FPS Nanotechnology Vocabulary
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
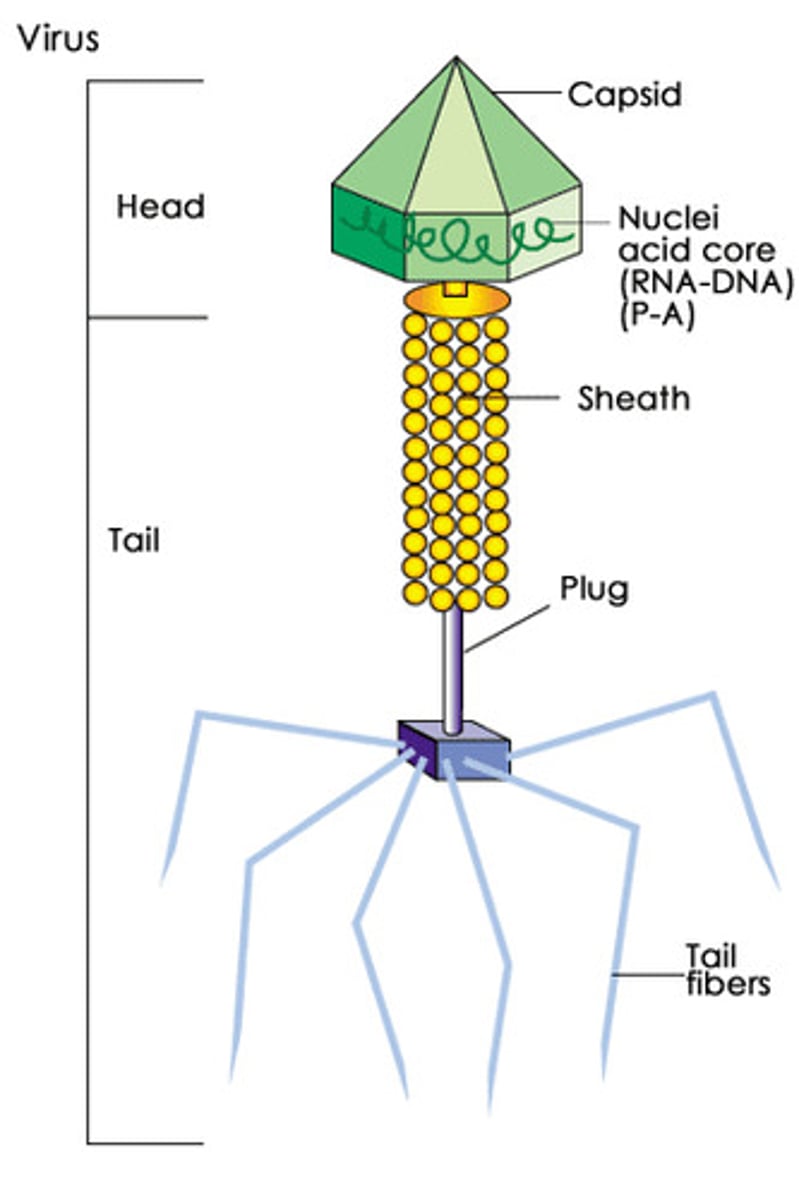
virus
an infectious organism that can only reproduce inside a host's body
toxic
poisonous, something that causes harm to living cells

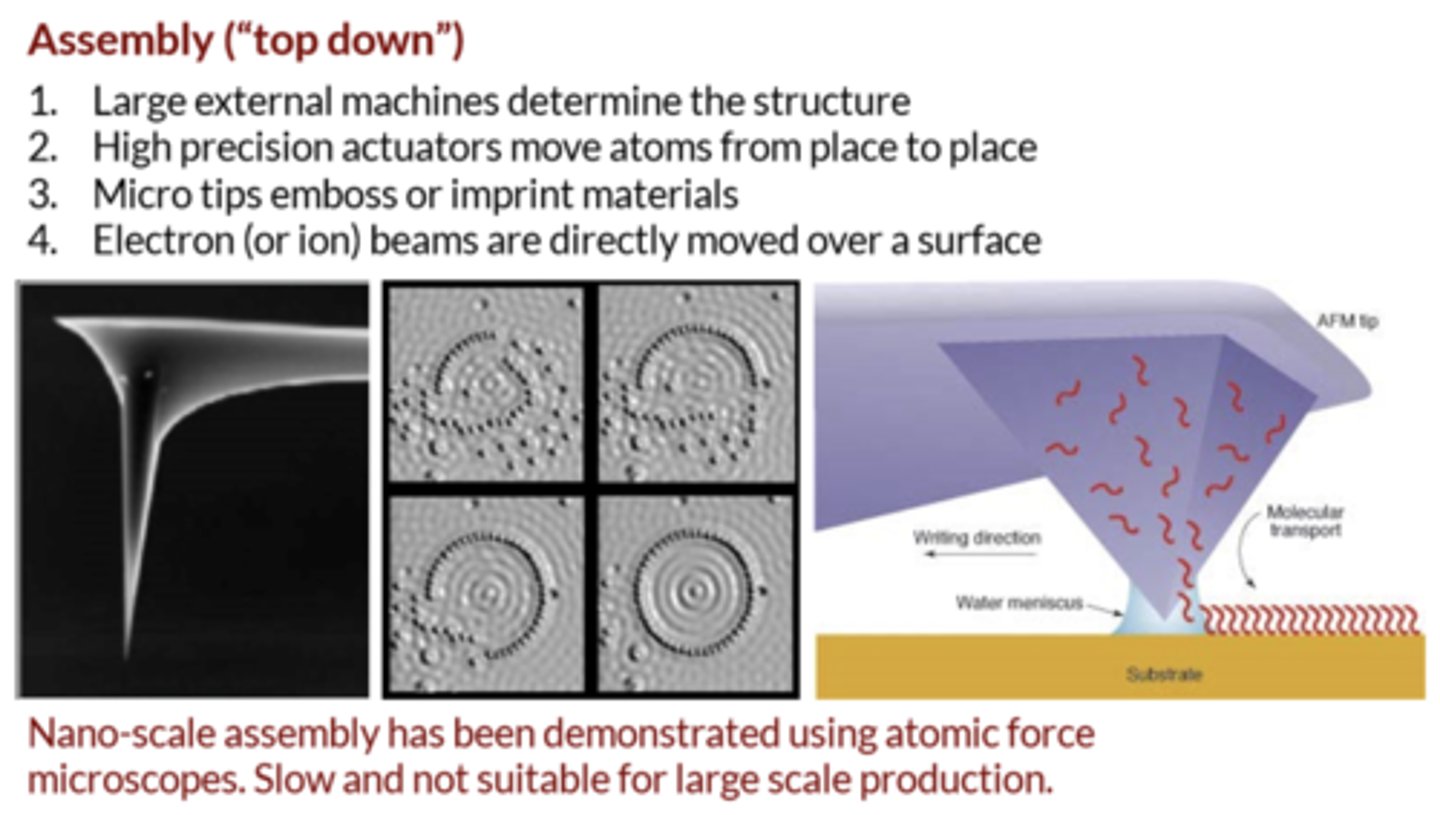
top-down assembly
breaking down of large materials to create nanoscale materials
involves the breaking down of large pieces of material to generate the required nanostructures from them
therapy
a treatment of a mental or physical disorder

textile
relating to fabric or cloth
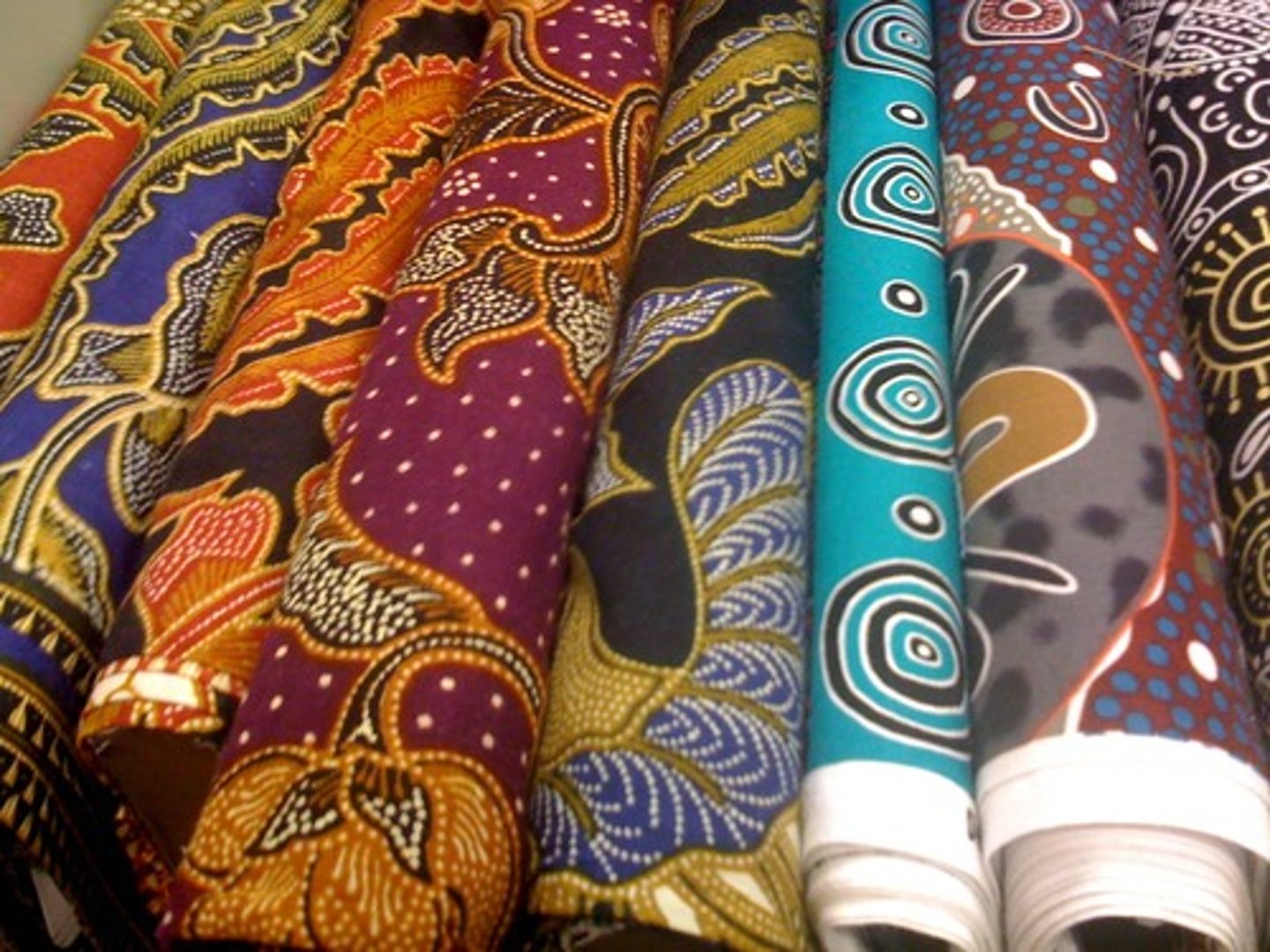

smart dust
tiny sensors capable of measuring and transmitting information on their environment
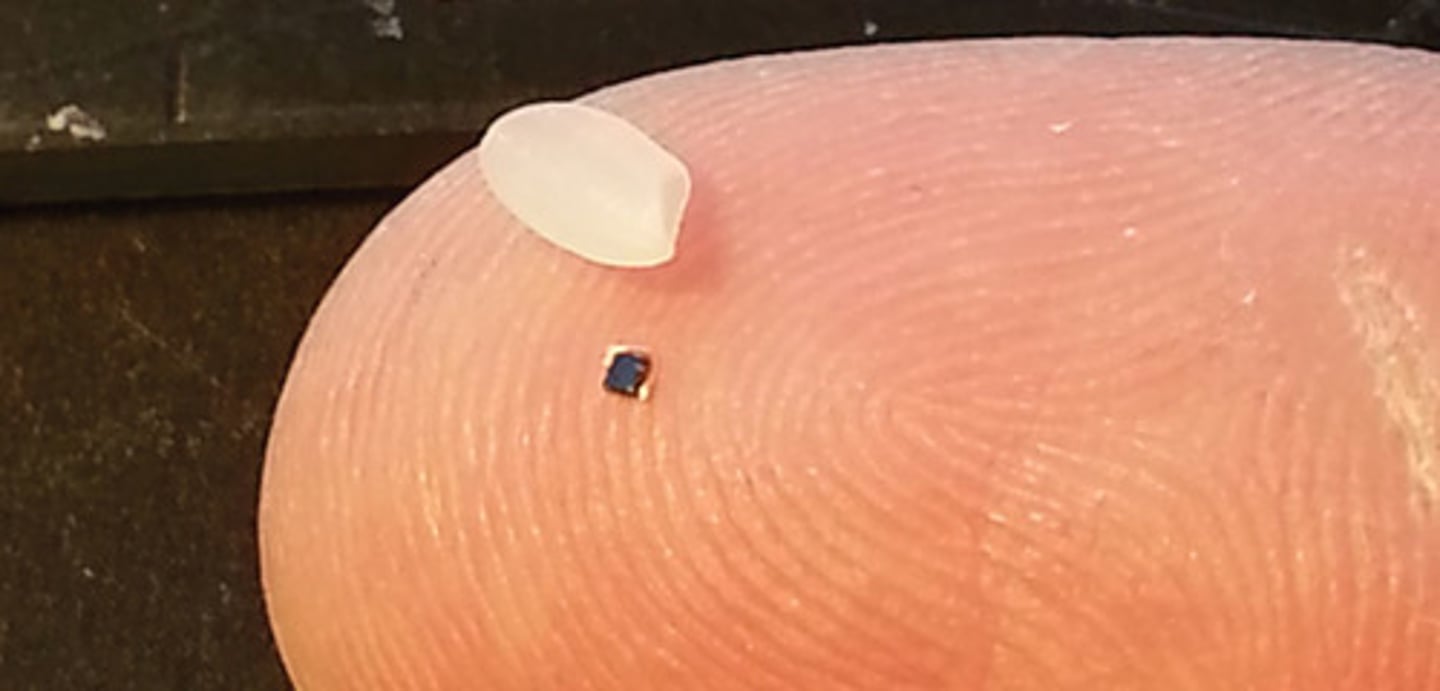

