Theme 1- Microbes and Us
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
What are the main prokaryotes
Bacteria and Archaea
What are the main eukaryotes
Fungi, Protozoan and Algae
Are viruses eukaryotic or prokaryotic
neither, are acellular
What is the bacteria’s cell wall made of
Peptidoglycan
Name three characteristics of archaea
lacks peptidoglycan
Lives in extreme environments
Not known to cause disease in humans
Extreme halophiles Archaea
Live in extremely salty conditions
Extreme thermophiles archaea
Live in hot sulphurous water
Methanogens archaea
Produce methane as a waste product from respiration
What are the unicellular fungi called
Yeasts

What are the multicellular fungi called
Mushrooms or mold
What are the cell walls of fungi made of
Chitin
How does bacteria reproduce
Binary fission - asexually
How do fungi reproduce
Asexually and sexually
Name three characteristics of Protozoa ( unicellular)
no cell walls
May be motile via pseudopods, cilia or flagella
Parasitic or free living
Name three characteristics of Algae
unicellular or multicellular
Asexual or sexual reproduction
Produce molecular oxygen and organic compounds by photosynthesis
What is the cell walls of algae made of
Cellulose
Name three characteristics of viruses
not considered living outside host cell
Core surrounded by a protein coat
Coat may be enclosed in a lipid envelope
What are the three domains based on cellular organisation
bacteria ( contains peptidoglycan)
Archaea ( lacks peptidoglycan )
Eukarya
Who developed the 3 domains based on cellular organization
Carl Woese
Who established the system of scientific nomenclature ( 1735)
Linnaeus
Who marked the beginning of the cell theory ( 1663-1665)
Robert Hooke
What does the cell theory state
All living things are composed of cells
Who observed the “animalicules” and found they were microbes ( 1623-1673)
Anton van Leeuwenhoek
Spontaneous generation
The hypothesis that life arises from nonliving mater, a “vital force” necessary for life
In 1668, who filled the hairs with decaying meat to show spontaneous generation
Francesco Reid
IN 1745, who put boiled nutrient broth ( microbial growth) into covered flasks to prove spontaneous generation
John Needham
In 1765, who boiled nutrient solution( no microbial growth) in sealed flasks
Lazzero Spallanzani
Biogenesis
The hypothesis that living cells arise only from pre-existing living cells
In 1858, who stated the hypothesis of biogenesis
Rudolf Virchow
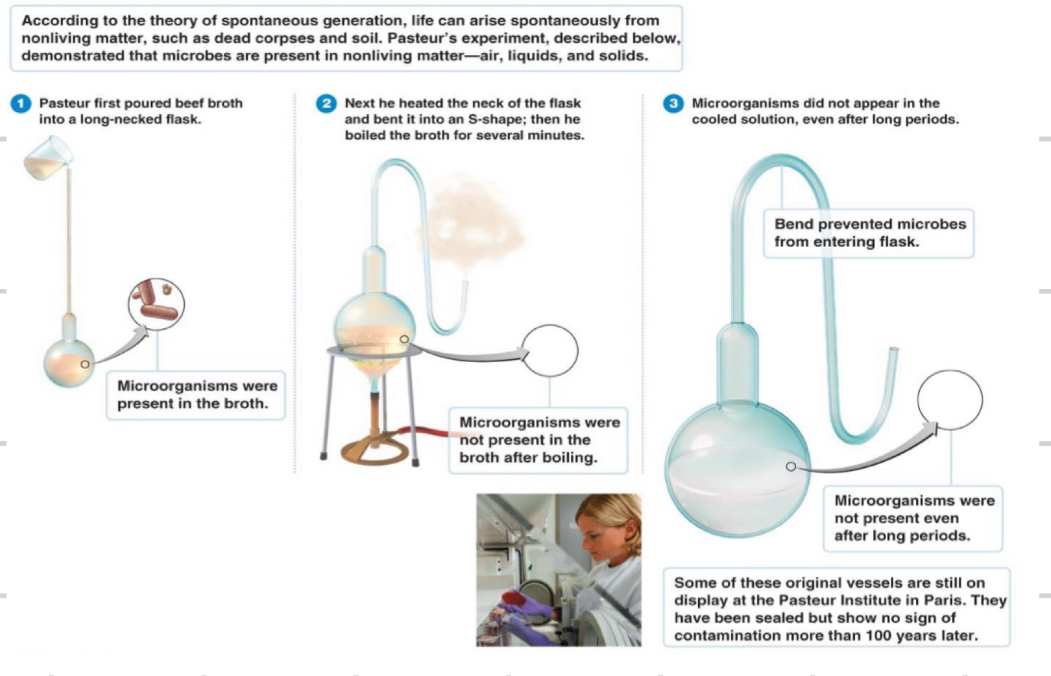
In 1861, who did experiments to that showed microorganisms are present in the air
Louis Pasteur
What conclusions came out of Pasteur’s work
microorganisms are present in air, liquids and solids
Heat can destroy microorganisms
Developed aseptic techniques ( prevent microbial contamination)
What occurred in the golden age of microbiology ( 1857-1914)
Used Pasteurs work to discover the relationship between microbes and disease, immunity and vaccines
Fermentation ( Pasteur showed microbes are responsible)
Microbial conversion of sugars to alcohols in the absence of air
Pasteurization
Application of high heat for a short time to kill harmful bacteria in beverages
Who showed that a silkworm disease was caused by a fungus
Agostino Bassi
Who advocated for handwashing to prevent the transmission of puerperal fever from one obstetrical patient to another
Ignaz Semmelweis
Who introduced the use of disinfectant to clean surgical wounds
Joseph Lister
In 1876, who proved that a bacterium causes anthrax and provided experimental steps, Koch’s postulates, to prove that a specific microbe causes anthrax specific diese
Robert Koch
Chemotherapy
Treatment of disease with chemicals
Antibiotics
Naturally produced by bacteria and fungi that inhibit or kill other microbes
Who developed the first synthetic drug, Salvarsan, to treat syphilis
Paul Ehrlich
Who discovered the first antibiotic, penicillin, on accident
Alexander Fleming
What are microbes that normally present in and on the human body called
Normal microbiota
What is the function of normal microbiota on our skin
prevents the growth of pathogens
Produce growth factors like vitamin B and K
What are biofilms
Microbes that attach to solid surfaces and grow into masses
Why are biofilms dangerous
Can cause infections and are often resistant to antibiotics
How do biofilms communicate
Quorum Sensing
Infectious disease
When a pathogen invades a host and overcomes the host’s resistance, disease results
Resistance
The ability of the body to ward off disease. E.g barrier of the skin, stomach acid
Emerging infectious diseases ( EIDs)
New diseases and diseases increasing in incidence
What does SARS stand for
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome
Covid 19
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Corona Virus ( MERS-CoV)
Bird flu and Influenza A virus
Avian influenza A ( H5N1 )
What does Ebola hemorrhagic fever ( EHF) cause
Fever, hemorrhaging and blood clotting which is transmitted via contact with infected blood or body fluids
What does AIDs stand for
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
What causes AIDs
Human immunodeficiency virus ( HIV)