Sample Collection, Transportation, Submission, Culture & Diagnosis of Bacterial and Fungal Diseases
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
- Clinician: collect and submit appropriate samples accompanied by sp requests or adequate history
- microbiologist: interpret results in relation to info supplied
Responsibilities of clinician and microbiologist in the interpretation of diagnostic results
- does not mean agent is not present
- means org did not grow
Interpreatiation of diagnostic results: negative report
- bacterium was overgrown by contaminants
- bacterium died on way to lab
- animal stopped shedding bacterium before sample was taken
Reasons why org may not grow (3)
- detection of org does not establish diagnosis
- result interpreted in light of: clinical signs, vaccinations, history, and normal flora
- animals may be shedders and org may not necessarily be causative org
Interpretation of diagnostic results: positive report
- Take from the affected site(s) early following onset of clinical signs
• Collect samples from clinical cases and in-contact animals esp if there is an outbreak of disease
• Samples should be taken from the edge of the lesion and include normal tissue
• Collect samples aseptically
• Inform lab whether treatment has started
• As far as possible submit a reasonable amount
• Avoid cross contamination
• Avoid human infs in the case of suspected zoonoses
Principles of sample collection (8)
- fine needle aspiration
- postmortem specimens
- swabs
Collection of specimens containing anaerobic bac
- normally sterile body fluids
