Seed Development, Structure, and Germination in Plants
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Doomsday Vault
Seed Bank
Seed
Develops from the fertilized ovule and includes the embryo and endosperm within a seed coat.
Double fertilization
Yields a diploid zygote (embryo) and a triploid central nuclei (endosperm).
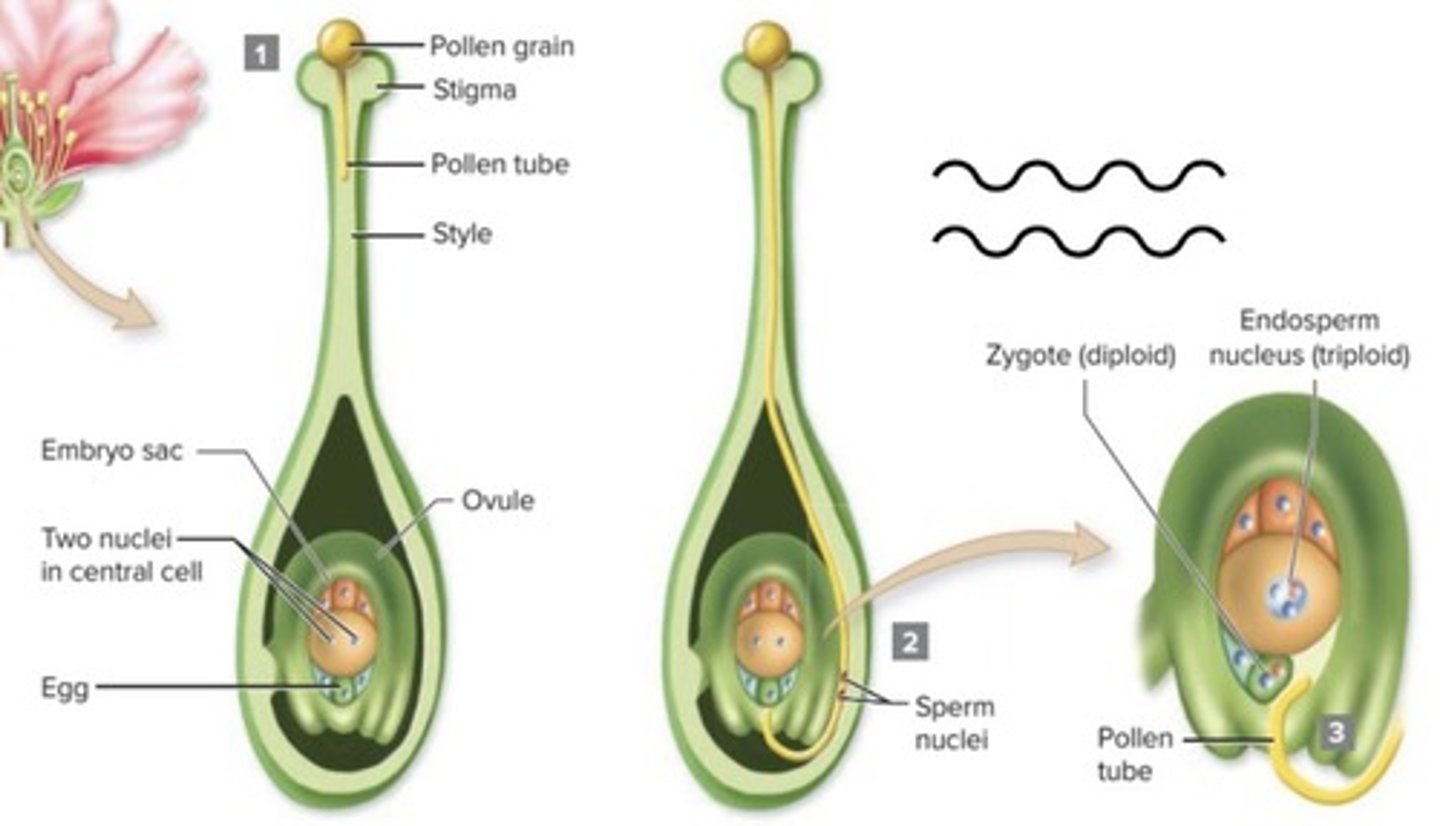
Endosperm Development
Usually develops first before the embryo.
