MCAT Physics: Circuits, Magnetism, Waves, and Sound
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Junction Rule
the sum of all currents entering a junction must equal the sum of the currents leaving (conservation of charge)
Elements in Series have equal
current
loop rule
The sum of the potential differences (voltages) across all the elements around any closed circuit loop must be zero
elements in parallel have equal
voltage
Power output by a battery
P=IV
Power dissipated across resistors due to thermal energy
P=I^2R=V^2/R
magnitude of force by a magnetic field
F=qvBsin(theta) (theta= angle between v and B)
right hand rule for the force by a magnetic wave
1. point your hand in the direction of velocity of the particle
2. curl fingers toward B
3. thumb will be in the direction of the force for a positive particle. MUST FLIP DIRECTION FOR A NEGATIVE CHARGE
The Force of the magnetic field is always perpendicular to
both the velocity and magnetic field
In a uniform magnetic field, an accelerated particle will exhibit
uniform circular motion; direction depends on the charge of the particle
Work done by a magnetic field
0
magnetic fields are created by
moving electric charges, like a current
the direction of a magnetic field for a current in a long wire
point your thumb in the direction of the current and curl your fingers around the wire. Your fingers represent the direction of the magnetic field around the wire.
the magnetic field at a point in space is __ compared to the field line
tangent
simple harmonic motion
back and forth motion with a restoring force proportional to displacement
Hooke's Law
F=-kx; restoring force is opposite the displacement from equilibrium and proportional to that displacement and the spring constant
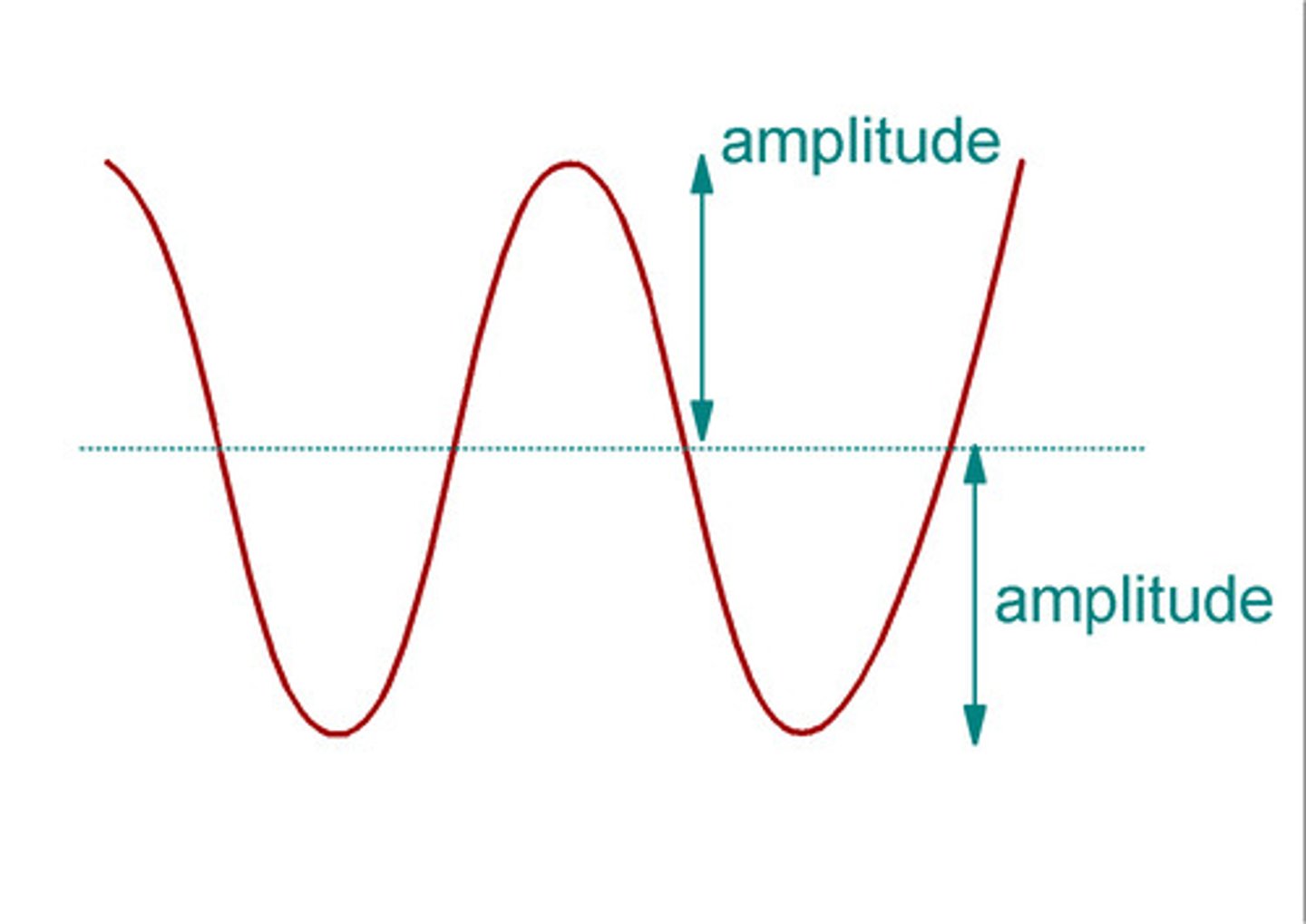
amplitude
+/-A: the greatest displacement from equilibrium during oscillation
