Neuro Lecture 10: Reticular Formation
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Where is the reticular formation located?
- Brainstem tegmentum
- Ventral to cerebral aqueduct
What is the reticular formation?
A complex network of specific nuclei and neurons
Does the reticular formation have distinct boundaries?
No
What is the function of the neurons and nuclei of the reticular formation?
- Multimodal
- Act as relay/integration centers to important brain centers
- Coordinates consciousness, attention, and arousal for survival
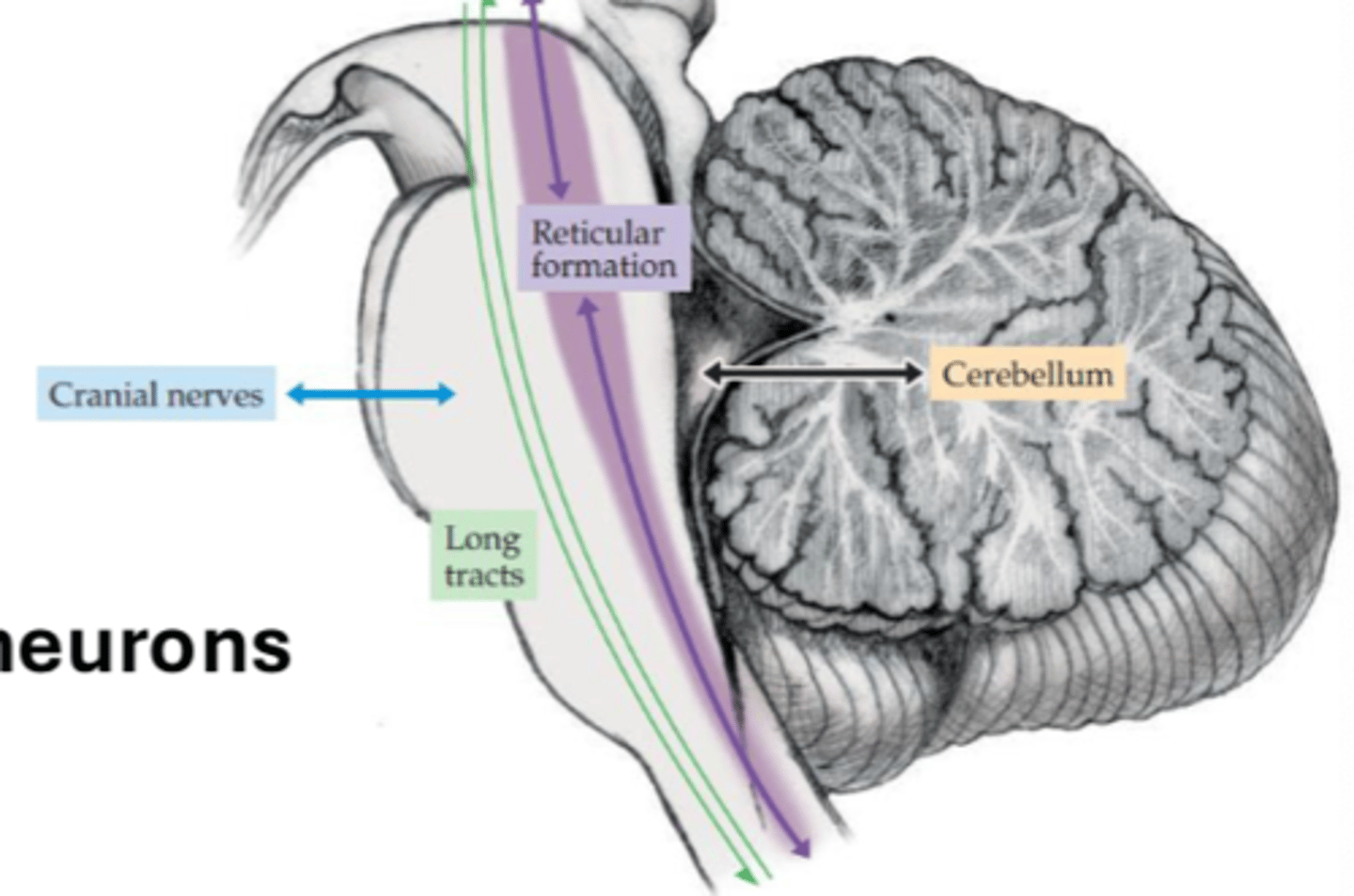
What are the major functions of the reticular formation? (7)
- Arousal
- Consciousness
- Circadian rhythm
- Coordination of motor movements
- Cardiovascular/respiratory control
- Pain modulation
- Habituation
What is the reticular formation rostrally connected to?
