AP psych terms (U1-U3)
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms

Humanism
Focus on personal growth & potential
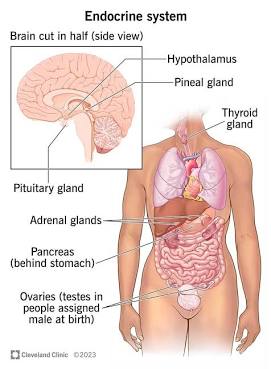
Endocrine system
Hormone producing glands
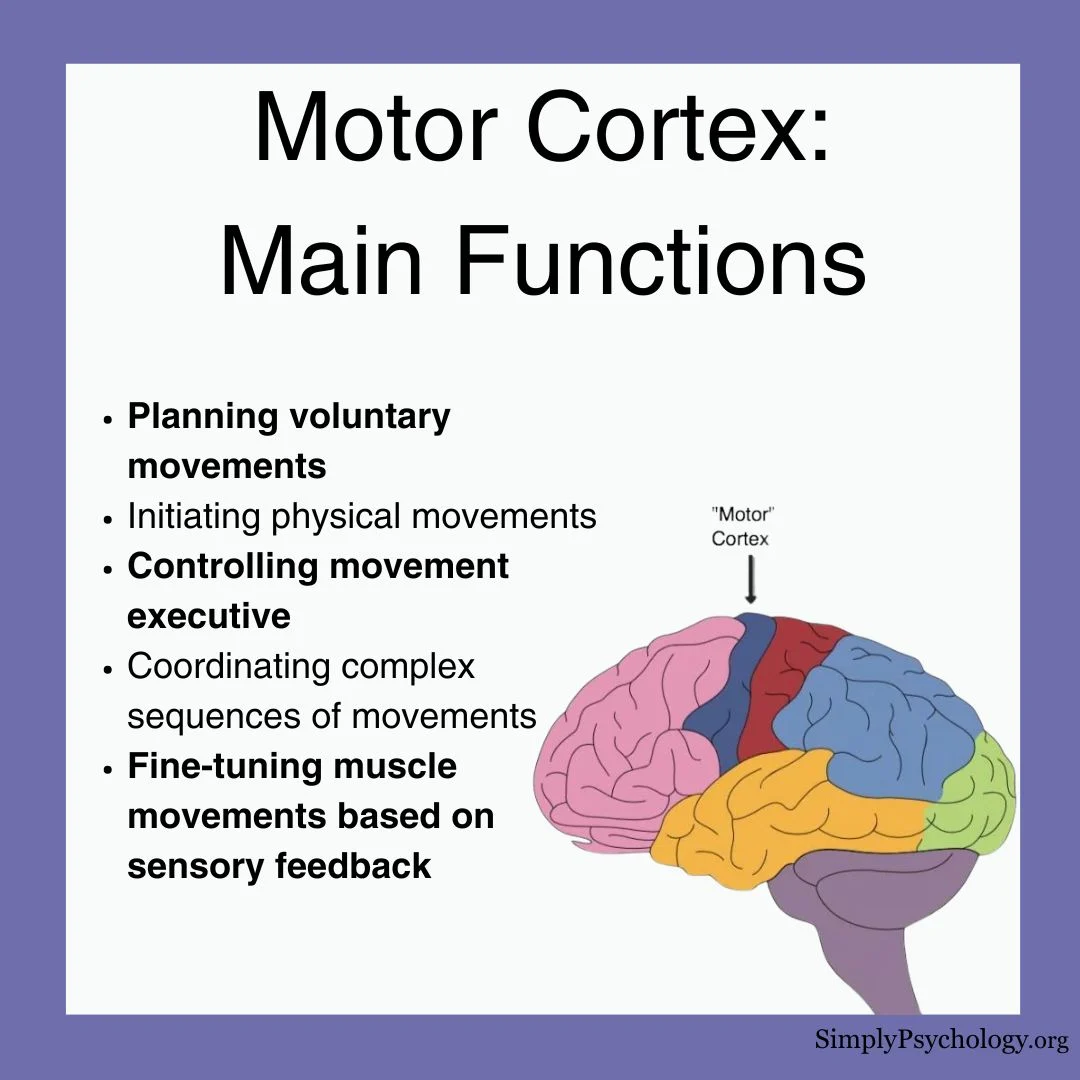
motor cortex
Controls voluntary movements
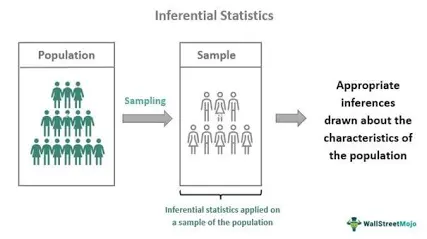
Inferential statistics
Drawing conclusions from data