energy stored in a spring as it stretches/compresses
PE=1/2 kx^2
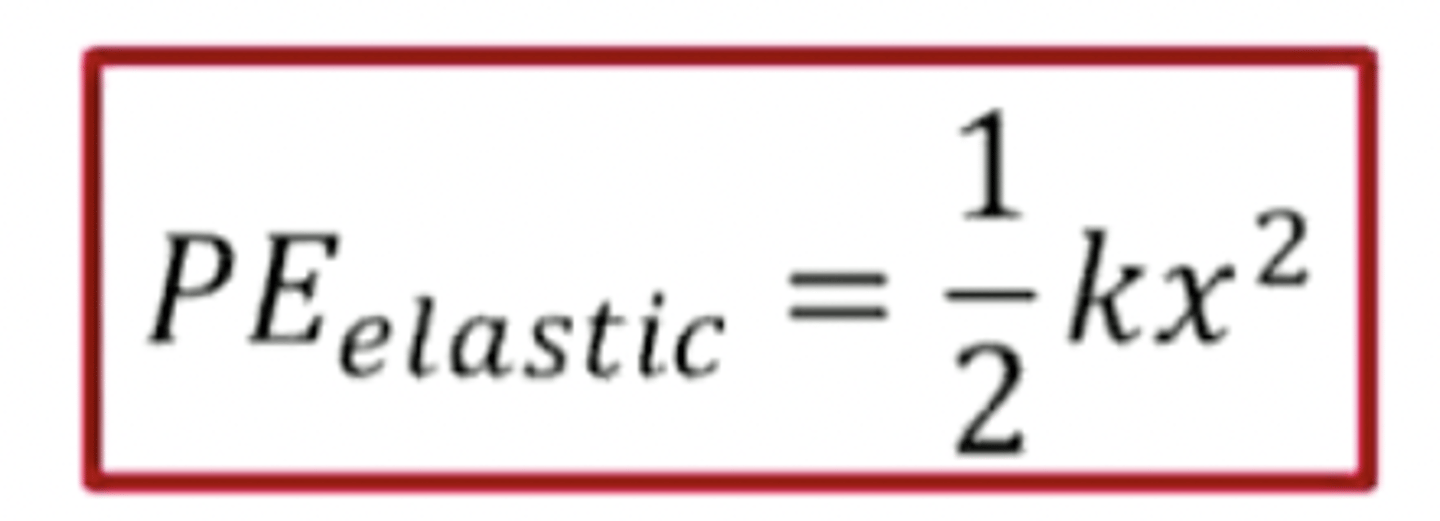
work done by the spring
= - delta PE
conservation of mechanical energy
KE₁ + PE₁ = KE₂ + PE₂; where there is no friction or air resistance (or other non-conservative forces)
period
time it takes to complete one cycle (returning to the same position and velocity); independent of amplitude
frequency
number of cycles that occur in one second (Hz)
relationship between frequency and period
f = 1/T
frequency of a spring
f = (1/2π)√(k/m)
propagating oscillations that transfer energy