self-repair
the ability of a material to partially or completely repair damage
scanning tunneling microscope
a microscope used for imaging surfaces at the atomic level
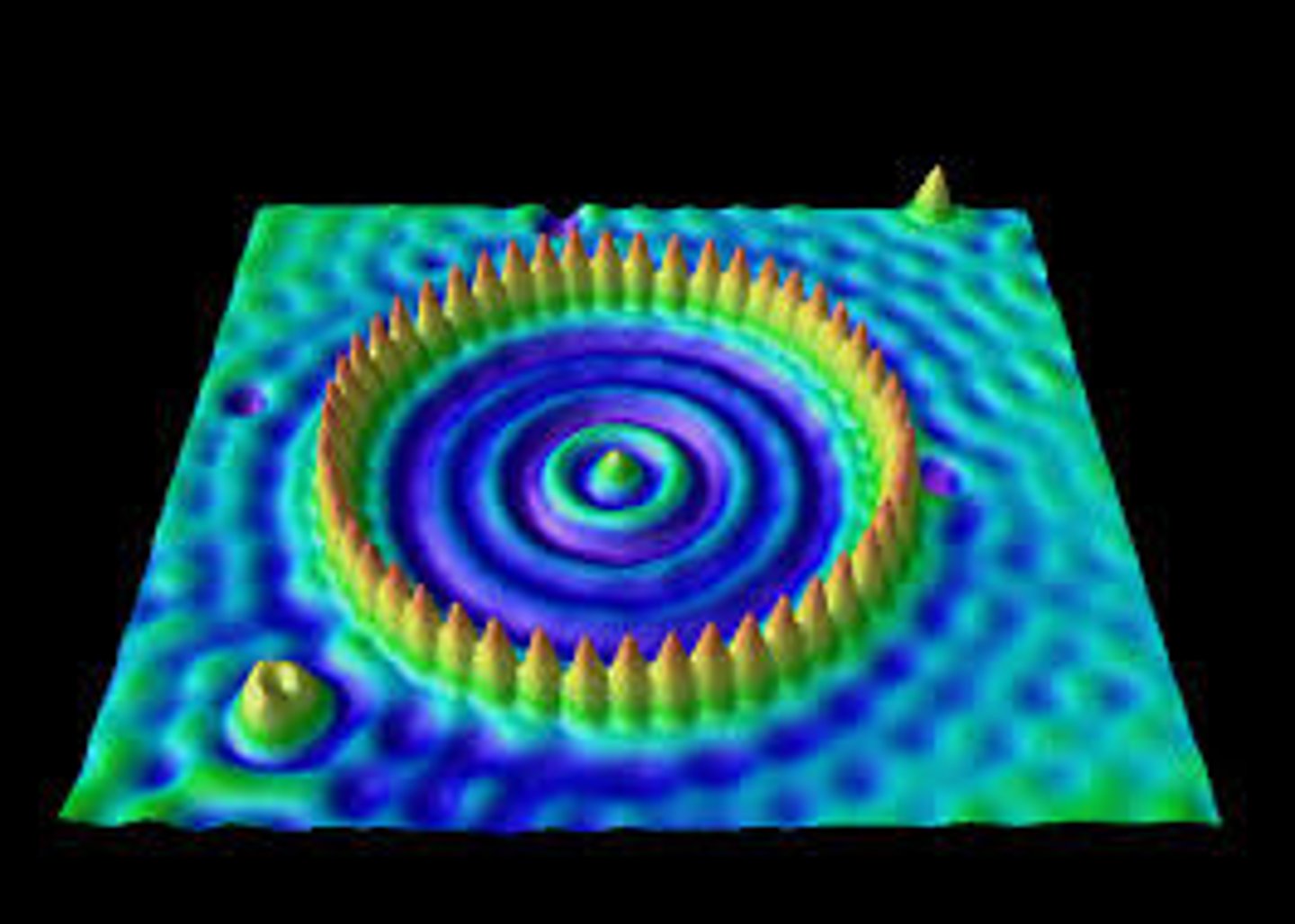
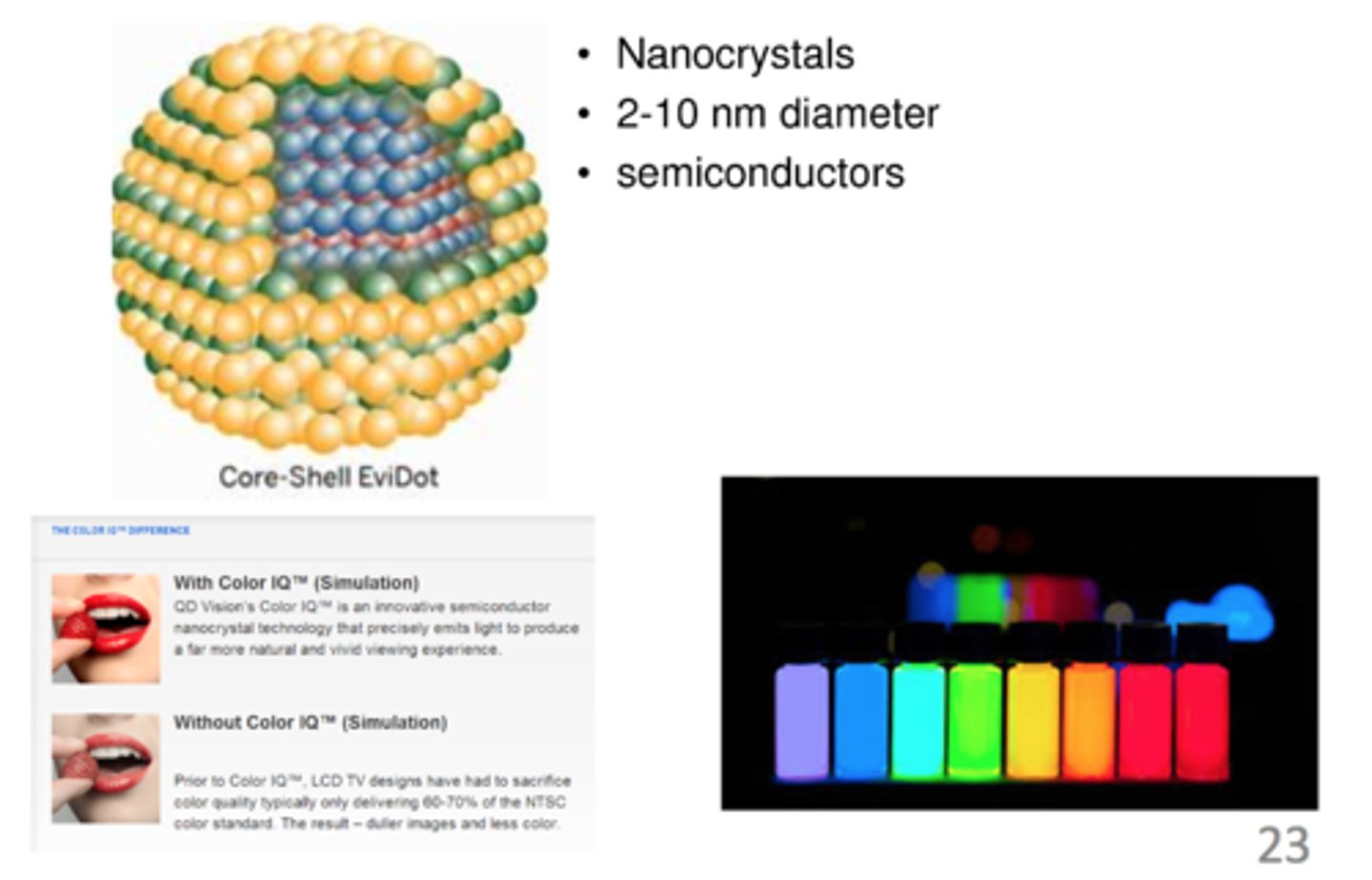
quantum dot
a smaller cluster of atoms, usually between 2 and 10 nanometers, usually made with conducive material such as zinc
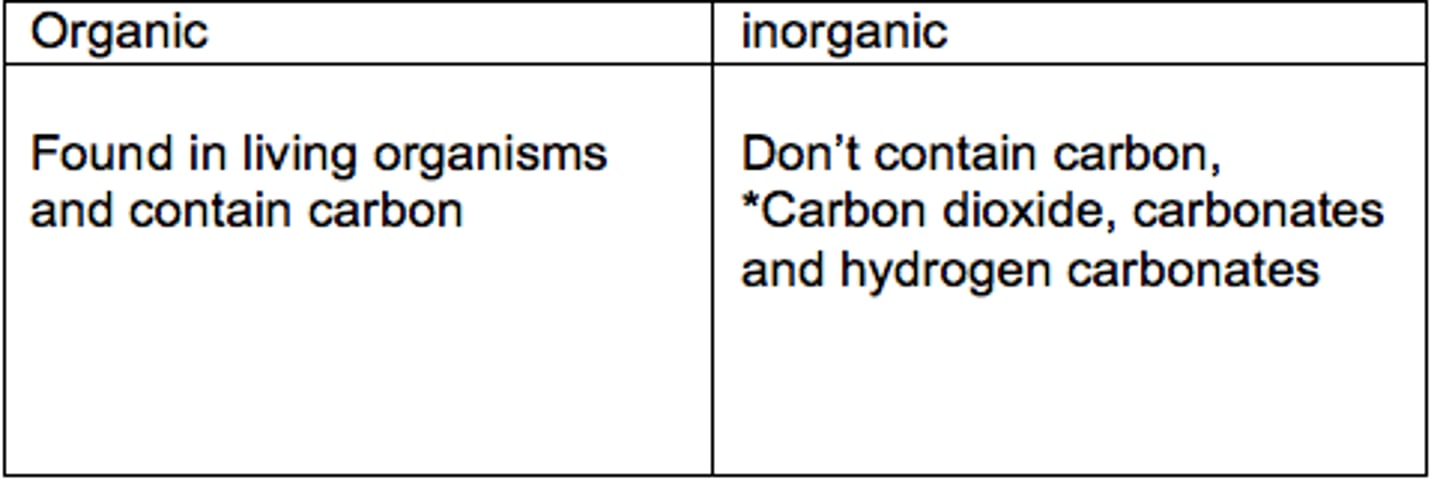
organic
relating to living things
optical
relating to how light reacts with a substance

nanotechnology
the science of designing, producing, and using devices and systems by manipulating atoms and molecules at the nanoscale

