L16 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Learning objectives
Identify and explain the functions of various regions within the peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Compare and contrast the divisions of the autonomic nervous system (ANS)
Be able to apply knowledge of the ANS (on a basic level) to situations
Identify and describe the structure of a nerves
Describe cranial and spinal nerves (don’t need to remember all)
Describe the dorsal and ventral roots and explain their importance
Recognise and describe the plexuses
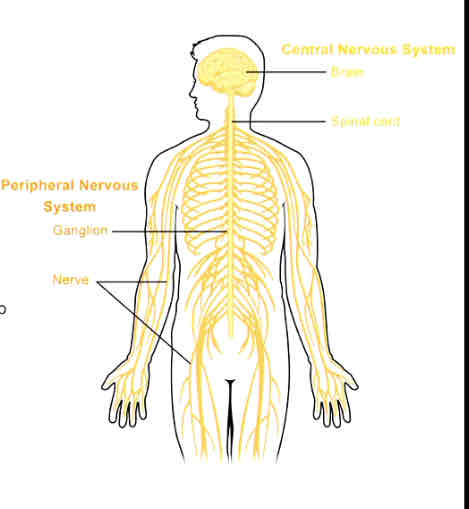
What is the peripheral nervous system (PNS)?
Everything outside of CNS
2 types of nerves:
cranial nerves (12 pairs)
Spinal nerves (31 pairs)
Ganglia
Enteric plexuses (GIT)
Other nerve plexuses
Sensory receptors
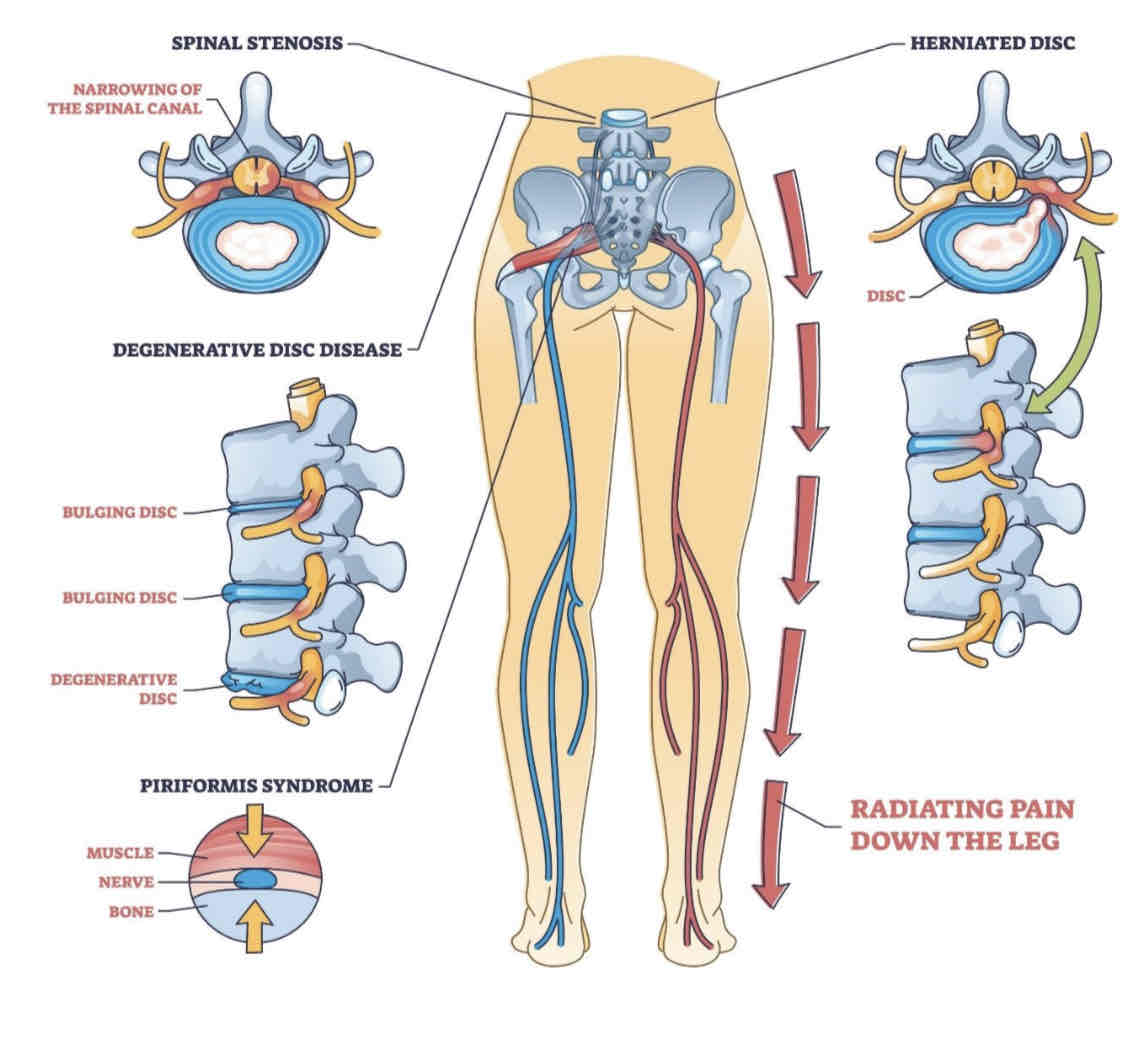
Why does the PNS?
