Combined CELLS
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
Describe the structure of the nucleus
The nucelus contains genetic matieral called chromatin and histone proteins bound in the membrane. Contains one or more nucleoli. The nuclear enevelope surronds the nucleus which nuclear pores between. There is also nucleoplasm in the nucleus.
nucleus function
contain genetic material of a cell in the form of chromosomes, holds instruction for protein synthesis, essential for cell divison, controls cell activity
Nuclear enevelope
double membrane that controls material entry and exit
Nuclear pores
Nuclear pores allow molecules to move in and out. For example, mRNA moves out during protein synthesis
Nucleolus
makes ribosomes (manufactores ribosomal RNA and assembles the ribosomes)
Chromatin
made of protein and DNA. it controls cell activity
Diff between pro and euk
eukaryotic has membrane-bound organelles
prokaryotic is smaller
pro has smaller ribosomes
Ribosomes description and location
contains RNA and protein. it is found at cytoplasm or on rough er. Ri
ribosome dont make proteins. Thats not scientific.. ribsomes
are the site of protein synthesis
Describe two ways in which the structure of the mitochondria membrane is related to teh function of a mitochondrian
highly permable to allow movement of molecules
it is the site of ATP synthesis
contains electron carriers
mitochondria organelles functions and mitochondria itself
mitochondria is the site of aerobic respiration
cristae- foldings formed by extensions of inner membrane of mitochondria, has increased SA where resp processes occur.
double membrane- outer controls flow of materials in/out
matrix- site of krebs cycle, contains enzymes needed for aerobic respiration
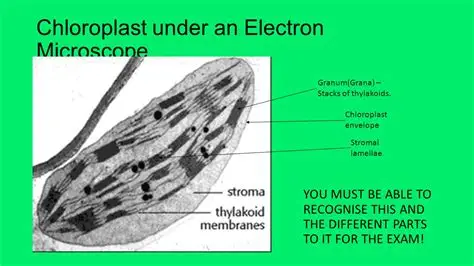
Chloroplast structures in depth
has compartmentalized sections to separate reactions of photosynthesis and maximize light absorption
granum contains chlorophyll pigments required for process of photosynthesis
large surface area formed by thylakoid stacks maximises space for enzymes and proteins required for photosynthesis
internal membranes form thylakoid sacs, which stack to make granum
lamella connect the thylakoid stacks, which allows for greater efficancy of photosynthesis
golgi apppartus function
forms lyosomes
transpors, modifies lipids
secretes carbs
adds non protein (carbs) to form glycoprotein
lyosome function
digests worn out organelles
breaks down dead cell - autolysis
release tehir enzymes outside of cell (exocytosis)) in order to break down other cells
digests material that have been ingested by the cell
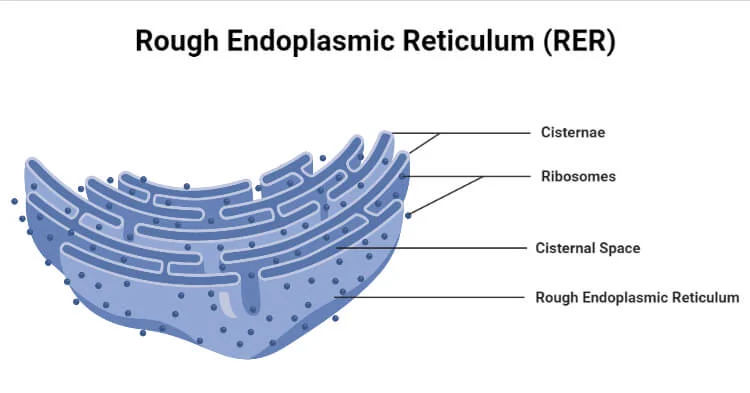
Endoplasmic Reticulum description
system of sheet like membranes throughout cytoplasm.
the two types of endoplasmic reticulum and their descriptions, and functions
ROUGH er- ribosomes at surface
processing of proteins for transport to the golgi apparatus
SMOOTH er - no ribosomes
stores and syntehsizes lipids
ALSO they both provide a structural skeleton to maintain cellular shape, provide a large SA for chemical reactions, provide a pathway for the transportation of materials thru cell
Rough ER and smooth draw it
rough smooth has the little tubes
All cells have an what?
Internal structure aka ULTRA STRUCTURE
Cell Vacuole (plants) description
contains cell sap made of weak solution of sugar and salts. has a surrounding membrane called a tonoplast.
