Ecosystem Services
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What are ecosystem services?
The benefits people obtain from ecosystems
Different types of Ecosystem Services:
- Regulating
- Supporting
- Provisioning
- Cultural

Difference between regulating service and supporting service
Regulating services help control and maintain ecosystem balance. For example, trees absorbing CO2 is a regulating service.
Supporting services are the foundation of all other ecosystem services. For example, soil formation and photosynthesis support plant growth.
- Regulating = Controls (like a thermostat)
- Supporting = Builds the base (like the foundation of a house)

Atmospheric Composition
Regulating
- Regulated by many abiotic and biotic processes which create a dynamic equilibrium
- Carbon dioxide and oxygen are largely regulated by photosynthesis and aerobic respiration
Biogeochemical Cycles
Supporting
- Living organisms are involved in these cycles
- Many of these are done by microbes such as bacteria or fungi
- Without these processes, waste products would build up and important nutrient resources would become depleted
Soil maintenance
Supporting
- Soil provides water and nutrients for the growth and survival of almost all plants.
Interspecies Relationships
Supporting
- Pollination
- Seed dispersal
- Habitat provision
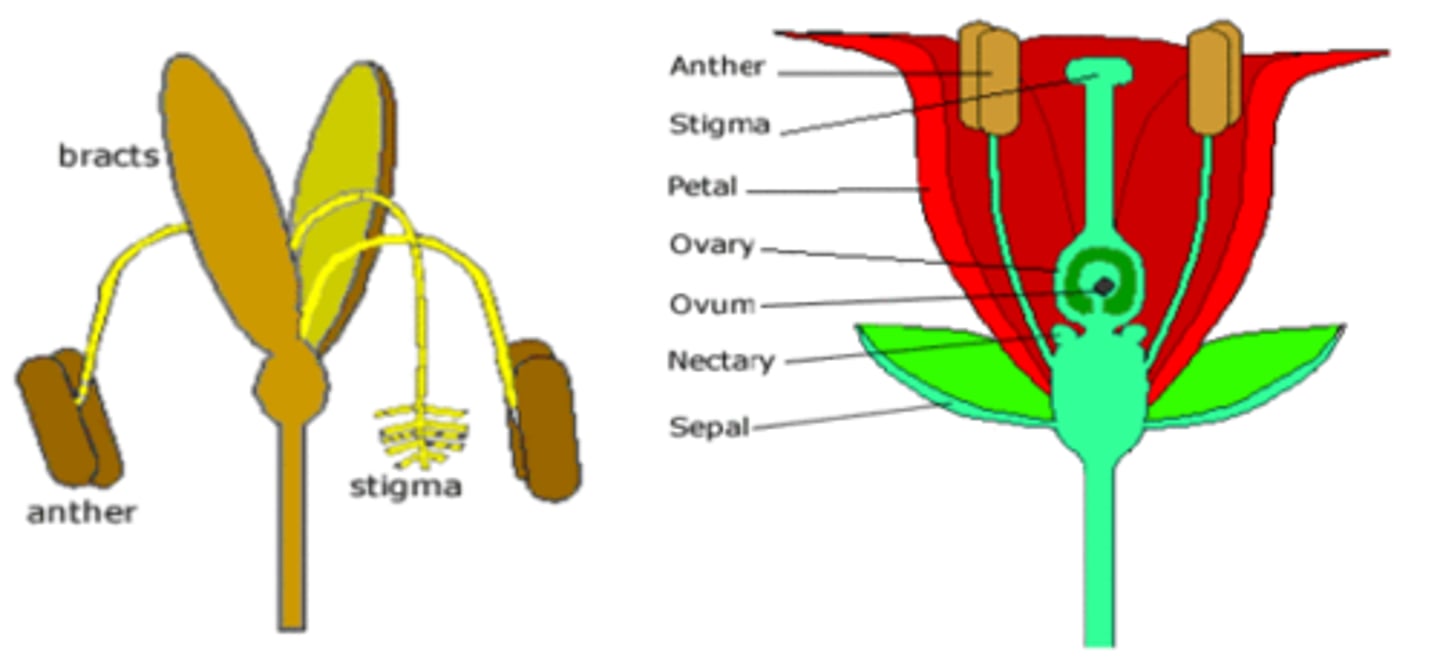
- Pollination
The transfer of pollen from the male part of a flower to the female part, allowing plants to reproduce.
