Astronomy Chapter 4: Atomic Physics and Spectra
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Blackbody
An ideal blackbody absorbs all of the electromagnetic radiation that strikes it.
Blackbody Radiation Laws
Laws that describe the emission of radiation from blackbodies, including Wien's law and the Stefan-Boltzmann law.
Wien's law
The peak wavelength of radiation emitted by a blackbody is inversely proportional to its temperature. λmax = 2.9 × 10-3/T
Stefan-Boltzmann law
An object emits energy per unit area at a rate proportional to the fourth power of its temperature in kelvins. F = σT4
Luminosity (L)
The total energy emitted by a spherical object each second. L = F • 4πr2 = σT44πr2
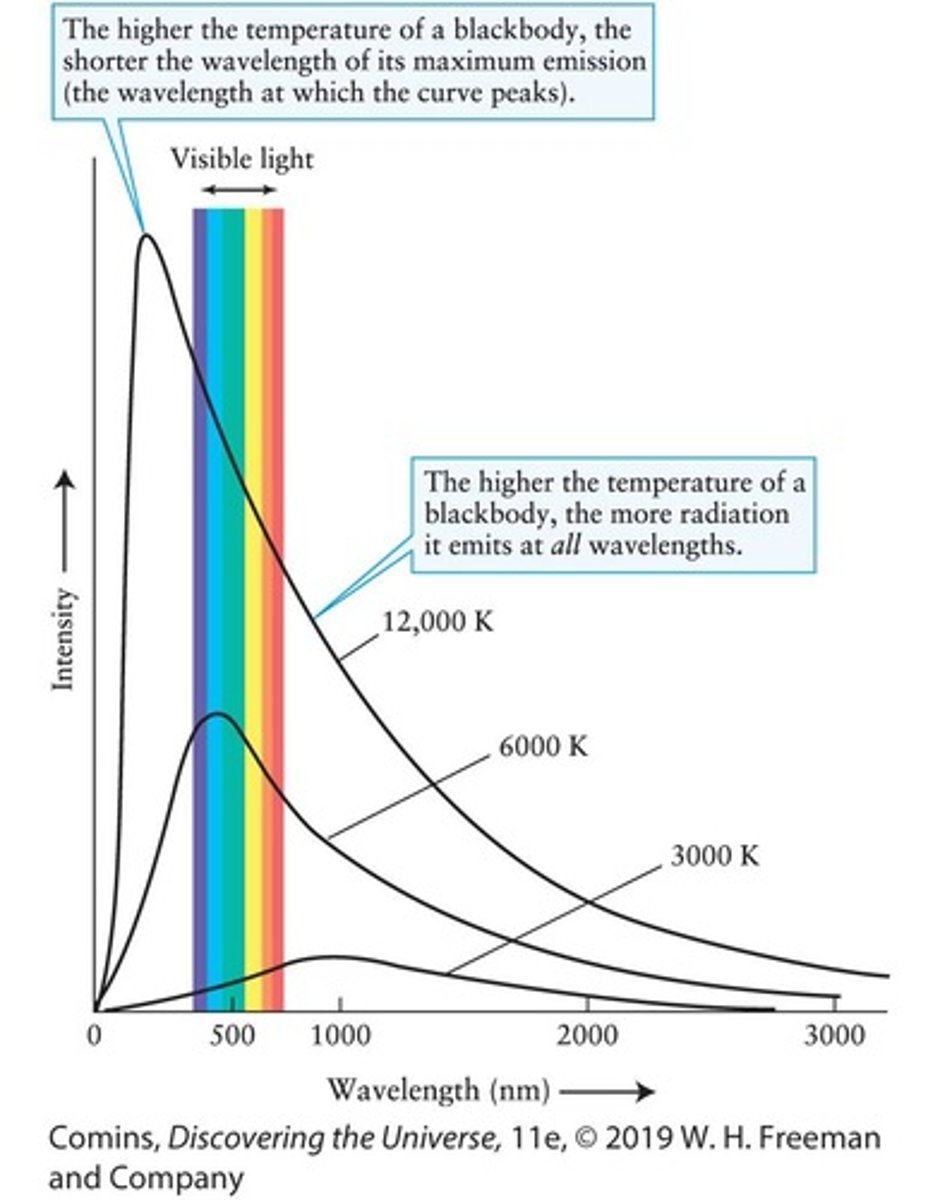
Blackbody Curves
