Metabolic Disorders in New Born Screening (Midterm Topic)
• 31 core conditions
• 25 secondary target conditions
• Procedure: tandem mass spectrophotometry
(MS/MS)
• Capable of screening infant blood specimens
for specific substances
- Congenital hypothyroidism (CH)
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH)
- Phenylketonuria (PKU)
- Glucose-6- phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD)
deficiency
- Galactosemia (GAL)
- Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD)
Newborn Screening Tests Summary
tandem mass spectrophotometry
(MS/MS)
What is the spectrophotometry procedure for newborn screening?
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
• 31 core conditions
• 25 secondary target conditions
• Procedure: tandem mass spectrophotometry
(MS/MS)
• Capable of screening infant blood specimens
for specific substances
- Congenital hypothyroidism (CH)
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH)
- Phenylketonuria (PKU)
- Glucose-6- phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD)
deficiency
- Galactosemia (GAL)
- Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD)
Newborn Screening Tests Summary
tandem mass spectrophotometry
(MS/MS)
What is the spectrophotometry procedure for newborn screening?
31 conditions
How many core conditions in NBS?
25 secondary target conditions
How many secondary target conditions?
disruption of normal metabolic PW
What is the cause of Overflow type?
Override the reabsorption ability of renal tubules
• Not reabsorbed from the filtrate
• Nonmetabolized substances in overflow type?
malfunctions in the tubular reabsorption mechanism
Cause of renal disorder?
Failure to inherit gene-producing enzymes
Cause of Inborn error of metabolism?
-Phenylketonuria
-Tyrosinemia
-Alkaptonuria
-Maple syrup urine disease
-Organic acidemias
-Cystinosis
-Porphyria
-Mucopolysaccharidoses
-Galctosemia
-Lesch - Nyhan disease
What are the Overflow inherited disorders? (examples)
-Infantile tyrosinemia
-Melanuria
-Indicanuria
-5-Hydroxyindoleacetic acid
-Porphyria
What are the metabolic disorders? (examples)
Hartnup disease
Cystinuria
What are the renal disorders? (examples)
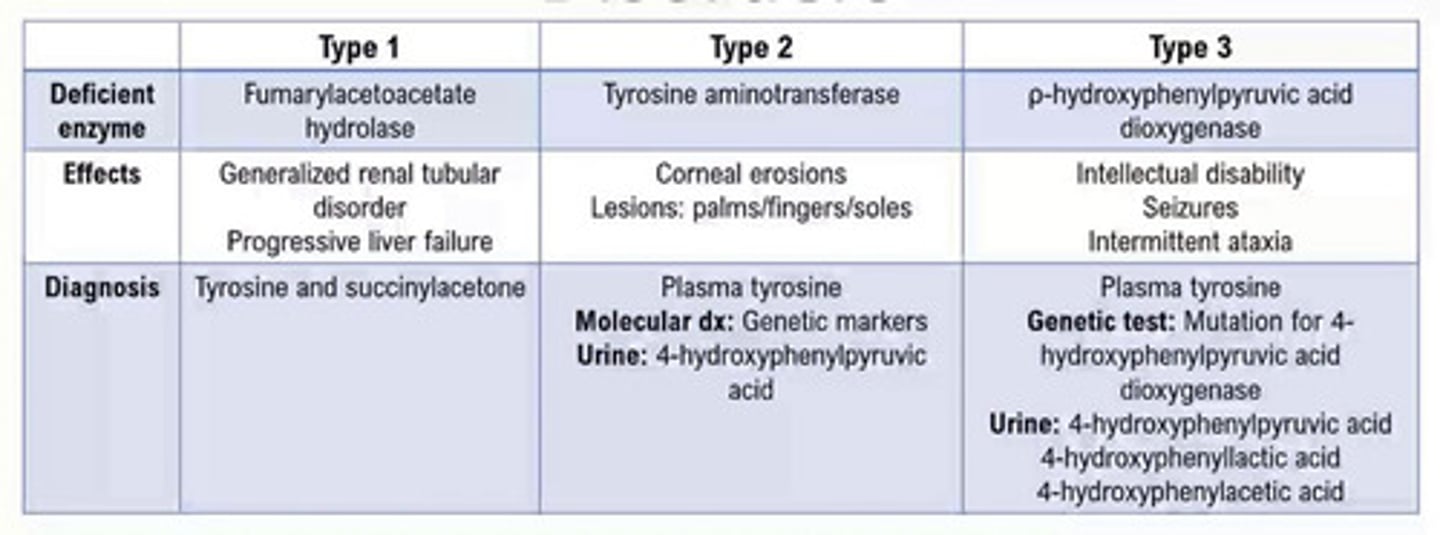
Phenylalanine and tyrosine metabolic pathway

Tyrosyluria
What disorder?