the medium is not propagated with the energy and oscillates with a series of identical oscillations, slightly out of phase
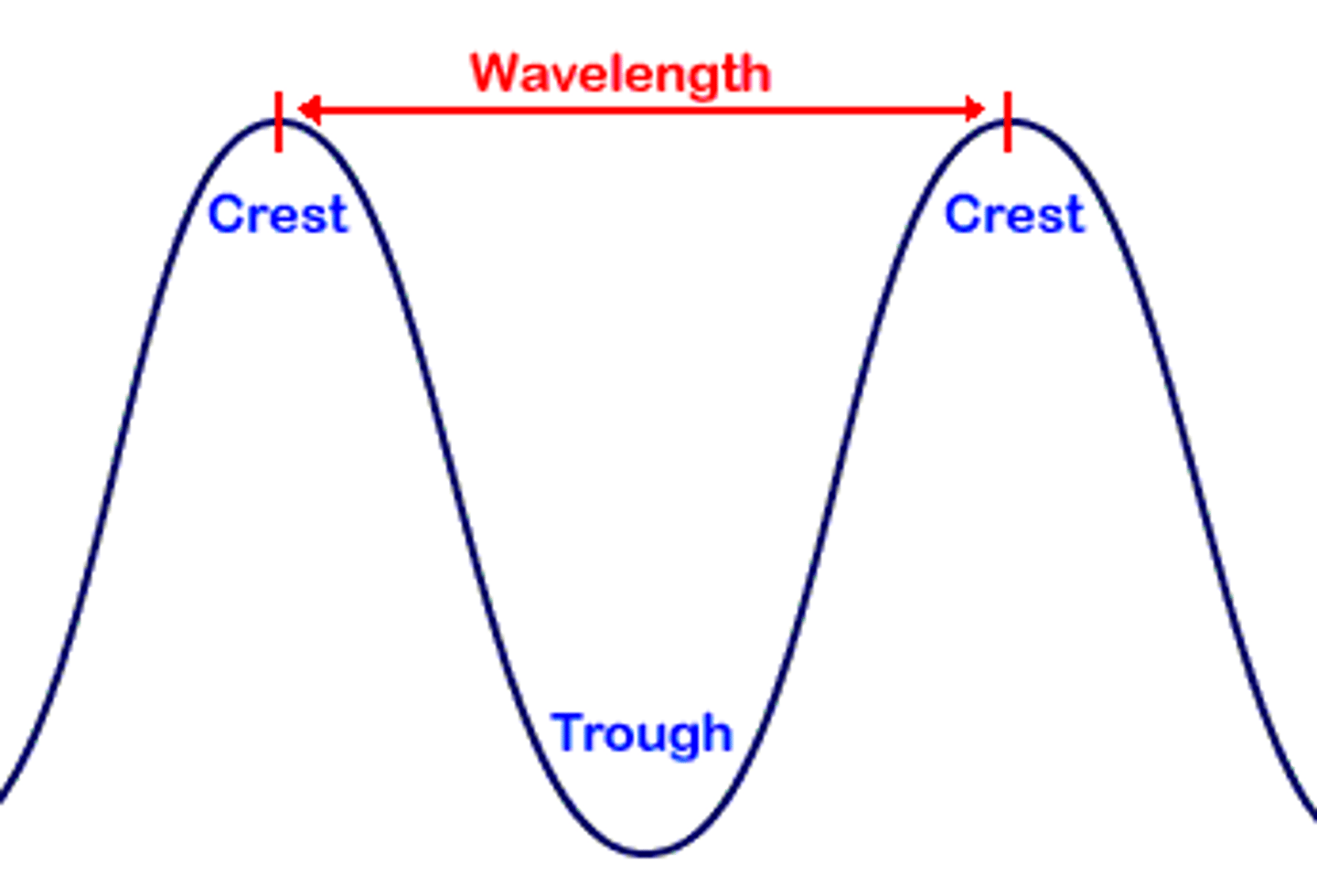
wavelength
length of one cycle
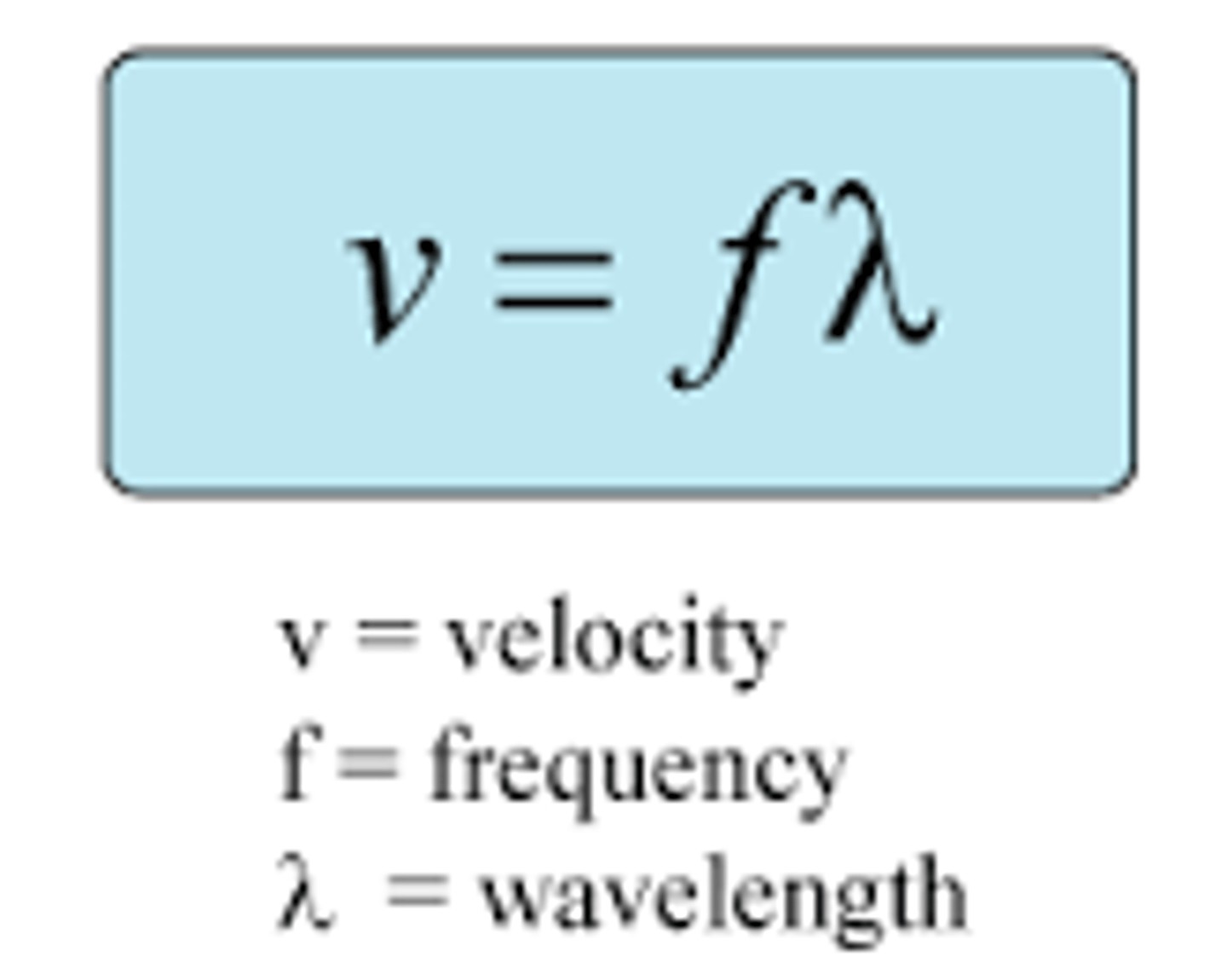
wave speed
the speed at which a wave travels through a medium. proportional to the wavelength times the frequency
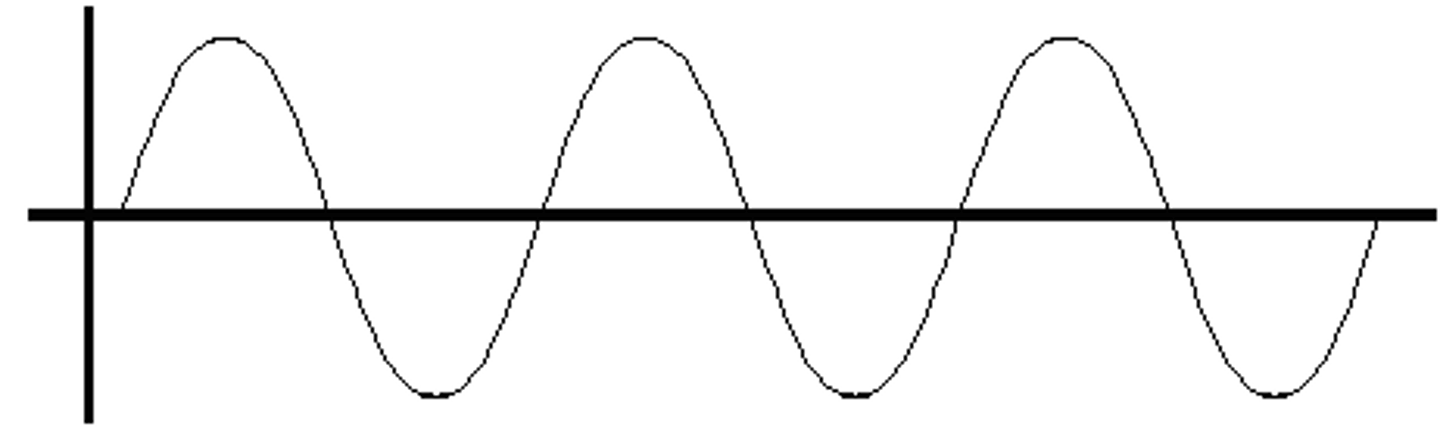
transverse waves
medium oscillate perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. Ex: ocean waves, waves on a string, electromagnetic waves
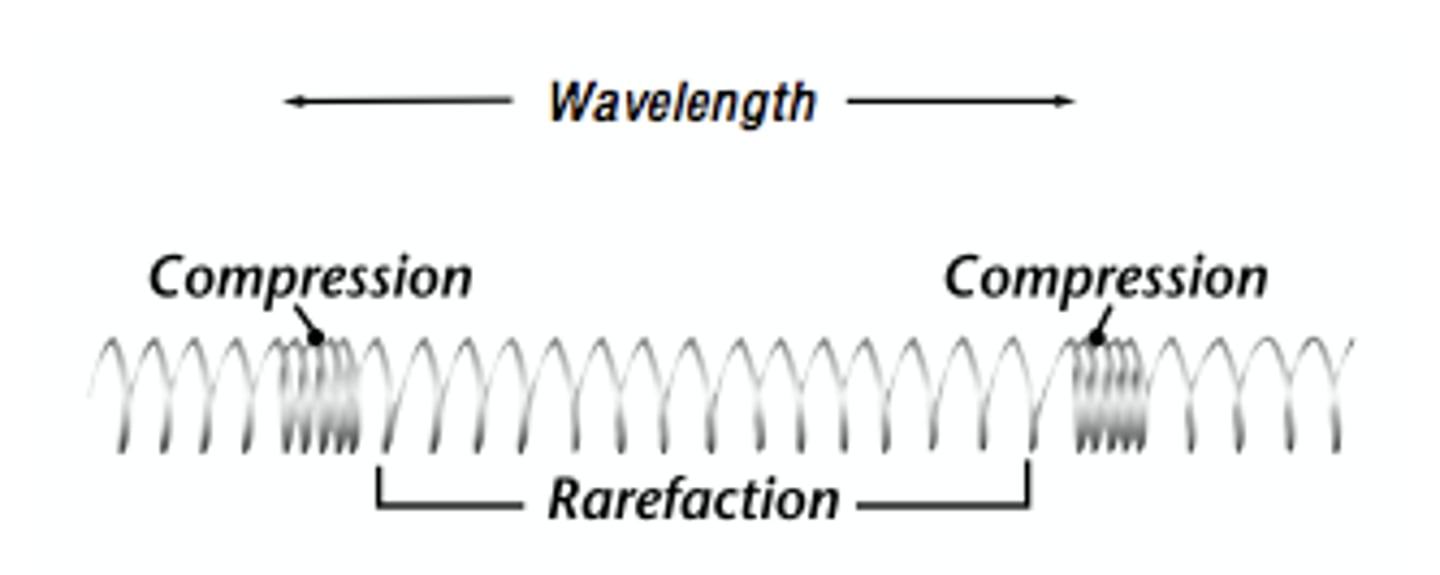
longitudinal waves