Graphs showing the intensity of radiation over a wide range of wavelengths emitted by a blackbody at a particular temperature.
Electromagnetic Radiation
Radiation consisting of waves of electric and magnetic energy moving through space.
Photon Energy
The energy carried by a photon, which varies with wavelength.
Cool Object Emission
A cool object emits primarily long-wavelength photons that carry little energy.
Hot Object Emission
A hot object emits mostly short-wavelength photons that carry much more energy.
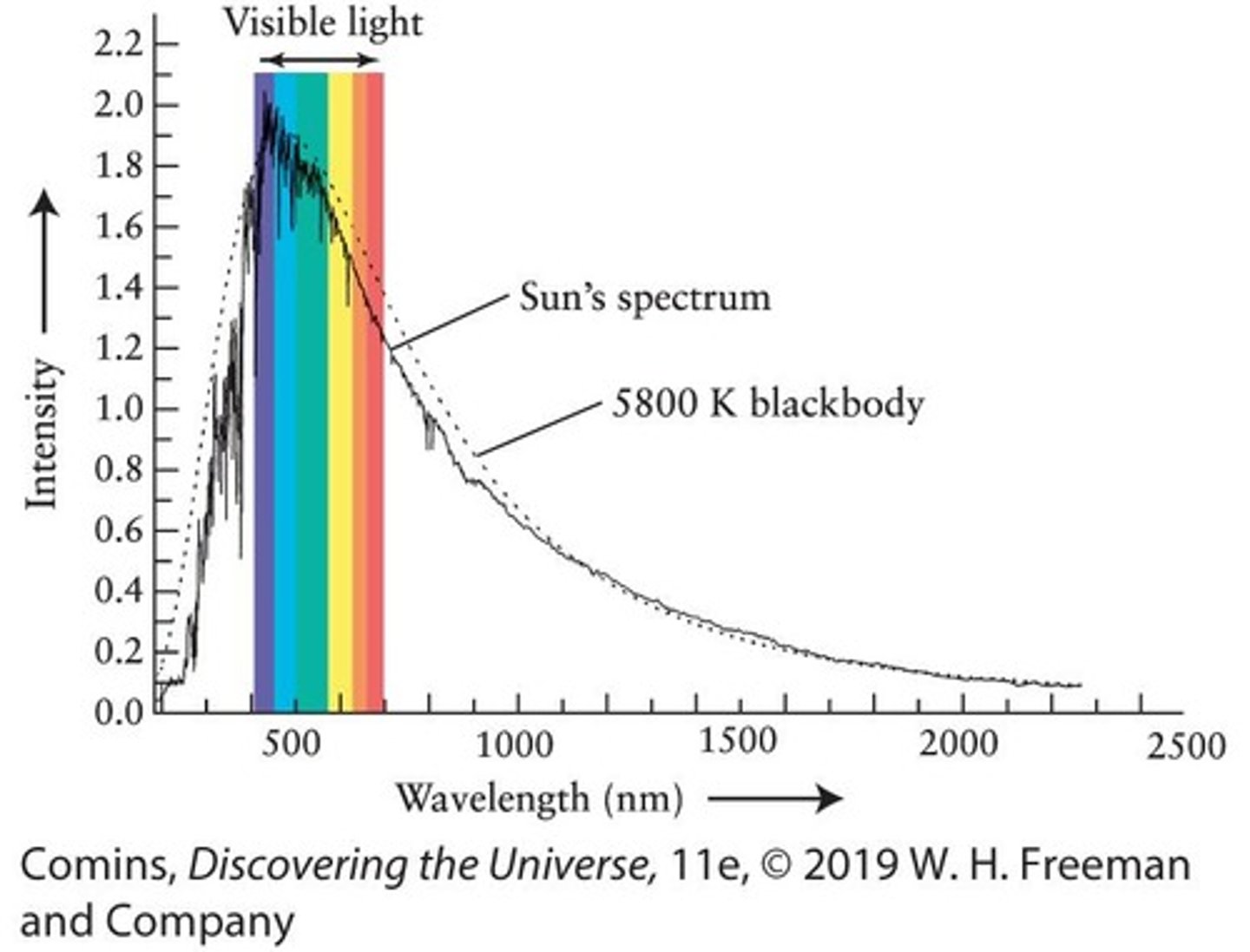
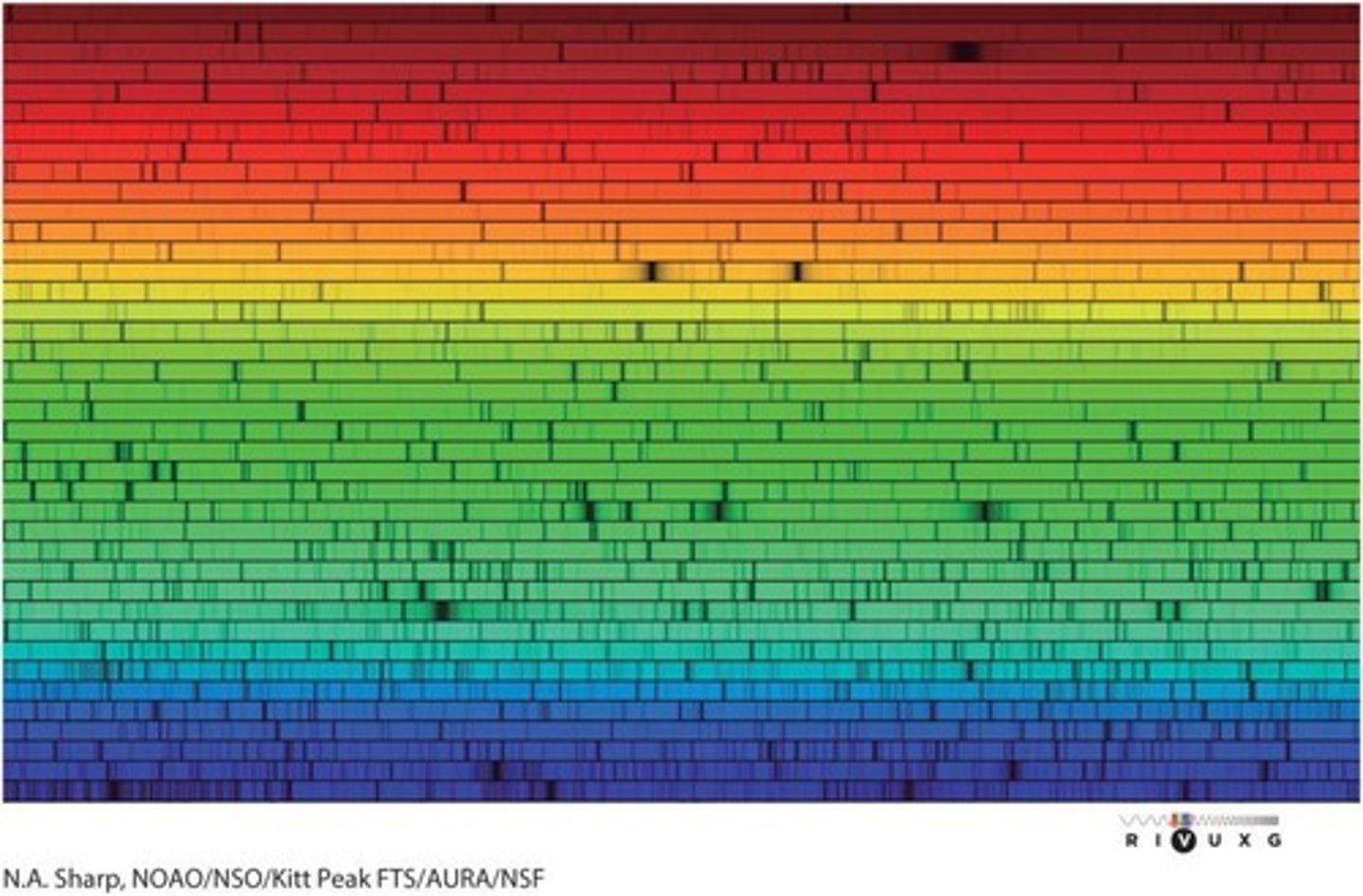
Solar Spectrum
The range of wavelengths emitted by the Sun, showing its intensity at different wavelengths.
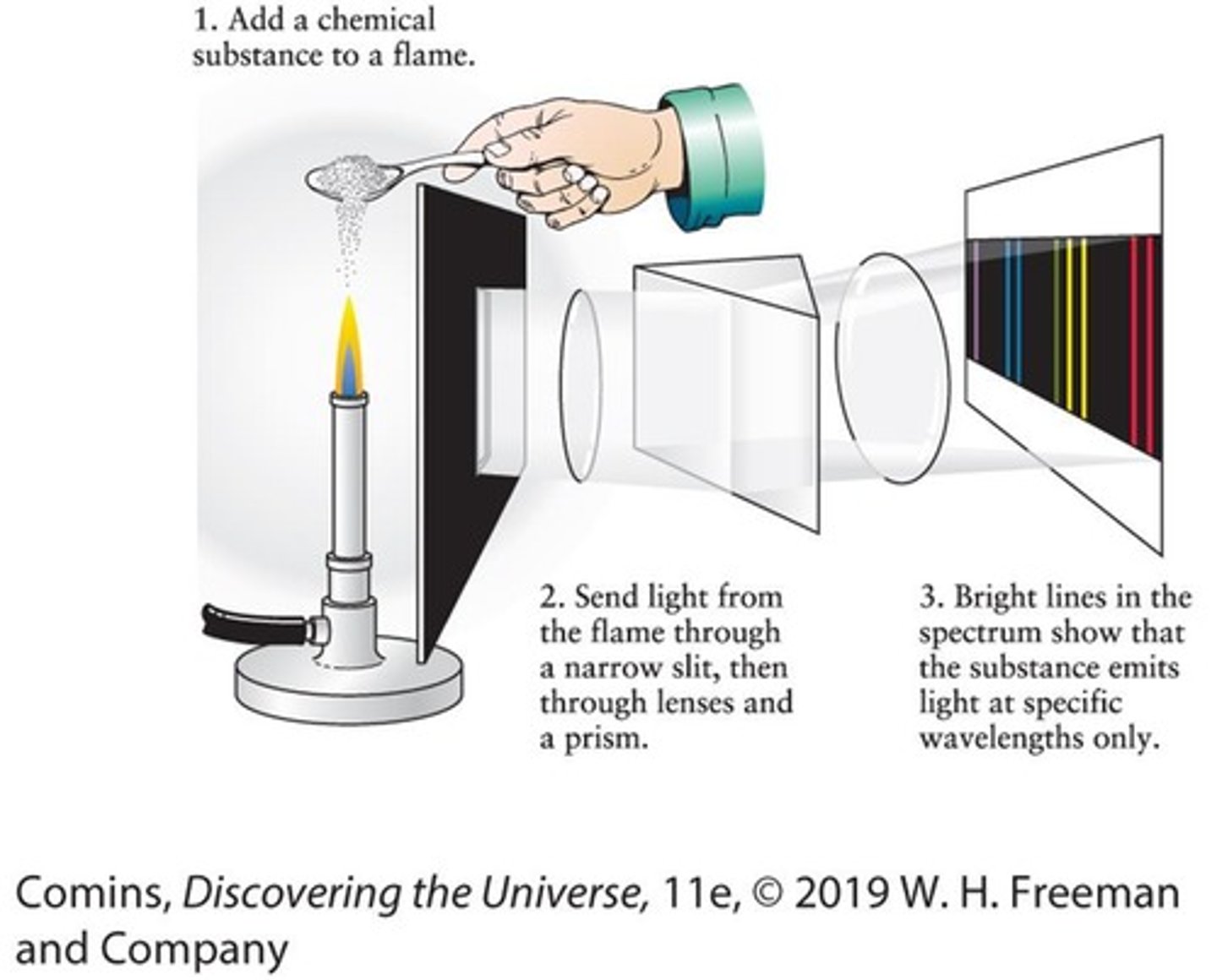
Spectroscope
An instrument used to observe the spectrum of light emitted by a chemical substance.