Cell Wall description
Rigid structure that surrounds cells in plants and fungi.
Cell wall function
supports cell, prevents them from changing shape
Microvilli description
Finger like projections of epithililal cells. NOT present in all cells
Microvilli….
increases surface area for absorption in order to increase the rate of exchange of substances
Cilia
Hair like projections made from microtubules
Allows the movement of substances over cell surface
Flagella
in specialized cells - provides cell movement
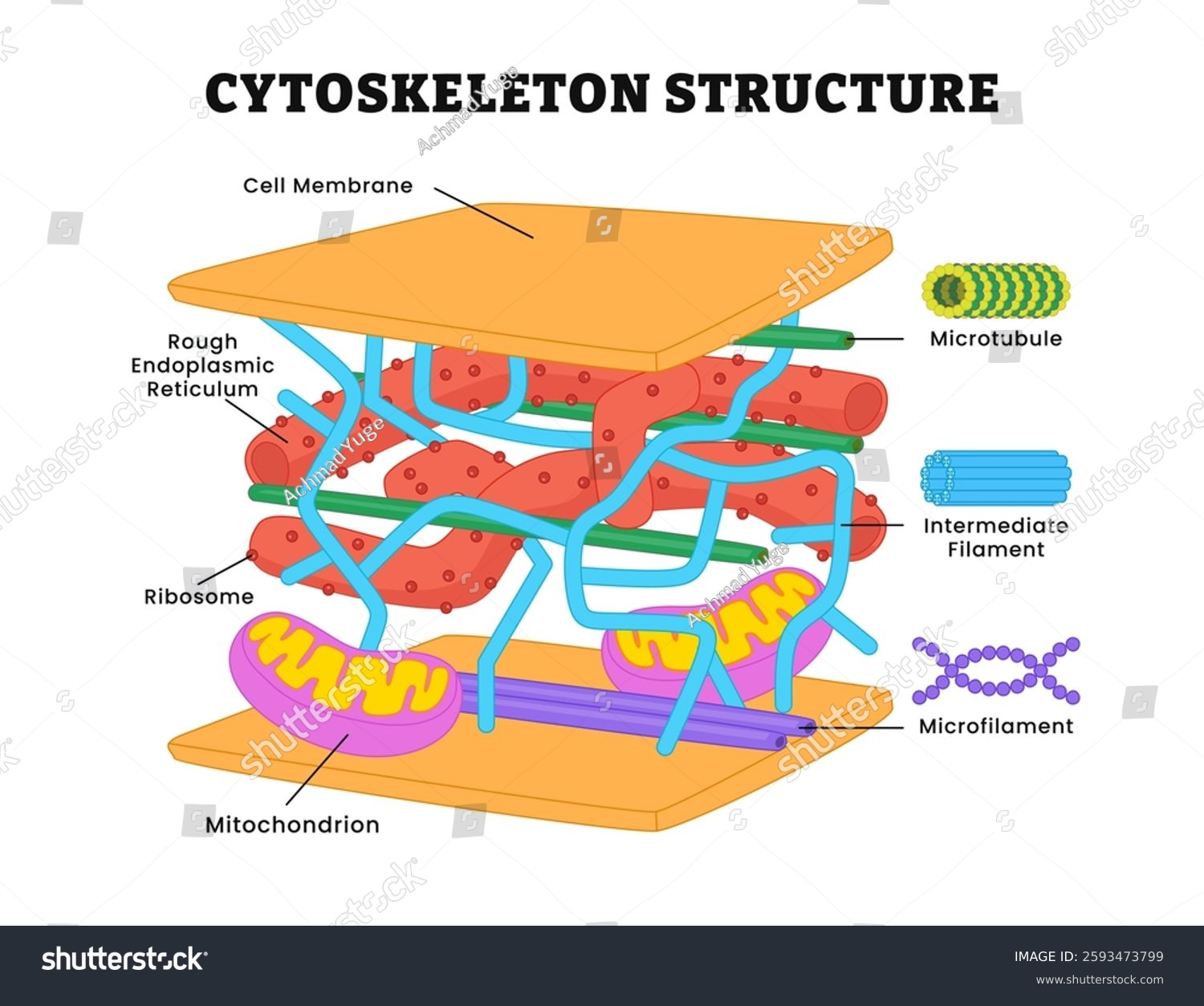
Cytoskeleton location
The cytoskeleton is located in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells, extending from the nucleus to the cell membrane
2 types of ribosomes and describe
80S type… eukaryotic cells
70S… prokaryotic, smaller
Cytoskeleton is made of up
2 main types of protein fibers -
micro filament
microtubules
Micro filaments
solid strands that are mostly made of the globular protein ACTIN.