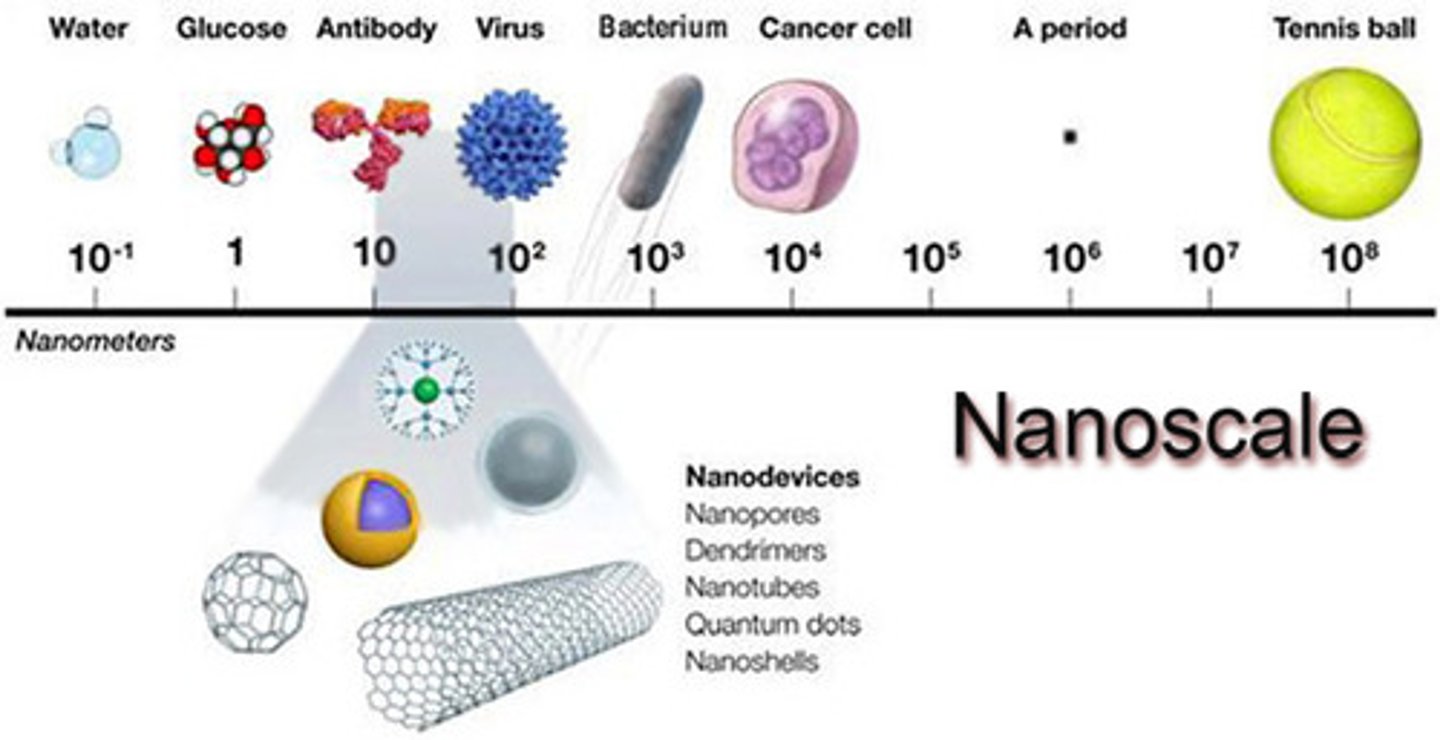
nanoscale
the scale of things from 1-100 nanometers
nanorobots
robots built to operate at the nanoscale, currently in the conceptual state but may be a reality in the coming decades
nanoparticles
particles that are between 1-100 nanometers
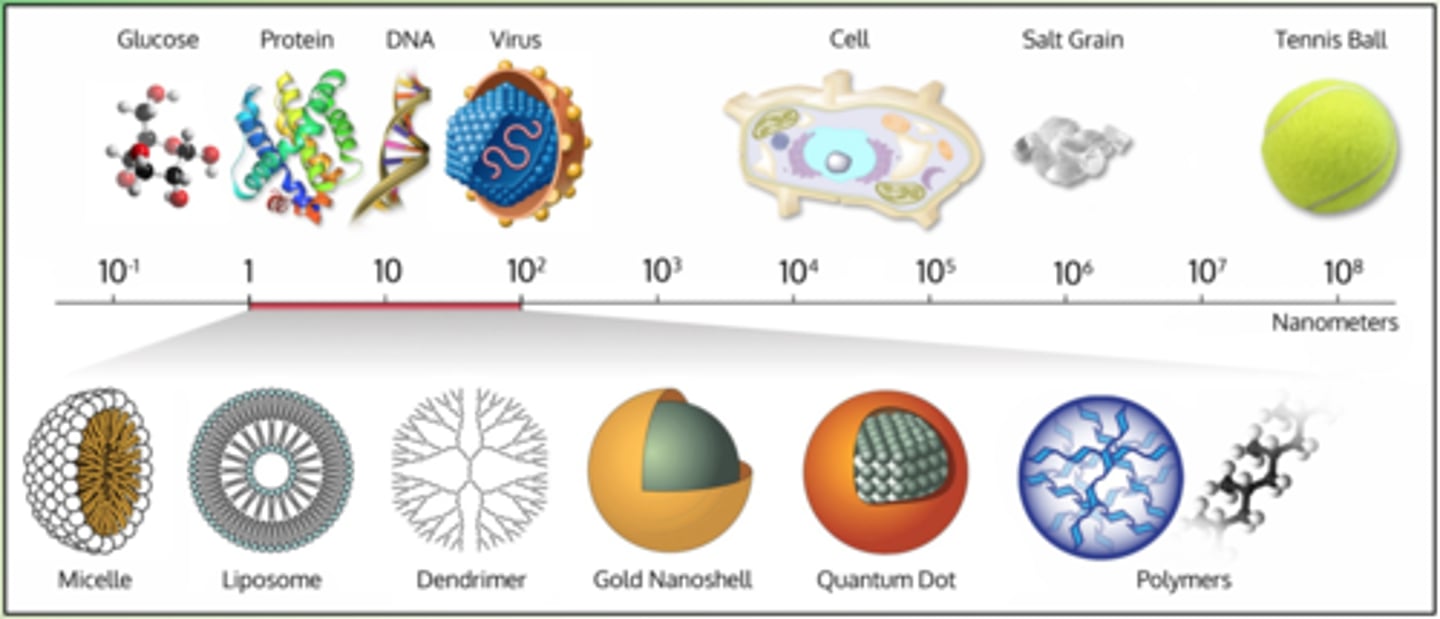
nanometer
one one billionth of a meter

nanomaterial
a material that has nanoparticles, or has been made using nanotechnology
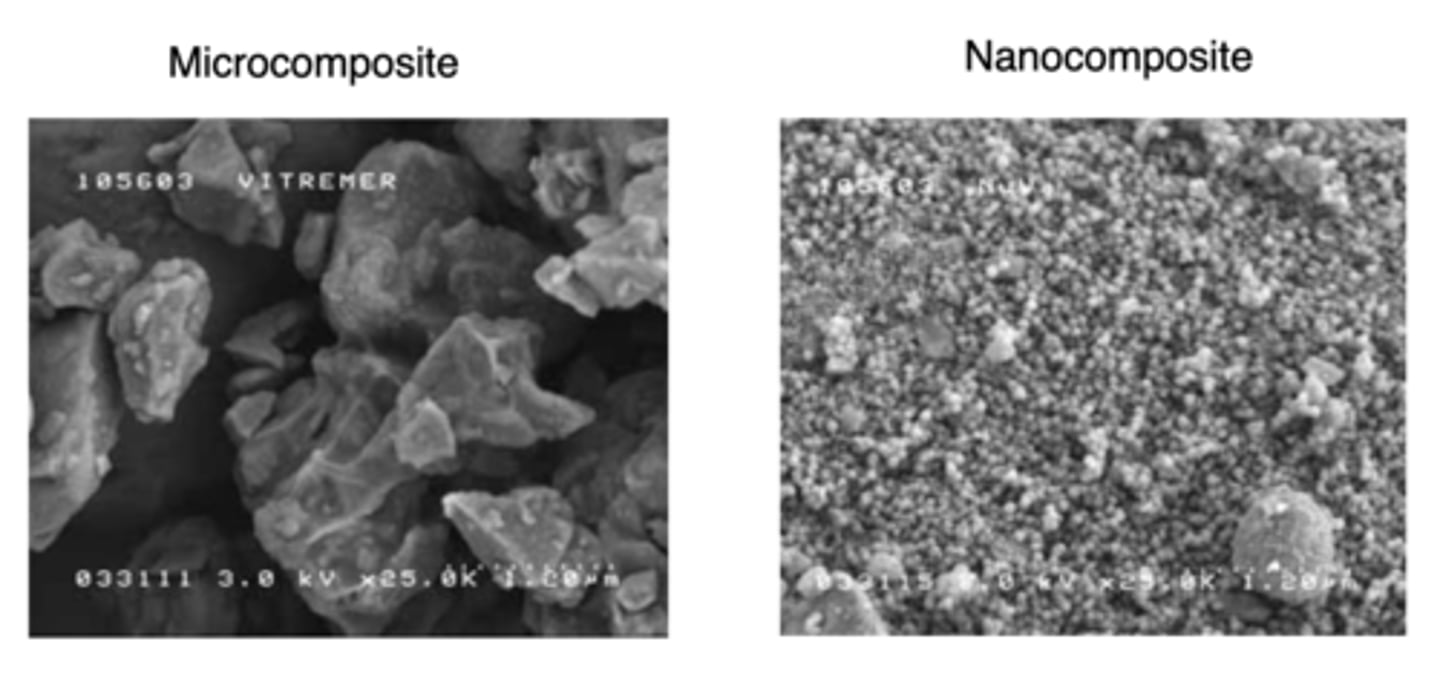
nanocomposite
a material that is made from two or more types of particle, at least one of which, is a nanoparticle
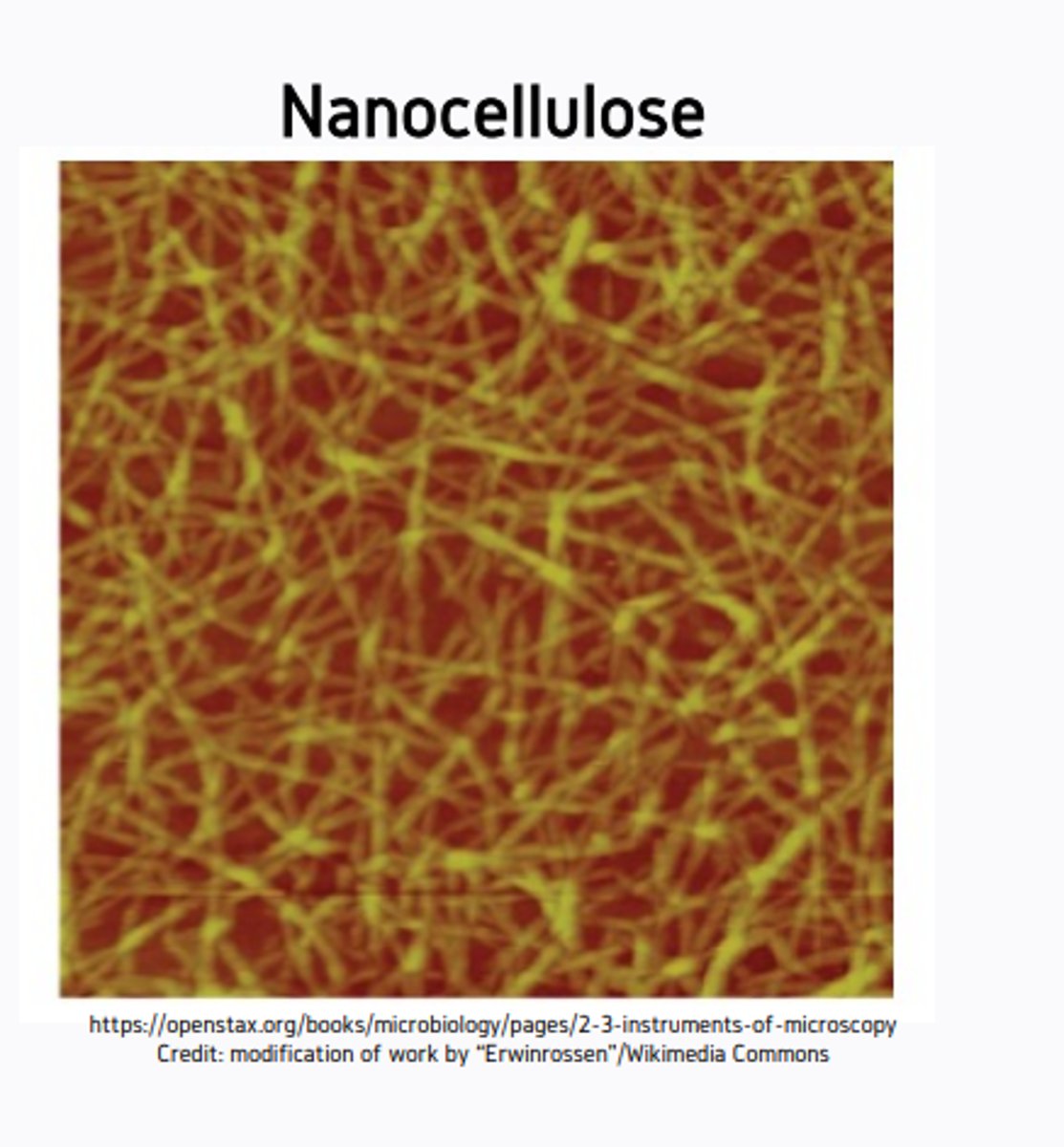
nanocellulose
a lightweight, strong, renewable material obtained from plant matter
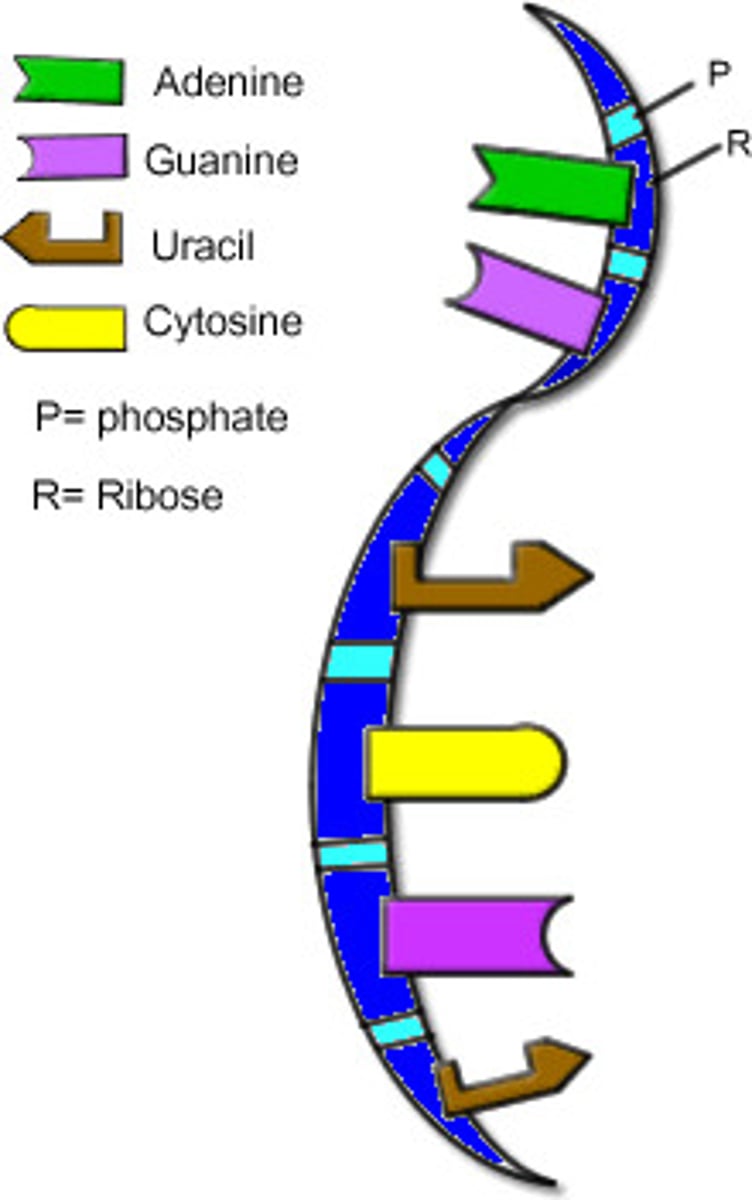
mRNA
messenger RNA; type of RNA that carries instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome to create specific proteins
mote
a small particle or a tiny piece of a substance
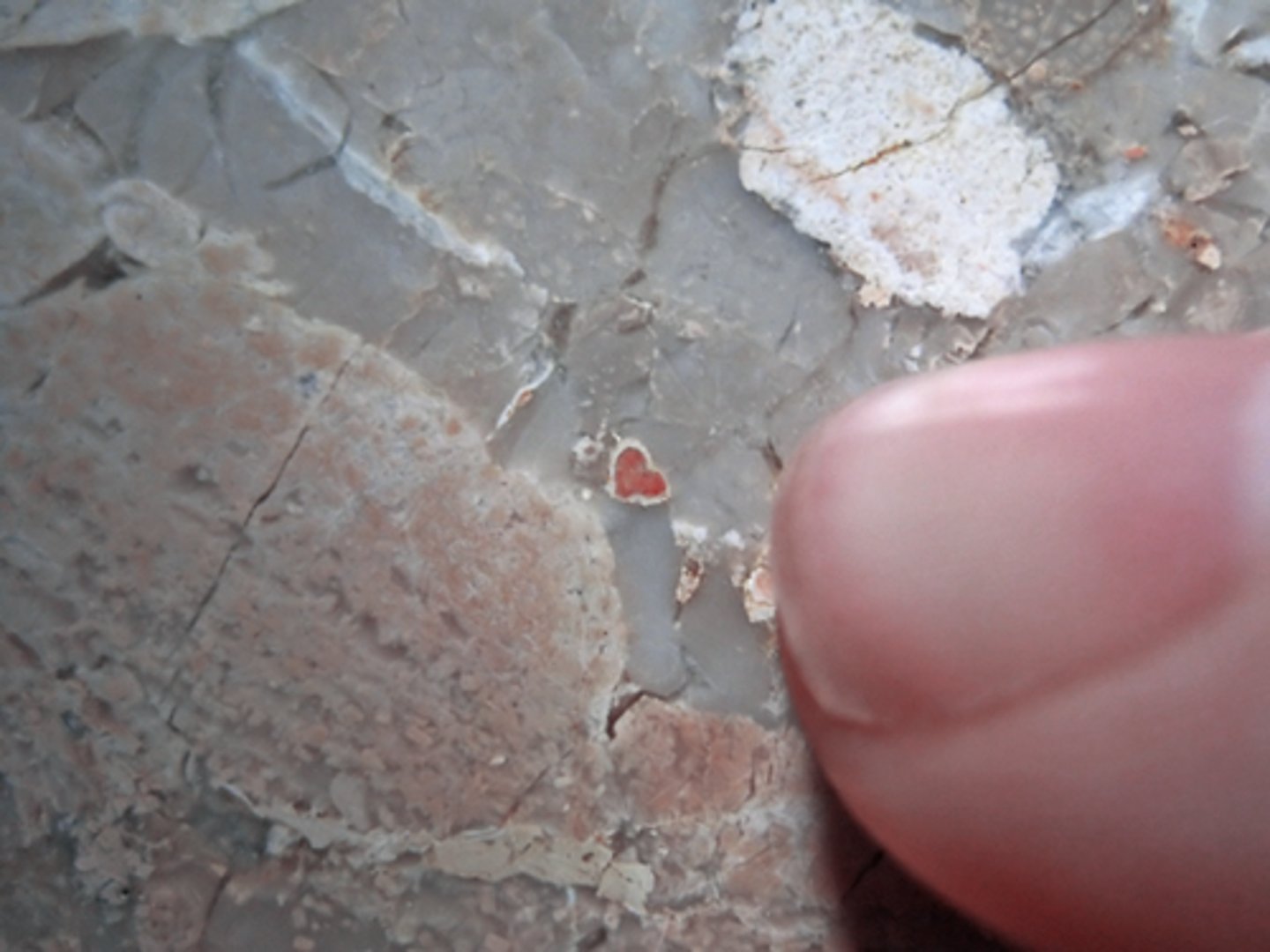