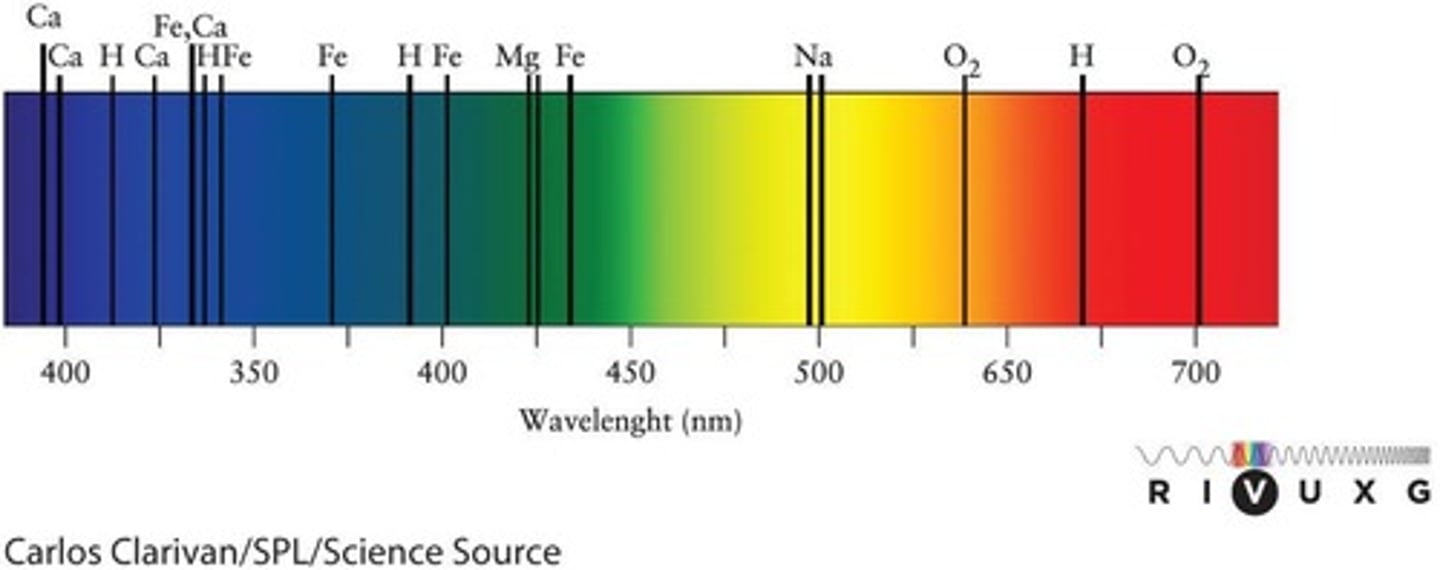
Spectral Lines
Bright lines in a spectrum that are characteristic of a particular chemical element or molecule.
Grating Spectrograph
An instrument that uses a diffraction grating to separate light into its component colors for analysis.
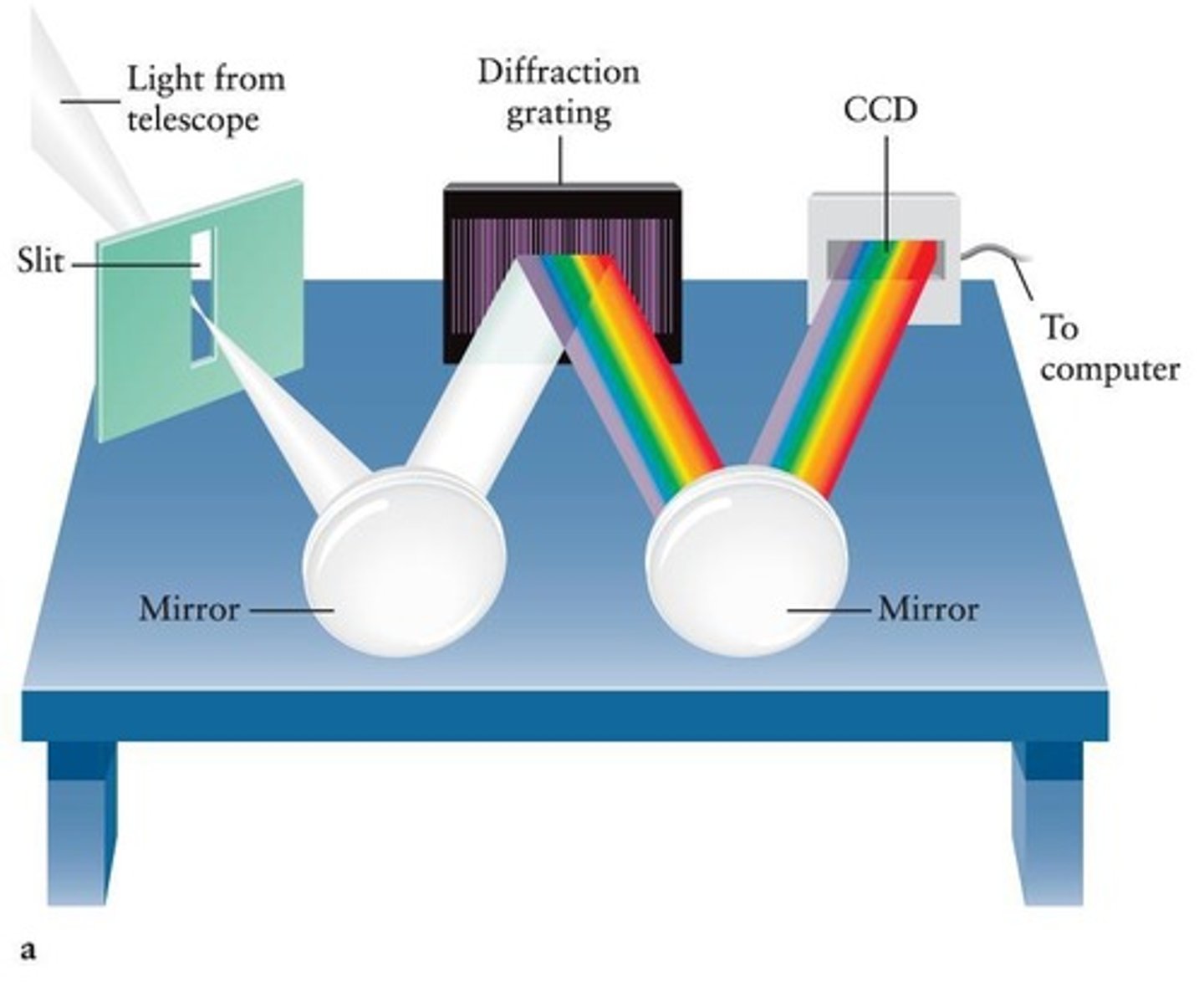
Diffraction Grating
A surface with many parallel lines that reflects light of different colors in different directions.
