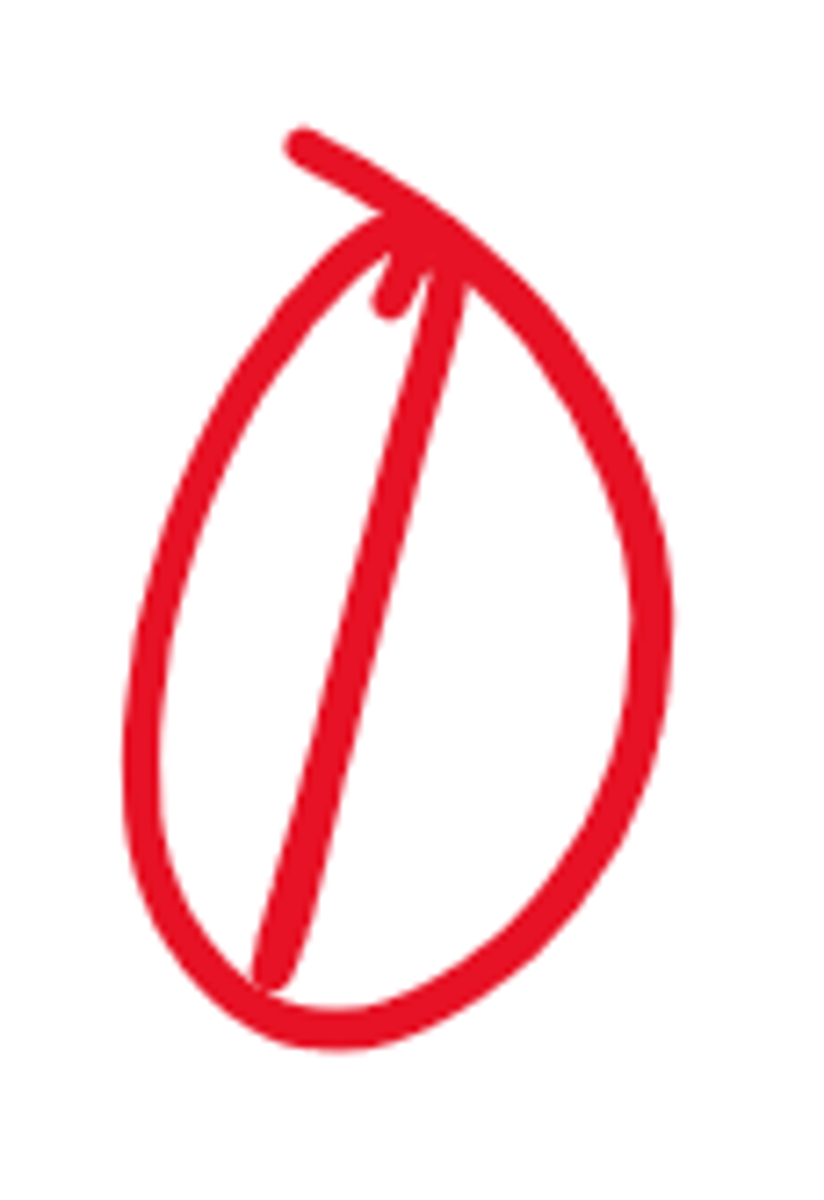
coffee bean sign
Colonic Volvulus may appear as the __________
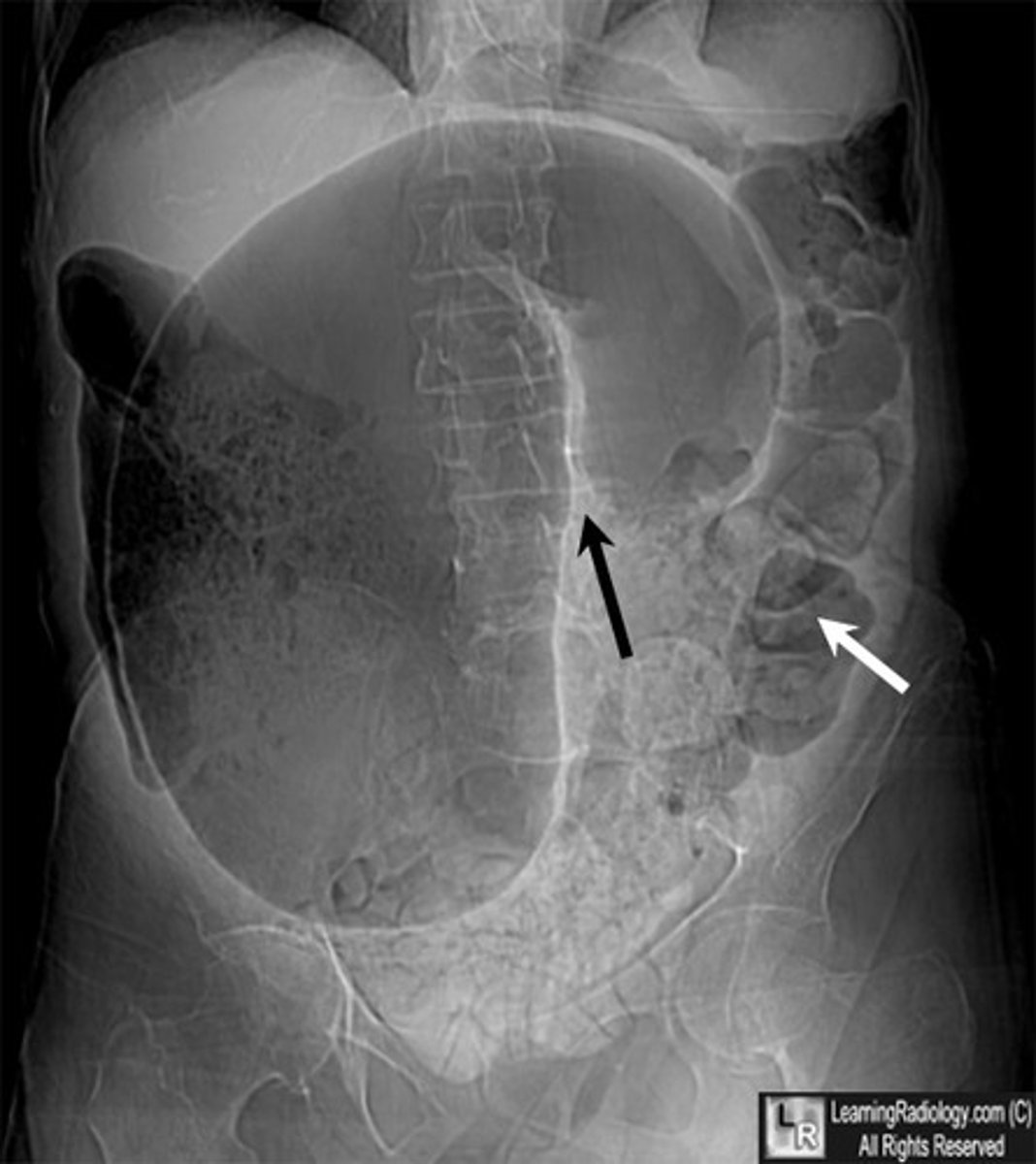
Cecum
this Coffee bean sign would be indicative of a Volvulus of the _____.

Sigmoid
this Coffee bean sign would indicative of a Volvulus of the _____.
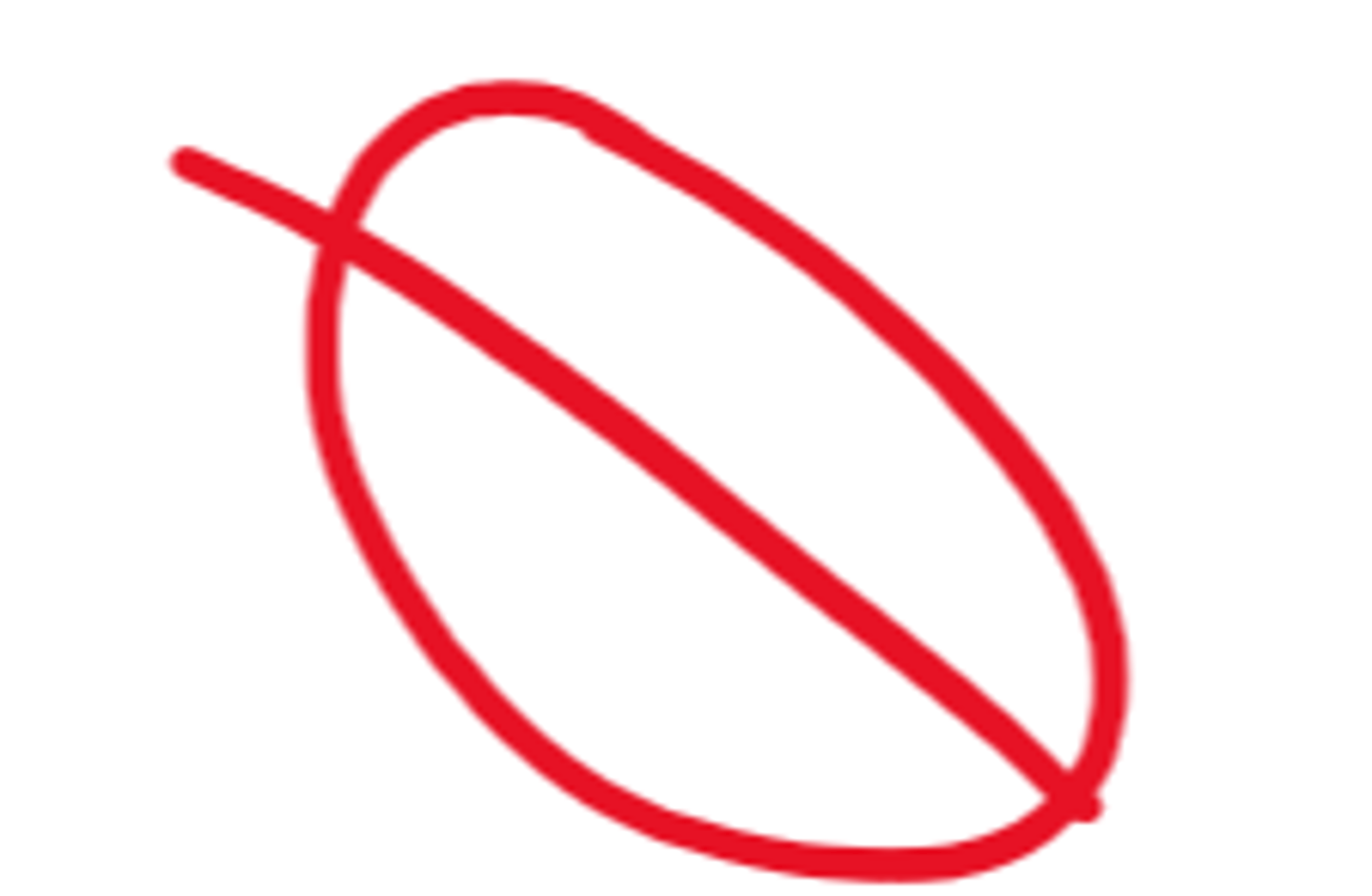

Sigmoid colon (most commonly)
Cecum
Colonic most commonly occurs at the...
