3. History of European Colonization: Chapter 3: the seventy years war (1744-1814)
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
overview: 1. the seven years war - Europe - india - america 2. the napoleonic wars - british expansion - the decolonization of latin america 3. the white settler colonies - canada - australia and new zealand - white settler colonies in the 19th and 20th century
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
first part of the second Hundred Years’ War
Nine Years’ War (1688-97)
weakened the Netherlands
Spanish Succession War (1700-1713)
Britain gained Gibraltar & Minorca from Spain
Britain gained Acadia from France
Austrian Succession War (1740-1748)
france occupied Madras, but returns it to Britain
=> wars fought both in Europe and colonies
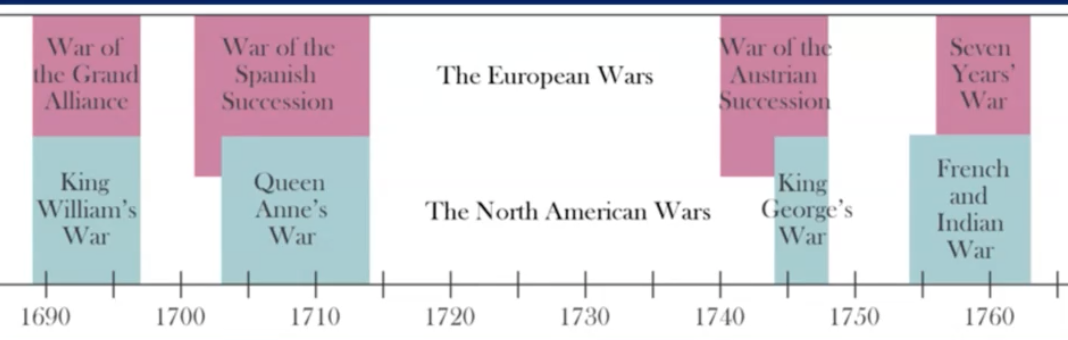
seventy years’ war
second part 100 years war
seven year’s war (1756-1763)
europe
india
america
the american independence war (1775-1783)
the napoleonic wars (1803-1815)
british expansion
decolonization of latin america
the white settler colonies
canada
australia and new zealand
white settler colonies in the 19th and 20th century
seven years’ war in Europe (1756-1763)
the great change of partners
century-old enemies France and Austria (and Russia, changes camp during war)
vs Britain (largest navy) and Prussia (largest land force)
outcome
900 000 - 1 400 000 deaths: first ‘world war’ (fought on different continents and massive impact on world)
change in the balance of power
the seven years’ war in india (britain)
calcutta
british fortify calcutta against frensh
after the experience with madras in 1746-1748
bengal nawab (ruler) conquers calcutta
robert clive (clive of india) reconquers calcutta (jan 1757)
bengal
clive supports new and dependent nawab
defeats the old nawab at plassey (june 1757)
defeats an indian coalition near buxar 1764
==> british conquest of bengal
other powers in india
french
1764 chandarnagar and pondichéry demilitarized (forced by brits to avoid repetition of what happened in 1740s)
moghuls (dynasty ruled india at the time)
ex jahangir,…
Taj Mahal (mausuleum to belated queen)
second half 16th century - 17th century
decline after aurangzeb (+1707) = pursued more rigid religious policy (muslim) => Moghul empire declined but still kept on existing until 19th century
saw europeans as interesting trade partners, looked down on their producs
delhi sacked by persians is 1739 (nader shah = napoleon of persia)
delhi sacked by afghans in 1748-61 (ahmad shah durrani = founding father modern afghanistan)
maratha empire
hindu empire in central india
defeated by afghans (battle of panipat 1761)
afghans: return to kabul after 1761
same period as 7 years’ war = britain was able to conquer because other powers had been weakened in india
seven years’ war in america
1754-1763: french and indian war
in particular: the control of the ohio country
different approach
france: let the colonies fight for themselves
—> french colonies lacked naval support
britain: avoid military commitment on the European continent (french were stronger there)
—> british colonies had numerical superiority
british victories:
1758: louisbourg
1759: Québec
1760: montréal
outcome
france loses Nouvelle france
choice between carribean and new france
everything east of mississipi river to britain
west of mississipi to spain
compensation for the loss of florida to britain
future developments
florida again spanish in 1783
louisiana and florida in 1800 to france
1803: napoleon sells louisiana to the United states
discussion about florida; spain cedes in 1819-1821
from BNA to USA
resentment in BNA
london wants compensation after Seven Years’ War
protection against france & native americans
BNA pays fewer taxes than carribean colonies
BNA reply: “no taxation without representation’
protest
tea act (1773): withdrawn after boston tea party
1774: first continental congress (philadelphia)
summer of 1775: battle of bunker hill
the independence war (1776-1783)
declaration of independence on july 4, 1776
Britain and Napoleon
several conflicts between britain and france
Egypt: shortcut to India (strategically and economically very important
French victory against Mamluks (Pyramids 21 july 1798)
british victory against french (nile 1-3 august 1798)
syrian expedition of france failed
oceans
trafalgar (21 october 1805)
metropoles occupied by france (either annexed by france or turned into public states, made his brothers kings)
—> british conquests of new colonies (napoleon wasnt interested in the colonies)
pain eg trinidad (1797-1802)
netherlands eg cape colony and ceylon (permanent)
why british expansion in india?