Iron in the Sun's Atmosphere
The presence of iron can be detected in the Sun's atmosphere through its characteristic spectral lines.
Color of the Sun
The appearance of the Sun varies depending on atmospheric conditions and the observer's location.
Temperature and Color
Stars with different surface temperatures emit different intensities of electromagnetic radiation.
Chemical Composition Determination
Astronomers can determine the chemical compositions of stars and interstellar clouds by studying the wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation that they absorb or emit.
Movement of Objects in Space
Astronomers can tell whether an object in space is moving toward or away from Earth.
Peak of Blackbody Temperature
The temperature at which a blackbody emits radiation most intensely.
Electromagnetic Radiation Wavelengths
Different ranges of wavelengths correspond to different types of electromagnetic radiation, such as radio, microwave, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, X-ray, and gamma ray.
CDs and DVDs
Store information on closely spaced bumps located on a set of nearly parallel tracks.
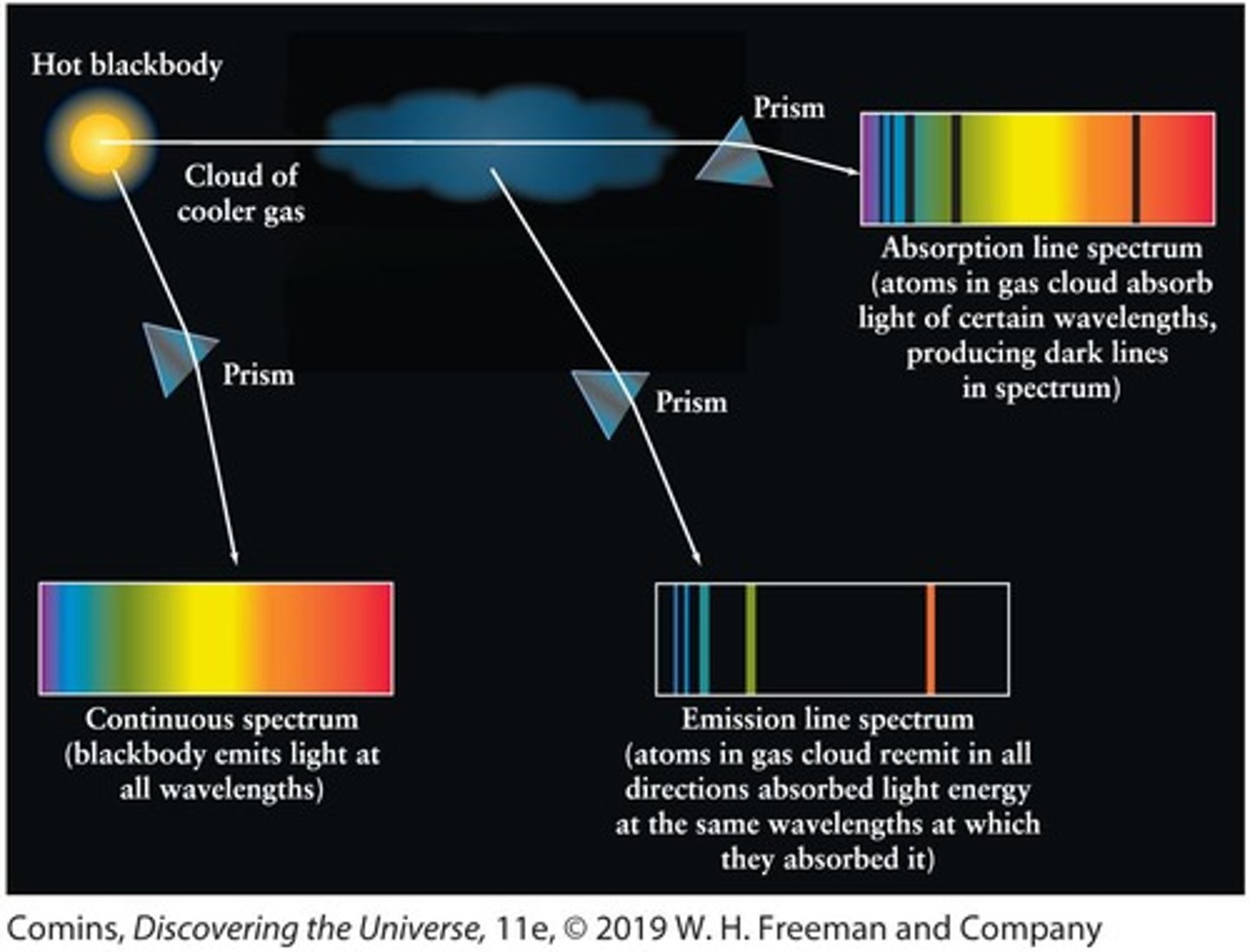
Law 1 of Kirchhoff's Laws
A solid, liquid, or dense gas produces a continuous spectrum, a complete rainbow of colors without any spectral lines.
Law 2 of Kirchhoff's Laws
A rarefied gas produces an emission line spectrum, a series of bright spectral lines against a dark background.
Law 3 of Kirchhoff's Laws
The light from an object with a continuous spectrum that passes through a cool gas produces an absorption line spectrum, a series of dark spectral lines among the colors of the rainbow.