Sciatica: a range of symptoms, including extreme back pain and radiating pain through the lower limbs
Compression or inflammation of sciatic nerve root = pain running down leg
Organisation of the PNS
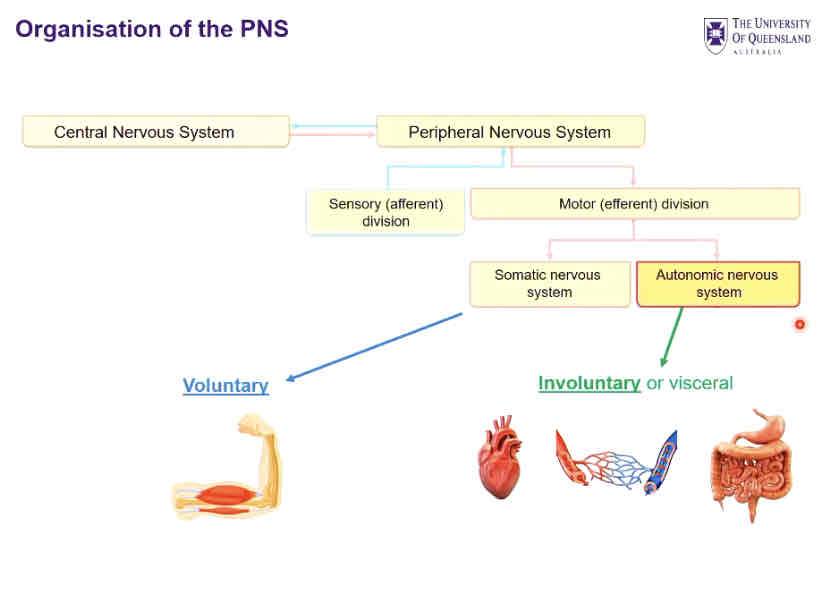
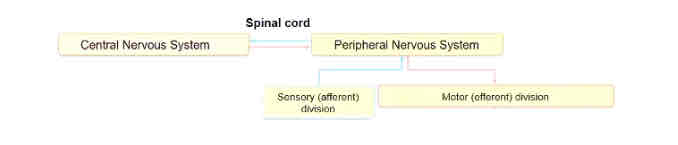
In/output from the PNS
Afferent sensory nerves carry info from sensory receptors to the CNS
somatic (skin, muscles, joints) - reflex action
Visceral (visceral organs)
Efferent (motor) nerves carry information away from the CNS to the effector organs
somatic motor nerves innervate skeletal muscle
Automatic nerves innervates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & glands (Parasympathetic and sympathetic)
Key anatomical differences between ANS divisions
1/ sites of origin
2/ fibre length
