Anatomy: digestive system
1/233
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
234 Terms
digestive system function
to break down food/drink into smaller units of absorbable nutrients which are used by your body to generate energy
your digestive tract is approximately 15-20 feet long. on average, how long do you think it takes for the sandwich you ate at lunch to completely pass through your digestive tract?
24 hours
alimentary canal
structures form long tube that breaks down food
- approximately 24 hours from ingestion to defecation
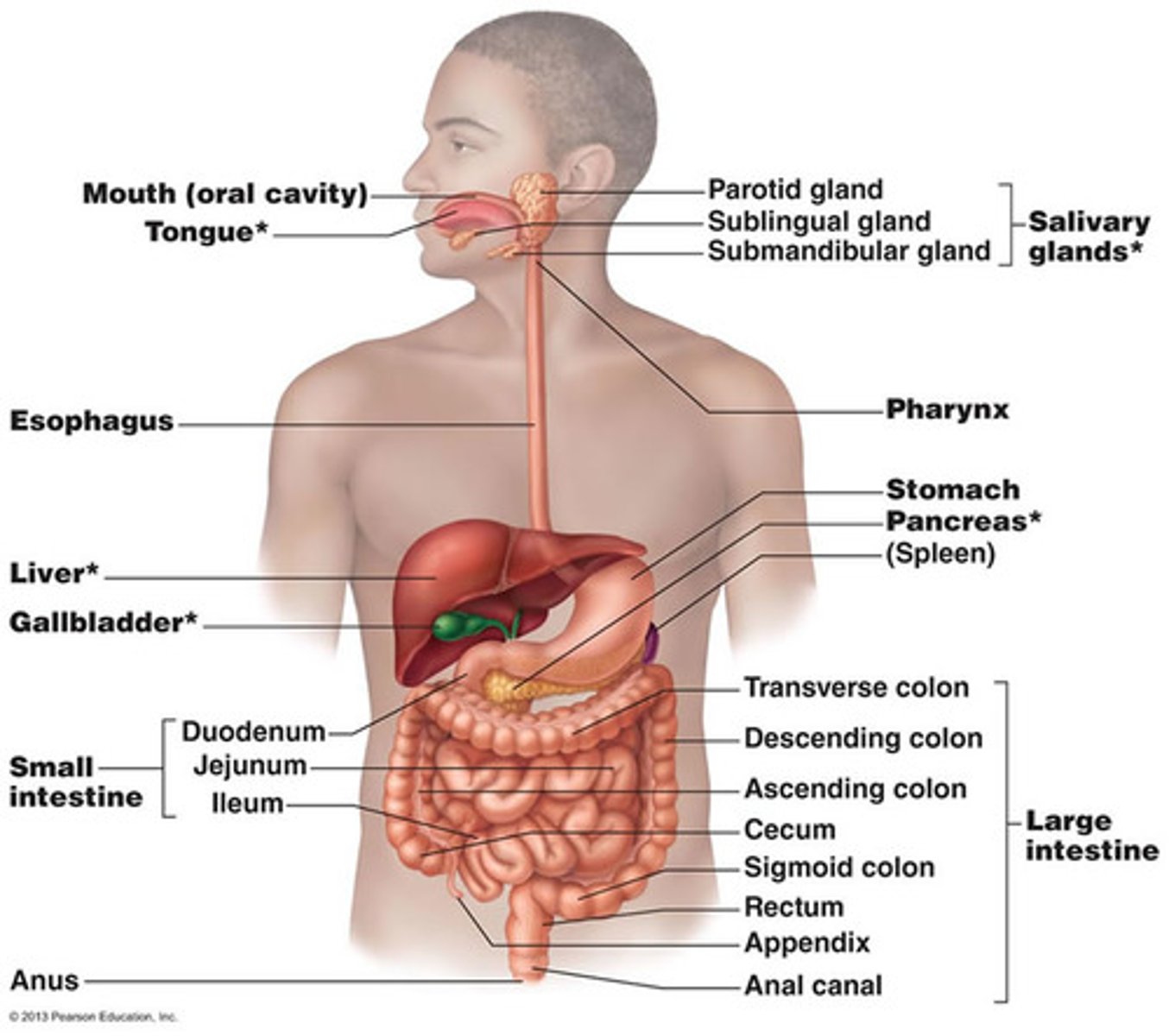
alimentary canal structures
1. mouth (oral cavity)
2. pharynx
3. esophagus
4. stomach
5. small intestine
6. large intestine
what makes up small intestine
duodenum, jejunum, ileum
accessory digestive organs
participate in digestive process but food does not pass through these structures
- tongue
- salivary glands
- liver
- gallbladder
- pancreas
ingestion
put food into mouth
propulsion
movement of food through canal
- swallowing -> voluntary
- peristalsis -> involuntary
peristalsis happens where
- esophagus
- stomach
- small intestine
peristalsis
an organized contraction and relaxation of smooth muscle layers that propels food through the alimentary canal in one direction
mechanical digestion
- physical breakdown of food particles
- chewing, churning, segmentation
segmentation
contractions of smooth muscle move chyme back and forth within canal to allow mixing and further break down
chyme
food product being digested
chemical digestion
enzymes break down food particles
absorption
particles (sugars, fatty acids, etc) transported from canal into blood and lymph capillaries
defecation
ingestible products eliminated from body as feces
anything passing through _______ is considered to be OUTSIDE the body and extracellular
the lumen of the alimentary canal
which processes are extracellular
- ingestion
- propulsion
- mechanical digestion
- chemical digestion
- defecation
which processes are intracellular
absorption
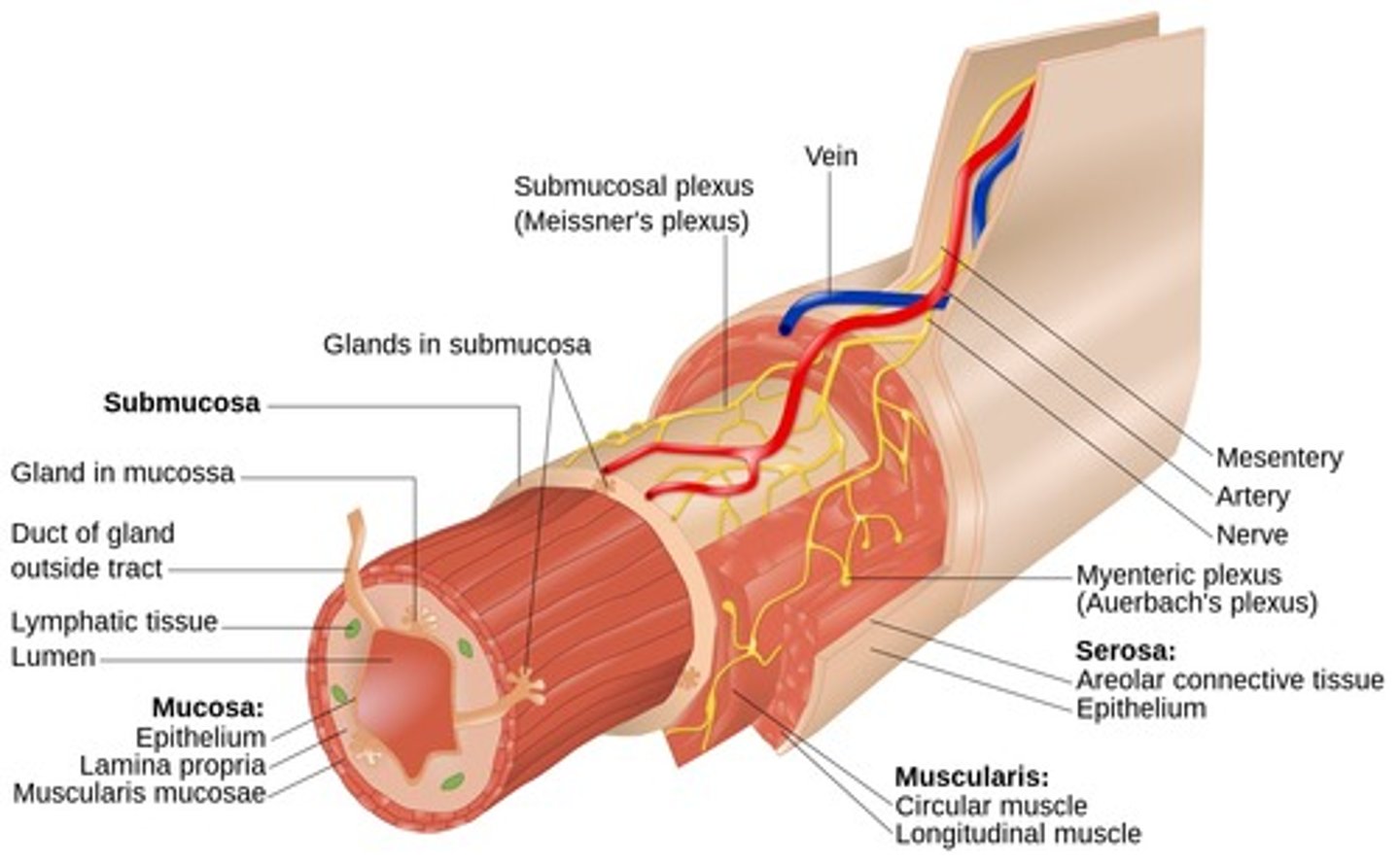
layers of organs of alimentary canal
1. mucosa
2. lines the lumen
3. muscularis externa
4. serosa
mucosa
- lines the lumen
- innermost layer
- 3 sublayers
- contains a stratified squamous epithelium
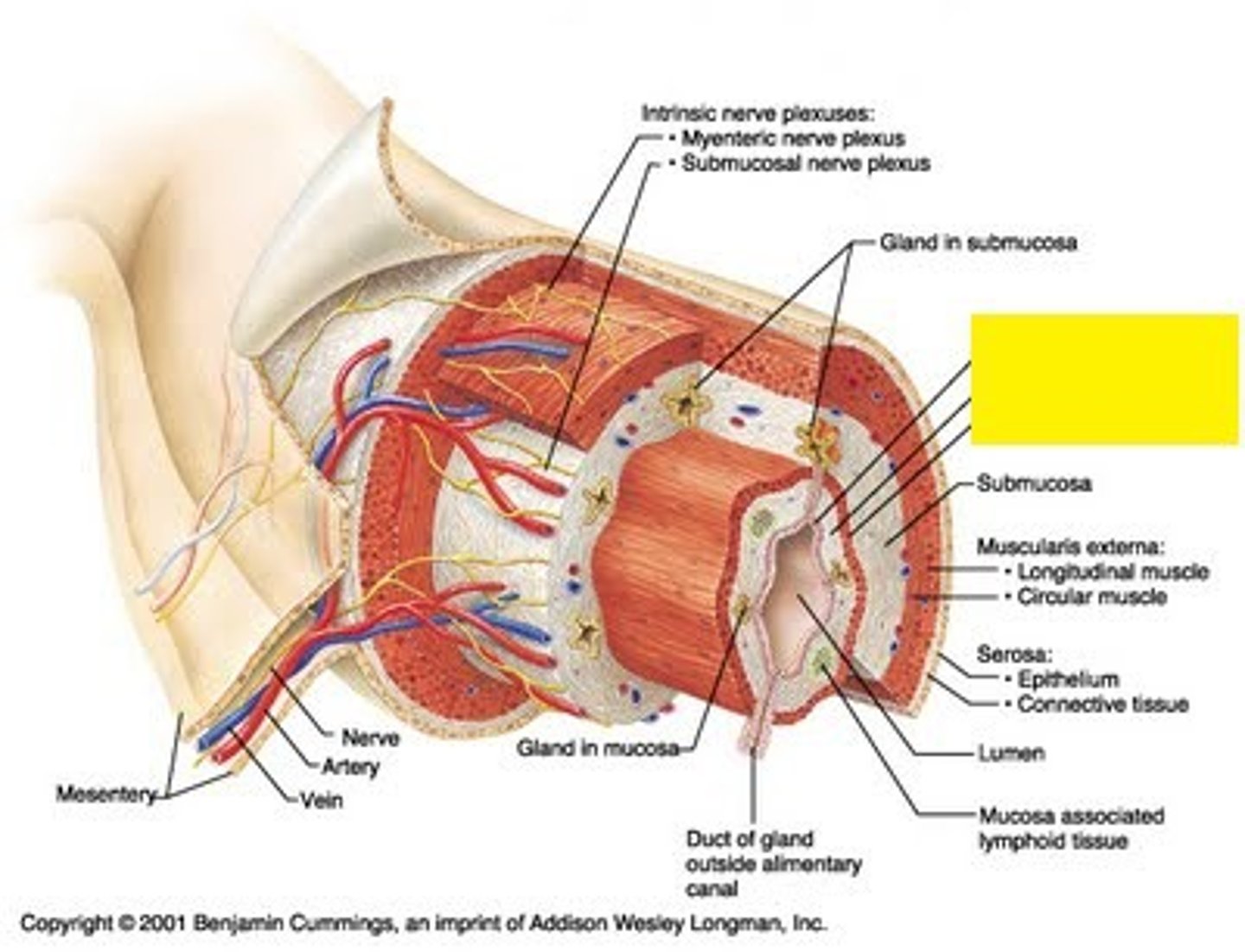
submucosa
support layer
- similar to loose areolar CT but higher concentration of collagen fibers provides more support
- highly vascularized