molecule
a group of atoms bonded together, representing the smallest fundamental unit of a chemical compound that can take part in a chemical reaction.
microplastics
extremely small pieces of plastic debris in the environment resulting from the disposal and breakdown of consumer products and industrial waste.

liposome
a tiny sphere of liquid that can carry liquids through the body
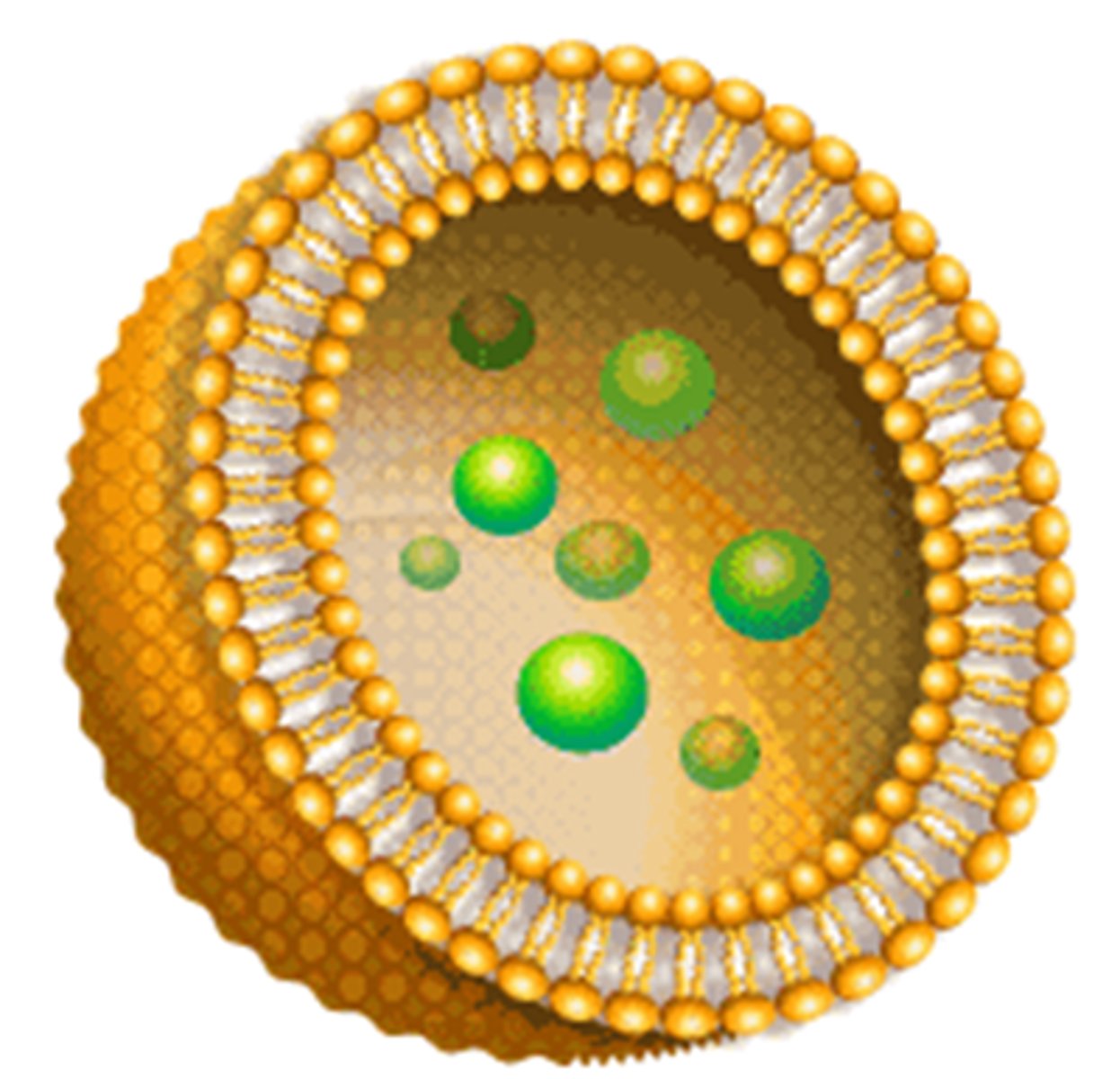
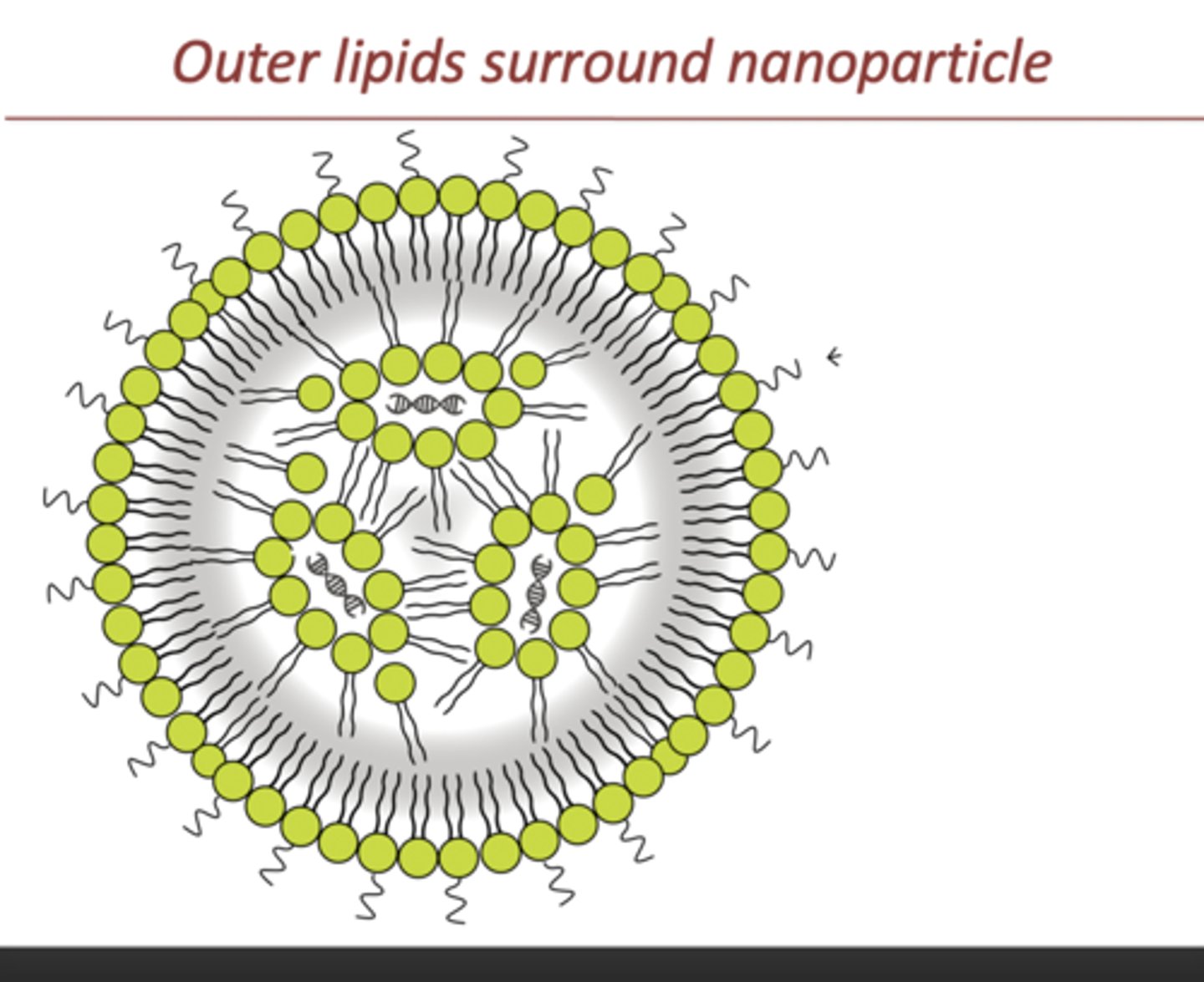
lipid nanoparticle (LNP)
spherical particles made of lipids (fatty molecules) that are used to deliver drugs by encapsulating them and other therapeutic agents to cells
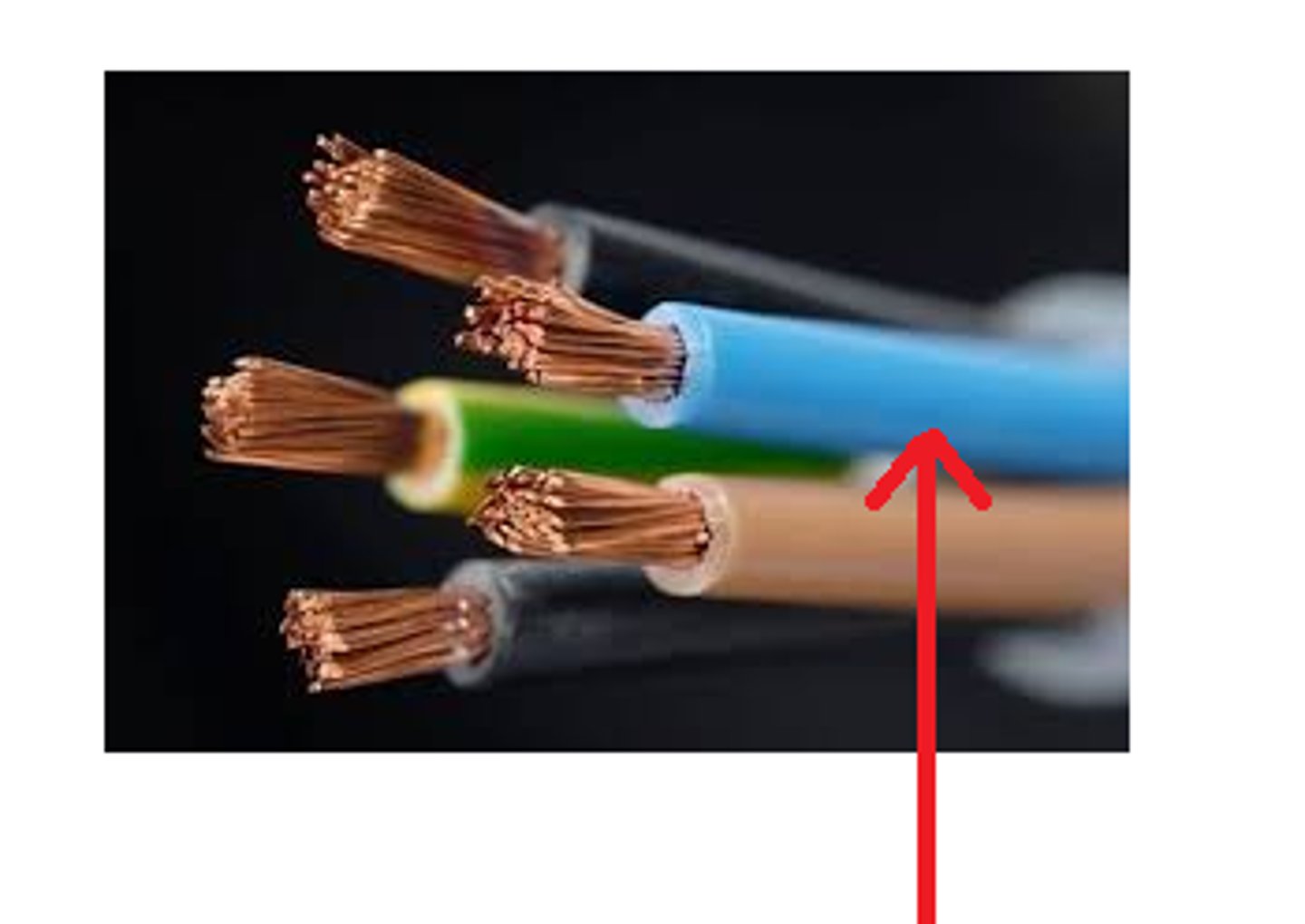
insulator
a substance that does not conduct heat or electricity, and prevents those things from passing through it
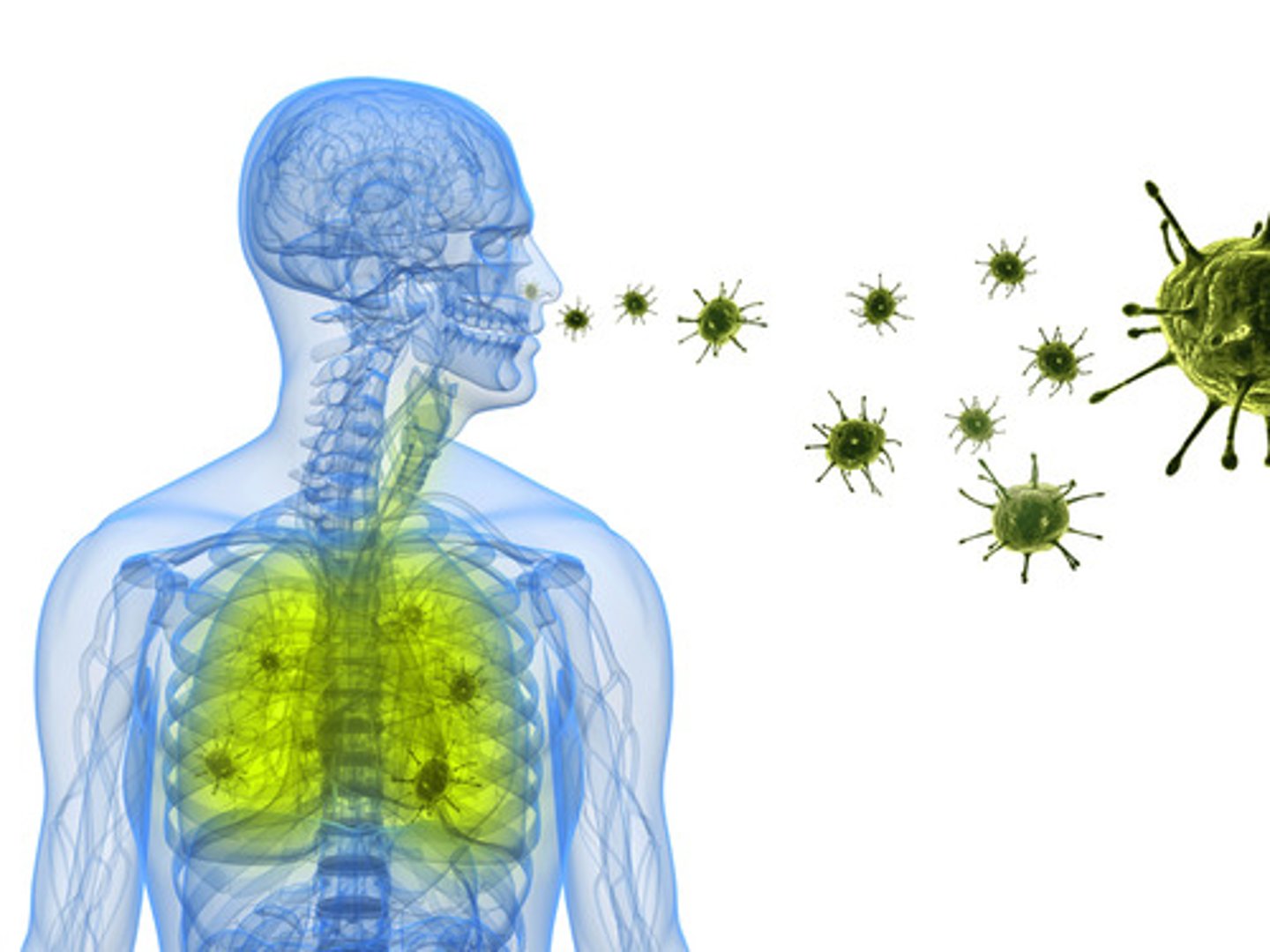
infection
illness caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi that enter the body and multiply
immune system
the network of cells and organs that defend the body against infection
greenhouse gas emissions
the release of harmful gases like Co2 in the atmosphere, also called carbon emissions

