Microscopic Anatomy and Organization of Skeletal Muscle Chapter 14
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
perimysium
connective tissue ensheathing a bundle of muscle cells
fascicle
Bundle of muscle cells.
sarcomere
contractile unit of muscle
fiber
a muscle cell
endomysium
thin reticular connective tissue surrounding each muscle cell
sarcolemma
plasma membrane of the muscle fiber
myofibril
a long filamentous organelle with a banded appearance found within muscle cells
myofilament
actin or myosin containing structure
tendon
cord of collagen fibers that attaches a muscle to a bone
List 3 reasons why the connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle are important.
1). Bundle the muscle fibers together, increasing coordination of there activity. 2). Add strength to the muscle. 3). Provide a route for entry and exit of blood vessels and nerves to the muscle fibers.
Why are there more indirect - that is, tendinous - muscle attachments to bone than there are direct attachments?
They conserve space (less bulky than fleshy muscle attachments) and are more durable than muscle.
How does an aponeurosis differ from a tendon structurally?
An aponeurosis is a sheet of white fibrous connective tissue, a tendon is a band of cord of the same tissue
How is an aponeurosis functionally similar to a tendon?
Both serve to attach muscles to bones or to other muscles.
The junction between a motor neuron's axon and the muscle cell membrane is
neuromuscular or myoneural
A motor neuron and all of the skeleton muscle cells it stimulates is called a ?
Motor Unit
The actual gap between the axon terminal and the muscle cell is called a ?
synaptic cleft