- surgical specimens from normally sterile sites
- deep abscess contents taken aseptically
- aspirates from deep wounds
- blood if collected properly
- specimens obtained by specialized procedures (i.e. tracheal aspirations)
Suitable specimens for anaerobic culture (6)
- Foul-smelling discharges
• Deep inf from penetration of cutaneous/mucosal surfaces
• Necrotic tissue, gangrene, pseudomembrane formation
• Gas in tissue or exudate
• Endocarditis with neg blood culture for aerobic bac
• Inf ass with malignancy or other disease-causing tissue destruction and impaired circulation
• Bite wounds
• Deep abscesses
• Septic pleuritis
• Aspiration pneumonia
• Fractures associated with trauma to soft tissue
• Infections following surgery of the gastrointestinal tract
• Septic processes such as pyometra
Clinical conditions suggestive of anaerobic inf
- macroscopic observations
- staining and microscopy (gram stain, dilute carbon rush in stain, and ziehl neelsen stain)
Tech used in direct examination of bacteriological specimens
- immunology and serology (detection of antigens or antibodies) (i.e. ELISA, precipitation, fluorescent antibody testing)
Indirect methods used to ID bac
- high throughput capacity
- rapid
- relatively low cost
- ease of use
- quantitative and qualitative
Advantages of immunology and serology to detect bac (indirect method) (5)
- detection limit for org/antigens with low abundance
- difficulties in generating selective antibodies
Disadvantages of immunology and serology to detect bac (indirect method) (2)