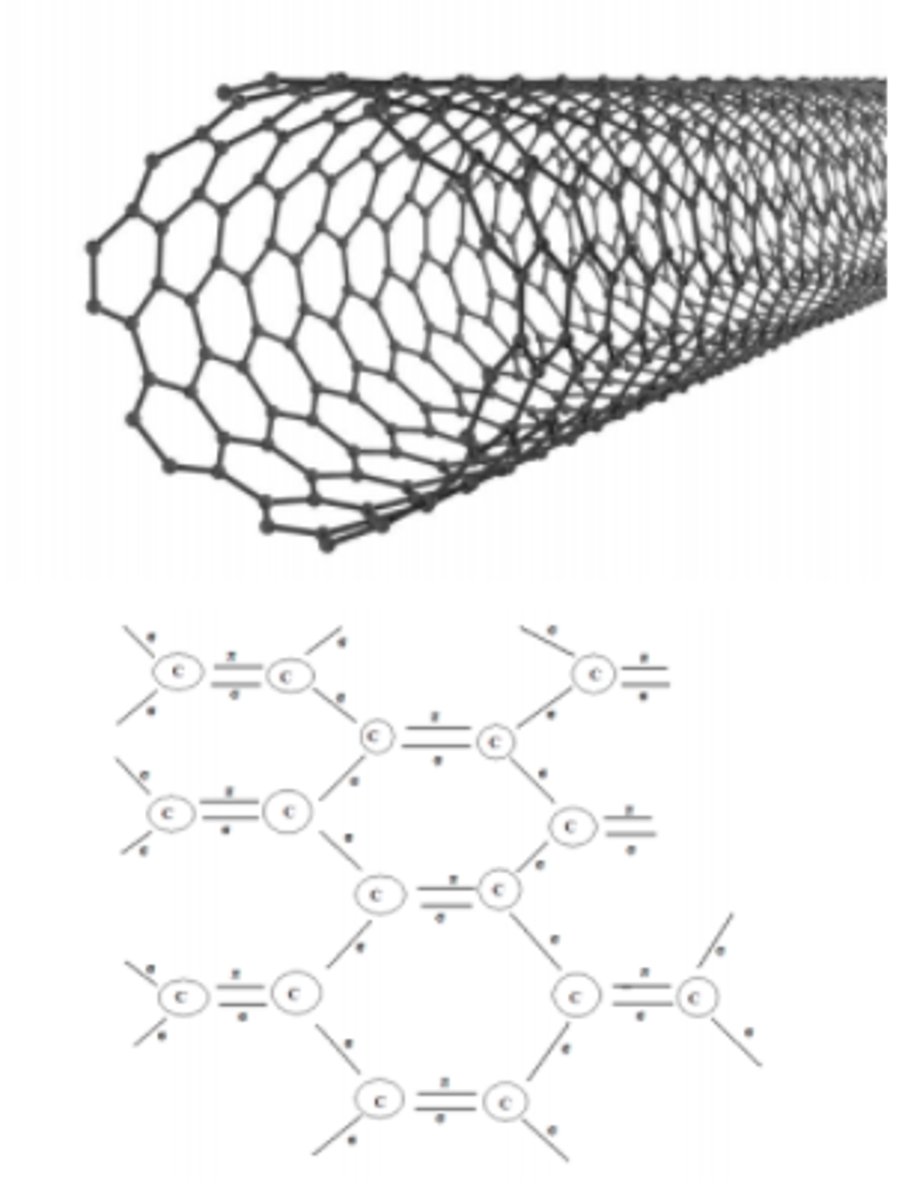
graphene
a net of carbon molecules one atom thick that can be formed into a lattice nanostructure
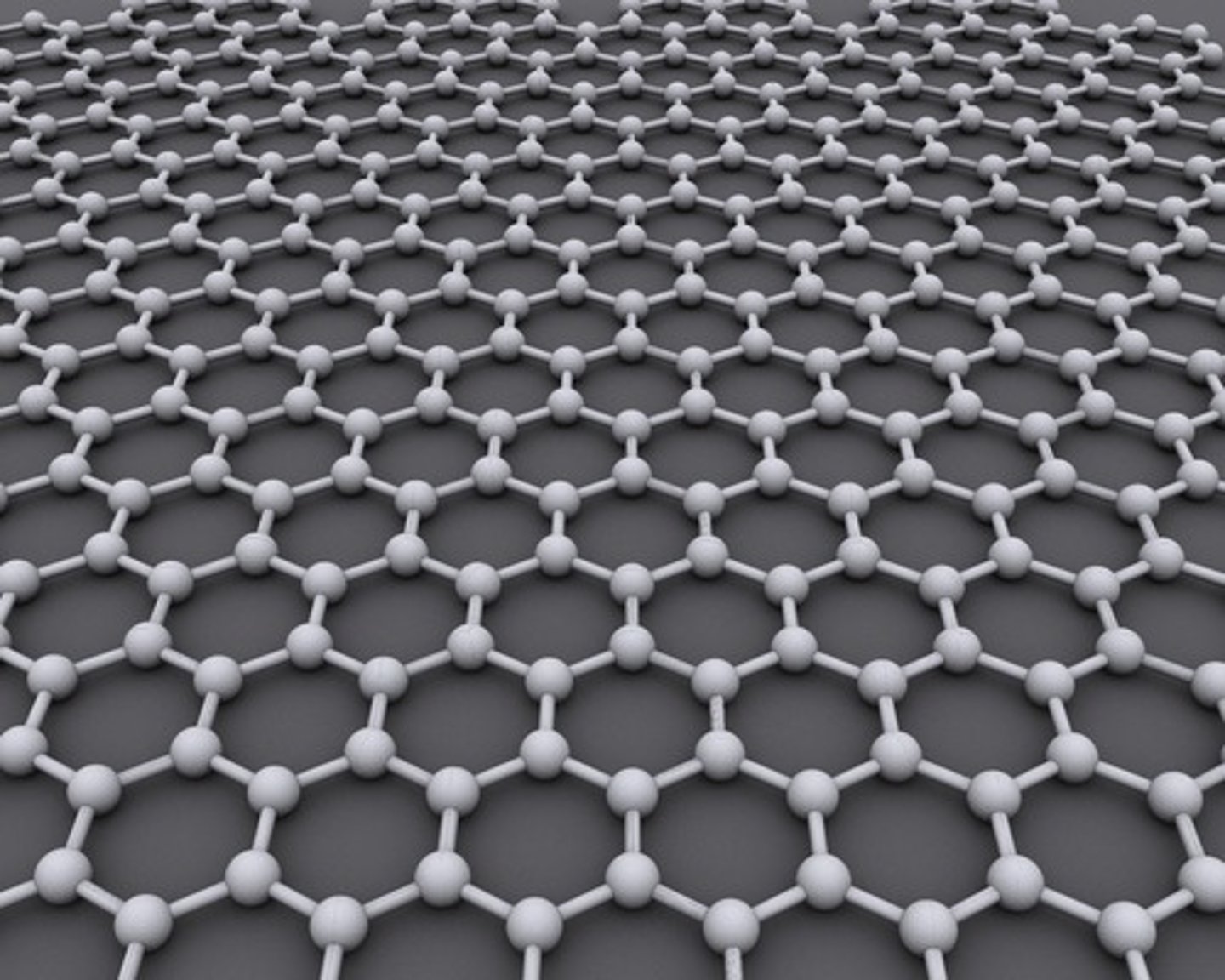
fullerene
a graphene sheet rolled into a tube or sphere; types of this are buckyballs and carbon molecules
encapsulate
to contain one substance into another