- Diencephalic nuclei (thalamus)
- Projections to cortical/subcortical structures
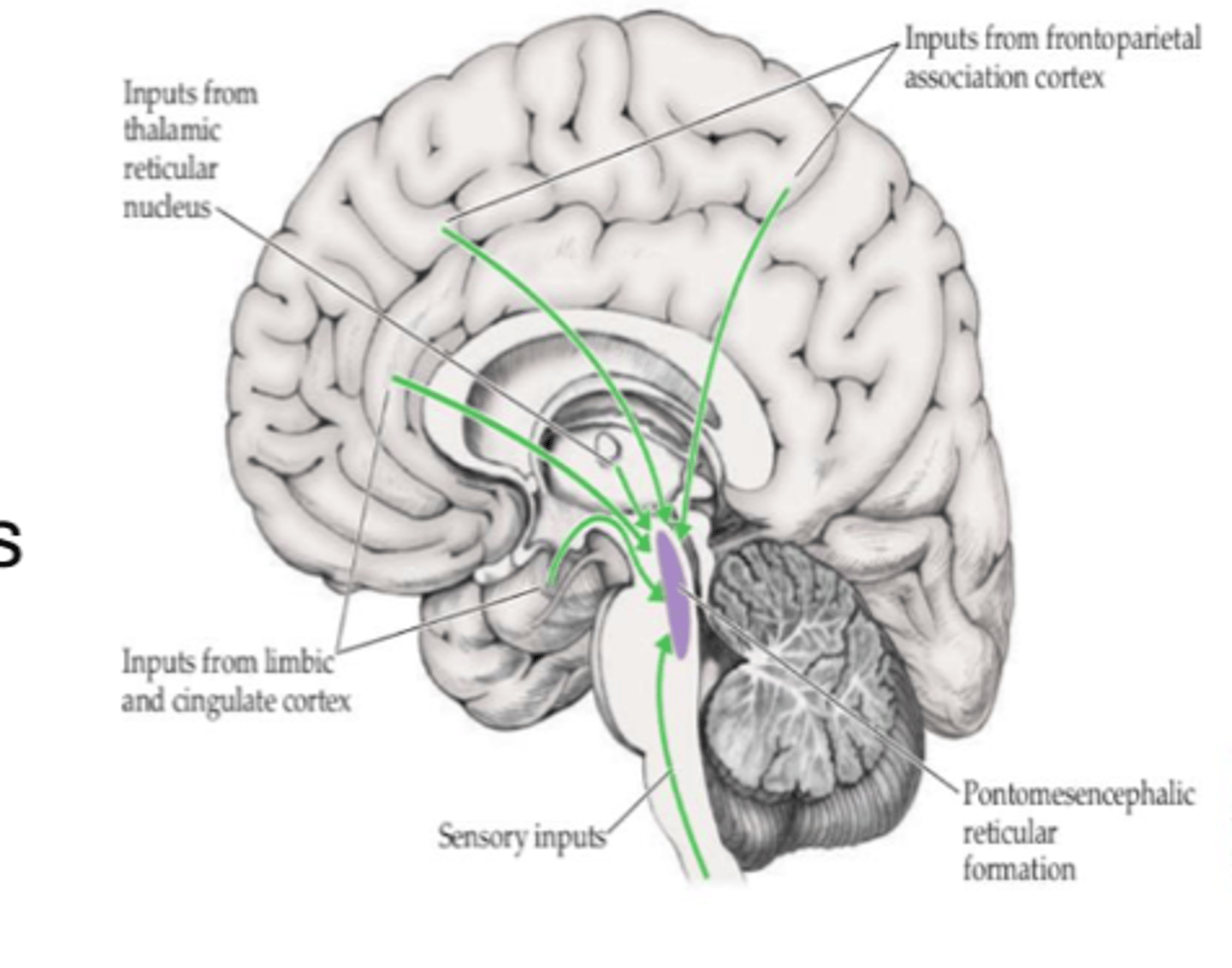
What is the rostral portion responsible for?
- Consciousness, attention, and arousal
- Sleep-wake cycle
What is the reticular formation caudally connected to?
- Intermediate zone of spinal cord (cervical)
What is the caudal portion responsible for?