Insect pollination vs wind pollination
Insect pollination allows plants to have dispersed populations as insects search over long distances for flowers. It is more reliable over long distances than wind pollination
Do insect pollinated plants need to produce more or less pollen than wind-pollinated plants?
Less, so the insect-pollinated flowers save energy
In what type of habitat is animal pollination especially important?
Forests, since trees reduce wind velocity.
Which group of animals are the most common pollinators?
Insects, especially bees.
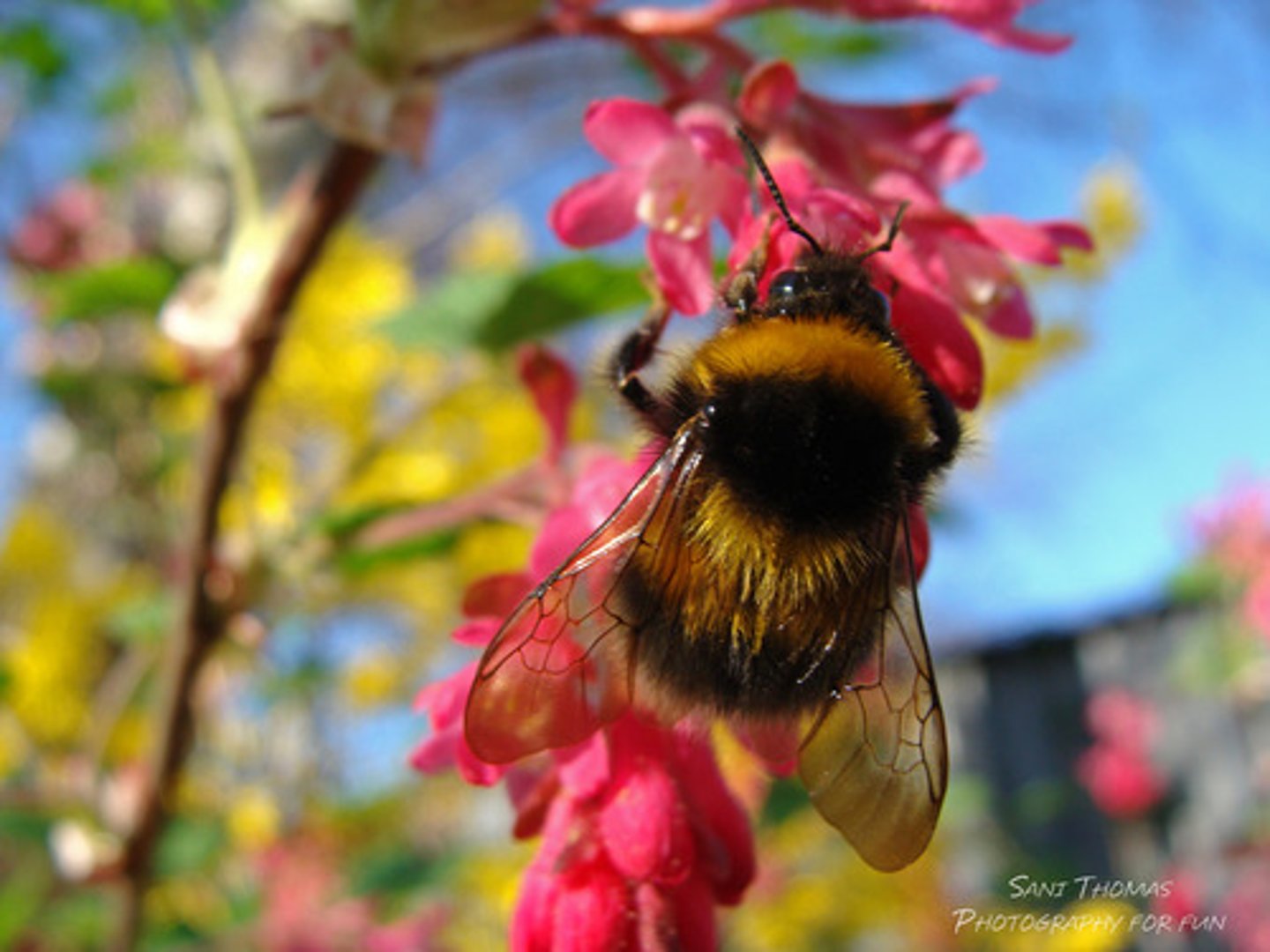

What other animals can act as pollinators?