3/ location of ganglia
1/ site of origin
PS: brain stem, sacral region
S: lumbar region, thoracic region
2/ length of fibres
PS: long preganglionic, short postganglionic
S: short preganglionic, long postganglionic
3/ ganglia location
PS: within/near visceral effector organs
S: close to spinal cord
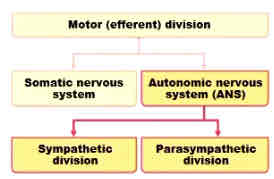
2 divisions of autonomic nervous system
Sympathetic (“fight or flight” → kicks in during stress)
Parasympathetic (“rest and digest”)
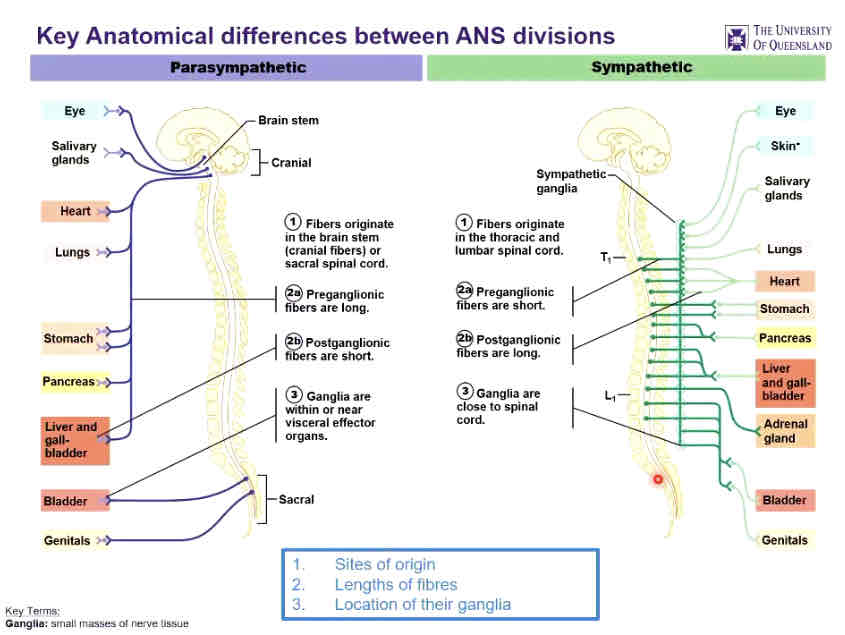
Key anatomical differences between ANS divisions
Parasympathetic
Fibers originate in brain stem/sacral spinal cord
Sympathetic
Fibers originate in the thoracic and lumbar spinal cord
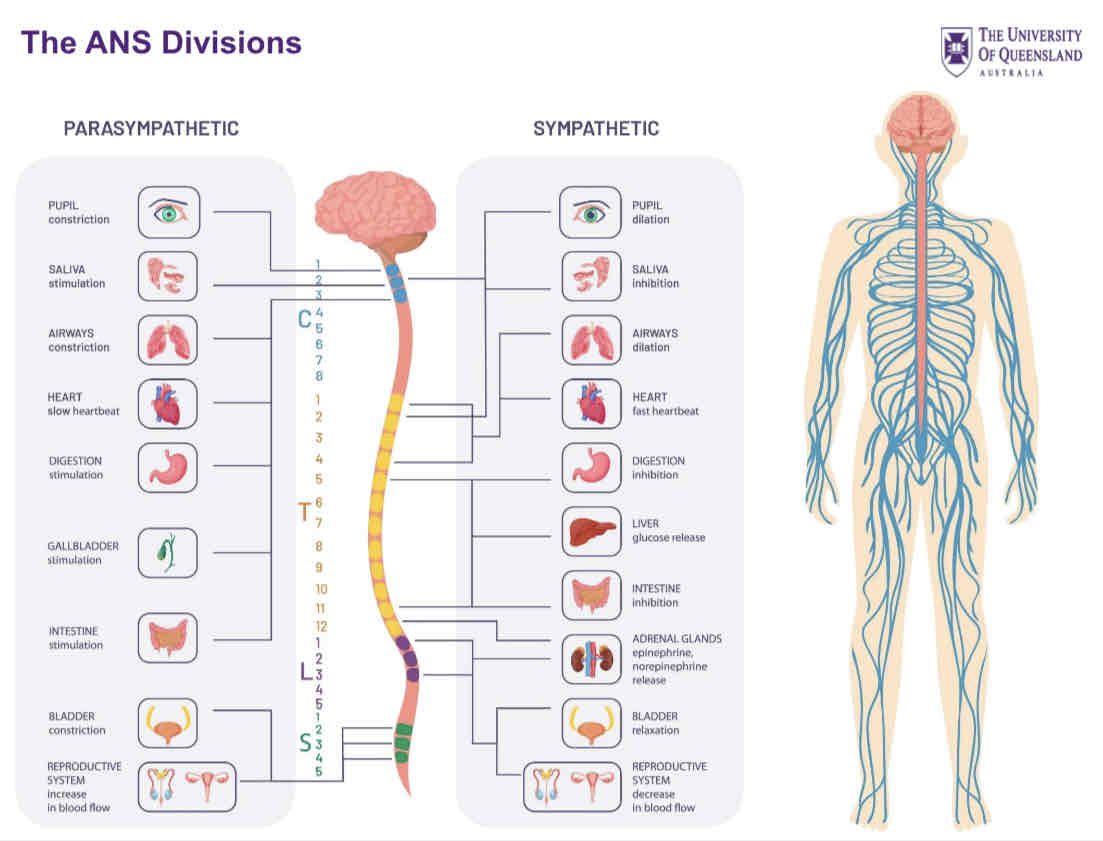
The ANS divisions
3 types of nerves
Sensory
Motor
Inter
