AP Pyschology Unit 2: Cognition
1/80
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Information Processing Model
compares mind to the computer
encoding
input is encoded when sensory receptors send impules that are registered by neurons
store
putting information in our brain
retrieval
the process of getting information out of memory storage upon demand
Multi-store model
describes memory as 3-part system that includes: sensory memory, short-term and long-term memory
sensory memory
A type of storage that holds sensory information for a few seconds or less; acts as breif stimuli through senses
iconic memory
a momentary sensory memory of visual stimuli; captures for fraction of a sec
echoic memory
a momentary sensory memory of auditory stimuli for abt 3-4 seconds (lets brain process spoken language)
short-term memory
activated memory that holds a few items briefly before the information is stored or forgotten typically for 15-30 secs (limited capacity)
short term mem examples
guides to a destination
long-term memory
stage where info is stored indefinitley with virtuall unlimited capacity; long-term retention for stuff
long term memory example
Recalling how to ride a bike, even after years of not having done the activity.
working memory
type of SHORT TERM memory that holds and manipulates info (short-term and long-term combine)
working memory example
as you cook, working memory is engaged to hold on sequence of steps and measuring ingridients
central executive
control center of working memory; manages attention, coordinates other components and integrates info from our senses
phonological loop
component of working memory responsible for processing/storing verbal+auditory information; has 2 parts: temp. holding sounds and words, and rehearsing info through vocal repetition
Visuospatial sketchpad
component of working memory that hand;es visual and spatial information, allows for temporary storage and manipulation of images (navigation, geometry, visual tracking)
long-term potientiation
long-lasting increase in signal transmission between neurons that results from simultaneous activation; considered one of the major cellular mechanisms that underlies memory and learning
Working memory challenge
we will demonstrate the limited capacity and active processing nature of working memory through tasks (number recall, word chain)
automatic processing
the unconcious encoding of information abt space,time freq and other well-learned tasks; routine of driving home from work
effortful processing
type of memory encoding that requires active work and attention to embed information into long-term memory; proces of learning languages
Levels of processing model
proposes that depth at which info is thought abt affects how well you remember it; study more remember more
shallow encoding
basic level of processing that focuses n surface characteristics of info like sound of words; involves minimal attention and leads to fragile memories
episodic memory
type of explicit memory that involves the recollection of personal experiences and specific events
autobiographical memory
type of memory that encompasses events and experiences from individuals life (combines episodic and semantic)
semantic memories
general personal information and knowledge that defines the self
implicit memories
type of memory does not require concious thought (fingers moving automatically to keys)
procedural memory
type of IMPLICIT memory that involved recall of how to perform tasks automatically (brushing ur teeth)
prospective memory
remembering to perform planned action or recall planned intention (remembering to pick up son from school at night)
massed practice "cramming"
cramming info over short period of times
spacing effect "distributed practice"
phenomenon where learning is more effective when study sessions are spaced out over time rather than crammed once
maintenance rehearsal
learning technique that involves repeatedly reviewing info to keep it in short-term memory
elaborative rehearsal
memory technique that involved deep processing of information by adding meaning or connecting to existing knowledge
retreival cues
stimuli that helps being previously learned info to mind, plays important role in process of retreiving memories (external or internal cues)
recall
A measure of memory in which the person must retrieve information learned earlier, as on a fill-in-the-blank test.
recognition
a measure of memory in which the person need only identify items previously learned when presented (familiarity and identification)
context-dependant memory
Process where people remember better when they attempt to recall information in the same context in which they learned it (physical surroundings and similar conditions)
state-dependant memory
The heightened ability to remember information when our internal state of conciousness matches those of when we learned/retained the information.