Microfilaments form the dynamic cytoskeleton, which gives structural support to cells and links the interior of the cell with the surroundings to convey information about the external environment.
Microfilaments provide cell motility. e.g., Filopodia, Lamellipodia.
During mitosis, intracellular organelles are transported by motor proteins to the daughter cells along actin cables.
In muscle cells, actin filaments are aligned and myosin proteins generate forces on the filaments to support muscle contraction.
MICROTUBULES
HOLLOW strands made of mostly the protein tubulin
Microtubules determine the cell structure.
Microtubules form the spindle apparatus to divide the chromosome directly during cell division (mitosis).
Microtubules provide transport mechanism for vesicles containing essential materials to the rest of the cell.
They form a rigid internal core that is used by microtubule-associated motor proteins (MAPs) such as Kinesin and Dyenin to generate force and movement in motile structures such as cilia and flagella.
chloroplast description. and function
Uses Light energy to produce sugars for photosynthesis
IMPORTANCE of cytoskeleton
strengthing and support
intercellular movement
cell movement
Importance of cytoskeleton - strengthing and support
provides cell with mechanical strength that forms sort of a scaffolding that helps to maintain the shape of the cell)
supports organelles - keeps them in psoitojn
Importance of cytoskeleton - intercellular movement + example
aids in transport within cell by forming tracks where organelles can move along
examples include movements of chromosomes to opposite ends of cell during cell division.
Importance of cytoskeleton - cellular movement
enables for cell movement via cilia and flagella
an stack of thylakoids aka
an granum
draw new organelles
plasma mebrane functions
regulates movement of substances in out of cell
receptor molecules on it allow it to respond to chemicals like horomones
golgi appartus description
similar structure to smooth er but more compact
has vessicles
vessicles are
flattened stacks of membranes with rounded structures
Golgi Vesicle
small fluid filled sac at cytoplasm
surrounded by a membrane
made by golgi appartus
golgi vesicle func
stores lipids and proteins made by golgi app and transports them out of cell by cell surface membrane
How does the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) contribute to protein formation?
RER has ribosomes attached; it folds and processes proteins after translation and transports them to the Golgi apparatus.
Which organelle is responsible for producing vesicles that transport proteins and lipids?
The Golgi apparatus – it packages modified proteins and lipids into secretory vesicles.
How are proteins and lipids secreted from the cell?
Vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane
all cellular organisms havew
ribosomes
How do lysosomes contribute to specialised cell function?
Lysosomes contain hydrolytic enzymes for breaking down waste, pathogens, or worn-out organelles – especially important in phagocytes like macrophages.
w is an amino acid in the cytoplasm secreted as a protein? ***
1. Nucleus
The process begins in the cell's nucleus, which houses the organism's DNA, the blueprint for all proteins.
Transcription: An enzyme called RNA polymerase creates a copy of a specific gene from the DNA. This copy is a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule.
mRNA processing: Before it leaves the nucleus, the newly created mRNA is modified. Non-coding regions called introns are removed, and the remaining protein-coding regions, or exons, are spliced together.
Exit: The mature mRNA molecule then exits the nucleus through a nuclear pore and travels into the cytoplasm.
2. Ribosomes
These are the cell's protein-building machinery. Ribosomes can be found freely floating in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER).
Translation: In the cytoplasm, the ribosome binds to the mRNA molecule and reads the genetic code in three-nucleotide units called codons.
tRNA delivery: Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules carry specific amino acids that match the mRNA codons. The ribosome links these amino acids together in the correct sequence to form a polypeptide chain.
Protein destination: If the protein is for use within the cell's cytoplasm, it is synthesized by free-floating ribosomes. If the protein is destined for secretion, another organelle, or insertion into a membrane, the ribosome carrying the mRNA attaches to the RER.
3. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
The RER is a network of membranes connected to the outer nuclear membrane and studded with ribosomes, which give it a "rough" appearance.
Insertion: As a ribosome on the RER synthesizes a protein destined for export, the new polypeptide chain is threaded into the RER's internal space, known as the lumen.
Folding and modification: Inside the RER, the polypeptide begins to fold into its correct three-dimensional shape. This process is assisted by chaperone proteins. Other modifications, such as the addition of carbohydrate groups (glycosylation), can also occur here.