Sigmoid Volvulus
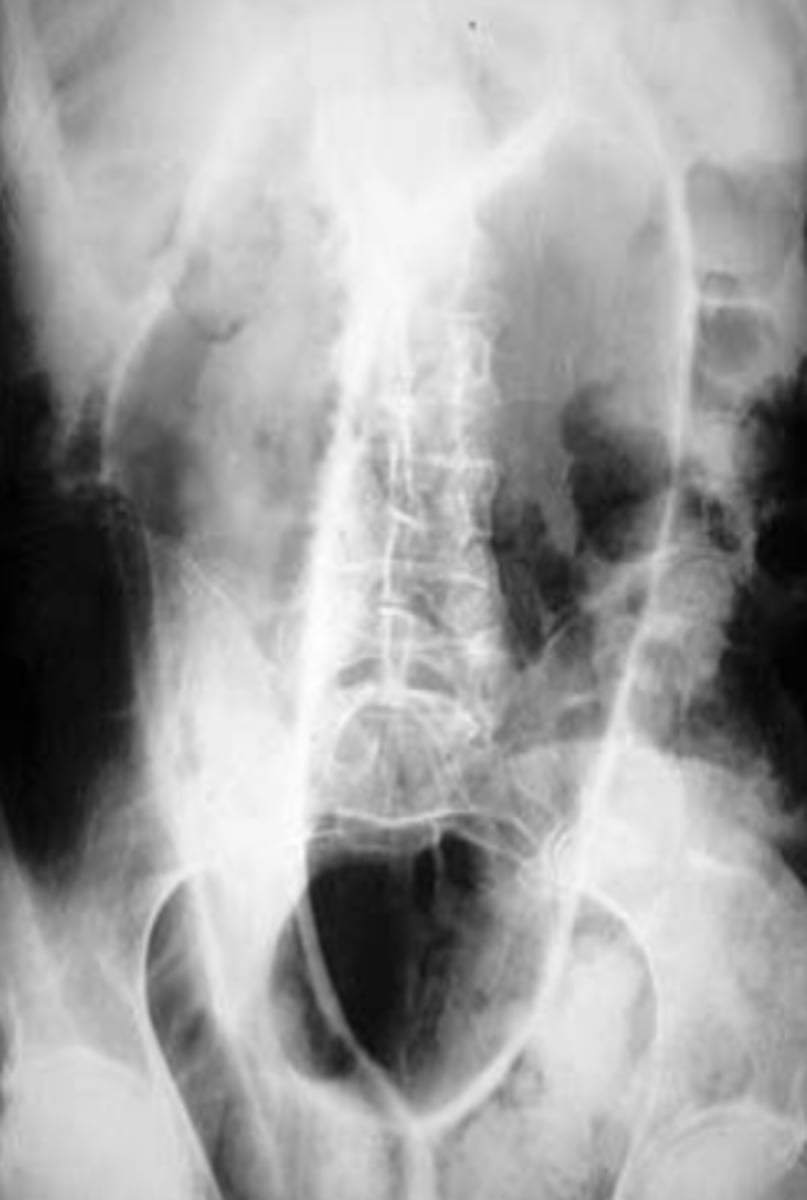
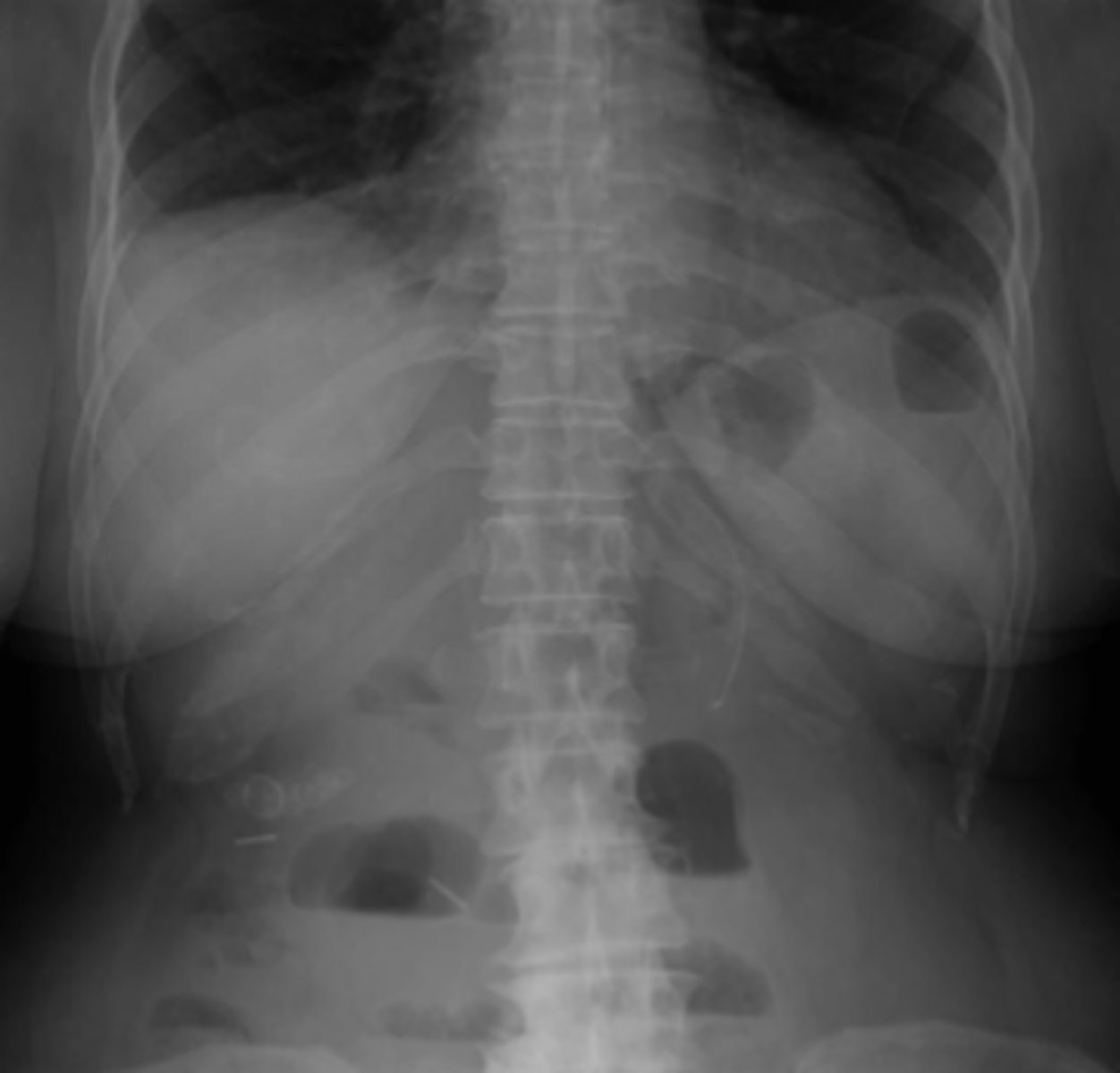
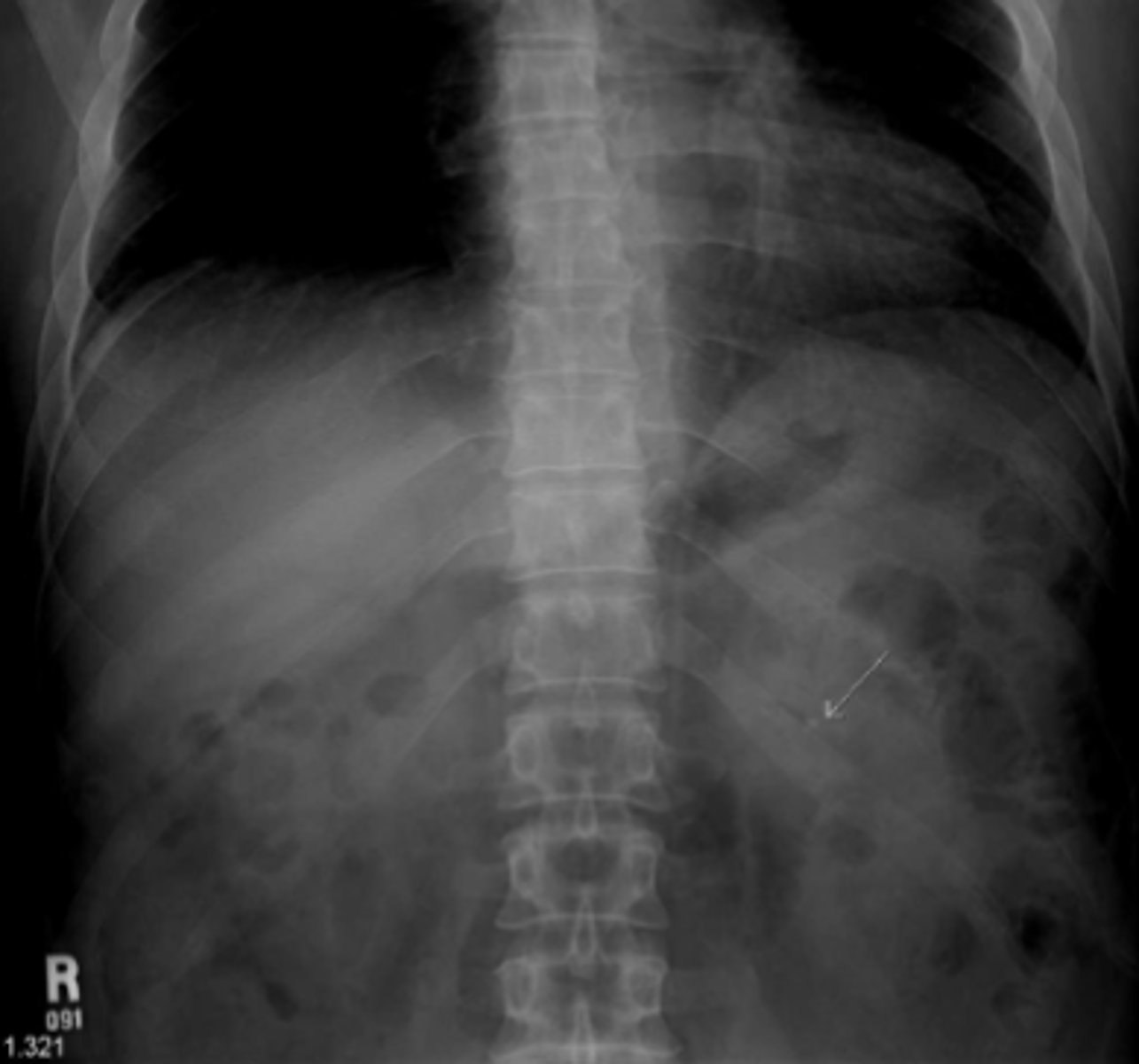
Pneumoperitoneum
free intraperitoneal gas that indicates perforated viscus. Most common causes include perforated peptic ulcer, rupture of an air containing loop of bowel, and trauma. Recognizable on imaging via air beneath diaphragm in upright film, falciform ligament sign, Rigler's sign
CT scan
choice of study for diagnosis of pneumoperitoneum.