Central nuclei
Divides to form a multinucleate 'supercell' with a milky consistency.
Coconut 'milk'
Example of liquid endosperm.
Coconut 'meat'
Example of solid endosperm.
Monocot Endosperms
The endosperm of grains such as corn, wheat, and rice occupies the bulk of the kernel and is the main energy reserve for the development of the young seedling.
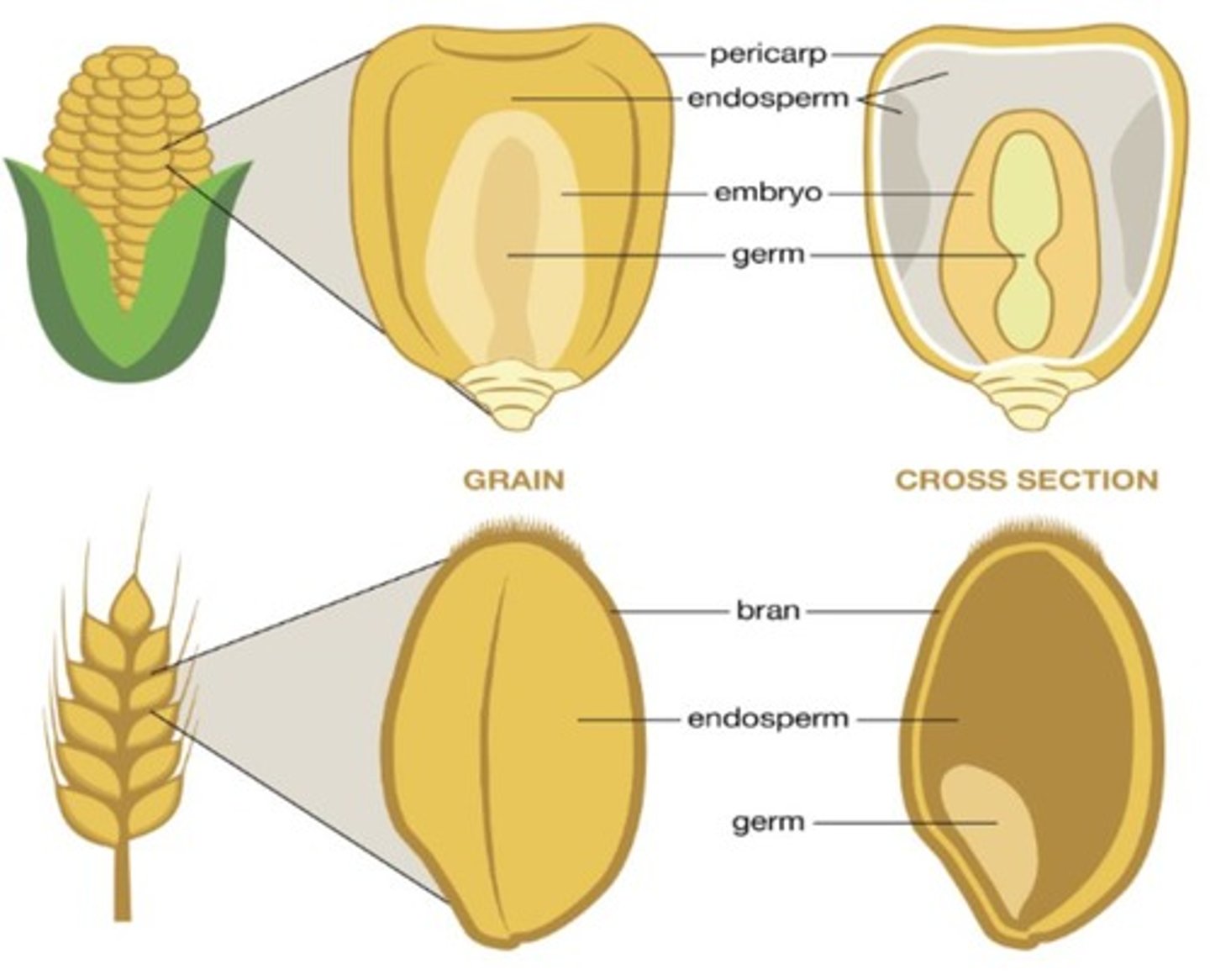
Monocot
Stores the bulk of its energy in the endosperm.