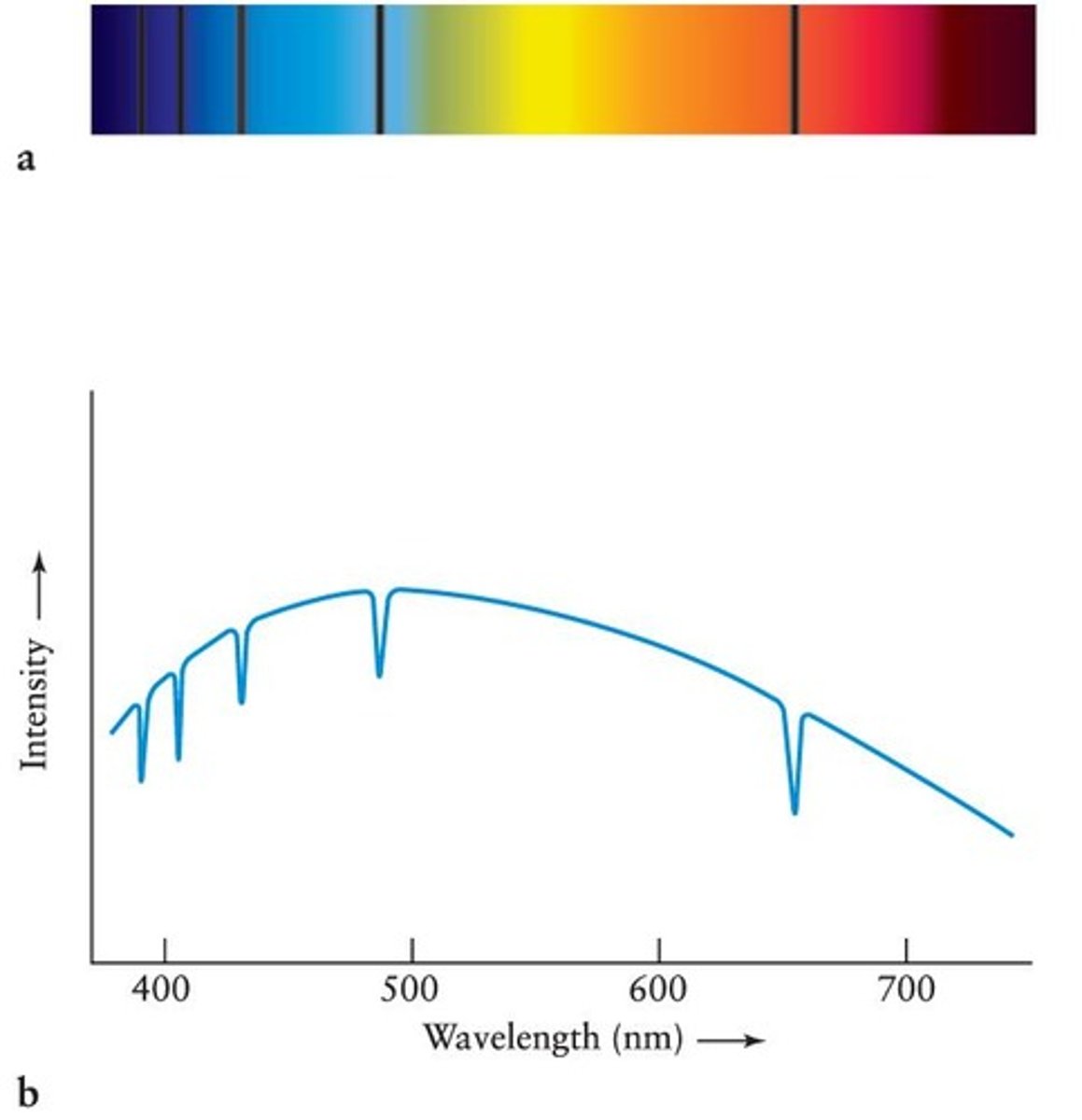
Absorption Spectrum of Hydrogen Gas
When a CCD is placed at the focus of a spectrograph, the spectrum is recorded from a hot object whose light shines through hydrogen gas.
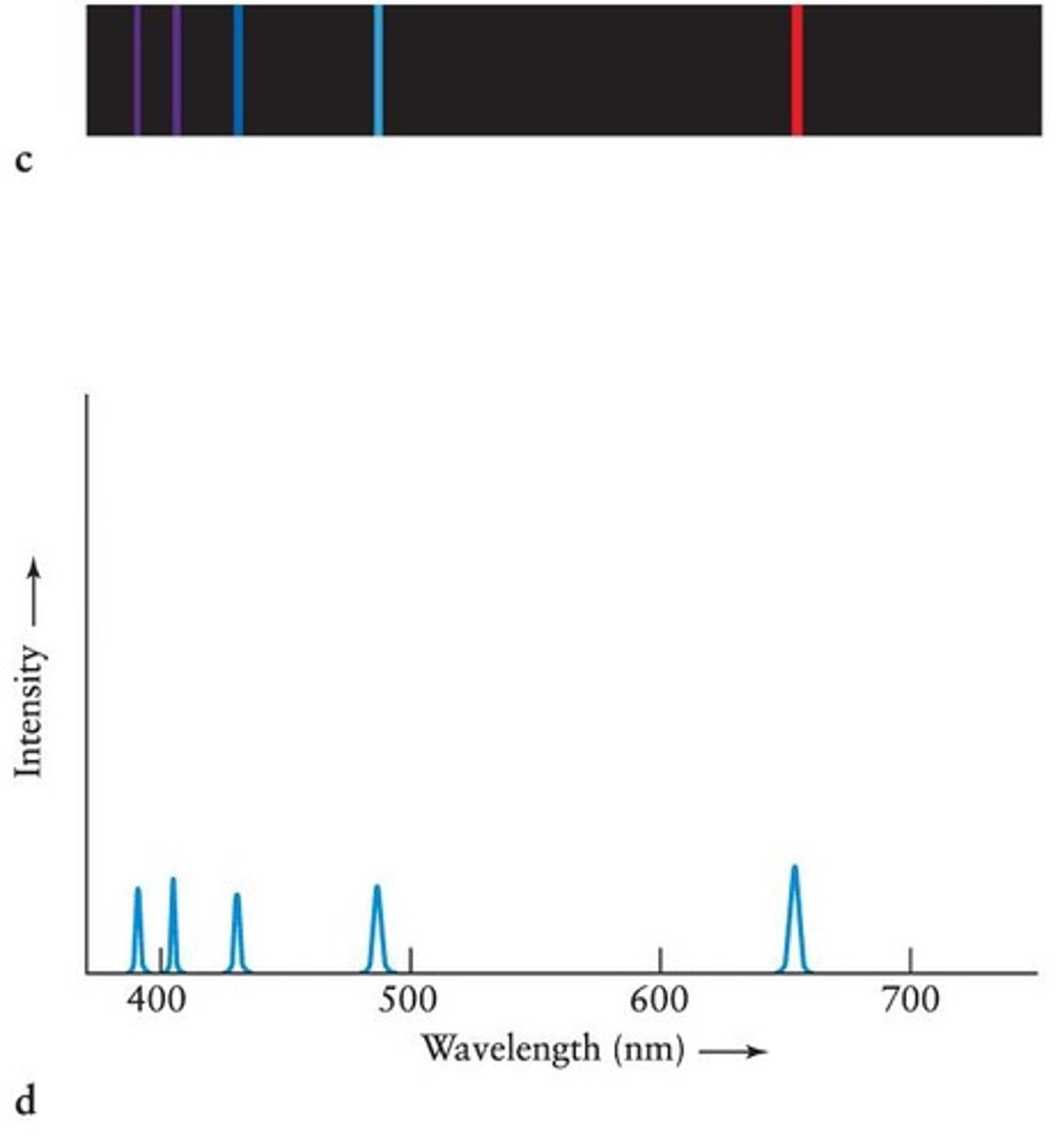
Intensity versus wavelength graph
The spectrum is converted by computer into a graph of intensity versus wavelength, with absorption lines appearing as dips.