- glands connecting to lumen may project into submucosa
- submucosal nerve plexus
- areolar connective tissue
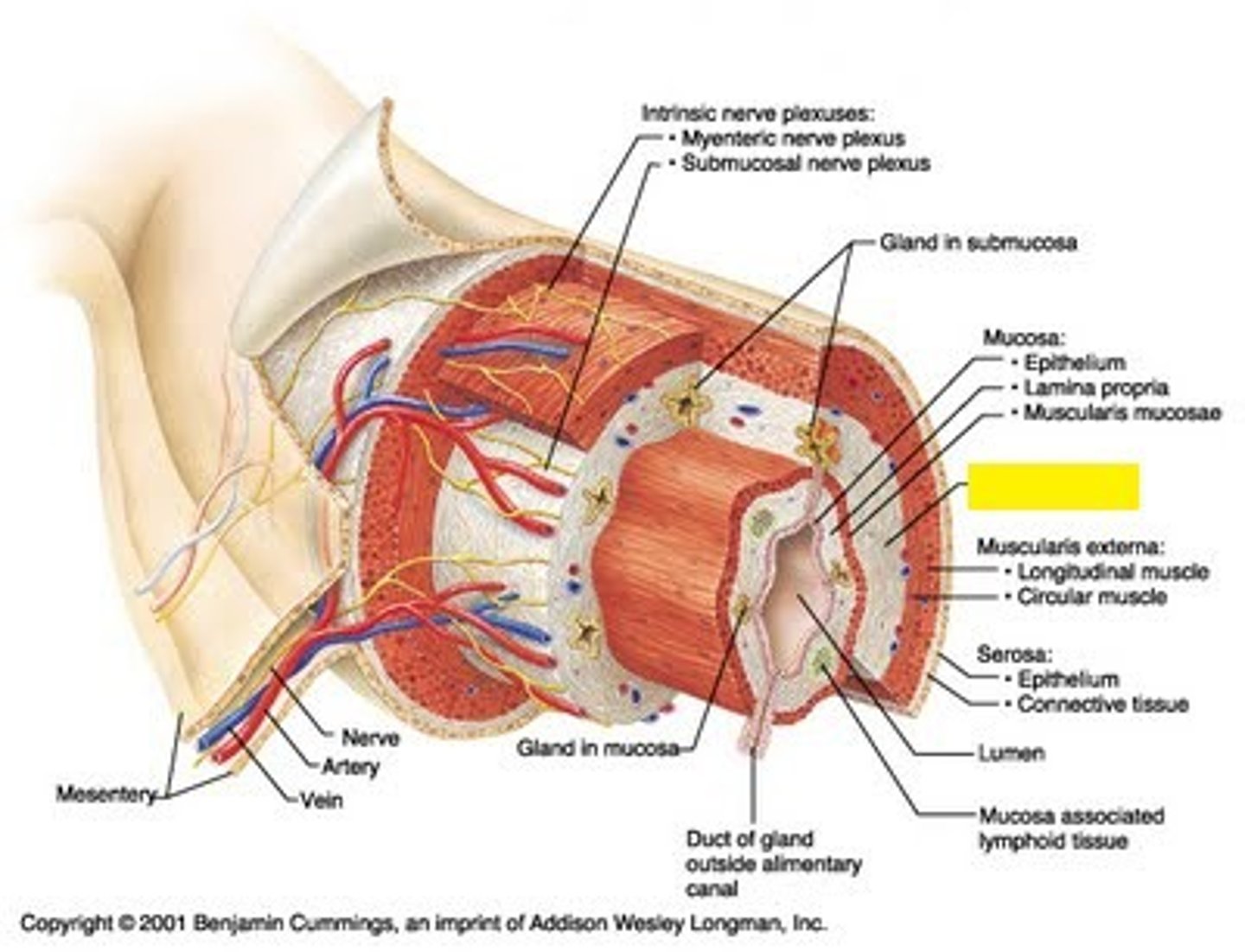
muscularis externa
muscle layer (red on diagram)
- 2 layers of smooth muscle
- myenteric nerve plexus
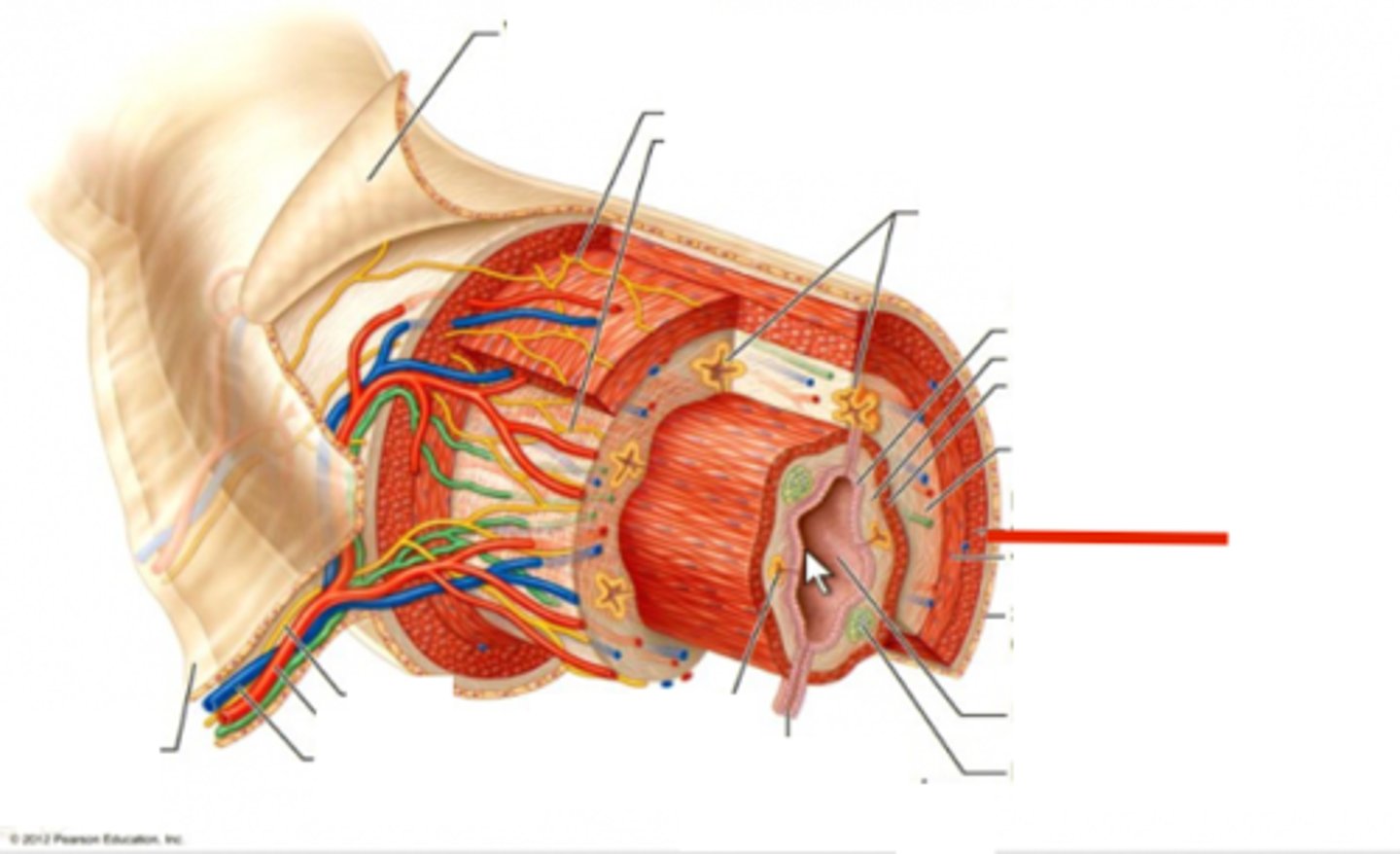
serosa
outer surface
- found around organs within abdominal cavity
- simple squamous epithelium with a thin loose areolar CT -> serous membrane
- visceral peritoneum
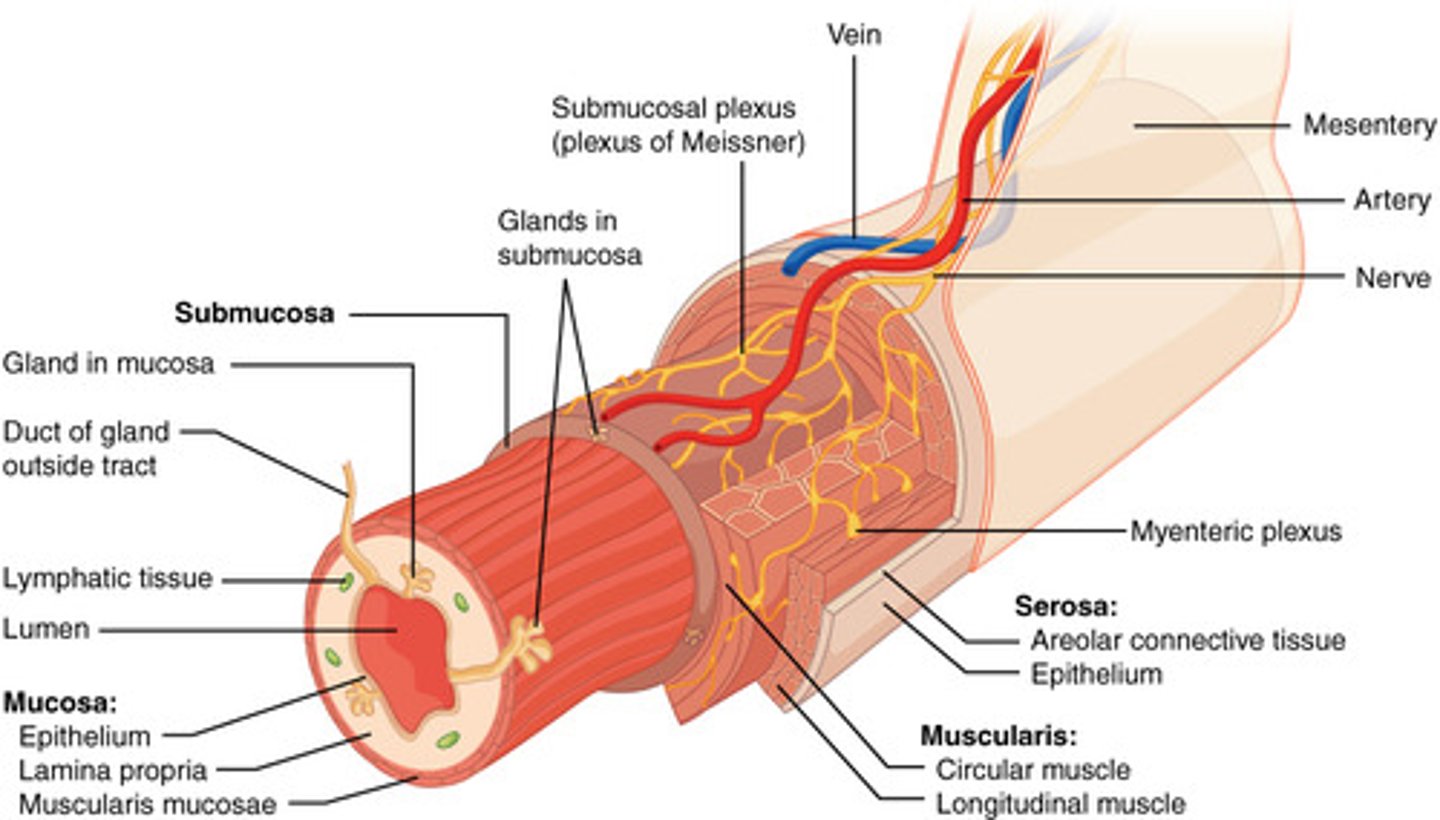
in which of the 4 main layers of the ailmentary canal would you expect to find an epithelium?
mucosa and serosa
3 sublayers of mucosa
1. epithelium
2. lamina propria
3. muscularis mucosa
epithelium
type varies by location
- mucus production, absorption, protection, etc
- continuous with many digestive glands
lamina propria
loose areolar CT
- MALT: Mucosa Associate Lymphoid Tissue provides defense against bacteria
muscularis mucosa
thin layer of smooth muscle
- localized movements
submucosa is highly vascularized
blood supply to mucosa for nutrient absorption
submucosal nerve plexus
control of muscle cells, glandular secretions, etc
- secretions of glands
- muscularis mucosa contractions
- within submucosa
2 layers of smooth muscle in muscularis externa
- circular layer
- longitudinal layer
circular layer of muscularis externa
inner layer, typically squeezes tube
longitudinal layer of muscularis externa
outer layer, typically shortens tube
- peristalsis and segmentation
the serosa is a simple squamous epithelium around organs that are within the abdominal cavity. another name for a serosa is:
visceral peritoneum
adventitia
fibrous CT that forms outer layer of esophagus (does not have a serosa)
- the esophagus is not contained within a body cavity lined by a serous membrane
nerve plexuses
- allow for localized response within visceral organs
- partly independent of CNS
intrinsic nerve plexuses
1. myenteric nerve plexus
2. submucosal nerve plexus
myenteric nerve plexus
- controls peristalsis and segmentation
- within muscularis externa
oral cavity
mouth
- ingestion of food
- mechanical digestion
- chemical digestion
oral cavity mechanical digestion
chewing
oral cavity chemical digestion
mixed with saliva which starts the breakdown of carbohydrates
which type of epithelium would you expect to find lining the oral cavity?
stratified squamous
why would you expect to see a stratified squamous epithelium in the oral cavity?