medium oscillates parallel to the direction of wave propagation. Ex: sound
the speed of a wave in a medium depends on the type of wave and physical properties of the medium
this means that v is constant in a medium regardless of the frequency or the wavelength
a wave moving from one medium to another will maintain the same frequency
the speed can change but the frequency of the wave doesn't change in relation to a change in medium
speed of sound waves in medium
slowest in gases, faster and liquids, and fastest in solids
standing waves
waves that are trapped where the endpoints determine which wavelengths can be trapped
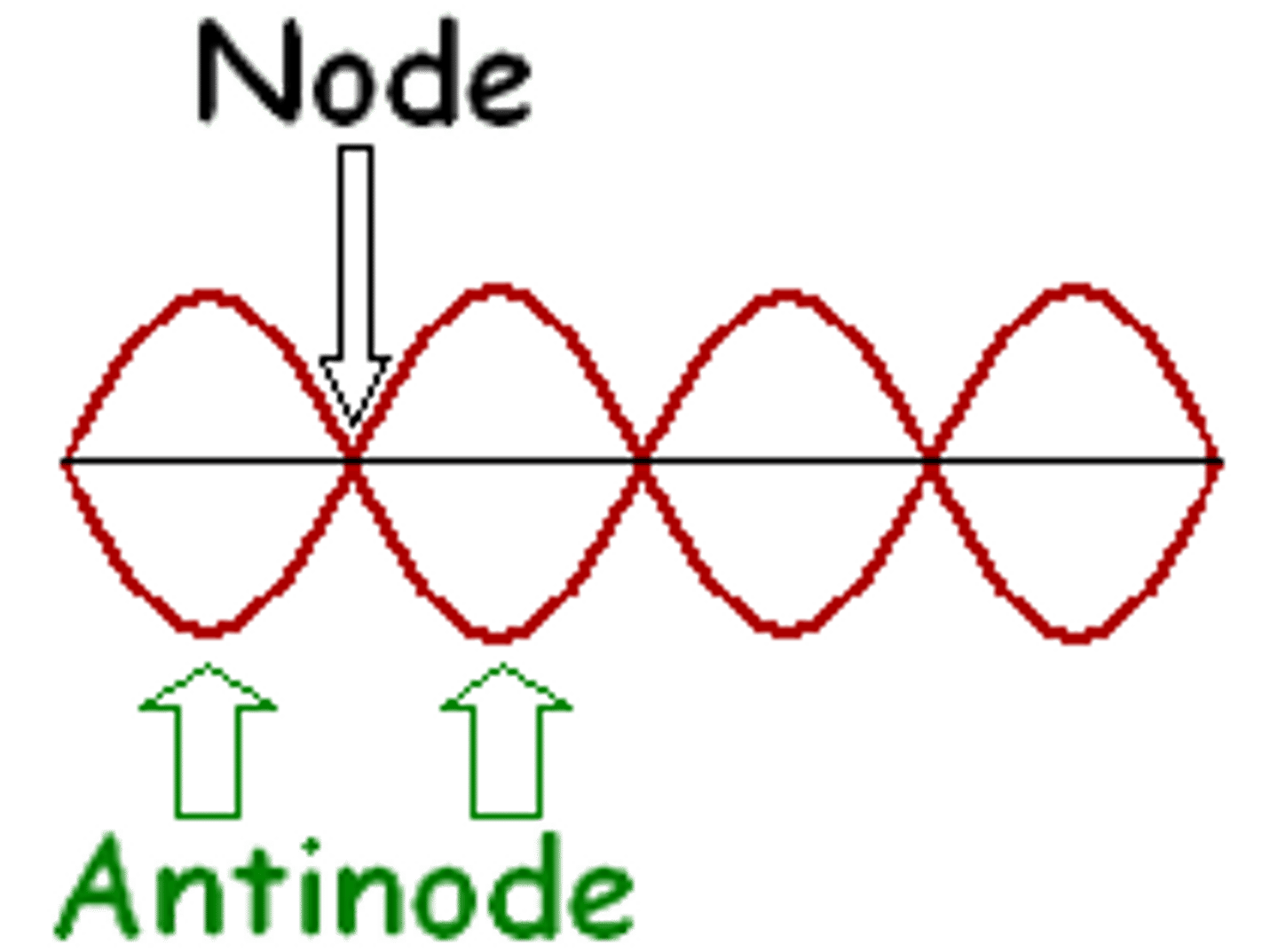
node
point of zero oscillation on a standing wave
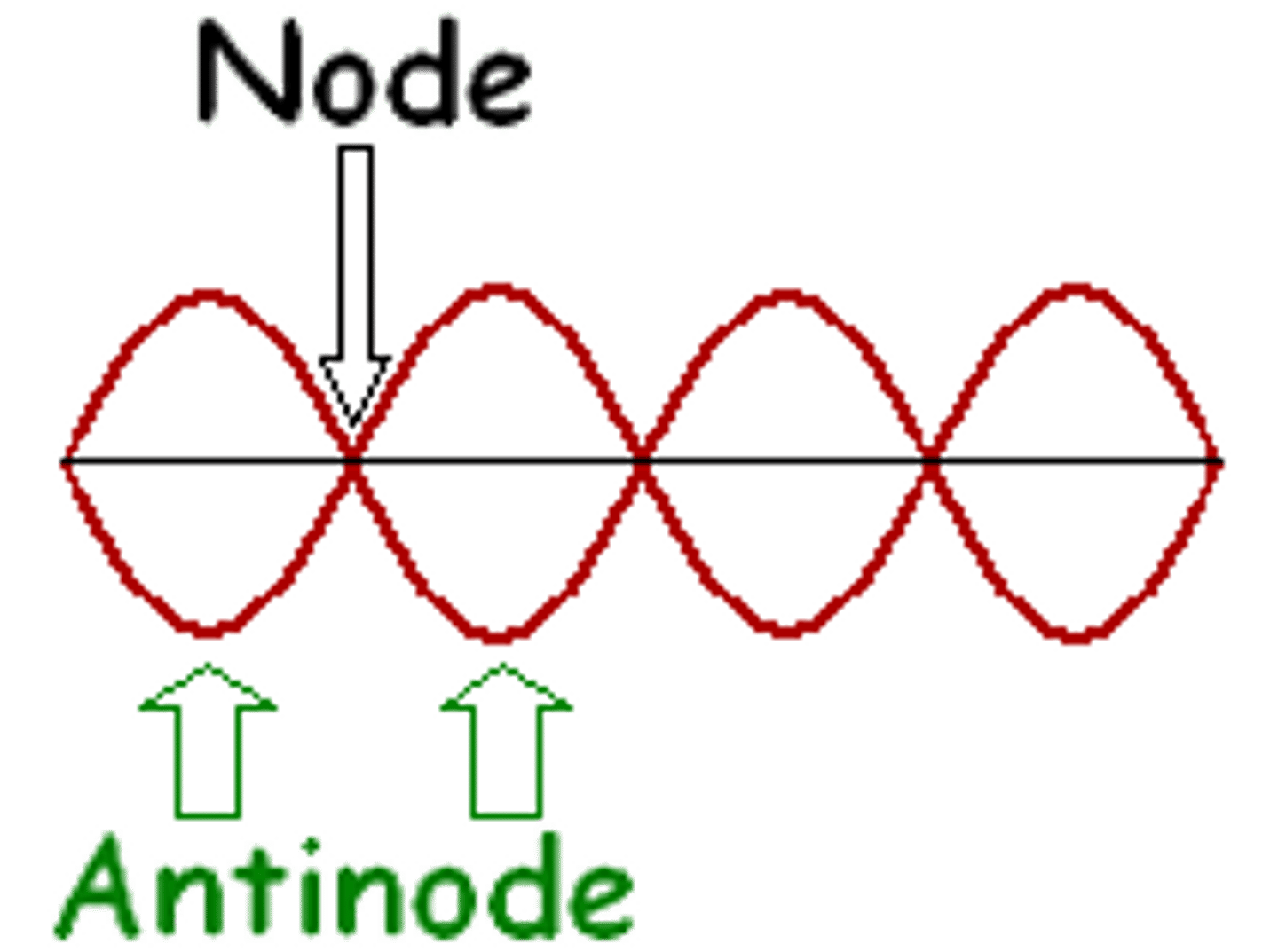
antinode
point of maximum oscillation on a standing wave
Standing waves in strings
displacement node at each end
frequency of a standing wave
f = nf1 (f1=frequency of the first harmonic) (n=harmonic integer)
first harmonic
fundamental frequency; longest wavelength standing wave that can exist on the string
wavelength of a standing wave
λ = 2L/n
Intensity
I=power/area
intensity of a spherical wave
I is proportional to 1/r^2
Intensity and amplitude
intensity is proportional to the amplitude squared