- Polymerase chain rxn (PCR)
- MALDI-TOF MS (matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry)
Molecular methods used to diagnose bac inf (2)
- based in nucleic acid (DNA/RNA) amplification
- amplifies a sp region of DNA within a few hrs
PCR
- conventional
- multiplex
- reverse transcription
- real-time
- microarrays
PCR types (5)
- rapid
- small amounts of sample required
- can detect fastidious in-culturable, slow growing, dangerous pathogens
- high specificity and sensitivity
PCR advantages (4)
- equipment may be expensive
- primers vary in specificity
PCR disadvantages (2)
- research
- diagnostics
- confirmation
- sequencing
PCR applications (4)
- Provides most detail
- unambiguous info
PCR whole genome sequencing: advantages (2)
- expensive
- detection limit for org with low abundance
PCR whole genome sequencing: disadvantages (2)
- high-throughput
- rapid
- gen easily interpretable spectra
- qualitative and quantitative data
- low overall operating costs
MALDI-TOF MS Advantages (5)
- det limit for org with low abundance
- host proteins and normal flora might overlap mass spectra
- high initial investments and maintenance costs
- lacking differentiation of closely related species
MALDI-TOF MS Disadvantages (4)
- sterile instruments
- suitable portions of specimen
- place in indiv polyethylene of leak proof container
- place in sterile screw capped jar
- postmortem mat collected asap after death
- long transport, use transport medium
- abortion: send whole fetus
- pieces of tissue
- pieces of placenta fetal
- abomasal contents (ruminants)