Dicot Endosperms
Most dicot seeds lack endosperms upon maturity.
Food reserves of the endosperm
Are completely transferred to the embryo in dicots.
Dicot
Stores its food in the two cotyledons.
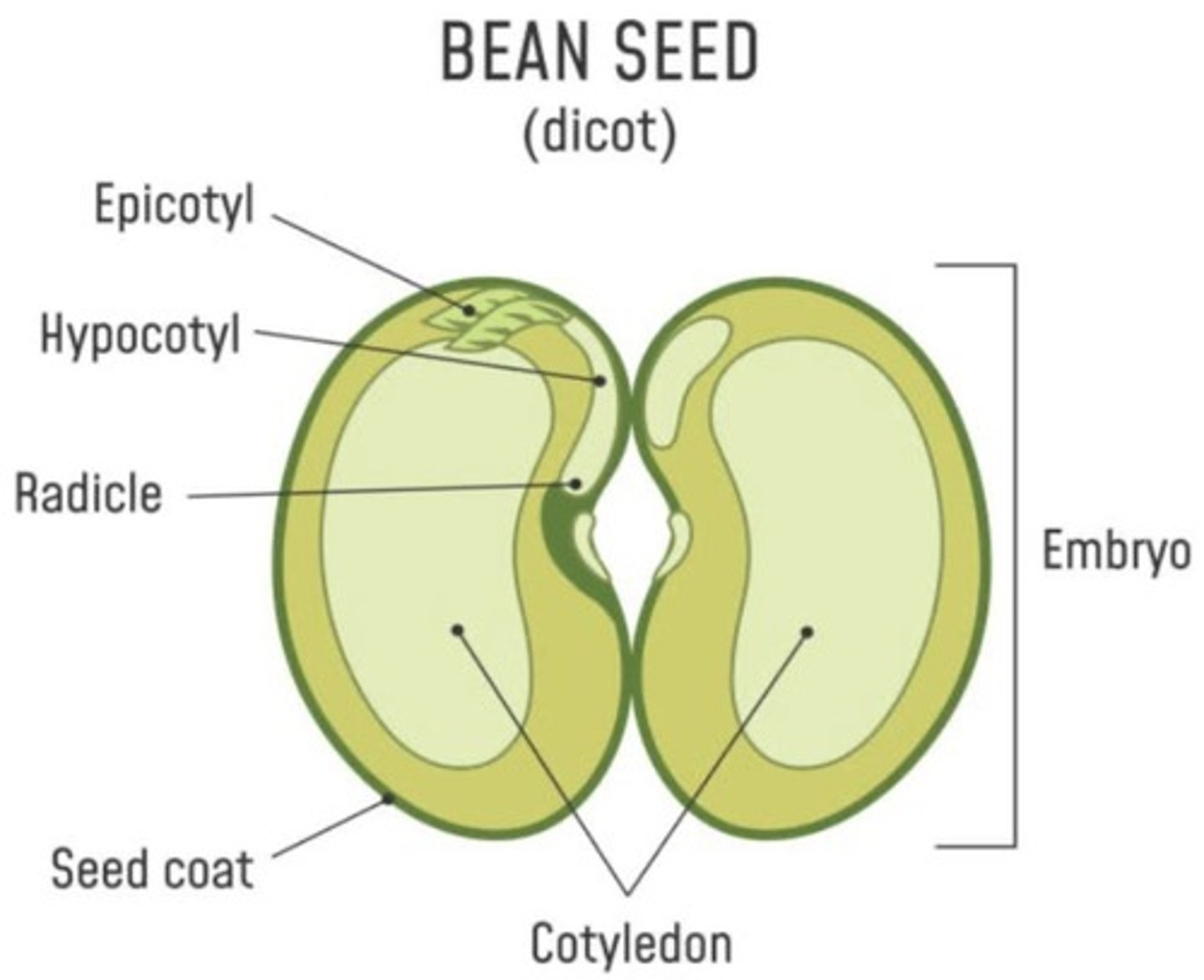
Seed Structure
Includes embryo, endosperm, seed coat, radicle, epicotyl, hypocotyl, and cotyledon.