- Regulates motor function
- Protective reflexes
- Autonomic functions of visceral organs (circulatory/respiratory)
- Muscle tone, posture, coordination
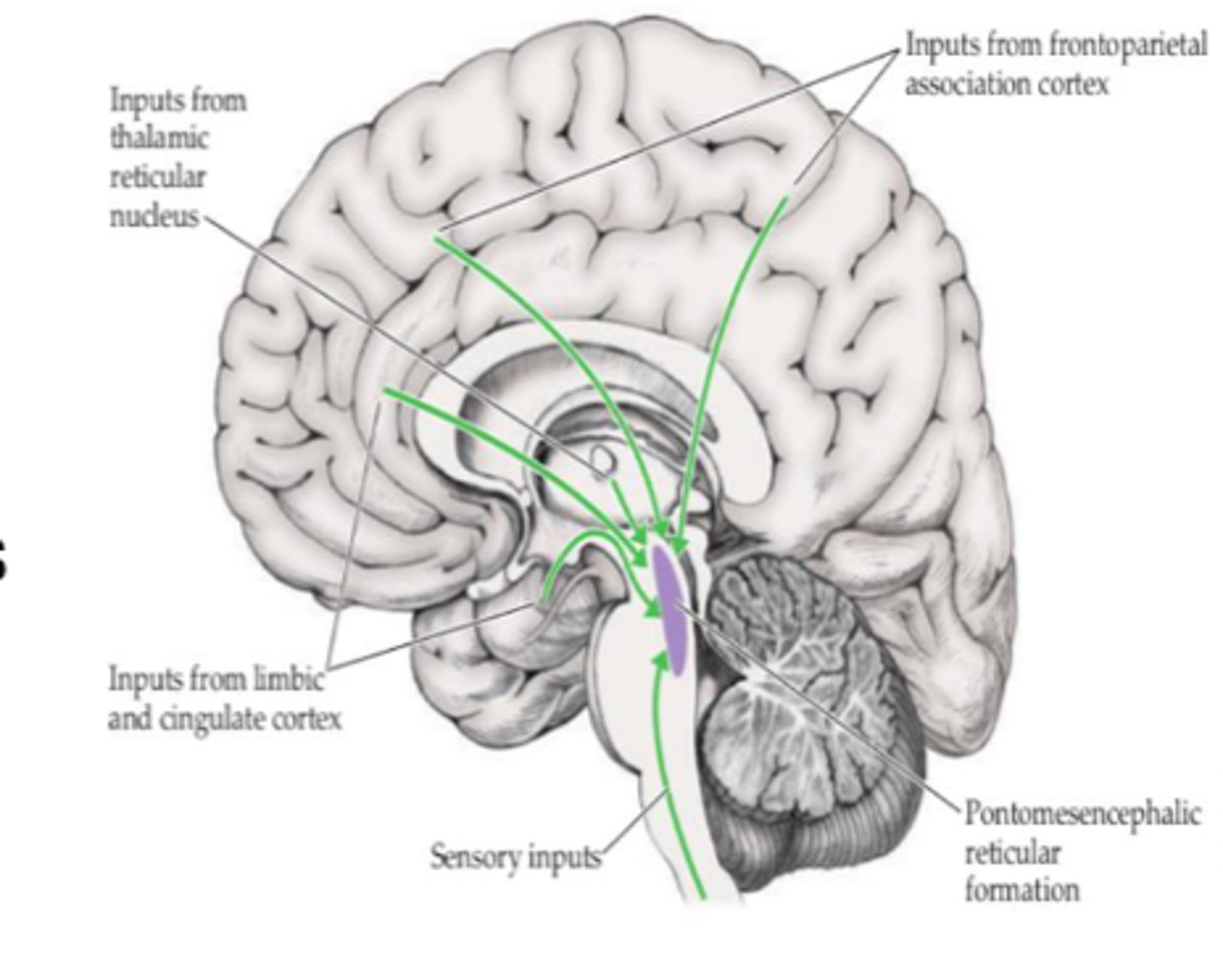
What is the rostral reticular formation also known as?
Pontomesencephalic RF
What structures are involved in the rostral RF?
