Occupational Hazards & Safety Issues (MSU VMT)
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Zoonotic diseases
Infectious diseases that can be passed from animals to humans
Reservoir
are essential and necessary for the survival and reproduction of the organism (replication of disease)
host
are living beings that offer an environment for maintenance of the organism, but they are not necessary for the organism's survival
direct transmission
requires close contact between reservoir and host; infected skin, mucous membranes, droplets from infected animal or human, soil or vegetation
Diseases transmitted directly
rabies from a bite, leptospirosis contaminated urine, brucellosis infected tissues
indirect transmutation
more complicated and involves intermediaries that carry the agent of disease from one source to another
Q fever
most commonly transmitted by air-borne transmission. It is transmitted by inhalation of the rickettsia, Coxiella burnetii, in dust from areas that are contaminated by tissue or excreta from infected animals. Can also be transmitted by direct contact through contact with wool, milk and other materials.
Various types of arthropods may serve as vectors. These may include mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas.
plague
best-known vector-borne disease involving the flea as a vector. The natural reservoir for plague is wild rodents, such as ground squirrels
food and water
vehicles of indirect transmission of disease. Both are sources of bacterial, viral, and parasitic diseases. Food-borne diseases are acquired by consumption of contaminated food or water and include food-borne intoxications and food-borne infections. Food-borne intoxications are caused by toxins produced by certain bacteria that may contaminate food, such as Staphylococcus aureus, Clostridium spp., and Vibrio spp
parasitic diseases
transmitted through food and water. Giardia is a protozoan that causes gastrointestinal disease in people; giardiasis can be quite serious in immunosuppressed individuals. Giardia is most often transmitted from person to person, it is also a source of water-borne outbreaks when people use mountain streams as community water sources without proper filtration techniques or drink the water during outdoor activities. Beavers and other domestic animals are reservoirs
Cryptosporidiosis (4.2 to 5.4 µm (microns))
attle and other domestic animals are reservoirs. Proper water filtration and treatment are essential in preventing water-borne diseases
animal bites
source of infections, trauma, and even zoonotic disease
Why was OSHA developed?