Within the axon terminal are many small vesicles containing a neurotransmitter substance called ?
Acetylcholine
When the _______ reaches the ends of the axon, the neurotransmitter is released and diffuse to the muscle cell membrane to combine with receptors there. The combining of the neurotransmitter with the muscle membrane receptors causes the membrane to become permeable to both sodium and potassium.
Action potential
The greater influx of sodium ions results in ______ of the membrane. Then contraction of the muscle cell occurs.
Depolarization
What is not true of skeletal Muscles?
1) It enables you to manipulate your environment. 2). It influences the body's contours and shape. 3). It is one of the major components of hollow organs. 4). It provides a means of locomotion.
It is one of the major components of hollow organs.
Because the cells of skeletal muscle are relatively large and cylindrical in shape, they are known as ?
Fibers
True or False? Skeletal muscle cells have more than one nucleus?
True
The two contractile proteins that make up the myofilaments of skeletal muscles are?
Actin and Myosin
Each muscle cell is surrounded by thin connective tissue called the?
Endomysium
A strong cordlike structure that connects a muscle to another muscle or bone is?
A tendon
The junction between a nerve fiber and a muscle cell is called a ?
neuromuscular or myoneural junction.
True or False - The neuron and muscle fiber membranes do not actually touch but are separated by a fluid - filled gap.
True
The bulk of the body's muscle is called?
skeletal muscle
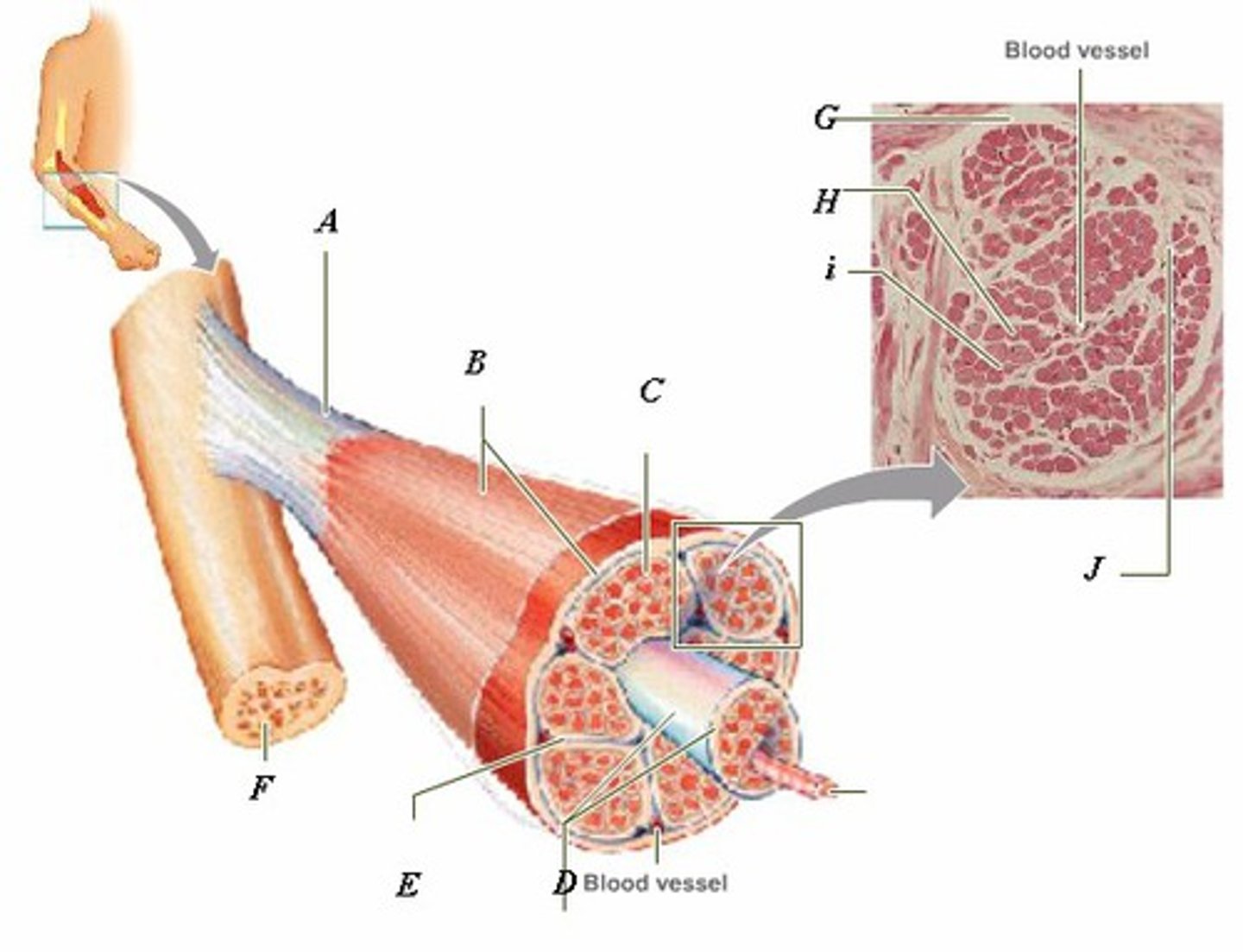
LABEL - TENDON
LABEL (A)
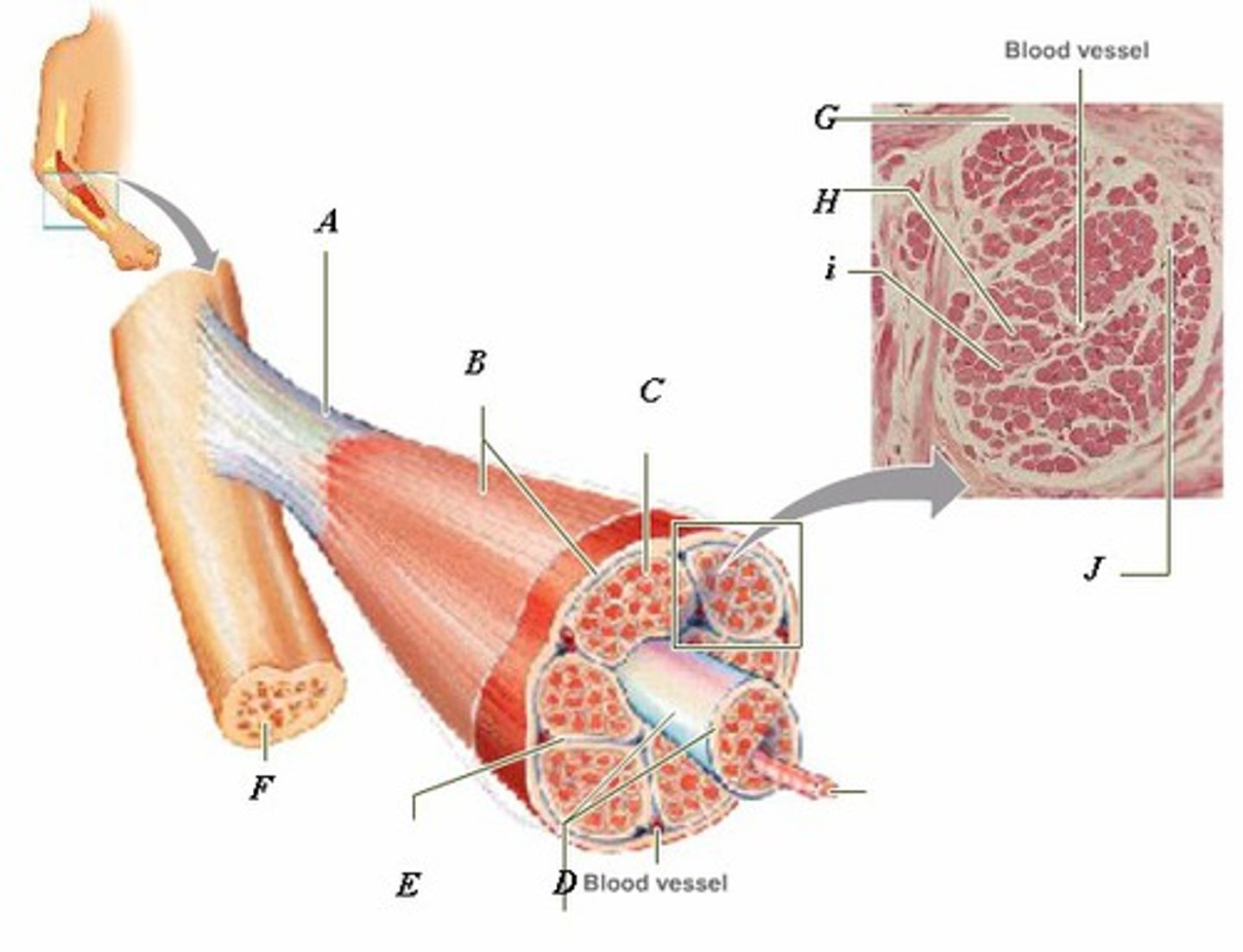
LABEL - EPIMYSIUM
LABEL (B)
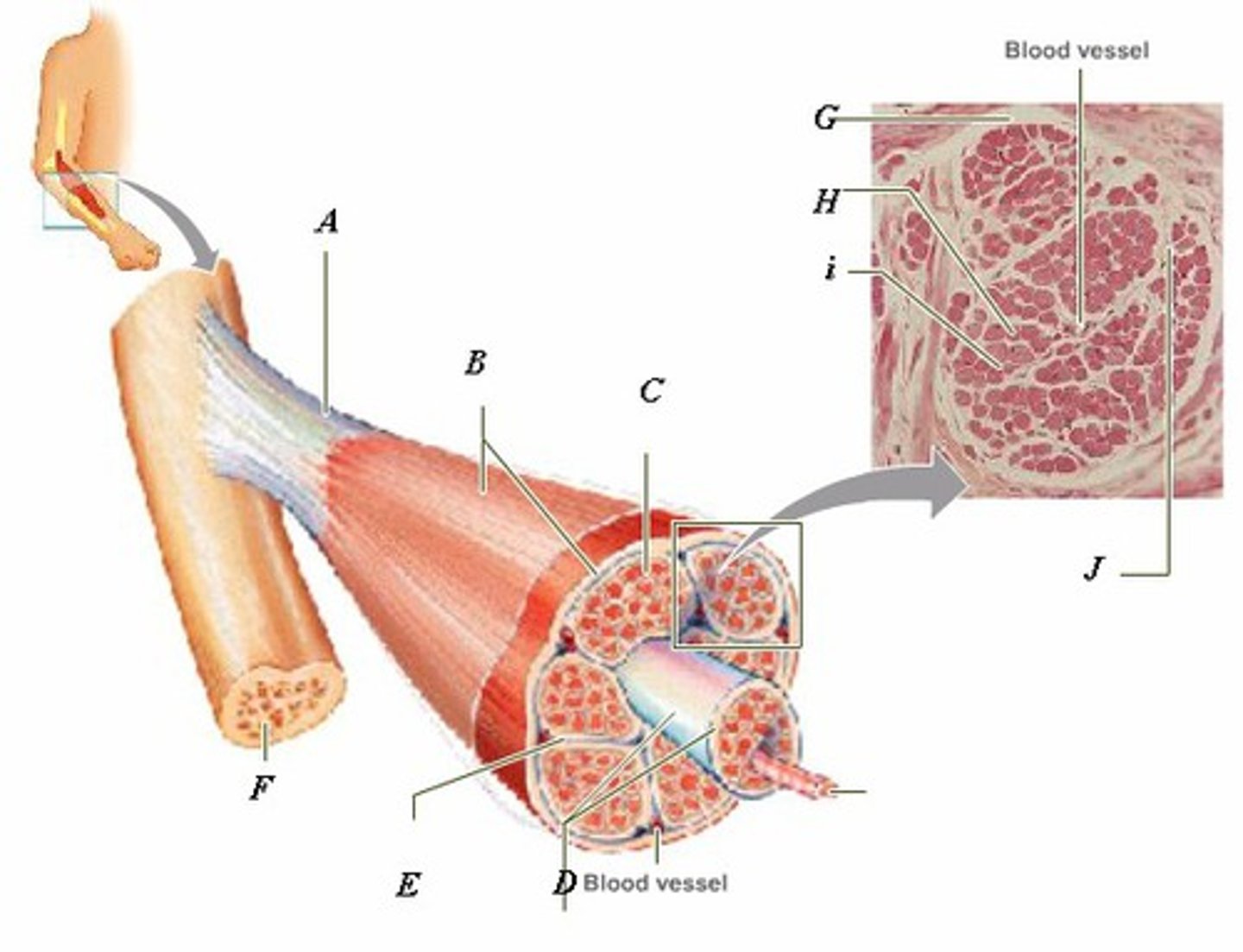