protection of trade and influence
french threat, more imagined than real
british conquest india
1792 & 1799: mysore (tipu sultan)
1801: Awadh/Oudh
1803: delhi (moghuls)
1802ff & 1818: marathas & rajputs
1816: treaty with nepal gurkhas
—> conquests went in steps
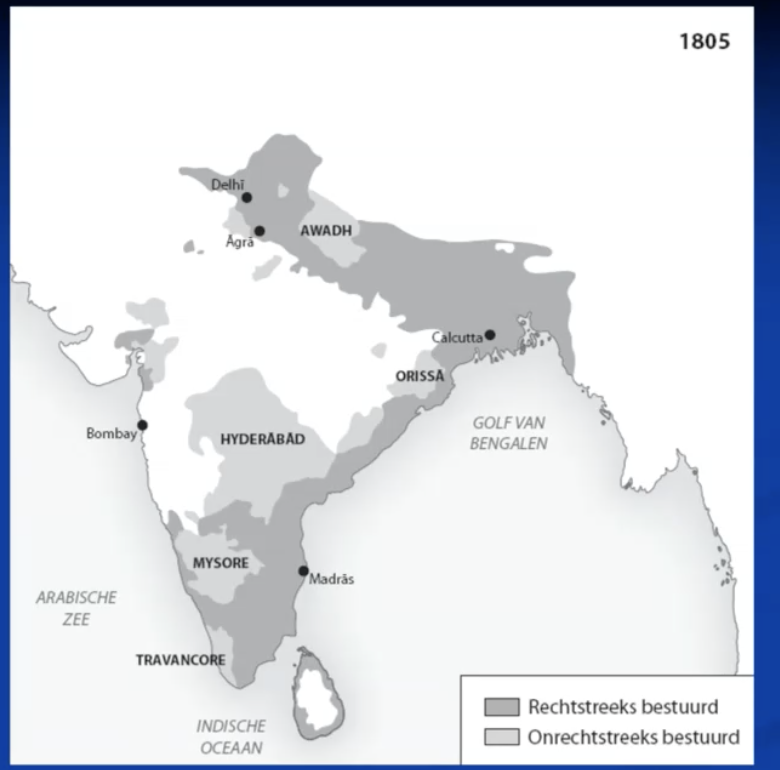
reasons for british succes
indian discord (castes, religions, ethnicities,…)
british technological and military superiority
overview decolonization latin america
first: french colony
saint domingue (haiti)
—> slaves’ insurrection
then: spanish colonies
—> related to napoleonic wars in europe
finally: portuguese colony
brazil (last)
not: guyana & caribbean (decolonization not complete)
—> deterrence effect from haiti (other colonies shocked => preferred to remain colonies)
==> “first wave of decolonization”
hispaniola
haiti
1492-1697 spanish
1697-1804 French
saint-domingue: richest colony in the world
insurrection under Toussaint L’Ouverture (1791-1803) = only successful slave insurrection in world history
Napoleon intervenes => Jean-Jacques Dessalines takes over rule (first emperor independent haiti)
1804 independence
dominican republic
for a while spanish
french
haitian
stereotype explanations haiti’s poverty
nature: mountains and rainfall
—> nonsense: in 18th century haiti was richest colony of the world
natural disasters (earthquake 2010 = buildings in ruins, people living in the streets)
—> less resistant but not main explanation
black emperors
—> “bad rulers” = “unable to create wealth and protect people”, racism, “incapable”
voodoo
—> racist stereotipicization = different religions in haiti turned into an image of horror and “bad religion” because Europeans were frustrated
==> to erase western role in poverty (deliberate amnesia)
french role haiti’s poverty
deforrestation and erosion under the french = exhausted soil of haiti (on top of slavery exploitation)
haiti’s debts to france after 1825 (to compensate for loss of colony) ==> by 1898 half of haiti’s government budget went to paying france and french banks, by 1914 that proportion climbed to 80 percent
haiti’s situation 19th and 20th century
political: international isolation & military priority (afraid of invasion that could end independence) => a lot of huge fortresses can be found in haiti even though they have never had to be used
social: new elite after disappearance of the white
economic: decline of plantation economy => less income
foreign interference in haiti 20th century
1915-1935: US occupation (confirming trauma of foreign treath
US support of dictators in the cold war and beyond papa doc and baby doc: françois & jean-claude duvalier = worst dictators during cold war, fully supported by US)
