Psy 200 Final Exam 4 Personality
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What is personality?
-Characteristic patterns of thinking, feeling, and behaving
-Multiple ways of viewing personality:
-Humanistic Persepective
-Psychoanalytic Perspective
-Trait Perspective
-Social learning perspective
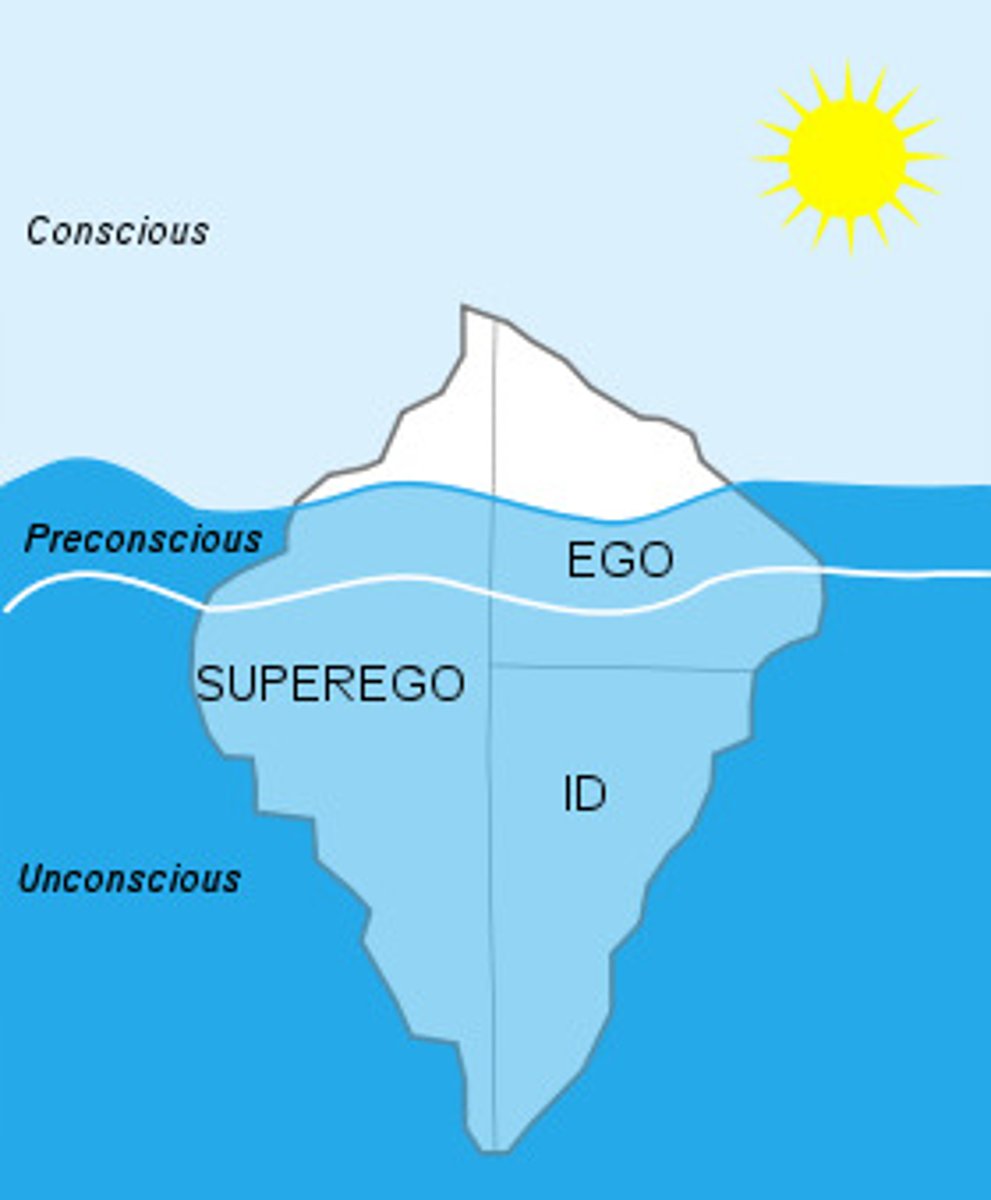
Id: (Psychoanyltyic theories: Fredian Personality Structure)
Primitive Drives, present at birth
Ego: (Psychoanyltyic theories: Fredian Personality Structure)
coordinates the needs of the id with reality-decision maker
Superego: (Psychoanyltyic theories: Fredian Personality Structure)
internalizes right/wrong, operates as our "conscience"
Charecterictics of (Psychoanyltyic theories: Fredian Personality Structure)
-Ideally, all 3 are balanced
-Imbalance leads to unhealthy behaviors
What are the levels awarness
-conscious
-preconscios
-unconscious
Repression (Freudian Defense Mechanism)
Expulsion from awareness of unacceptable ideas or motives
The return of behavior that is typical of earlier stages of development
Regression (Freudian Defense Mechanism)
The return of behavior that is typical of earlier stages of development
Displacement (Freudian Defense Mechanism)
The transfer of unacceptable impulses away from their original objects onto safer or less threatening objects
Denial (Freudian Defense Mechanism)
Refusal to recognize a threatening impulse or desire
Reaction formation (Freudian Defense Mechanism)
Behaving in a way that is the opposite of one's true wishes or desires in order to keep these repressed
Rationalization (Freudian Defense Mechanism)
The use of self-justifications to explain away unacceptable behavior
