chapter 4 biology notes
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
name the 5 main components of a eukaryotic cell
nucleus
plasma membrane
cytoskeleton
cytosol (gel like) & cytoplasm
other organelles
give 3 main structural differences between plant and animal cells
cell walls
chloroplasts
central vacuole
rough ER function
protein process
smooth ER function
detoxify harmful substance
mitochondria function
makes energy or ATP
chloroplast function
site of photosynthesis
lysosomes function
get rid of worn-out organelles
ribosomes function
protein synthesis
Golgi complex function
processes, sorts, and tags proteins
transport vesicles function
carries proteins to other organells
centrosomes function
organizing centers
why do red blood cells burst if put into fresh water but plant cells don’t burst in fresh water
water is hypotonic; both plant and blood cell will absorb water however plants have cell wall for stability
cell pic
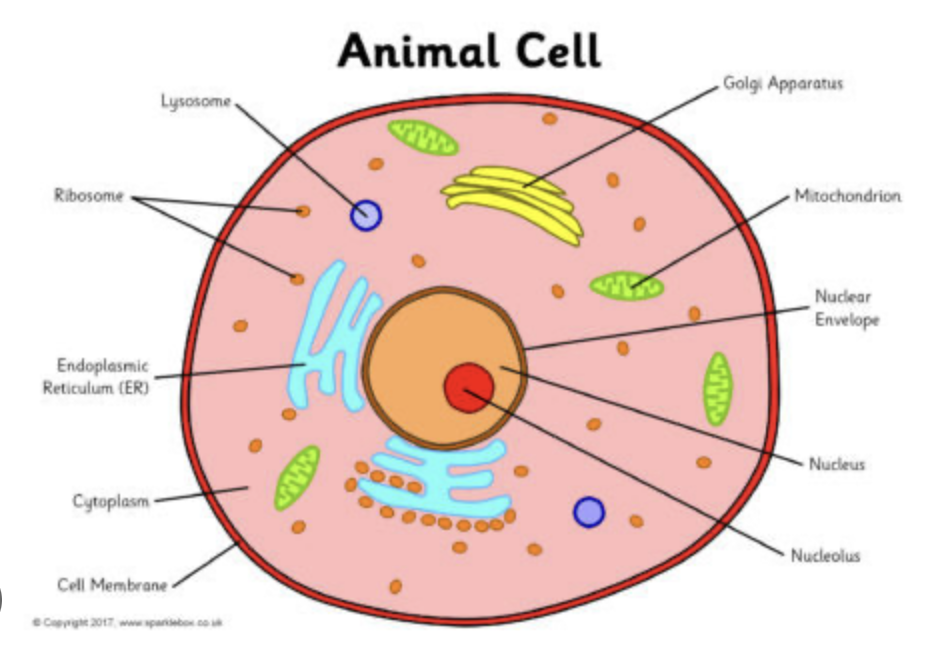
what are the two different types of cells
prokaryotic and eukaryotic
prokaryotic cells include
bacteria and archaea
eukaryotic cells include
plant cells
fungi cells
animal cells
protista
unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
prokaryotic cell
prokaryotic cells are located in
the nucleoid
prokaryote cell structure includes:
cell wall, unique structures; capsules, pili, and flagella
prokaryotic cells:
DNA: Nucleoid region
Cell size: small
Organization: single-celled
metabolism: may not need O2
Organelles: none
eukaryotic cells:
DNA: nucleus
Cell size: larger
Organization: multi-cellular
metabolism: usually needs O2
Organelles: has organelles
nucleus is made out of:
nuclear envelope with pores
nucleoplasm (semi solid fluid)
DNA-chromatin
nucleolus (synthesize ribosomes)
DNA, Chromatin, Chromosomes, and nucleolus are all found in:
the nucleoplasm
DNA + Protein =
chromatin
how many chromosomes do bacteria have
one
how many chromosomes do humans have
46 (23 pairs)
plasma membrane
a phospholipid bilayer with proteins and cholesterol embedded in it
ribosomes are attached to surface:
rough ER
ribosomes are NOT attached to surface
smooth ER
ribosomes are made out of:
ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins
during protein synthesis, ribosomes:
assemble to convert mRNA to amino acids
mitochondria is the:
powerhouse of the cell
the food we eat converts into ATP during a process called:
cellular respiration
lysosomes are considered the:
garbage disposals of the cell
protein production in animal cells:
in nucleus DNA is copied to mRNA (messenger RNA)
mRNA carries info to ribosomes, exiting nucleus through nuclear pores
amino acid chain dropped inside ER and folded into protein
Golgi complex does addition; processing and sorting
protein moves to plasma membrane for export (exocytosis)
in protein synthesis, ribosomes are known as:
work benches
endomembrane system
group of membrane and organelles that work together to modify, package, and transport vesicles.
cytoplasm
the region between plasma membrane and the nuclear envelope
cytoplasm contains
70-80% of water
cytoskeleton is:
made out of protein fibers that help maintain the shape and mobility of a cell, position of organelles, and movement on vesicles
cell wall:
is made out of cellulose
central vacuole in a plant is :
90% of cell volume
plastids
pigment containing organelles
plant cells do not have
lysosomes or centrosomes