Vesicle transport: Once the protein is properly folded, it is packaged into a transport vesicle, a small, membrane-bound sac that buds off from the RER.
4. Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus, or Golgi complex, is a stack of flattened, membrane-bound sacs called cisternae.
Receiving: Transport vesicles from the RER fuse with the receiving (cis) face of the Golgi, releasing the proteins inside.
Further modification: As proteins move through the Golgi, they are further modified, sorted, and tagged with molecular "shipping labels" that determine their final destination.
Packaging and export: At the opposite (trans) face, the finished proteins are packaged into new vesicles. Some vesicles transport the protein to other organelles, while others move to the cell membrane for secretion via exocytosis.
5. Mitochondria
While not directly involved in protein synthesis, the mitochondria supply the energy necessary for this complex, multi-step process.
Smooth Er
storage of carbs and lipids
function of chloroplast
Uses light to produce sugars for photosynthesis
how is a plant cell adapted for photosynthesis
Chloroplast - absorbs light
Vacuole - pushes chloroplast to edge of the cell
Cell wall - thin and permeable cell wall absorbs the CO2 needed for photosyntehsis
identify- chloroplast parts
identify- mitochondrian (also… the cristae is the what
the cristae is the extensions of the inner membrane that have been folded.
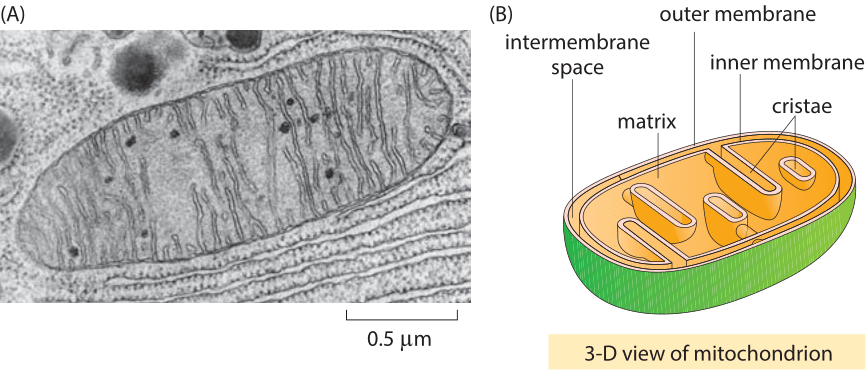
when there are metabollically active cells, not only does the number of ___ increase, but thenumber of ___ increases as well bc..
the number of mitochondria increase, as does the number of cristae bc cristae is where the respiratory processes occur due to its increased SA
Mucus is a
glycoprotein
Organelles involved in protein production
1- nucleosus manufacture ribosomes for protein synthesis
2- nucleus manufacture mRNA (needed by ribosomes to make proteins)
3- ribosomes in RER to make protein
4- RER processed proteins sent to vesicles
5- GOLGI APP modified proteins and sends them in vesicles fuse with plasma membrane for EXCYTOSIS
Be able to identify GOBLET cells
structures only in animal cells
Centrioles and Microvilli
Plasmodesmata
Plasmodesmata are tiny cytoplasmic bridges that connect adjacent plant cells, enabling the direct exchange of substances such as ions, sugars, hormones, and signaling molecules.
Plants can control the size (permeability) of plasmodesmata:
Open wider to allow more movement during growth.
Narrow or close during stress or infection to prevent the spread of pathogens or toxins.
Lamelle
Forms the grana
Types:
Granal lamellae: stacked membranes that form the grana (where light-dependent reactions happen).
Stromal lamellae (intergranal lamellae): unstacked membranes that connect the grana.
specialised cell
A cell with particular adaptions in order to carry out its specific function.
Prokary cell wall is made of what
Murein
Thykaloids site of
Light dependent stage
Stroma site of
Calvin Cycle
DRAW DETAILED ORGANELLES
Centrioles
Centrioles are cylindrical structures composed of nine sets of microtubule triplets arranged in a characteristic arrangement. They are found in most eukaryotic cells, typically as a pair known as a centrosome, located near the nucleus.