- the oral cavity is a continuation of the skin
- food is abrasive
- food and drink temperatures vary considerably
anatomy of the mouth
- stratified squamous epithelium
- thin submucosa layer anchored directly to underlying bone
- NO muscularis externa or serosa/adventitia
- lips: margin between skin and oral cavity
lips
margin between skin and oral cavity
- keratinized like skin
- no suderiferous or sebaceous glands
teeth
- accessory digestive organs
- heterodont dentition
- deciduous teeth
- permanent teeth
heterodont dentition
different shapes of teeth for different jobs
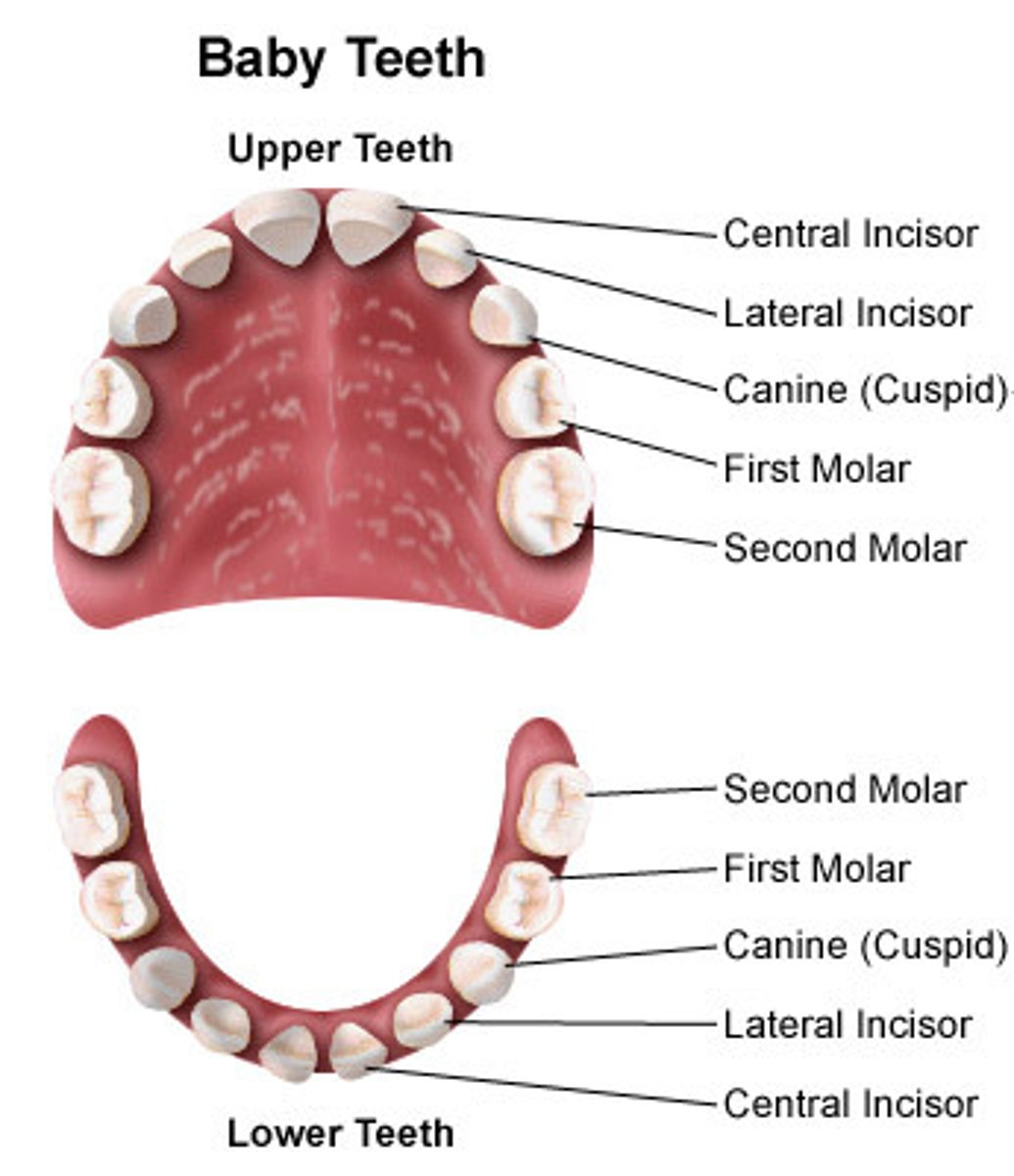
deciduous teeth
20 total erupt typically between ages 6 mo -> 6 yr
permanent teeth
32 total gradually replace deciduous
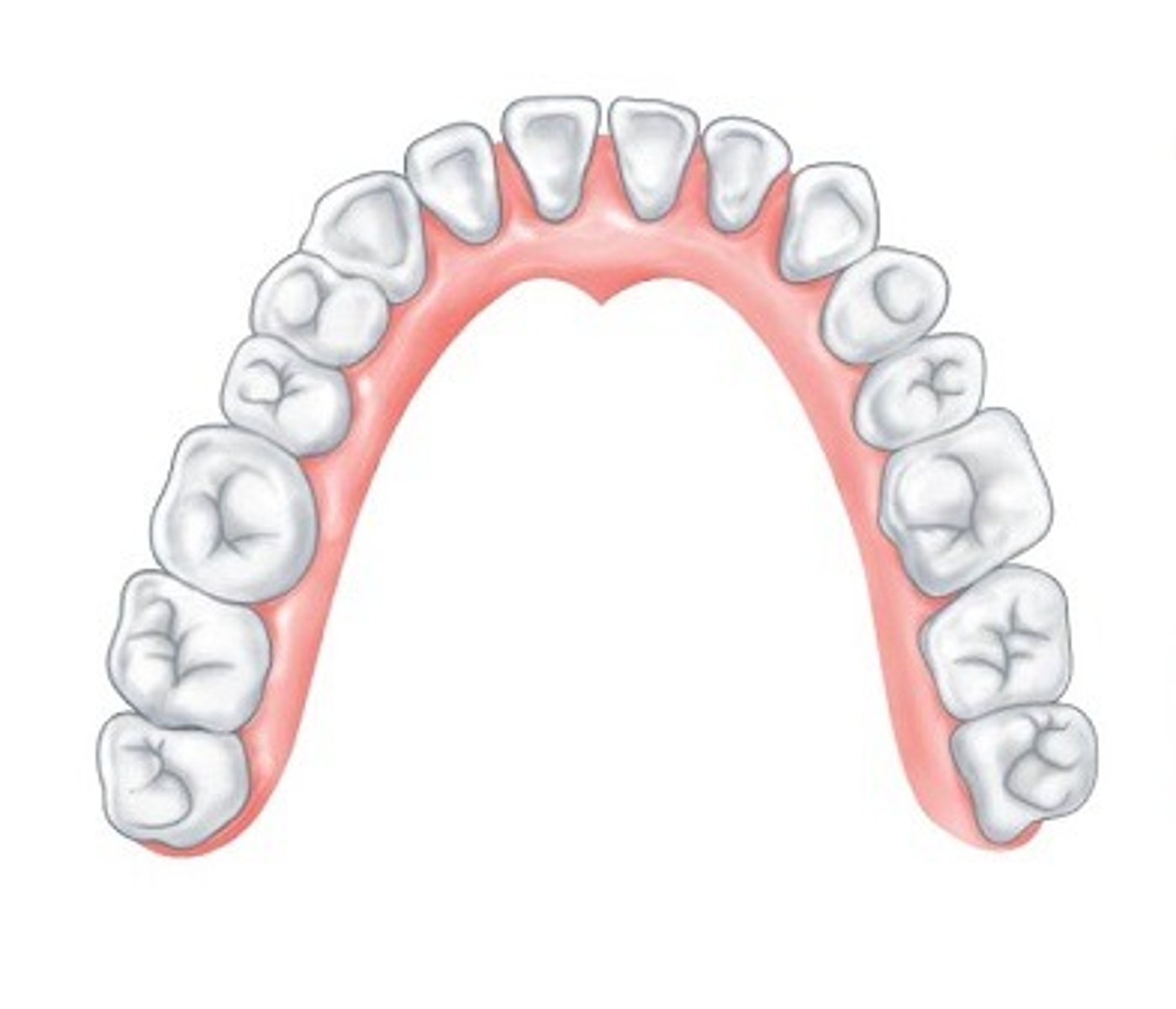