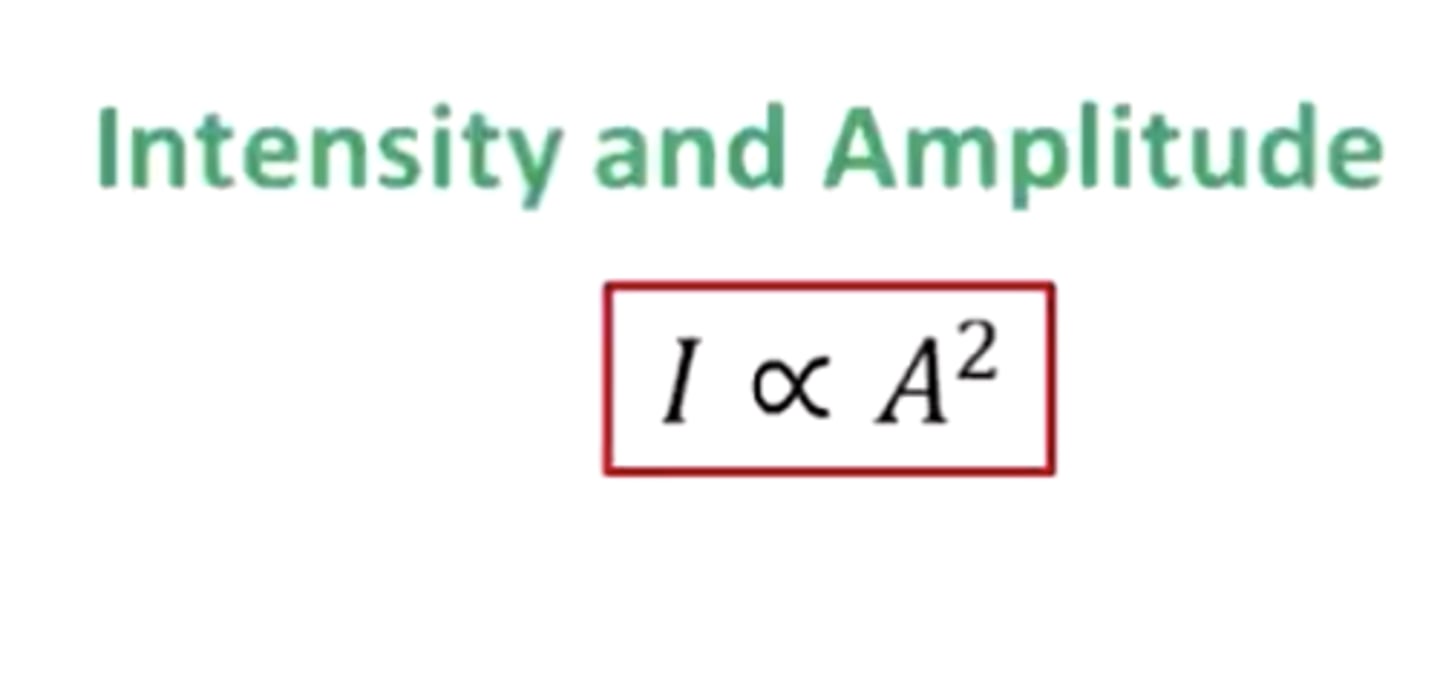
sound level
beta = 10 (log intensity +12)
For every increase in the intensity by a factor of 10
add 10 to the sound level
for every decrease in the intensity by a factor of 10
subtract 10 from the sound level
doppler shift
shift in the detected frequency of a wave due to the relative motion between the detector and the sound source.
In general:
as they get closer: higher frequency is detected
as they get further: lower frequency is detected
doppler shift equation (frequency detected)
fd=fs ((350+/-vd)/(350-/+vs))
- "top" sign is towards
- bottom sign is away