- uterine discharge
Guidelines for bac isolation from selected specimens: Tissues and organs
- fluids preferable to swabs
- greater the volume greater liklihood of det org
- bac susceptible to desiccation esp if collected on dry swab
- short cotton swabs unsatisfactory for nasopharyngeal
specimens of epithelial cells and mucus for the investigation of respiratory diseases of large animals
- Guarded swabs necessary for certain bacteriological examinations where contamination by normal flora may pose problem
Guidelines for bac isolation from selected specimens: stipulations of swab use
- preferred way of submitting specimens from: nasal passage, pharynx, tonsil, eye, ear, vagina, and cervix
- drying of specimens should be avoided
- suitable transport media available
Guidelines for bac isolation from selected specimens: Swabs and discharge
- obtained directly from rectum in manner it avoid contamination
- samples size of end of thumb may be sent to lab without transport medium
- rectal swabs often don't have enough fecal matter for agent det
- fecal swabs should be placed in medium to avoid desiccation
- leak proof containers
- transport immediately
- some org shed intermittently and samples must be collected over several days
Guidelines for bac isolation from selected specimens: feces
- as soon as mastitis is observed
- sample should be collected in sterile vials or tubes
- clean udders before taking sample
Bac isolation from milk in indiv cows
- pretense or absence of bac
- ID of prominent bac groups
Blue tank milk
- no after treatment