Accumulation of excess tyrosine in the plasma (tyrosinemia)
• Inherited or metabolic defects
p-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid
• p-hydroxyphenyllactic acid
Degradation products of tyrosine
Transitory tyosinemia
Most frequently seen in premature infants
• Underdevelopment of liver function
Acquired severe liver disease
Produces tyrosyluria
• Urinary crystals: Leucine and Tyrosine
Leucine and Tyrosine
Urinary crystals in acquired severe liver disease?
Nitroso-naphthol test
Test for tyrosyluria?
5 - Hydroxyindoleacetic Acid (5 - HIAA)
Degradation product of serotonin
• Used in the stimulation of muscles
•From tryptophan by the argentaffin cells
Elevated urinary 5 - HIAA
what is the cause of Carcinoid tumors (argentaffin cells)?
2-8 mg
Normal daily excretion of urinary 5 - HIAA?
> 25mg/24 h
Argentaffin cell tumor what amount?
Silver nitroprusside test
testing for tryptophan disorder?
HPLC and Fluorescence detection
plasma method for tryptophan testing?
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Most well-known of the aminoacidurias
• 1 of every 10,000 to 20,000 births
Norway, 1924
Ivan Folling identified PKU in (country, year?)
mousy odor
Urine odor of PKU?
Failure to inherit the gene producing phenylalanine hydroxylase
cause of PKU?
• Blood: increased levels of phenylalanine
• Excretion of urinary pheny|pyruvic acid: 2 to 6 weeks
• Can be detected as early as 4 hours after birth
• Testing: 24 to 48 hours after birth
screening of PKU?
Test: Ferric chloride tube test
testing for PKU?
Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD)
Accumulation of one or more early A degradation products
