bio 109- CHAPTER 2- redox reaction and forces of attraction
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
element
a substance which cannot be brok en down into other substances
compound
contains 2 or more elements, held together by inTRAmolecular forces
molecule
2 or more atoms held together in a stable association, held together by inTRAmolecular forces
ionic
atom/molecule with a full electrical charge
compounds that involve a metal binding with either a non-metal or a semi-metal opposite charges attract
redox reaction creates ions
not actually bonded just strongly attracted
polar
asymetrical- unequal sharing of electrons
electronegativity difference >0.5
create dioples
strong inTRAmolecular forces
non-polar
symetric- equal sharing of electrons
electronegativity difference < 0.5
electronegativity
atoms ability to attract electrons
ranges from 4.0 (f) - 0.7 (Cs)
differences affect electron distribution within a covalent bond
covalent bond
chemical bond formed when two electrons are shared between two atoms
more electrons shared= greater strength of the bond
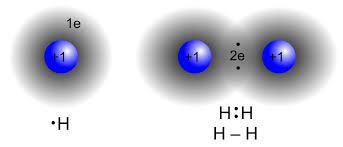
what kind of bond is this
covalent bond
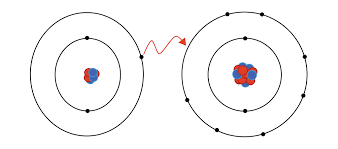
what kind of bond is this
ionic bond
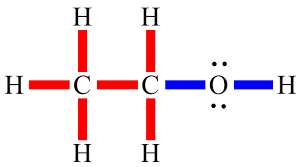
what kind of bond is this
polar
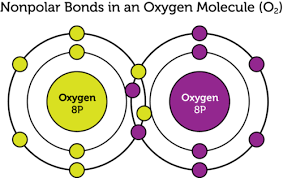
what kind ofbond is this
non polar
inTRAmolecular forces
hold adjacent atoms together WITHIN a molecule
inTERmolecular forces
attract DIFFERENT MOLECULES (or parts of molecules) together
what are atoms composed of?
protons
neutrons
electrons
protons
positive charge, located in the nucleus
neutrons
no charge, located in the nucleus
electrons
negative charge, found in orbitals surrounding the nucleus, have potential energy related to their position- farther away from nucleus=more energy
OIL
RIG
oxidation is loss of an electron (and energy)
reduction is gain of an electron (and energy)
weak electronegativity
carbon- 2.5
sulfur- 2.5
hydrogen- 2.1
phosphorus- 2.1
strong electronegativity
oxygen- 3.5
nitrogen- 3.0
chlorine- 3.0
dipole - dipole interactions
attractions of opposite partial charges
depends on polar inTRAmolecular forces
ex- polar cov bond
weaker inTERmolecular forces
London dispersion forces (LDF)
general attraction between any 2 molecules
more electrons in atom= stronger forces
WEAKEST force of attraction
catalyst
substance that speeds up a chemical reaction, or lowers the temperature or pressure needed to start one, without itself being consumed during the reaction
buffers
substances that resist changes in pH
releasing H+ when a base is added
absorbing H+ when acid is added
overall effect= keeps [H+] relatively constant
bases
combines with H+ in water to decrease [H+] (increase pH)
pH greater than 7
conduct electricity
slippery to touch
acids
dissociates in water= increase [H+] (lower the pH)
pH less than 7
acids are electrolytes
react with active metals to yield hydrogen gas
are strong ionic compounds water souluble
they are less water soluble, harder to dissociate ions
does dissolving glucose create ions
no
cohesion
dipole-dipole (hydrogen bond) inTERmolecular forces
creates surface tension
adhesion
water molecules attracted to other polar molecules
dipole dipole (hydrogen bond) inTERmolecular forces
properties of water
high specific heat- lots of energy to change temp, many dipole- dipole forces
high heat of vaporization- lots of energy for phase change, many dipole-dipole forces
water is more dense than ice- fixed dipole- dipole, more empty space, ice floats in water
can form ions
are nonpolar molecules soluble
no they are insoluble, cannot form dipole- dipole attractions
hydrophobic
are polar molecules and ions soluble?
yes they are soluble, form dipole- dipole, or ion- dipole
hydrophilic