neoliberal measures imposed by the IMF (Jean-Bertrand Aristide = good candidate for president <=> only got American and international support if he accepted neoliberal reforms that served Haiti but also US and western world ex basically banning import tariffs)
overview of decolonization Latin america
french colony
saint domingue (haiti)
—> slaves’ insurrection
spanish colonies
related to napoleonic wars in europe
portuguese colony
brazil
<=> not: guyana & caribbean
deterrence effect from haiti
spanish colonies (south america) decolonization
periphery
new granada: simon bolivar (north)
la plata: josé san martin (south)
center
lima: san martin and bolivar
new spain
general observations decolonization spanish colonies
disintegration independent states
—> great-colombia 1830 (colombia venezuela and exuador
—> peru falls apart
—> federal republic of central-ameri
violence
between european powers
between europeans and colonials
between colonials
interconnection
continuity
new granada independence
1810: simon bolivar starts armed struggle
1813: caracas (venezuela)
1814: bogota (colombia)
1819: republic of great colombia
1830: disintegration of great-colombia
colombia
venezuala
ecuador
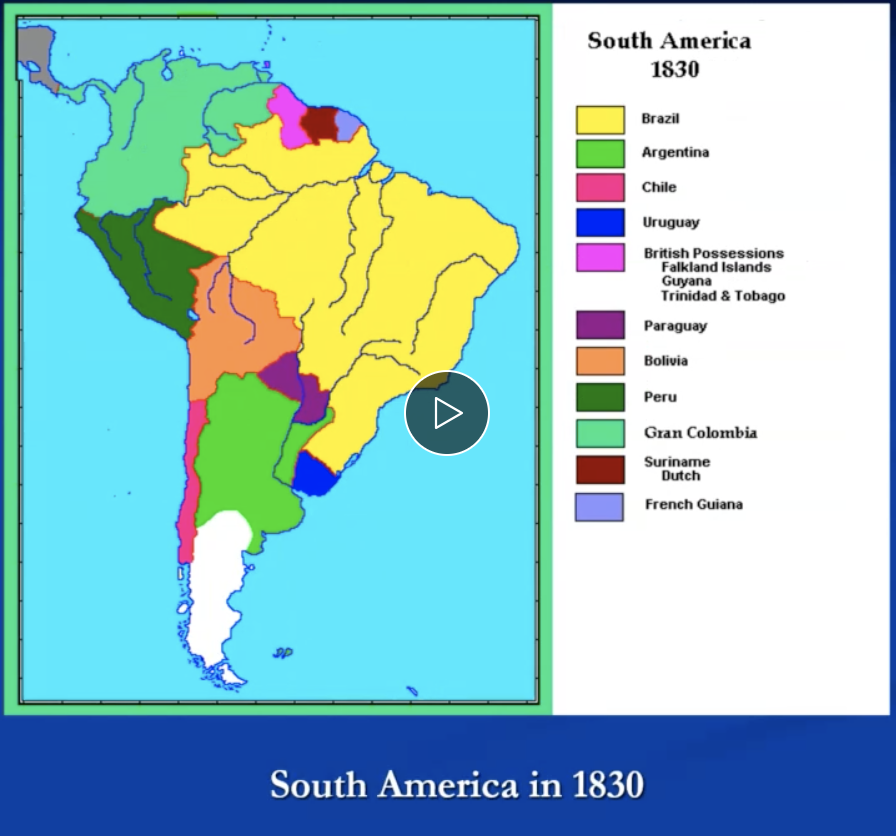
la plata and lima independence
1810: provisional junta in buenos aires
1816: declaration of independent argentina
1817: josé de san martin crosses andes
1818: conquers chile with bernardo O’higgins (irish)
1821: conquers lima
1822: meeting with bolivar behind closed doors (unclear what is established)
peru pesident inter alia
martin (1821-22)
bolivar (1824-27)
1825: republic bolivia
bolivar first president
new spain 2 parts (independence)
mexico
1810-1815: pro-napoleon insurrections
defeated by loyals to spanish throne
—> remained with spain (not for long)
1821: new spanish constitution (too liberal for elite in new spain)
conservative revolution
—> independence
federal republic of central-america (1823-1840)
disintegration due to
mexican interference
conflicts between conservatives and liberals
independence brazil
1808: portuguese king joao VI settles in Brazil
remains there after 1815
1821: joao returns to libon
restoration old balance between lisbon and brazil
dom pedro (son of joao) regent in brazil
frustration in brazil
dom pedro supports nationalists
1822: brazilian independence under emperor pedro
—> independence under House of Braganza
violence during decolonization of latin amerca
between european powers, especially France-britain
ex carribean (1793-96) and egypt (1798-1801
between europeans and colonials
in 9/20 independent countries
colonials often supported by other europeans
la fayette (french officer) in US
britain supports haiti and spanish colonies
between colonials