• Inborn error of metabolism
Leucine/Isoleucine/Valine
Amino acid disorder in MSUD?
a -ketoisovaleric
a-ketoisocaproic
a -keto-B-methylvaleric
keto acids in MSUD?
maple syrup
odor of MSUD?
2, 4 - DNPH Test for MSUD
• Plasma AA (PAA)
test for MSUD?
Alkaptonuria
1 of the 6 original IEM (Garrod in 1902)
"alkali lover"
3rd major defect in the phenylalanine-tyrosine PW
Brown-stained/black-stained cloth diapers/reddish-
stained disposable diapers
failure to inherit the gene-producing
homogentisic acid oxidase
cause of alkaptonuria?
accumulates in the blood,
tissues, and urine
homogentisic acid accumulates where?
• Ferric chloride
• Clinitest
GC-MS
Homogentisic acid test
testing for alkaptunoria?
Alkaptonuria
Melanuria
Melanuria
2nd metabolic PW for tyrosine
• Melanin
• Thyroxine
• Epinephrine
• Protein
• Tyrosine sulfate
• Dark urine
• Proliferation of melanocytes
• Malignant melanoma
• 5, 6 - dihydroxyindole
Increased melanin in urine causes the following?
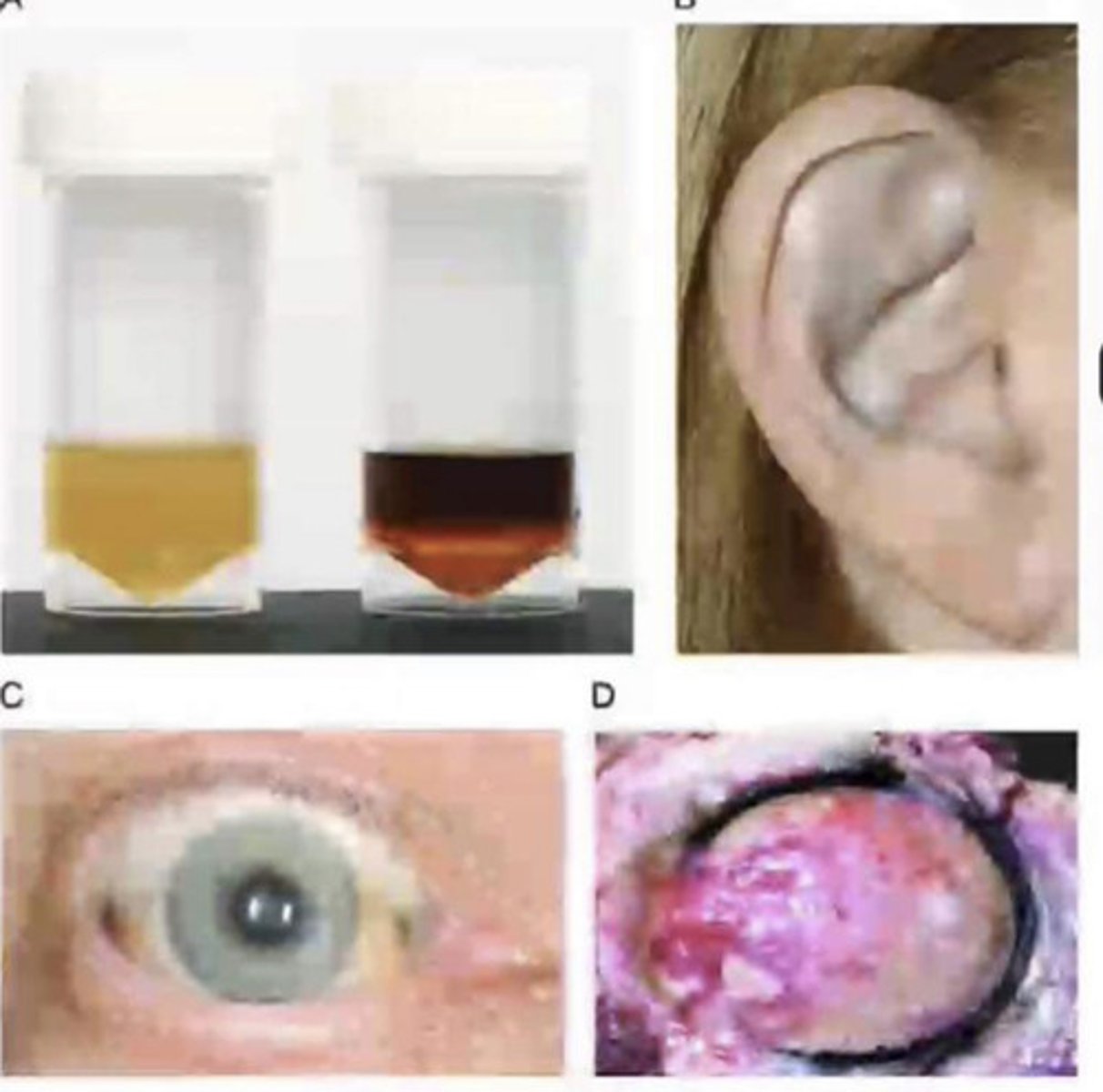
indicanuria
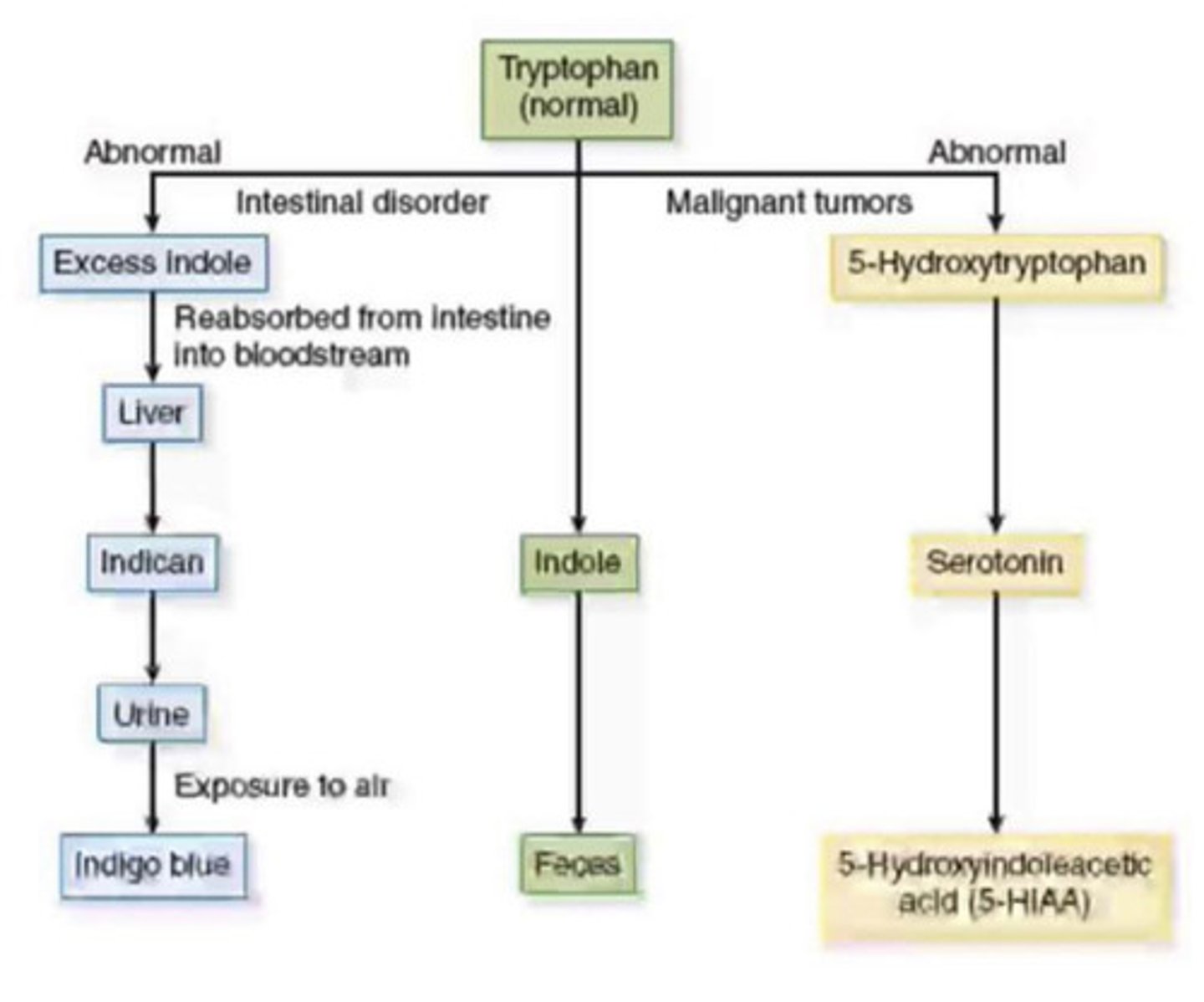
indicanuria
Increased amounts of tryptophan what disease?
Indole:
reabsorbed and circulated becomes indican?
indicanuria
colorless to indigo blue, what disease?
Hartnup disease
Blue diaper syndrome
• Affects the following:
• Intestinal reabsorption of tryptophan
• Renal tubular absorption of other amino
acids (generalized aminoaciduria)
isovaleric acidemia
propionic acidemia and methylmalonic acidemia
organic acidemias?
Isovaleric acidemia
Urine odor: sweaty feet
• Accumulation of isovalerylglycine: deficiency in isovaleryl coenzyme A
• Propionic acidemia and Methylmalonic acidemia