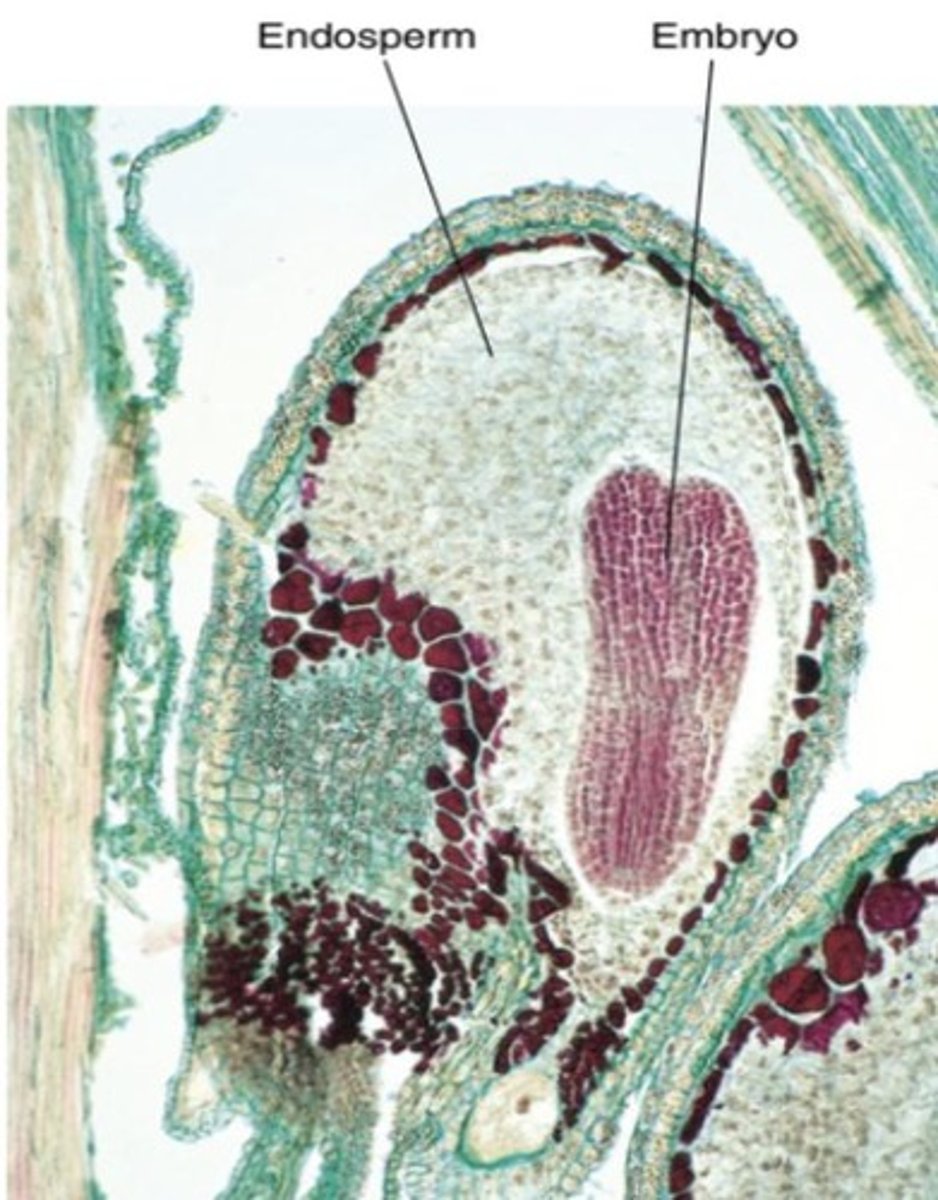
Embryo
Young plant.