loyalists (to the british throne) and revolutionaries in the US
slave insurrection in haiti
most quiet country: Brazil
interconnection events decolonization america
observation and participation in BNA/US
dominican (haitian) mulattos in french army BNA
south american revolutionaries
direct influence
US support to haitian insurrection in 1790s
haitian asylum to bolivar (2X)
reverse consequences (independence war strengthens ties colony and metropole
canadian nation grows out of anti-revolutionarism
carribean landowners prefer colonial status-quo to repetition of haiti
continuity between colonial era and decolonial era america
social:
elite: white and affluent minority
exceptions: US (majority) and haiti (black)
US and Brazil maintain slavery (only abolished in 19th century)
political
empires (just like metropoles in Europe): haiti, brazil, mexico
exception: constitutional confederation in the US
other confederations fail
economic
produced goods, free trade,…
the white settler colonies
canada
australia and New Zealand
white settler colonies in the 19th and 20th century
the US and canada
british since 1764 but large french population
US (revolutionaries wanted to include canada in independence claims) attempts to conquer north (1775-1777)
took montreal and attacked quebec
not successful in mobilizing french population (thought they were better of under British)
—> britain had respected language, religion and property
continuing hostility (british colonies in canada and newly independent US)
britain (canada) supported native americans (enemies US)
britain prevented trade US-france
new failed invasion by US in 1812-1815 War (britain was involved in napoleonic wars)
developments in canada in end 18th century, first decades of 19th century
immigration of 40.000 to 60.000 loyalists
18th c: majority of inhabitants of french origin
mid 19th century: majority of british origin
constitutional act (1791)
to accommodate english-speaking settlers
division of the province of quebec (still today)
canada west/upper canada (ontario): english law (named after river)
canada east/lower canada (quebec): french law
durham report (1838)
rebellion of 1837 in the canadas (BNA)
house of assembly neglected by london governor
like US two generations earlier (“no taxation without representation”)
lord durham (experienced politician) detects two problems
ethnic conflict between french and english
1840: act of union (united province of canada)
encouraged immigraiton from britain to canada (countering the french speaking majority)
people’s representation and control
power and control to legislative assembly (remained british colony)
1848: responsible government in nova scotia
==> everything happens gradually —> success of canada?