Pneumoperitoneums
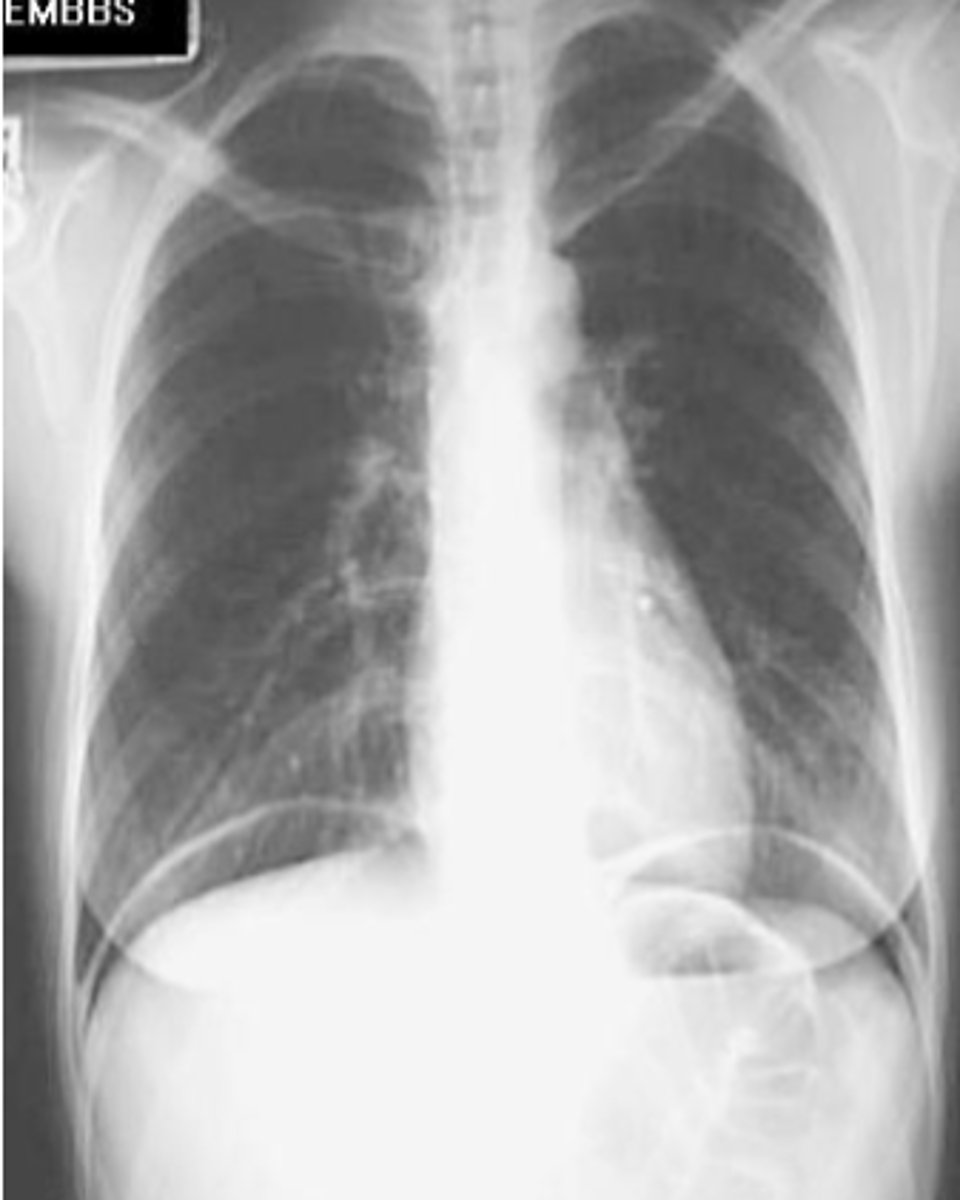
Rigler's sign
pneumoperitoneum
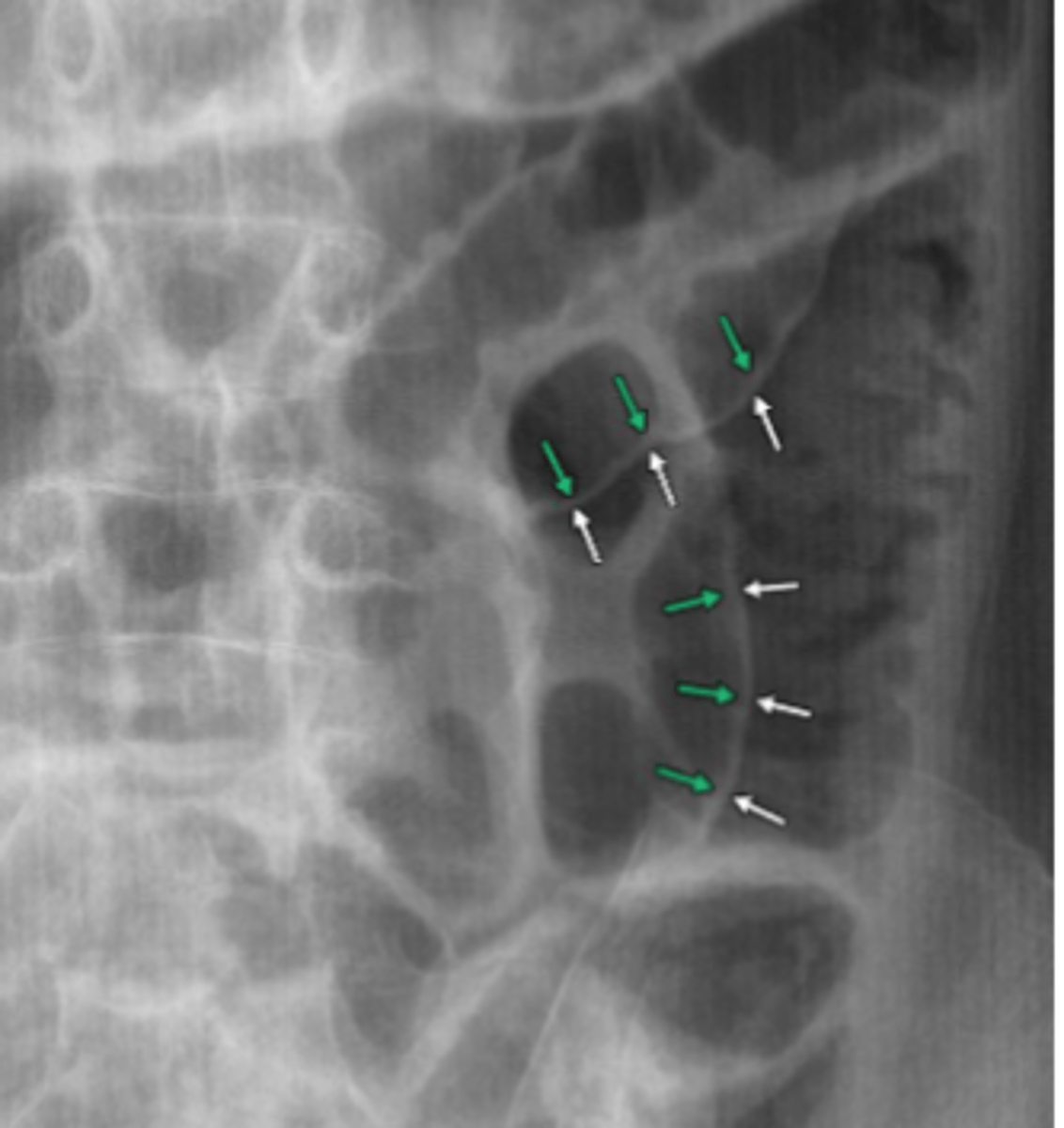
Rigler's sign
ability to see both sides of the bowel wall. Requires a large amount of air to present in order to visualize.