Emission Spectrum of Hydrogen Gas
When a gas emits only a few wavelengths, its emission spectrum appears as a series of bright lines, converted into peaks on a graph of intensity versus wavelength.
Continuous spectrum
A spectrum emitted by a hot, glowing object that shows a complete range of colors.
Absorption lines
Dark lines that appear in a spectrum when light from a continuous source passes through a cool gas.
Emission lines
Bright lines that appear in a spectrum when a gas is viewed against a cold, dark background.
Atom
The smallest particle of a chemical element that still has the properties of that element.
Nucleus of the atom
Contains protons and neutrons, with electrons normally orbiting around it.
Atomic number
The number of protons in an atom's nucleus, which determines the element of that atom.
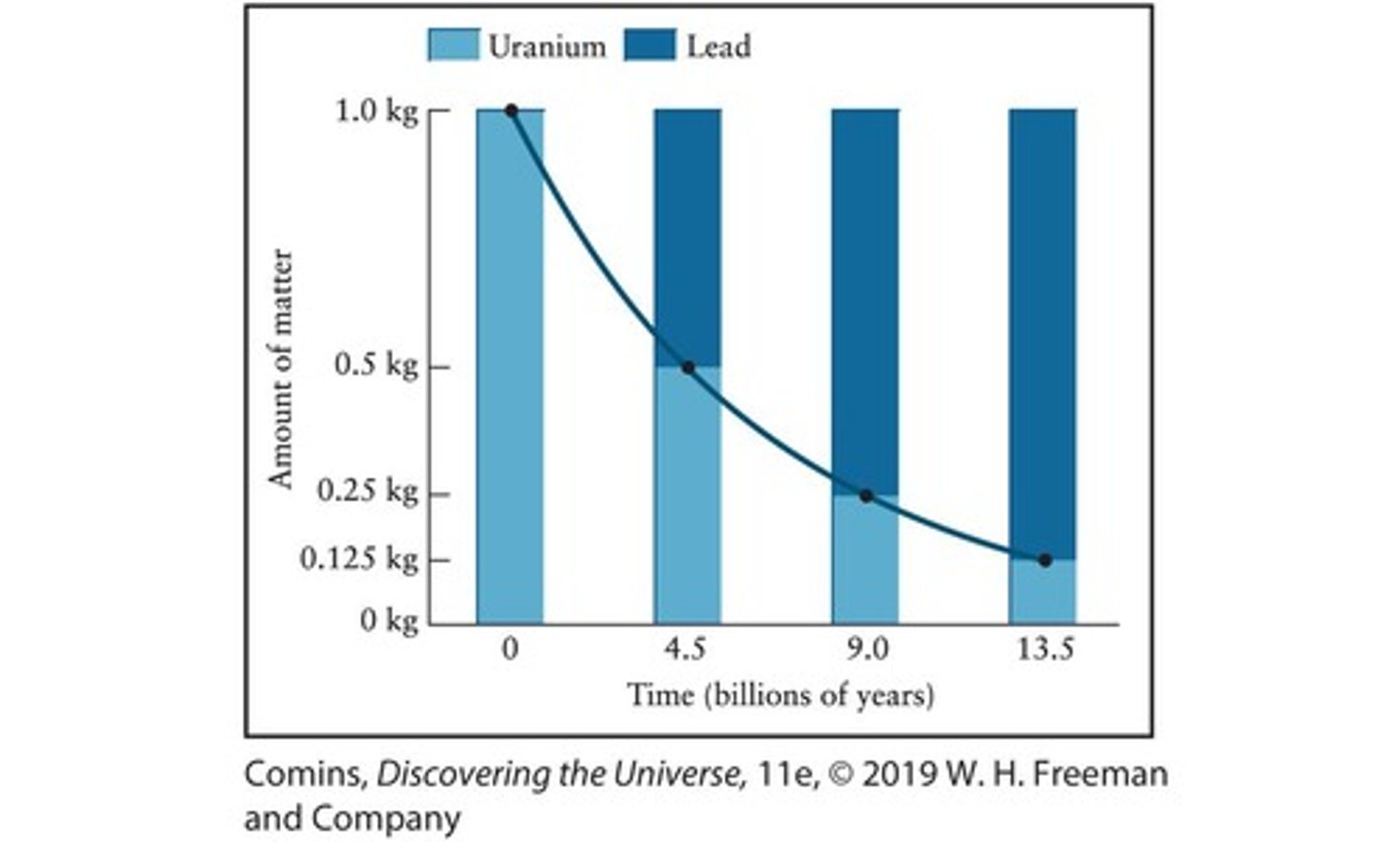
Isotope
Each different combination of protons and neutrons in an atom.
Electric charge
A property of electrons and protons where like charges repel and opposite charges attract.
Radioactive element
An element that naturally and spontaneously transforms into another element by emitting particles over time.
Quantum mechanics
Explains that electrons in atoms can exist in only certain allowed orbits around their nuclei.
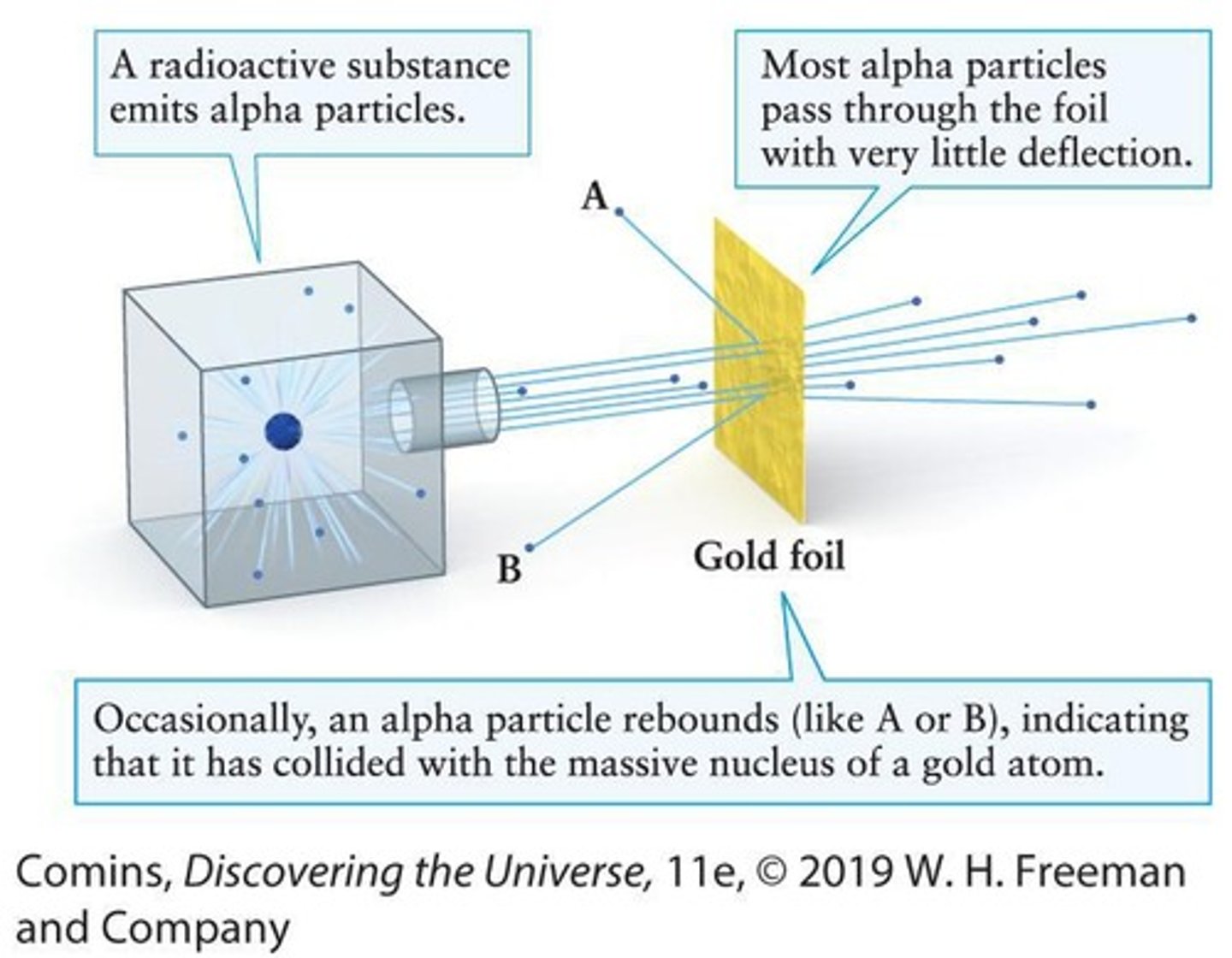
Rutherford Scattering Experiment
An experiment showing that most helium nuclei scatter slightly while some scatter backward, indicating dense, compact objects.