Hindsight bias
I knew it all along effect
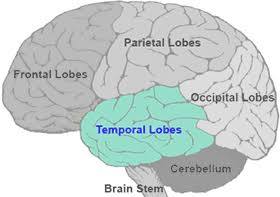
Temporal lobe
hearing, memory, language comprehension

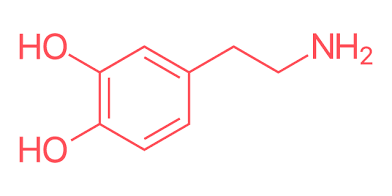
Dopamine
reward, motivation, pleasure, movement
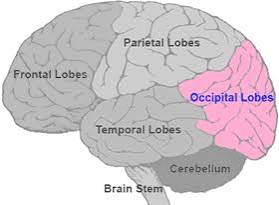
Occipital lobe
Processing visual information

Behaviorism
Study observable behavior only (Watson Skinner)
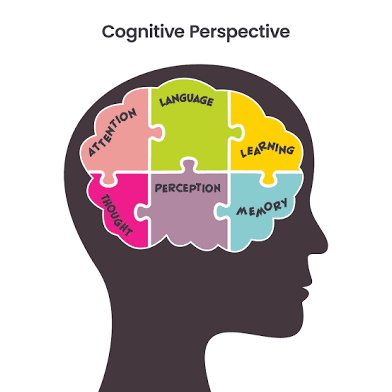
Cognitive psych
How we think know remember
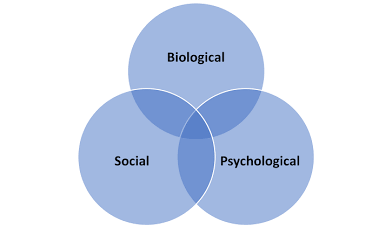
Biopsychological
Mix of biology, psychology, social factors

Glutamate
Prepares nuerons for memory (formation/processing)
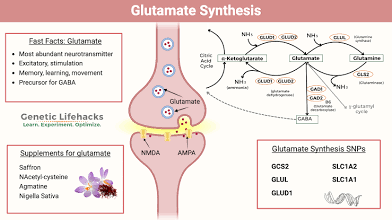

GABA
Quiets neural activity

Functionalism
How mental processes help us adapt (James)
Hypothesis
Testable prediction

Operational Definition
How you measure a variable
Random assignment
Assign to groups by chance
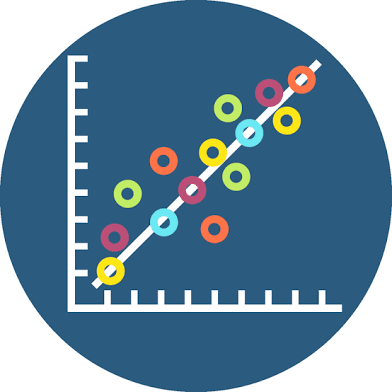
Correlation
How two things relate