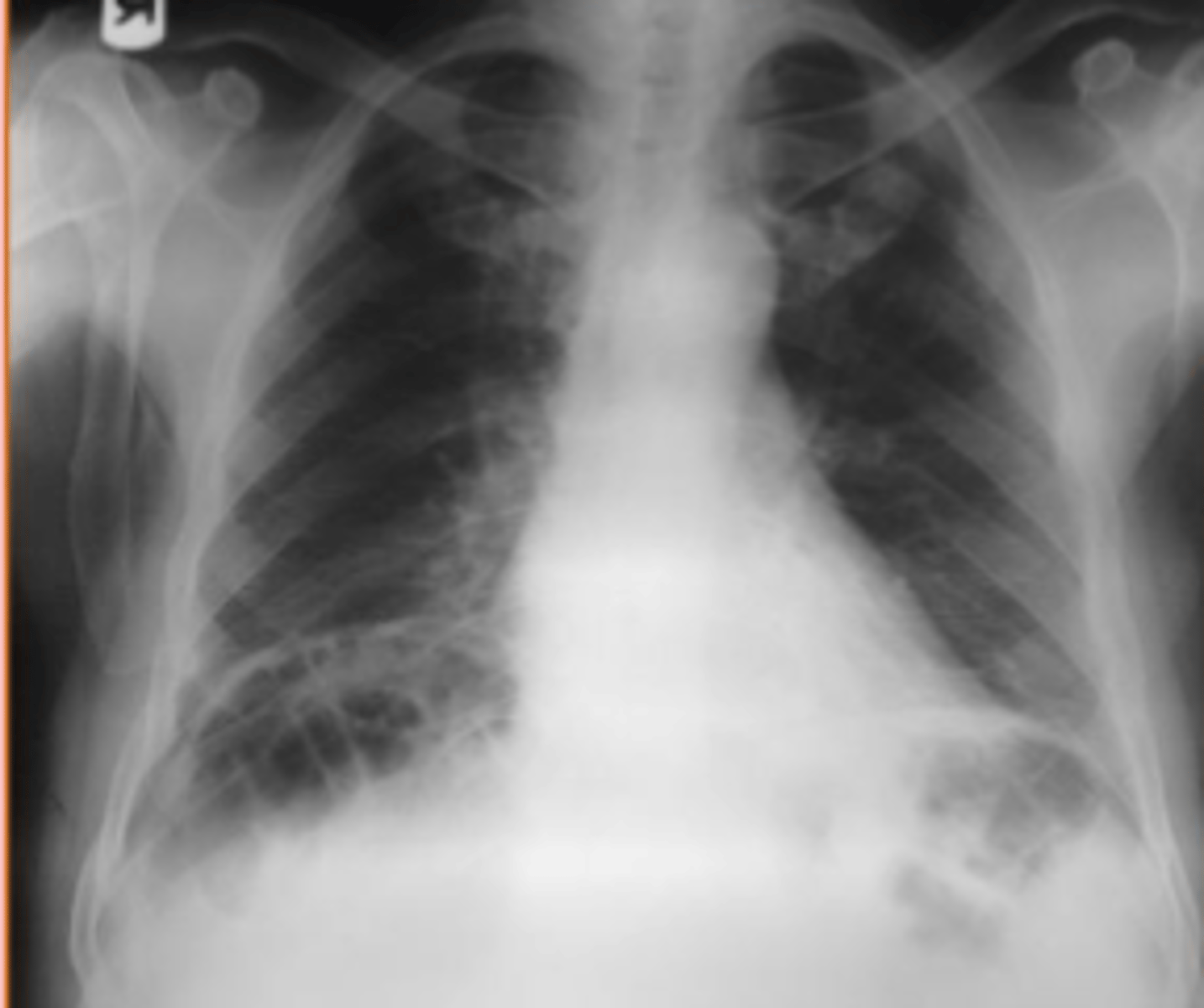
Chilaiditi's Syndrome
asymptomatic interposition of the bowel between the liver and the right hemidiaphragm. Usually an incidental findings that may look like pneumoperitoneum.
Chilaiditi's syndrome
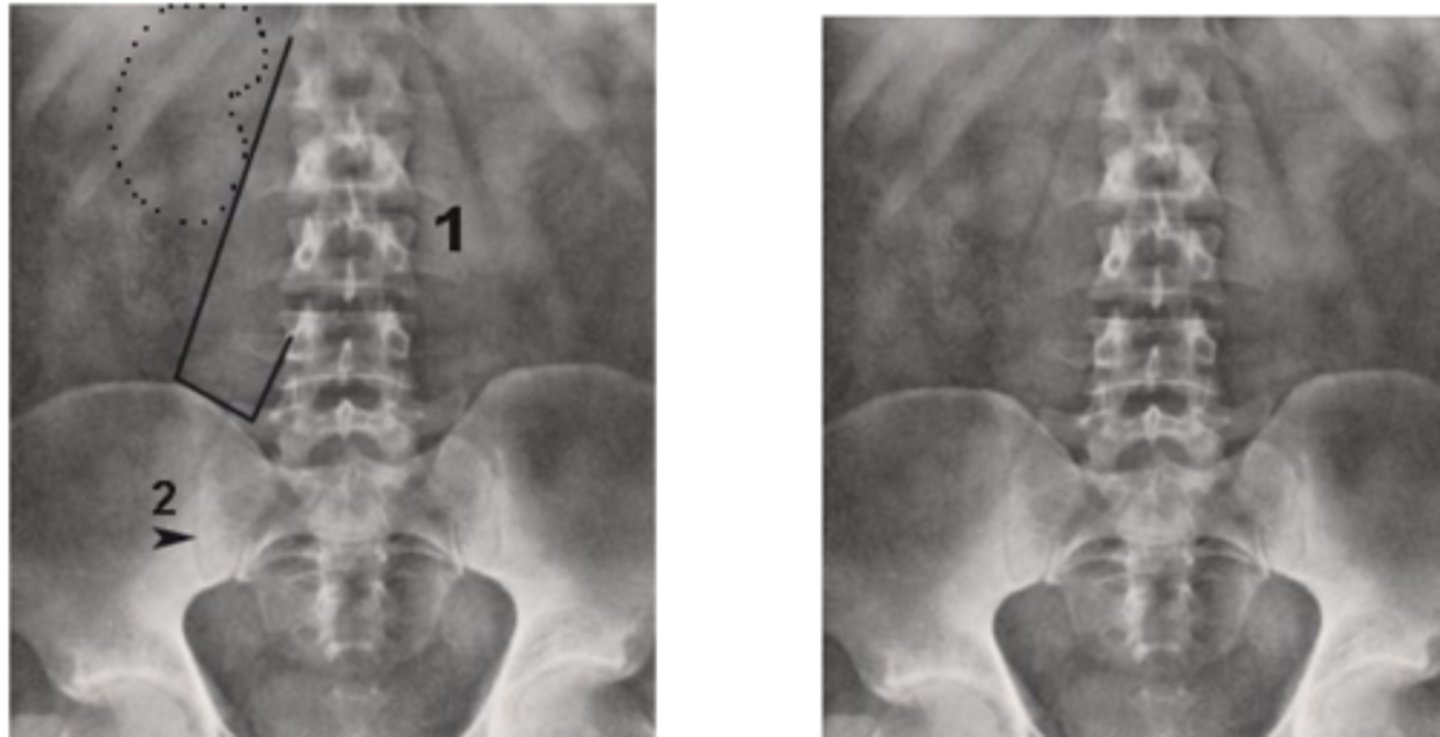
Psoas
muscle that is almost always seen on AXR when exposure is technically adequate.