Birds, bats, and monkeys.
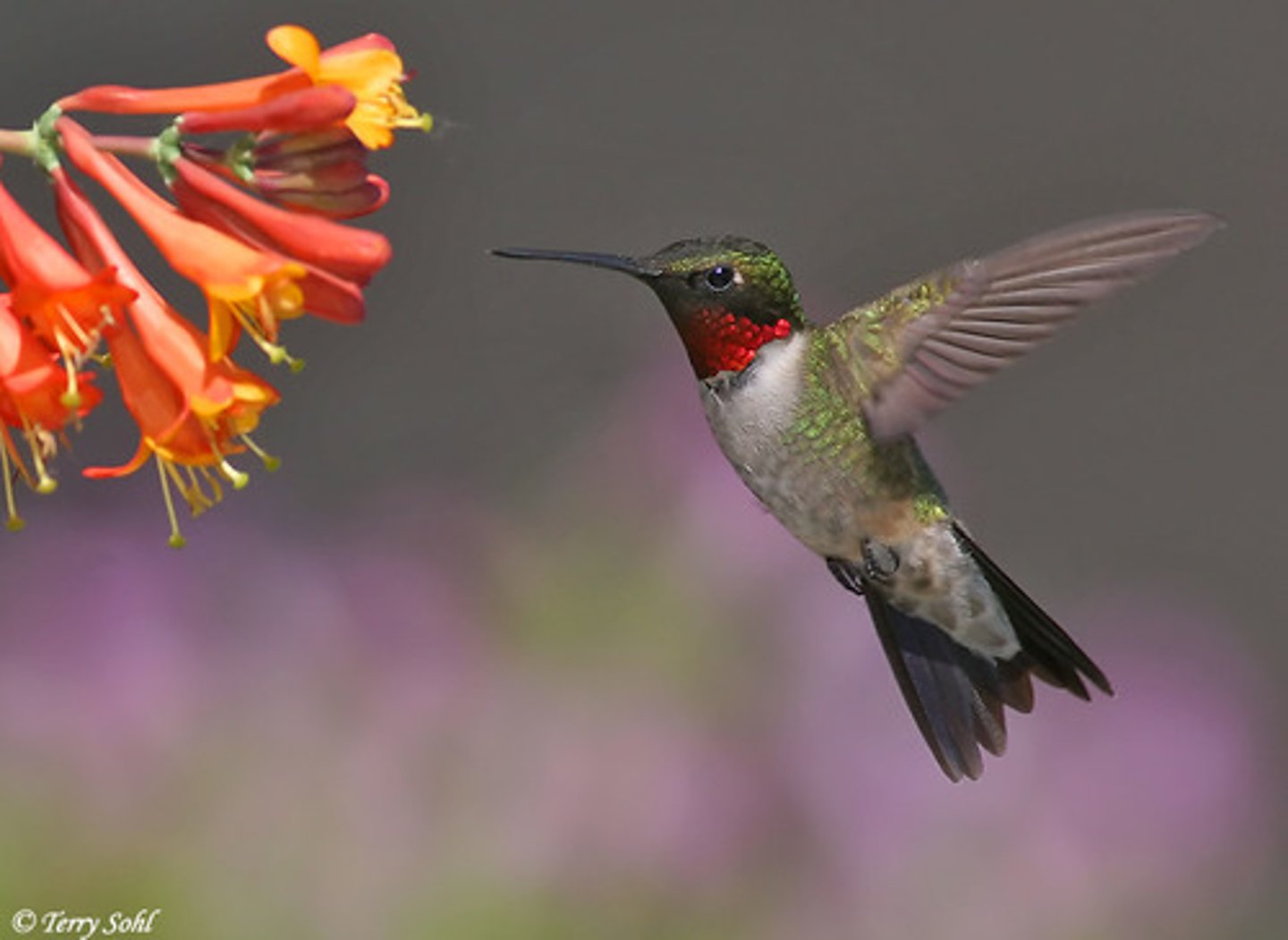

What do pollinators seek from flowers?
