Chapter 1: Skin & Hair Anatomy
1/215
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
216 Terms
What is the pilosebaceous unit?
The hair follicle and its appendages.
Where does skin color derive from?
Melanin produced in the stratum germinativum.
Carotene, a yellowish pigment
Concentration of blood vessels found in the dermis.
Where is skin the thickest and thinnest? And approximately how thick and thin?
Thickest in the soles of the feet; 1/5th of an inch
Thinnest in the eyelids; 1/12th of an inch
The skin is the body’s largest organ covering up to ? on the average person.
20 square feet
Skin is made up of which two types of tissue?
Epithelial Tissue (“No Blood”/Epidermis)
Connective Tissue
What are the three main layers of the skin?
Epidermis
Dermis
Subcutaneous
What are the other names for Epidermis?
Scarf
Cuticle
No Blood
Epithelial
What are the other names for the dermis (has blood)?
Living Tissue
Living Layer
Corium
Connective Tissue
Cutis Vera
Derma
True Skin
What are the other names for subcutaneous?
Hypodermis
Subcutis
Adipose Tissue/Fat
The epidermis consists of layers made of ? .
Stratified epithelium (no blood)
The process of living cells moving upwards and changing to dead cells is known as ? .
Keratinization
The 2 main zones of the epidermis are:
The Horny Zone
The Germinal Zone (Living/Basal Zone)
The Horny Zone consists of which layers?
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Lucidum
Stratum Granulosum
The Germinal Zone consists of which layers?
Stratum Spinosum
Stratum Germinativum
Tell me about the Stratum Corneum:
Also known as the outermost layer of the skin or “superficial layer”, this is where dead skin cells are constantly shed, even through the friction of changing clothes. These cells are predominantly bound by sebum (the skins natural lubricant).
Tell me about the Stratum Lucidum:
Only found in the palms and soles of the feet where the epidermis is thickest, not found in thin skin. Gets its name from the transparent nature of the cells that contain eleidin (a clear protein), a clear substance derived from keratohyalin granules.
Tell me about the Stratum Granulosum:
Grand Slam = Baseball Players = Have Calluses
Persistent friction and pressure cause areas to thicken for protection and form calluses. It is thickest on soles of feet, followed by palms. Also known as the granular layer. The lower cells have nuclei and are still living. As these cells are pushed upwards by new cells, they lose their nuclei and die. This layer gives skin its opaque appearance due to presence of keratohyalin granules in the cytoplasm.
Tell me about the Stratum Spinosum:
Also known as the prickle cell layer because of the cells’ prickley (spiney) shape.
Tell me about the Stratum Germinativum:
Also known as the Basal Layer, Innermost Layer or Lowest Layer of the Epidermis.
Cell division (mitosis) occurs here, new epidermal tissue is formed and begins migrating to the surface of the skin, replacing dead skin cells that have been shed. This process is known as desquamation and takes approx. 28 days (much less is babies/younger skin and longer in mature adults, usually late 20s and older). This is where melanocytes exist and melanin is produced.
True or False: People of different races have approximately the same number of melanocytes. People with dark skin have melanocytes that are more active and produce more melanin.
True: The color of skin depends on the melanin produced.
What is the Malpighian Layer?
A layer made up of the stratum mucosum and stratum germinativum. The stratum mucosum is only a single cell layer above the stratum germinativum.
The Dermis, made up of connective tissue, is divided into what two layers?
The Papillary Layer
The Reticular Layer
Tell me about the Papillary Layer:
The strongest portion of the dermis, lies directly below the epidermis and is made of elastic collegenous and reticular fibers that are cone-shapes, finger-like projections called papillae.
Tell me about the Reticular Layer:
The thickest layer of the skin, is composed of dense bundles of collagen fibers. It includes numerous appendages: arrector pili muscles, blood vessels, fat cells, hair follicles, lymph vessels, nerve endings, sebaceous glands, and sudoriferous glands.
Name the sensation associated with the following:
End of Bulb Krause
Pacinian Corpuscle
Ruffini’s End Organ
Meissner’s Corpuscle
Merkel’s Disc
Cold
Pressure
Heat
Touch
Light Touch
What are these appendages (found in the reticular layer) responsible for?
Arrector Pili Muscle
Sebaceous Gland
Sudoriferous Gland
Goosebumps
Oil
Sweat
Lymph glands produce lymph, which is made of ? .