Psoas muscle
Liver
soft tissue structure that normally displaces all bowel gas from the RUQ
12th rib
the spleen usually doesn't project below the _____
4 lumbar vertebrae
the kidneys are approximately the height of ______
uterus
____ if seen sits on top of and may indent the bladder. It is often not seen on plain films.
Prostate
___ sits deep in the pelvis, usually only seen if calcified.
Splenomegaly
bladder
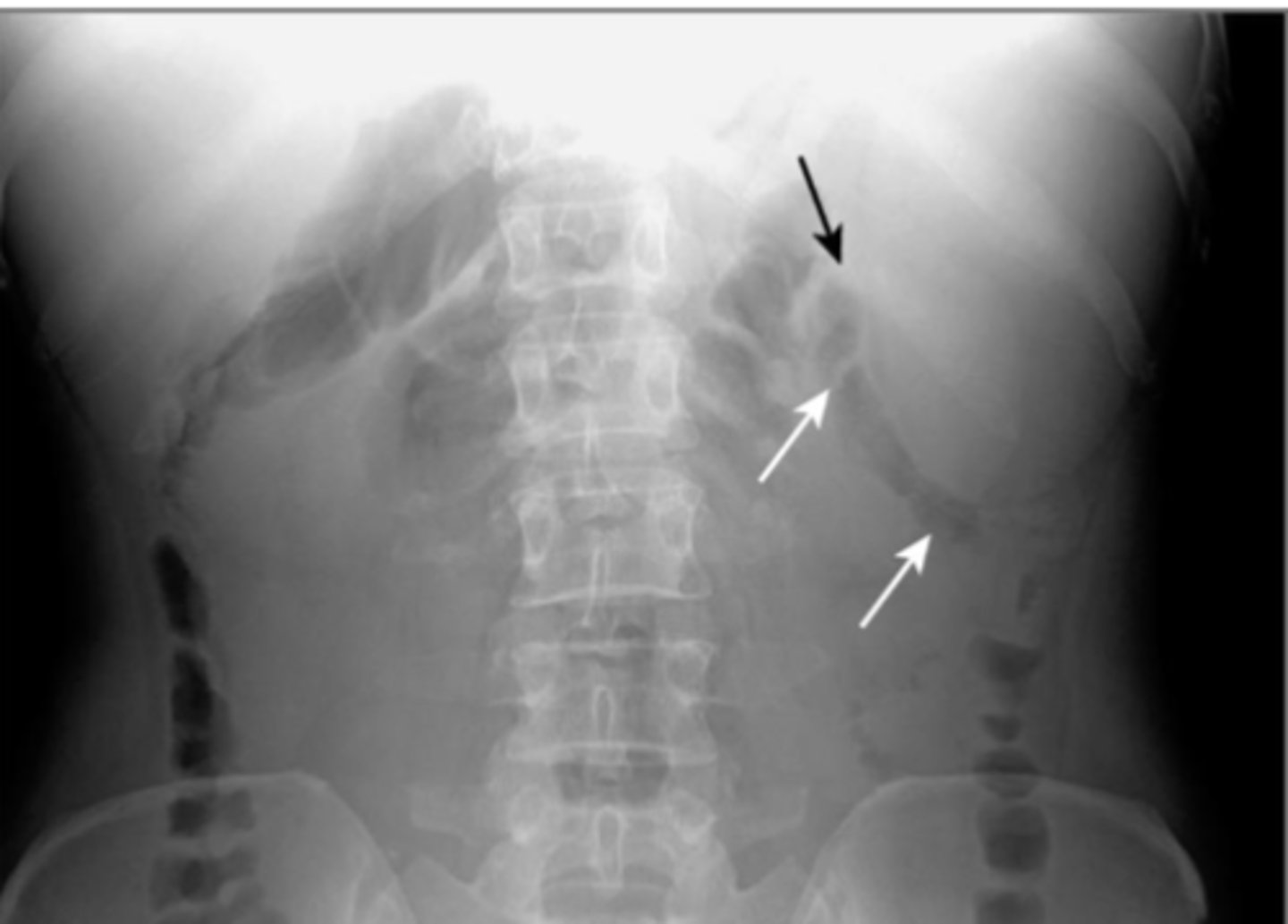
Phleboliths
normal findings
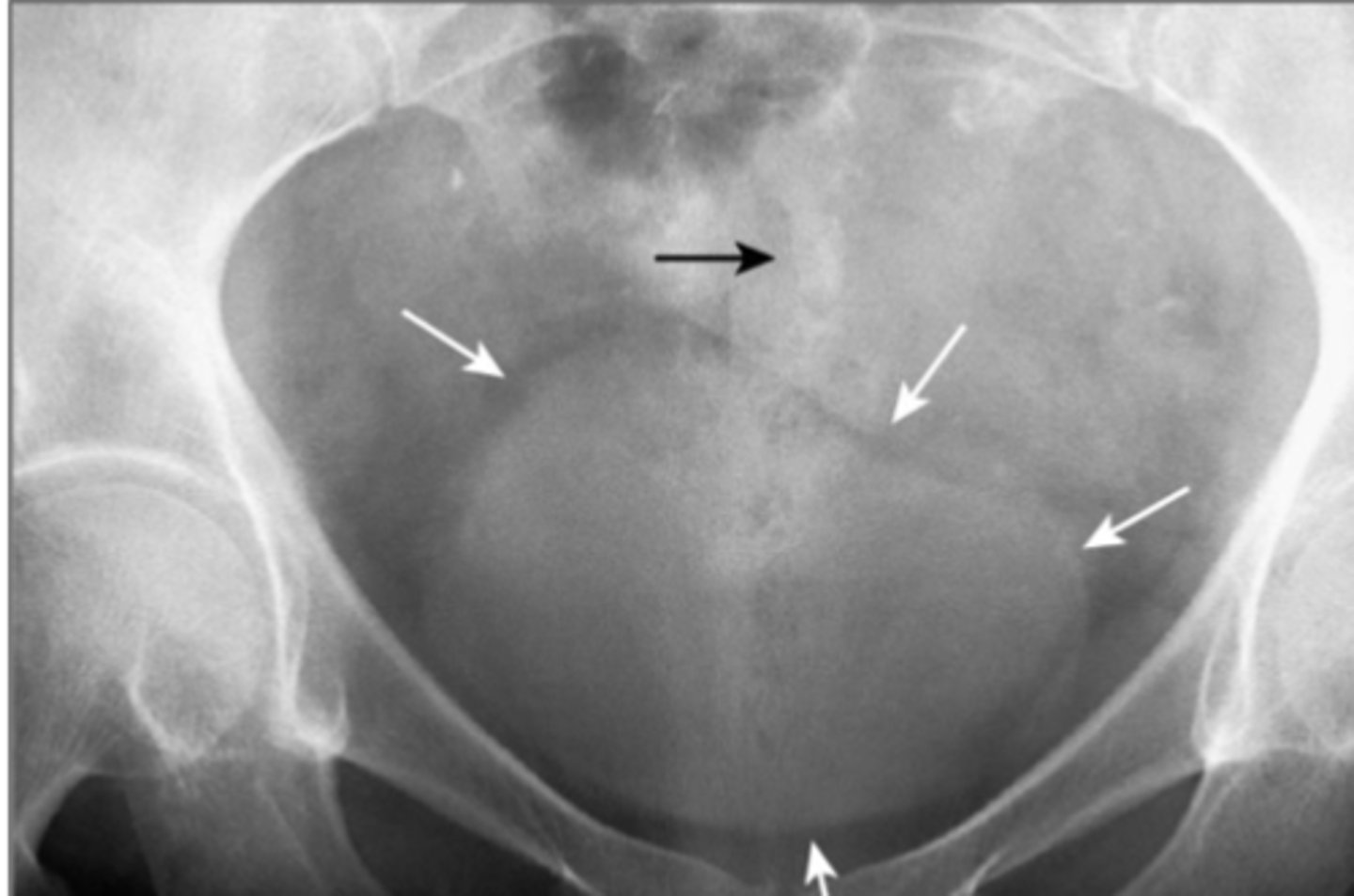
Calcified mesenteric Lymph nodes
normal finding
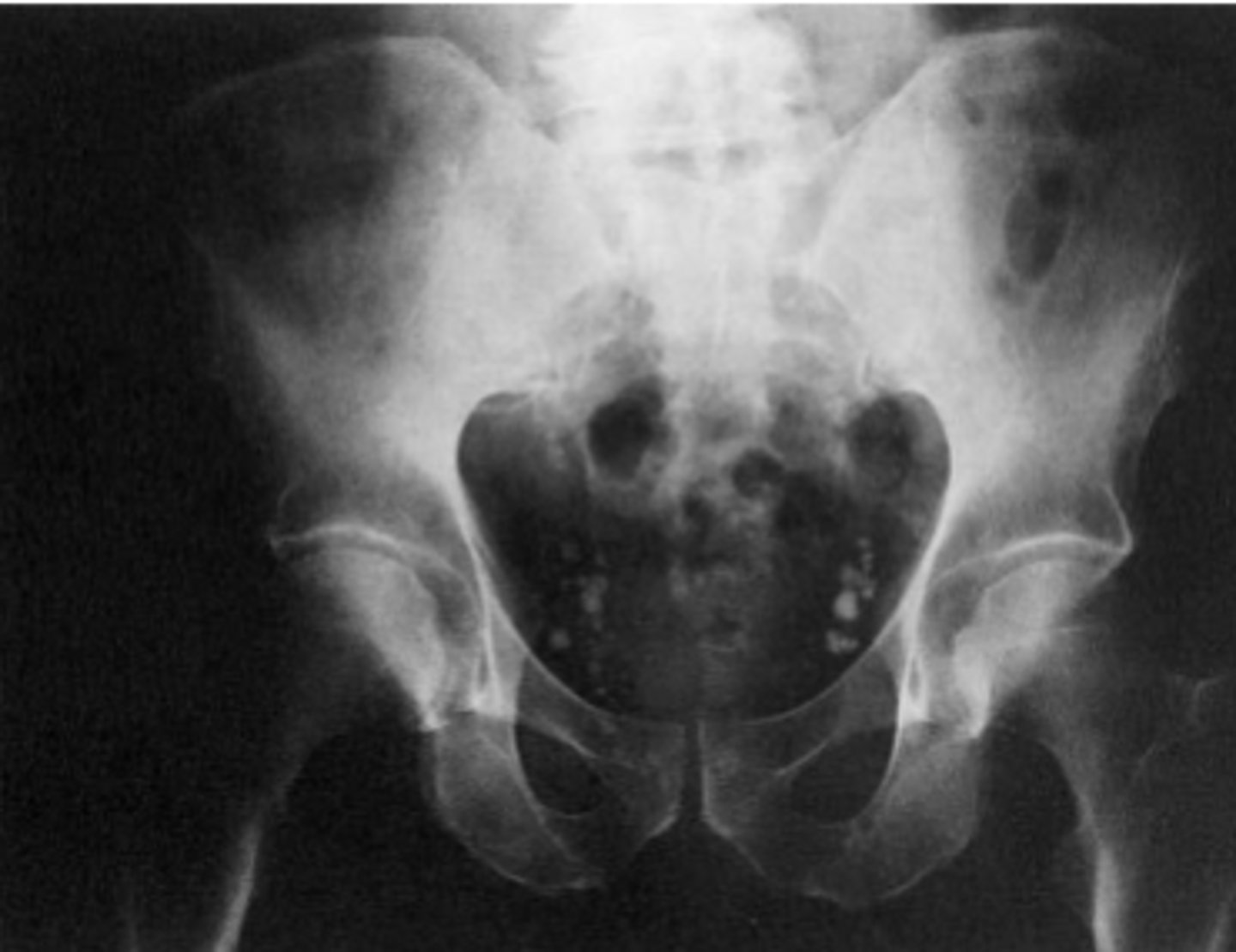
Costal cartilage, phleboliths, prostate gland, mesenteric lymph nodes
normal calcifications that can be seen on AXR
Abnormal calcifications
finding on AXR that can indicate underlying pathology. Can actually be pathology themselves.