- udder shouldn't be rinsed with water unless very dirty (teats should be wiped with 70% ethyl alcohol on cotton wool, special attention to teat sphincters)
- if washed, dry throughly
- start with teats furthest away
- hold sterile narrow necked collecting bottle almost horizontally
- discard first milk from each teat
- for composite sample, take a little milk from each teat
- collect from nearest teat first
Guidelines for bac isolation from selected species: milk
- conjunctival swab may be taken gently holding palprebrae apart
- scrapings can be taken with fine, sterile spatula
- carefully wash cells into transport media
Guidelines for bac isolation from selected specimens: eyes
- bac microscopy and culture for bac viable count
- collect by cystocentesis, catheter, or midstream urine
Guidelines for bac isolation from selected specimens: urine
- if possible, collect 3 ml of pus with scrapings from wall
- pus at center often sterile
- pus from freshly formed abscess can yield best cultural results
- anaerobic bac can often be cultured from abscesses
Guidelines for bac isolation from selected specimens: abscesses
- If there are intact pustules or vesicles present the surface should be disinfected with 70% ethyl alcohol
• Allow to dry
• Aspirate material with a sterile syringe and fine needle
• A swab may be taken from the raw surface of the ulcer
• A biopsy of the wound should be collected after the superficial area has been cleaned and debrided
• When ringworm is suspected, hair should be plucked from the lesion and the edge of the lesion should be scraped with a blunt scalpel until blood begins to