Placebo effect
Thinking something works makes you feel good
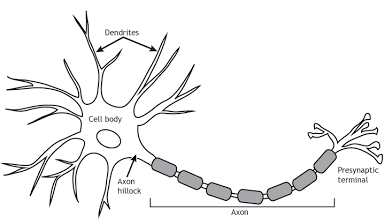
Neuron
Nerve cell
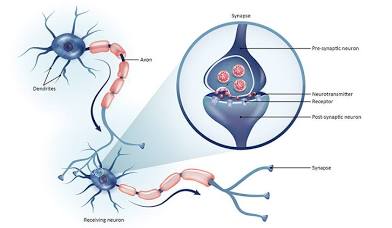
Synapse
Gap between two neurons (where messages are passed)
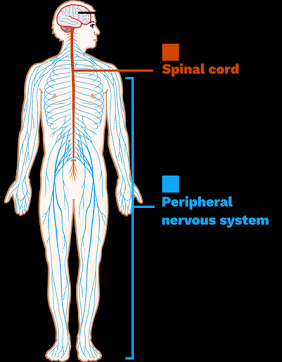
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain + spinal cord.
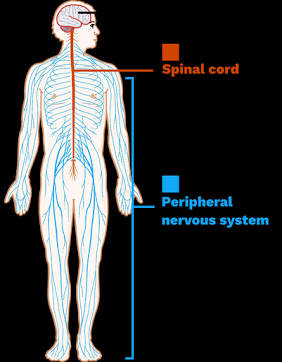
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
– All the nerves outside the CNS.
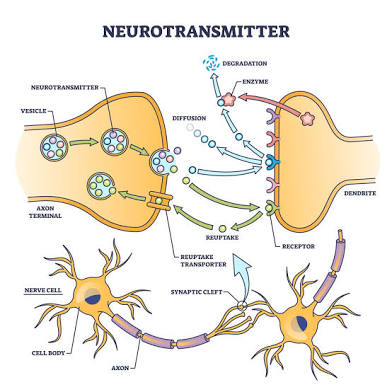
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers: serotonin and dopamine
plasticity
Brain can change and organize
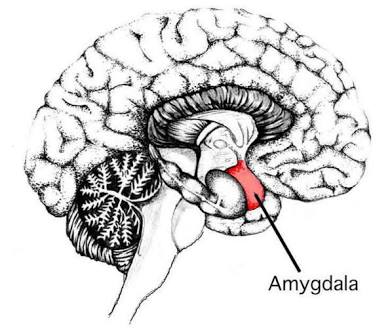
Amygdala
Fear and emotion
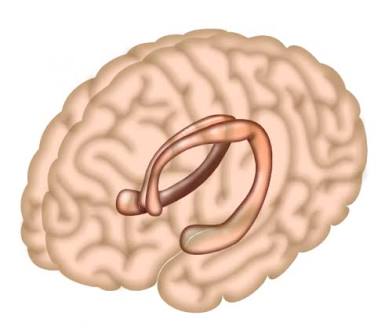
Hippocampus
Memory
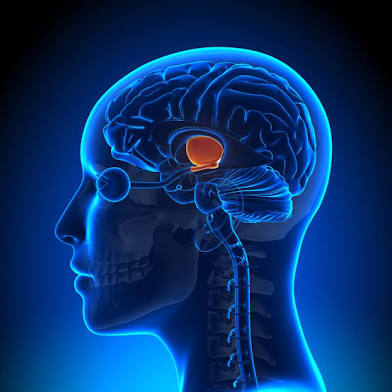
Hypothalamus
Hunger thirst temp sex drive
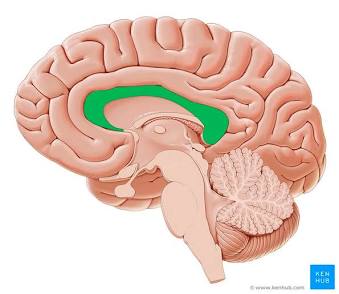
Corpus Callosum
Connects brain hemispheres
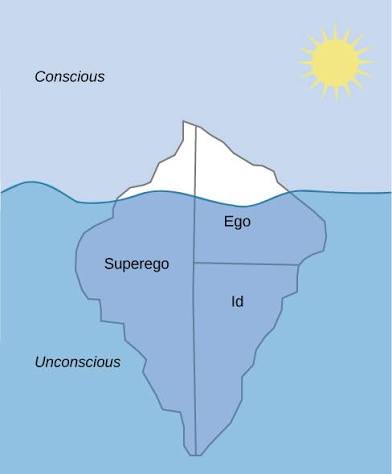
Psychodynamic
Behavior = unconscious drives + early childhood. Freuds playground.
Independent variable
The thing you change in an experiment
Dependent variable
The result you measure in an experiment
Control group
group with no real treatment used for comparison
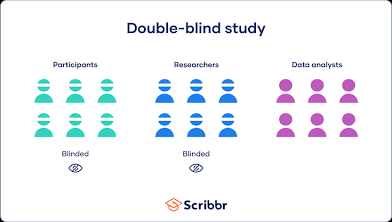
double blind procedure
Participants nor researchers know who’s in which experiment group- prevents bias