Pollinators drink the sugar-rich nectar, picking up pollen in the process.
How have plants and insects evolved wrt pollination?
Many plants have evolved flowers that attract particular insects, and many insects have evolved to feed from the flowers of particular species.
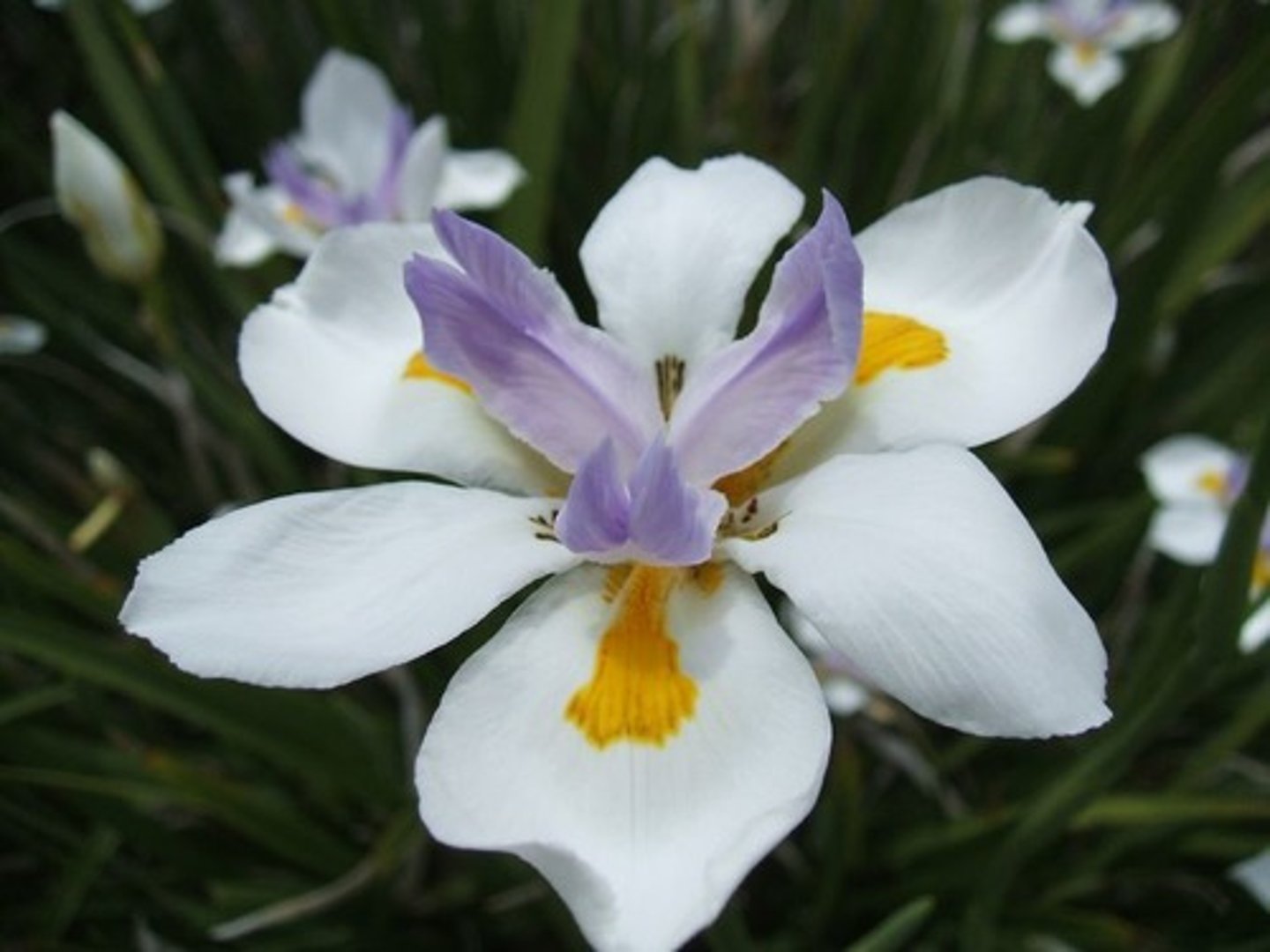

Where is Darwin's Orchid found?