responsible government in canada timeline (after durham report)
governments responsible to parliament rather than to monarch or the imperial government
1848: nova scotia
1849: province of canada
1851: prince edward island
1854: new brunswick
1855: newfoundland
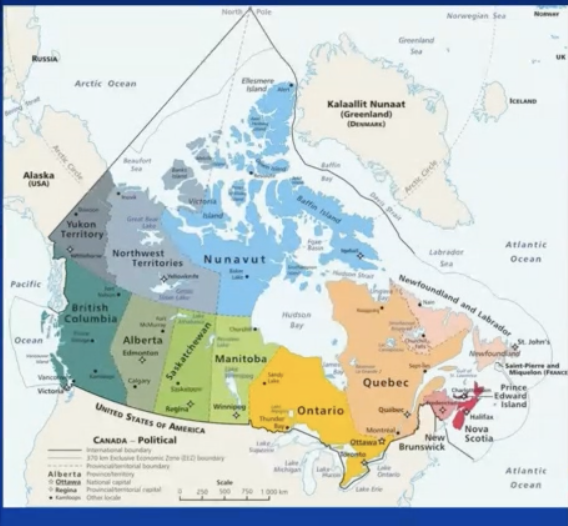
creation of dominion of canada
constitution act (1867
united province of canada (1840-) impracticable
three colonies formed into four provinces
ontario
quebec
new brunswick
nova scotia
canada: a federal dominion with own institutions
autonomous polity nominally under british sovereigbty
later addtions inter alia:
1871: british columbia
1873: prince edward island
1898: yukon
1905: saskatchewan & alberta
why exploration of the pacific
continuity with previous centuries (in 18th century)
also future centuries: africa (19th century)- poles (late 19th century, beginning 20th century) - space
culture
fascination with the far away and the savage
science (enlightenment)
myth of a large southern continent: terra australis
initially unable to travel longer distances due to scurvy => 1753: a treatise of the scurvy (vitamin C)
political
great britain vs Dutch cape of good hope
france: loss of footholds in india and north america
early voyages in the pacific in 18th century
Easter island
Strait between asia & america: Vitus Bering
falklands (britain)
tahiti
1766: first frenchman who circumnavigated the globe
George vancouver charted North america’s northwestern pacific coast regions
Matthew flinders: brit circumnavigation of australia (gave it name instead of new holland)
the voyages of james cook
1768-1771
mapped new zealand (circumnavigated)
landed at botany bay and claims land for britain (today: sydney) = kickstart british colonization of canada
1772-1775
crossed antarctic circle and nearly encountered mainland antarctica
1776-1779
again in pacific => more north
hawaii and coastline california-alaska
killed by hawaii locals on return
creation of australia
need for new penal colony
BNA: 40.000 convicts by 1777 (after british defeat in american independence war they needed new prison)
1787: first ships with criminals to sydney
26 january 1788: establishment of new penal colony
australia’s national day
convicts liberated after some years
only 1/14 returns home, rest starts new life
1828: for first time more free people than convicts
1868: last convicts’ transportation
==> “a nation of shoplifters”
australian society
white colony
procreation (eight months on sea)
steep decline of population of 350.000 aboriginals
disease, resettlement, cultural disintegration
tasmania: regulated genocide (diseases deliberately introduced)
economic development
land acquisitions from aboriginals
urban development (governor lachlan macquarie “founding father of australia”) => created sydney
sheep and gold
territorial expansion australia
initially (1788): New South Wales
eventually: six colonies
inter alia
van diemen’s land (tasmania): 1803 settled, 1825 colony
1829: britain claims western part of australia