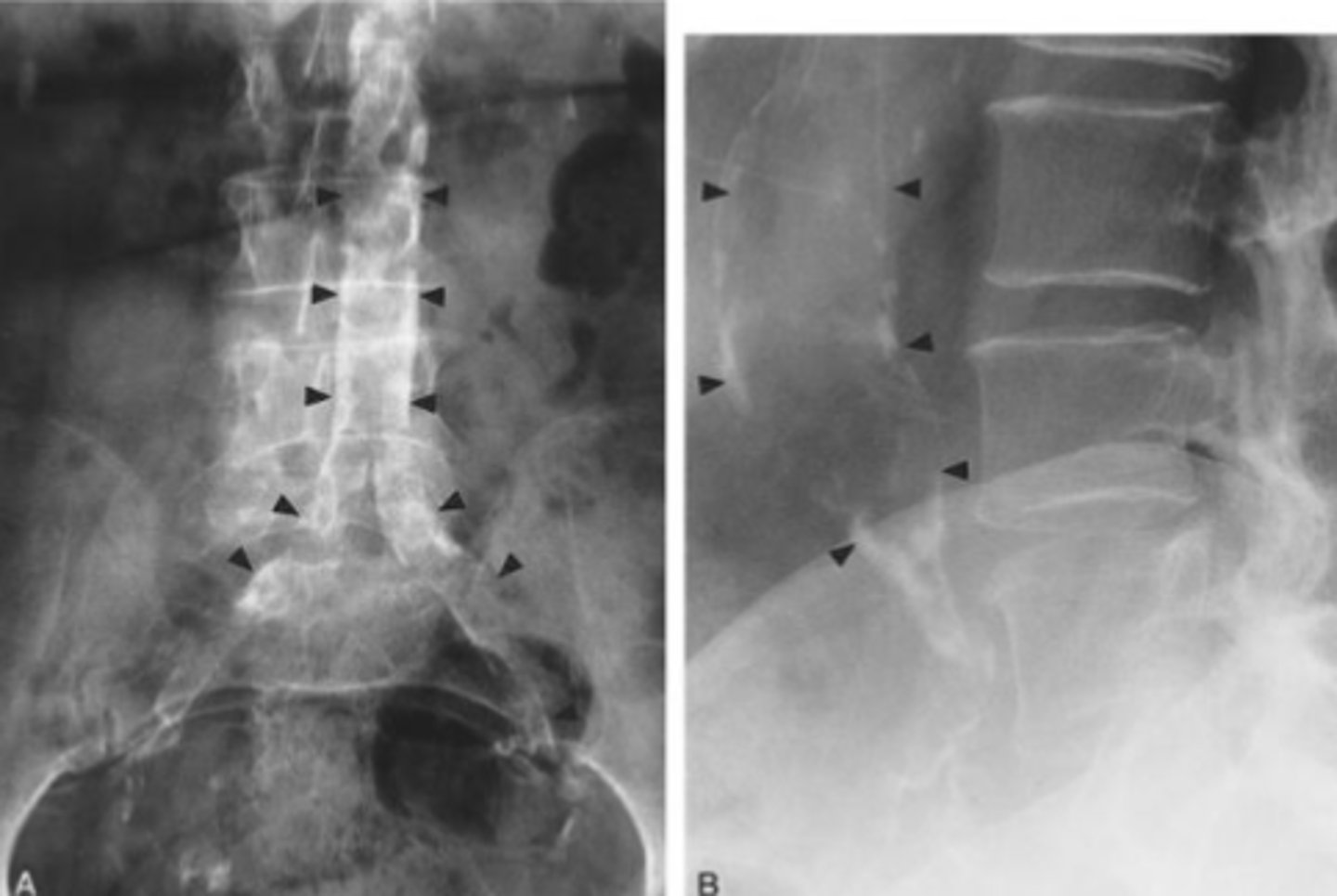
- Rimlike (AAA, porcelain GB)
- Linear
- Lamellar (renal calculi, gallstones)
- Cloudlike/popcorn (Chronic pancreatitis, uterine fibroids)
Patterns of Calcifications on AXR...
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
Ultrasound
the study of choice when asymptomatic pulsatile abdominal mass is palpated.
CT scan
defines the absolute size of AAA, extent of mural thrombus and presence of dissection.
Porcelain Gallbladder
inflammatory scarring of the wall of the gallbladder, along with dystrophic calcification within the wall. Increased incidence of GB cancer.