White blood corpuscles and plasma. HIV stores in lymph, as well as blood and other body fluids.
Where are sudoriferous glands (sweat) found?
Deep in the dermis, have tubular ducts extending all the way up to the pores in the epidermis.
Where are apocrine glands found?
The underarms (axillae) and genitals; believed to excrete pheromones which play a role in sexual attraction.
Where are eccrine glands found?
All over the body; increased number on the forehead, palms and soles of the feet. Excrete mainly water with a little bit of salt, urea, and water soluble substance. (Sweet Sweat)
True or False: The sebaceous glands vary in size and shape and in their production of a waxy, oily substance, called sebum, which lubricates the skin and hair.
True
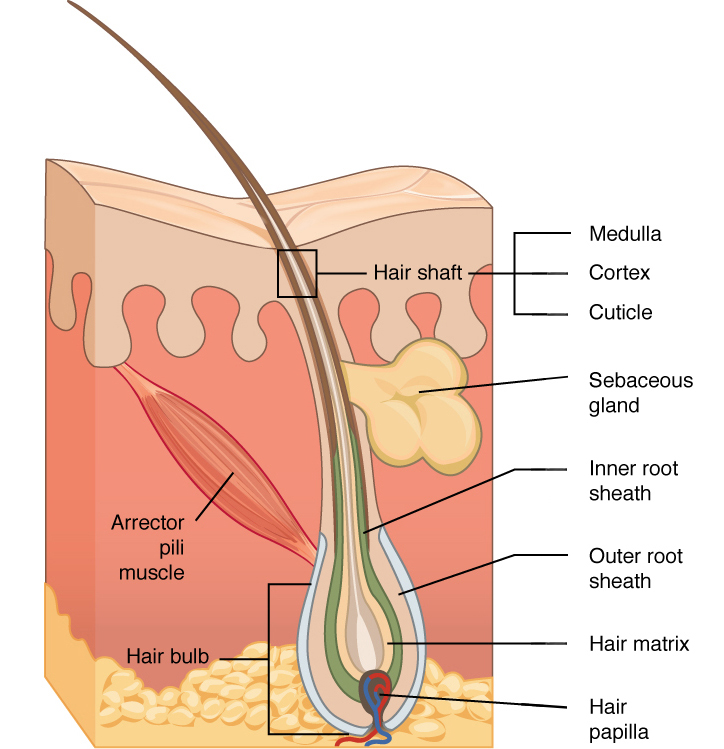
Where are sebaceous glands found in greater numbers?
The scalp, T-Zone (forehead, nose, chin), and the cheeks
What influences hair growth at different ages in males and females?
Hormones and genetic inheritance
The root or papilla of the mature terminal hair is found in the ? , and the hair shaft reaches up to its ? .
lower part of the dermis; follicular opening in the epidermis
The arrector pili muscles is an appendage that is attached to ? .
The hair follicle; it is responsible for lifting the hair to trap a layer of air on the skin’s surface.
Tell me about the subcutaneous layer:
Also known as the subcutis or adipose tissue; a fatty layer at the base of the dermis. This layer varies in thickness depending on the individual’s sex, age, and overall health. Many of the arteries, veins, and lymphatic circulate through this area, as do nerve endings and an abundance of fat cells. This layer protects against impact, i.e. hits and falls.
Healthy ? is continually growing, shedding, and being replaced.
Hair
The hair sits in a ? in the skin.
Pocket / indentation / depression
The outer sheath of the follicular canal is formed from what?
Basal cell layer
The inner side of the follicular canal (external root sheath) is made up of what?
Horny Epidermal Tissue
True or False: The hair shaft is lined with epidermal tissue and in full-grown, active hair stage extends downward, through the dermis to the subcutaneous tissue.
True
What is responsible for producing the hair follicle and the hair matrix?
Epidermal Cells
The base of the follicular canal widens (enlarges) to something called the ? .
Hair Follicle Bulb
What is the area where the hair grows and contains the dividing cells of hair matrix?
The Bulb
What does the hair matrix do?
Produces the hair and the protective external and internal root sheath
What is the dermal papilla?
Located at the base of the hair bulb, it is an indentation which is the layer of dermal tissue that attaches itself to the epidermis with protrusions called papillae. These papillae contain the blood supply needed for providing nutrients for growth as well as hormones that stimulate hair growth.