Madagascar.
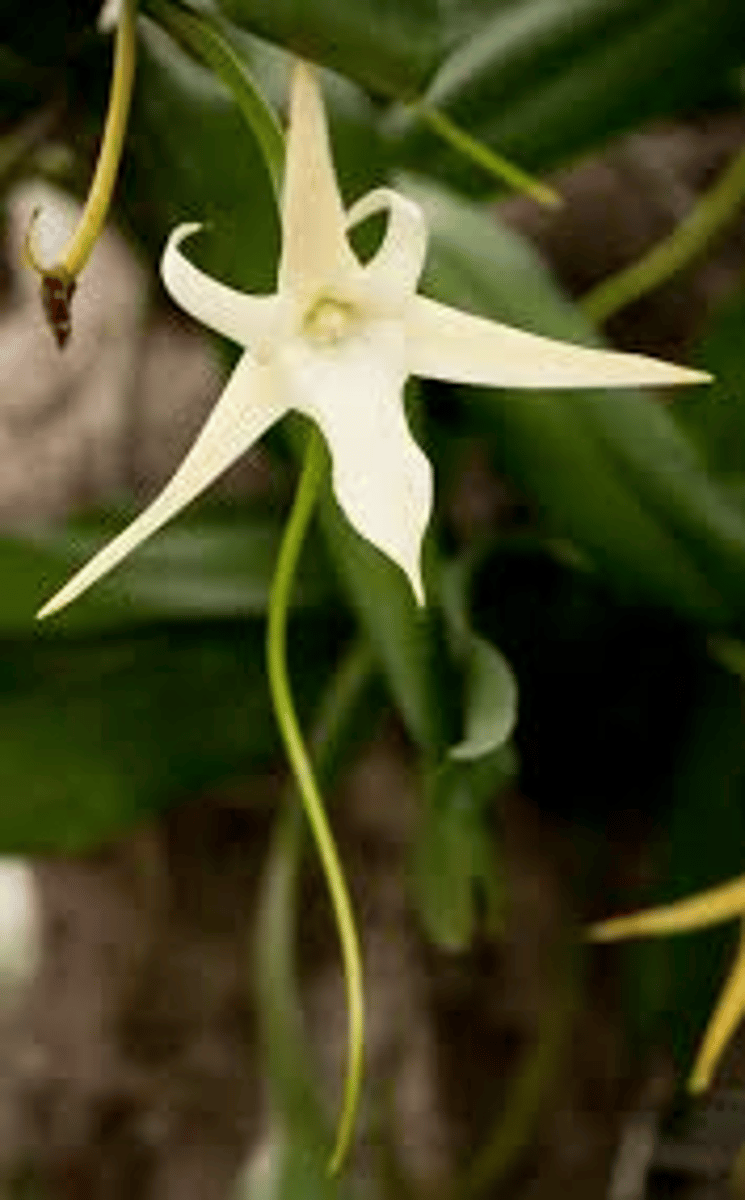

What is unique about the nectar of Darwin's Orchid?
The nectar is found at the end of a 30cm long tube, which only the Sphinx Moth can reach.