Porcelain gallbladder
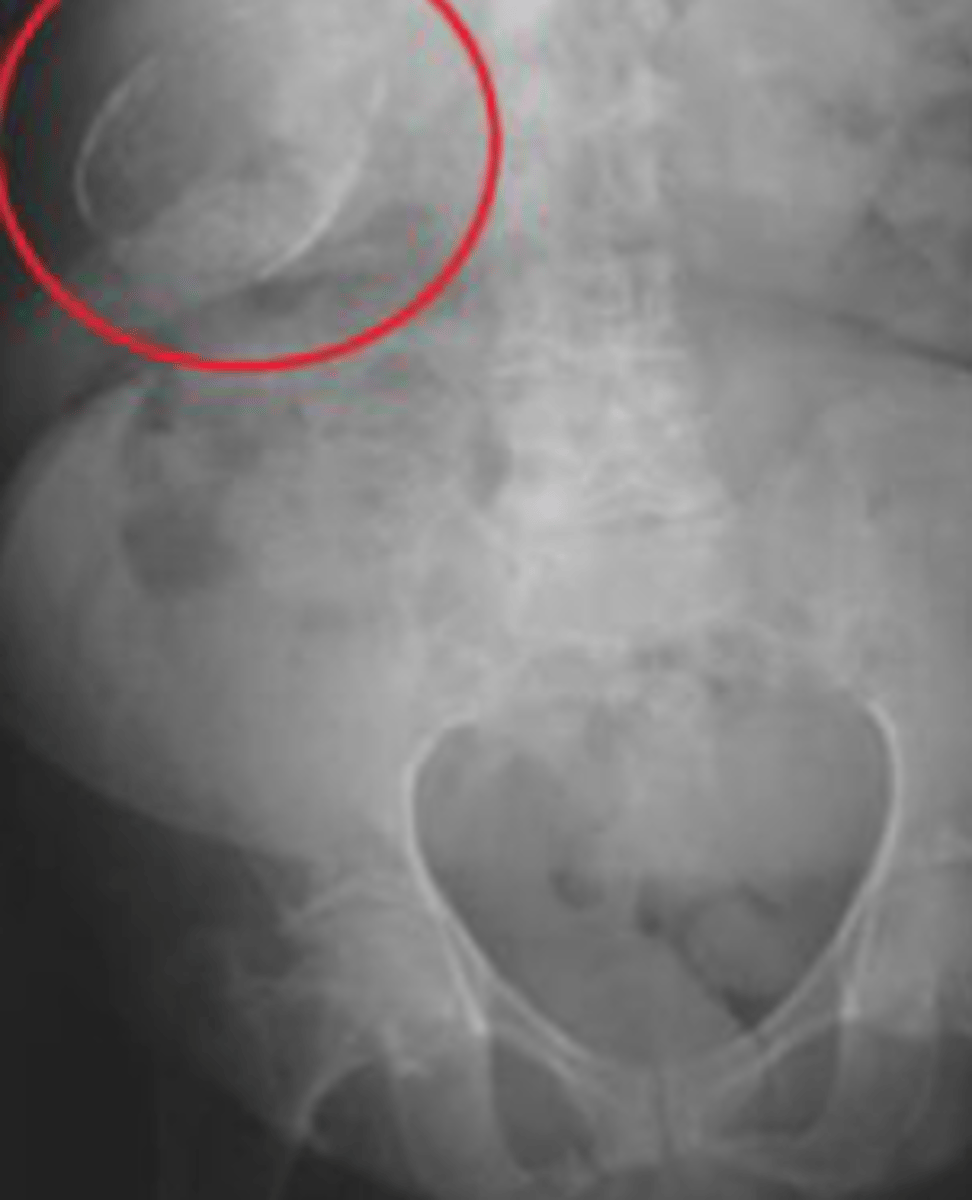
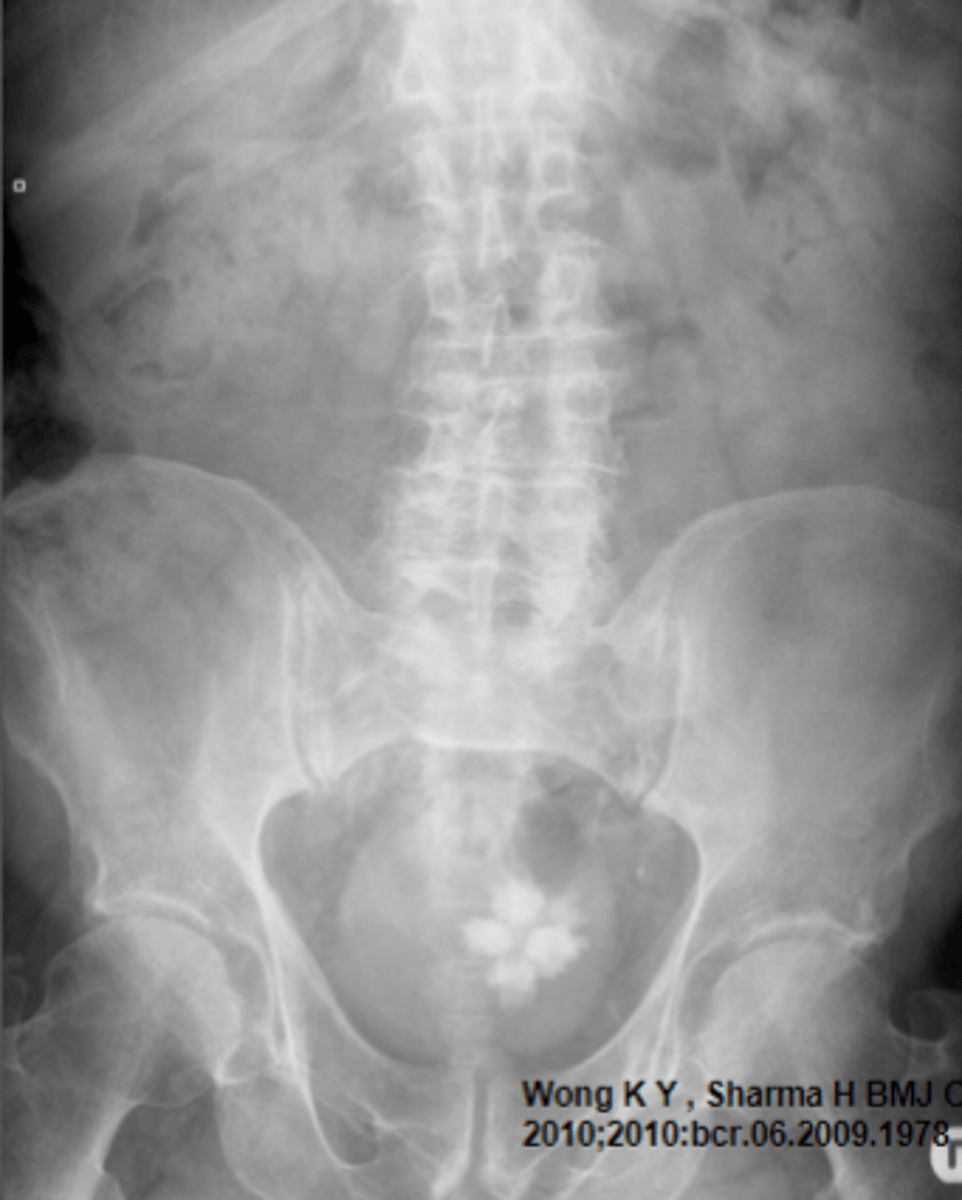
Bladder calculi
gallstones
gallstones on CT scan
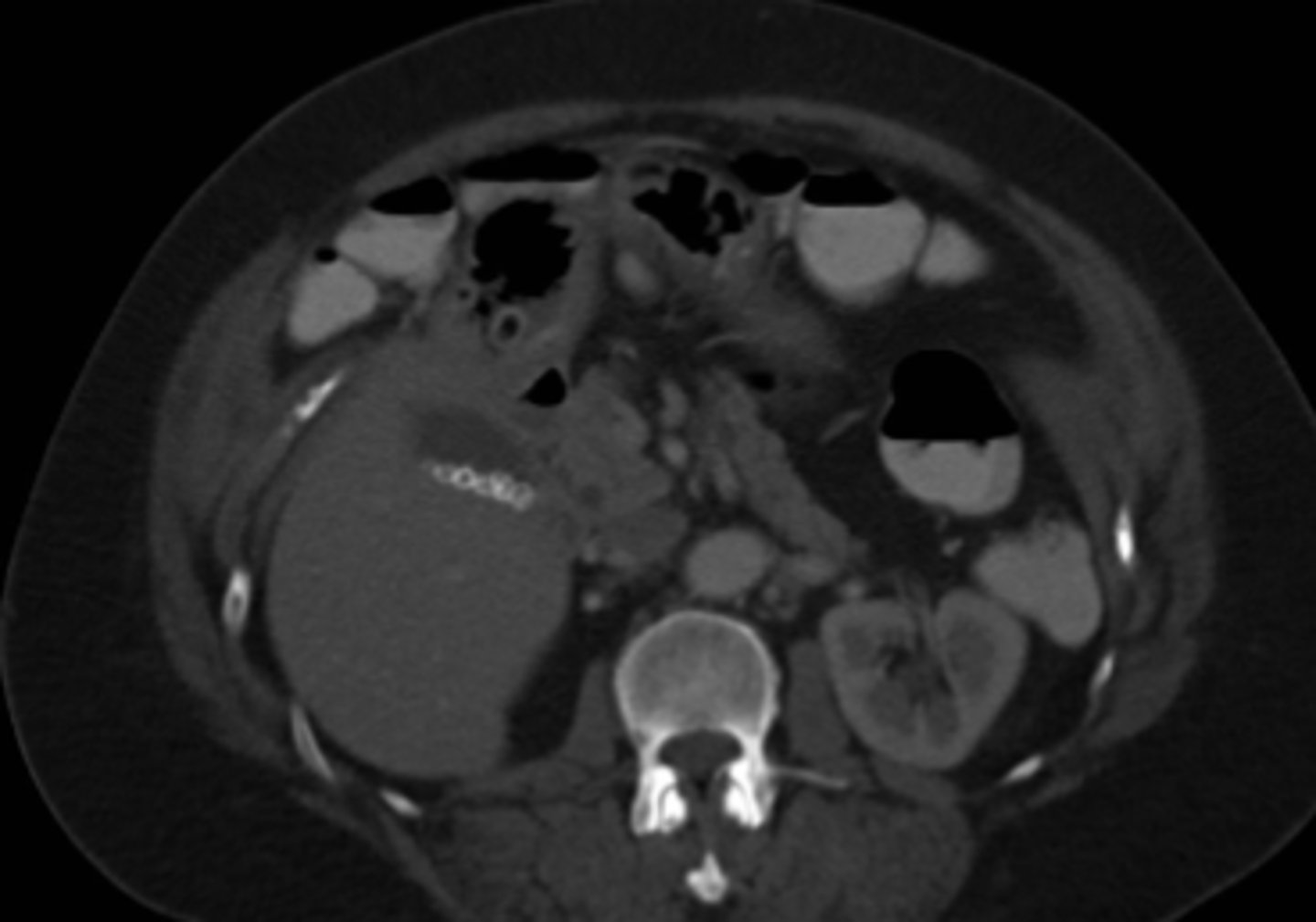
nephrolithiasis
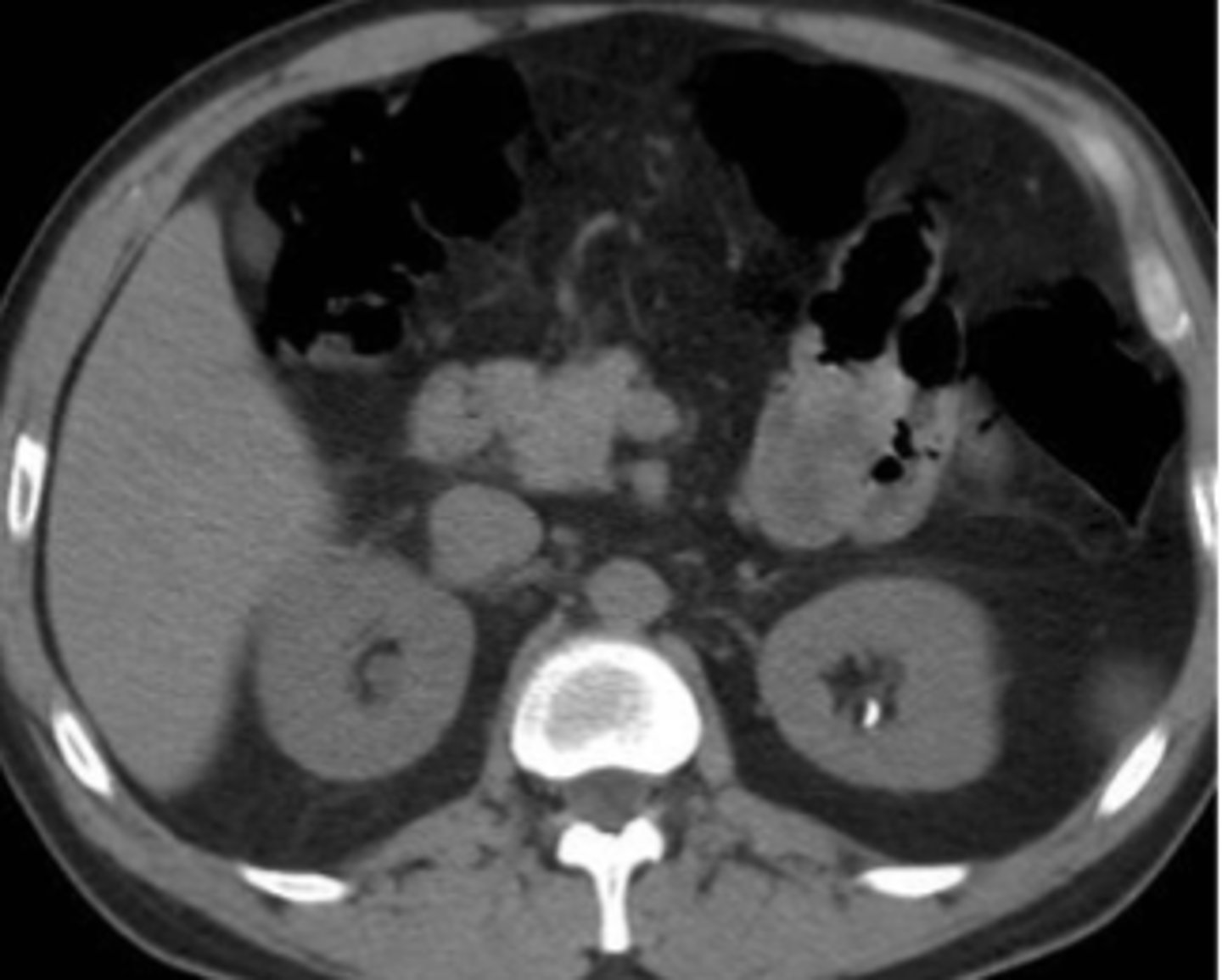
nephrolithiasis on CT scan
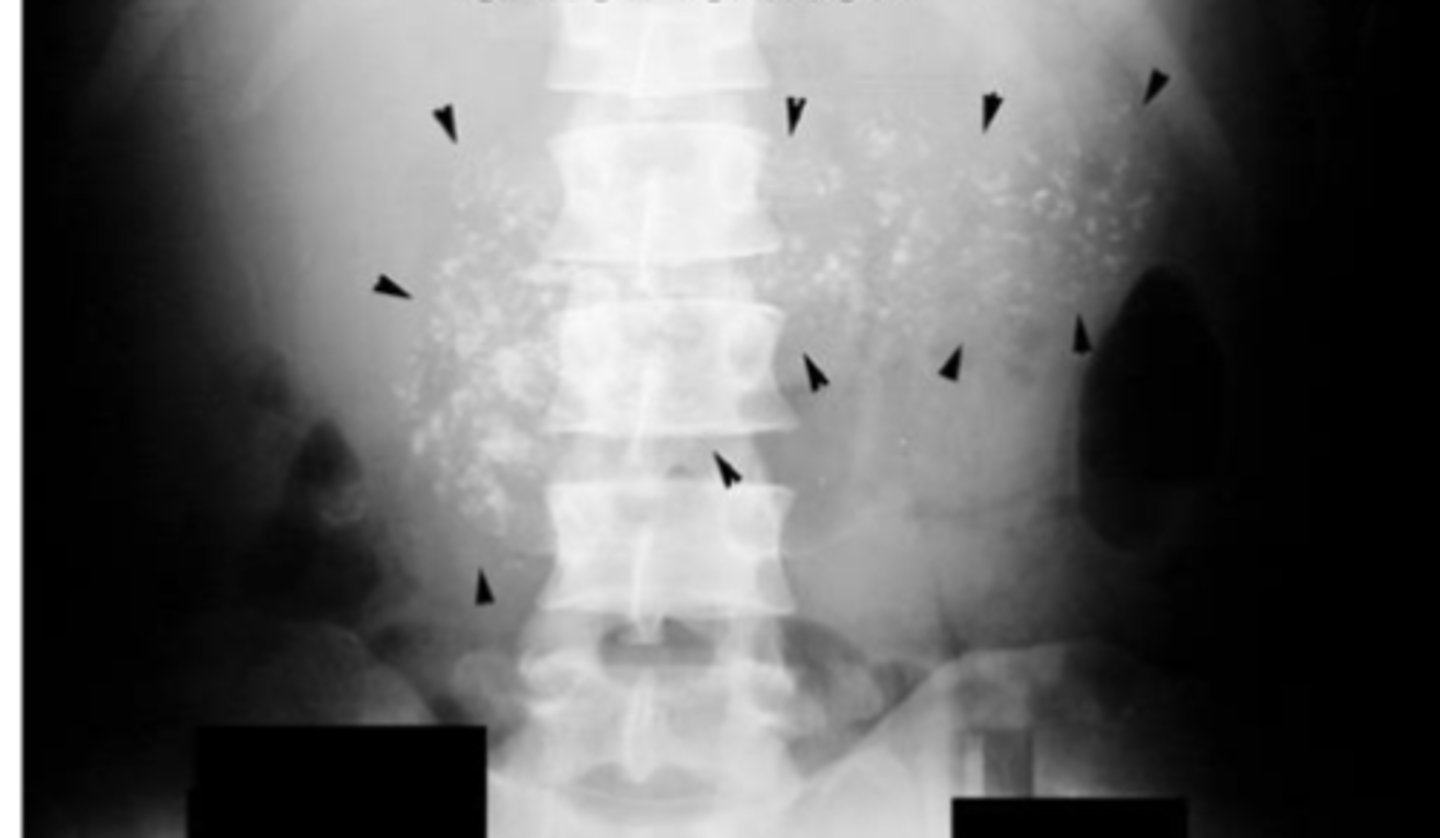
chronic pancreatitis
- feces
- iatrogenic (surgical clips, IUDs, stents)
- Accidental (bullets, per rectum objects)
- Projectional findings (pajama buttons, coins, body piercings)
Incidental findings on AXR include...