Endosperm
Stored food for embryo.
Seed coat
Encases the seed.
Radicle
Embryonic root.
Epicotyl
Embryonic shoot.
Hypocotyl
Junction between roots and shoots.
Cotyledon
Seed leaf.
Embryogenesis
Zygote undergoes mitotic division and gives rise to terminal and basal cell.
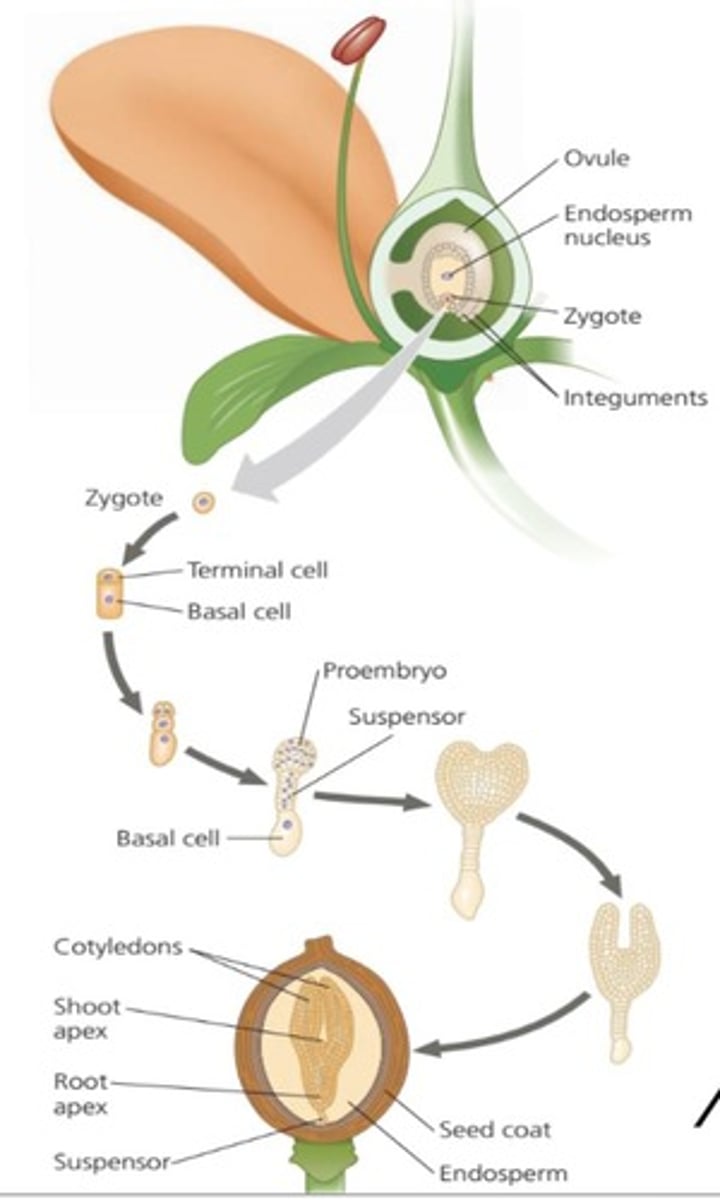
Suspensor
Helps in transferring nutrients to the embryo.
Seed Dormancy
A survival mechanism by which seeds can delay germination until the right environmental conditions for seedling growth and development.
Germination for Dicot
The first organ to emerge is the radicle.