4 types of teeth (permanent dentition)
1. incisors
2. canines
3. premolars
4. molars
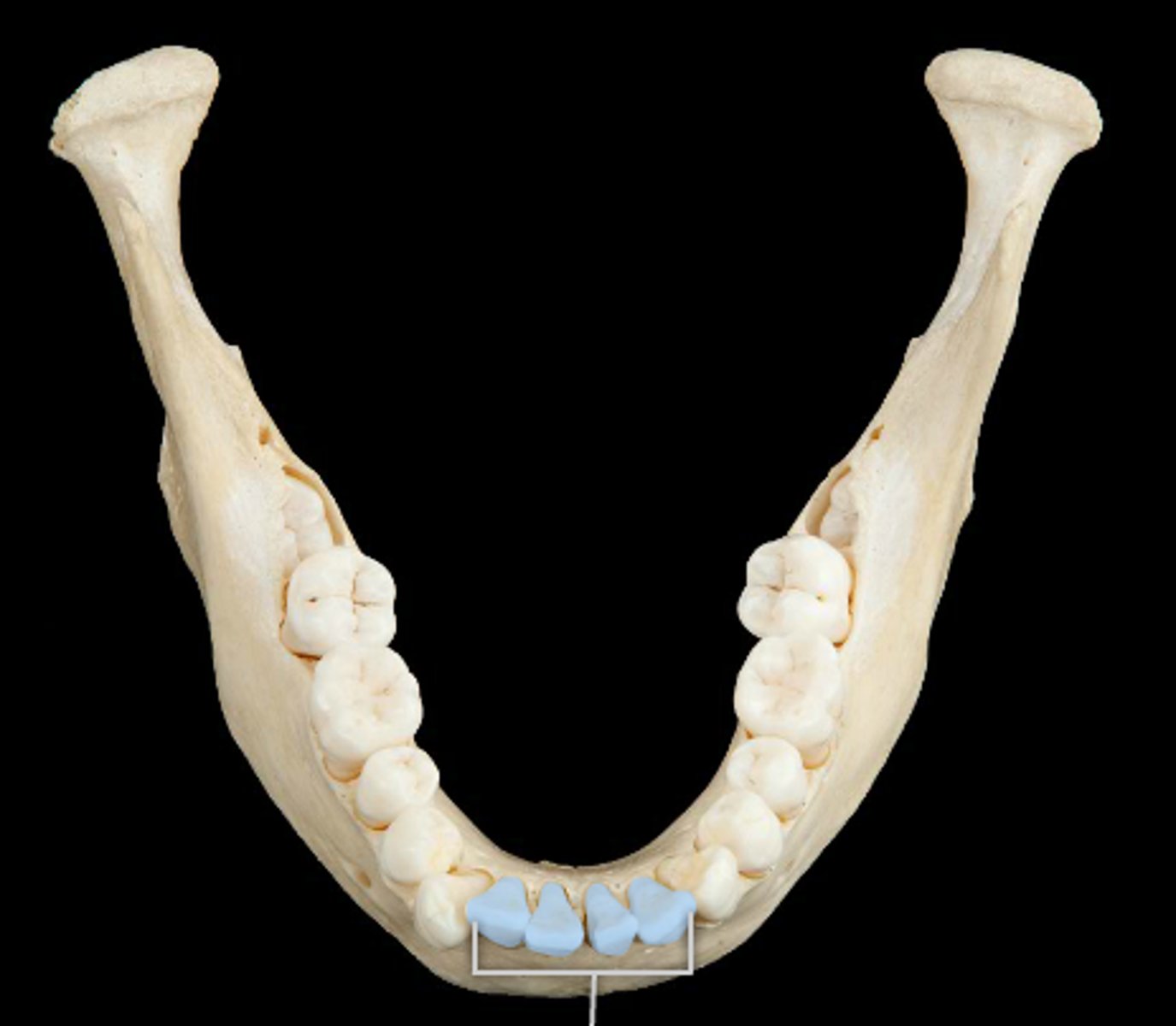
incisors
4 pairs
- surface good for cutting and shearing food
- 1 root
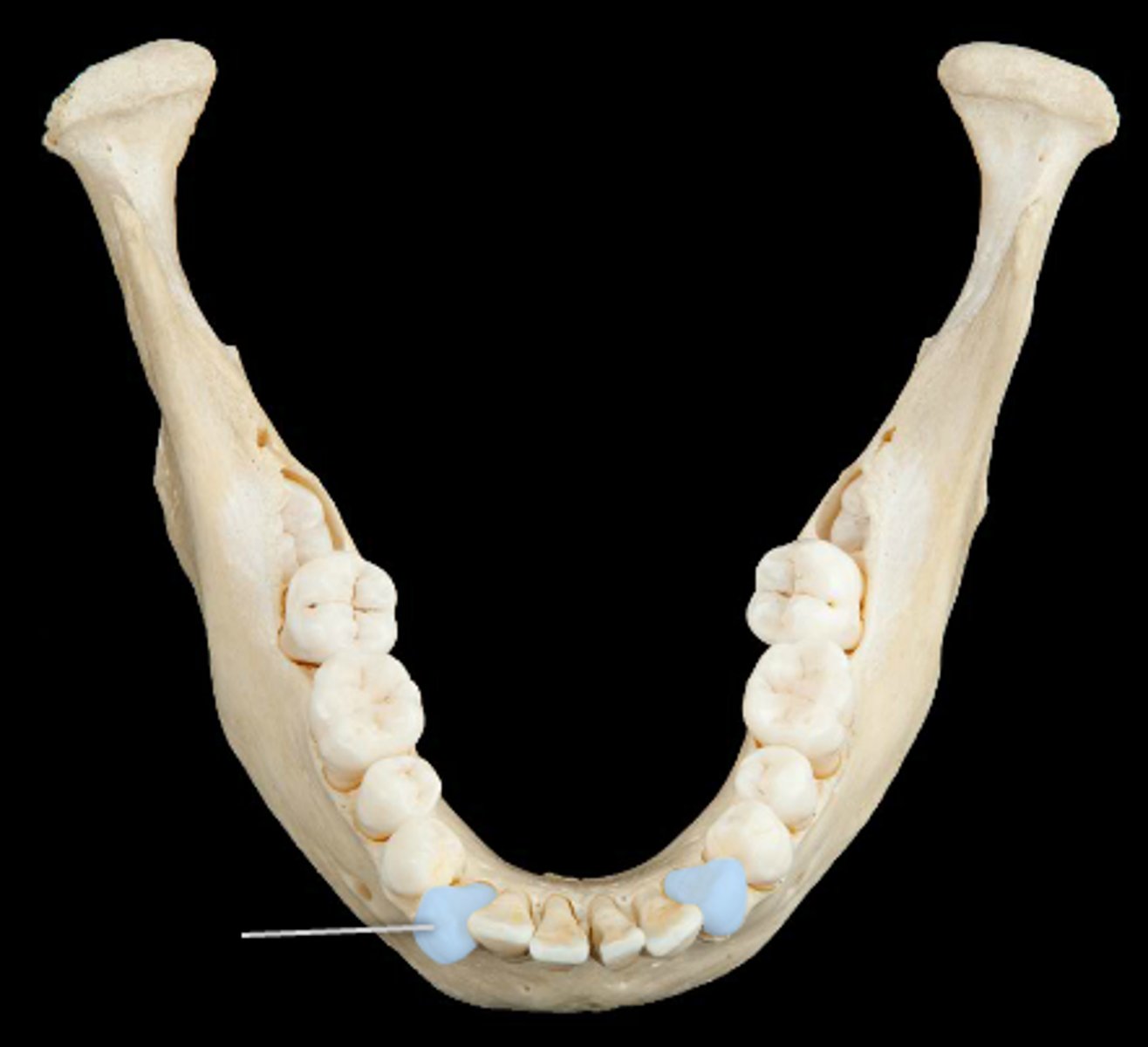
canines
2 pairs
- surface good for holding and tearing
- 1 root
premolars
4 pairs
- rounded, broad surface good for grinding
- at least 2 cusps
- 1 or 2 roots
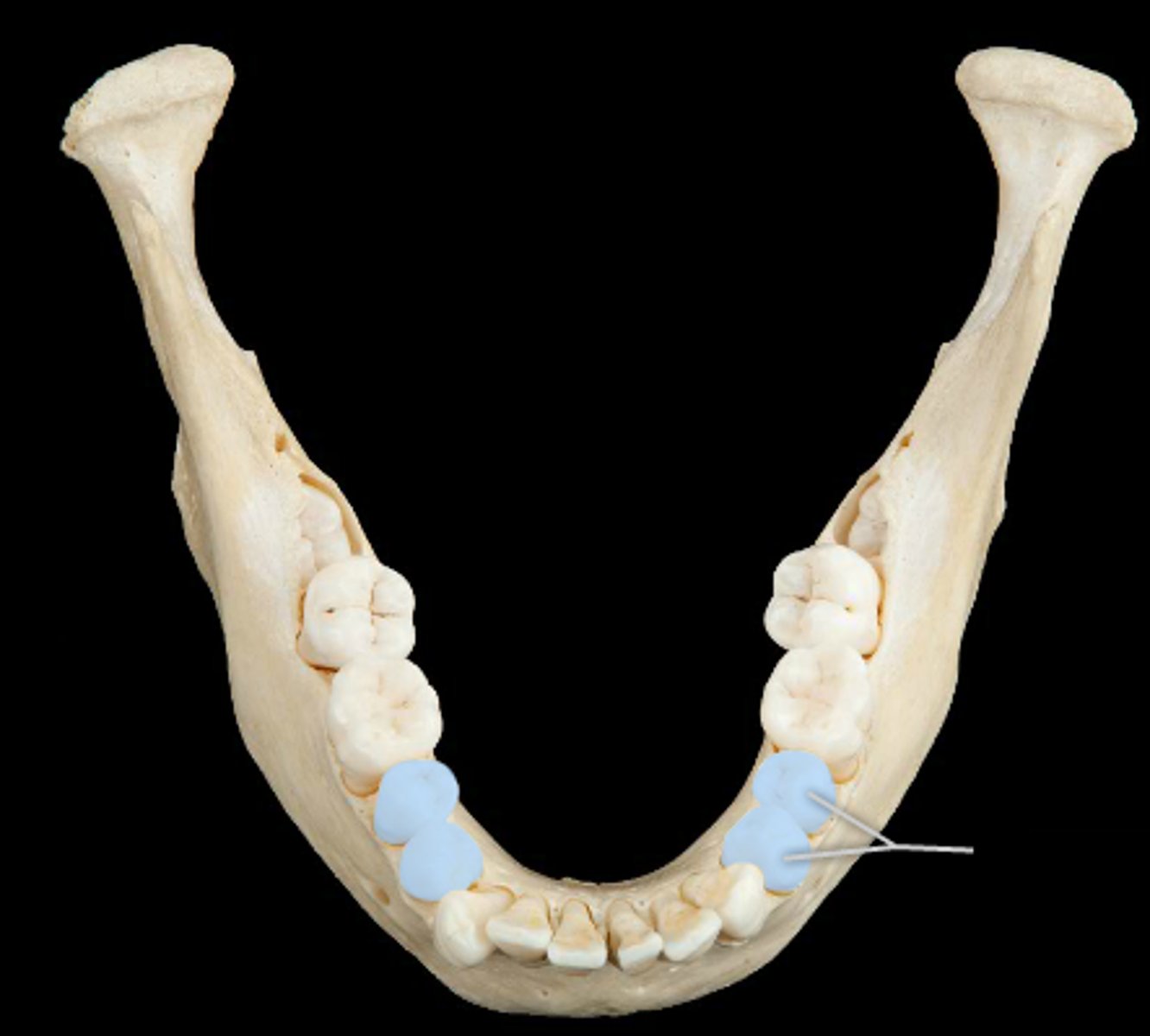
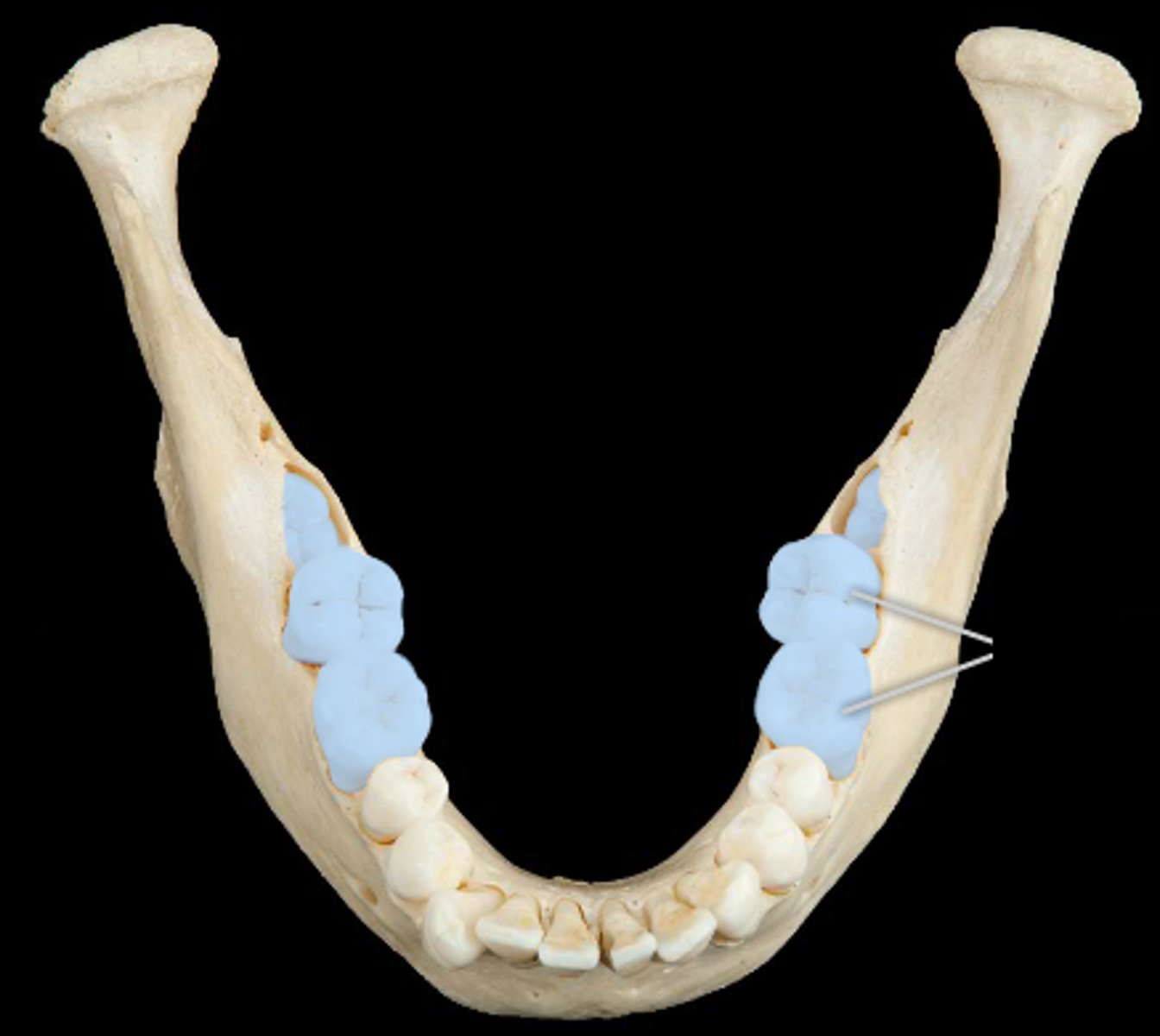
molars
6 pairs
- grinding surface
- 4-5 cusps
- 2-3 roots
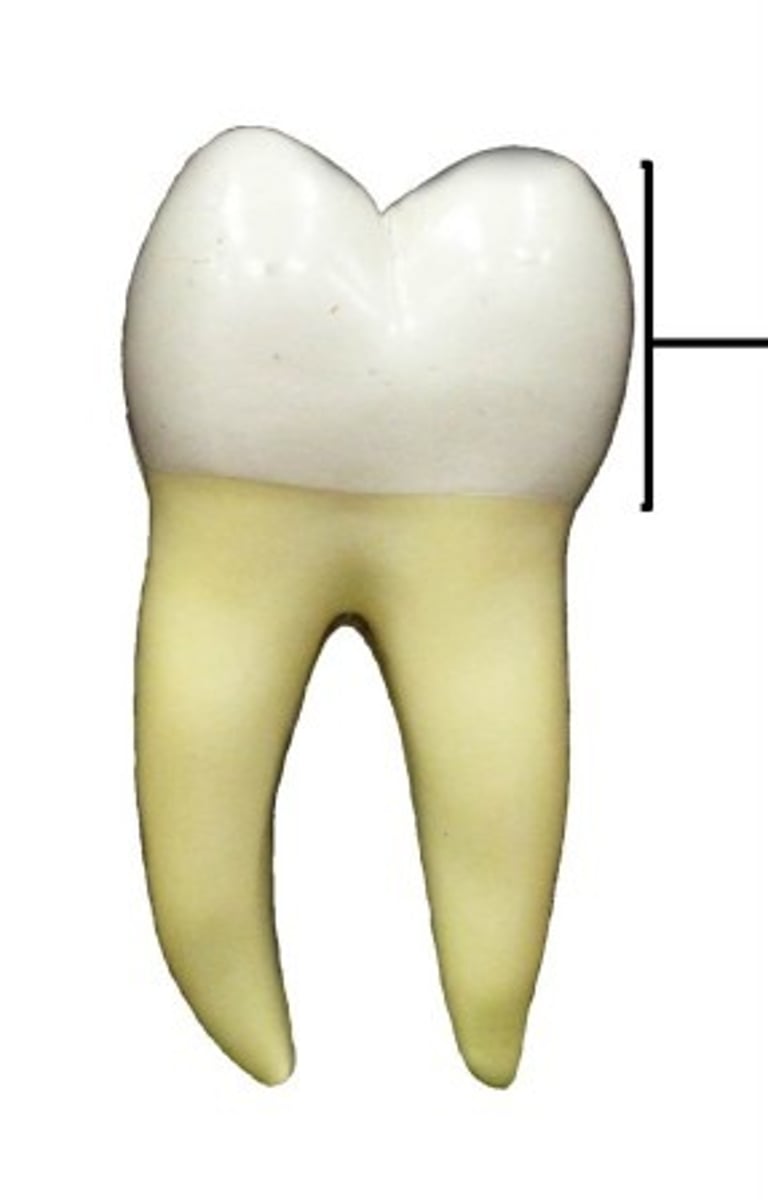
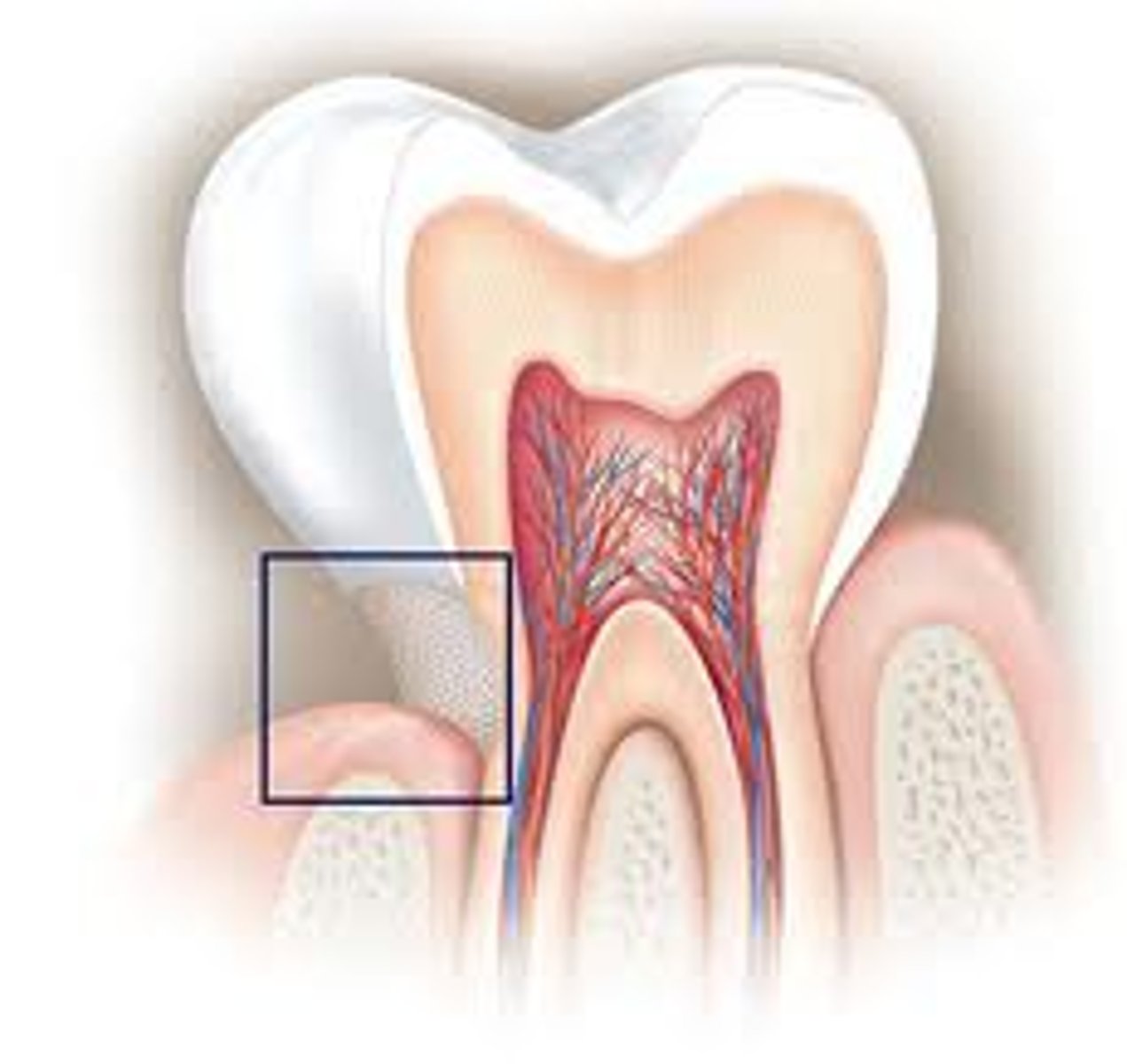
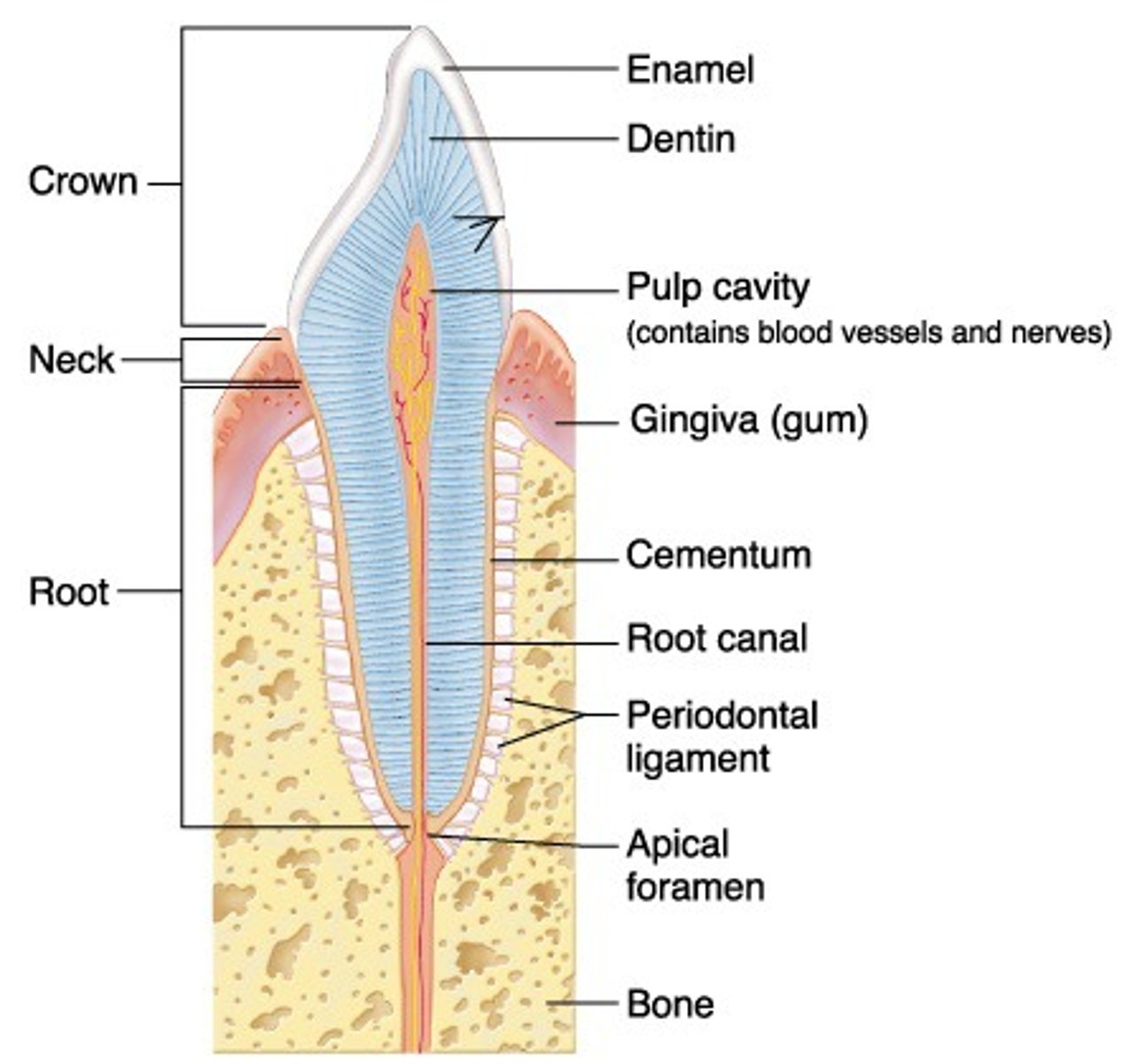
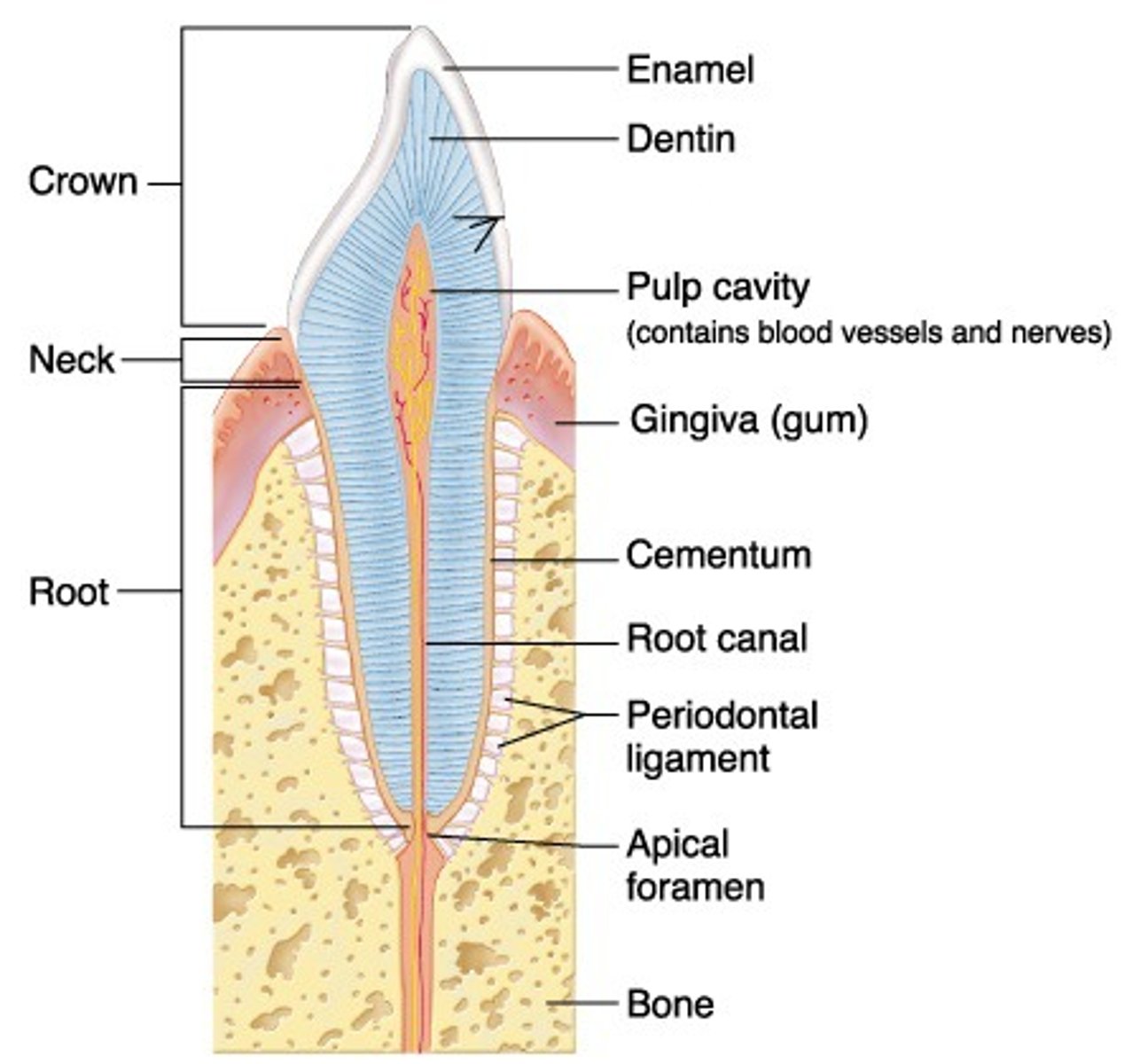
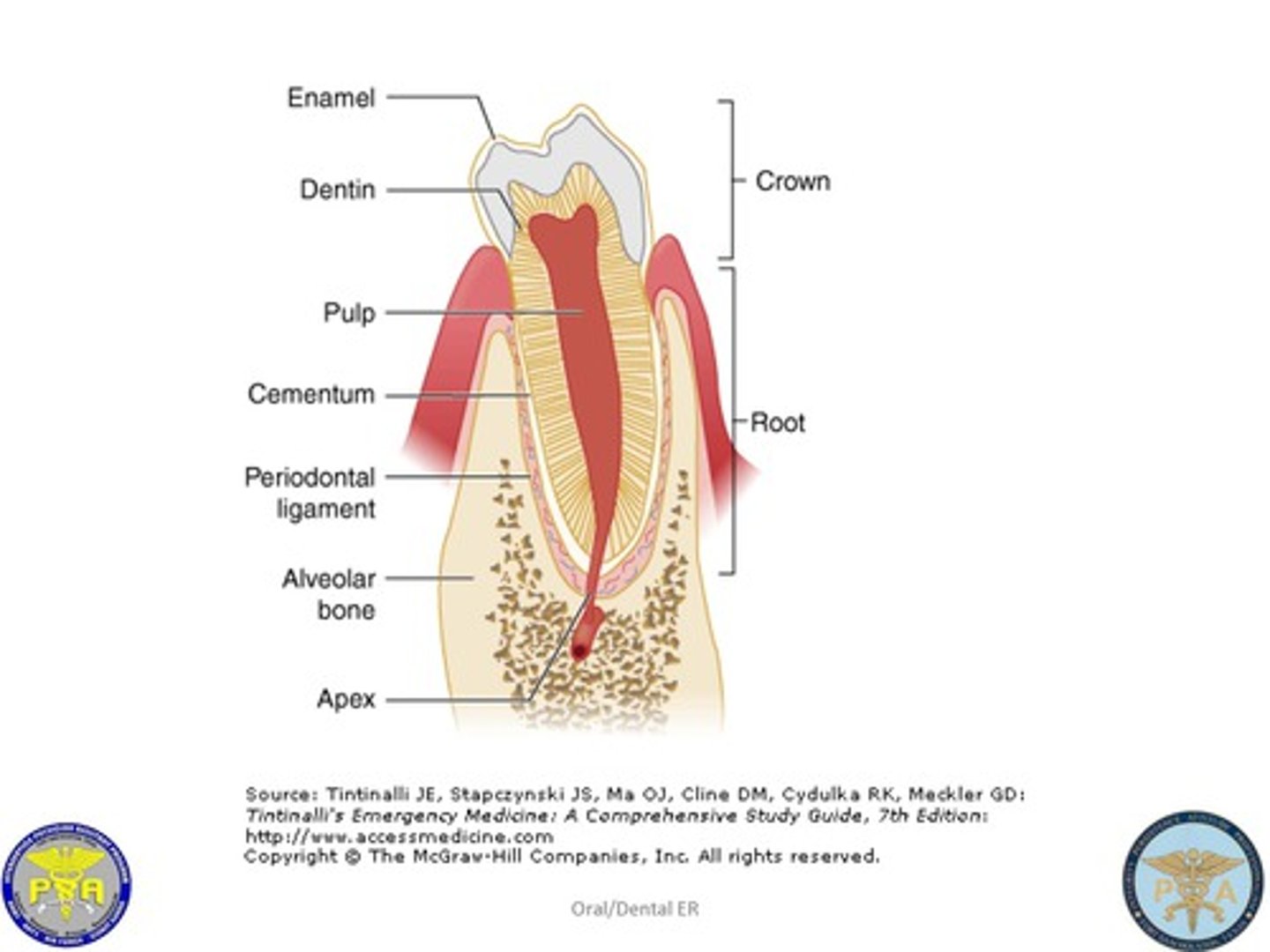
regions of a tooth
- crown
- neck
- root
crown of tooth