ooze
• The plucked hair and skin scrapings (wit
Guidelines for bac isolation from selected specimens: skin lesions
Lag phase
1
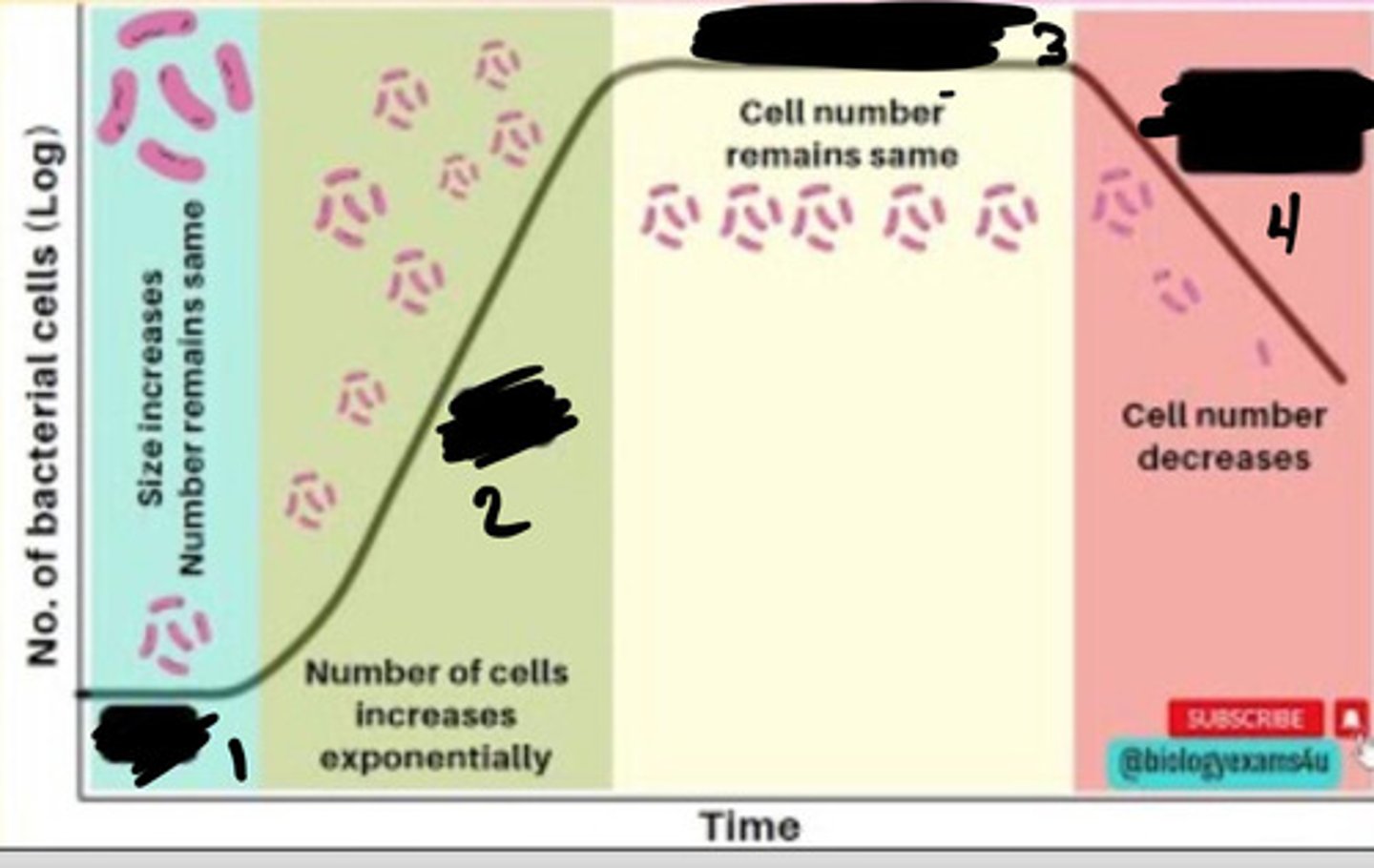
Exponential phase
2
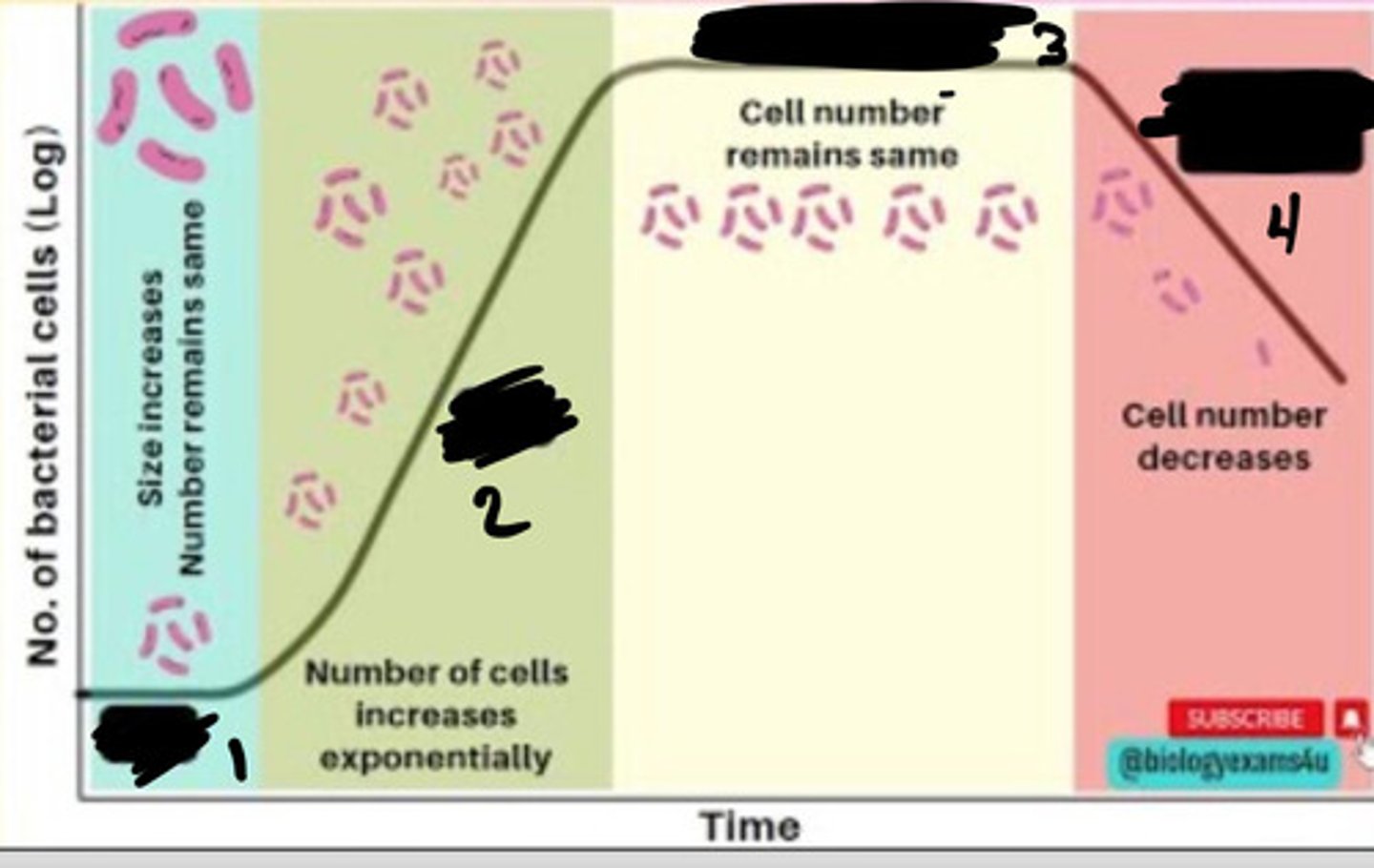
Stationary phase
3
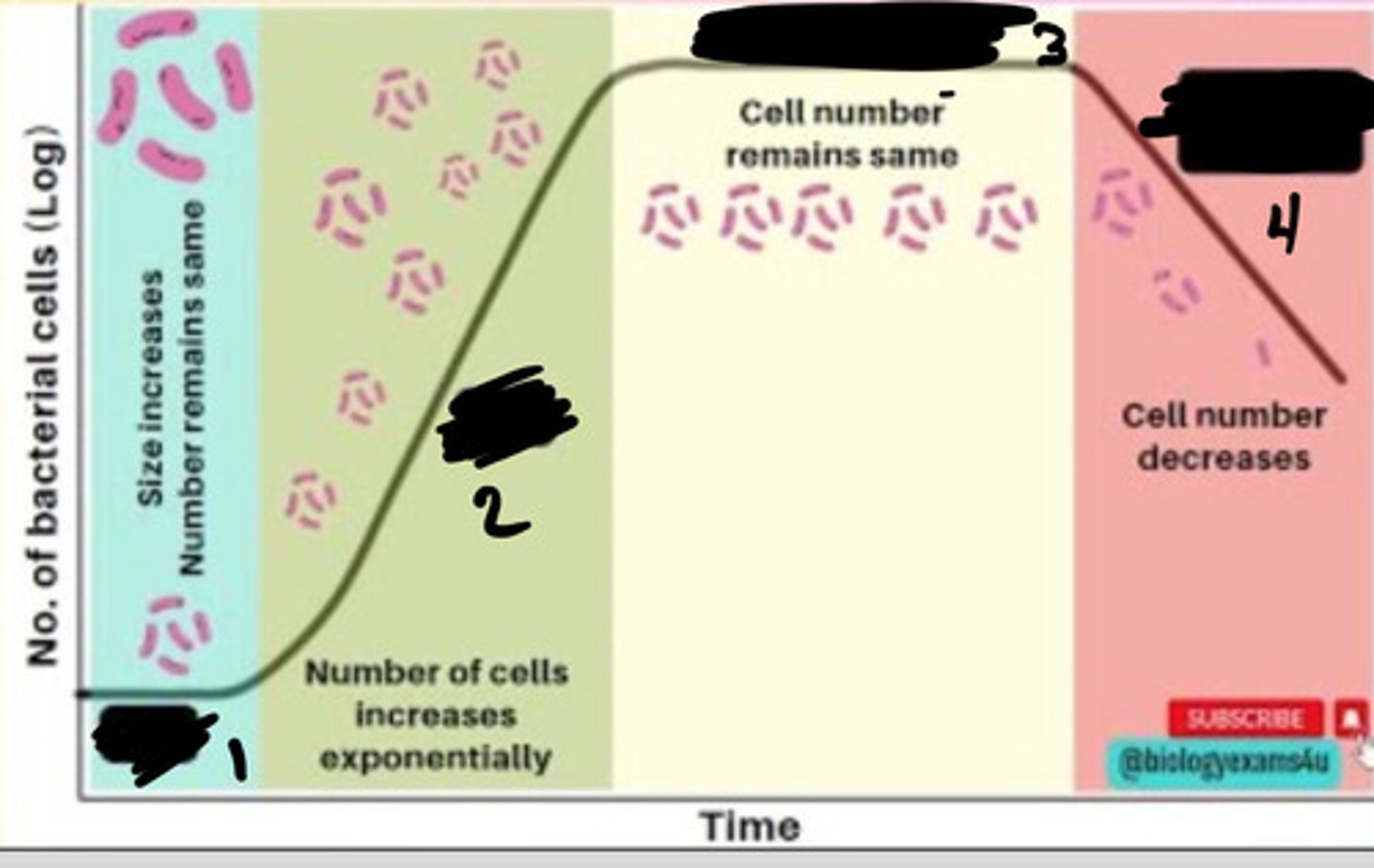
Decline phase
4
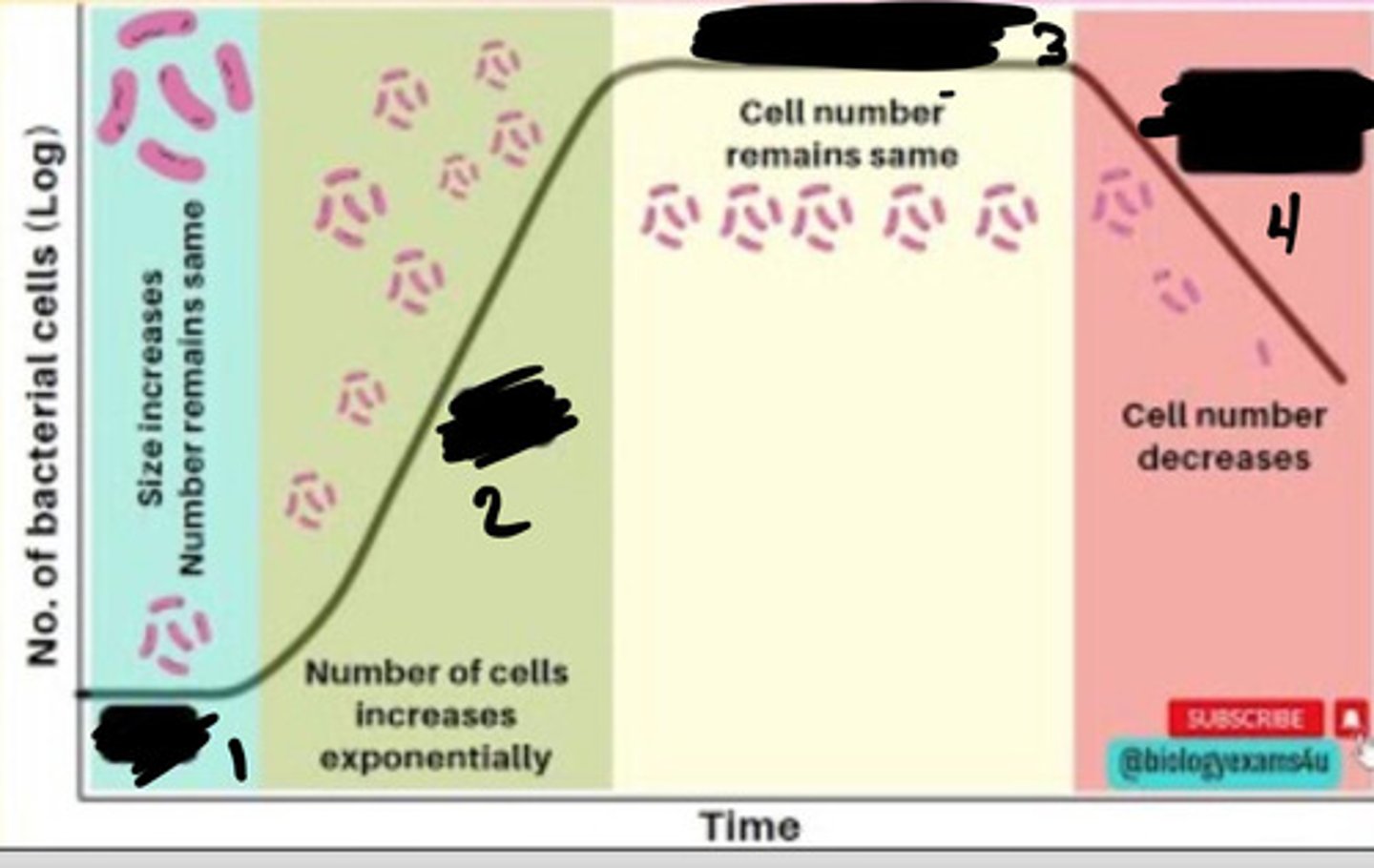
- Generation times vary
- many pathogens need blood agar
- most grow on cell-free media as colonies
- few require cells in which to grow (obligate intracellular bac)
Bac growth in labs: time, media
- temp
- hydrogen ion conc
- availability of moisture
- atmospheric comp
- osmotic pressure
Growth of bac in a culture influenced by: (5)
- broth
- semisolid
- solid
Types of media based on consistency (3)

- use in test tubes, bottles, and flasks
- bac grow uniformly
- turbidity production
- certain aerobic bac and those containing fibrin form thin film-surface pellicle
- no agar
- nutrient broth
Liquid media/broths
- type of liquid media
- gen purpose
- grows non-fastidious bac
- contains yeast extract, peptone, sodium chloride, and nutrients
Nutrient broth
- .2-.5% agar
- fairly soft
- can demonstrate bacterial motility
Semi-solid agar
- liquid media can be rendered solid by adding solidifying agent
- agar most common
- polysaccharide obtained from algae
- used at conc of 1-3%
Solid media
- supports most non-fastidious bac
Basal media
- extra nutrients added (blood and serum)
- i.e. blood agar, chocolate agar
Enrichment media
- inhibits unwanted commensal or contaminating bac
