newtons laws of motion, force and the use of technology
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
whats newtons 1st law of motion
‘ a body continues in a state of rest or uniform velocity unless acted upon by an external or unbalanced force
law of inertia, inertia is the resistance of a body to change its state of motion
A golf ball will remain still unless acted on by the golf club
what is newtons 2nd law of motion
‘ a body’s rate of change of movement is proportional to the size of the force applied and acts in the same direction as the force applied’
law of acceleration, as acceleration is proportional to the size of force applied
when the velocity of the golf ball been hit is proportional to the amount of force used to on it
what is newtons 3rd law of motion
‘ for every action force applied to a body there is an equal and opposite reaction’
law of reaction and states
When you jump, your feet apply force to the ground, and the earth applies an equal and opposite reaction force that pushes you into the air
what is velocity
the rate of change of displacement
Velocity(s)= displacement/ time taken
what is momentum
the quantity of motion possessed by a moving body
momentum= mass x velocity
what is acceleration
Acceleration= (final velocity - initial velocity) / time taken
measured in M/S
What is force
force is a push or pull which alters the state of motion of a body
Force= mass x acceleration
F=MA
Measured in newtons N
Types of force
internal force
contraction of skeletal muscles
external force
from outside the body
weight, reaction, friction and air resistance
what are the five effects force can have
can create a motion
can accelerate a body
can decelerate a body
can change direction of a body
can change the shape of a body
what is net force
the sum of all forces acting on a body( resultant force)
if net force is 0 then there is no change in motion
describe the vertical forces
weight
the gravitational pull that the earth exerts on a body
weight= mass x acceleration due to gravity
10 m/s
Reaction
is the equal and opposite force exerted by a body
measured in Newtons
what are the horizontal forces
Friction
the force that opposes the motion of two surfaces in contact
Measured in newtons
Air resistance
force that opposes motion of body travelling through the air
measured in newtons
what are the factors that can affect friction
roughness of the ground surface
roughness of the contact surface
temperature, if higher temp friction is higher
size of normal reaction
what are the factors affecting air resistance
velocity
shape( streamlining)
frontal cross sectional area
smoothness of surface body( lycra suits for cyclists)
whats a free body diagram
a clearly labelled sketch showing all of the forces acting on a body at one particular time
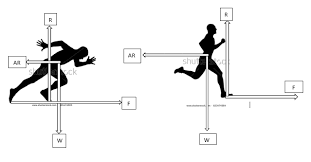
what is limb kinematics
the study of movement in relation to time and space, allowing limb displacement, velocity and acceleration to be assessed
what are force plates
used to measure the size and direction of ground reaction forces on the athlete and can be used to asses acceleration, work and power output
what are wind tunnels
used to measure air resistance and aim to improve the flow of air around an object streamlining its path through the oncoming air
what is the centre of mass
the point in which the body is balanced in all directions
the centre of mass can also move outside the body and act as a point of rotation
whats the Fosbury flop technique
in high jump to move the centre of mass outside the body and below the bar
what is stability
the body’s ability to resist motion and remain at rest
also to withstand a force applied and return to its original postion
what are the factors affecting stability
mass of the body( more mass better stability)
height of the centre of mass( lower is better)
Base and support
line of gravity
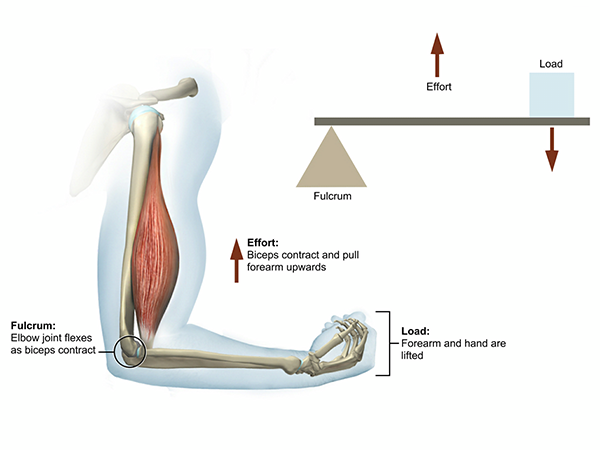
what are the components of lever systems
lever(bone)
fulcrum(joint)
effort(muscular force)
load(weight or resistance)
what is the 1st class lever
E-F-L
L-F-E
fulcrum is in the middle
extension of neck when preparing to header a football
what is the 2nd class lever
E-L-F
F-L-E
load is in the middle
ball of the foot at the take off phase of a high jump
what is the 3rd class lever
L-E-F
F-E-L
effort is in the middle
flexion at the elbow in. bicep curl
describe the efficiency of the lever system
the order and distance of the lever components from the fulcrum is important for their function
the distance from the fulcrum to the effort is known as ‘effort arm’
the distance from the load to the fulcrum is know as the ‘load arm’
the greater the distance of the effort or load to the fulcrum the more significant the effort or load becomes
describe the efficiency of the lever system (2)
longer levers can generate more force as the load arm becomes longer therefore greater acceleration to projectiles
the length of the effort and load arm gives a lever system a mechanical advantage or a mechanical disadvantage
second class lever has the mechanical advantage to move a large load with small effort
the third class lever has the mechanical disadvantage requiring a large effort to move a relatively small load, however can generate lots of acceleration over a large range of movement