Chapter 15 - Wars of Religion and the Clash of Worldviews 1560-1648 - The Making of The West - HIST 1111 / HIST 1112
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Catherine de Médicis
Italian-born mother of French king Charles IX (r. 1560-1574); she served as regent and tried but failed to prevent religious warfare between Calvinists and Catholics.
Pg. 389

Edict of Nantes
The decree issued by French king Henry IV in 1598 that granted the Huguenots (French Calvinists) a large measure of religious toleration.
Pg. 390

politiques
Political advisers during the sixteenth-century French Wars of Religion who argued that compromise in matters of religion would strengthen the monarchy.
Pg. 390
Philip II
King of Spain (r. 1556-1598) and the most powerful ruler in Europe; he reigned over the western Habsburg lands and all the Spanish colonies recently settled in the New World.
Pg. 391
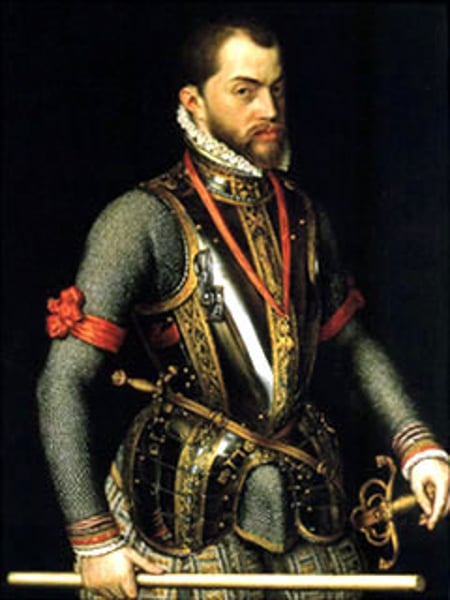

Lepanto
A site off the Greek coast where, in 1571, the allied Catholic forces of Spain's king Philip II, Venice, and the papacy defeated the Ottoman Turks in a great sea battle; the victory gave the Christian powers control of the Mediterranean.
Pg. 392

Elizabeth I
English queen (r. 1558-1603) who oversaw the return of the Protestant Church of England and, in 1588, the successful defense of the realm against the Spanish Armada.
Pg. 393

Puritans
Strict Calvinists who in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries opposed all vestiges of Catholic ritual in the Church of England.
Pg. 393

Peace of Westphalia
The settlement (1648) of the Thirty Years' War; it established enduring religious divisions in the Holy Roman Empire by which Lutheranism would dominate in the north, Calvinism in the area of the Rhine River, and Catholicism in the south.
Pg. 397

raison d'état
French for "reason of state," the political doctrine, first proposed by Cardinal Richelieu of France, which held that the state's interests should prevail over those of religion.
Pg. 398
secularization
The long-term trend toward separating state power and science from religious faith, making the latter a private domain; begun in the seventeenth century, it prompted a search for nonreligious explanations for political authority and natural phenomena.
Pg. 404

scientific method
The combination of experimental observation and mathematical deduction used to determine the laws of nature; first developed in the seventeenth century, it became the secular standard of truth.
Pg. 405
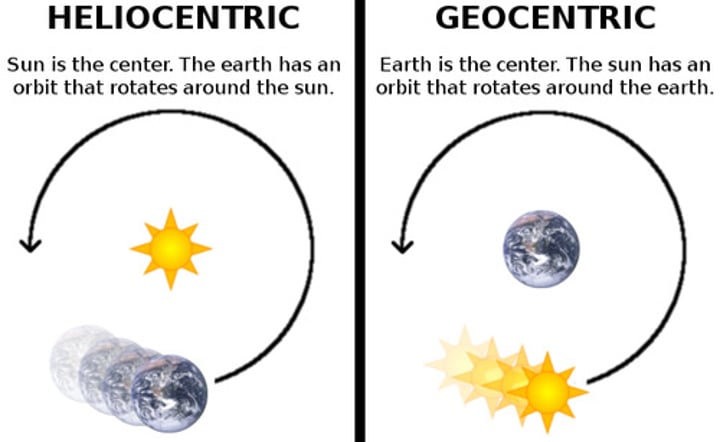
heliocentrism
The view articulated by Polish clergyman Nicolaus Copernicus that the earth and other planets revolve around the sun.
Pg. 406
baroque
An artistic style of the seventeenth century that featured curves, exaggerated lighting, intense emotions, release from restraint, and even a kind of artistic sensationalism.
Pg. 410