to ensure employee safety
How do you clean an animal bite?
Clean wound with Betadine scrub for 5 minutes; rinse well
biohazards
blood, glass, needles (discarded in a sharps container)
Chemotherapy Agents
Personal protection equipment, CSTD (closed system transfer device), Animal bedding, Spill kit
What is ethylene oxide?
Ethylene oxide (EtO) is a flammable, colorless gas at
temperatures above 51.3 ºF (10.7 ºC) that smells like
ether at toxic levels
Glutaraldehyde is used for?
to disinfect medical and dental equipment
What is formaldehyde used for?
used to fix tissue samples, carcinogen
NFPA Label
National fire protection association. The higher the number (max. is 4), the greater the hazard (check msds).
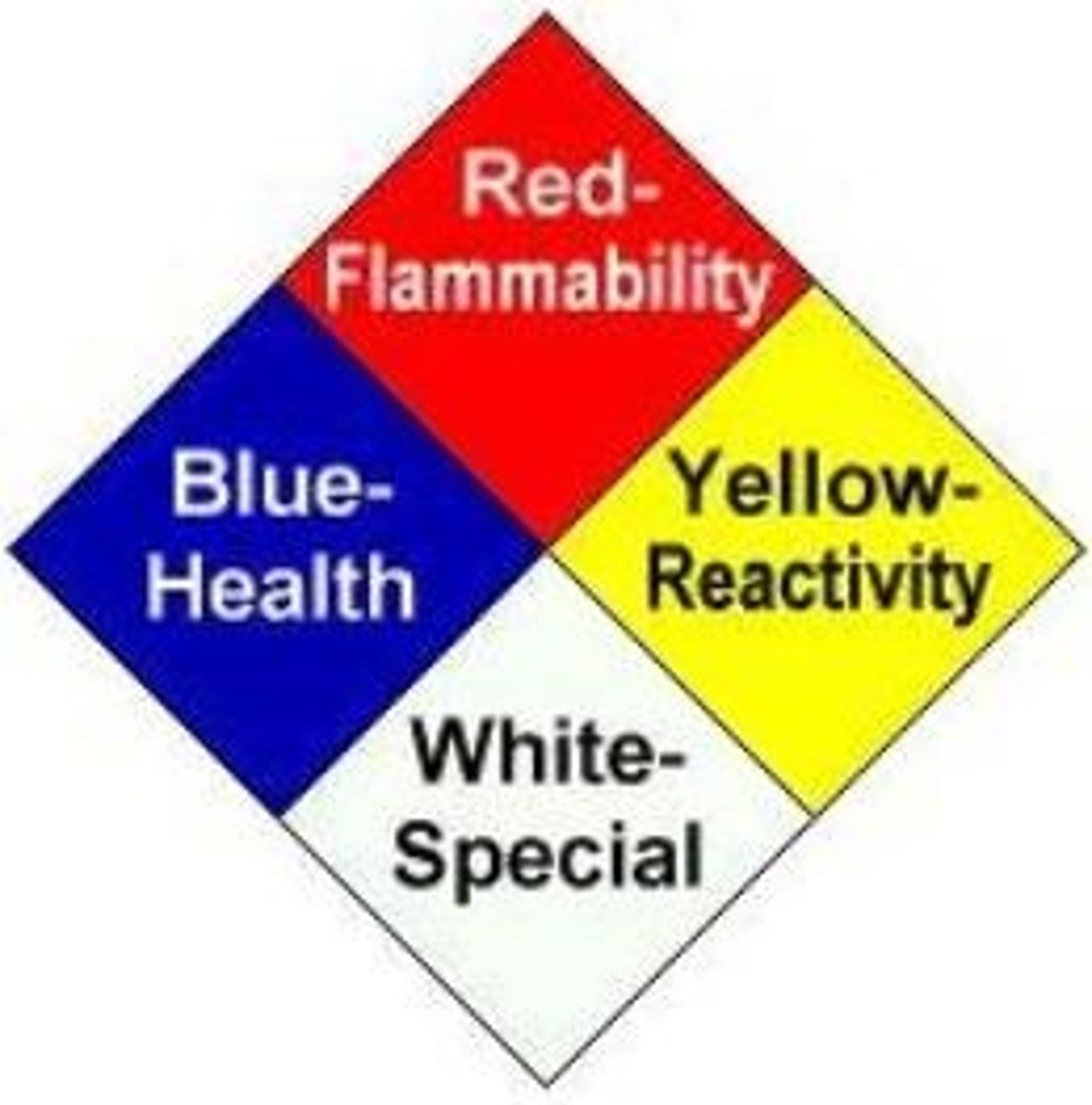
Red section of NFPA
Flammability
Blue section of NFPA
health hazard
Yellow section of NFPA
Reactivity
White section of NFPA
other hazard information
Five levels of hazard potential
zero (0) used to indicate no special hazards and
four (4) for severe or extreme hazard potential.
Health Hazards (NFPA)
based on the form or condition of the material, as well as its inherent properties
Health Hazards ratings (NFPA)
A rating of 1 is for slightly hazardous (toxic) material which require only minimal protection in addition to normal work clothing to work with safely
A rating of 2 is for moderately toxic or hazardous material which require additional PPE or equipment in addition to that required for less toxic material. Consult the MSDS for specific health hazard and proper PPE to use with this material.
A rating of 3 or 4 is for highly to extremely toxic (deadly) material (and any carcinogen, mutagen, or teratogen). These materials will require specialized equipment beyond that required for moderately toxic material. You must consult the MSDS and/or other safety information to determine the hazard (acute or chronic) and the proper PPE and engineering controls to safely use of this material
What is the most common reason for fire?
overloaded electrical circuits
Right to know law
equires that you be informed about all chemicals you may be exposed to while doing your job. The Right to Know Law also requires you to wear all safety equipment that is prescribed by the manufacturer when handling a chemical. The safety equipment must be provided by the employer at no cost to you. It is not optional; you must wear what is prescribed
Secondary Container Labeling
Mandated by OSHA, all materials dispensed out of the primary storage unit must be properly identified with MSDS information to include: health hazard, flammability, reactivity, and personal protection