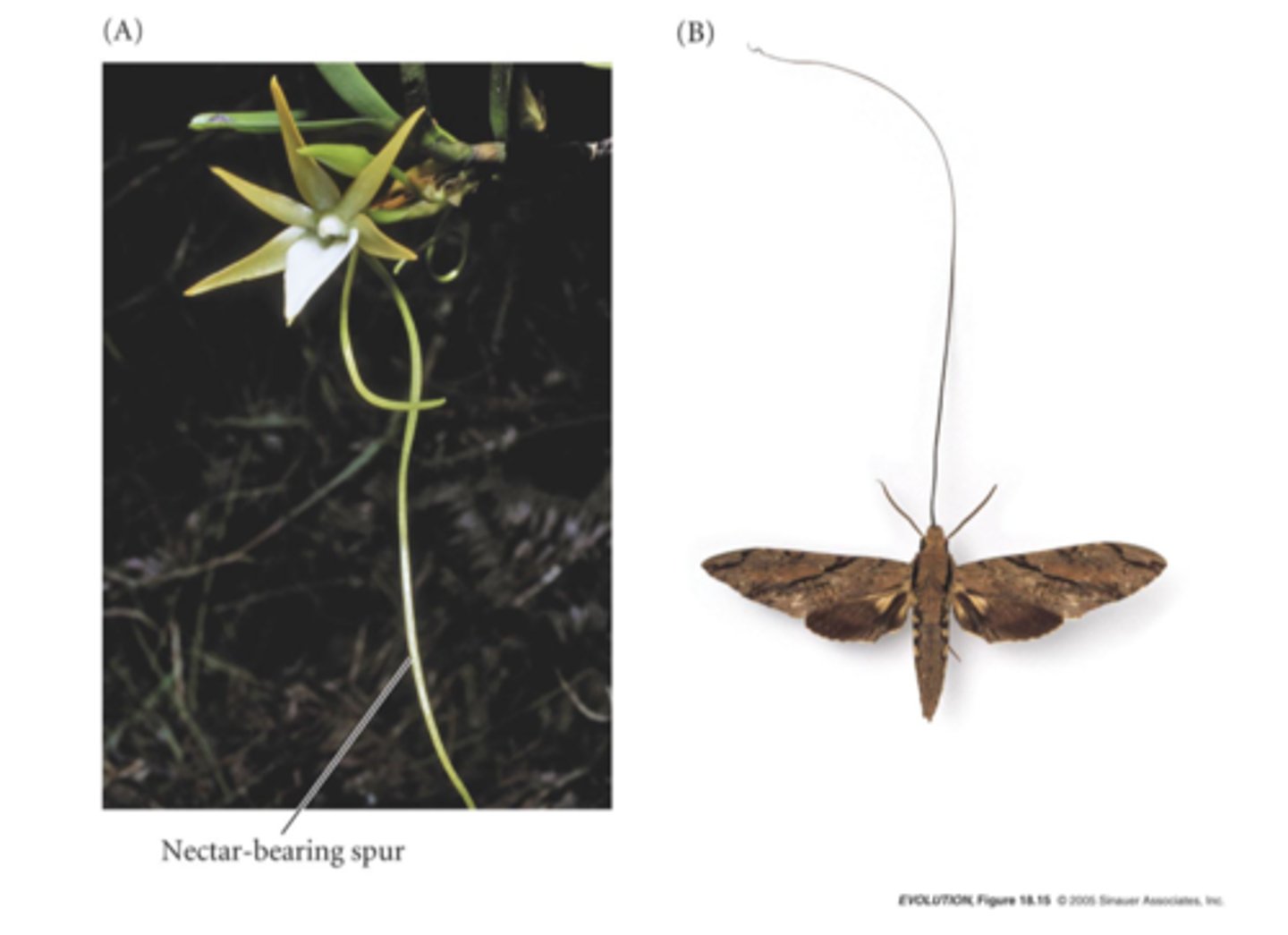
Sphinx Moth in pollinating Darwin's orchid
The Sphinx Moth carries pollen only between the flowers of Darwin's Orchid, ensuring that pollen is not wasted on other plant species.