Errors in the metabolic PW converting the following to succinyl COA
• Isoleucine
• Valine
• Threonine
• Methionine
Propionic acid
the immediate precursor to methylmalonic acid
3 types of phenylalanine-tyrosine disorders
Hurler syndrome
Effect: Abnormal skeletal structure
Intellectual disability
Affects cornea
notes: fatal during childhood
what disease? (syndrome)
Acid-albumin turbidity test
• CAB turbidity test
• Metachromatic staining spot test
tests for mucopolysaccharide disorders?
porphyrin disorders

porphyrias
Inherited or acquired
• Porphyrinuria: red or port wine urine color
Ehrlich reaction
• Fluorescent technique
tests for porphyrin disorders?
hunter syndrome
cause: Abnormal skeletal structure
Intellectual disability
notes: Sex-linked recessive
Rarely seen in females
Fatal during childhood*
what disease?
sanfilippo syndrome
effects: Intellectual disability
notes: Tx: Bone marrow transplant**
Gene replacement therapy**
what disease?
- Defect in methionine metabolism
-Test for homocysteine is included in the NBS program.
Homocystinuria Cause:
Homocystinuria
Effects:
- Failure to thrive
- Cataracts
- Intellectual disability
- Thromboembolic problems
- Stroke
- Death
Increased urinary homocysteine
• (+) Cyanide - nitroprusside test
Additional test: Silver-nitroprusside
Only homocysteine will react, what additional test?
Cystinuria
Elevated amounts of cystine in the urine.
• Cause: the inability of the renal tubules to reabsorb cystine filtered by the
glomerulus.
• Amino acids: Cystine/Lysine/Arginine/Ornithine
Modes of inheritance:
• Reabsorption of all four amino acids is affected.
• Reabsorption of cystine and lysine is affected.