portion above gumline
neck of tooth
narrow portion contained within gum tissue
root of tooth
contained within bone
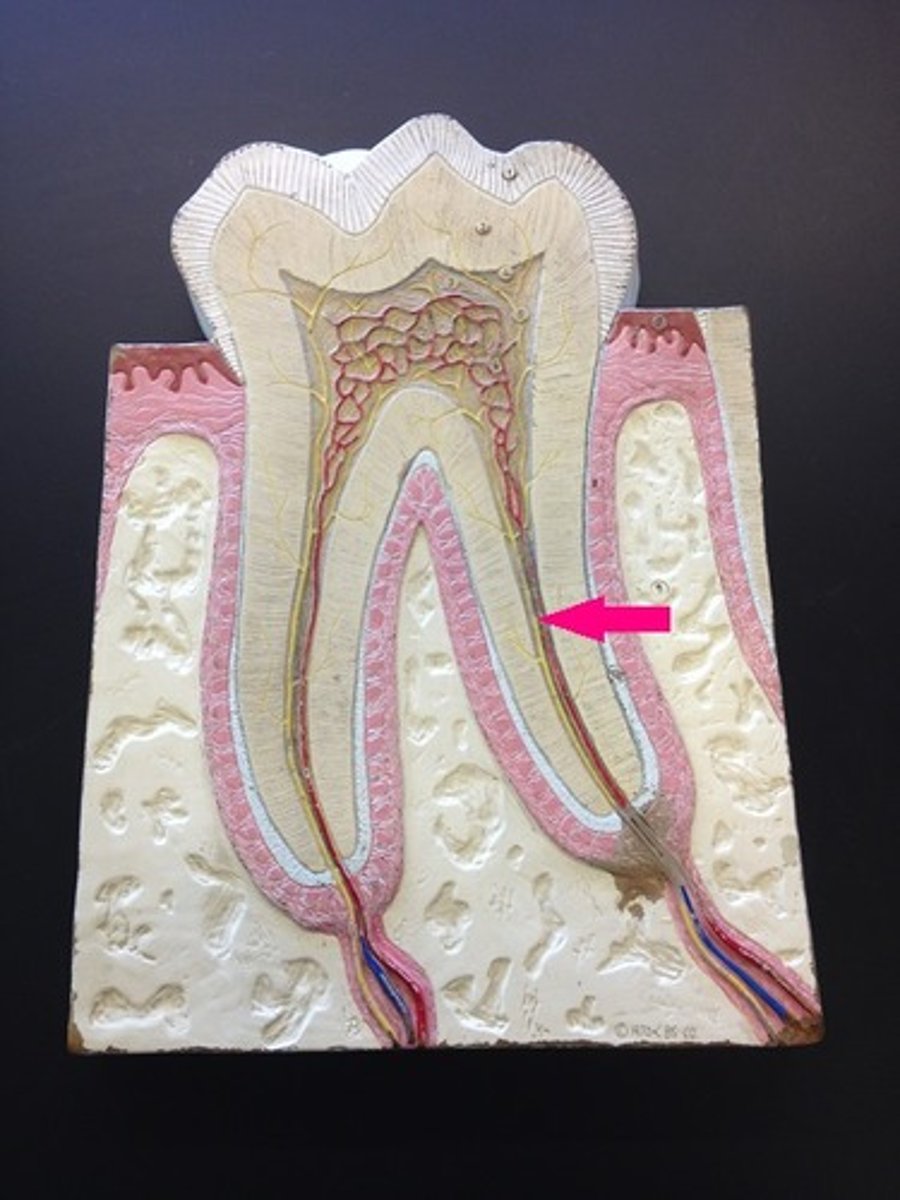
layers of a tooth
- pulp
- dentin
- enamel
- cementum
- periodontal ligaments
pulp layer of tooth
- loose areolar CT
- provides nutrients and sensation to tooth
- odontoblasts
loose areolar CT in pulp layer of tooth
blood vessels and nerves
odontoblasts
create dentin
dentin layer of tooth
- collagen (from odontoblasts) and minerals
- no cells or blood vessels
- harder than bone
enamel layer of tooth
- 99% calcium
- no cells or blood vessels
- layer is added during tooth development by ameloblasts
cementum layer of tooth
- calcified connective tissue similar to bone
- cementoblasts continually replace
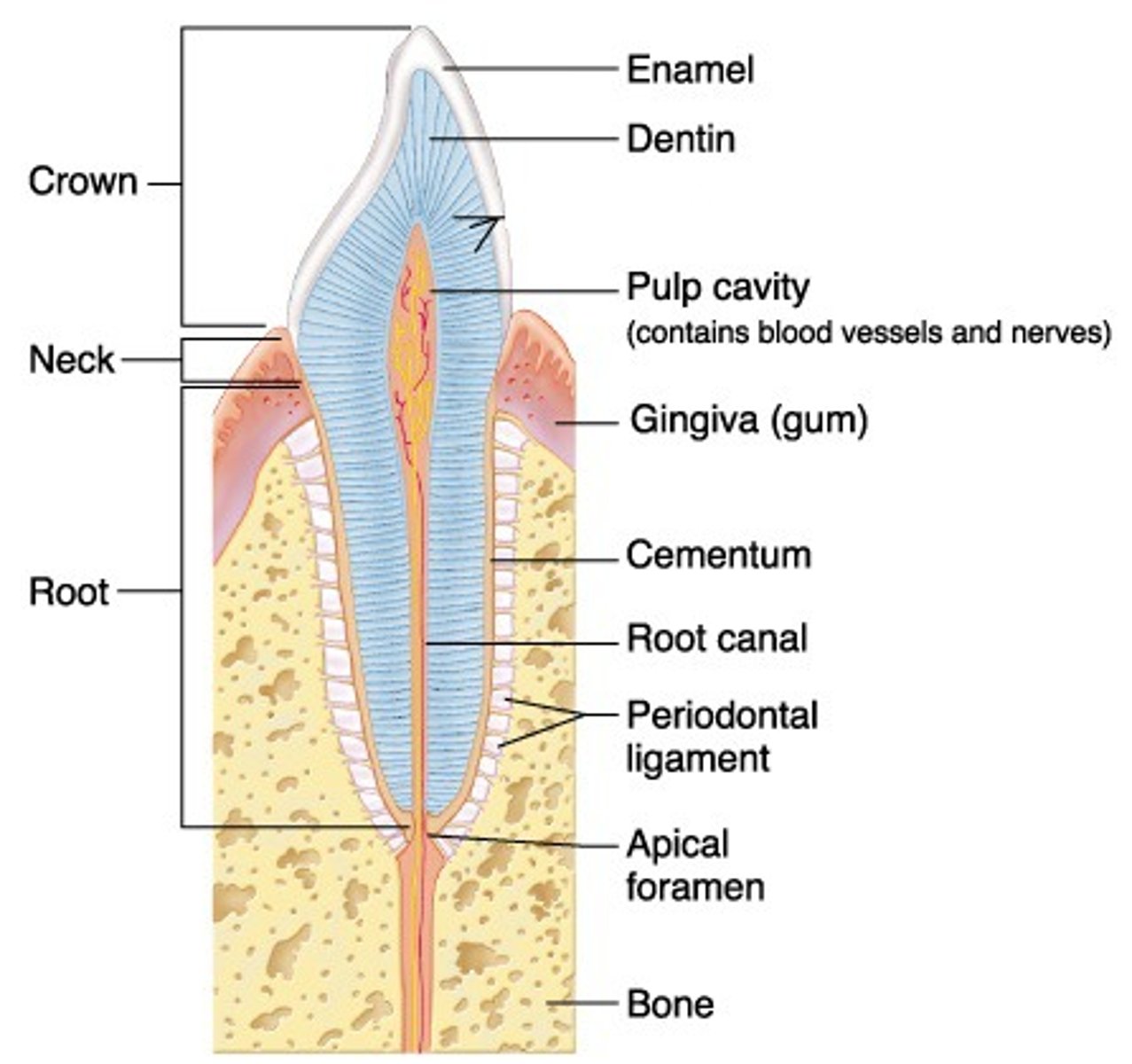