- RF of mesencephalon
- Upper pons
- Thalamus connected with cortical structures
- Forebrain connections
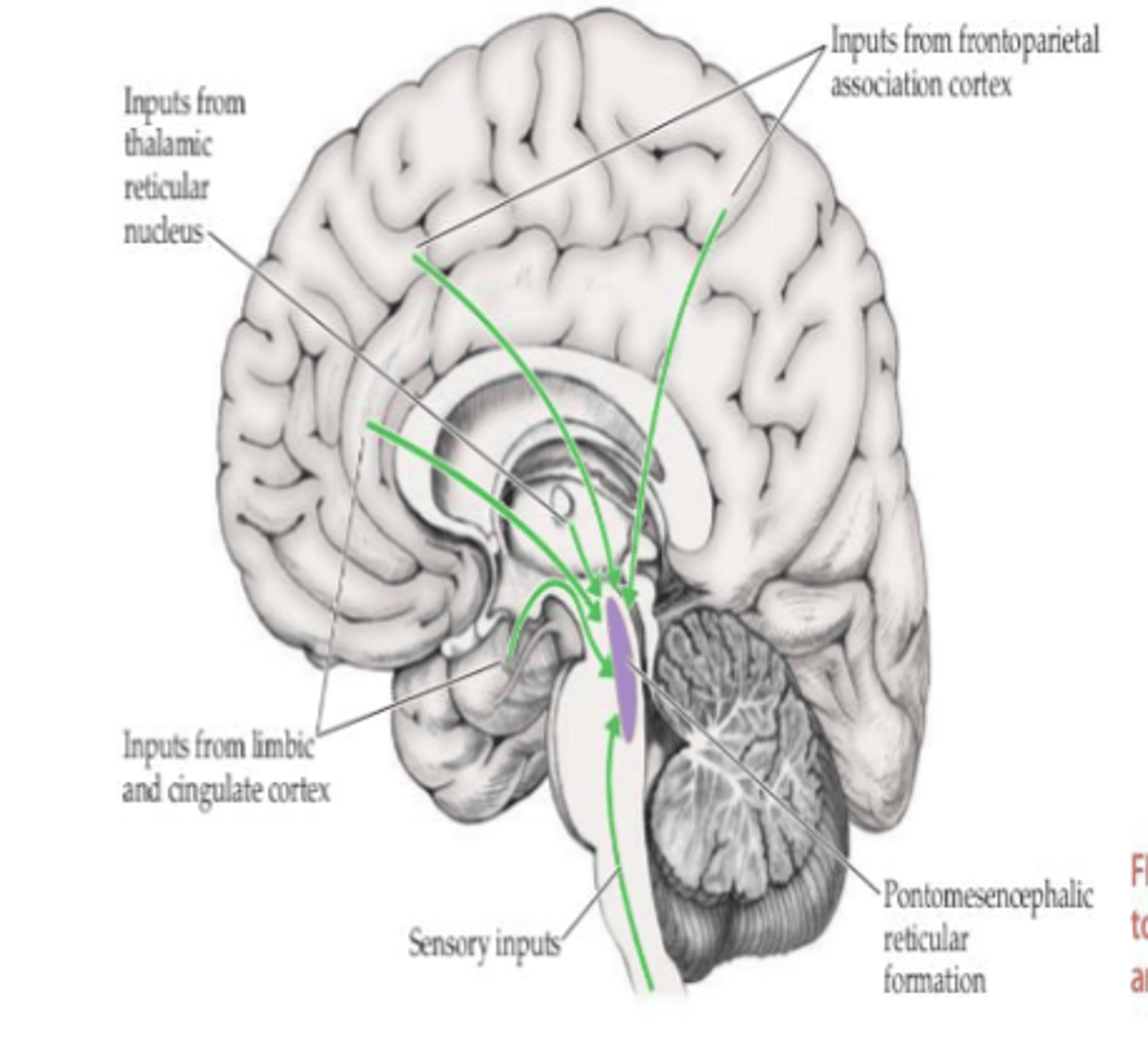
What structures are involved in the caudal RF?
- Lower pons
- Medulla
- CN nuclei and spinal cord
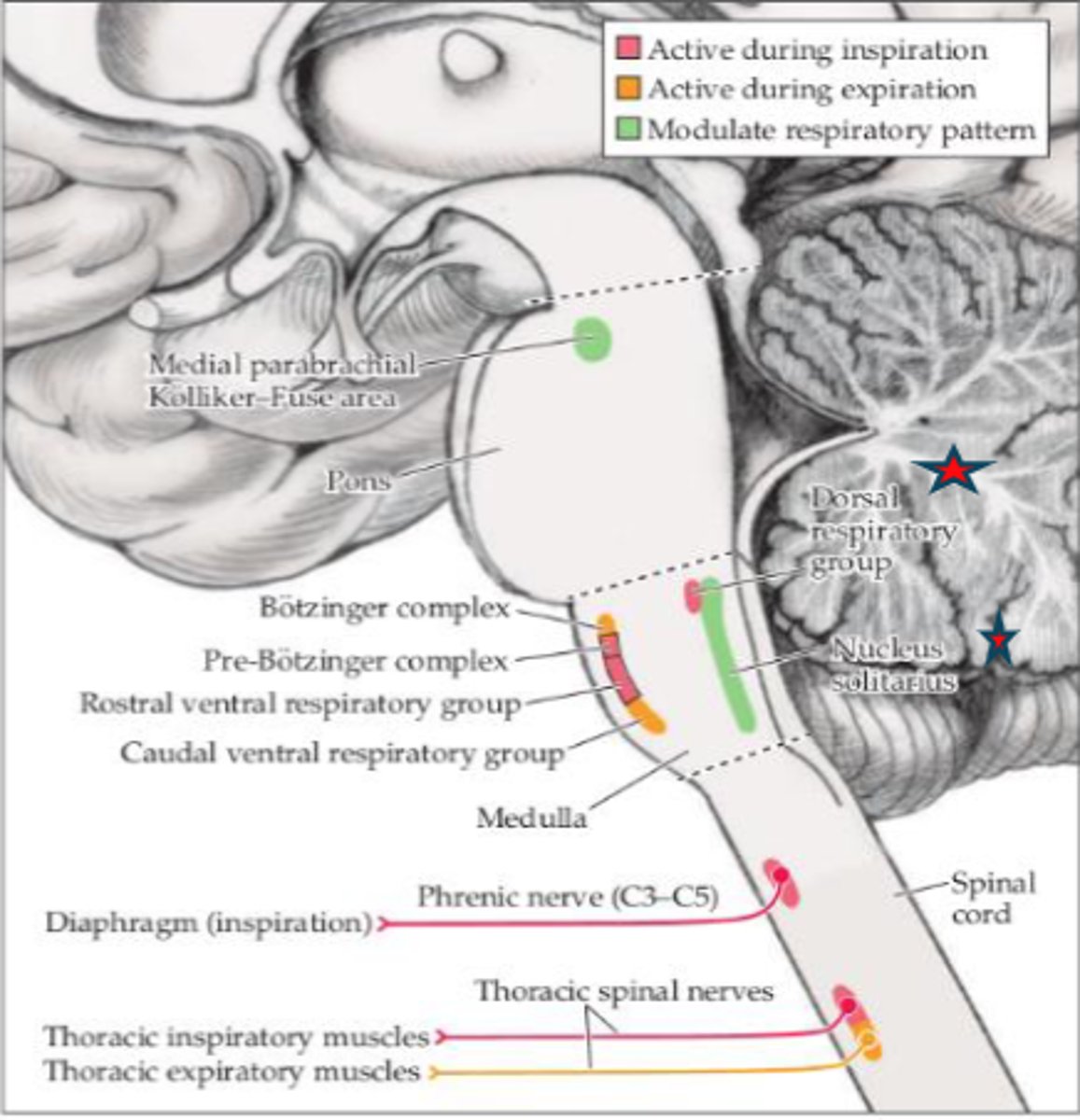
What is consciousness?