- Seed dispersal
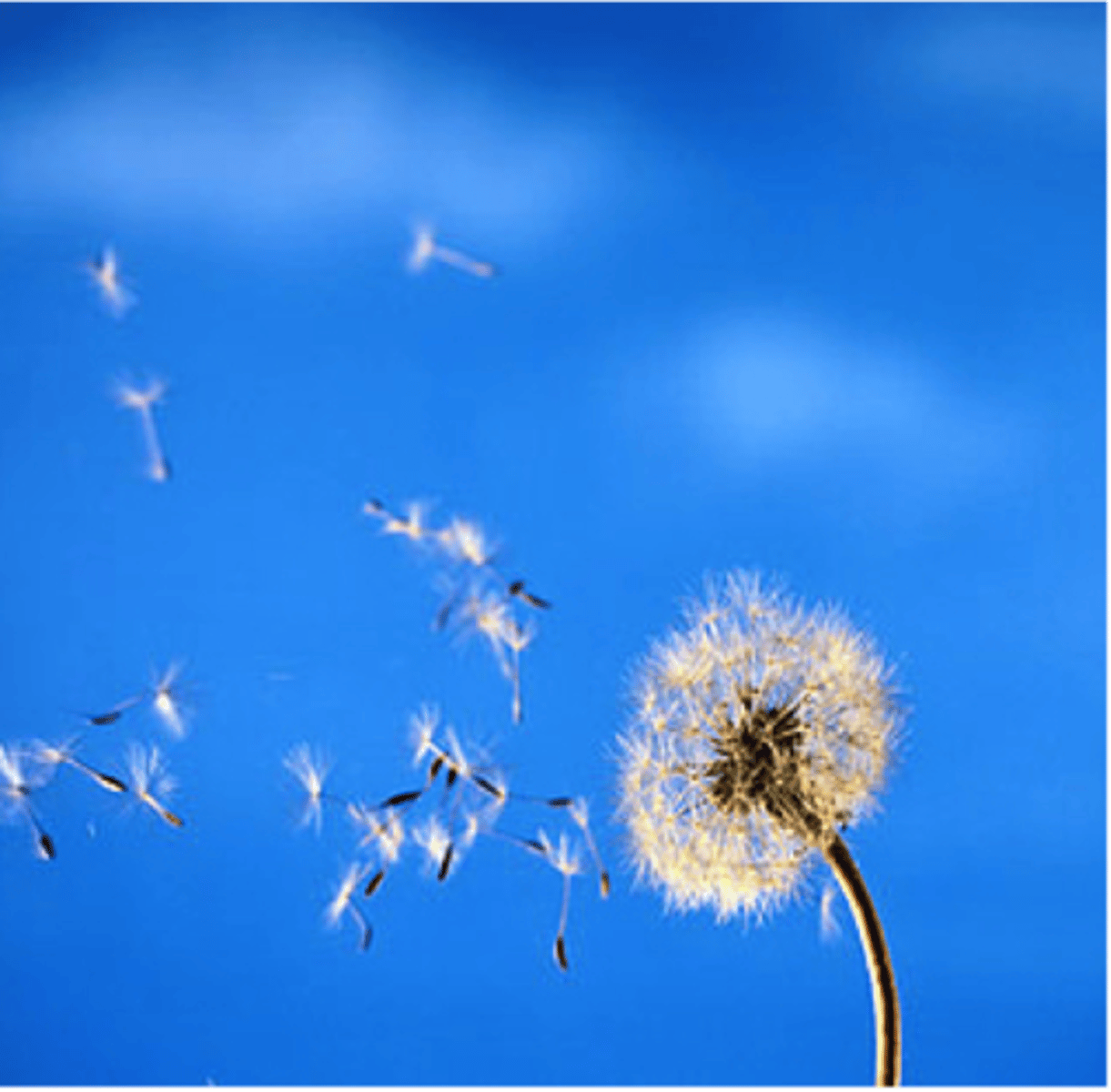

What are the advantages of seed dispersal by animals compared to wind dispersal?
Seeds can be carried longer distances.

Why are animals likely to carry seeds to suitable locations?
Animals live in the same habitat as the plant, increasing the chances of seeds being carried to locations where they can survive.
How do larger seeds benefit from animal dispersal?
Larger seeds contain more nutrients for the growth of young plants, increasing their survival.
How do plants attract animals for seed dispersal?
Plants often attract animals using brightly coloured fruit that tastes good.

Seeds consumed by animals
Seeds may be passed through the animal's gut and be carried to a suitable habitat in faecal material, which acts as fertiliser.
Many seeds are stimulated to germinate in the intestines of the animals that disperse them.