periodontal ligaments
dense CT that attaches cementum of tooth to bony socket
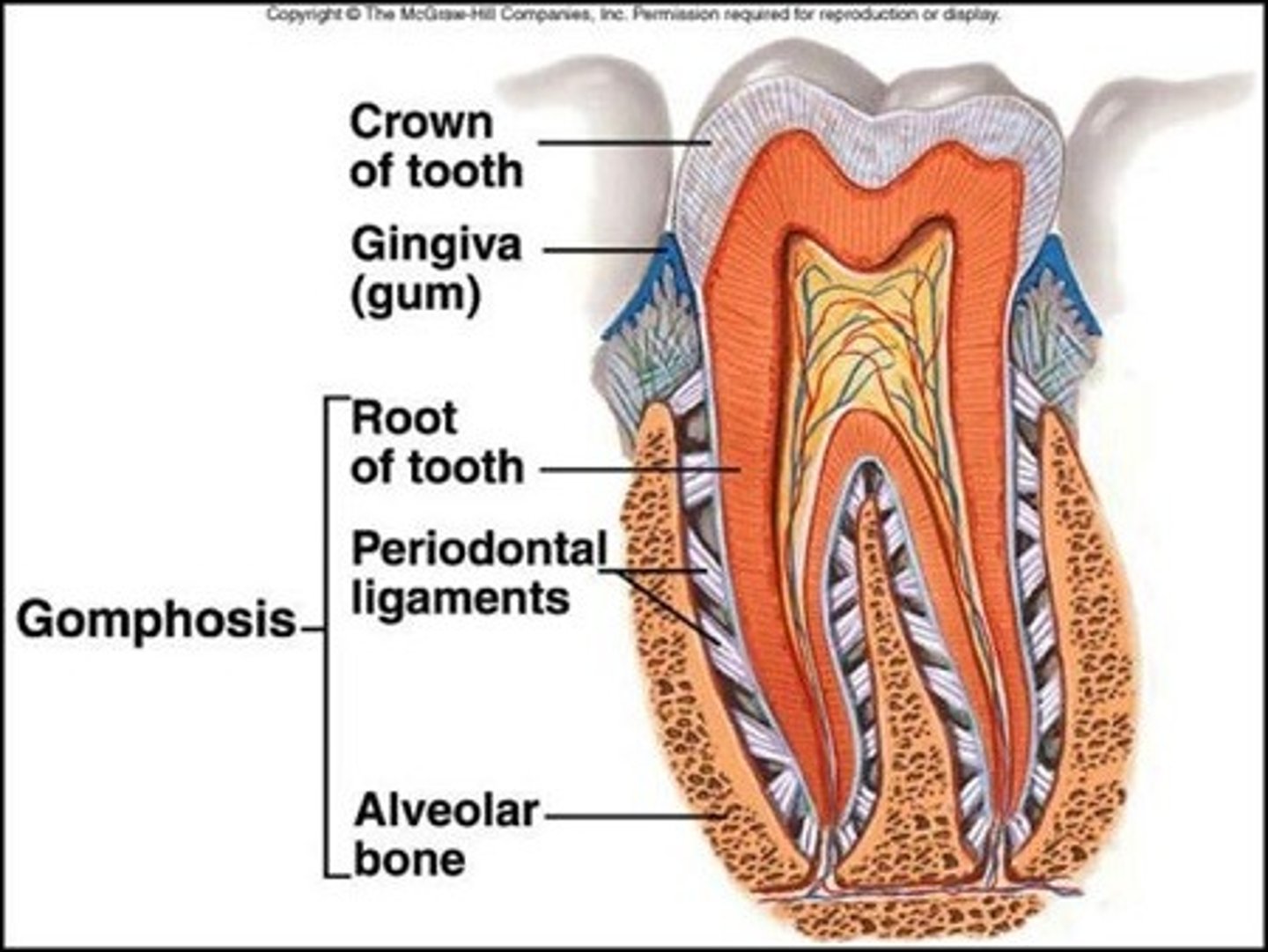
the periodontal ligaments are part of what type of joint?
gomphosis
cavities
enamel and eventually dentin erode when plaques formed of sugars and bacteria form on teeth. bacteria feed on the sugars and produce acids that demineralize the tooth surface
root canal procedure
- procedure may be required when pulp within the canal becomes infected
- pulp is drilled out -> tooth is now "dead"
- cavity is sterilized and filled
- tooth is capped off to help strengthen it
permanent teeth in children who suffer from Celiac Disease may lack enamel, a condition known as hypoplastic dentition. This is not a symptom found in individuals who develop Celiac Disease as adults. Why?
