Chapter 9: Price management and pricing tactics
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Price
1) Importance of price
2) Price management
Influencing factors
Price positioning
3) Price setting
4) Alternative methods of pricing
Break-even analysis
5) Pricing existing vs new products
6) Price as a marketing instrument
Immediate sales tactics
Extended sales tactics
Limits on promotional pricing
1) Importance of price
Important in following situations
New product intro: skimming vs penetration
Competitor action / reaction to price change
When the economy “changes”
When prices of substitutes change
With changing government regulations
With technological breakthroughs
2) Price management
Influencing factors on price management

Price vs Quality
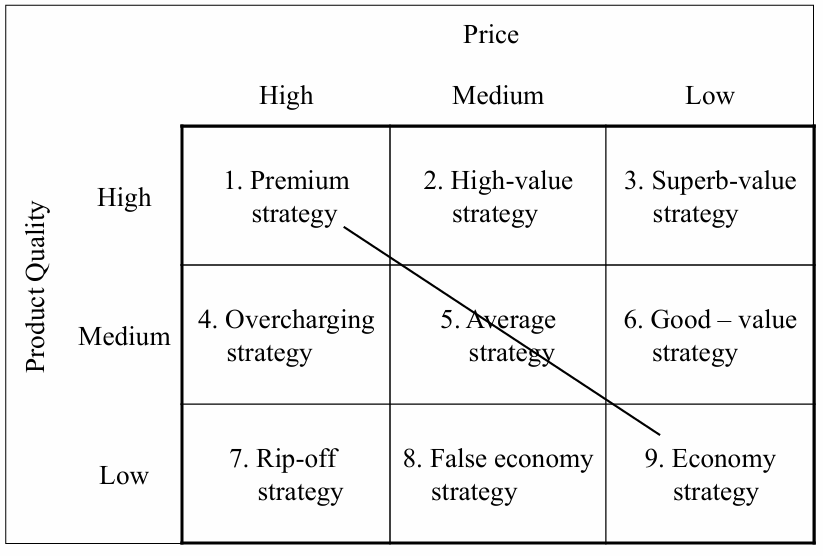
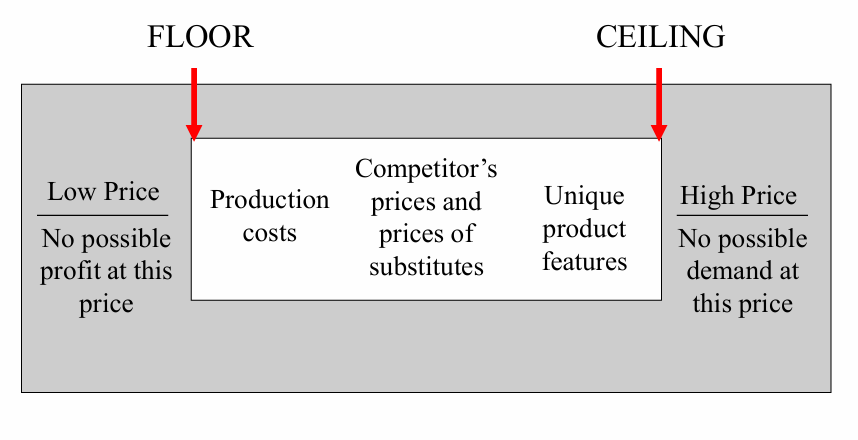
3) Price setting
Determining the overall price level
Floor and Ceiling price level
Floor (minimum) | Ceiling (maximum) |
|
|
4) Alternative methods of pricing
Cost-oriented or cost-based pricing
Competition-oriented pricing
market (demand) - oriented pricing
4) Alternative methods of pricing: Cost-oriented or cost-based pricing
Own cost structure as the basis
Knowledge of the cost structure is required
Selling price = Average total cost + Margin
Margin depends on speed of rotation (eg. margin on fast rotating mineral water is usually smaller than the margin on slow rotating exclusive wines)
Break-even analysis
Profit = Total Revenue - Total Costs
Total Revenue (TR) = P x Q
Total Costs (TC) =VC x Q + FC
Profit = P x Q - VC x Q - FC = (P - VC) x Q - FC
Break-even: P and Q where TC = TR
Target rate of return
Financial goal (eg. 20% on investment)
Added to “fixed costs” in break-even analysis
Return on investment
Accounts for “turnover”
Number of times a company uses its investments per year
Payback period
How long it takes before original investment is recovered
Payback period = (break even sales) / (annual demand)
4) Alternative methods of pricing: Competition-oriented pricing
Price of competitor as the basis
Somewhat cheaper or somewhat more expensive ?