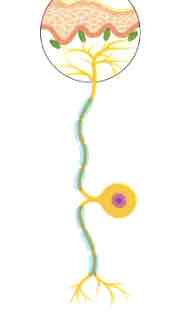
Sensory neuron
Activated by external physical or chemical stimuli
Picking up signals from the environment and send them affluently into our NS
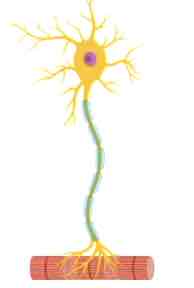
Motor neuron
Found in the spinal cord that connect to organs, muscles, and different types of glands in the body
Efferent: sending signals out onto our organs, muscles, and glands

Interneuron
Connect motor neurons to sensory neurons, allowing signalling between the 2
High concentration of inter neurons in the spinal cord
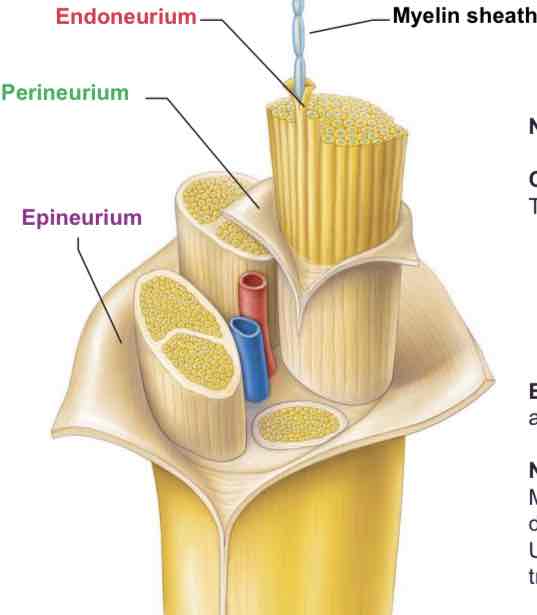
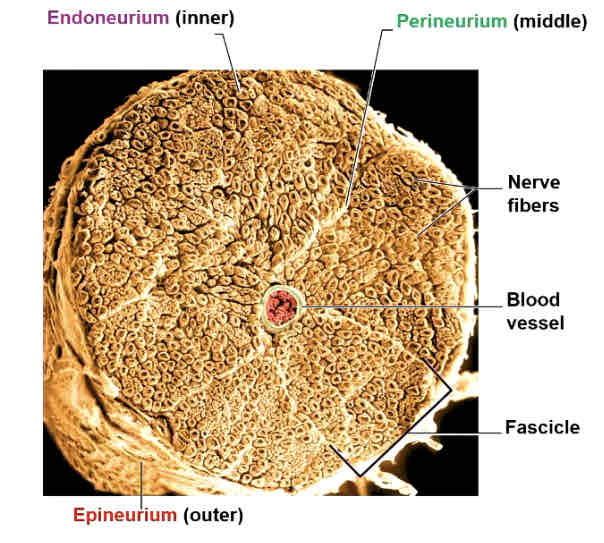
3 layers in connective tissue
Endoneurium: surrounds individual axons within a fascicle
Perineurium: wraps around each fascicle