Strong nuclear force
The strongest fundamental force, with a strength of 1, acting inside atomic nuclei.
Electromagnetic force
A fundamental force with a strength of 1/137, acting throughout the universe.
The interaction between charged particles; one of the four fundamental forces in nature.
Weak nuclear force
A fundamental force with a strength of 10^25, acting inside atomic nuclei.
Gravitational force
A fundamental force with a strength of 6 x 10^-39, acting throughout the universe.
Allowed electron orbits
Specific orbits around the nucleus where electrons can exist, each with a well-defined energy.
Allowed Electron Orbit
Each allowed electron orbit has a well-defined energy associated with it.
Unique Set of Allowed Orbits
Every different type of atom and molecule has a unique set of allowed orbits.
Photon Absorption
Electrons can absorb only those photons with energies exactly enough to boost them up to a higher-energy allowed orbit.
Unstable Excited States
Electrons in excited states are unstable and must emit a photon to transition down to a more stable state.
Photon Emission
The emitted photon has energy equal to the difference between the energies of the starting and final allowed orbits.
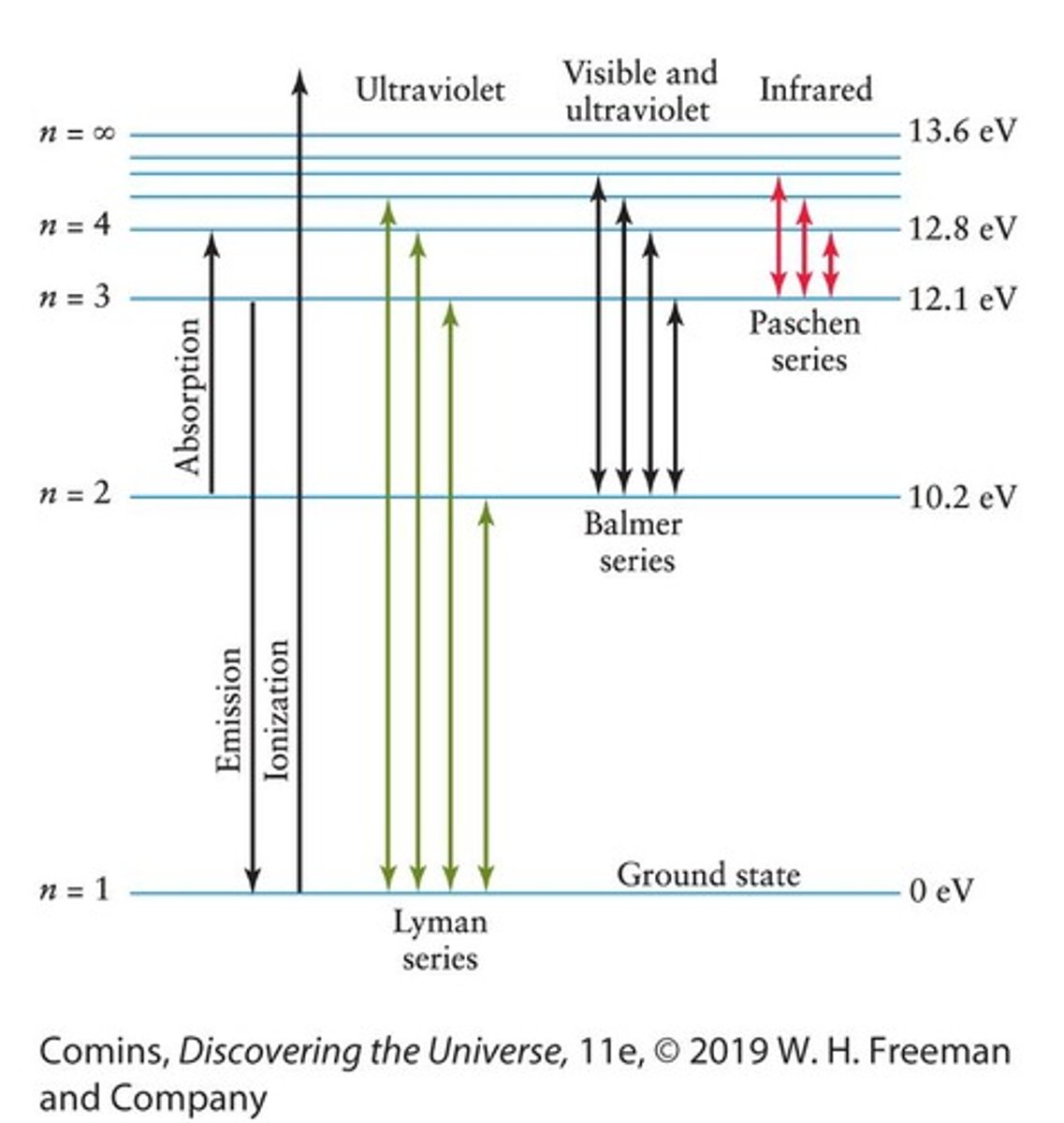
Photoionization
If an electron orbiting in a hydrogen atom encounters a photon with more than 13.6 eV, that photon is absorbed and knocks the electron completely out of orbit.