State of awareness of self and the embedded environment
What structures are involved in the consciousness system?
- Frontoparietal association cortex
- Arousal circuits in upper brainstem and diencephalon
What 2 components make up the consciousness system?
- Level of consciousness
- Content of consciousness
What is the level of consciousness component responsible for? (4)
- Arousal
- Alertness (arousal circuits and cortex)
- Attention (arousal circuits, cortex, frontoparietal)
- Awareness (subjective/personal)
What is the content of consciousness component responsible for?
- Sensory
- Motor
- Memory
- Emotional functions
How many stages occur in a sleep cycle?
4
What occurs in stages 1-3?
- Non-rapid eye movement (Non-REM)
- Physical restoration
What occurs in N1 of the sleep cycle?
Falling asleep
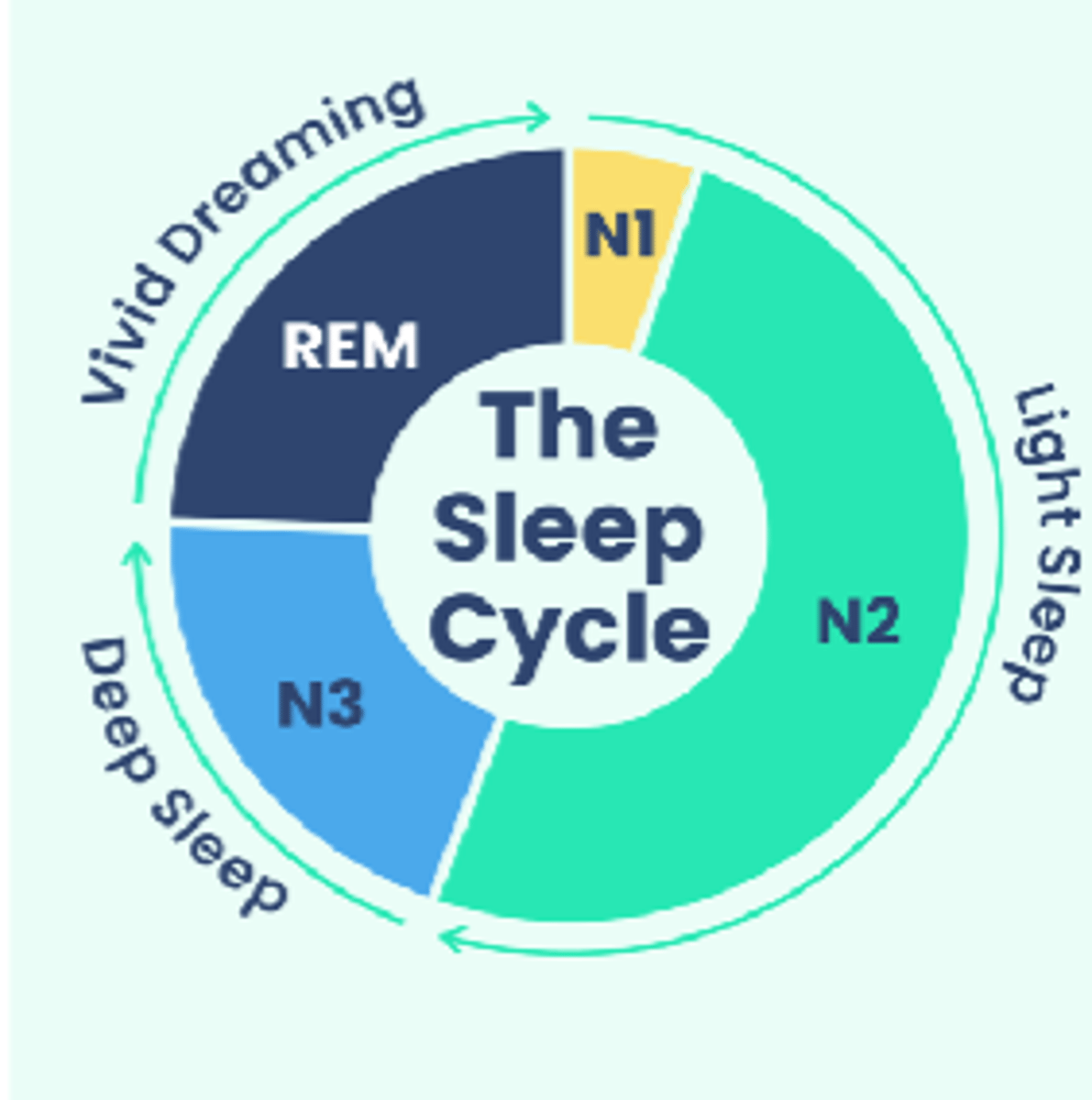
What occurs in N2 of the sleep cycle?