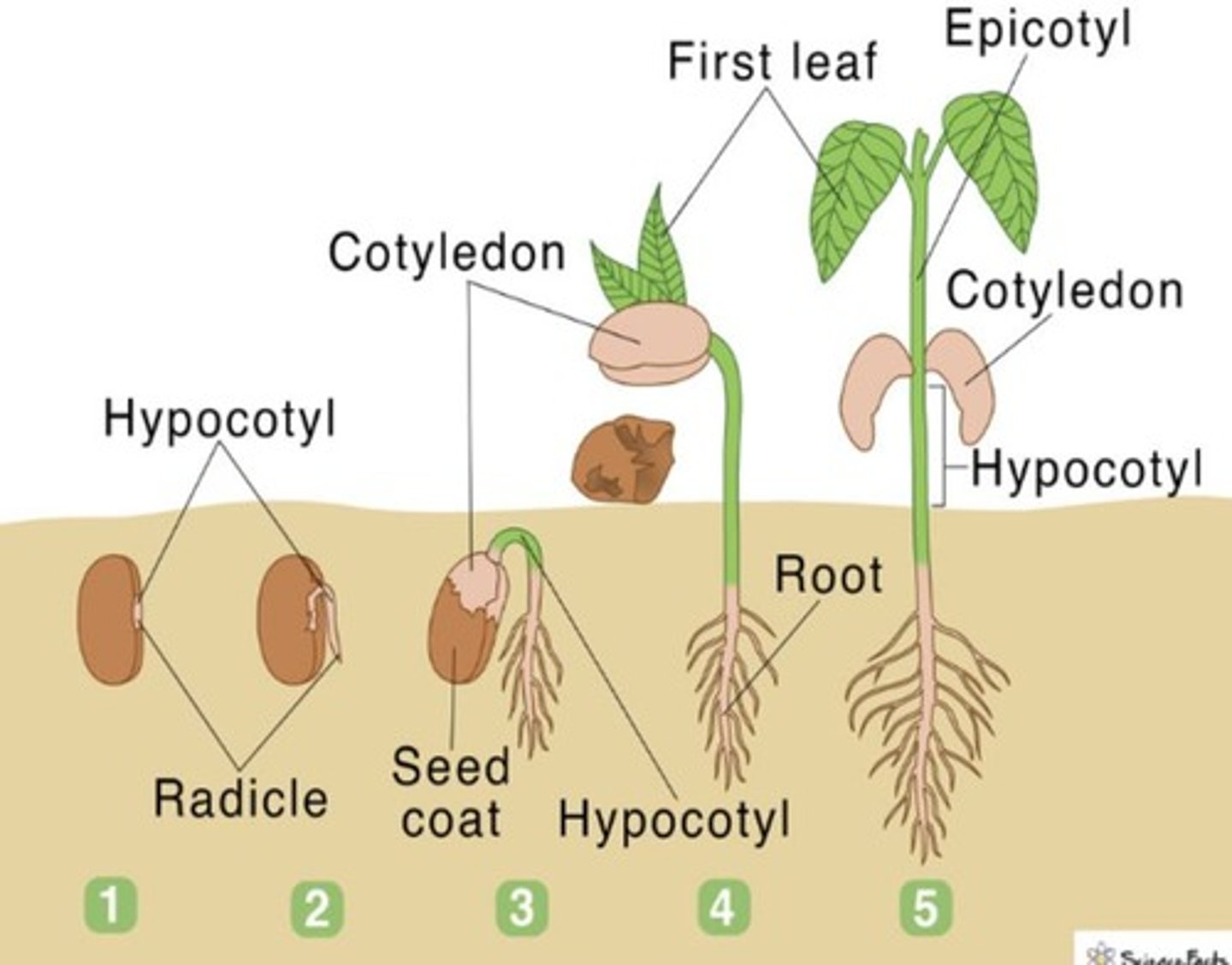
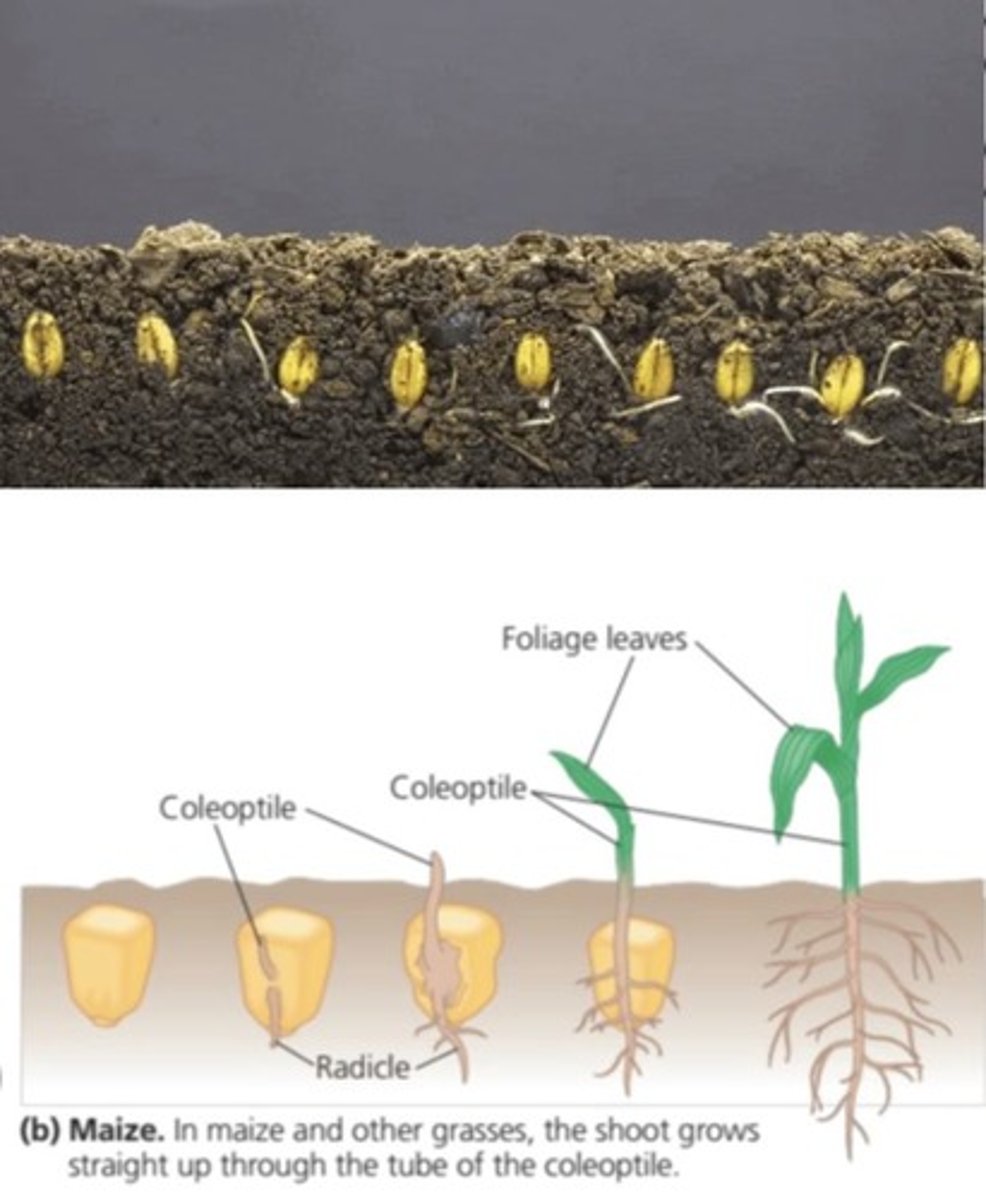
Germination for Monocot
Shoot tip grows through the coleoptile (sheath) once it has pushed through the surface of the soil.