Epineurium: encases all the fascicles to form the whole nerve
Blood vessels
Provide oxygenated blood
Take away deoxygenated blood + other wastes
Nerve fiber types
Myelinated (white matter) axons: rapidly transmit impulses over long distances
Unmyelinated (grey matter) axons: slower or shorter-distance transmissions
Structure of a nerve
31 spinal nerves attach to the spinal cord
8 cervical
12 thoracic
5 lumbar
5 sacral
1 coccygeal
Mixed spinal nerves
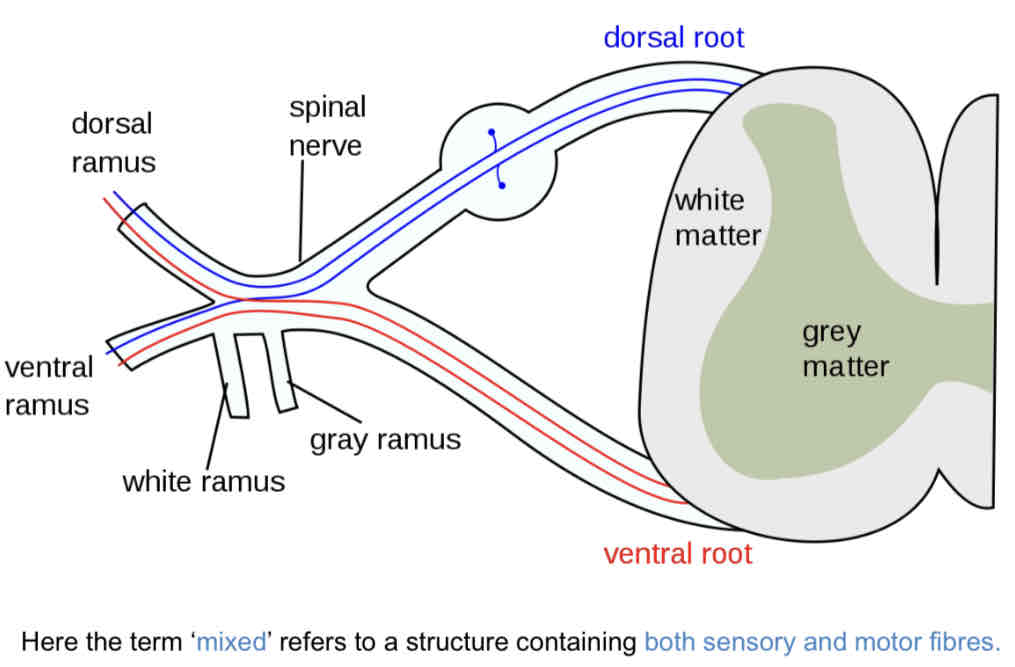
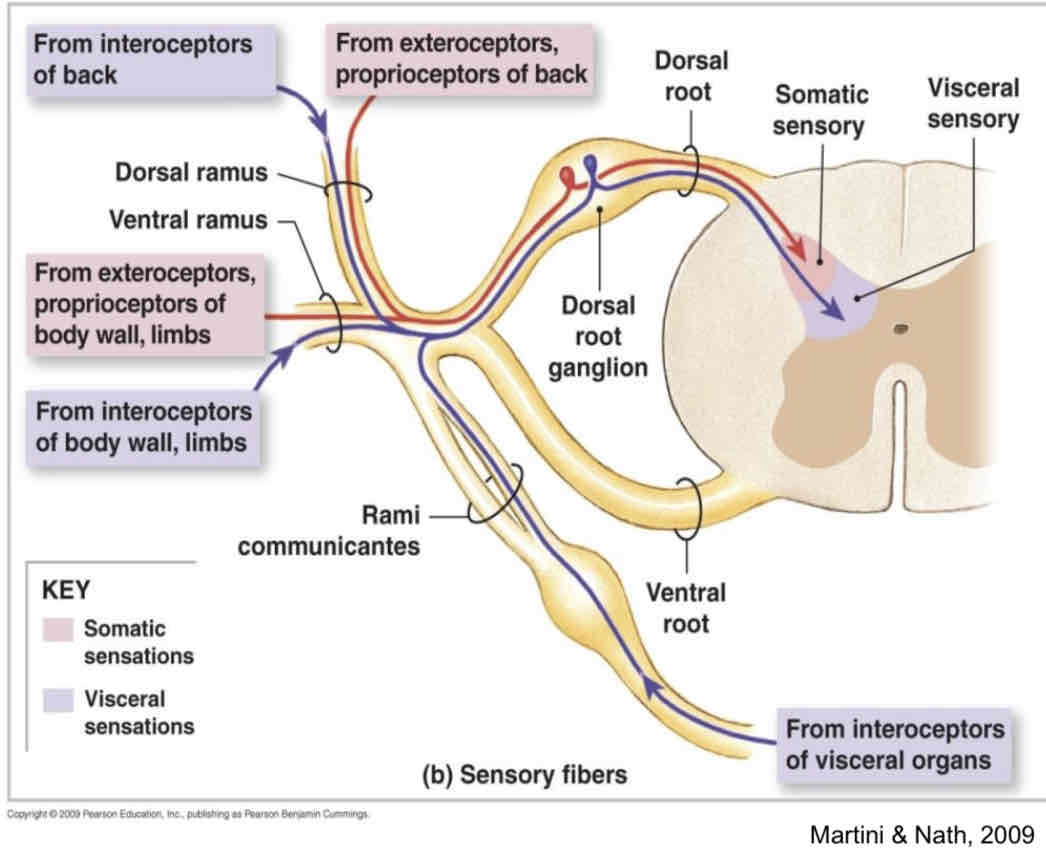
Spinal nerves branch to form dorsal and ventral rami
Dorsal rami
Innervation to the skin + back muscles (smaller)
Ventral rami
Innervation to the rest of trunk and limbs (larger)
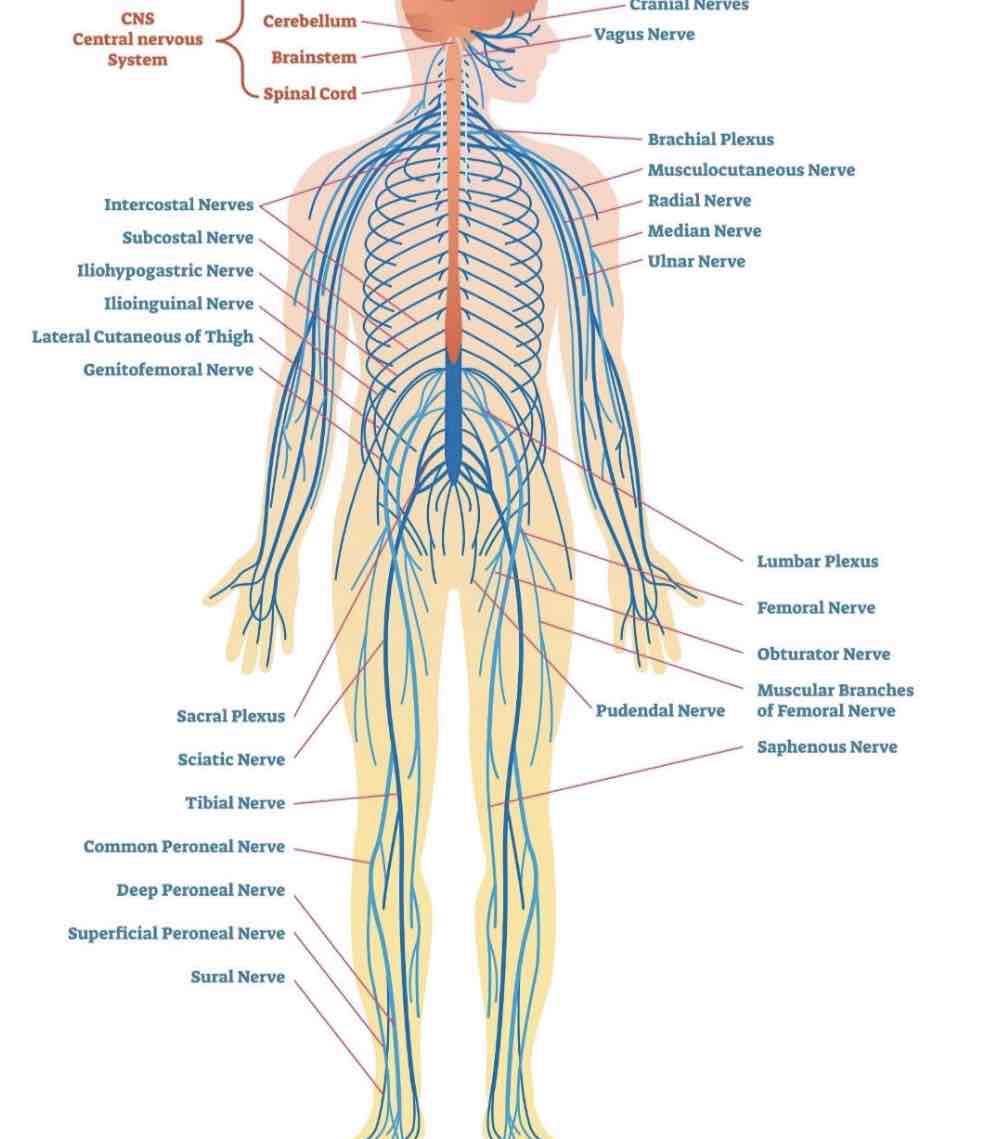
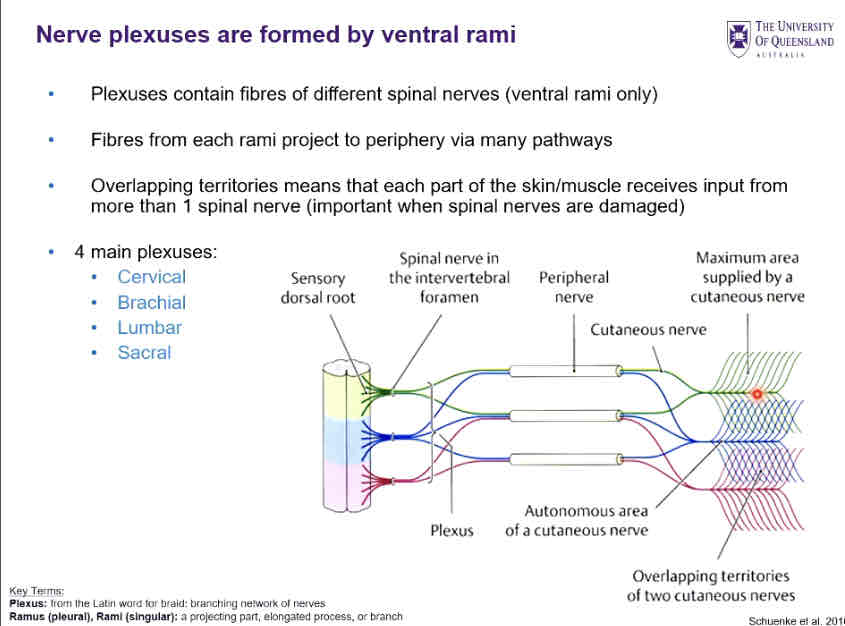
Nerve plexuses ???