Procedures with competing bids (procurements)
Entails risks from neglecting
Own cost structure (underestimating own costs)
Market demand and customer’s ability and willingness to-pay
4) Alternative methods of pricing: Market-oriented pricing
Based on demand elasticity
Market responsiveness to price changes
Generic vs brand demand elasticities
Simulation studies
5) Important considerations when pricing new products
Price positioning strategy
Target market choice
Value to the consumers
Multiple segments, versions, prices
5) Important considerations when pricing new products: Strategic options with pricing
When introducing new products to the markets
Skimming strategy
High prices
Big profit margins
High returns on investment
Rapid payback of investment
Price penetration strategy
Low prices
Rapid market share gain
Stimulate product trial
Strategic options with pricing of existing products
Build: P lower than competition
Hold: maintain P
Harvest: premium P
Reposition: change P
6) Price as Marketing Instrument: Immediate sales tactics
Off-season discounts
Seasonal demand
Offset storage costs
Level out productioon schedule
Quantity discounts
Volume discount
Cash discount
Discount for cash payment
Special sale prices
Discount coupons
6) Price as Marketing Instrument: Extended sales tactics
Trade discounts
List price vs actual price
For performing a specific marketing function
One price vs Variable price
Price flexibility
One price: inflexible, consumers’ trust
Variable prices: flexible, bargaining
Pricing multiple products
Overall goal vs individual goal
Price lining
Offering a price range: cheap to expensive version
Resale price maintenance
control of the price level at retail level
Suggest or enforce: on-label or on-pack?
Psychological pricing
Odd pricing
Demand curve effect
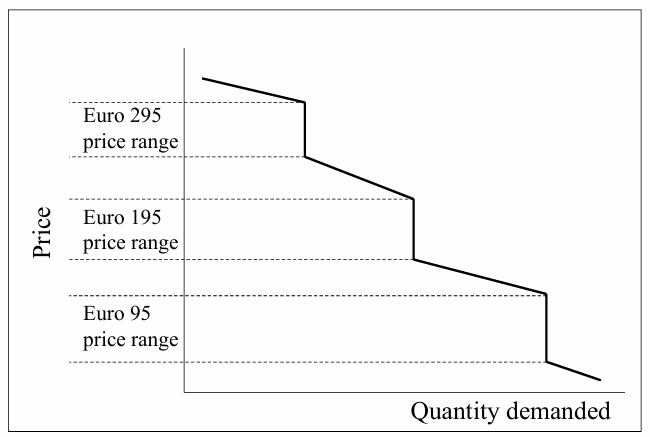
6) Price as Marketing Instrument: Limits on Promotional pricing
Techniques at retail level
Loss Leader pricing (eg. Lotus (€1,79) → Colruyt (€1,89) vs Carrefour (€1,69) = loss leader pricing)
Pricing below costs
Objective = realise revenues from
sales other products
develop shopping habits
attract new buyers
Bait and Switch (2+5 in AH)
Price special
Quick supply run out
Convince customers to buy more expensive alternative
Forbidden by law
General limitations
No selling at price below costs
Specials should be available to all interested buyers
Rules of thumb for price policy
Put the price up when everyone else does
Not too much at any one time
Not too often
Move something down when you move up
Look after your key accounts
Provide sound and true explanations