- HR and breathing slows
- Muscles relax
- Temperature drops
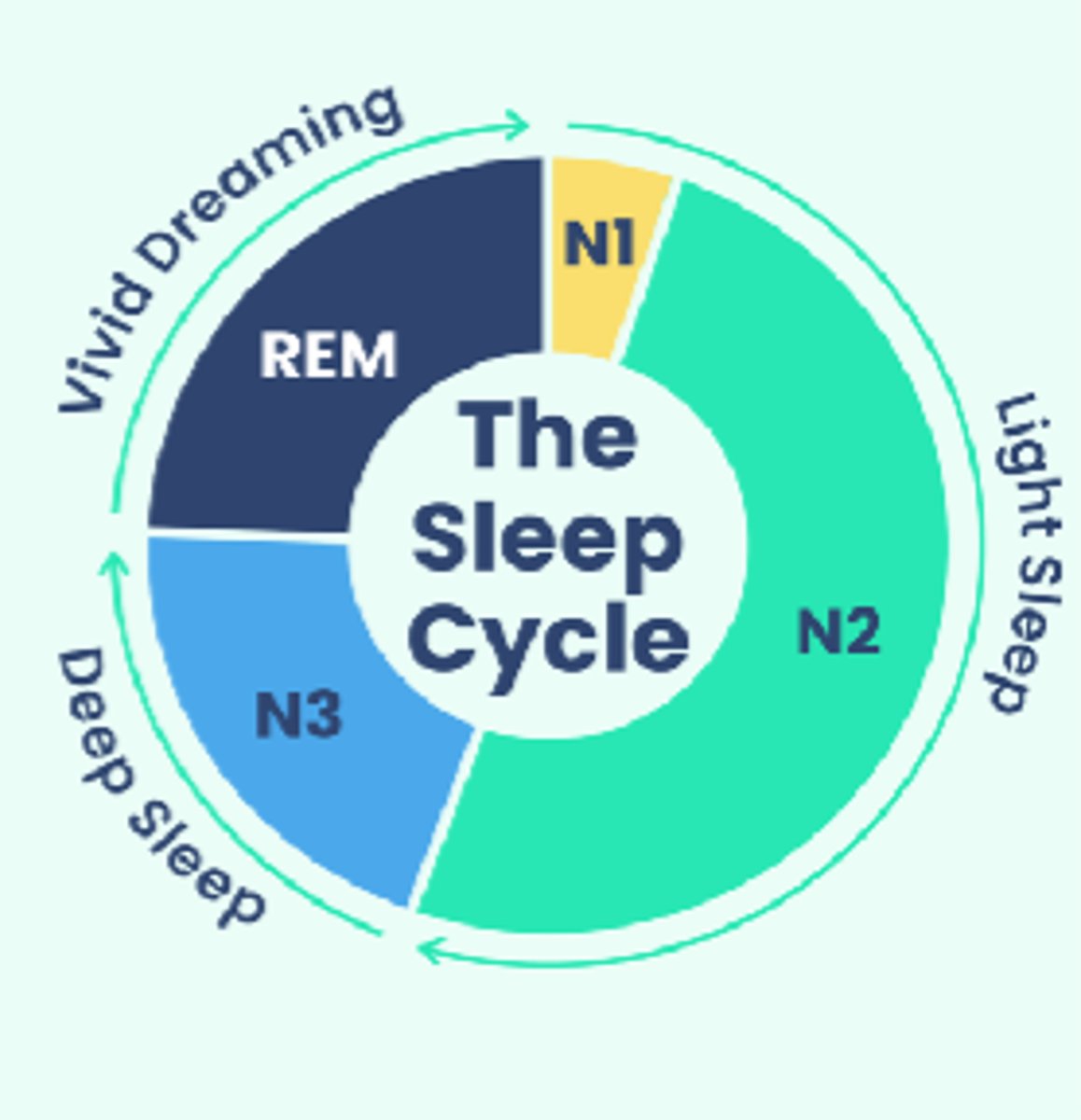
What occurs in N3 of the sleep cycle?