Militant French Catholic nobles followed the lead of which family?
The House of Orange
The Guise family
The Bourbon family
The Médicis
The Guise family
The most militantly Catholic nobles took their cues from the Guise family. The Huguenots followed the lead of the Bourbon family, who stood first in line to inherit the throne if the Valois kings failed to produce a male heir.
Who led the successful revolt against the Spanish occupation of the Netherlands in the 1570s?
Catherine de Médicis
Elizabeth I
William of Orange
Henry of Navarre
William of Orange
Prince William of Orange led the Netherlands' seven predominantly Protestant northern provinces into a military alliance with the ten mostly Catholic southern provinces and drove out the Spaniards.
Which of these events marked the beginning of the Thirty Years' War?
The invasion of northern Germany by Christian IV of Denmark
The invasion of northern Germany by Gustavus Adolphus of Sweden
France's declaration of war on Spain
The deposition of Ferdinand II by rebellious Czechs
The deposition of Ferdinand II by rebellious Czechs
The Czech rebellion was suppressed by imperial forces, but that did not bring the war to an end.
Which of these fared relatively well during the economic recession of the first half of the seventeenth century?
Italy
The Holy Roman Empire
The Dutch Republic
Spain
The Dutch Republic
The only country that emerged unscathed from this downturn was the Dutch Republic, thanks to a growing population and a tradition of agricultural innovation. During this period, their foreign trade, textile industry, crop production, and population all grew.
The seventeenth-century scientist Isaac Newton is most famous for his work on which of the following?
Empiricism
The law of universal gravitation
The law of inertia
Heliocentrism
The law of universal gravitation
Newton's law of gravity had the advantage of explaining the whole universe in a unified system.
Which of these explains the defeat of the Spanish Armada?
French intervention on the English side
The superior size and quality of the English fleet
Poor planning by the Spanish
English fire ships and bad weather
English fire ships and bad weather
The English scattered the Spanish Armada by sending blazing fire ships into its midst. A great gale then forced the Spanish to flee around Scotland.
Which of these is a major contributing factor to the outbreak of the Thirty Years' War?
A contested succession
Peasant uprisings
Ethnic competition
Inflation and other economic problems
Ethnic competition
The fighting that devastated central Europe from 1618 to 1648 had its origins in a combination of religious disputes, ethnic competition, and political weakness.
Which of these is an accurate description of the demographic and economic trends in the second half of the sixteenth century?
Population declined and prices rose.
Population grew and prices rose.
Population grew and prices fell.
Population declined and prices fell.
Population grew and prices rose.
Population grew and prices rose in the second half of the sixteenth century. England's population grew by 70 percent, and in parts of Spain the population grew by 100 percent (that is, it doubled). Food prices rose particularly fast, climbing 400 percent over the course of the whole century.
Descartes argued which of the following?
That human reason was an inadequate tool for discovering the secrets of the universe
That human behavior is essentially irrational
That scientific investigation should begin with observation and experiment
That mathematical and mechanical principles provided the key to understanding all of nature
That mathematical and mechanical principles provided the key to understanding all of nature
In his Discourse on Method (1637), Descartes argued that mathematical and mechanical principles provided the key to understanding all of nature, including the actions of people and states.
Why did the French kings fail to stop the spread of Calvinism within their realm?
Preoccupation with foreign wars
A series of family tragedies
Near-universal popular support for Calvinism
Their indecision and apathy
A series of family tragedies