Projection (Freudian Defense Mechanism)
Imposing one's own impulses or wishes onto another person
Sublimation (Freudian Defense Mechanism)
The channeling of unacceptable impulses into socially constructive pursuits
(Neo-Freudians: Alfred Adler)
inferiority complex, overcompensation, birth order
Inferiority
overwhelming feelings of inferiority
Overcompensation
response to inferiority, attempt to seek appearance of superiority
Birth Order
first to suggest that parents and siblings may influence development. Encouraged attention to birth order.
Personal unconscious (Neo-Freudians: Carl Jung)
same as Freud!
Collective unconscious
common human predisposotions passed from generation to generation
Archetypes
classic ways of unconsciously thinking about topics like power, death, darkness
Introversion
dimension of personality in which people tend to withdraw from excessive stimulation
Extroversion
how outgoing, talkative, sociable, and assertive a person is
Evaluating Freudian Theory
-Strong influence on culture
-Little empirical support
-Operationalizing constructs difficult
-Questions about the effectiveness of psychoanalysis
Humanistic Theories
Personality results from motivation
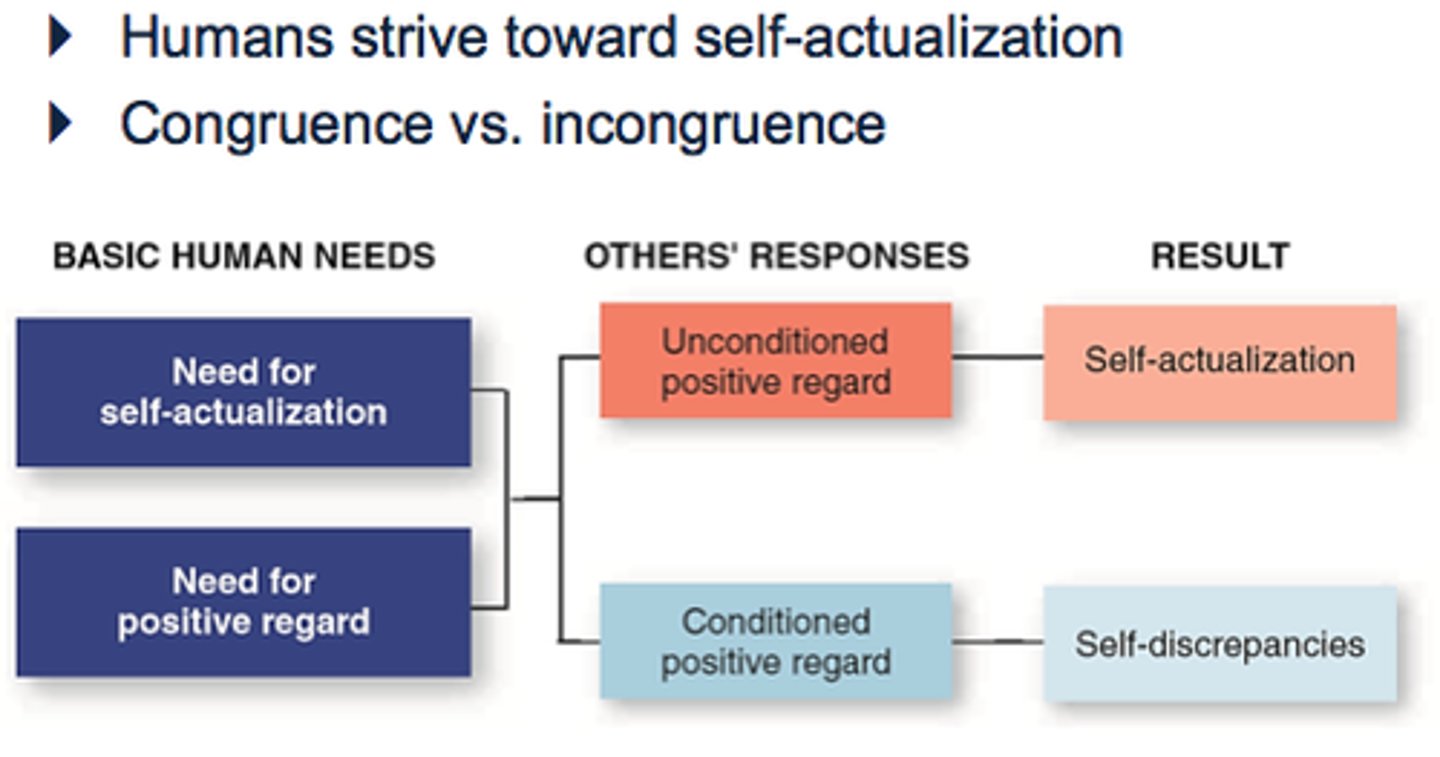
Humanistic Theories (Carl Rogers)
-Humans strive toward self-actualization
-Congruence vs. incongruence
Collectivistic (culture and personality)
communal, interdependent
Individualistic (culture and personality)
(individuality/uniqueness) cultures
Culture and Personality
-Collectivistic vs Individualistic cultures
-Often used to explain differences in personality across culture