LABEL - ENDOMYSIUM
LABEL (C)
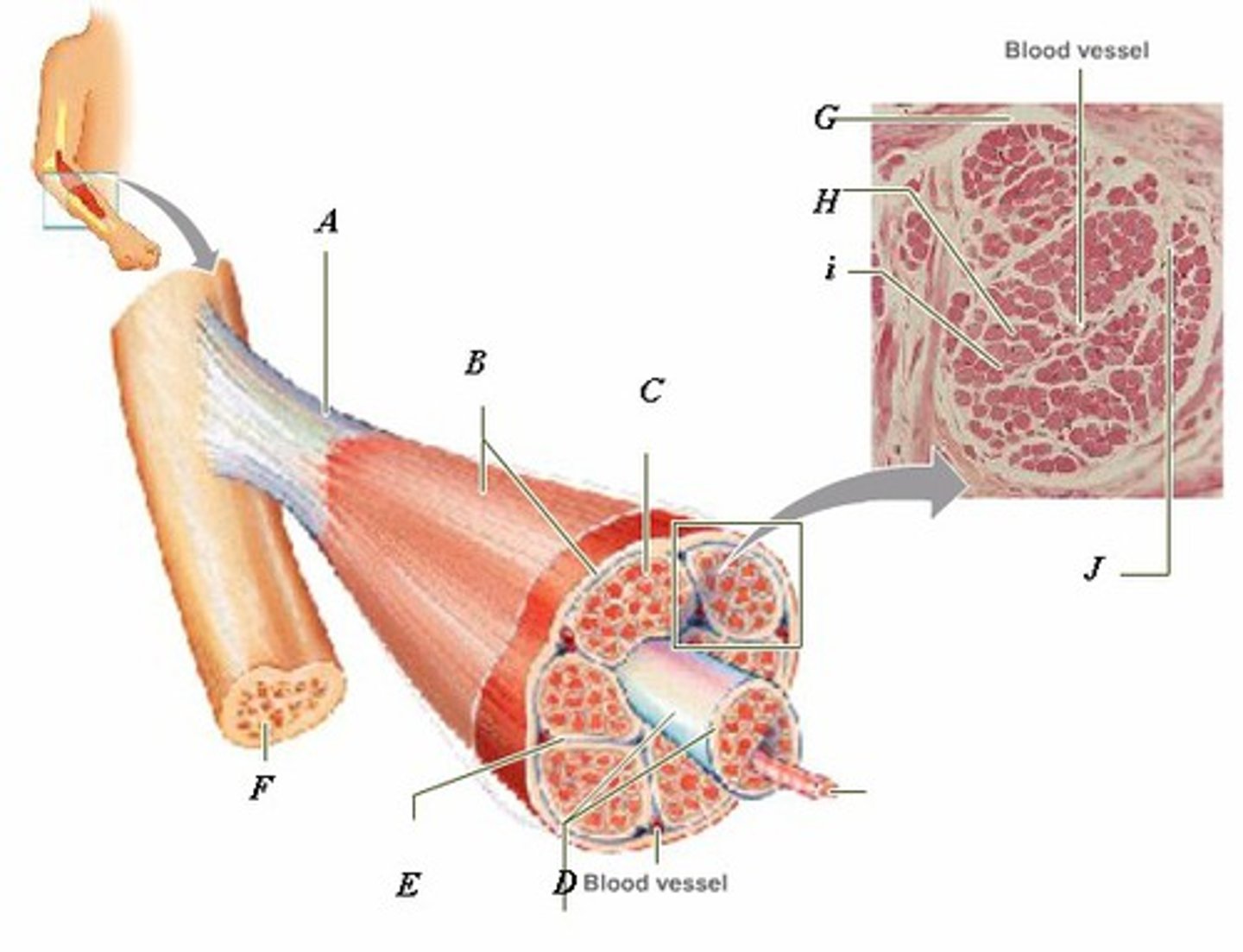
LABEL - FASCICLE
LABEL (D)
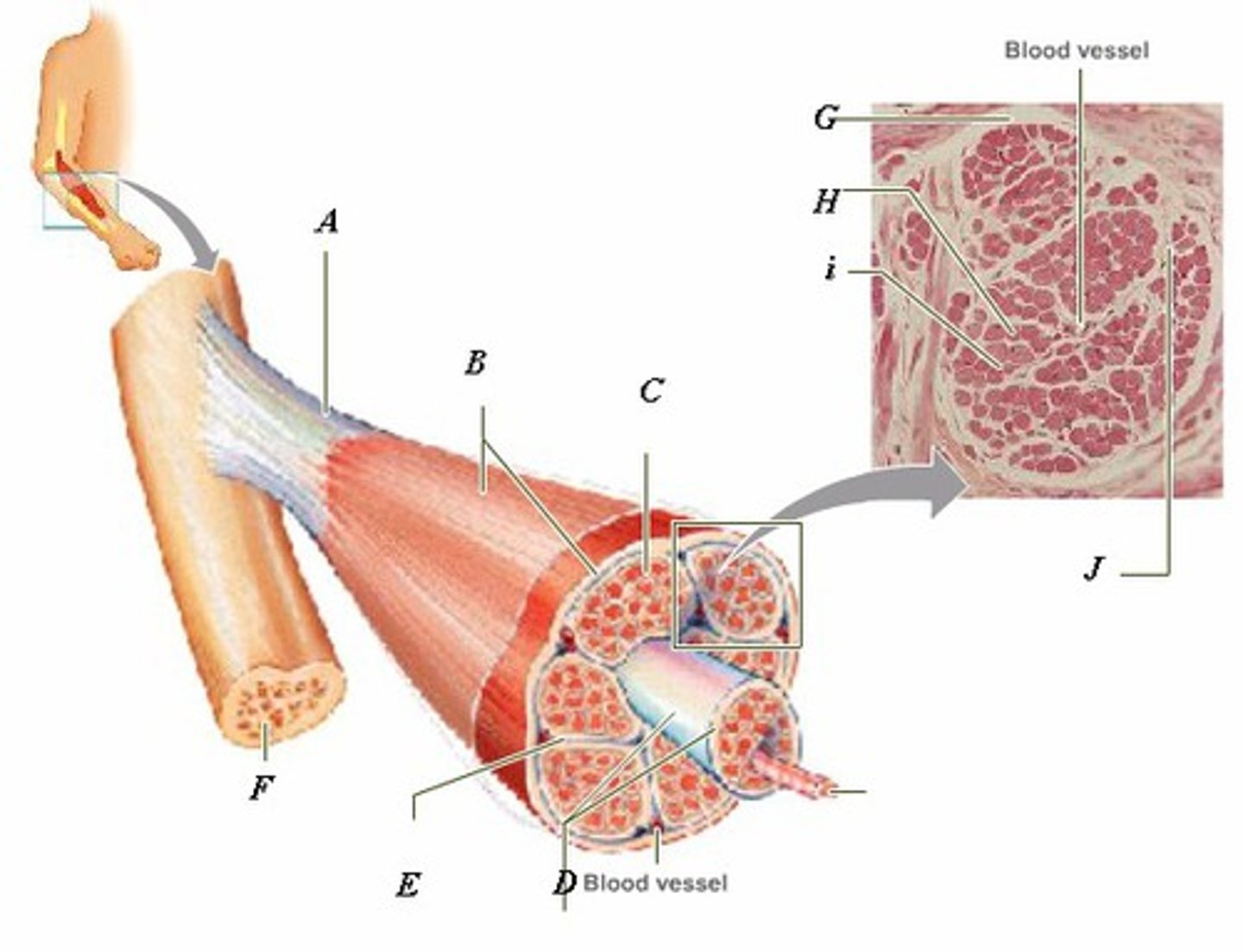
LABEL - PERIMYSIUM
LABEL (E)
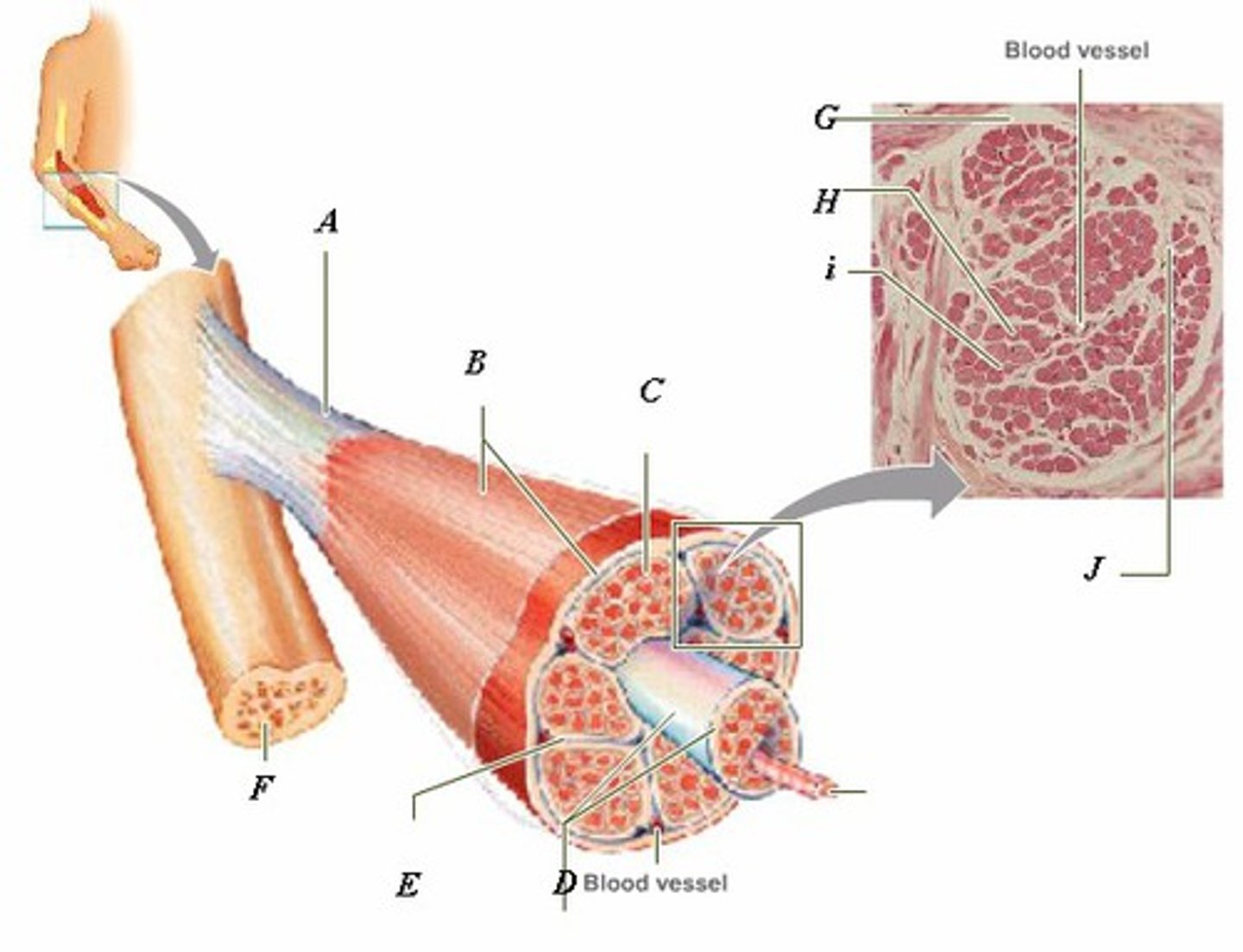
LABEL - BONE
LABEL (F)
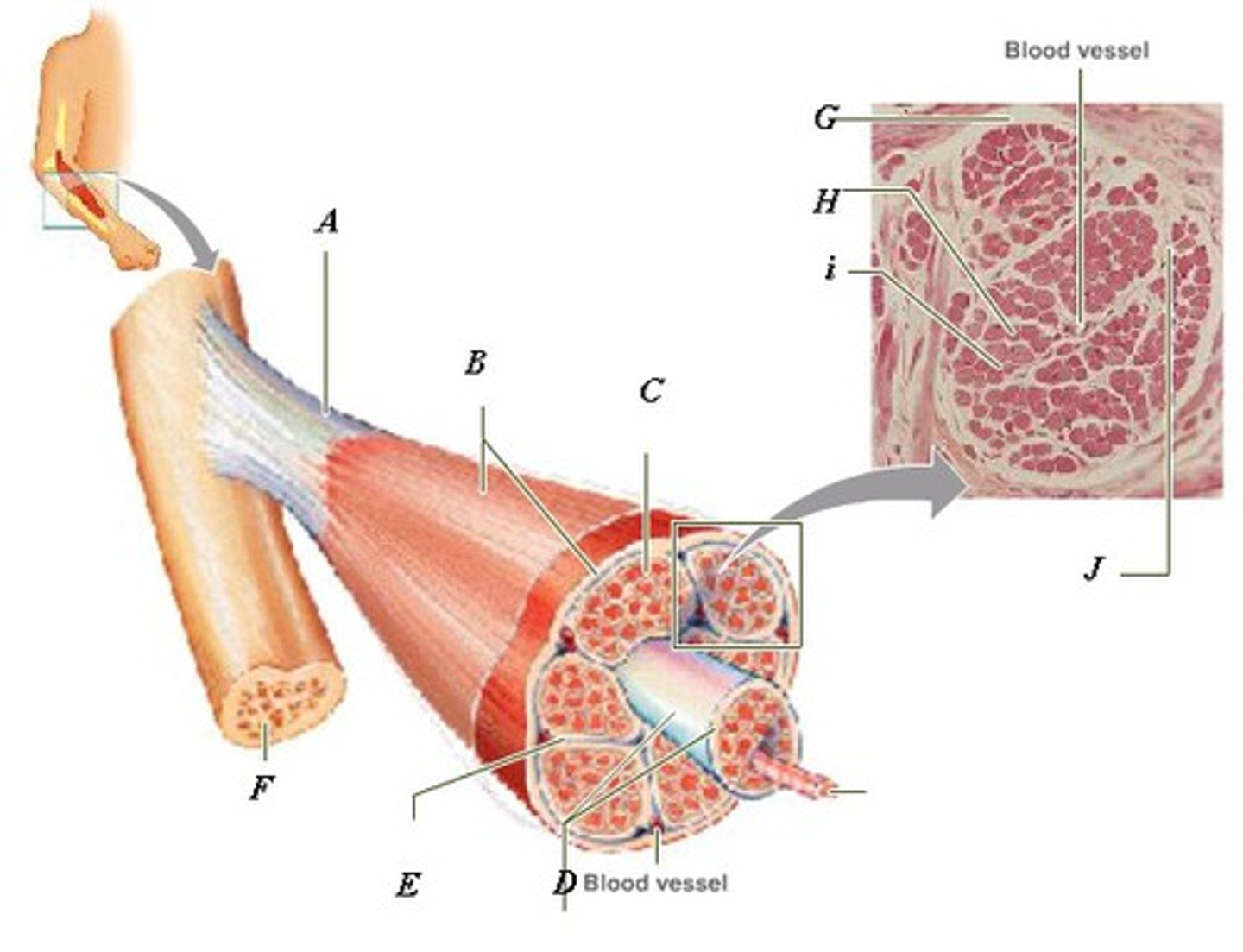
LABEL - EPIMYSIUM
LABEL (G)
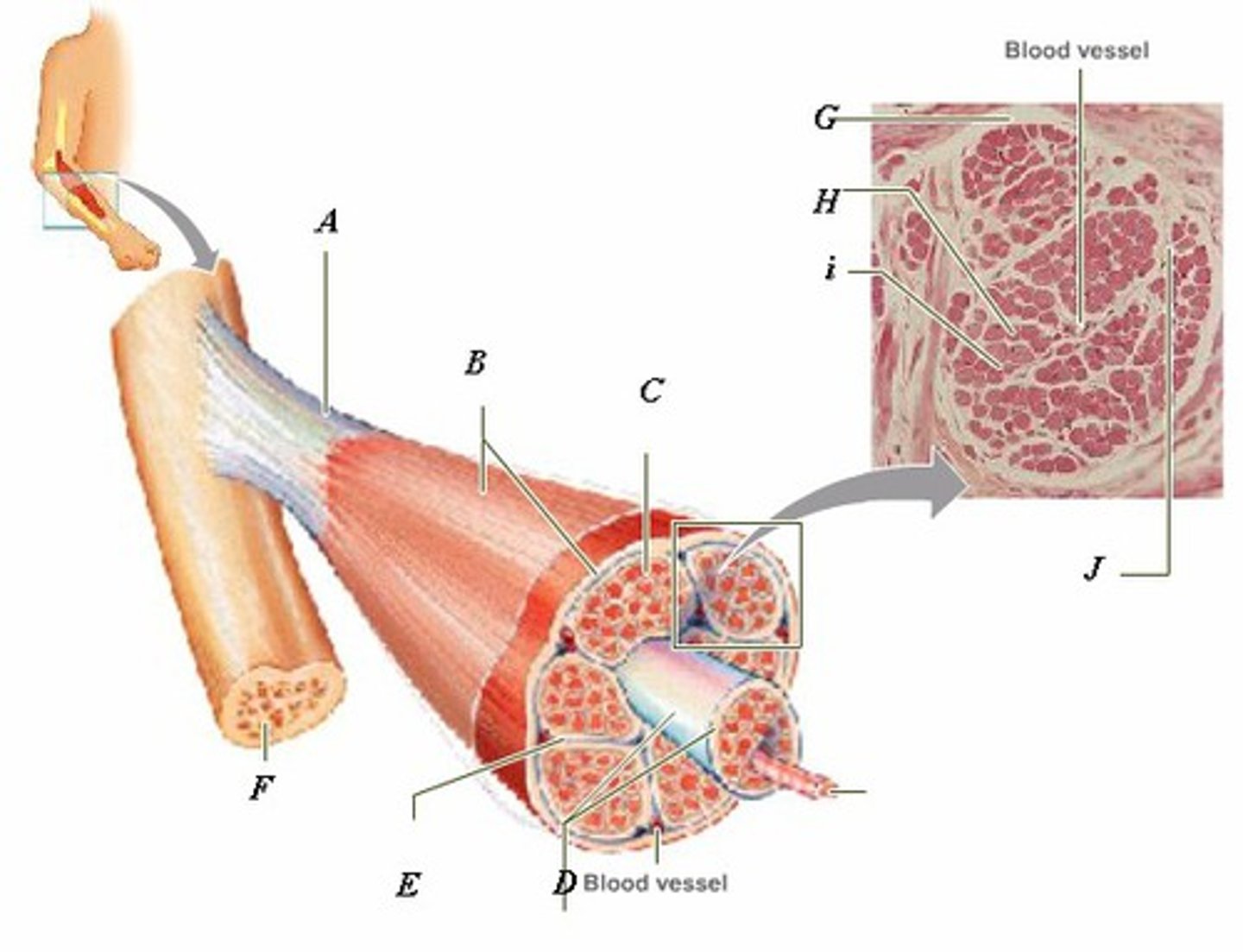
LABEL - MUSCLE FIBER
LABEL (H)
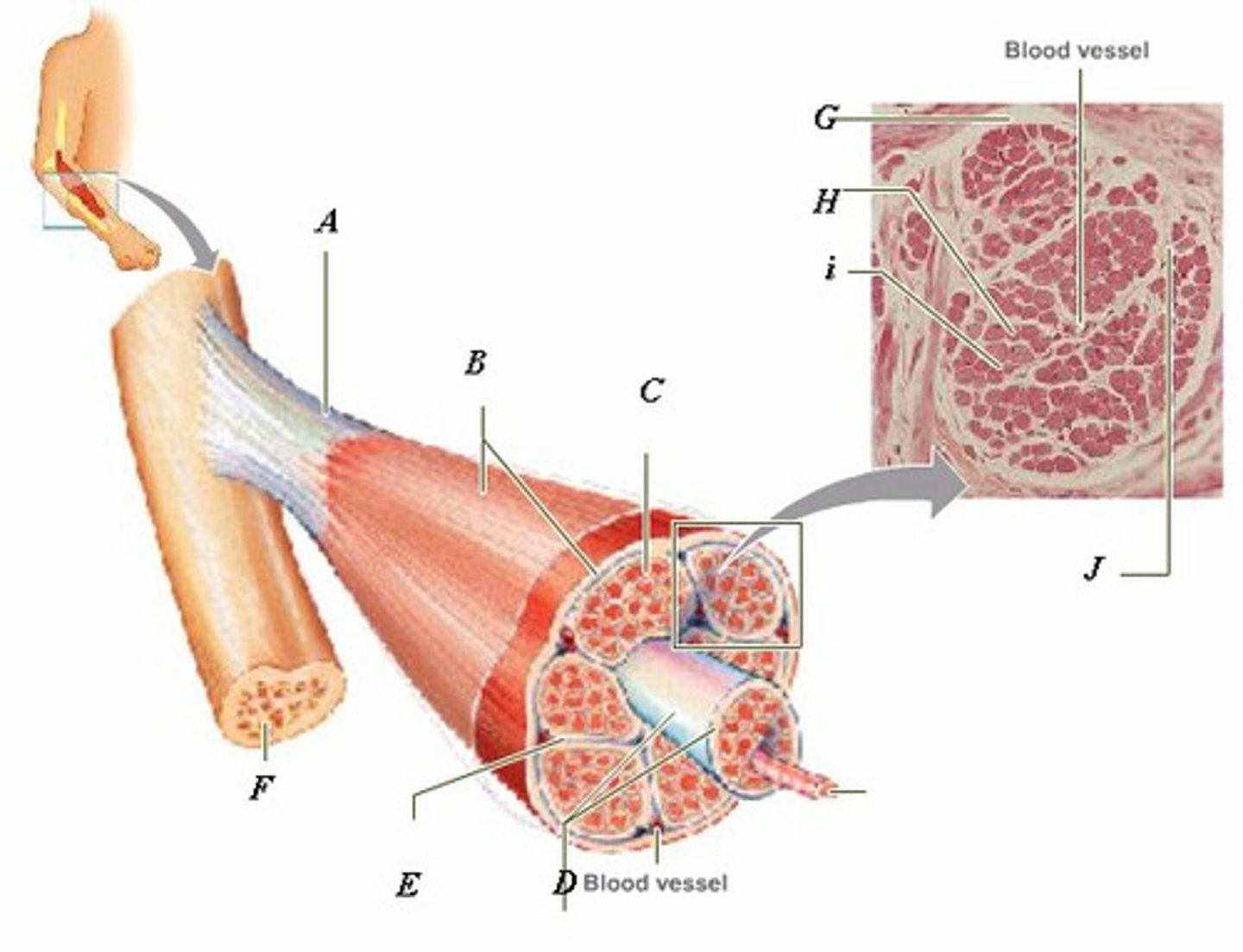
LABEL - ENDOMYSIUM
LABEL (I)
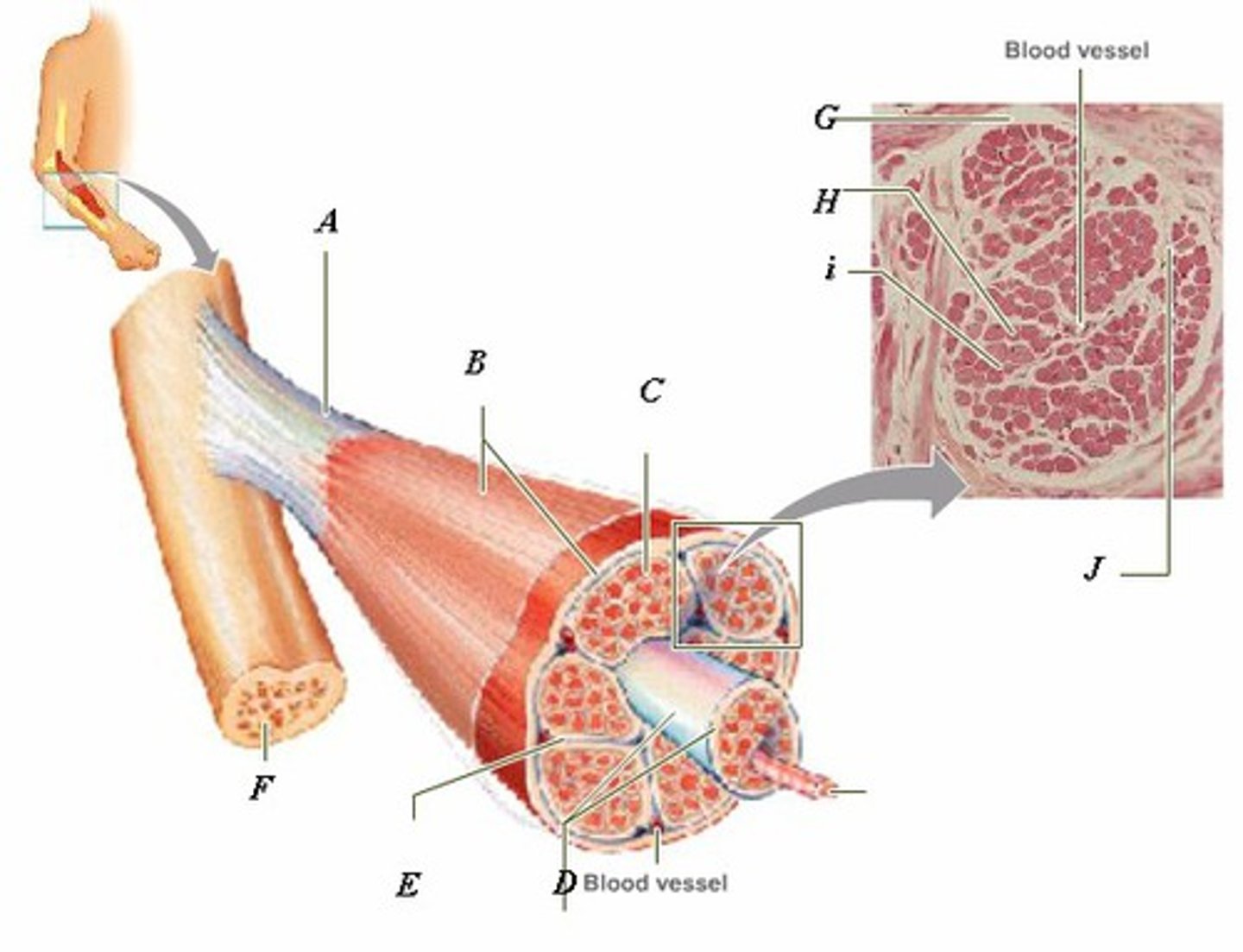
LABEL - PERIMYSIUM
LABEL (J)
All of the following are functions of muscle EXCEPT -
body support.