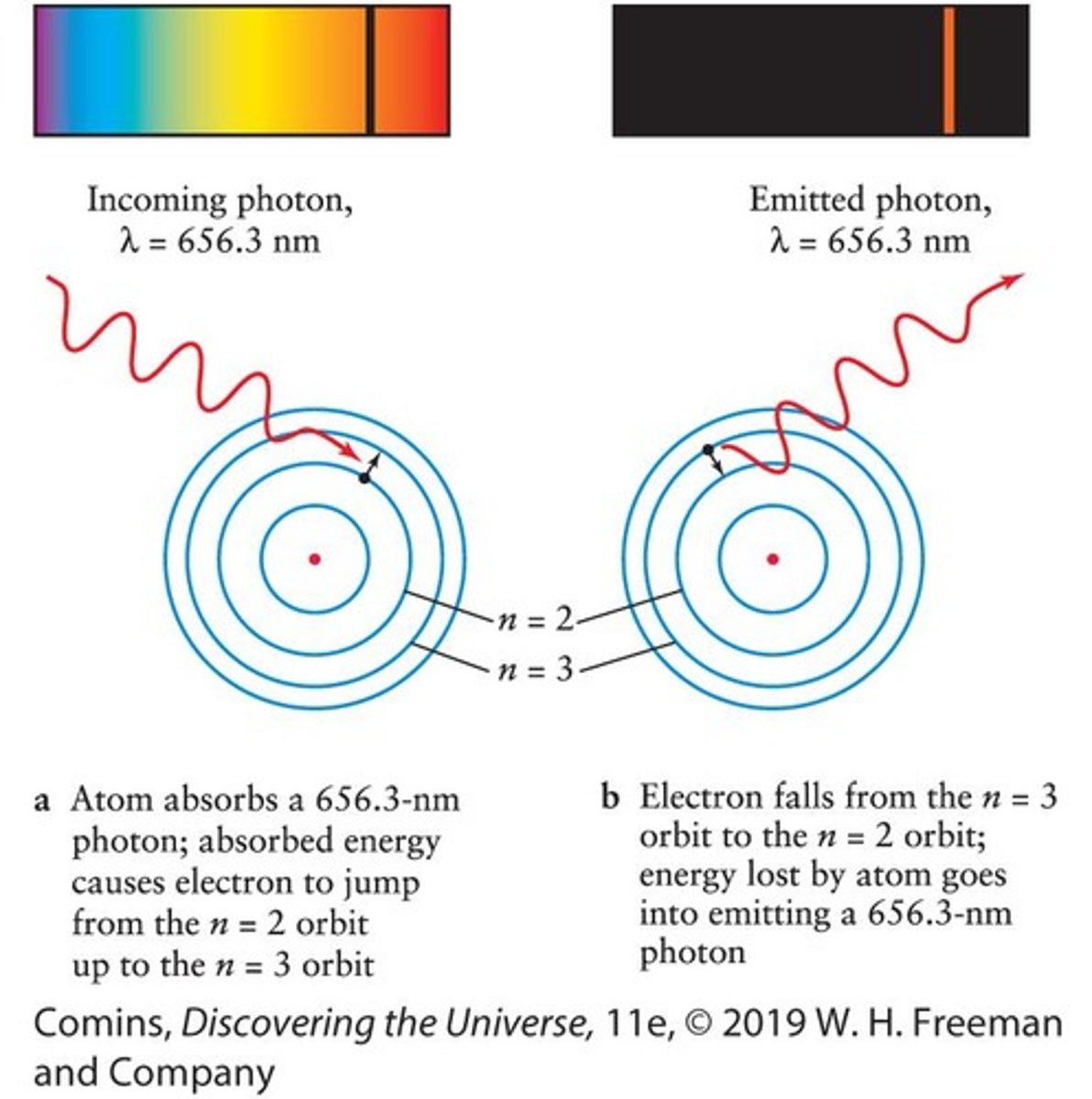
Hα Photon
An Hα photon is red and has a wavelength of 656.3 nm.
Energy Level Diagram
A diagram showing some of the energy levels, labeled n, at which the electron can exist in orbit.
Electron Jumps
Electron jumps, or transitions, produce the most prominent lines in the hydrogen spectrum.
Blackbody Spectra
Stars in interstellar gas clouds emit blackbody spectra.
Electron Absorption in Gas Clouds
Electrons in the cloud's hydrogen gas absorb and reemit red light from stars.
Doubly Ionized Oxygen
Doubly ionized oxygen atoms (O III) in the cloud emit 501-nm photons.
Doppler Shift
The waves are compressed in front of the source but stretched out behind it.
Blueshift
Wavelengths appear shortened (blueshifted) if the source is moving toward the observer.
Redshift
Wavelengths appear lengthened (redshifted) if the source is moving away from the observer.
Radial Velocity
The speed of an object toward or away from us is called its radial velocity.
Transverse Velocity
The speed in kilometers per hour perpendicular to the radial velocity is called its transverse velocity.
Proper Motion
The angular motion of the star across the celestial sphere is called proper motion.
Barnard's Star Proper Motion
Barnard's star has the largest known proper motion of 10.3" per year.
Distance to NGC 2363
NGC 2363 is located some 10 million light-years away.
Distance to NGC 604
The nebula NGC 604 is located 2.7 million light-years away.
Distance to Rosette Nebula
The Rosette Nebula is 3000 light-years away.
Spectroscopy
The study of the wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation emitted and absorbed by astronomical objects.
Stefan-Boltzmann Law
Shows that a hotter blackbody emits more radiation at every wavelength than does a cooler blackbody.
Kirchhoff's Laws of Spectral Analysis
Describe the conditions under which absorption lines, emission lines, and a continuous spectrum can be observed.
Stable Nuclei
Nuclei of some atoms that do not spontaneously split into pieces.
Spectral Lines of Atoms
Correspond to the various electron transitions between allowed orbits of that element.
Balmer Series
The spectrum of hydrogen at visible wavelengths that arises from electron transitions between the second energy level and higher levels.
Charged Atom
An atom that has more protons than electrons or vice versa.
Doppler Shift Equation
States that the size of a wavelength shift is proportional to the radial velocity between the light source and the observer.
Absorption Line
A dark line in a spectrum that corresponds to a specific wavelength of light absorbed by an atom.
Absorption Line Spectrum
A spectrum that contains dark lines corresponding to wavelengths absorbed by a substance.
Blackbody Curve
A graph showing the intensities of radiation emitted at various wavelengths by a blackbody at a given temperature.
Emission Line
A bright line in a spectrum that corresponds to a specific wavelength of light emitted by an atom.
Emission Line Spectrum
A spectrum that contains bright lines corresponding to wavelengths emitted by a substance.
Electron
A negatively charged subatomic particle usually found in orbit about the nucleus of an atom.
Energy flux
The amount of energy emitted from each square meter of an object’s surface per second
Excited state
The orbit of an electron with energy greater than the lowest energy orbit (or state) available to that electron
Ground state
The lowest energy level of an atom
Ion
An atom that has become electrically charged due to the loss or addition of one or more electrons
Ionization
The process by which an atom loses or gains electrons
Molecule
Two or more atoms bonded together
Neutron
A nuclear particle with no electric charge and with a mass nearly equal to that of a proton
Periodic table
A listing of the chemical elements according to their properties; created by D. Mendeleev.
Planck’s law
The relationship between the energy carried by a photon and its wavelength
Proton
A heavy, positively charged nuclear particle
Radioactive
Unstable atomic nuclei that naturally decompose by spontaneously emitting particles.
Spectral analysis
The identification of chemicals by the appearance of their spectra.
Spectrograph
A device for photographing a spectrum
Transition (of an electron)
The change in energy and orbit of an electron around an atom or molecule.
H alpha (H a)
The longest wavelength Balmer line
H beta (H B)
The second longest wavelength Balmer line
H gamma (H y)
The third longest wavelength Balmer line
H infinity (H ∞)
The shortest wavelength Balmer line
Oxygen-rich gas clouds
Emits many green photons, making oxygen-rich gas clouds glow green