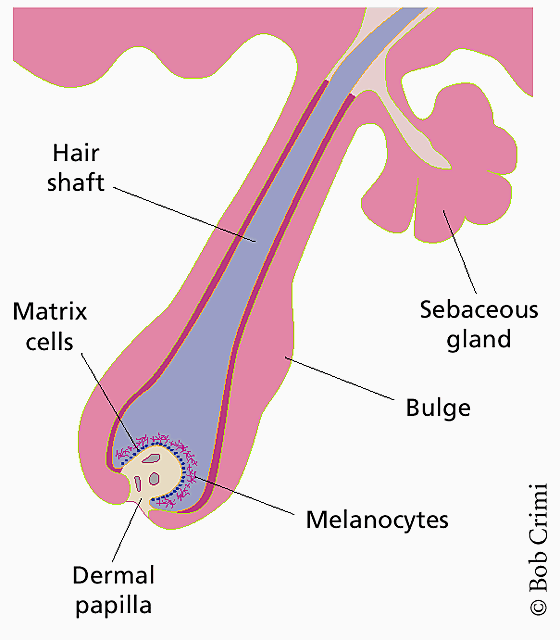
True or False: The arrector pili muscle is an appendage to the hair follicle that is attached to the underside of the follicle, midway between the bulb and the sebaceous gland.
True
Which appendage is partially responsible for heat regulation?
Arrector Pili Muscle
What causes the arrector pili muscle fiber to contract, lifting the hair straight up and resulting in goosebumps?
Fear and cold stimuli
The sebaceous glands help prevent the epidermis from what?
Drying and cracking, and preventing bacteria and germs from entering the skin
What are the 3 layers of the hair from outer to inner most?
Cuticle
Cortex
Medulla
What is the cuticle layer of the hair?
The outermost layer composed of transparent cells that overlap like scales, its purpose is to protect the inner layers of the hair.
What is the cortex layer of the hair?
The middle layer of the hair made of elongated cells of fibrous tissue and pigment that gives hair its color. The cortex is also the layer that gives hair its strength and elasticity.
What is the medulla layer of the hair?
The innermost layer of the hair made of round cells, also known as the pith or marrow. Fine hair lacks the medulla, but the medulla can be found in wavy hair. Generally the curlier the hair, the stronger the medulla.
What are the three main types of hair?
Lanugo
Vellus
Terminal
What is lanugo hair?
Soft, downey hair, also called fetal hair because it is on fetuses in utero and on infants at birth, covering their bodies and scaps. Can have pigment - light or dark. It often sheds a few weeks after birth, eventually the permanent hair begins to grow in.
What is vellus hair?
Present through adulthood. It is fine, short, and often called “peach-fuzz”. Vellus hair often has no pigment or medulla. Women are believed to have 55% more vellus hair than men, it can be found of womens faces where men produce beard and mustache hair at puberty and onward.
What is terminal hair?
Longer, coarser, medullated and pigmented hair that covers the scalp and is found on the arms and legs of both males and females. At puberty, it is also found in the groin area and axillae of both males and females, as well as on the face, chest and back of men.
Growth of vellus and terminal hair is affected by what?
Age, genetics, health and the hormonal changes of puberty, pregnancy and menopause.
The three main stages of hair growth are:
Anagen
Catagen
Telogen
Tell me about the anagen phase:
The Growing Phase. The hair’s active growing phase, when the hair follicle is at its deepest. At this stage, the hair matrix is active, encapsulating the dermal papilla, and the bulb of the hair is visibly darker.
Once a growing anagen hair has reached its full length, it can remain there, depending on location for what varying amounts of time?
A few weeks on the fingers to eight years on the scalp.
Tell me about the catagen phase:
The Transitional Phase: Also known as the involution phase; the shortest hair-growth phase, lasting for only a few days to a few weeks. The hair follicle separates from the dermal papilla, the follicle shrinks to about a third of its anagen size. Club hair starts in this phase.
Tell me about the telogen phase:
The Resting Phase; the base of the hair looks like a club, hence the name club hair. The bulb is usually white. Telogen hairs increase (i.e. more hair loss) during illness, after child birth, and when an individual is experiencing stress.
Will excess androgens lead to a longer or shorter telogen phase?