1859: queensland
unification
1901: commonwealth of australia
1908-1927: construction of canberra (capital territory)
growing autonomy
canada: responsible government and dominion
New zealand timeline
1839: new zealand company
promotion of settlement and trade
1840: treaty of waitangi with maori chiefs
new zealand as bi-cultural society but
differences between english and maori versions
ignored by settlers and courts
maori wars 1845-1847 & 1860-1872
maori population:
1841: 70000-90000 vs 2000 europeans
1896: 42000 vs 701000 europeans
pacific colonies
tahiti
1797: british missionaries
1842: french military ship annexes island
new caledonia
annexed for france in 1853
major prison colony (10500 convicts in 1901)
major settlers’ colony (54000 french in 1983
new guinea: netherlands, brits and german (kaiser wilhelmsland)
…
migration in white settler colonies
1500-1783
1,4 million European migrants to the new world
1815-1914
22,6 million people left the british isles
62% to the US
mainly Irish
1918-
white australia policy (1901-1949/73) = white people more easily allowed in Australia
1922: canada attracts migrants (empire settlement act) = especially farmers, agriculturalists, bio-engineers,…
1924: immigration quotas in the US
responsible government white settler colonies
governments are responsible to parliament rather than to the monarch or the imperial government
1848-1855: canada
other white settler colonies
1855: victoria
1856: new south wales, new zealand, south australia, tasmania
1872: cape colony
1890: western australia
1893: natal
1906 transvaal
1907: orange river colony
semi-independent polities under british sovereignty (dominions)
1867: canada
1907: australia, new zealand and newfoundland
1910: south africa (also white settler colony)
1922: irish free state (until 1937)
autonomous communities within Empire 1926
1926: second balfour declaration: dominions ‘equal in status’ to metropoles so ± independence
—> first about palestine and jews
1931: statute of wistminster: legal status (dominions independent states with great ties to england)
commonwealth of nations
1949
now 56 member states
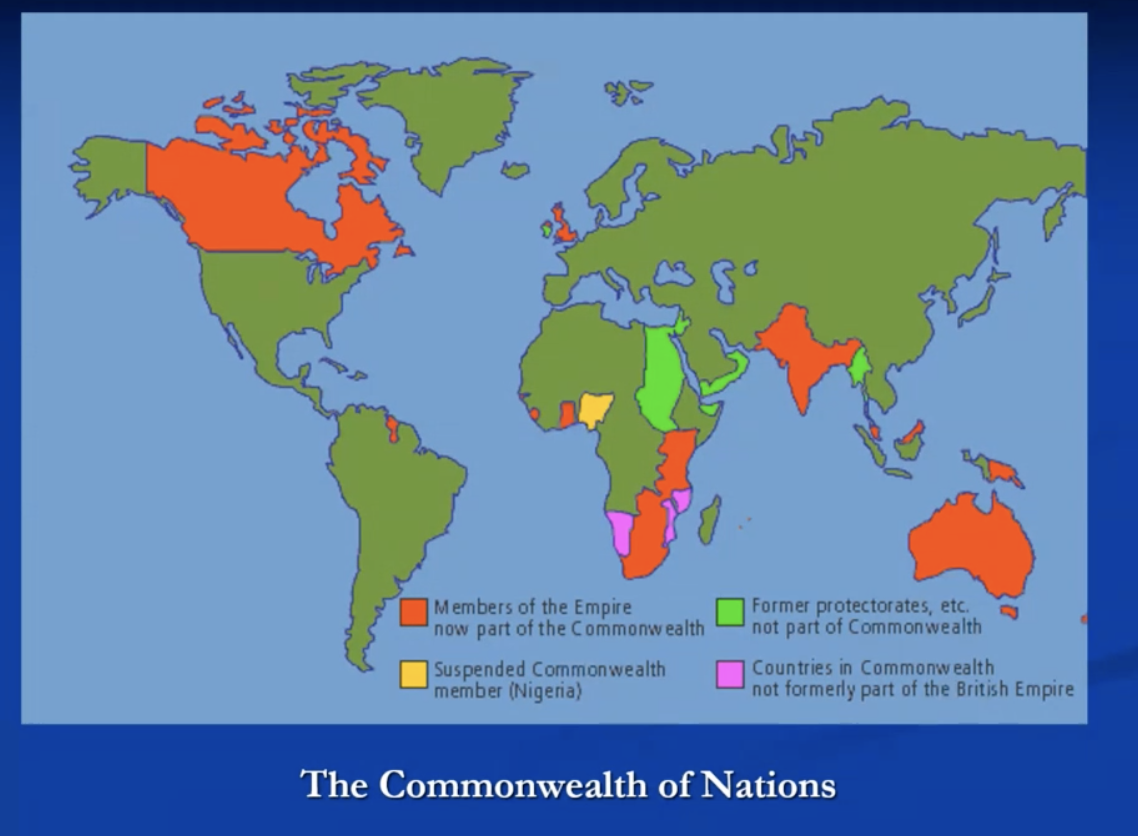
interconnectedness commonwealth
plethora of networks
family, business, education, press, sport,…
many shared experiences => common history, identity
wars & crises
progressive political culture (in white settler colonies)
responsible government & dominions
secret ballot: australia 1850s, 10 years before UK
female suffrage: New Zealand 1893, UK 1918
universal male suffrage: NZ 1893, 1U 1902, UK 1948
gradual erosion white settler colonies
collapse of the concept of imperial citizenship
1935: irish free state asserted its own citizenship
canada follows in 1946
Australia, New Zealand and South Africa follow 1948-49
leaving the commonwealth: Ireland 1949, South africa 1961
“Queen of Canada” 1952, “Queen of Australia” 1973
1965: maple leaf flag instead of union jack
1982: canadian constitution
present-day debates