- helps to recover pathogen from mixture of bac
- media can be made sensitive by addition of: antibiotics, dyes, chem, and pH
- liquid media that serves to favor growth of one org over another
Selective media
- diff bac can be recognized on basis of colony morphology
- approaches include: incorporation of dyes and metabolic substrates
- i.e XLD agar
Differential media or indicator media
Non-selective
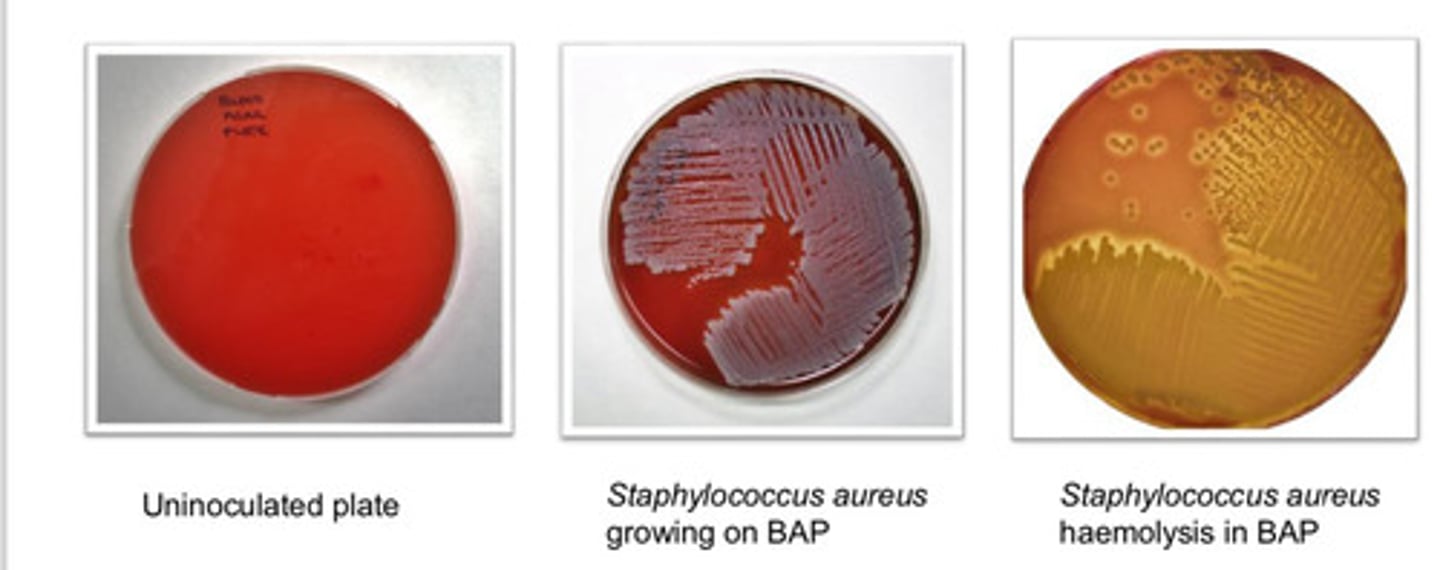
Blood Agar Plate (BAP): agar type
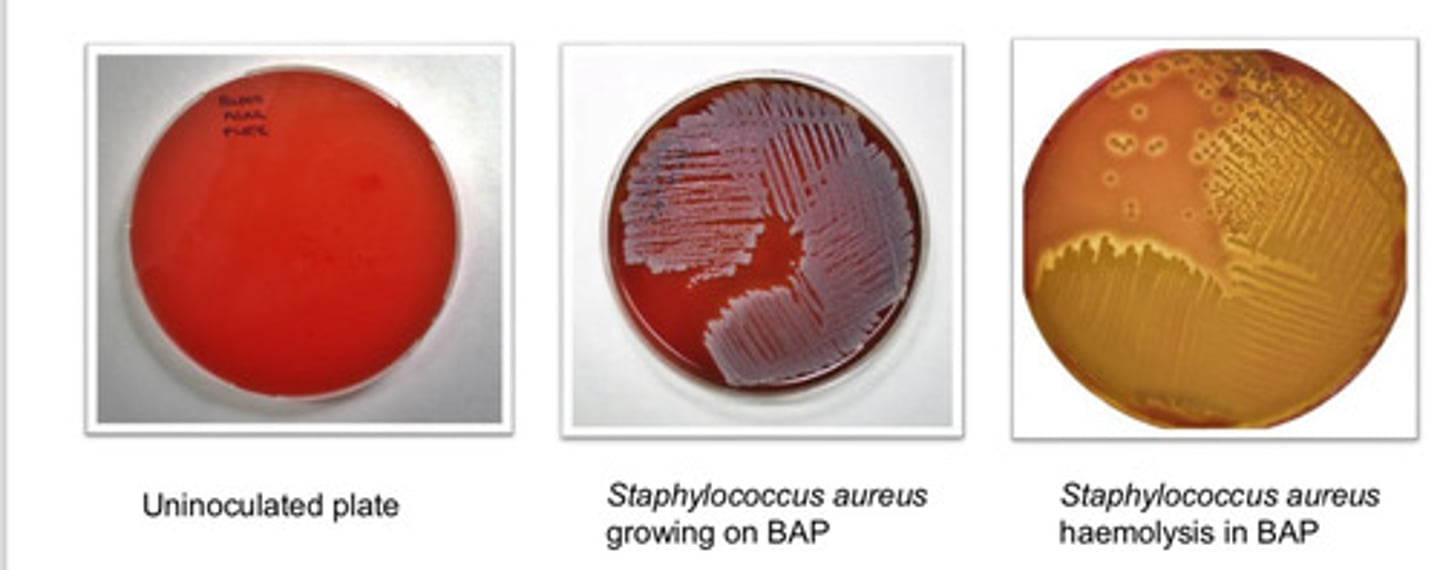
- can grow wide range of org (fastidious and non-fastidious)
- can visualize variations on hemolysis
Blood Agar Plate (BAP): purpose
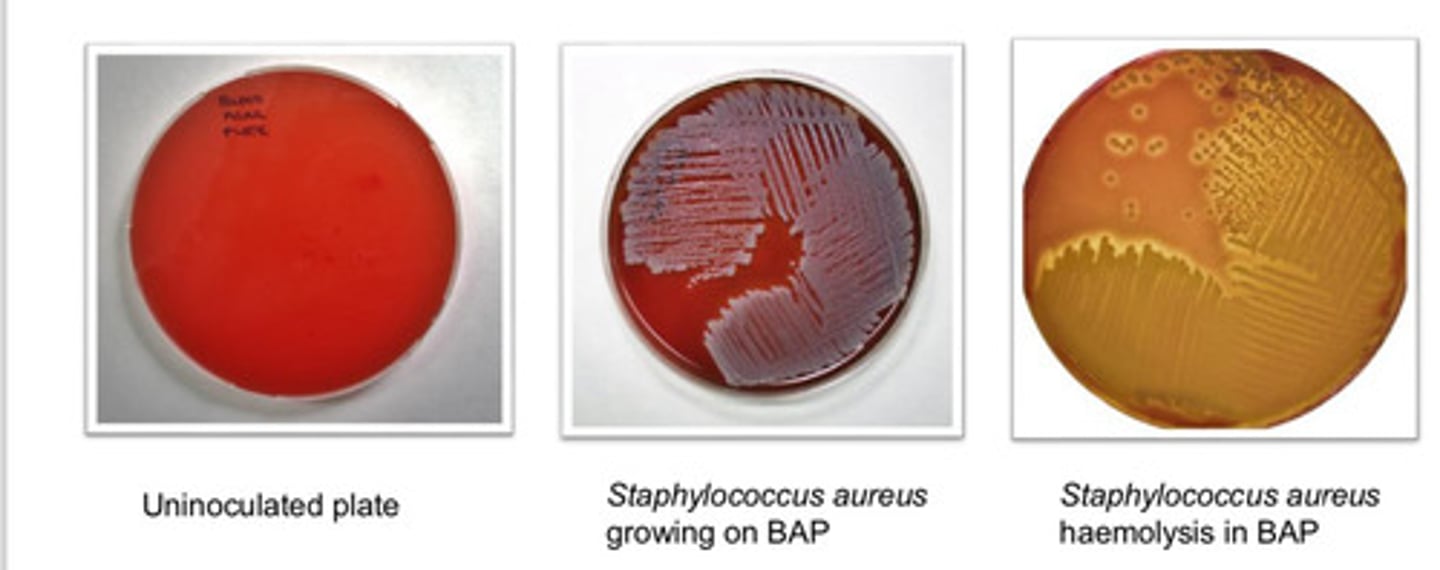
- based on hemolysis
- alpha hemolysis: incomplete
- beta hemolysis: complete
- gamma hemolysis: none
Blood Agar Plate (BAP): colony appearance
Selective and differential
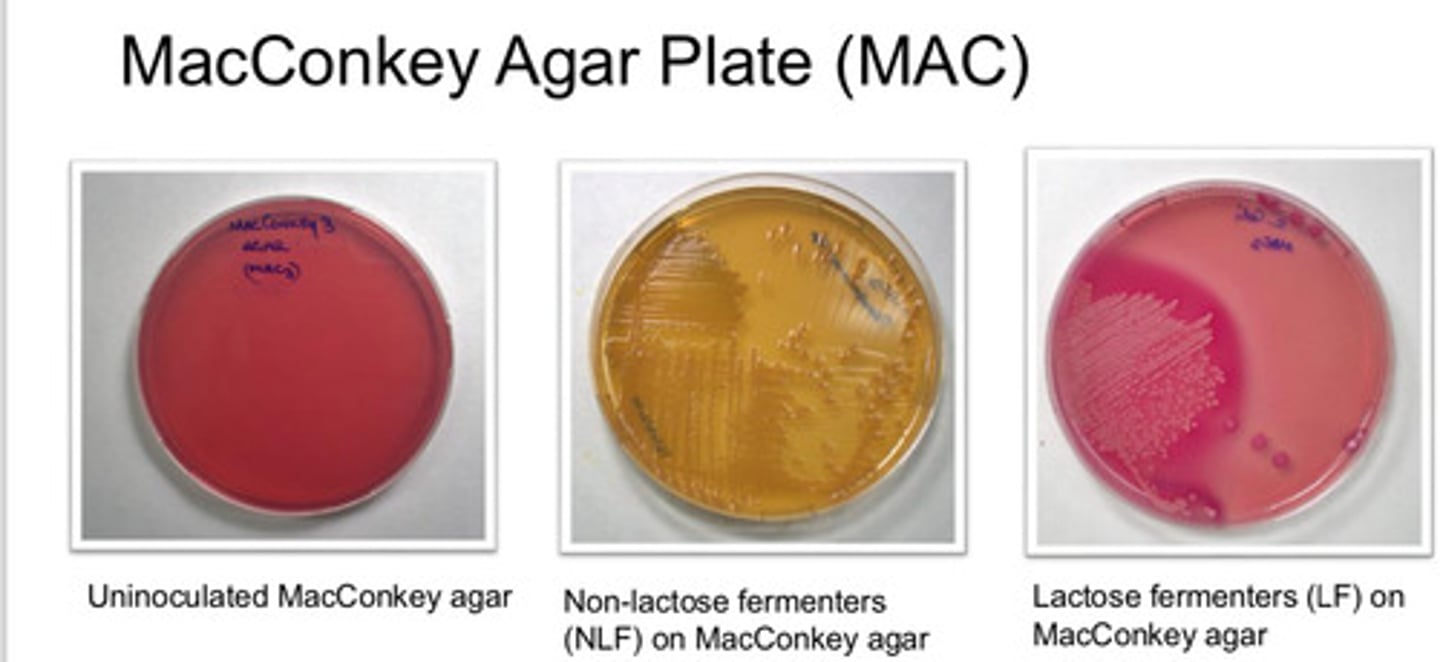
MacConkey Agar Plate (MAC): agar type
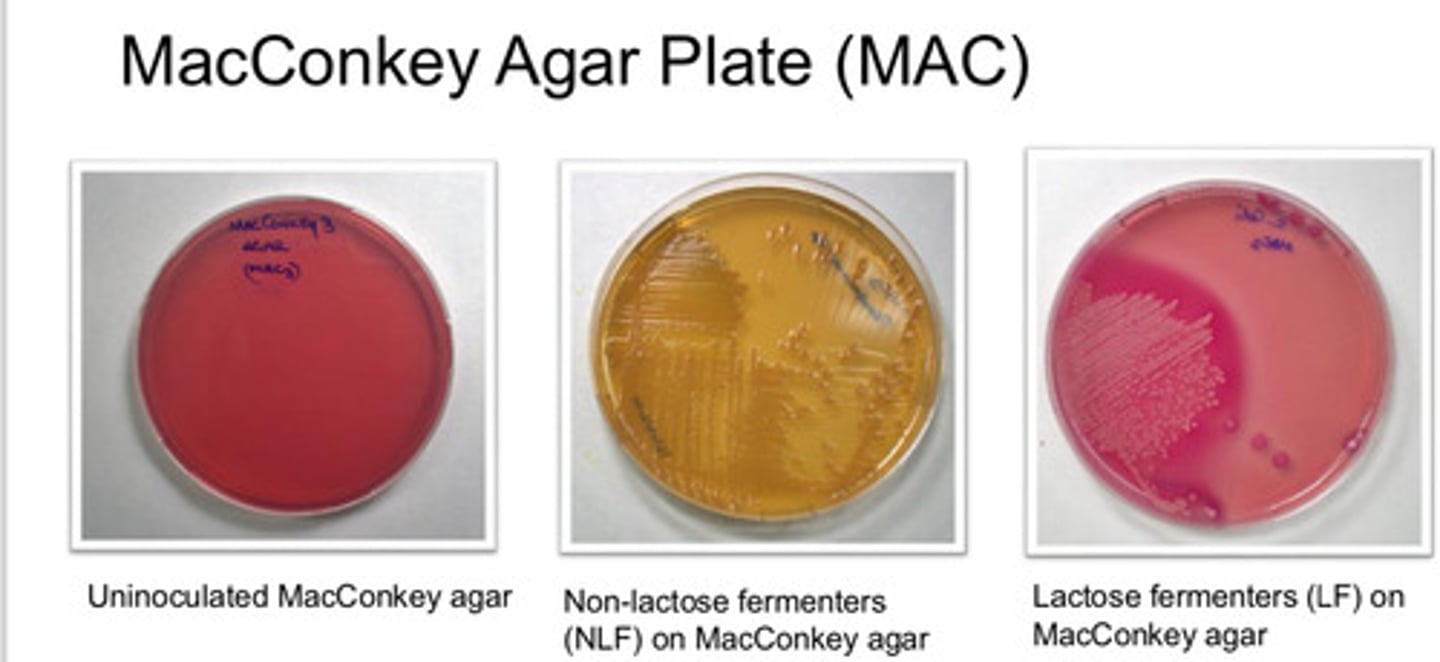
- useful in recognition of Gram-neg
- differentiate those which ferment lactose from those which do not ferment lactose
MacConkey Agar Plate (MAC): purpose
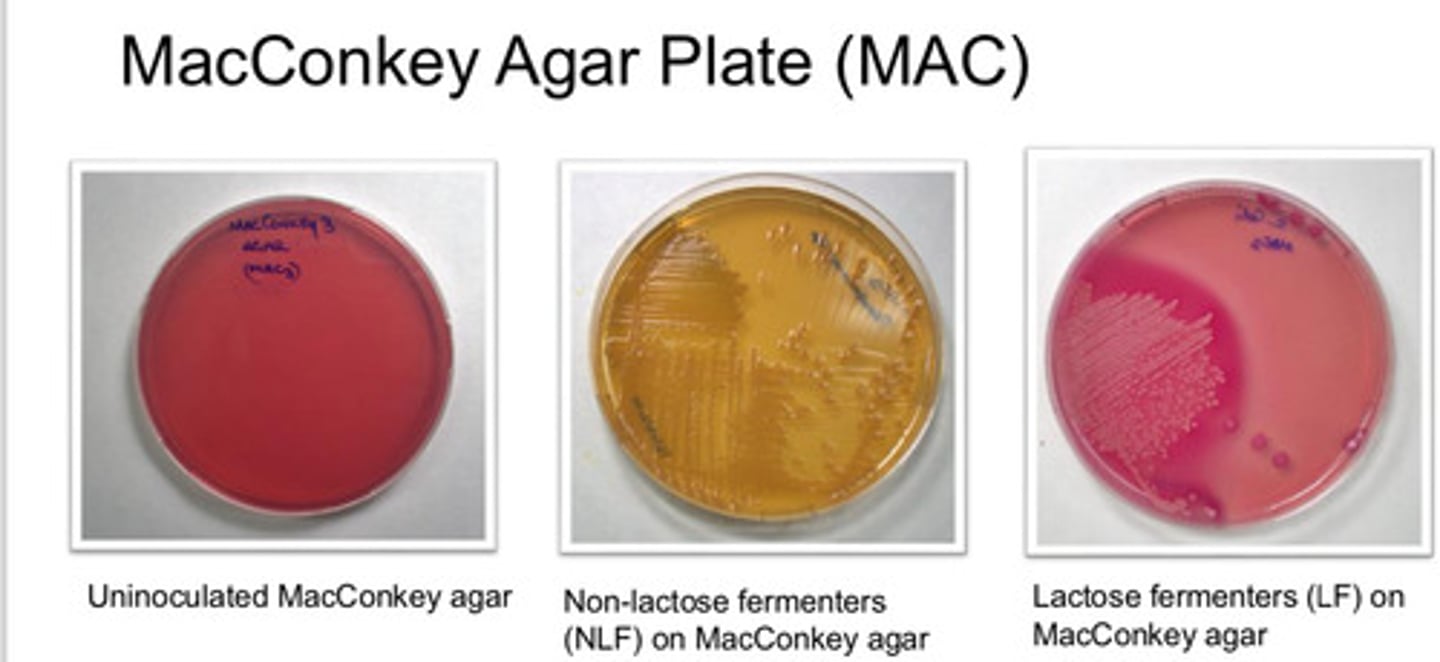
- lactose fermenting bac grow red/pink
- non-lactose fermenting colonies are pale/white and agar turns yellow
MacConkey Agar Plate (MAC): colony appearance
- Antimicrobial susceptibility testing medium which may be used in internationally recognized standard procedures
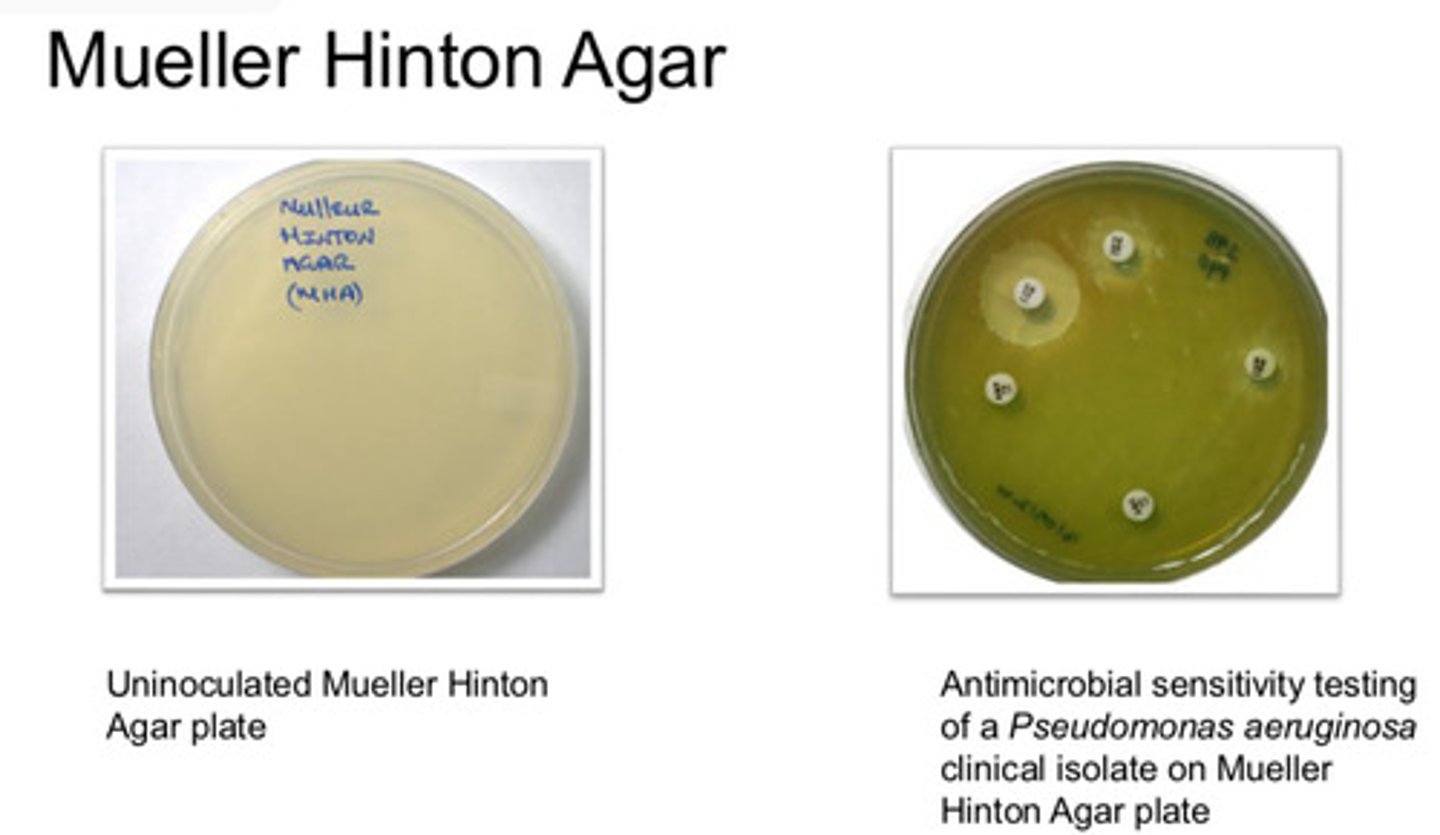
Mueller-Hinton Agar: agar type/purpose
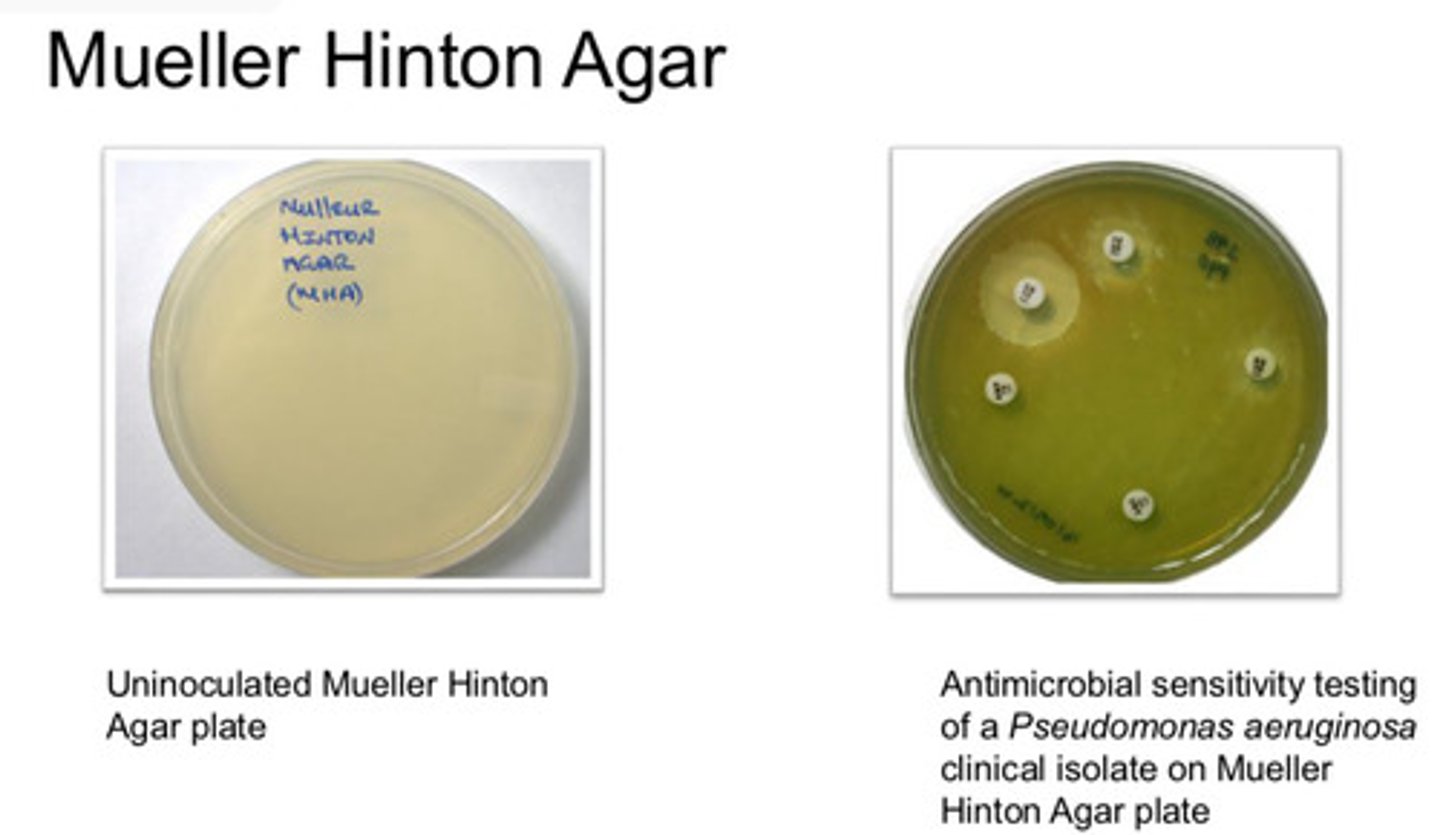
