DNA + RNA
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Heredity
The passing of features from parent to offspring by means of genes.
Genes
A section of DNA that causes the production of protein
Gene expression
the way genetic information is decoded and used to make a protein
Chromosomes
Made up of 60% protein and 40% DNA.
Protein helps to tightly pack it in.
Genes are spread along the length of the chromosome.
DNA (2 types)
Coding + non-coding (junk)
DNA (deoxyribonucleaic acid) Structure
Made up of nucleotides.
Nucleotides (3 parts)
Phosphate group (PO4).
Sugar (Deoxyribose, 5 carbon molecule).
Bases (Nitrogen containing)
DNA structure (4 bases)
Adenine, Guanine = purines.
Thymine, Cytosine = pyrimadine
The Genetic Code
Genes code for a protein.
Each amino acid is coded by a unique sequence of 3 bases. called triplet or codon.
e.g. the codon CAA codes for the amino acid valine.
What shape is DNA
Double helix
DNA Replication (4 steps)
1.Double helix unwinds
2.Enzyme breaks the bond between complementary base pairs and the 2 strands separate.
3.DNA bases enter from the cytoplasm and attach to the exposed complementary bases on each strand.
4.Each new double helix strand rewinds to form a double helix.
DNA profiling (Genetic fingerprinting)
A method of making unique patterns of bands from the DNA which can be compared to the DNA profile of another person.
DNA Profiling (Crime)
To compare a persons DNA profile to that of a DNA sample found at a crime scene. this can incriminate someone if they match or rule them out as a suspect.
DNA profiling (Medical)
Determine paternity. the bands in a persons DNA profile match their biological mother and fathers bands.
Method of DNA profiling (4 steps)
1.DNA is released from the cells
2.DNA is cut into fragments using restriction enzymes. Each restriction enzyme cuts DNA at specific base sequences.
3.Fragments are placed on sugar based gel. electric current is applied based on size, smaller fragments move faster through gel, photograph is taken as permanent record.
4.Patterns are compared between different samples.
Genetic Screening (Detects mutations in gene)
Radioactive piece of DNA is added to sample of DNA. The probe will only attach to a normal gene, if it does not attach, gene is mutated.
Genetic Screening (Adult Screening)
used to see if an adult is a carrier for a genetic mutation, e.g. cystic fibrosis, gives a person information of the chance of them having a kid with the condition.
Genetic Screening (Foetal Screening)
A sample of cells is removed from the embryo. cells are then tested.
Ethics of genetic screening (Adult + Foetal)
: there could be possible insurance issues if you are likely to get a condition.
: If a mother finds that their child has a condition (Down Syndrome) then they cand decide to abort it.
RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) Vs DNA
It has ribose sugar instead of deoxyribose
RNA is single stranded
It has the base Uracil instead of thymine
Protein Synthesis (Transcription + Translation)
Making of mRNA using a DNA template.
Making of protein using the mRNA code.
Transcription (3 steps)
Enzyme starts to unwind the double helix in the nucleus.
Complimentary RNA bases join to the exposed DNA strand to form mRNA.
The enzyme RNA polymerase joins the RNA bases together to form mRNA.
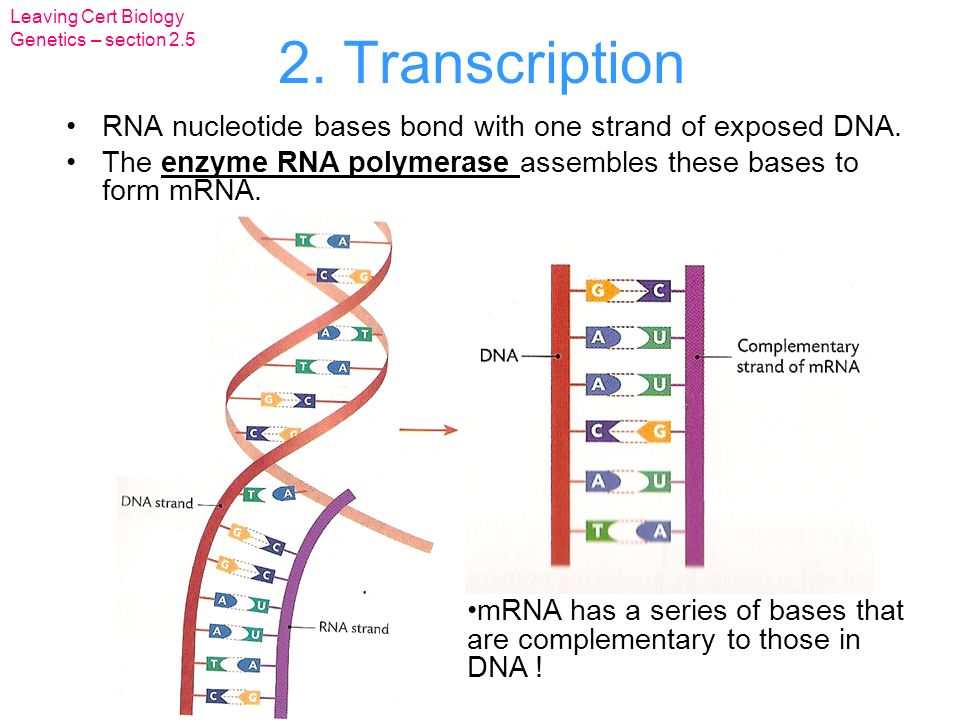
Each mRNA strand has:
1.a start codon
2.a series of codons represent different amino acids.
3.a stop codon
Translation (Steps 1-4)
1.mRNA moves from nucleus - cytoplasm.
2.rRNA is found in the ribosome.
3.mRNA moves into ribosome and forms a weak bond with the rRNA.
4.tRNA is found in the cytoplasm. tRNA contains an anticodon attached to an amino acid.
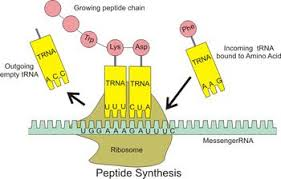
Translation (Steps 5-7)
5.tRNA is attracted to the mRNA in the ribosome. anticodon on tRNA compliments codon on the mRNA.
6.while the tRNA attach to the mRNA in the ribosome, it brings an amino acid.
7.when the tRNA attach to the mRNA in the ribosome, the amino acids detach from the tRNA and bond together to form a new protein.
Translation (Steps 8-9)
8.tRNA leaves the ribosome without any amino acids and pull the mRNA strand out of the ribosome.
9.The process stops once it has reached the stop codon. a new protein has been produced and becomes functional when it folds.
Coding DNA
Has genetic instructions to produce a protein
Non coding DNA
Has genetic instructions that do not produce a protein
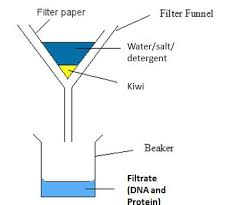
Experiment (Isolate DNA)
Chop up kiwi (Break down cell).
Add sodium chloride to washing up liquid in distilled water (Release DNA from cells)
add kiwi.
place in water bath at 60 C for 15m (denatures enzyme)
Place in ice bath for 5m (slow breakdown of DNA)
blend for 3s (Break down cell walls to release DNA)
filter solution (So DNA can pass through it)
with a syringe place in boiling tube.
add protease enzyme (Breaks down proteins around DNA) + ethanol (slowly).
Twist a glass rod at the interface of the liquids, DNA should attach (So DNA attaches)
Ensure safety goggles are worn.