ductility
of metal, the property of being able to be drawn out into a wire

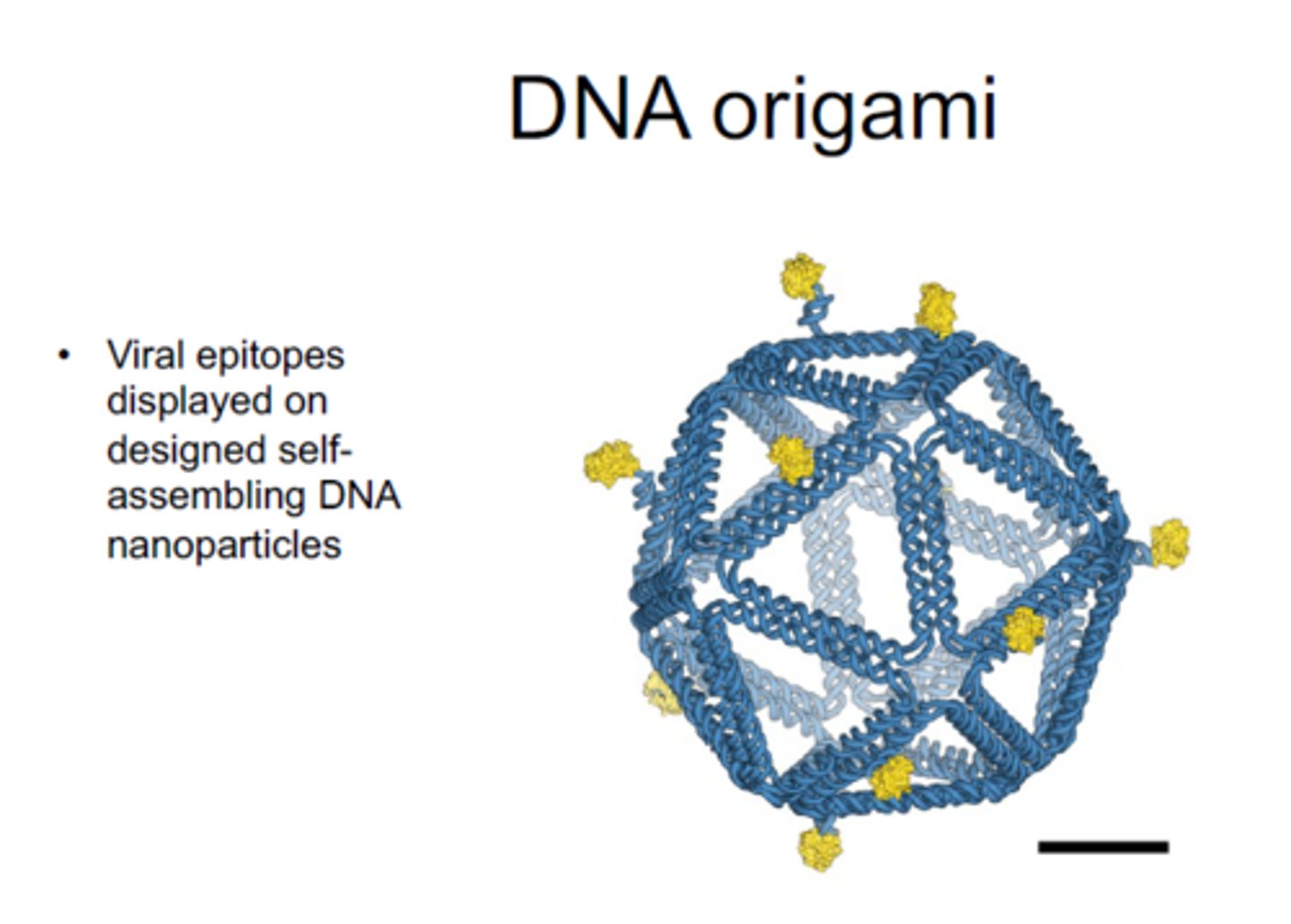
DNA origami
folding of DNA at the nanoscale level to create complex structures
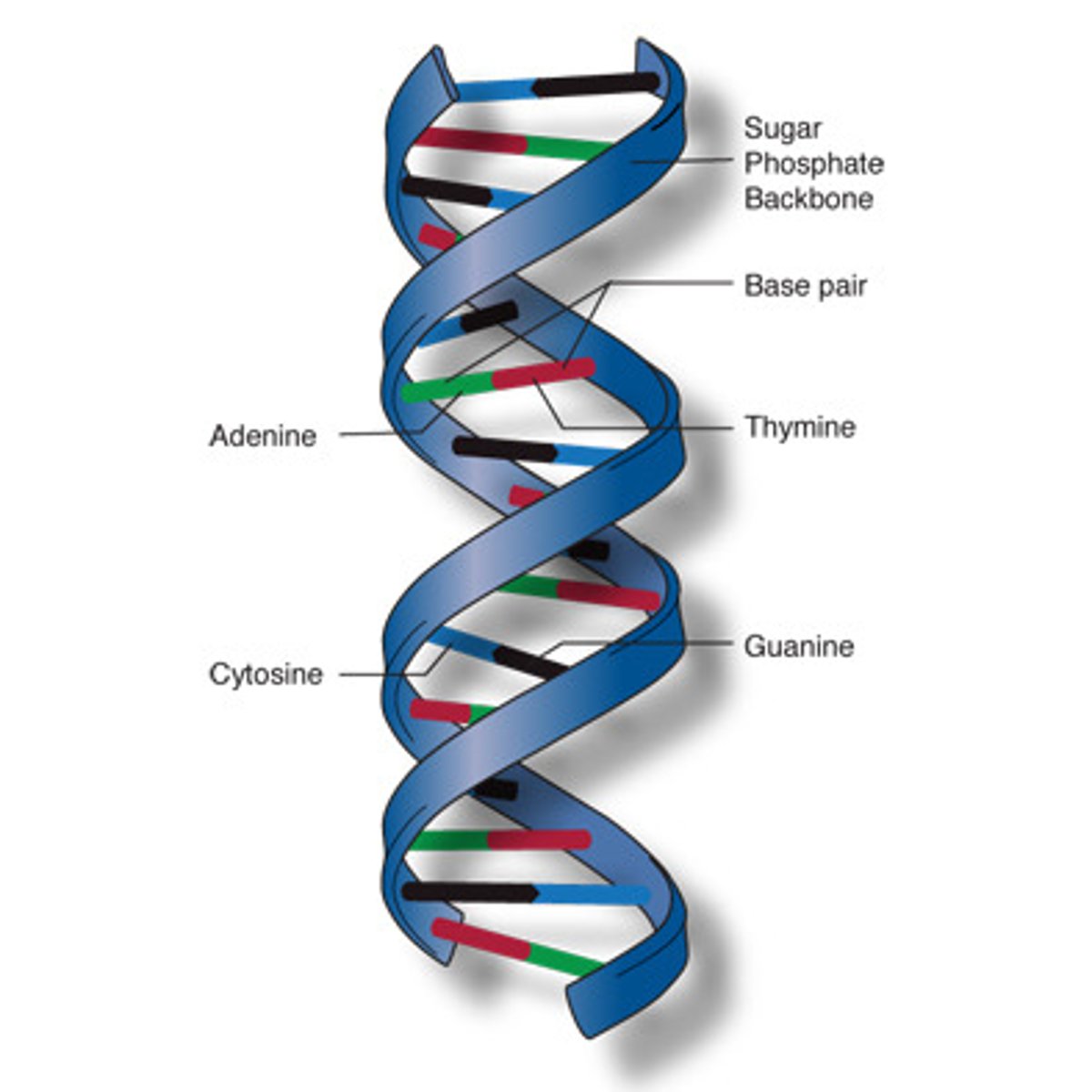
DNA
molecule that carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth
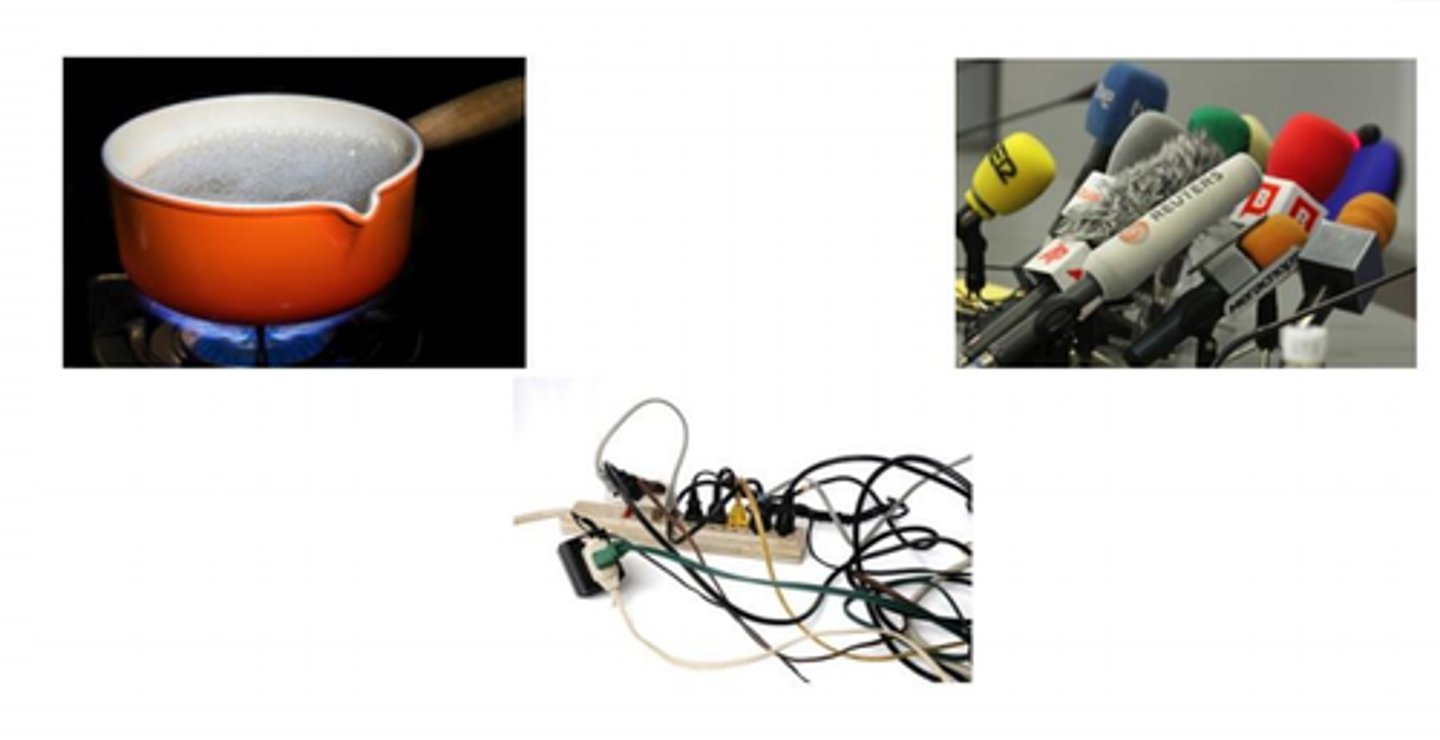
conductivity
the property of allowing heat or electricity to travel through a substance
composite
a substance made of more than one element
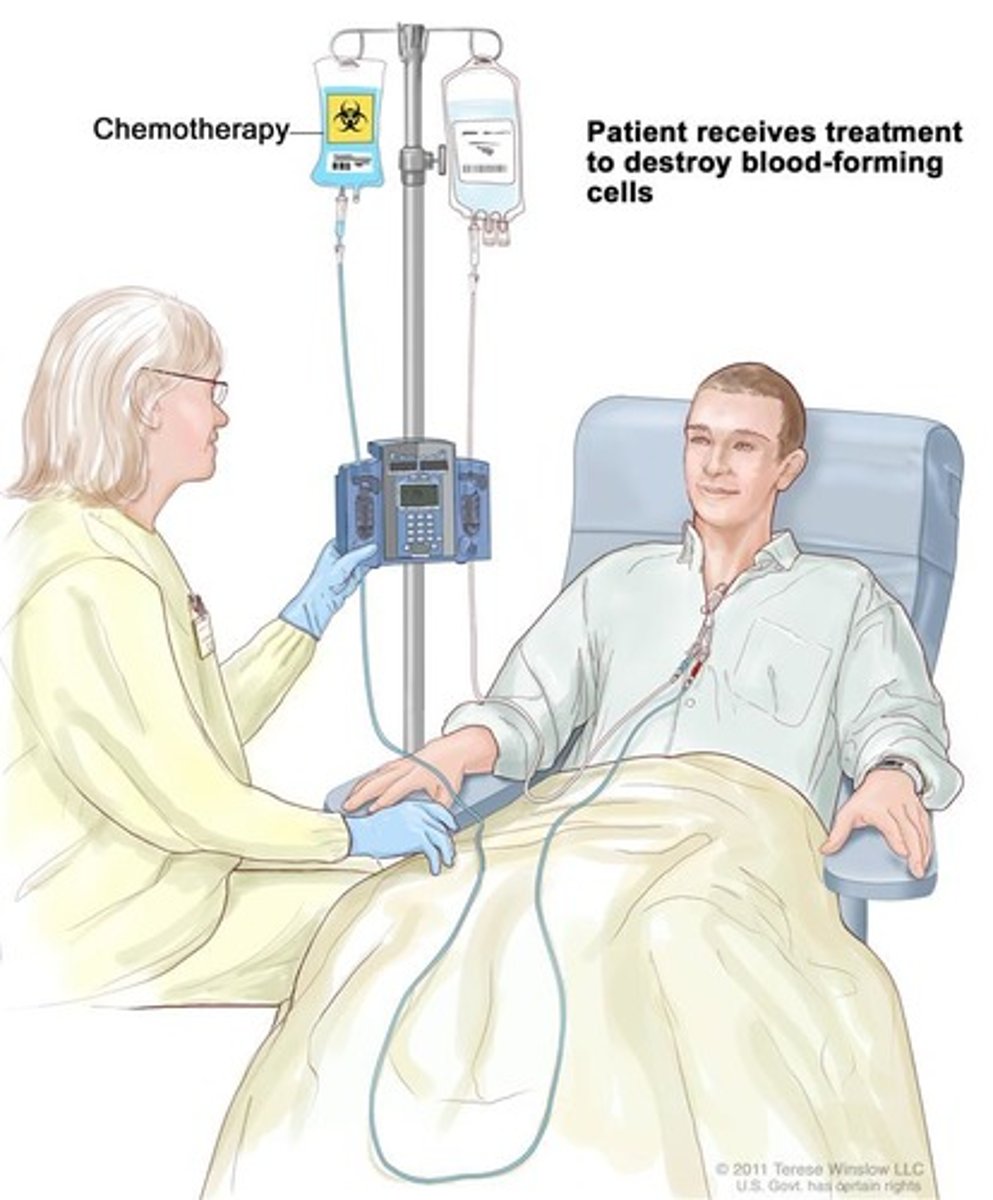
chemotherapy
the treatment of a disease, often cancer, using chemical substances
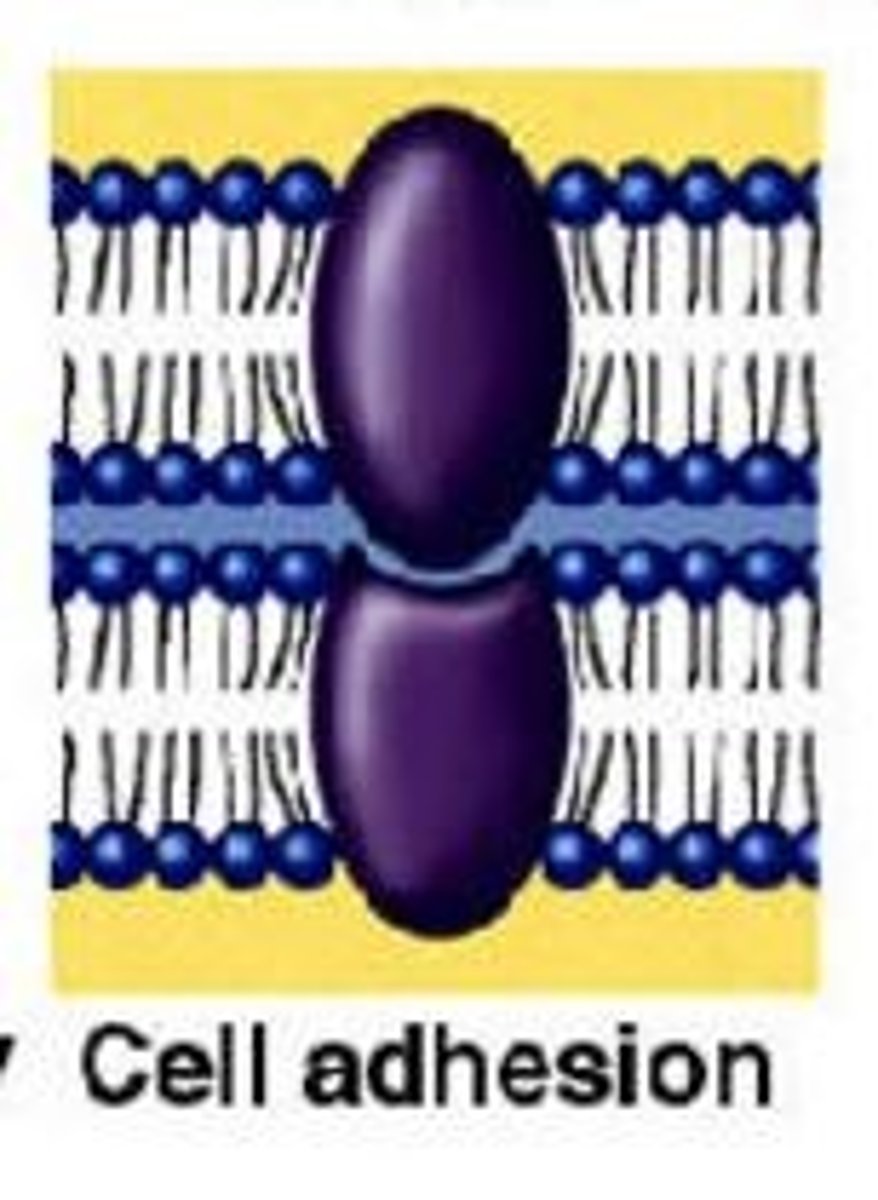
cell adhesion
the bonding of cells to surfaces or to other cells
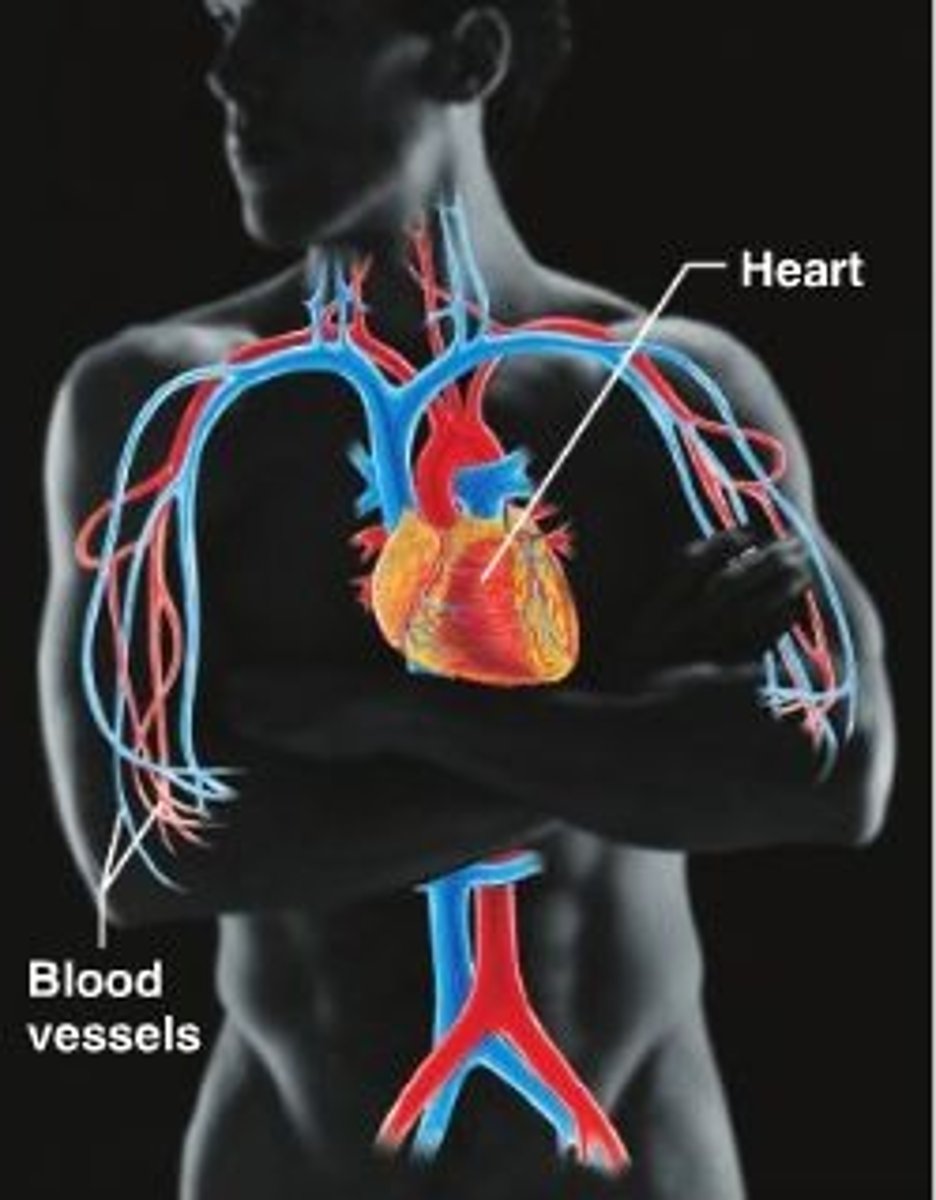