- after all the permanent teeth have erupted, adults no longer have the cells needed to create enamel
- malabsorption of calcium could only impact tooth enamel levels while the enamel is being added to the tooth during its formation within the bone
- permanent teeth develop within the bone during childhood, so any abnormalities of the tooth would form at this time
tongue
- accessory digestive organ
- primarily skeletal muscle
- covered in keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
- moves food, helps mix with saliva to form bolus
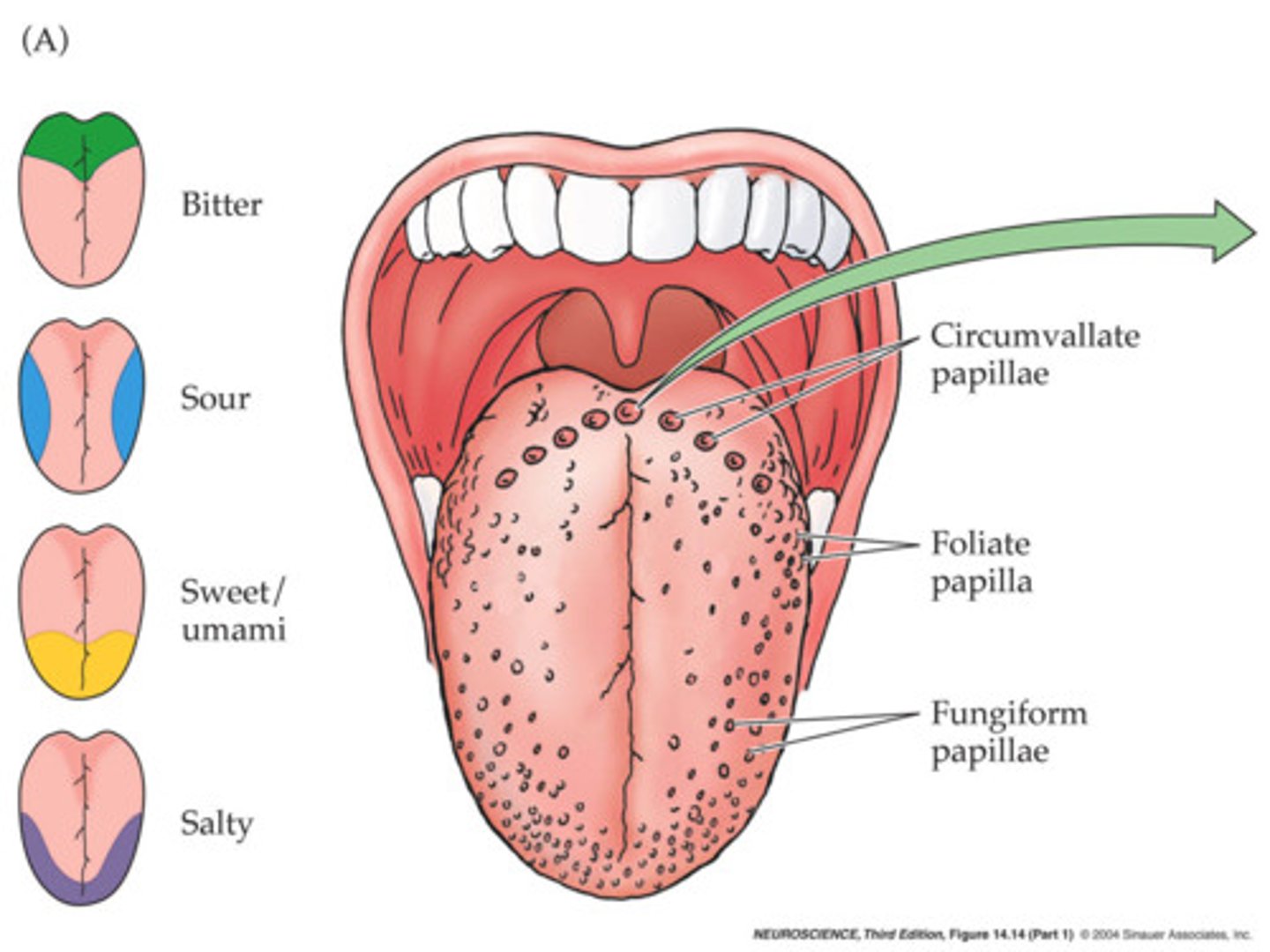
- fusiform papilla
- fungiform and circumvallate papilla
fusiform papilla
rough surface
fungiform and circumvallate papilla
contain taste buds
lingual frenulum
- fold of mucosa layer
- connects tongue to floor of mouth
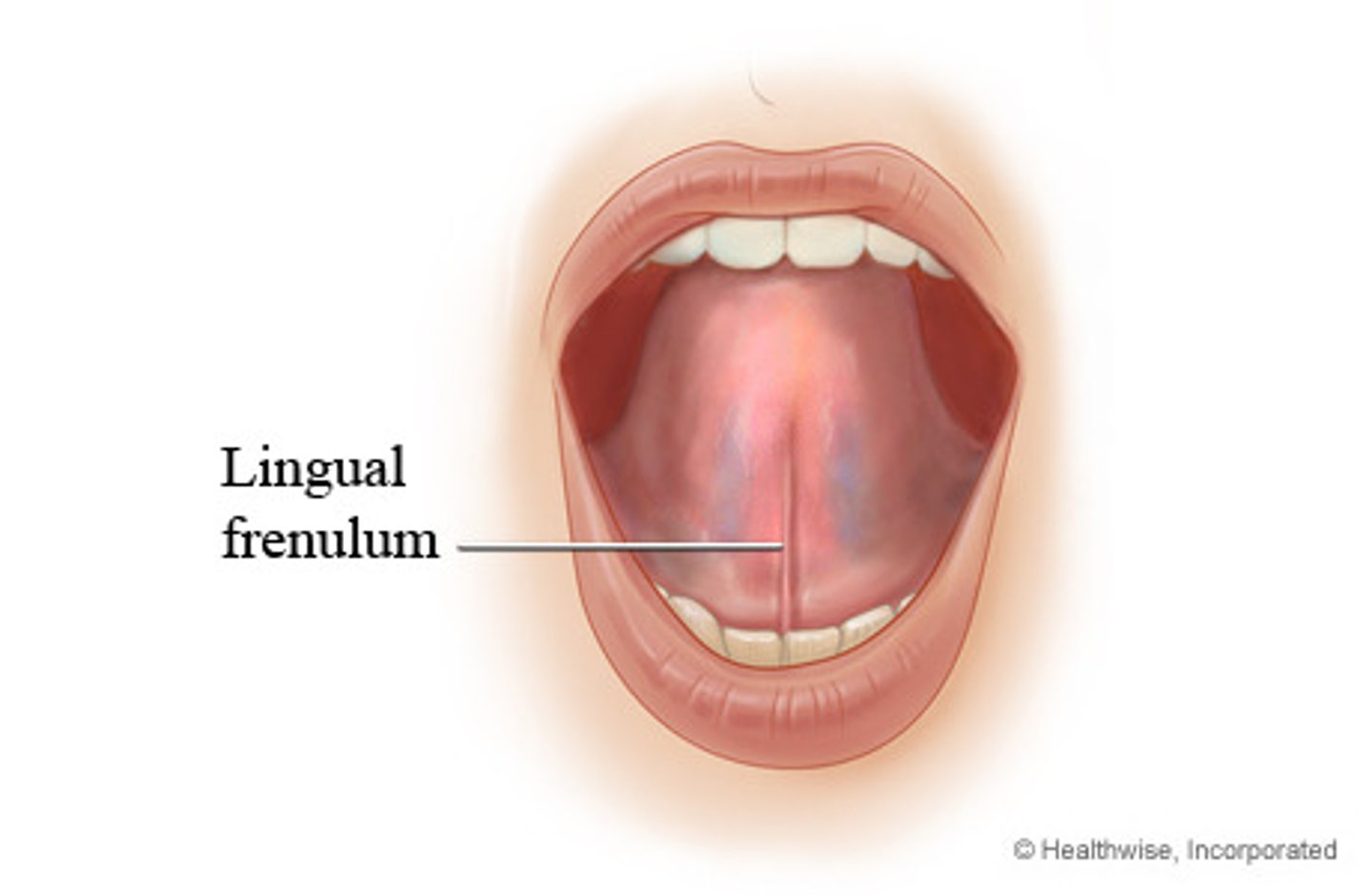
"tongue tied"
if lingual frenulum extends too far forward, the tip of the tongue cannot move and speech is difficult
which layer of the alimentary canal lines the lumen of a digestive organ?
mucosa
salivary glands
- accessory digestive organs
- exocrine glands
- produce saliva
saliva
- solvent
- dissolve food
- contains digestive enzymes
- contains mucus
- two types of cells: serous and mucous
saliva as a solvent
cleanse teeth
saliva for dissolving food
taste
saliva contains mucus
helps swallowing
salivary gland cell types
serous cells and mucous cells
serous cells of the salivary glands
secrete digestive enzymes
mucous cells of the salivary glands
secrete mucus
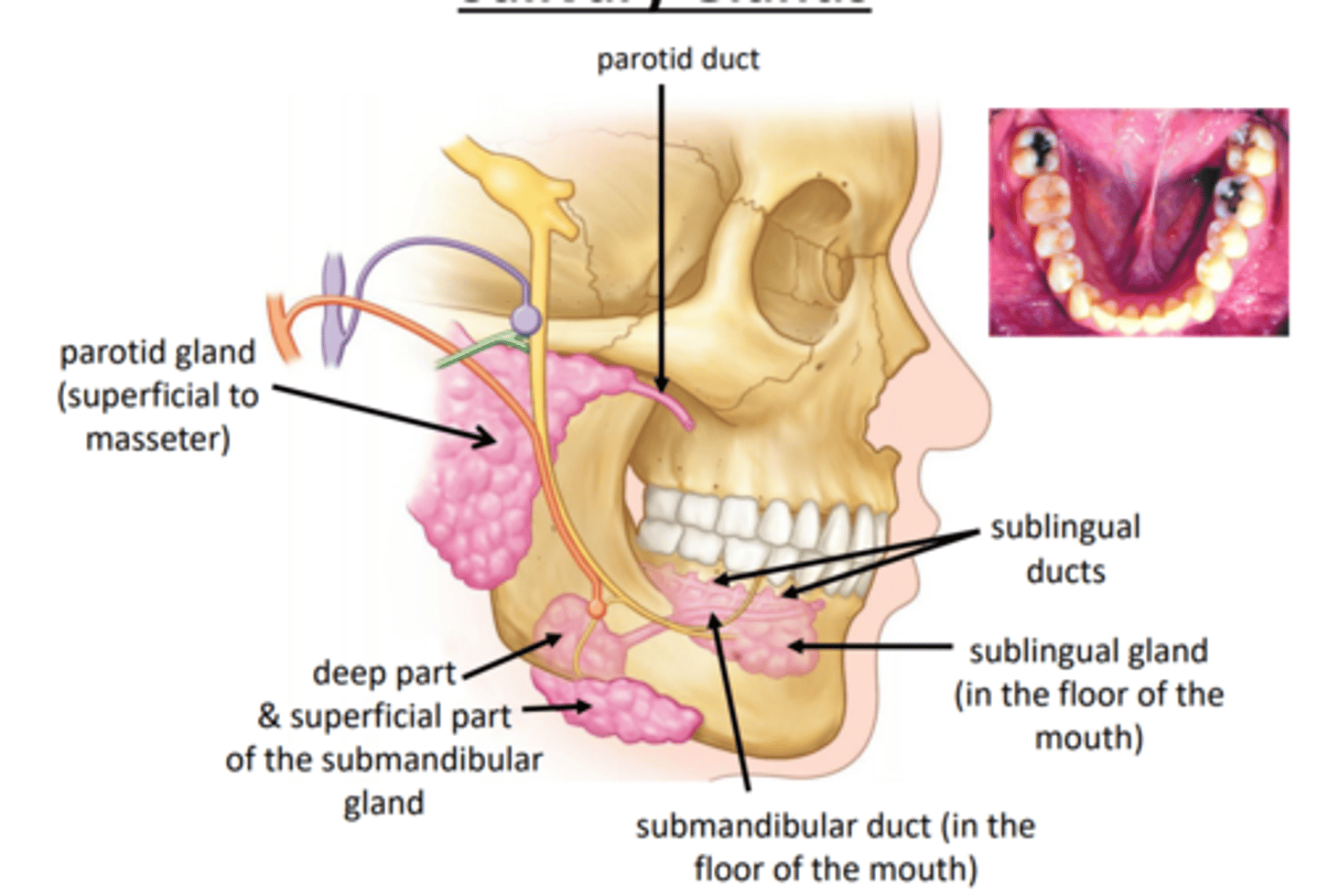
primary salivary glands