Formed by ventral rami of spinal nerves
Cervical
Brachial
Lumbar
Sacral
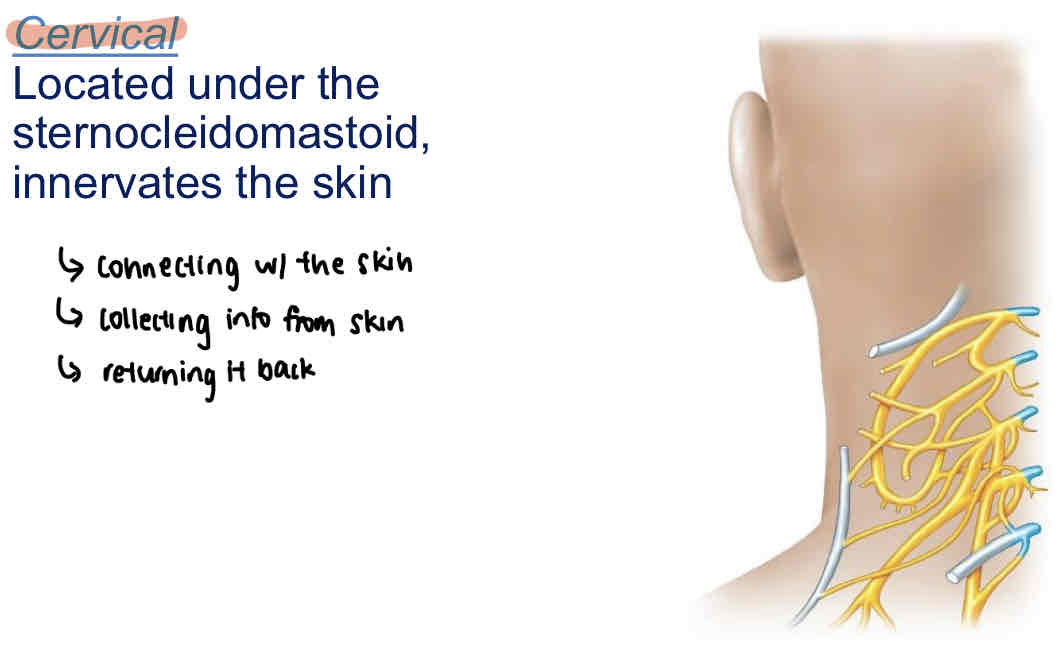
Cervical
Located under the sternocleidomastoid, innervates the skin
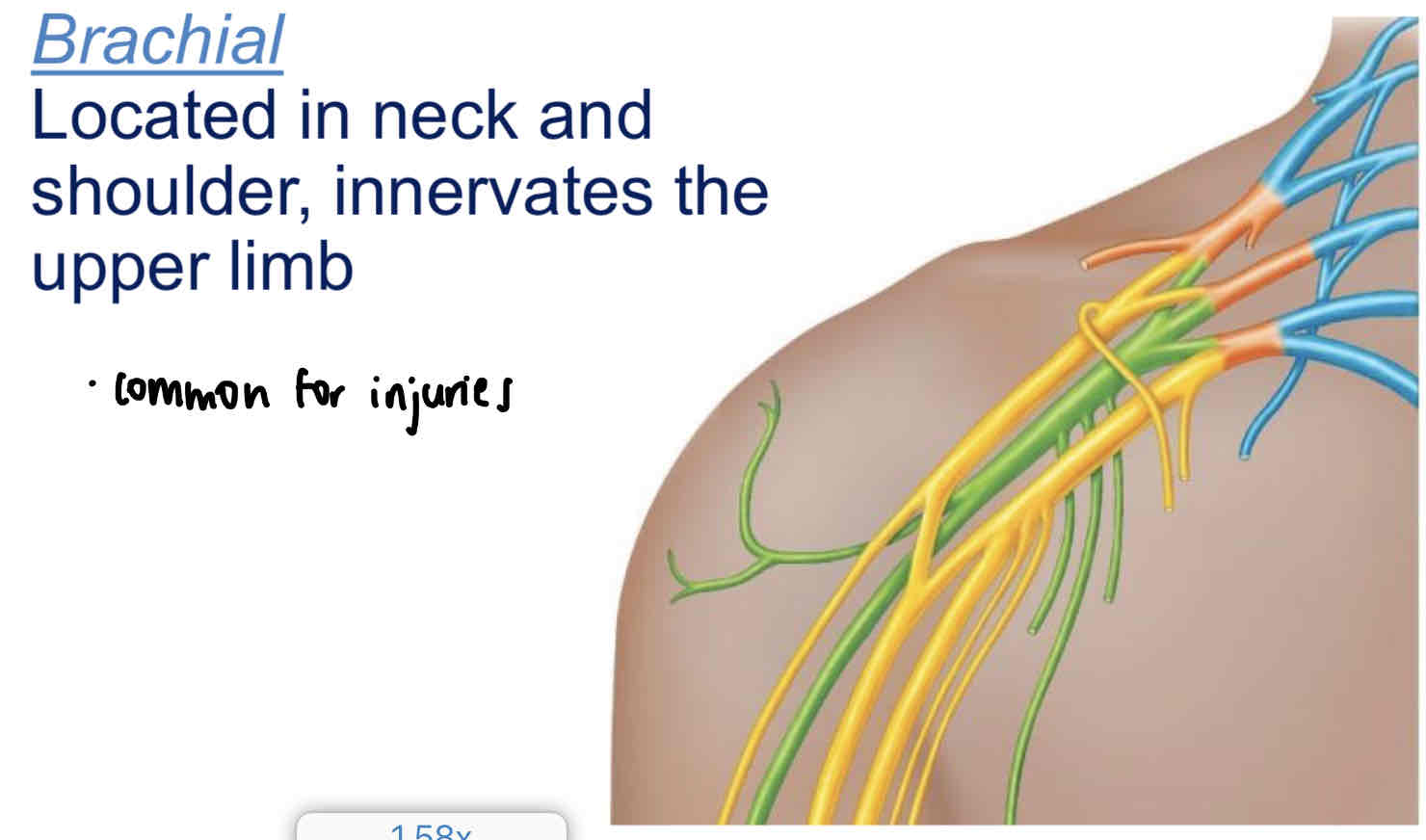
Brachial
Located in neck and shoulder, innervates the upper limb
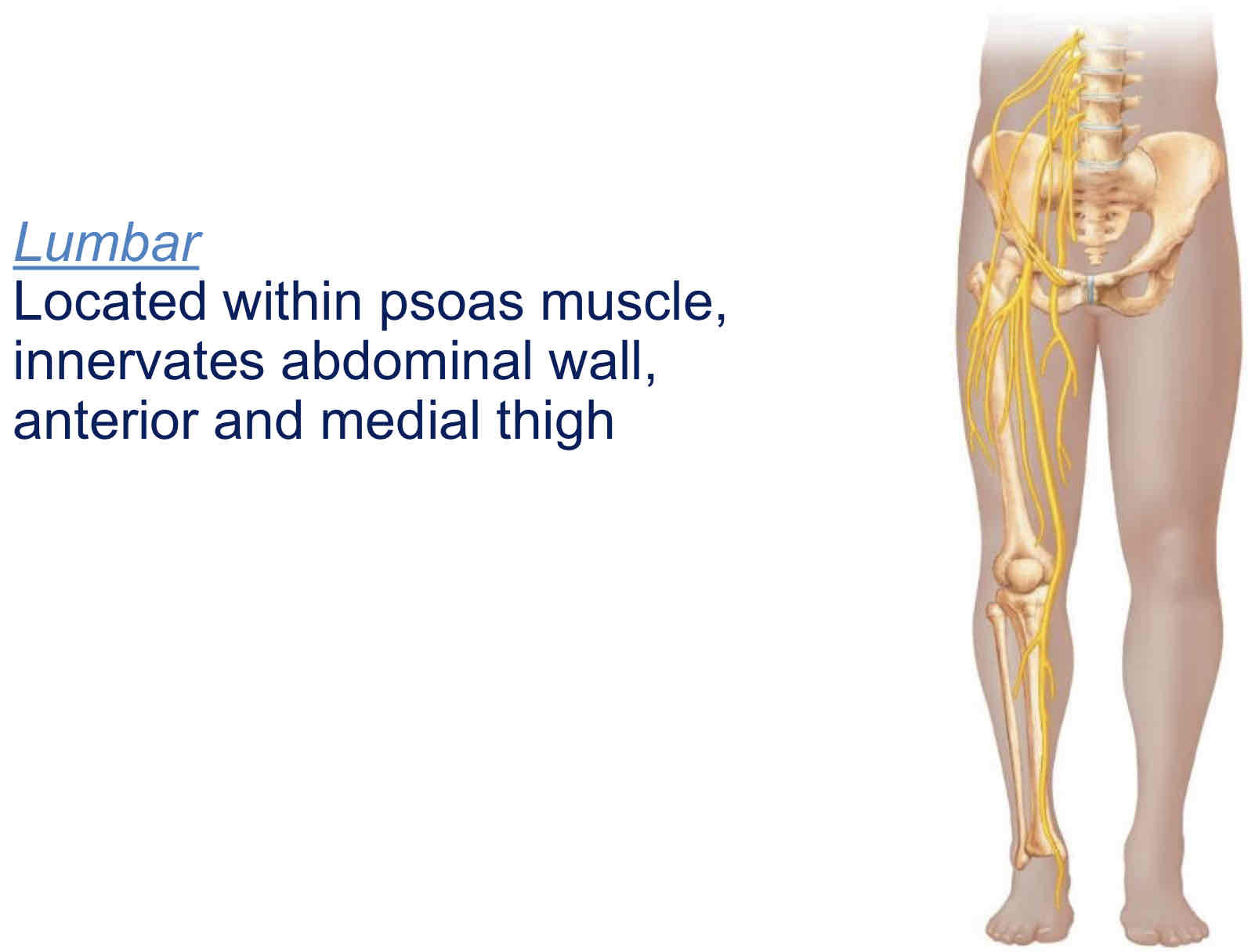
Lumbar
Located within psoas muscle (hip), innervates abdominal wall, anterior and medial thigh