cardiovascular disease
a disease affecting the heart and/or blood vessels
carbon nanotube
a sheet of graphene rolled into a tube
carbon
a nonmetallic element found in all living things
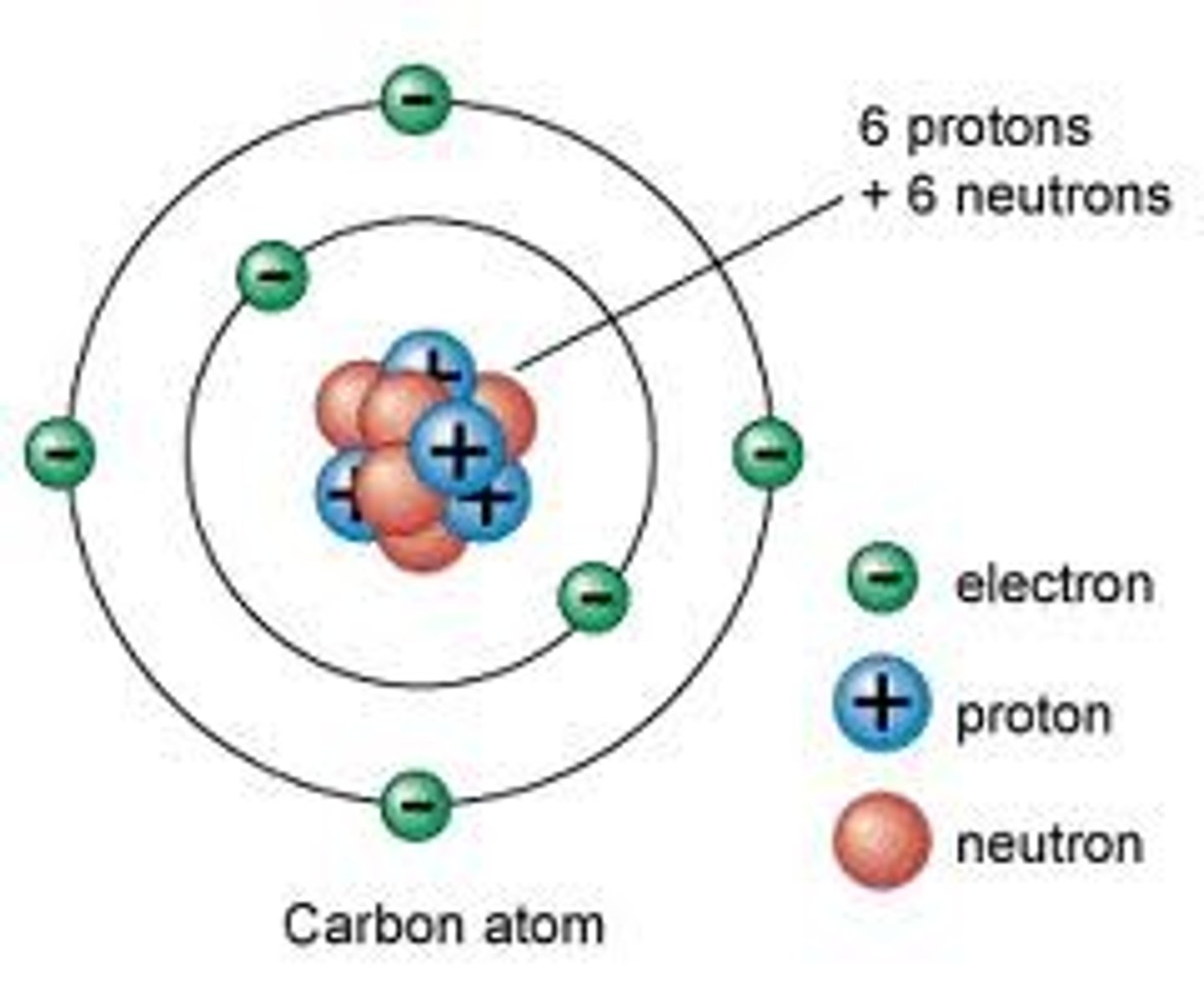
bulk materials
particles that are larger than 100 nanometers in all dimensions
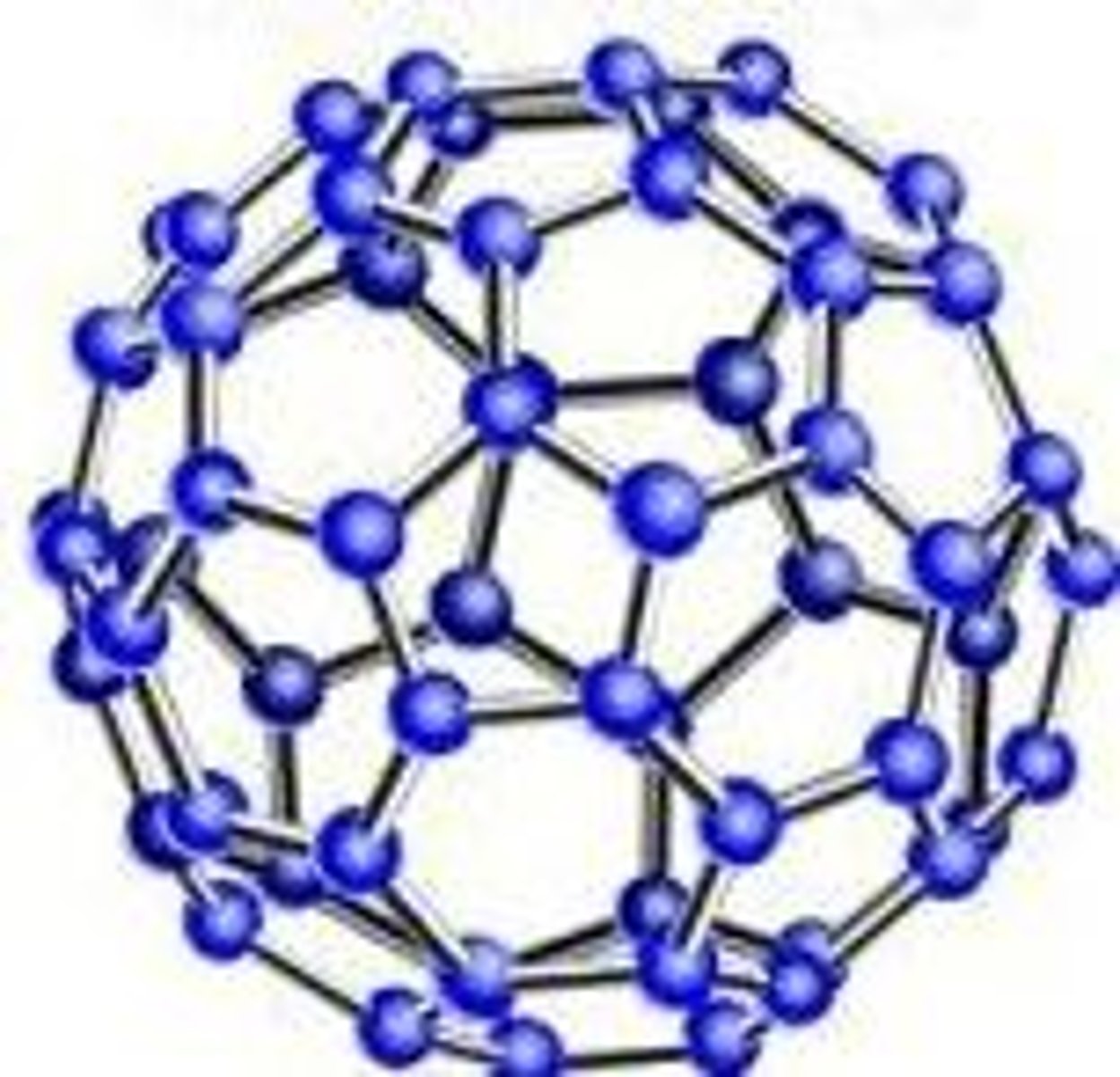
buckyball
graphene that is shaped into a sphere; extremely stable and can maintain their shape under extreme pressure and in outer space
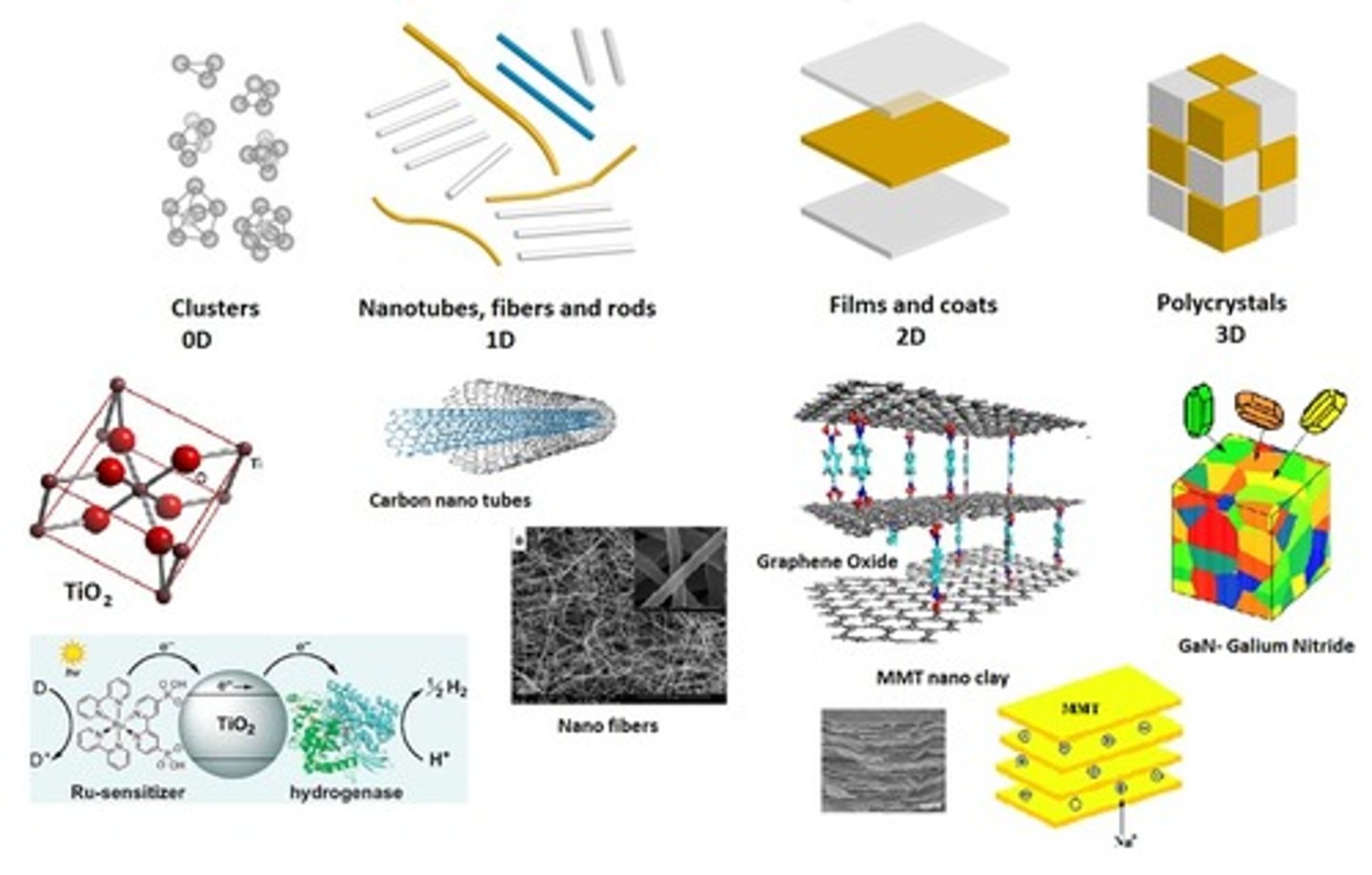
bottom-up assembly
building products assembling single atoms and molecules into larger nanostructures
biodegradable
a substance that can be decomposed by bacteria or other living organisms, and therefore does not cause pollution

