Lab 6: Green Algae and Seedless Plant Diversity
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Green Algae
A group of photosynthetic organisms that are not land plants, eukaryotic, most are protists, contain chlorophyll for photosynthesis, can be uni or multicellular, primarily aquatic, and fall into the charophyte group.
Plants
Photosynthetic organisms that have complex tissues evolved for living on land that are eukaryotic, photosynthetic, multicellular, and primarily terrestrial
Plants and Green Algae
Primary producers and autotrophs
Challenges preventing desiccation
Protective cuticle(waxy covering)
Challenge: support for body
Vascular tissues(roots absorb water and minerals, green shoots conduct photosynthesis)
Challenge: gas exchange
Stomata
Challenge: fertilization of gametes
Gametangia (protective gamete housing, antheridia for sperm and archegonia for eggs)
Diploid multicellular stage
Sporophyte generation
Haploid multicellular stage
Gametophyte generation
Sporophyte (2n)
A spore(n)is a haploid cell for asexual reproduction and a sporangium is the location of spore production in meiosis
Gametophyte(n)
Gametangia is the location of spore production by meiosis, antheridium(n) is the location of sperm production, and archegonium(n) is the location of egg production
Evidence chlarophytes are the closest relatives to terrestrial plants
Similar mechanisms for forming cell plates, similar nuclear and chloroplast genes, cell walls with high cellulose concentration, flagellated sperm similar to land plants, and the genus chara produce gametes within gametangia which was a key feature that allowed plants to colonize dry land.
Genus Spirogyra
Are haploid(n) and reproduce asexually under normal conditions, use sexual reproduction under deteriorated conditions via conjugation resulting in a zygospore(2n) with a thick coat
Conjugative filament phases
a) vegetative filament(n)
b) formation of conjugation tubes
c) gamete(n) from a filament migrate to the other
d)fusion of two gametes form a zygospore(2n)
Genus Chara
Reproduce via archegonium(contain eggs) and antheridium(contain sperm)
Bryophytes(mosses)
Seedless plants, reproduce with spores, earliest land plants, most abundant plant until 285 MYA, and many species are adapted to grow on rocks
Non vascular Bryophytes
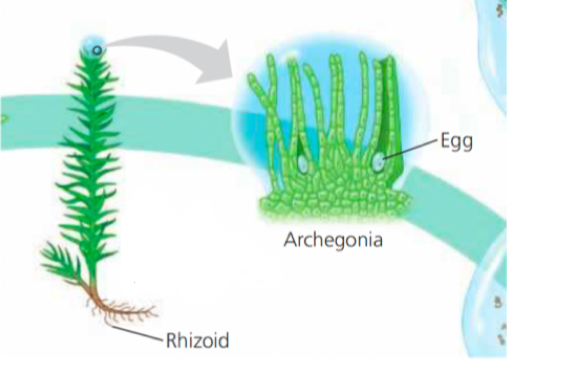
Rely on diffusion and osmosis, anchored to rocks by rhizoids, gametophyte(n) is the dominant generation, depending on on gametophytes for energy and nutrition
Moss antheridium are located
At the top of the gametophyte(n) and contain sperm inside