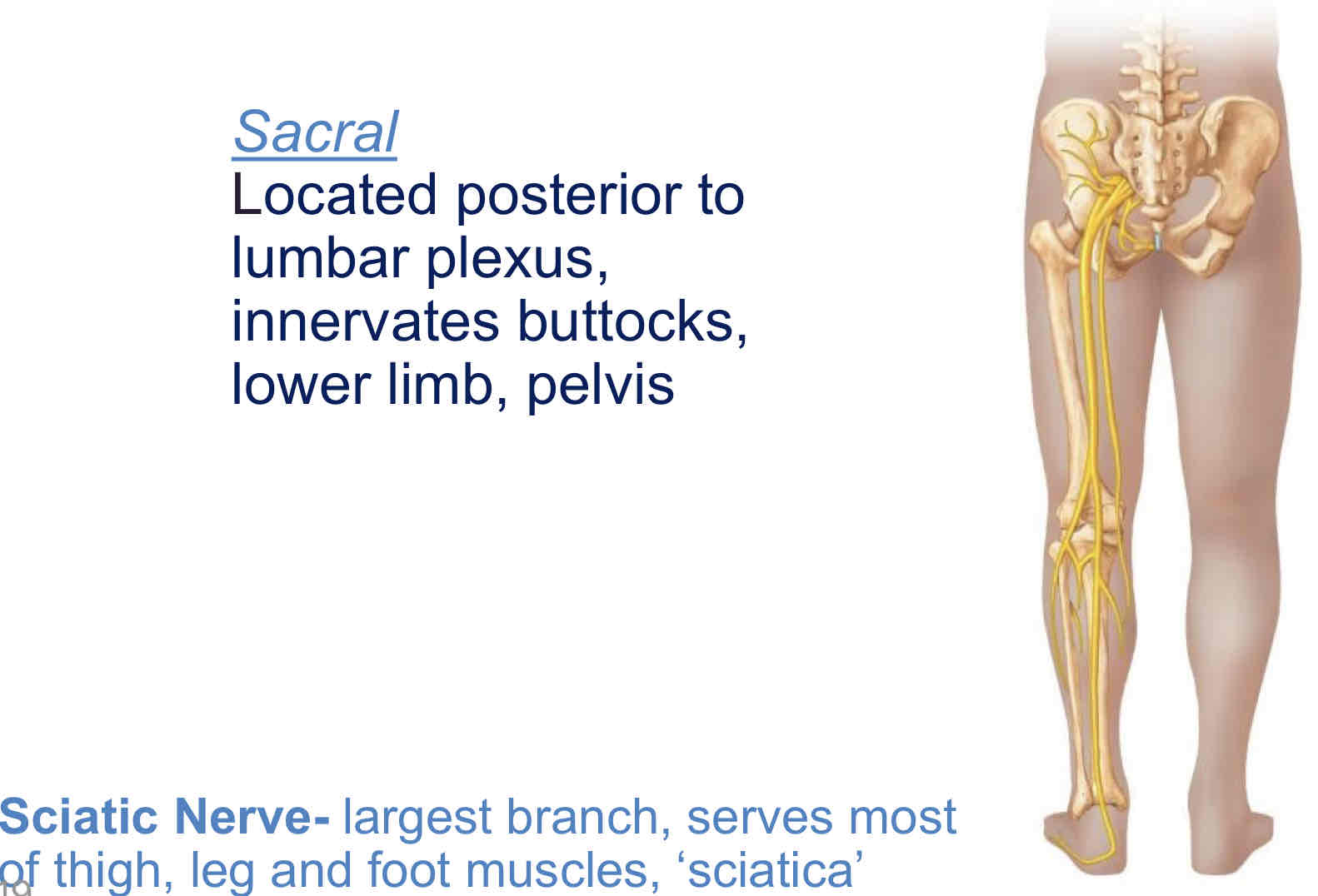
Sacral
Located posterior to lumbar plexus, innervates buttocks, lower limb, pelvis
Brachial plexus injuries
Injuries to brachial plexus are common - can weaken or paralyse arm
Ulnar nerve is very vulnerable (“funny bone” - ulnar nerve is superficial, rests against medial epicondyle)
Eg.
carpal tunnel syndrome - median nerve is compressed
Brachial plexus birth palsy
Any injury to brachial plexus during difficult delivery (nerves are stretched or torn)
Most recover in 3-6m with physical therapy, otherwise surgery
Cranial nerves
12 pairs: sensory, motor, or both (mixed)
Arranged along the longitudinal axis of brain:
CNI attaches to the cerebrum
CNII attaches to diencephalon
CNIII-XII attach to the brain stem

Compare vs. contrast parasympathetic + sympathetic