Shorter telogen phase as they can stimulate terminal hair to regrow faster (anagen).
What are the multiple functions of the skin?
Protection, heat regulation, excretion, secretion, absorption, sensation, and the synthesis of vitamin D.
What should health skin have?
Hair
What is hair nourished by?
Blood and hormones
What are the percentages of anagen, telogen and catagen hair on the scalp?
Anagen: 85% (Duration of anagen; 2-6yrs)
Catagen: 1-2%
Telogen: 13%
What is the name for the skins built-in protective aid which has a pH of 5 to 5.6?
The acid mantle
The acid mantle is caused by the combined activity of what?
Sweat and sebaceous glands. Perspiration is acidic, as it lies on the skin’s surface it can act as a bactericide by inhibiting the growth of bacteria.
Unwanted organisms are recognized by ? in the epidermis that warn against invading microorganisms. ? are then released to engulf and destroy the invading organisms.
Langerhans’ Cells (Immunologic function); Leukocytes
True or False: The adipose tissue provides a source of energy.
True
A healthy body temperature is usually around what?
98 degrees F; 37 degrees C
Evaporation of perspiration of the skins surface produces cooling, also known as?
Thermoregulation
True or False: The skin can absorb oil and fat based substances to differing levels but it cannot absorb water.
True
What is the most common skin cancer vs. the most dangerous (can be deadly)?
Most common = Basal Cell Carcinoma
Most deadly = Malignant Melanoma
The bacteria killing/inhibiting layer made of sweat and lipids (fat); Built in protective aid, with a pH of 5 to 5.6. Caused by the combined activity of the sweat and sebaceous glands. Perspiration is acidic, as it lies on the skins surface it acts as a bactericide.
Acid Mantle
Also known as: Hypodermis, Subcutis, or subcutaneous layer; Connective tissue in animal bodies that contains fat, it is a layer of fat that provides insulation, cushioning, and energy storage.
Adipose Tissue
Glands in the axillae (underarm) and groin (genitals/pubic/triangle region) that secrete sweat and substances that produce body odor when contaminated with bacteria.
Apocrine Glands
A small muscle/appendage attached to hair follicles that causes hair to stand upright when contracted, often referred to as "goosebumps."
Arrector Pili Muscle
The deepest layer of the epidermis where new skin cells are generated - living layer of dividing cells that continuously change and push upward, consisting of the Stratum Spinosum and Stratum Germinativum.
Basal Zone
The thick layer of skin beneath the epidermis, composed of connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerve endings, providing structural support and housing various skin appendages. Contains the papillary layer and the reticular layer, which contribute to the skin's strength and elasticity.
Dermis
The process of shedding dead skin cells from the outermost layer of the skin, exfoliation.
Desquamation
Sweat glands found throughout the skin, that excrete mainly water and salt.
Eccrine Glands
A translucent/clear intracellular protein found in the stratum lucidum of the skin, involved in the process of keratinization.
Eleidin
Also Known As: Cuticle, Scarf, No Blood, Epithelial Tissue
The thin (0.05-1.5mm) outermost layer of skin, providing a protective barrier and containing several sub-layers, including the stratum corneum and stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, stratum germinativum. CLGSG (Come Let’s Get Sunburned, Girls)
Epidermis (CLGSG)
The tissue that forms a thin protective layer on bodily structures.
Epithelial Tissue
The inner side of the follicular canal which is made of horny epidermal tissue.
External Root Sheeth
The depression or indentation in the skin that houses the entire pilosebaceous unit
Follicular Canal
The layer of skin where cells divide
Germinal Zone
The outermost portion of the epidermis
Horny Zone
The skin and its accessory organs, such as the sebaceous and sweat glands, sensory receptors, hair and nails
Integumentary System
A protein found in the skin that helps guard against invasion
Keratin
The change of living cells to dead ones
Keratinization
Cells found in the epidermis that warn against the invasion of microorganisms and respond to that invasion; immunologic function. Derived from bone marrow and constitute about 5% of cells within the epidermis.
Langerhans’ Cells
Colorless, watery fluid that circulates through the lymphatic system; similar in composition to blood plasma
Lymph
A skin layer made of the stratum mucosum and stratum germinativum
Malpighian Layer
Nerve endings in the skin that are sensitive to touch
Meissner’s Corpuscles
Grains of pigment that give your hair and skin color
Melanin