production of body heat.
movement.
protection.
posture maintenance.
protection.
An entire skeletal muscle is surrounded by
epimysium
As an axon enters a muscle, it branches into a number of axonal terminals, each of which forms a neuromuscular junction with a single muscle fiber. A motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it supplies is called a
motor unit
During muscle contraction, all of the following occur EXCEPT -
hemoglobin concentration in muscle fibers increases.
myosin heads bind to actin.
calcium concentration in the sarcomere increase.
the I bands shorten and H zones disappear.
ATP is hydrolyzed
hemoglobin concentration in muscle fibers increases
What is the ion released from the terminal cisternae that combines with troponin and removes the blocking action of tropomyosin, resulting in formation of cross bridges?
Ca2+
Each skeletal muscle fiber is controlled by a neuron at a single
neuromuscular junction
In a skeletal muscle fiber, which of the following best describes the composition of the structure known as a triad?
Terminal cisterna, transverse tubule, and terminal cisterna
In the sliding filament model of muscle contraction, the myofilaments slide over each other, resulting in an overlapping of actin and _________.
myosin
Interactions between actin and myosin filaments of the sarcomere are responsible for
muscle contraction
The all-or-none response of a muscle fiber means that
a muscle fiber responds maximally to threshold stimulation or NOT at all.
The dense layer of collagen fibers that surround an entire skeletal muscle is the
epimysium
The functional unit of a skeletal muscle fiber is the
sarcomere
Which statement below does NOT represent a role of ionic calcium in muscle contraction?
Triggers sliding of myofilaments and ATPase activity
The action potential triggers Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Promotes glycogen breakdown and ATP synthesis
Promotes neurotransmitter release
Triggers diffusion of Na+ out of the cells
Triggers diffusion of Na+ out of the cells
The space between the neuron and the muscle is the
synaptic cleft
The term that means a continued mild or partial contraction of an entire muscle is muscle
tone
The type of muscle contraction in which the muscle fibers produce increased tension but the muscle neither shortens nor lengthens is called
isometric
What is the role of calcium ions in the contraction of skeletal muscle?
Calcium ions bind to the troponin-tropomyosin complex and remove their inhibitory action on actin/myosin interaction.
Which of the following statements about smooth muscle is true?
Fibers are small and spindle-shaped.
Which of the following statements is INCORRECT?
Skeletal muscle contractions help maintain body temperature.
Skeletal muscles are responsible for the pumping action of the heart.
Skeletal muscles support the weight of some internal organs.
Skeletal muscles are responsible for guarding the openings of the digestive and urinary tracts.
The contractions of skeletal muscles pull on tendons and move elements of the skeleton.
Skeletal muscles are responsible for the pumping action of the heart.
Which of the following types of muscle is found in the eye and are used to regulate the size of the pupil?
Multiunit smooth muscle
Which of the following substances increases in quantity during repetitive muscle contraction?
Lactic acid
The sequence of electrical changes that occurs along the sarcolemma when a muscle fiber is stimulated is known as the
action potential
In the early stage of repolarization, the sarcolemma is restored to its initial polarized state initially by
K+ diffusing rapidly out of the muscle fiber.
During repolarization, the initial events restore only the electrical conditions while the Na+/K+ pump restores the
ionic conditions.
Which of the following moves Ca2+ back into the tubules of the SR after a contraction?
The ATP-dependent calcium pump
Which of the following allows recoil of the muscle fiber when contraction ends?
Elastic filaments
Which one of the following binds calcium ions in a smooth muscle causing contraction?
Calmodulin
Which of the following events is something a smooth muscle can do but cardiac and skeletal muscle can not do?
Grow by hyperplasia or an increase in the number of cells.
What is the protein found on thick filament
Myosin
What is the protein found on thin filament
Actin
What are the features of skeletal muscle
Voluntary, striated
What is the contractile unit of muscle?
Sarcomere
Light bands have
Only Thin filament
A motor unit consists of
Muscle fibers and motor neuron
A bundle of muscle fibers is called
Fascicle
The areolar connective tissue that enclose each muscle fiber is called?
Endomysium
ACh is a(an) ______ released by the axon terminals
Neurotransmitter
Are skeletal muscle cells multinucleate?
yes