King Henry II was accidentally killed during a jousting tournament in 1559, and his fifteen-year-old son, Francis, died soon after. Ten-year-old Charles IX became king, with his mother, Catherine de Médicis, as regent, or acting ruler. This situation left the crown weak and unable to control the religious violence that soon engulfed France.
Of the following families or states, which of these lost the most as a result of the Peace of Westphalia?
The Habsburgs
Sweden
England
The Ottomans
The Habsburgs
The Habsburgs were forced to recognize Dutch independence; give the German princes the right to establish Lutheranism, Catholicism, or Calvinism as their state religion; and give up considerable territory in the west.
Which of these was a long-term consequence of the recession of the early 1600s?
Greater economic equality in the countryside
Increased outbreaks of famine and disease
An increase in economically motivated migration
A new pattern of late marriages and smaller families
A new pattern of late marriages and smaller families
European families reacted to economic downturn by postponing marriage and having fewer children.
With which of these statements would Ptolemy have agreed?
The earth is at the center of the cosmos.
The sun is at the center of the cosmos.
The planets revolve in elliptical orbits.
The earth is more perfect than the heavens.
The earth is at the center of the cosmos.
According to the Greek astronomer Ptolemy, the earth was at the center of the cosmos. Above the earth were fixed the moon, the stars, and the planets in concentric crystalline spheres.
Chall
Why did French regent Catherine de Médicis arrange the marriage of the king's Catholic sister, Marguerite de Valois, to Henry of Navarre, a Huguenot and Bourbon?
She was a Huguenot.
She feared the rise of Guise influence.
She wanted control of his lands.
She wanted his help in the event of civil war.
She feared the rise of Guise influence.
Catherine de Médicis feared the rise of Guise influence. To counter this, she brought a Huguenot noble, Henry of Navarre, into the royal family.
Which of these was true of armies during the later phases of the Thirty Years' War?
Most soldiers were motivated by religious convictions.
Most soldiers were unpaid draftees.
Mutinies were frequent.
Armies grew increasingly professional and reliable.
Mutinies were frequent.
As the war dragged on, governments were increasingly short of funds and often failed to pay the troops. The result was frequent mutinies, looting, and pillaging.
Which of these was true of seventeenth-century marriage and childbirth patterns?
Family sizes shrank.
The average family had eight children.
The number of births out of wedlock reached 20 percent.
The average age of marriage fell from the late twenties to the early twenties.
Family sizes shrank.
Which of these was true of the period that followed the Thirty Years' War?
The Habsburgs emerged as Europe's preeminent power.
Europe remained at peace for almost fifty years.
States grew increasingly decentralized.
Religion was no longer the underlying cause of international warfare.
Religion was no longer the underlying cause of international warfare.
After 1648, international warfare would be undertaken for reasons of national security, commercial ambition, or dynastic pride rather than to enforce religious uniformity.
American colonial enterprises among the Swedes, Danes, Britons, and Dutch differed from those of the Spanish and Portuguese in that only the Swedes, Danes, Britons, and Dutch
chartered joint-stock companies initially.
colonized the Caribbean.
established colonies in South America.
imported African slaves to their colonies.
chartered joint-stock companies initially.
Northern European colonializing was accomplished through private joint-stock companies to enrich investors by importing fish, furs, tobacco, and precious metals (if they could be found) and to develop new markets for European products.
How did Hugo Grotius define natural rights?
Employment, health, shelter, and autonomy
Life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness
Faith, freedom, property, and salvation
Life, body, freedom, and honor
Life, body, freedom, and honor
To be in accord with natural law, Grotius argued, governments had to defend natural rights, which he defined as life, body, freedom, and honor.