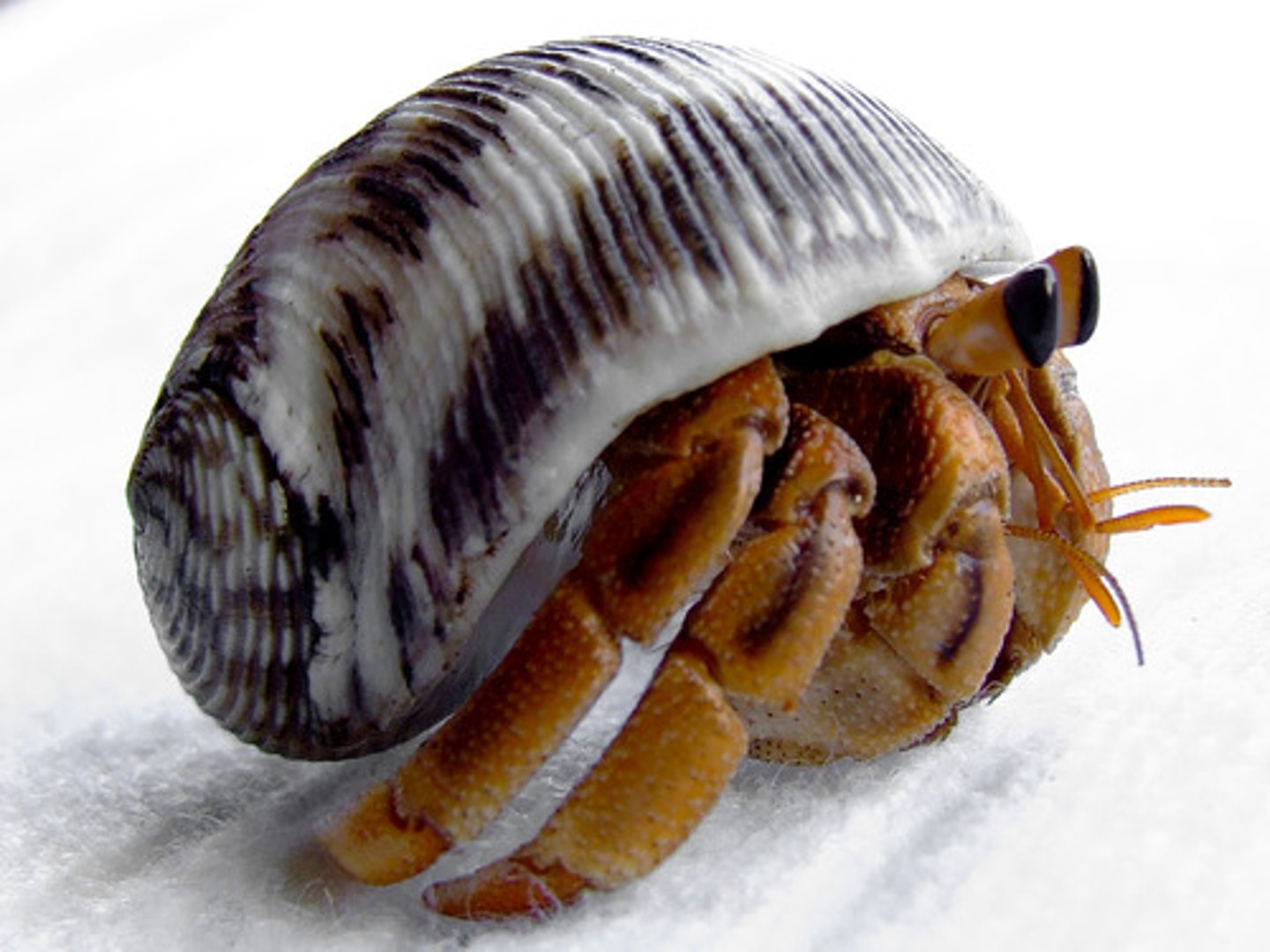
- Habitat provision
One species may provide habitats for other species.
Hermit crabs live inside the shells of dead molluscs

Trees
- Trees provide nest sites for birds
- Trees also control the abiotic conditions beneath the canopy, such as light levels, wind velocity, etc. This may provide conditions that are suitable for species that cannot survive in more exposed locations.