- Delta waves
- Hard to arouse
- Physical restoration
- Strengthening immune system
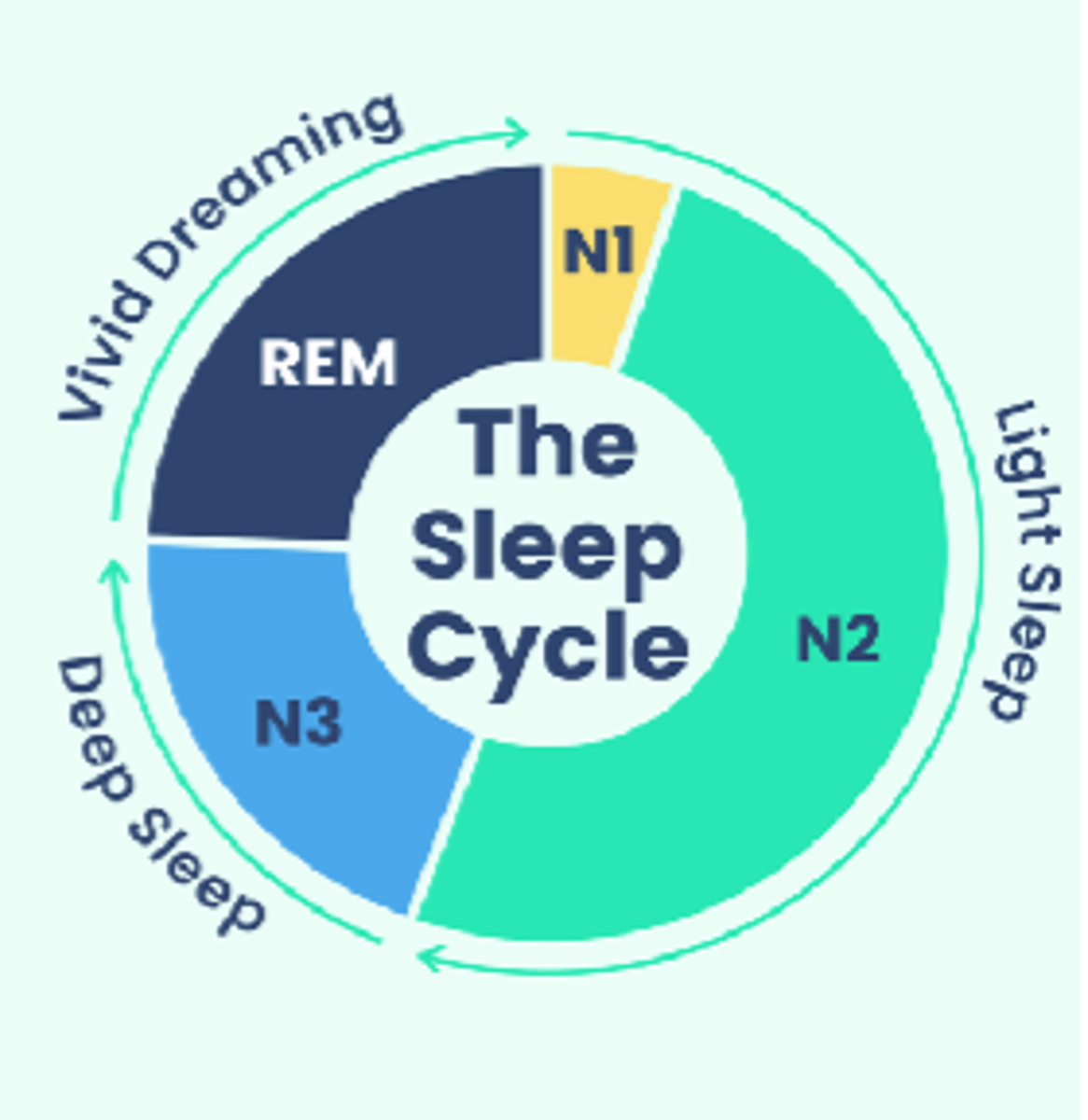
What occurs in stage 4 of the sleep cycle?
- REM
- Restores mind
- Vivid dreams
- Active brain processing events of day and saves in LTM
- No muscle activity
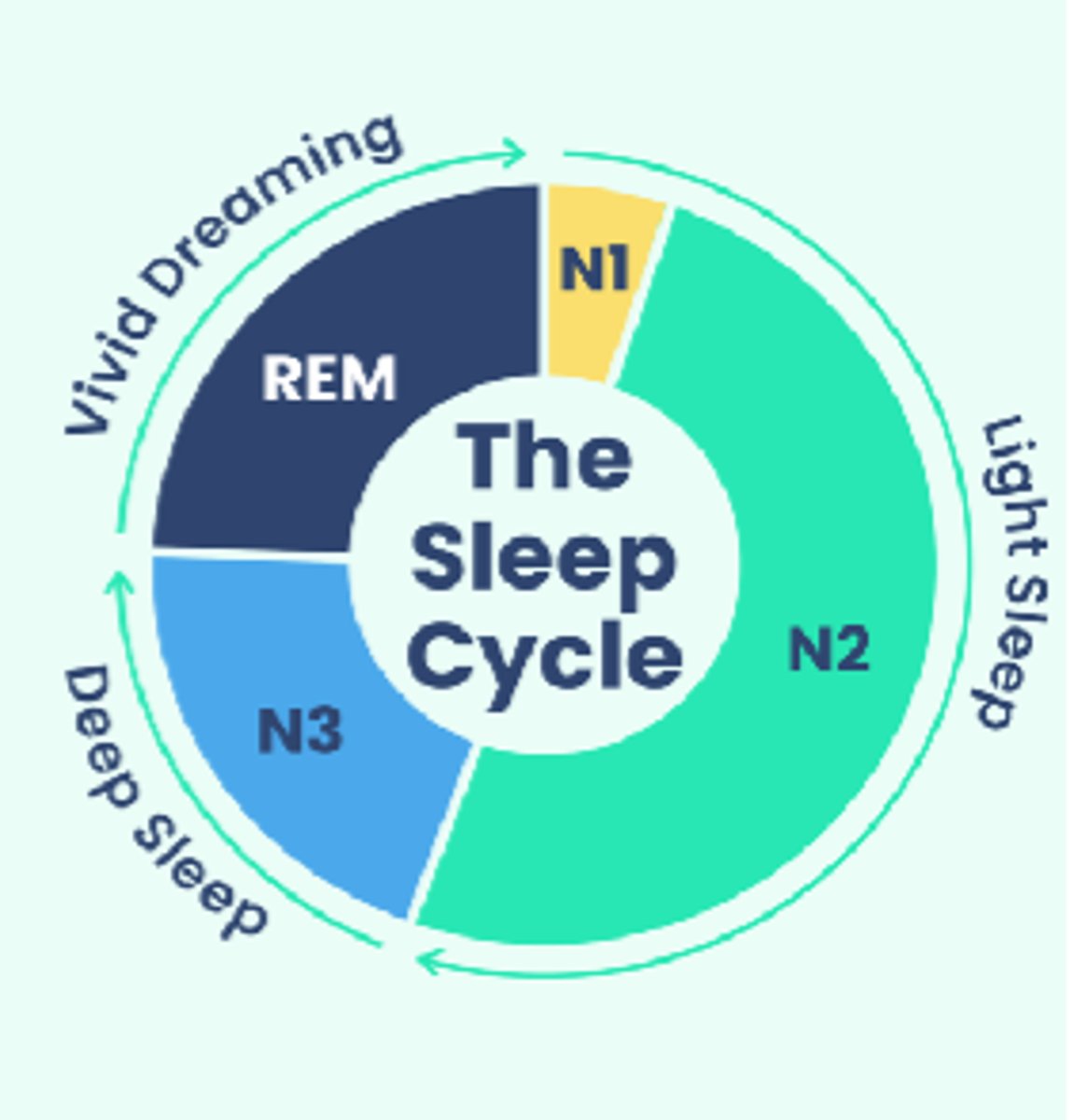
What does a midbrain transection lead to?
Coma (hypersomnia)
What does a lower pons transection lead to?
Reduces sleep (insomnia)
What is a coma?
- Unarousable
- Lying with eyes closed
What can cause a coma?
- Damage at pontomesencephalic RF
- Damage to bilateral large areas of cortex
- Bilateral lesions of thalamus
What is the presentation of a coma? (6)
- May show reflexive eye movements (vestibulo-ocular reflex)
- May show respiratory movements
- Posturing
- No purposeful movements
- No response to painful stimuli
- Not permanent (may deteriorate/improve)
Where is the site of a lesion leading to decorticate posturing?
- Forebrain
- Diencephalon rostral to midbrain
- Above red nucleus
What is decorticate posturing also known as?
Flexor posturing
What are signs of decorticate posturing?
- Closed hands
- Legs are internally rotated
- Feet turned inward
- Arms adducted, flexed against chest
Where is the site of a lesion leading to decerebrate posturing?
- Below mid brain
- Vestibular nuclei not modulated
What is decerebrate posturing also known as?
Extensor posturing
What are signs of decerebrate posturing?
- Head and neck arched
- Legs straight
- Toes pointed downwards
- Arms straight, extended
- Hands curled
What is a vegetative state?
An extreme case of alertness without awareness
What is the presentation of a vegetative state?
- Open their eyes
- Responses to stimuli, but not meaningful