stool
fluffy mid-density material throughout the abdomen, multiple small bubbles of gas, mottled appearance.
stool
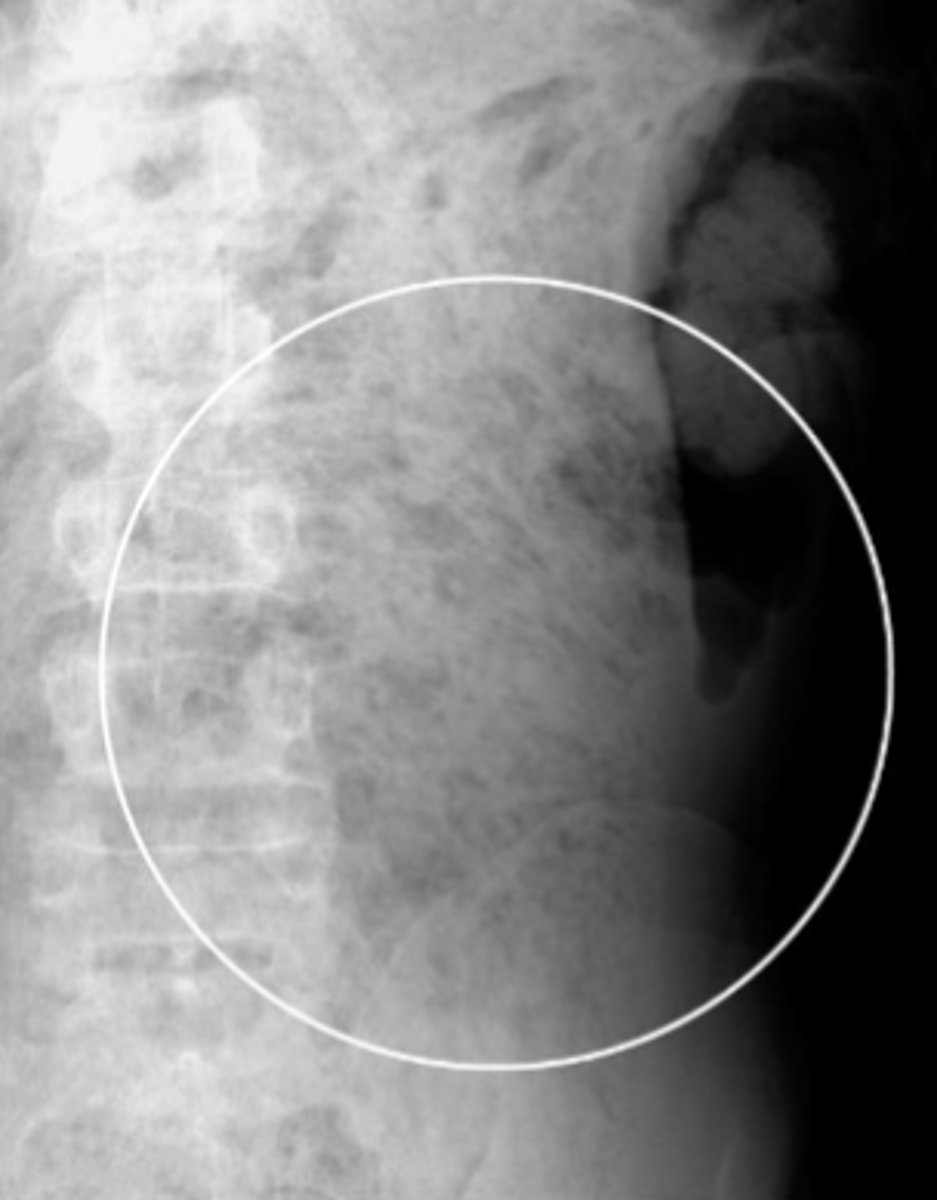
stool
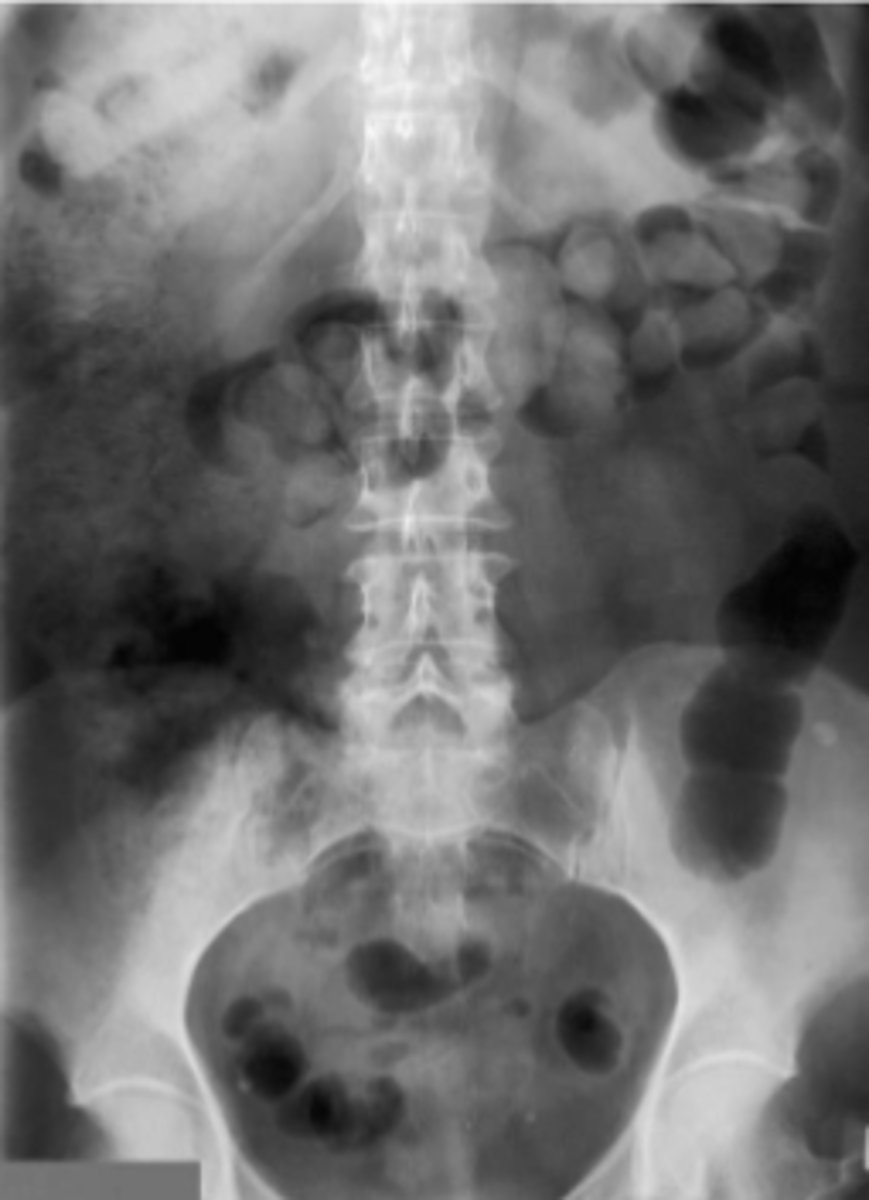
constipation
lots of stool backed up