Endorphins
Natural painkillers brain releases during stress or exercise
Medulla aka brain stem
Controls heart beatbreathing- basic survival functions
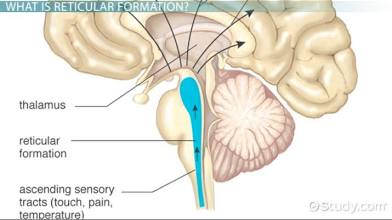
Reticular formations
Keeps you alert + awake. Damage of this = coma
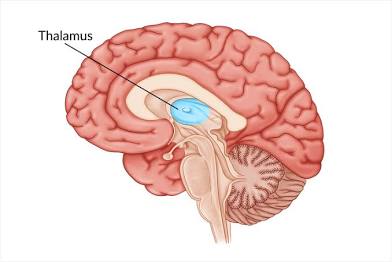
Thalamus
routes info to right parts of brain. All senses go here first

Myelin Sheath
Fatty layer around axons- speeds up neural messages
Psychology
science of behavior and mental processes
Nature vs. Nurture
Are we more shaped by genetics (nature) or experience (nurture)?

Case Study
Studying one person or group deeply.
Confounding Variable
Something else that could affect the outcome.

Experiment
A test to find cause and effect.

Naturalistic Observation
Watching behavior without interfering.

Survey
A quick way to collect data by asking questions
Axon
a long fiber on a neuron: sends messages to other neurons muscles
Dendrites
Branches on a neuron that receive messages.

Frontal lobe
CEO of brain= plans and makes conditions

Operant conditioning
Learning by action and consequences (reward or punishment)
Spinal reflex
Super fast body reaction without waiting for brain (auto pilot)
Absolute Threshold
Smallest signal your body can detect
Selective attention
Focusing on one thing and ignoring the others
Scatterplot
Graph showing how two variables relate

Willhelm Wundt
Father of psychology started first lab in 1879

B.F Skinner
Contributed to operant conditioning
William James
Studied purpose of mind and behavior: birthed functionalism
Sympathetic Nervous system
Speeds body up for fight/ flight
Para sympathetic
Calms body down rest/ digest
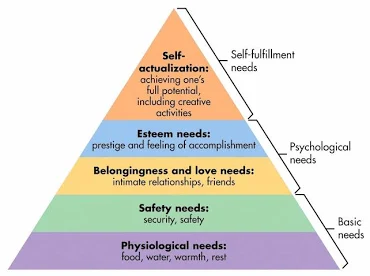
Hierarchy of needs
Needs that motivate people

John B. Watson
Founder of behaviorism
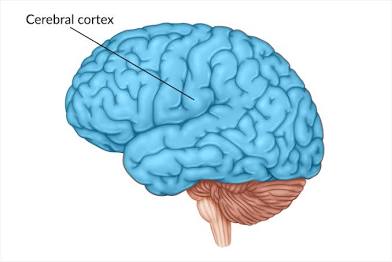
Cerebral cortex
Outer brain level for high level thinking
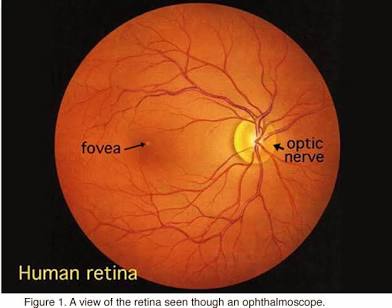
Retina
Back of eye that senses light
Cones
See color, works best in light
Transduction
Changing sensory input to brain signals

Sigmund Freud
Psychologist who developed psychoanalytic field
Psychoanalysis
Freud’s theory about unconscious thoughts shaping behavior.
Unconscious mind
Hidden thoughts and feelings that influence you without awareness.

Psychologist
Studies behavior/mental processes

Psychiatrist
Medical doctor who diagnoses mental illness and prescribes meds.

Therapist/counselor
Talks with people to help mental health and emotions.
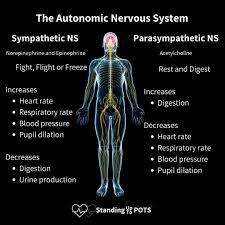
Automatic nervous system
Para sympathetic vs sympathetic
Variable
The thing that changes