Moss archegonium are located
At the top of the gametophyteand contain eggs inside
Moss capsule
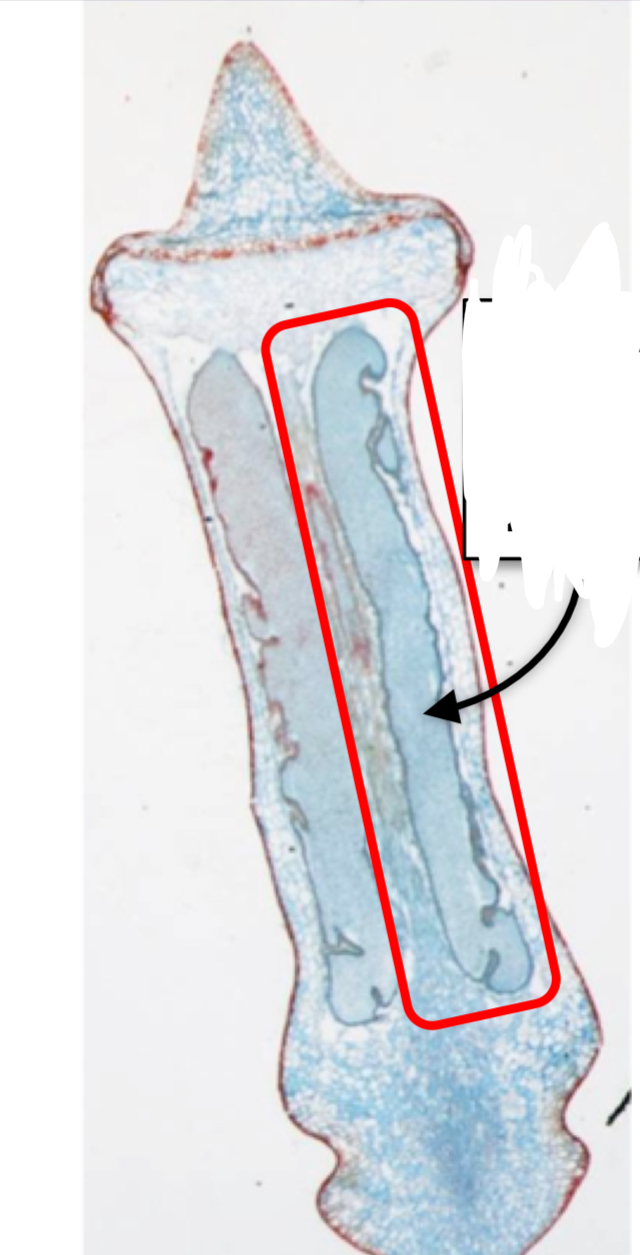
Located at the top of the sporophyte(2n) and contains sporangium(2n)
Sporangium
2n
Spores
N
Ferns
Seedless vascular plants(contain roots, leaves, and stems, dominant generation is sporophyte(2n), both generations are free willing(neither depend on the other)
Gametophytes in ferns are
Reduced or smaller
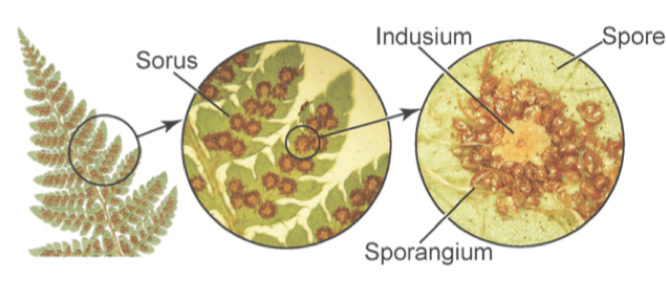
What is on the underside of Fern fronds(leaves)
Sori
Sori
Contain sporangia where meiosis takes place to produce spores
Fern gametophyte contain
Male and female Gametangia
Both fern and moss sperm
Require a little bit of water to swim to the egg
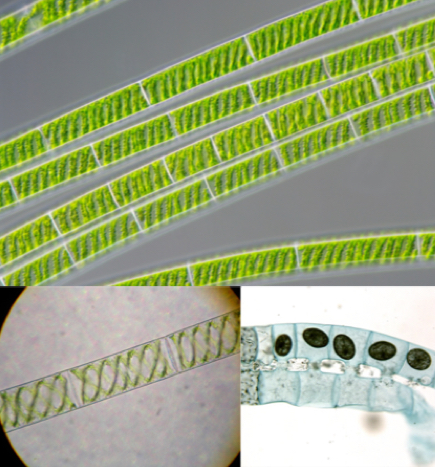
What is this
Spirogyra
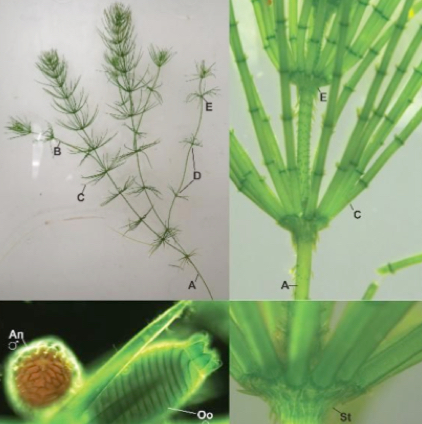

What is this
Chara
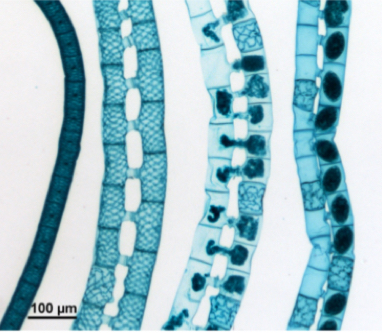
What is this
Spirogyra sexual reproduction
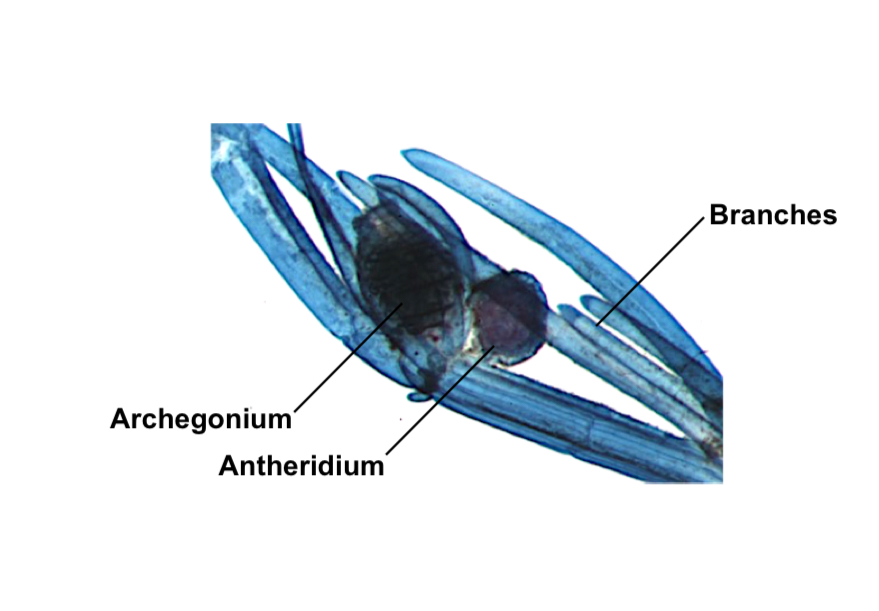
What is this
Chara reproduction
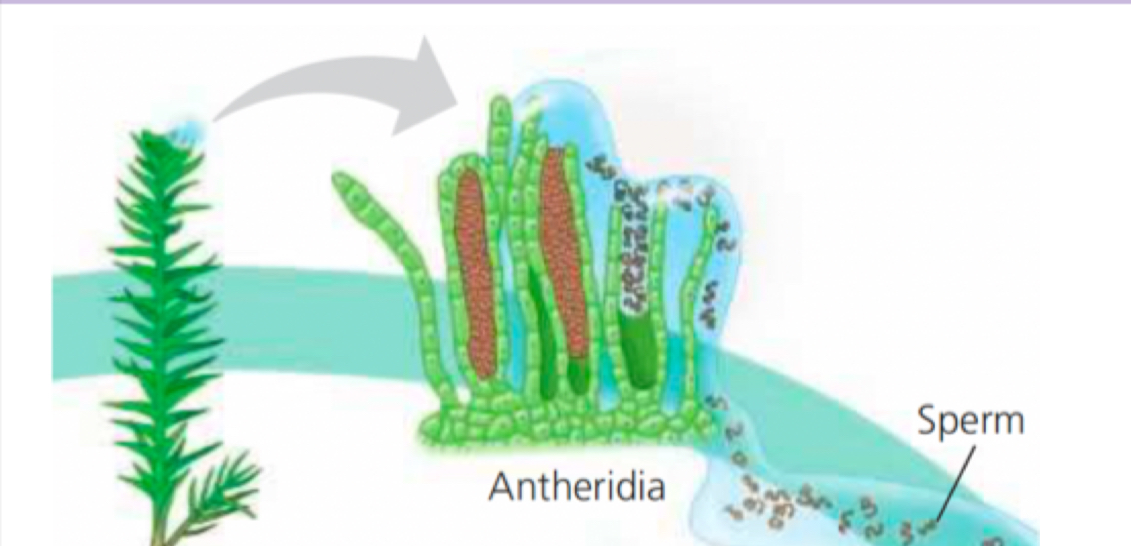
What is this
Male moss gametophyte
What is this
Female moss gametophyte
What is this
Moss capsule
What is a fern leaf
Sporophyte(2n)
What is this
Fern sporophyte
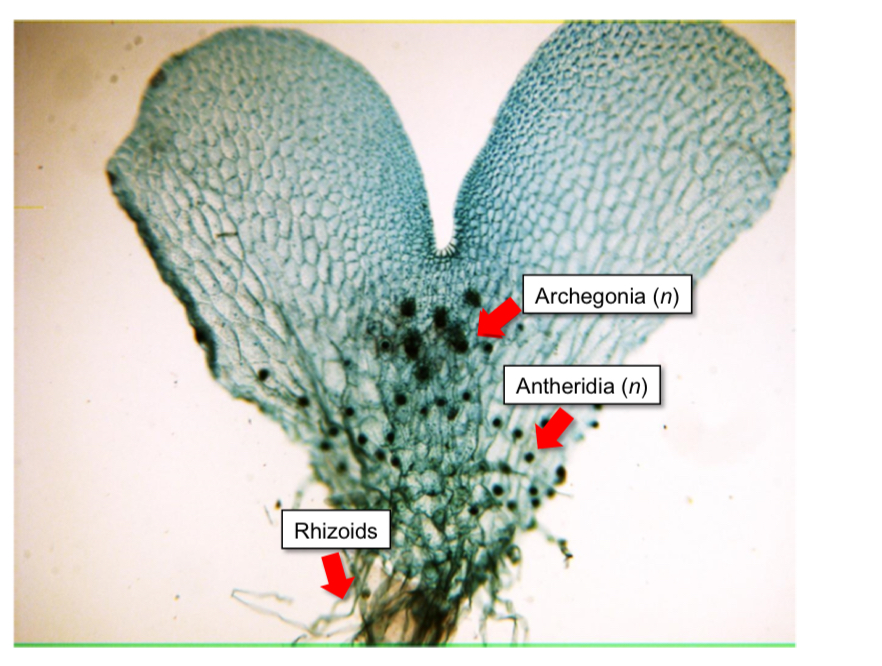
What is this
Fern gametophyte