• Test: Cyanide
- Nitroprusside Test
types of cystinuria
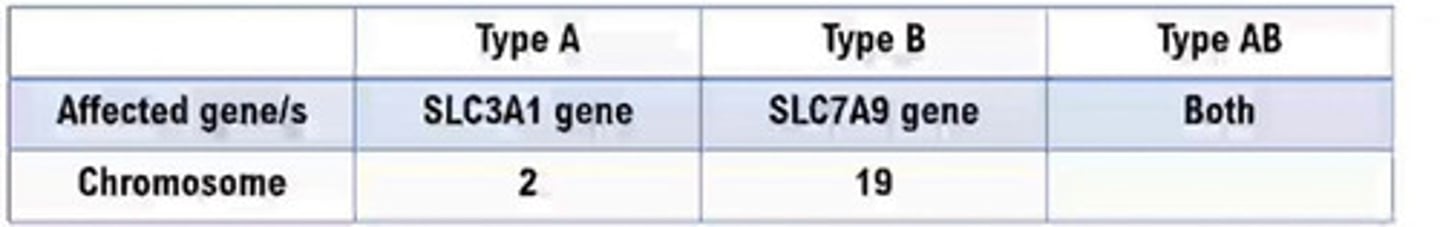
Cystinosis
Genuine inborn error of metabolism
• Cause: defect in the lysosomal membranes
• PCT: affected by the cystine deposits
• Nephropathic cystinosis
• Infantile
• Late-onset
• Intermediate cystinosis
• Nonnephropathic cystinosis
• Types of Cystinosis:
Molecular testing
• Test for Cystinosis
porphyrin disorder table
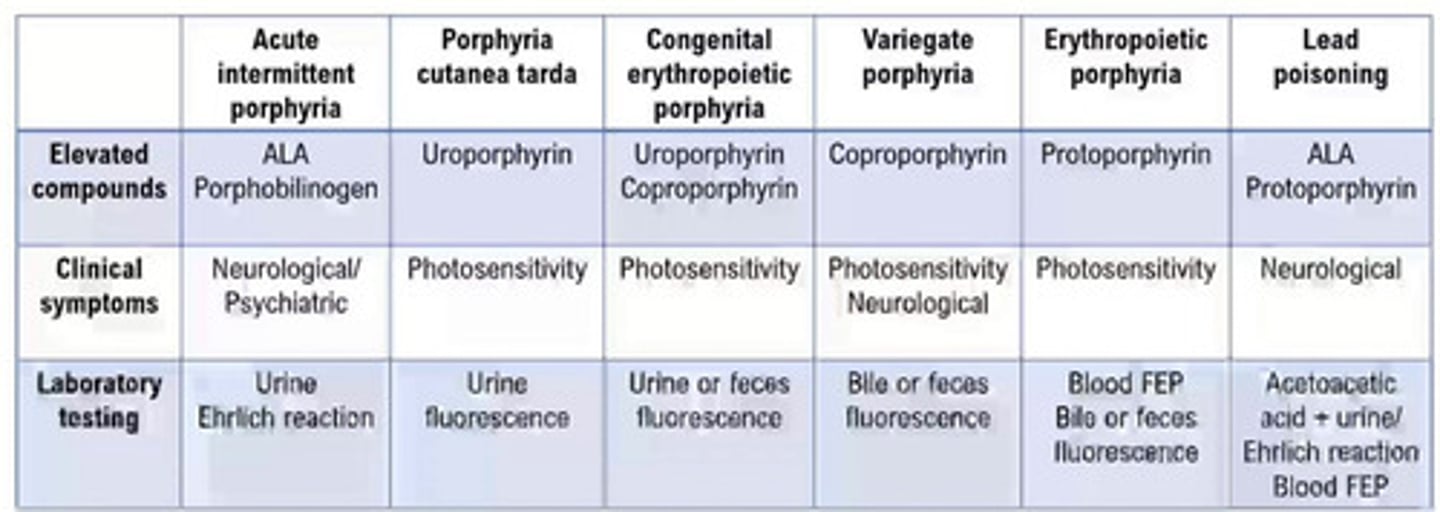
Porphyrin
intermediate compounds in the
production of heme.
Uroporphyrins
Coproporphyrins
Protoporphyrins
Three primary porphyrins:
Alpha-aminolevulinic acid (ALA)
• Porphobilinogen
Porphyrin precursors:
Blood
Bile
Feces
Urine
Specimens: for porphyrin
Mucopolysaccharides/Glycosaminoglycans(GAGs)
• Large compounds in the connective tissues
• Protein core with polysaccharide branches
• Products found in the urine:
• Dermatan sulfate
• Keratan sulfate
• Heparan sulfate
• Hurler syndrome
• Hunter syndrome
• Sanfilippo syndrome
• Mucopolysaccharidoses (MPSs) what syndromes?