biorisk
the risk associated with biological materials

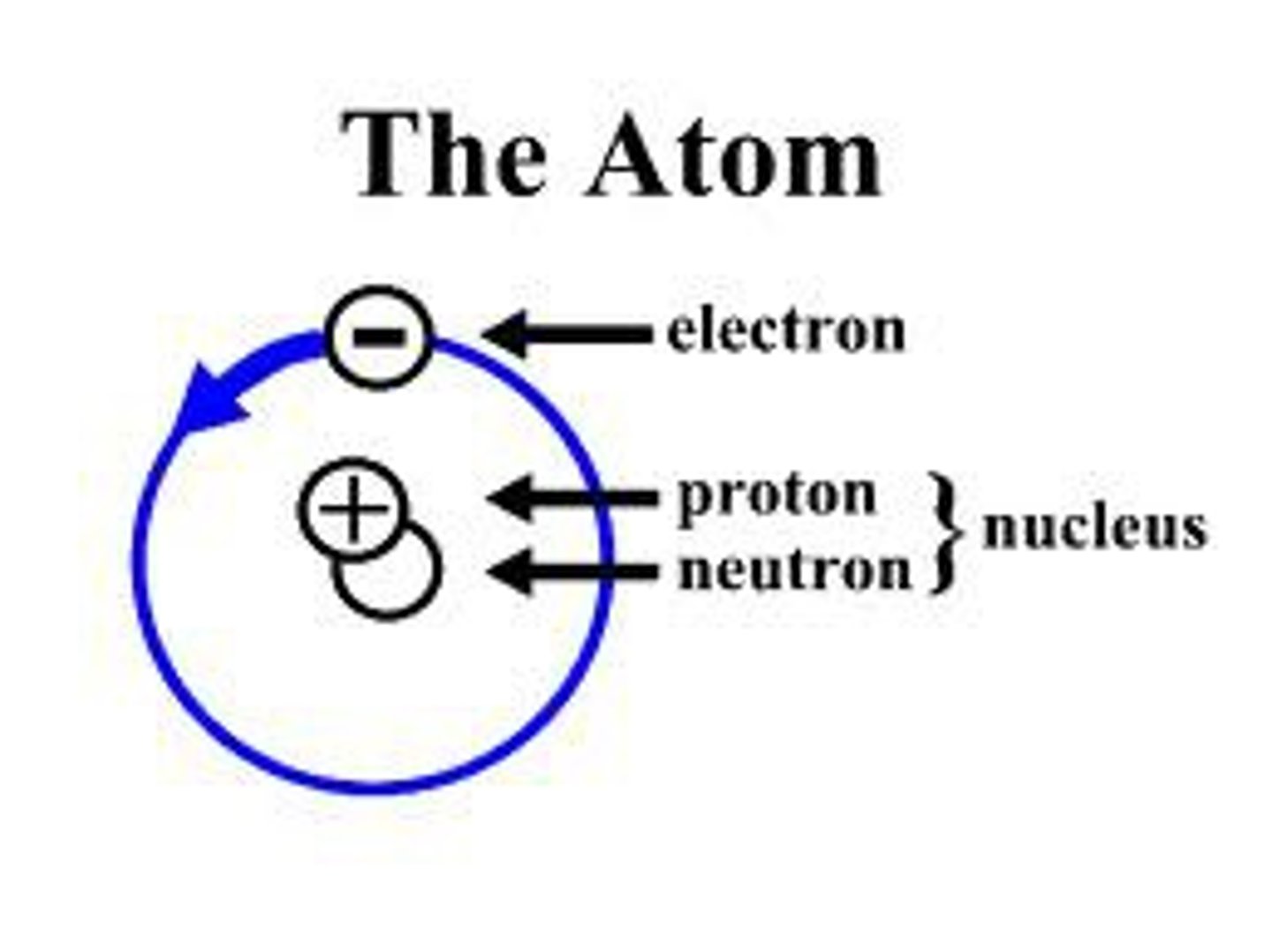
atom
basic unit of a chemical element
artificial
man-made, not found in nature

antibacterial
preventing bacteria from growing or spreading

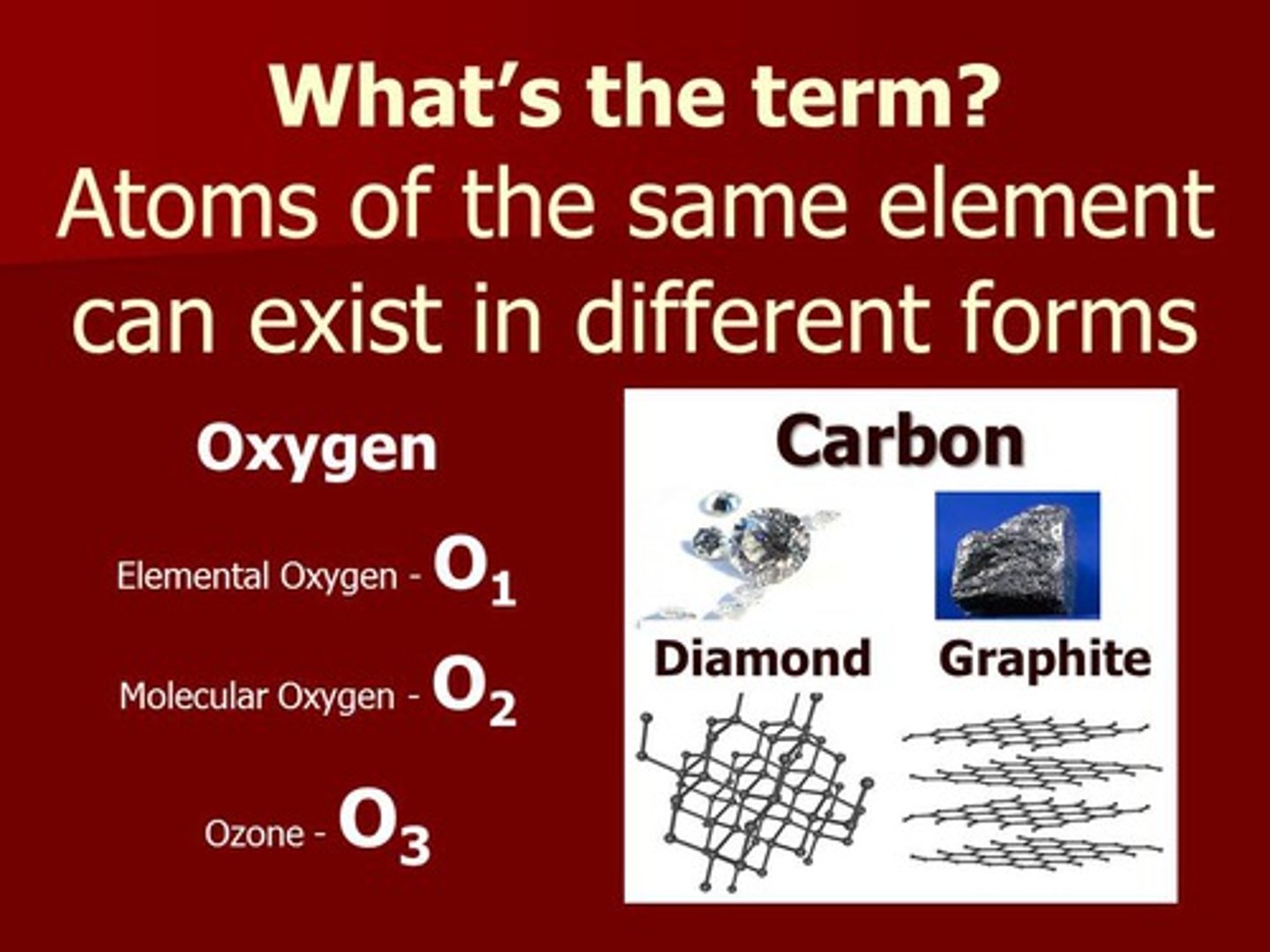
allotrope
different forms of the same element, e.g., carbon in the forms of diamond and graphite