mood-congruent memory
tendency to recall info that is consistant with current mood
serial position effect
tendency to remember items at beginning and end of a list
primacy effect
cognitive phenomenon where people remembers items presented at beginning of list better than after
recency effect
same thing as primacy, except they remember end of list better
testing effect
enhanced memory after retrieving, rather than simply rereading, information through testing
metacognition
awareness and understanding of one's thought process ("i learn better visually")
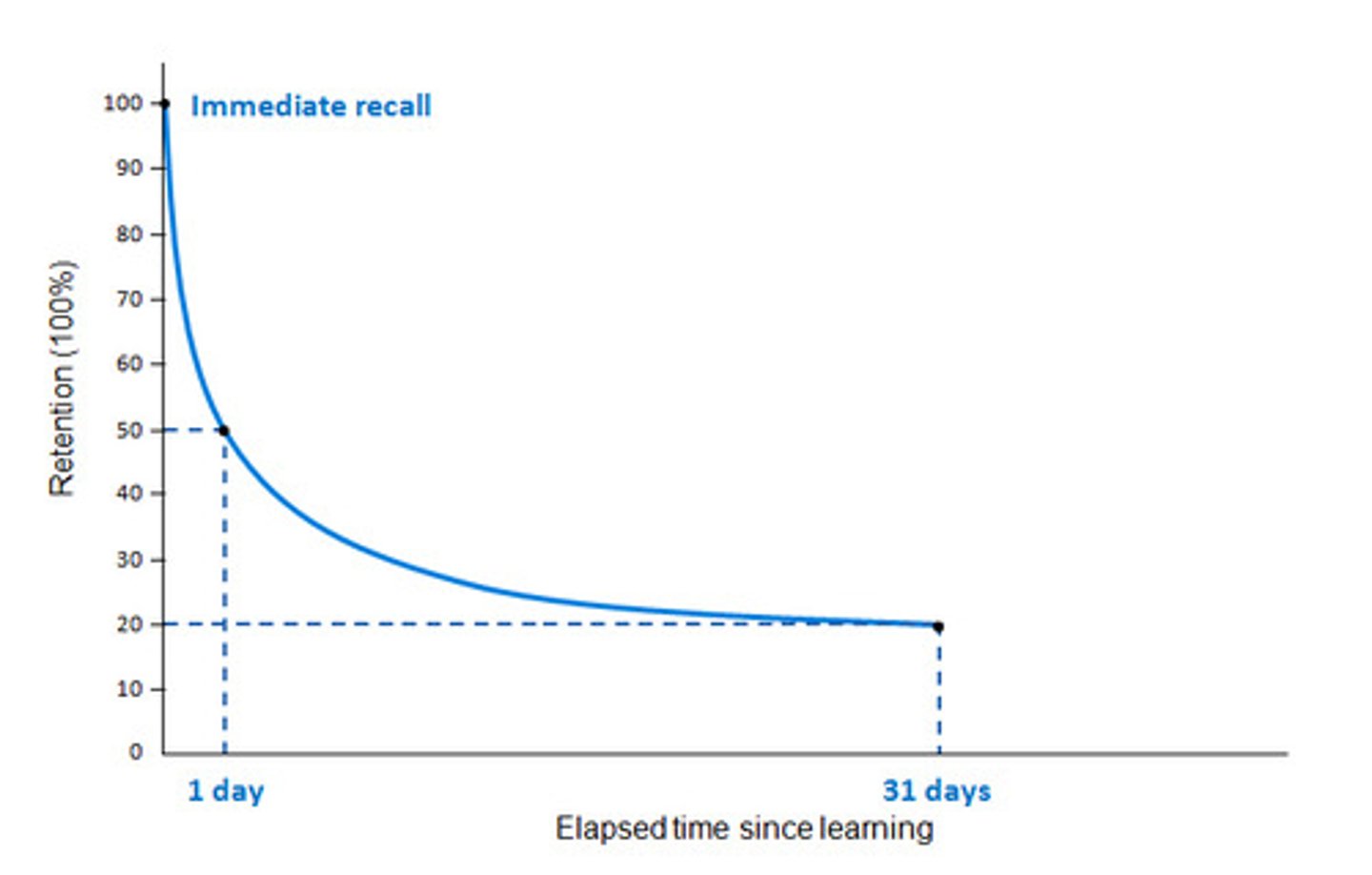
forgetting curve
graphical representation @ rate where memory fades over time
encoding failure
failure to process information into memory
proactive interference
when older memories inhibit ability to learn and remember new info
retroactive interference
occurs when new learning impairs recall of previously encoded info
tip-of-tounge phenomenon
common memory experience where someone feels confident that they know a word or name but cant immediately recall it
source amnesia
faulty memory for how, when, or where information was learned or imagined, while retaining factual knowledge
anterograde amnesia
an inability to form new memories
retrograde amnesia
an inability to retrieve information from one's past
infantile amnesia
the inability to remember events from early childhood, typically before 3-4 years
alzheimers
progressive neurological disorder leads to memory loss, cognitive decline and behavioral changes
repression
keeping distressing thoughts and feelings buried in the unconscious
constructive memory
a process by which we first recall a generalized schema and then add in specific details; memories are not retreived but actively reconstructed
misinformation effect
incorporating misleading information into one's memory of an event
schemas
mental frameworks help us organize
perceptual set
tendency to precieve aspects we expect
Gestalt Psychology
a psychological approach that emphasizes that we often perceive the whole rather than the sum of the parts
Figure ground
ability to distinguish foreground from background
Binocular working cues
visual info needs both eyes to precieve distance and depth
retinal disparity
each eye sees slightly diff picture bc of position
convergence
when our eyes move inwards as we see objects closer
monocular depth cues
visual indicators of distance and space are perceived as one eye
relative clarity
if object is closer, it is clearer
relative size
if object is closer, it is perceived as larger
texture gradient
the way we perceive texture if objects are closer
linear perspective
parallel lines appear to converge in the distance

interposition
when one object overlaps another leading us to perceive the overlapping object as closer
perceptual constancies
our brains ability yo see objects as unchanging even when image changes
bottom-up
detials to big picture
top-down
big picture to details
selective attention
focusing on specific aspect of info while ignoring others
cocktail party effect
focus on single convo n noisy environment
inattentional blindness
failure to notice unexpected thing in visual field
change blindness
failure to notice large changes in environment when change occurs
shape constancy
ability t percieve an object as having the same shape even if distance/angle changes
size constancy
perception that object remains same size when its distance changes
color constancy
ability to perceive colors of object as stable under lighting conditions
apparent movement
perception of motion when no actual movement