- May turn head/eyes toward tactile/auditory stimuli
What sets apart a persistent vegetative state?
- >1 month of no meaningful motor/cognitive function
- Absence of awareness of themselves/environment
What is a persistent vegetative state > 6 months considered (traumatic vs. nontraumatic)?
Nontraumatic
What is a persistent vegetative state > 12 months considered (traumatic vs. nontraumatic)?
Traumatic
What is the prognosis of a persistent vegetative state?
Poor
What is a minimally conscious state?
Do not have reliable interactive verbal/nonverbal communication
What is the presentation of a minimally conscious state?
- Visual tracking
- Minimal level of responsiveness
What is the Glasgow Coma scale used for?
Determine severity
What responses does the Glasgow Coma scale measure?
- Eye opening
- Verbal
- Motor
What is the Rancho Los Amigos Levels of Cognitive Functioning (LOCF) scale used for?
Communicate the cognitive/behavioral state and planning intervention
What causes Locked-in Syndrome?
Lesion in ventral pons affecting the bilateral corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts
What is the presentation of Locked-in Syndrome? (5)
- Absent motor function (no voluntary movement)
- Reticular activating system spared (conscious)
- Intact sensation and cognition
- Vertical eye movements spared
- Eyelid elevation spared
What causes Horner's Syndrome?
Interruption of sympathetic nerve arising from T1, T2
What are the symptoms of Horner's Syndrome?
- Miosis
- Ptosis
- Anhidrosis
- Dilation of blood vessels on face and head
What is miosis?
- Decreased pupil size
- Loss of SNS innervation to pupillary dilator
What is ptosis?
- Drooping of upper eyelid
- Loss of innervation to superior tarsal muscle (Müller's muscle)
What is anhidrosis?
Decreased sweating