Which of these was a major seventeenth-century social and economic trend?
International trade quickened, especially in the Mediterranean.
Prices rose precipitously.
In most places, population growth slowed.
With a few exceptions, agricultural yields slowly increased.
In most places, population growth slowed.
In most places, population growth slowed, and in many places, population actually declined.
Why were Philip II's forces victorious at the 1571 Battle of Lepanto?
The Muslim forces had poor luck with the weather and were separated in a massive gale.
Spanish forces effectively used fire ships against the Turkish forces.
Christian forces employed six heavily armed Venetian ships that rode high in the water.
Spain and its Dutch allies effectively trapped the Muslim forces on the Spanish coast.
Christian forces employed six heavily armed Venetian ships that rode high in the water.
The Christian allies had the advantage of six big Venetian vessels that rode too high in the water to be boarded and carried many artillery pieces.
Bodin's ideas helped lay the foundation for which of these?
Constitutionalism
Federalism
Republicanism
Absolutism
Absolutism
Bodin's ideas helped lay the foundation for absolutism — the idea that the monarch should be the sole and uncontested source of power.
Which of these was an important difference between witchcraft beliefs and accusations before 1400 and beliefs and accusations during the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries?
Before 1400, witchcraft accusations were concentrated in central Europe.
Before 1400, witchcraft accusations were much more common.
Before 1400, nearly half of the accused were men.
Before 1400, people of all social groups believed in witchcraft.
Before 1400, nearly half of the accused were men.
In the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries, 80 percent of accused witches were women. In sharp contrast, before 1400 nearly half of the accused were men.
In the seventeenth century, Galileo provided further evidence for the Copernican hypothesis by doing which of the following?
Developing the law of inertia
Experimenting with centripetal force and acceleration
Writing at length on cosmic harmonies and elliptical motion
Discovering the first four moons of Jupiter
Discovering the first four moons of Jupiter
The existence of moons around Jupiter clearly suggested that Jupiter could not be embedded in an impenetrable crystal sphere.
Which of these was true of patterns of agricultural labor in seventeenth-century Europe?
Serfdom remained strong in western Europe.
Slavery replaced serfdom in much of Europe.
In general, eastern European peasants had more freedom than western European peasants.
Eastern European nobles reinforced their dominance over peasants.
Eastern European nobles reinforced their dominance over peasants.
In eastern Europe, nobles reinforced their dominance over peasants, and the burden of serfdom increased. Although serfdom produced short-term profits for landlords, in the long run it retarded economic development in eastern Europe.
The development of baroque art in the later sixteenth century was encouraged by which of the following?
The revitalization of the Catholic church
Artists who wanted to minimize the influence of religion on culture and art in society
The emotionalism of the Protestant Reformation
A renewed interest in the Renaissance
The revitalization of the Catholic church
The church hoped that a meaningful art movement might help rekindle the faith of ordinary churchgoers.
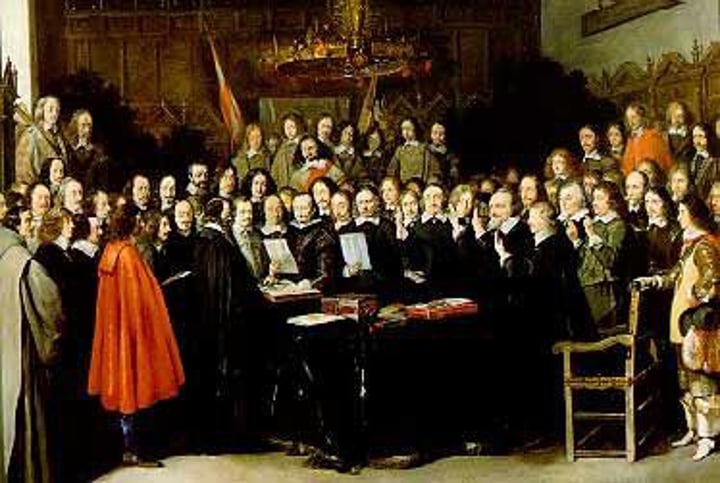
How did the Peace of Westphalia differ from earlier peace treaties?
It was the first to be signed by government ministers and not rulers themselves.
It was the first to bring warring parties together a few at a time.
It was the first to employ a diplomatic congress.
It was the first to establish an international body to settle future disputes.
It was the first to employ a diplomatic congress.
For the first time, a diplomatic congress convened to address international disputes, and those signing the treaties guaranteed the resulting settlement. A method still in use, the congress was the first to bring all parties together rather than two or three at a time.