Centrioles are key cellular structures that play a central role in organizing microtubules and facilitating cell division, as well as forming basal bodies for cilia and flagella.n
Microtubules
Found in all ekatyoktic
MAKES UP THE CYTOSKELETON OF CELL
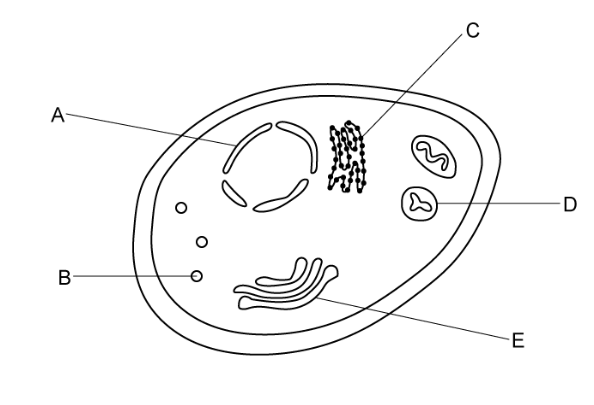
the little dots in a cell pic
B is lysosomes. A is nuclear envelope
what is magnification?
how many times larger an image appears compared to the actual size of the object
What is resolution?
the minimum ability to be able to see different objects as two separate enitities.
on the stage micrometer 1 division
0.01 mm
2 main microscopes
optical microscope and electron microscope
electron microscopes types
transmission electron microscope (2d)
scanning electron (3d)
in light microscopes, why can’t we see the organelles?
max resolution and mag
200nm and mag is 1500x
how electron microscope works - TEM
coats spectrum in resin to form solid block
thin slices are made, and stained with heavy metals
electrons pass thru the thin slice of material and are absorbed by the heavier stained metals. As they pass, they are photographed by electromagnets on the film.
TEM captures . SEM captures _.
tem organelles. sem is whole cells, tissues, organisms
scanning is about
how it’s reflected
steps of how scanning electron microscope works
specium coated w/ thin layer of metal (like gold, tungsten, silver) to improve conductivity
electrons are reflected from the surface of specium, producing a 3D shape
limits of electron microscope
complex, expensive, can’t look at living cells, ARTEFACTS can be made from preperation, black and white
how to observe the cells in a prepared slide using light microscope
clip slide onto stage
select lowest powered objective lens
use course knob to bring stage just below objective lens
look down the eyepiece and use coarse knob to move stage down till image is roughly focused
adjust focus with fine knob till image is clear
if greater magnification is required refocus using a higher powered objective lens
artefact
things that shouldn’t be there bc of staining in electron microscope
Temporary mount
where the specimen is suspended in a drop liquid on the slide. the microscopy which Enchances colour of the spec
Why is the resolution of Electron microscope higher than the resolution of a image using optical
electrons have much shorter wavelengths than photons (light particles), allowing them to resolve smaller details
how to measure for size of a structure (real)
measure image in mm and divide by mag
convert image to micrometres
divide image size by length of scale
multiply real length of scale bar
Why is it important for a leaf tissue to be very thin when observed
Thiness allows for light to pass thru specimun
What are the measurement conversions needed for magnification?
describe the steps to preparing a microscope slide using a temporary mount?
- begin by pipetting a small drop of water onto the centre of the slide.
2
- you will then need to place a thin section of your specimen on top of the water drop through using tweezers.
3
- add a drop of stain. stains are used to highlight objects in a cell.
4
-add a cover slip.
-do this by standing the slide upright on the slide, next to the water droplet.
-carefully tilt and lower so specimen is covered.
-ensure no air bubbles are seen. they'll obstruct view of specimen.
describe how you could make a temporary mount of a piece of plant tissue to observe the position of starch grains in the cells when using an optical light
add a drop of water to glass slide
obtain thin slice of plant tissue and place slice on drop pf water
stain with iodine in potassium odiine
lower cover slip using mounted needle
Cell and cellular structures are often . This makes it difficult to visualize components while using a light microscope. Staining techniques use coloured dyes to . Using multiple diff dyes to stain diff parts of specimen is known as ____ staining. For example, _____ is a dye which stains cell red.
Transparent, distinguish organelles, differiential, phloroglucinol
Prokaryotic Cell
organism without a membrane boudn organelles
tyoes of prokary
bacteria and archaea
ex of bacteria
e coli, chloera, cyanobacteria
List of prok structures
cell wall, capusle, cell membrane, dna, plasmids, cytoplasm, ribosome, mesosome, pilli,
How does cell division occur
Binary Fission, no spindle
Pilli
For attachment to other cells, involved in sexual rep
How do cells divide in eurkaryote
Mitosis or MEIosis and involves a spindle to seperate chromosomes
description of structures… dna
aka the nucleoid/genophore
free in cytoplasm