- used in Antimicrobial sensitivity testing (AST) where a lawn is required
Mueller-Hinton Agar: colony appearance
Selective and differential
Mannitol Salt Agar Plate (MSA): agar type
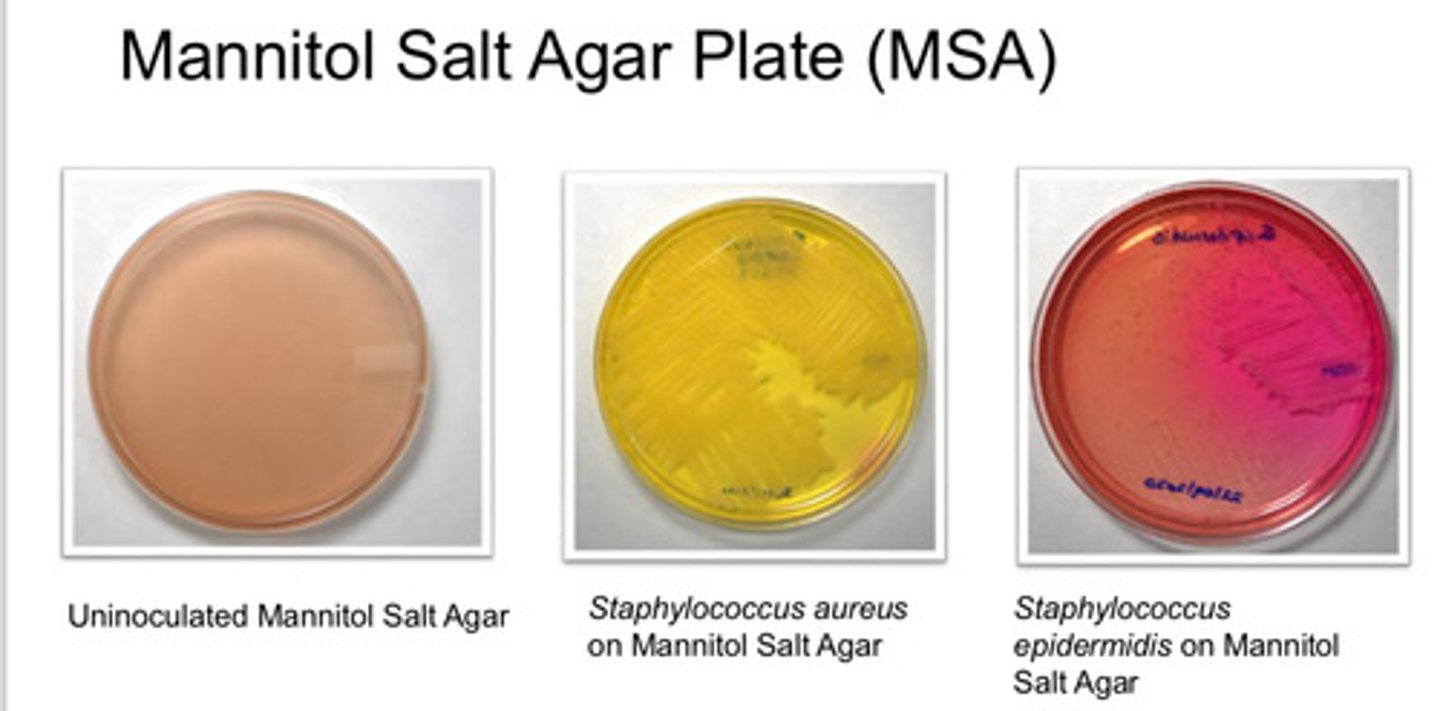
- isolation of pathogenic stapylococci (coagulate-positive)
Mannitol Salt Agar Plate (MSA): Purpose
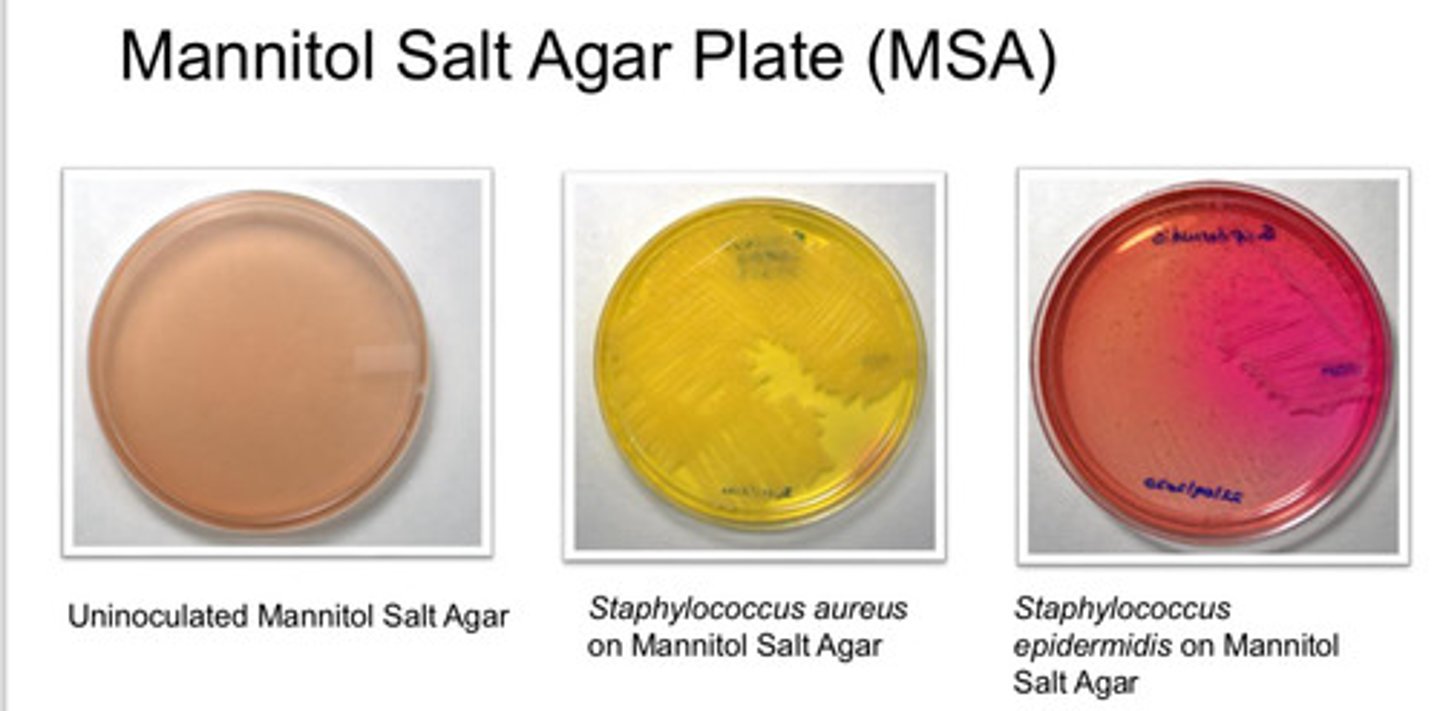
- 7.5% NaCl inhibit growth of other bac
- coloration due to Phenol red: red at alkaline condition, yellow at acidic condition
- Staphylococcus aureus is yellow
- Staphylococcus epidermis is red
Mannitol Salt Agar Plate (MSA): colony appearance

- selective media for cultivation of yeasts, molds, and aciduric bac
Sabouraud Dextrose Agar (SAB): agar type

- growth and maintenance of pathogenic/non-pathogenic fungi
- used for recovery and total counting of yeasts and molds from environmental samples
Sabouraud Dextrose Agar (SAB): purpose

- yeasts: Candida spp, Aspergillus spp.
Sabouraud Dextrose Agar (SAB): colony appearance

Principles of sample collection
collect samples from clinical cases and exposed animals, sample taken from edge of lesion including normal tissue
Aerobic bacterial samples
FNA, postmortem specimens, swabs, sterile body fluids, surgical specimens, blood
Clinical conditions of anaerobic infections
foul-smell, deep infections, necrotic tissue, gas, bites, deep abscesses
Indirect methods used to identify bacteria
immunology & serology
Molecular methods used to identify bacteria
PCR, MALDI-TOF MS
Bacterial growth characteristics
30 min - 20 hours, viable but non-culturable