-Ignores the great variation within groups
Trait Theories
theories that endeavor to describe the characteristics that make up human personality in an effort to predict future behavior
Early Trait theories - allport and cattell
a perspective that views personality as being composed of stable, enduring traits or characteristics.
Early Trait theories - Eysenk
-Unstable
-Introverted
-Extroverted
-Stable
Openess to experience (The big 5)
tendency to be original, have broad interests, be open to a wide range of stimuli, be daring and take risks
Conscientiousness (The big 5)
the personality dimensions that includes dependability, cautiousness, organization, and responsibility ; people low in this dimension are impulsive, careless, disorderly and undependable
Extroversion (The big 5)
The personality dimension that includes enthusiasm, dominance, and sociability; people low on this dimension are considered introverted
Agreeableness (The big 5)
the personality dimension that includes friendliness, cooperation, and warmth ; people low in the dimension are cold, quarrelsome and unkind
Neuroticism (The big 5)
the personality dimensions that includes nervousness, tensions and anxiety ; people low on this dimension are emotionally stable, calm and contended
Genetic contributions (implications to trait theories)
temperament; neurotransmitter functioning
Situational factors (implications to trait theories)
person-situation interactions
Social Cognitive Theories (Albert Bandura)
reciprocal and self efficacy
Reciprocal
interaction between cognitive factors, environment and behaviors
Self-efficacy
-key to this interplay
-One's expectations of success