- parotid gland and duct
- submandibular gland and duct
- sublingual gland and duct
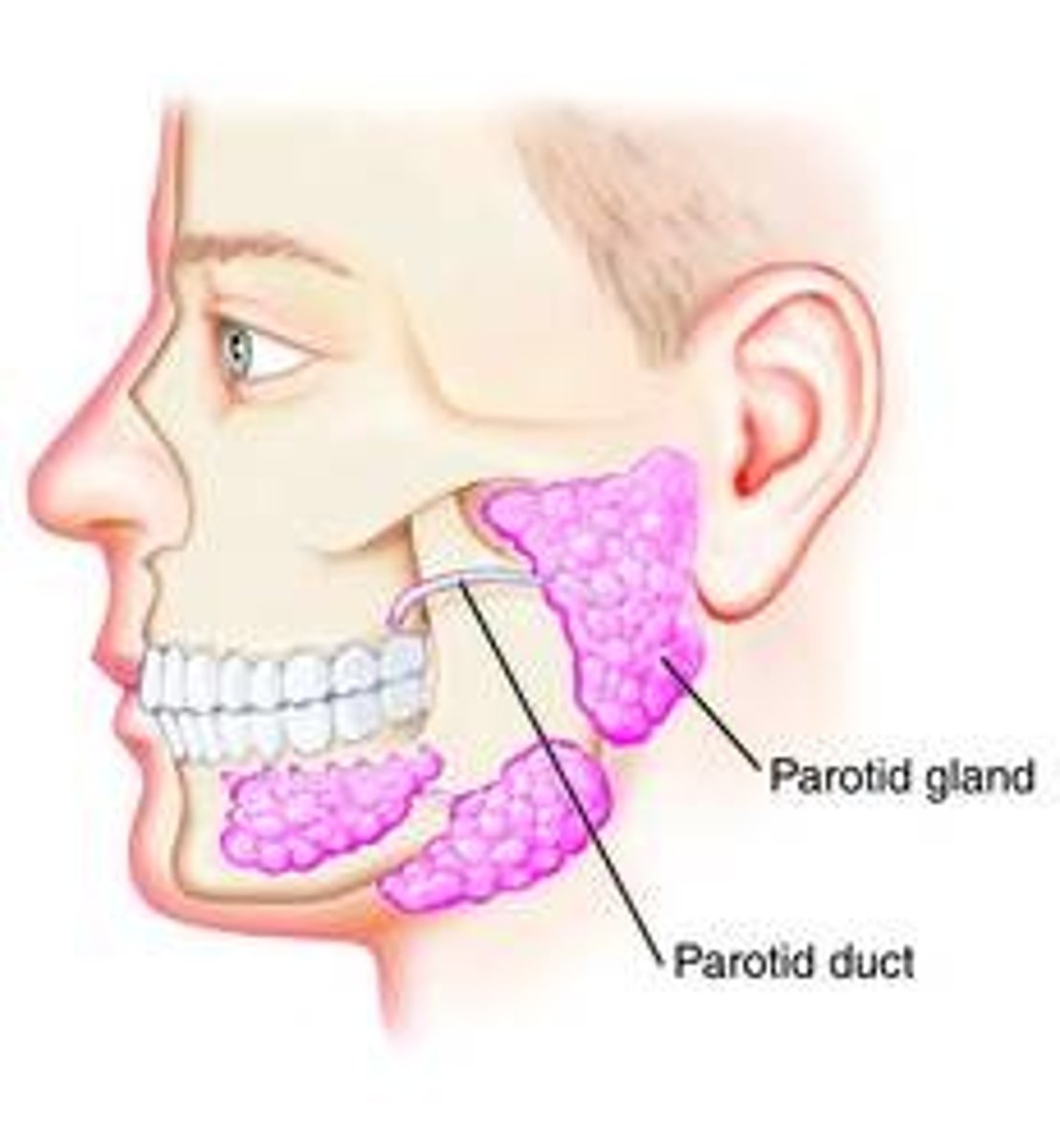
parotid gland and duct
- largest
- contains serous cells -> watery enzyme rich secretion
- ducts open lateral to lingual frenulum
submandibular gland and duct
- approximately 50/50 serous to mucous cells
- ducts open lateral to lingual frenulum
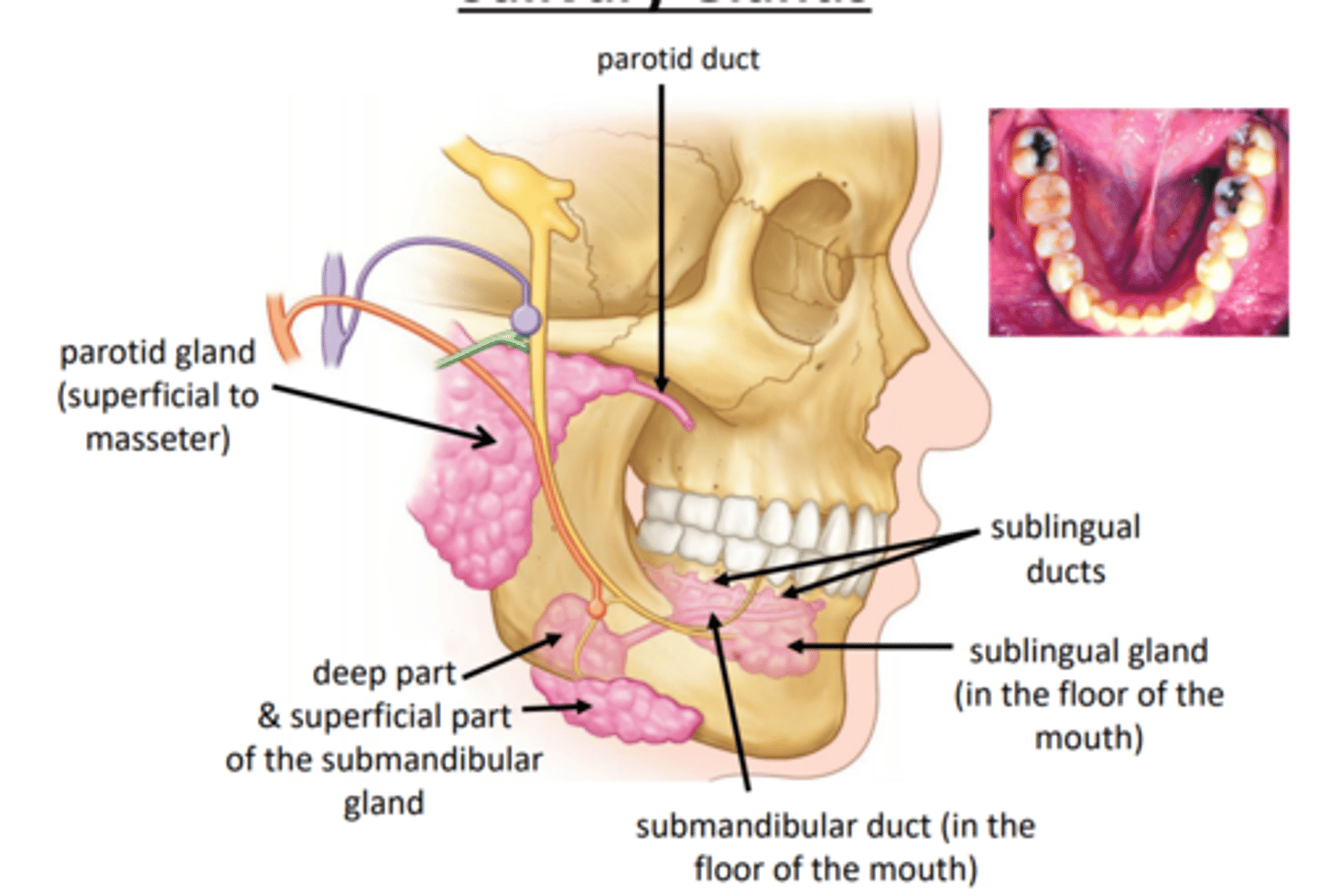
sublingual gland and duct
- mucous cells -> mucus secretion
- several ducts empty below tongue
which process of digestion does not typically take place in the oral cavity?
absorption of nutrients
pharynx
connects oral cavity to esophagus and nasal cavity
- muscularis externa has skeletal muscle for swallowing
parts of pharynx that are considered part of the digestive system
- oropharynx
- laryngopharynx
oropharynx
stratified squamous epithelium
laryngopharynx
stratified squamous epithelium
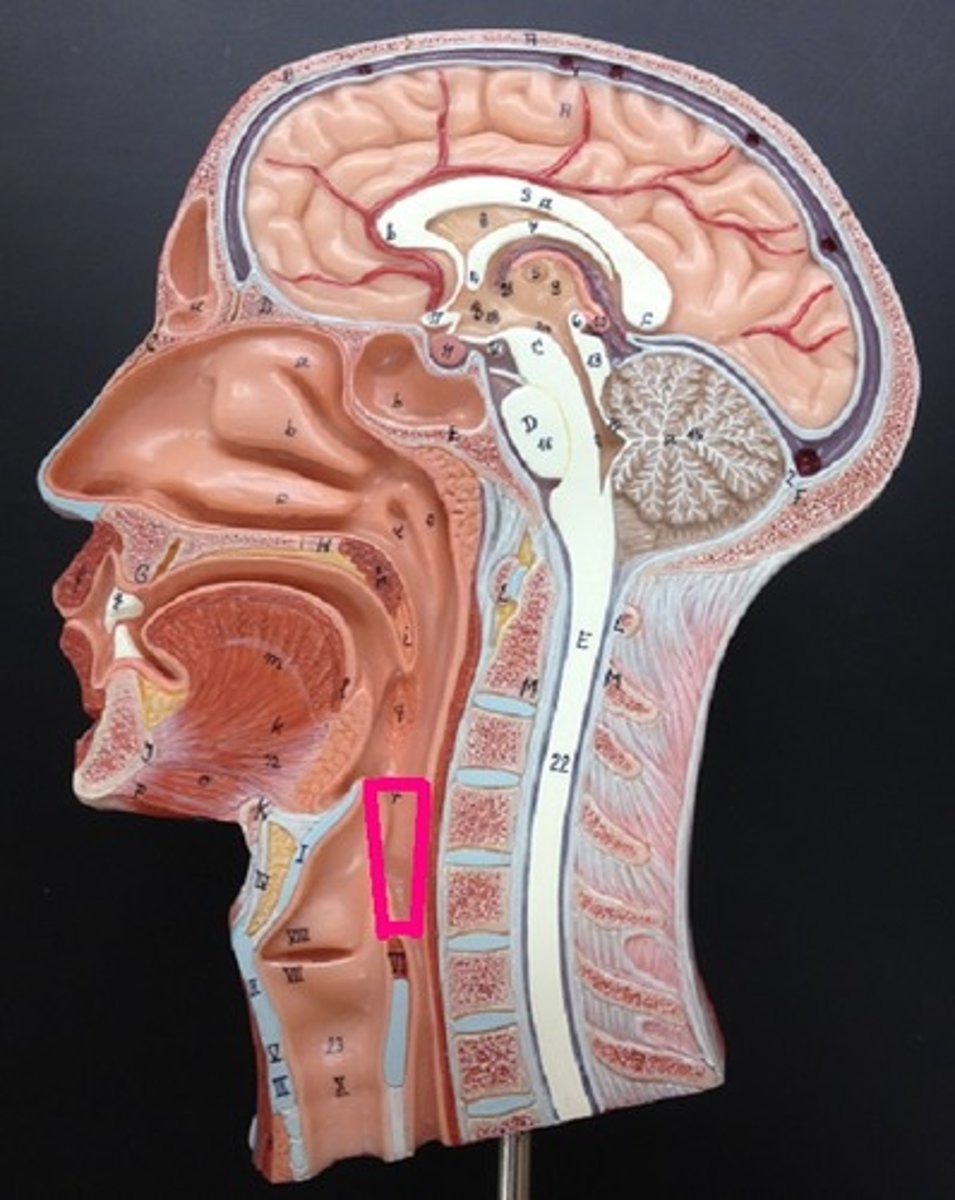
esophagus
- connects pharynx to stomach
- stratified squamous epithelium
- mucous glands in submucosa and mucosa secrete mucus to lubricate as bolus of food passes through
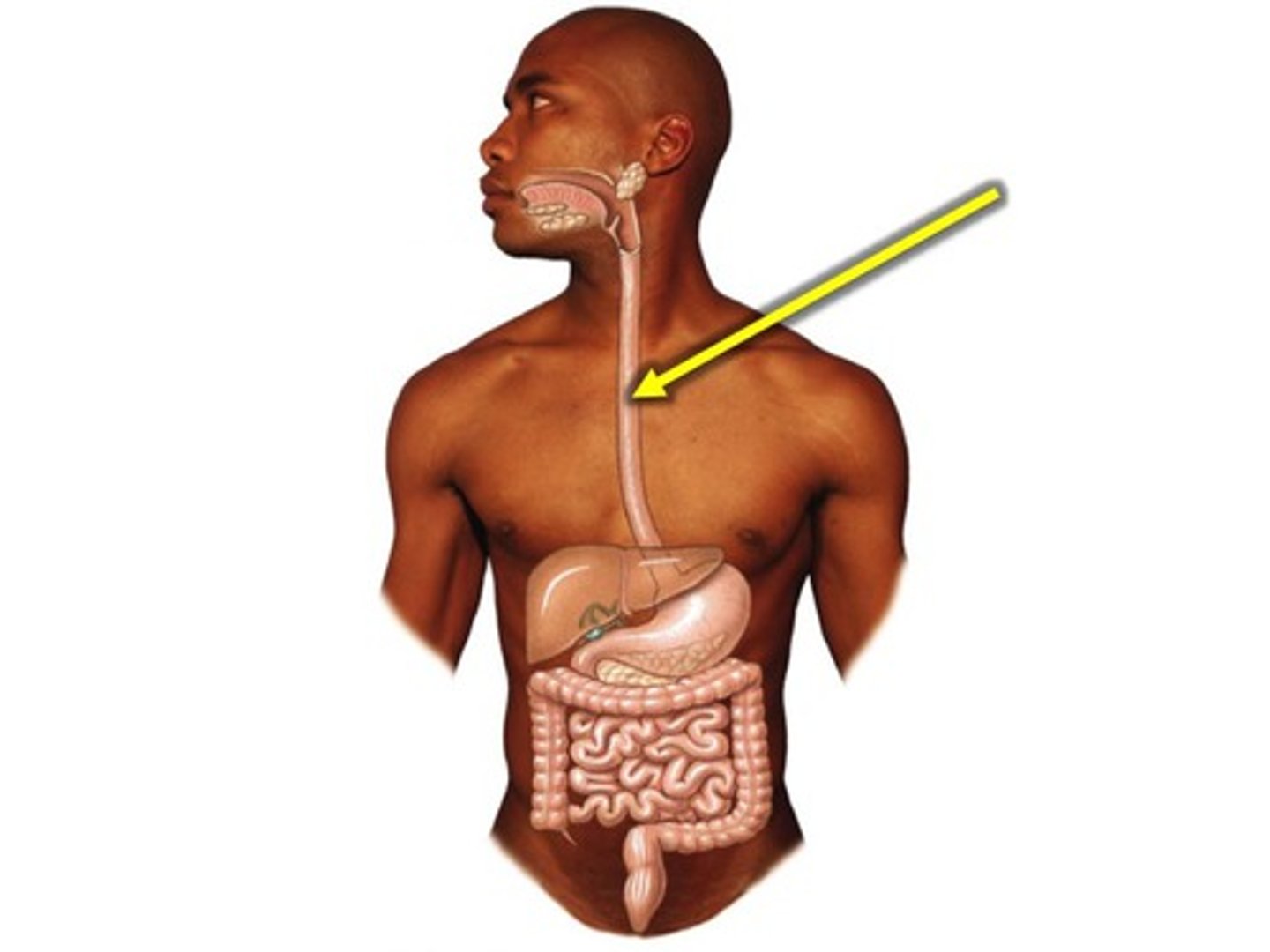
upper 1/3 of muscularis externa of esophagus is what kind of muscle
skeletal muscle
middle 1/3 of muscularis externa of esophagus is what kind of muscle
mix of skeletal and smooth
lower 1/3 of muscularis externa of esophagus is what kind of muscle
smooth muscle
the outer layer of the esophagus is called the _____
stomach
- food spends ~4 hours in stomach being turned into chyme
- simple columnar epithelium
- absorption